APHG Unit 1 Review
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
reference maps
maps designed for people to refer to for general informatioin about places. Examples include political maps, physical maps, road maps and plat maps.
physical map
reference map that shows identifiable natural landmarks such as mountains, rivers, oceans
political map
a reference map that shows political boundaries
e.g. countries, cities, capitals, etc.
thematic maps
maps used to display specific types of information (theme) pertaining to an area
cartogram
a thematic map that shows statistical data by transforming space (the size of ocuntries are shown according to some specific statistic)
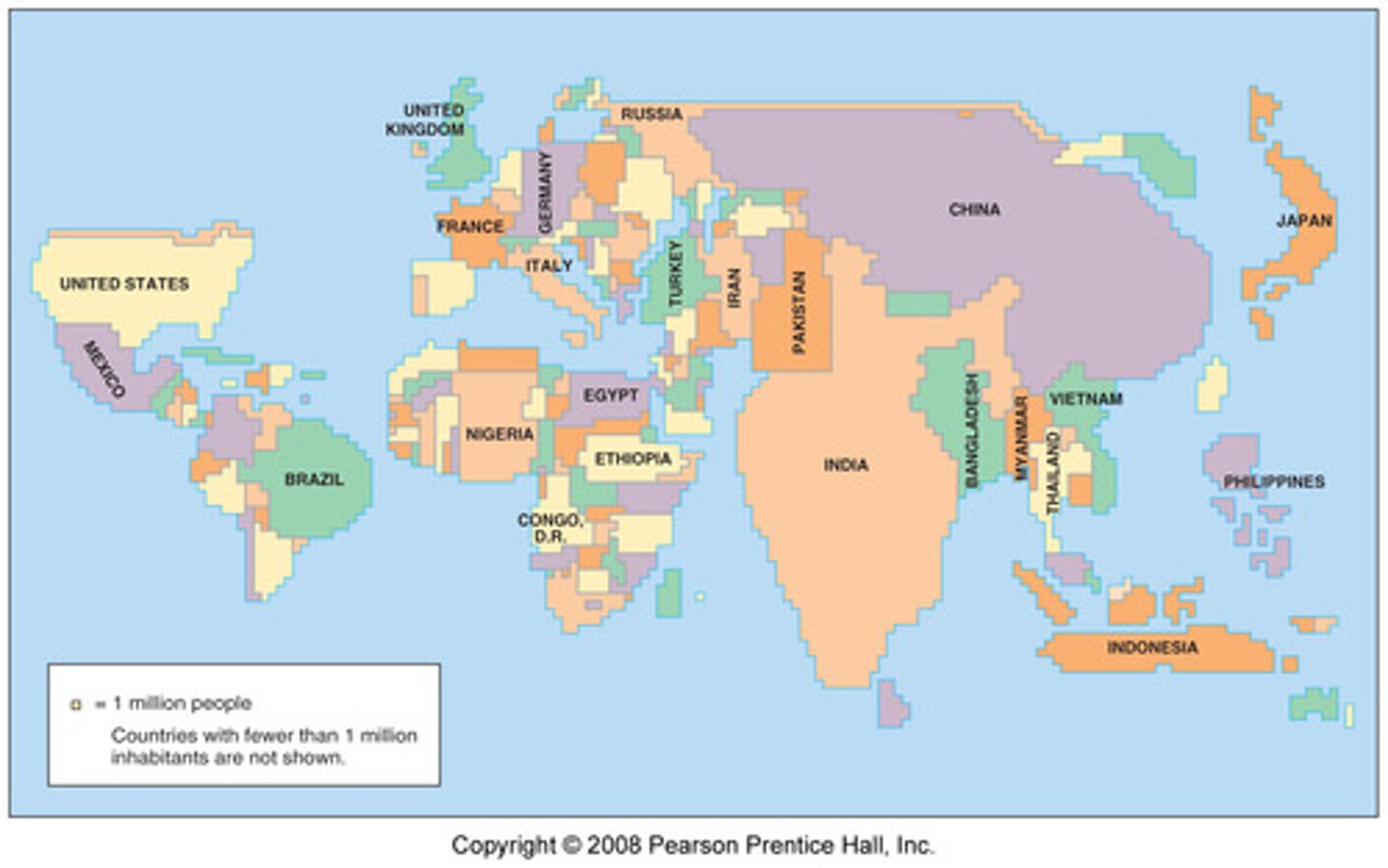
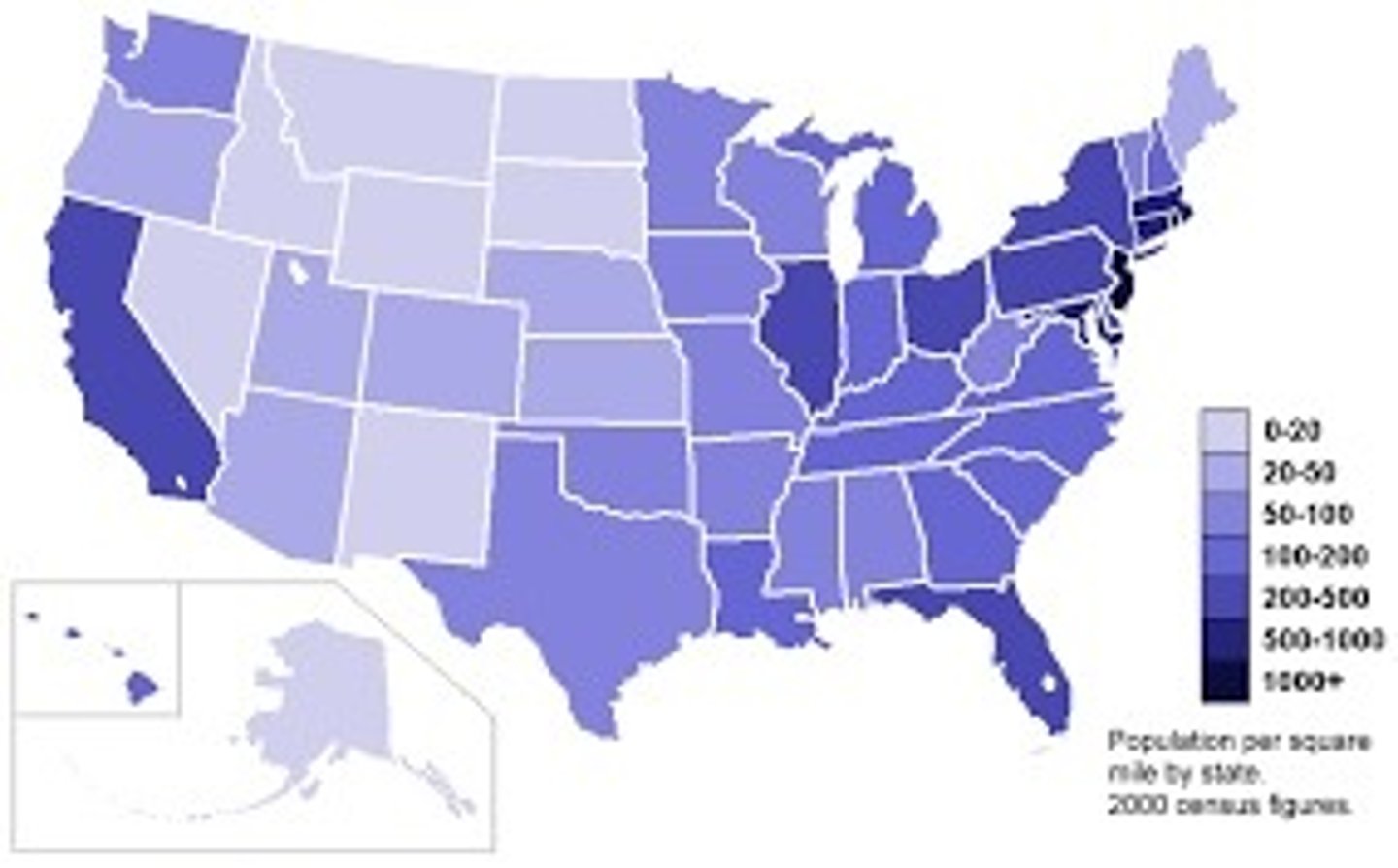
choropleth map
