BE 450 PPT 7 Physical Properties - Exam 2
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
physical
what kind of properties are the following? mechanical, hydrophobicity, crystallinity, porosity, surface area, surface topography
chemical
what kind of properties are the following? amine groups, carboxyl groups, surface charge, elemental makeup, degradability
biocompatibility
what kind of properties are the following? toxicity, protein adsorption, hemo-compatibility, cellular response, animal studies
mechanical testing
systematic process used in engineering and material science to evaluate the physical and mechanical properties of materials, components, or products when subjected to various external forces, stresses and environmental conditions
mechanical testing
informs design decisions, ensures safety and reliability, critical in the development of new materials
tensile, compressive, shear
types of mechanical testing: elastic modulus, strain, ductility, toughness, ultimate strength etc.
torsional
types of mechanical testing: rotational force
cyclic
types of mechanical testing: repeated tensile or compressive forces
biaxial
types of mechanical testing: loading in 2 directions simultaneously
3 or 4 point bending
types of mechanical testing: both compressive and tension forces
rheological
types of mechanical testing: viscosity measurement
wear
types of mechanical testing: resistance to repeated mechanical forces
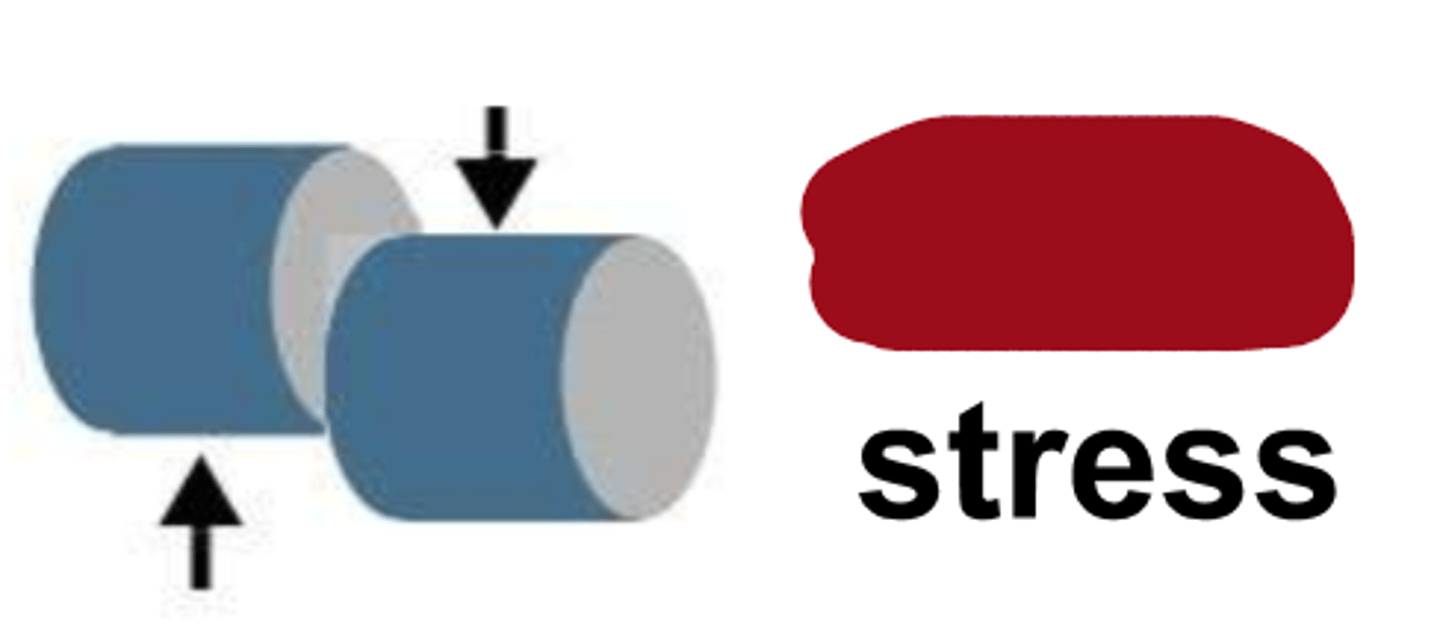
stress
mechanical testing basics: load applied to a certain cross-sectional area of an object
tensile
type of stress?