a thematic map that uses shading or coloring to show statistical data; data is showen in defined area; great for showing rates of something
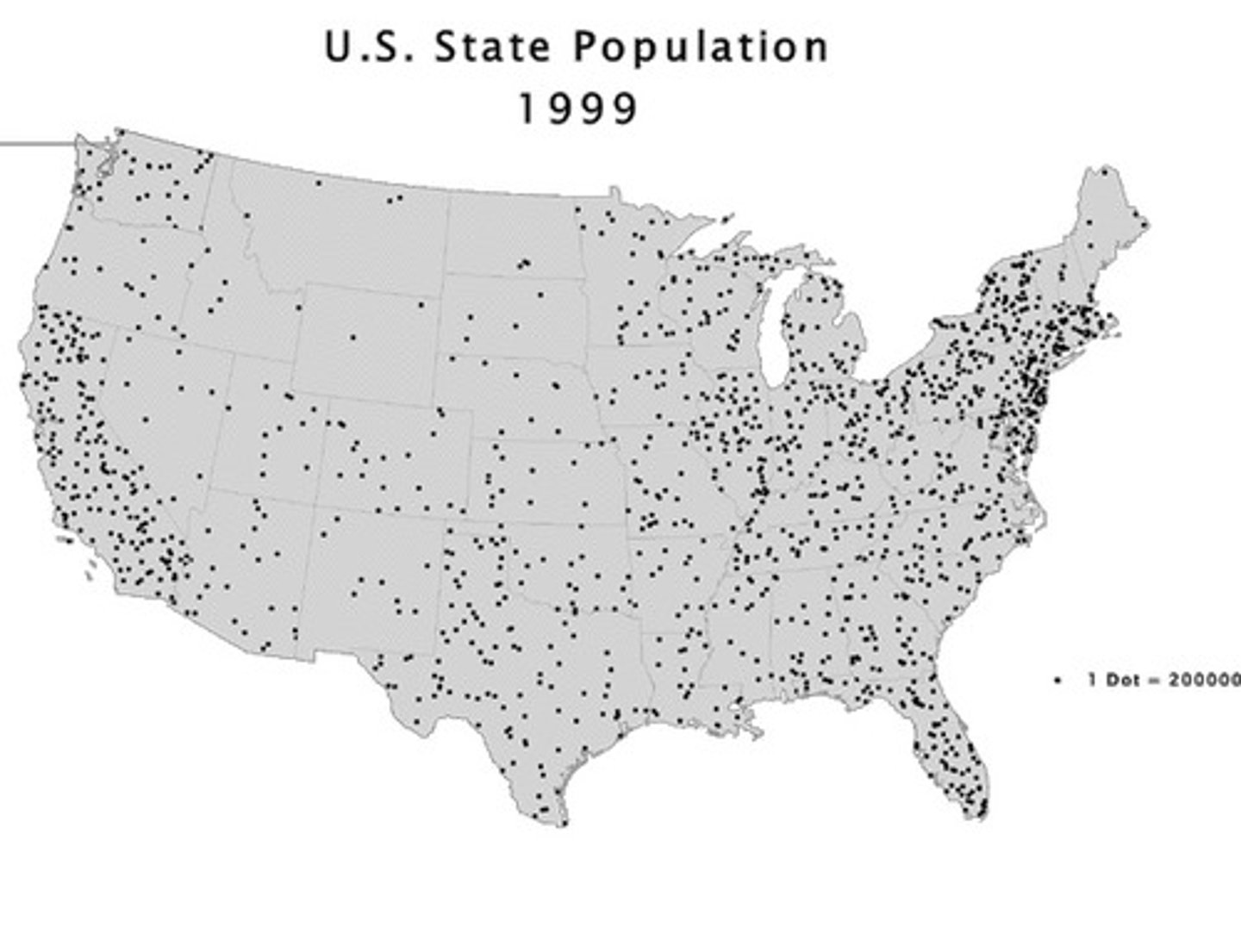
dot distribution map
a thematic map that uses dots to indicate a feature or occurrence; each dot represents a specific quantity; great for showing specific location and distribution
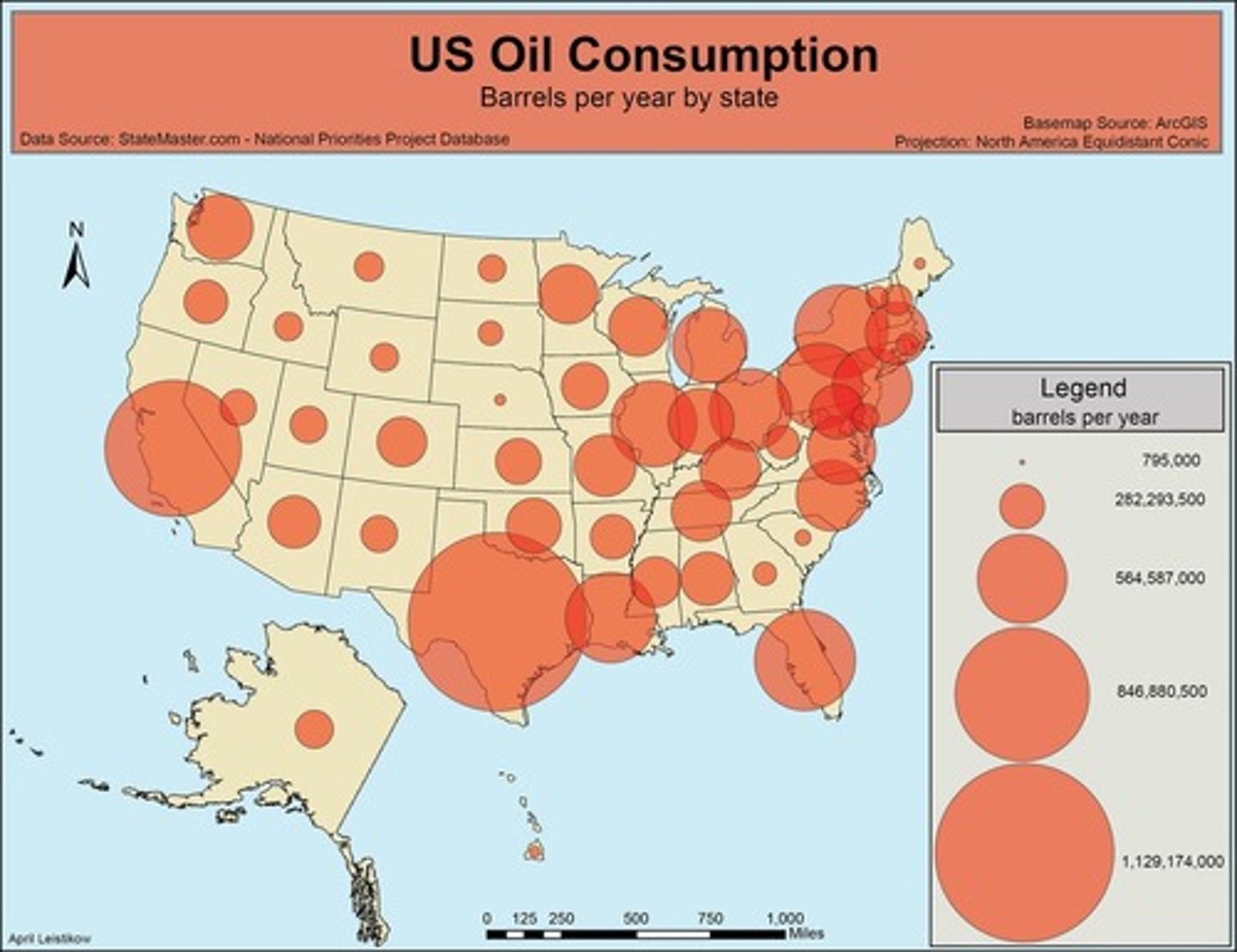
graduated symbol map
a thematic map that uses symbols of different sizes to indicate different amounts of something; make it easy to see where the largest and smallest of some phenomena are; also called proportional symbol map
relative location
description of where someting is compared to things around it
absolute location
Precise spot of where something is; most widely used system is latitude and longitude or street address
agglomerated
objects that form a group; cliustered
distribution
The arrangement of something across space (clustered, linear, dispersed, circular, geometric, random)
elevation
height above or below sea level
map distortion
a change in the shape, size, or position of a place when it is shown on a map
map projection
a way to transfer the 3-dimensional early onto a 2-dimensional map to deduce distortion in area, distance, shape, and/or direction
geospatial technologies
technology that provides geographic data that is used for personal, business, and governmental purposes
GIS (geographic information system)
a computer system that can capture, store, query, analyze, and display geographic date
GPS (global positioning system)
a system that accurately determines the precise position of something on Earth
census data
geospatial data collected through the quantification (counting) of a population; gathered by the U.S. government annually (in smaller counts) and every ten years (in a larger count)
absolute location
describes the precise location of a place using the earth's latitude & longitude
relative location
describes the location of a lace relative to other human and physical features
space
relational concept that acquires meaning and sense when related to other concepts
place
describes an area on the surface of the Earth with distinguishing human & physical features
human-environment interaction
The dual relationship between humans and the natural world and the connection and the exchange between them.
distance decay
the idea that the likelihood of interaction diminishes with increasing distance
time-space compression
term that refers to the greatly accelerated movement of goods, information, and ideas during the 20th century made possible by technological innovations
flow map
a type of thematic map that shows the movement of objects between different areas with line symbols of different widths.
sustainability
meeting an increased demand for resources in a way that protects that ability of future generations to meet their own needs
natural resources
something found in nature and is necessary or useful to humans
environmental determinism
the theory that a society is formed and determined by the physical environment, especially the climate.
environmental possibilisim
the theory that the environment sets certain constraints or limitations, but people use their creativity to decide how to respond to the conditions of a particular natural environment
region
an area of Earth distinguished by a distinctive combination of cultural and physical features
Formal (uniform) region
region marked by shared trait (cultural, physical, etc.) that is measurable and holds true across the entire region.
Functional (nodal) region
a type of region marked by a particular set of activities that occur; united networks of communication, transportation, or pother interactions.
Perceptual( vernacular) region
a type of region that exists as an idea; vary widely based on the person who is defining them.
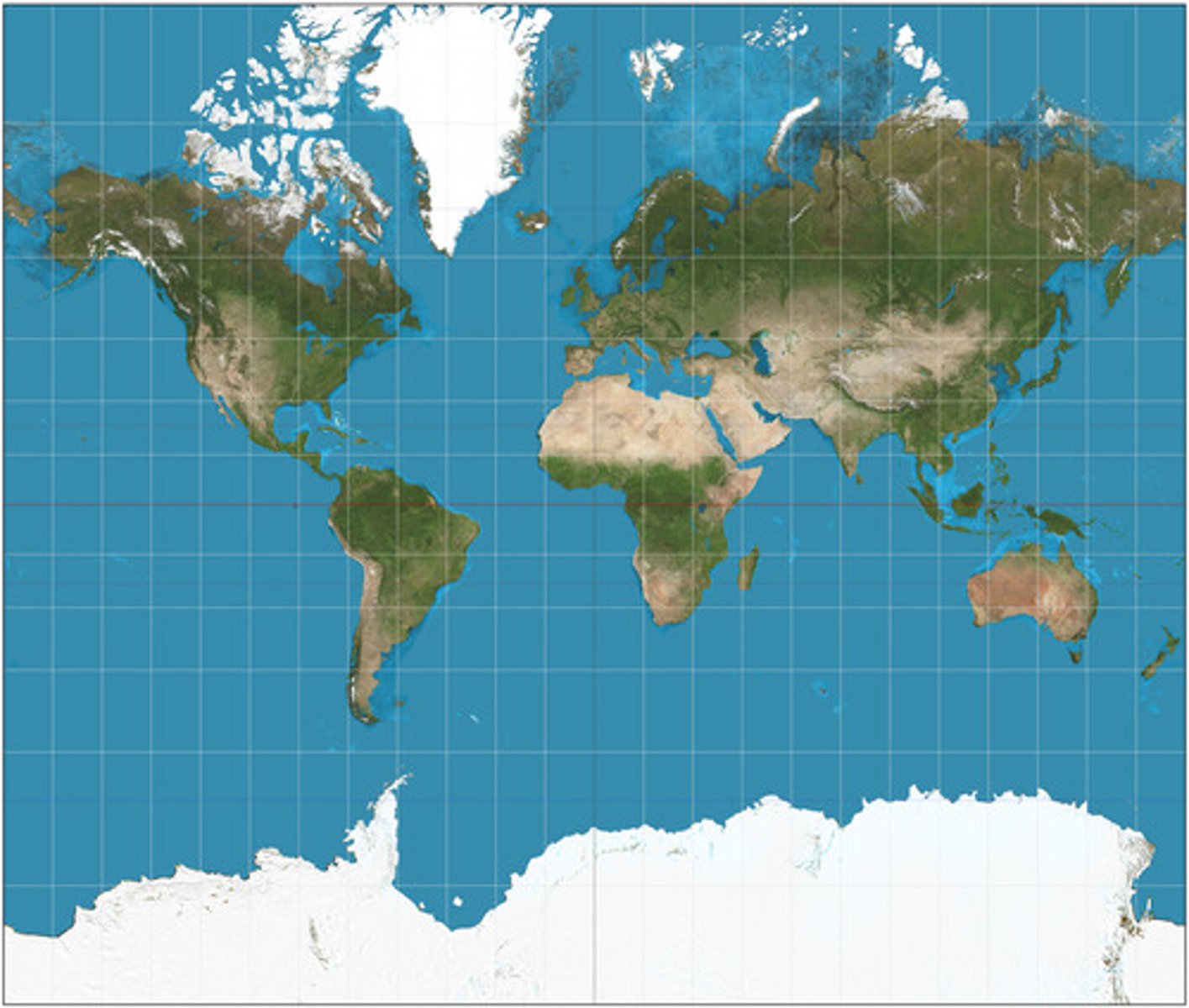
Mercator projection
a projection that is particularly useful for navigation because it maintains accurate direction; area is significantly distorted in polar regions
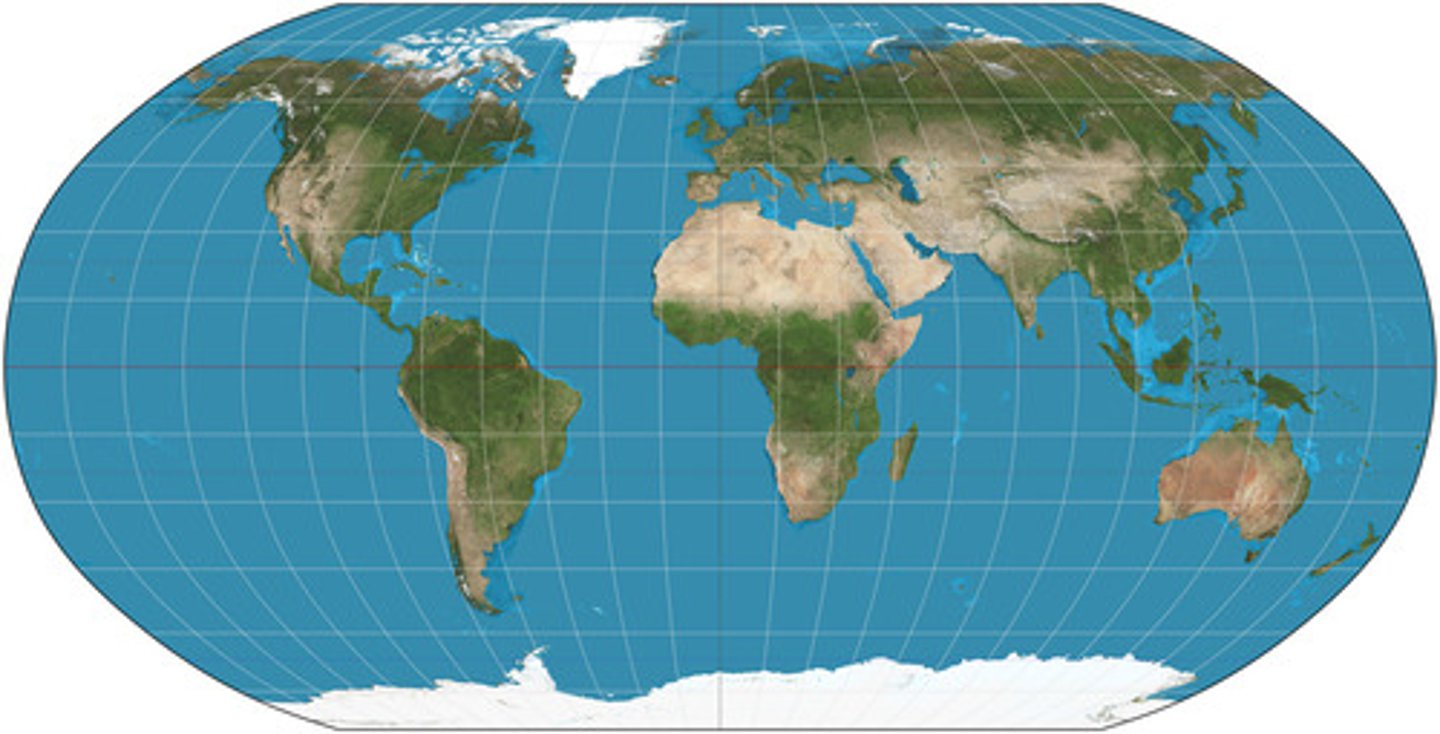
Robinson projection
Projection that attempts to balance several possible projection errors. It does not maintain completely accurate area, shape, distance, or direction, but it minimizes errors in each.
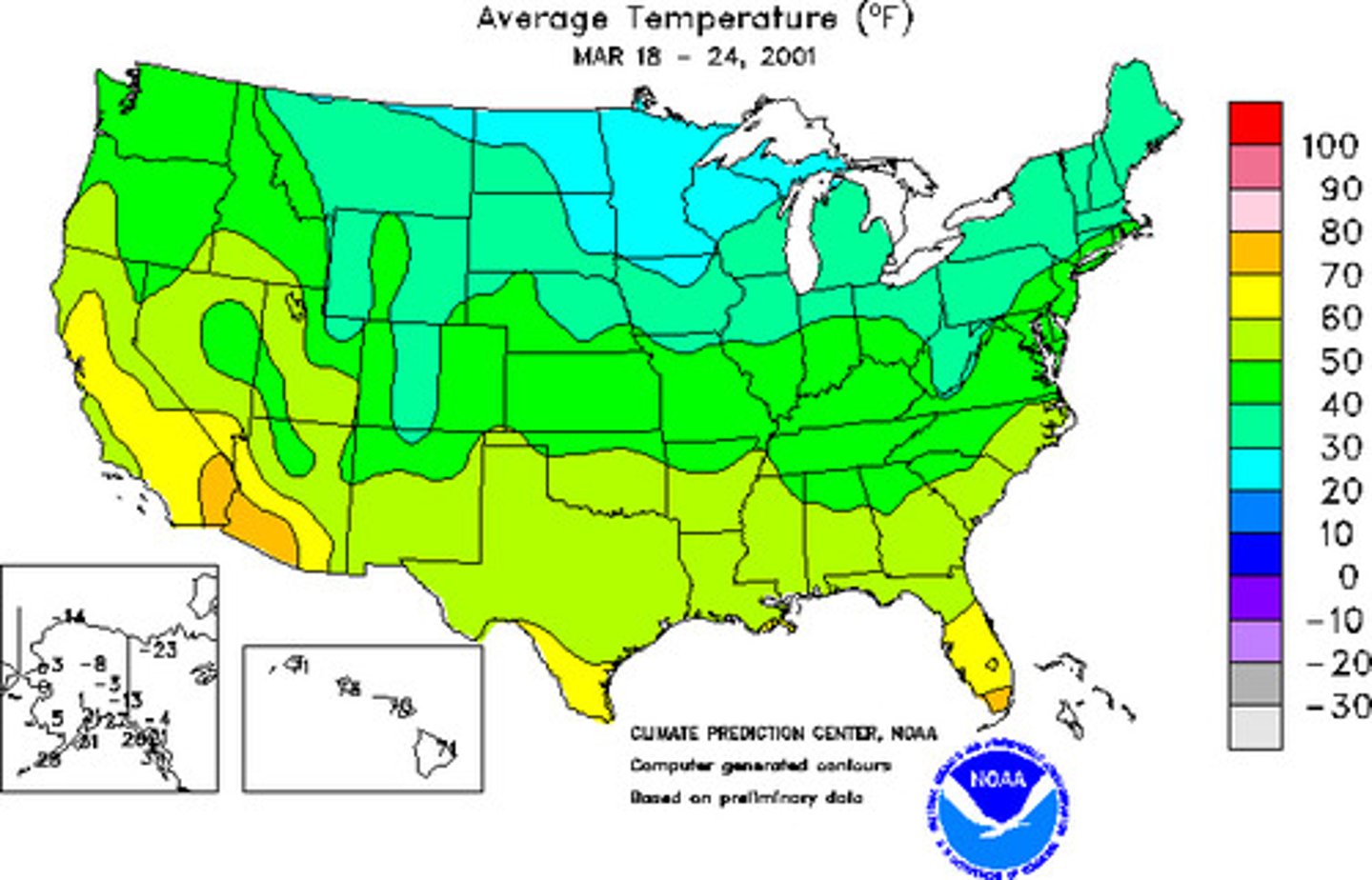
isoline map
A thematic map with lines that connect points of equal value.
remote sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite, aircraft, drone or other long-distance methods using a camera or other sensors
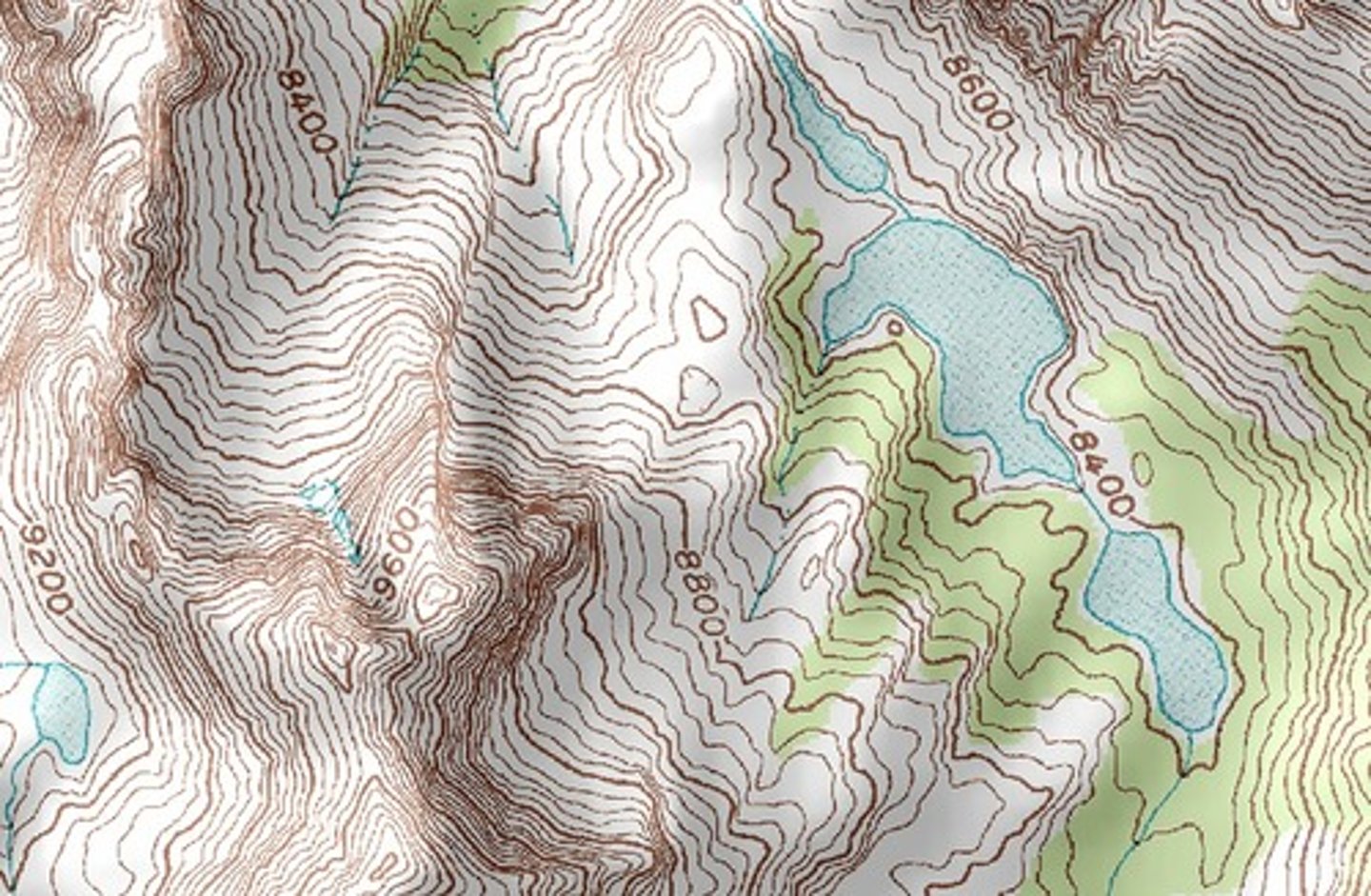
Topograpic map
the most common type of isoline map; points of equal elevation are connected on these maps, creating contours that depict surface features.
absolute direction
A compass direction such as north or south.
relative direction
Directions such as left, right, forward, backward, up, and down based on people's perception of places
cartographic scale
refers to the ratio between distance on a map and the actual distance on the Earth's surface; also called map scale
geographic Scale
the amount of territory that a map represents (global, national, regional, sub-national, county, city, neighborhood, etc)
scale of data / scale of analysis
The scale at which the data on a map is being disaggregated (separated/broken down) i.e. national, subnational, regional, state, city, county...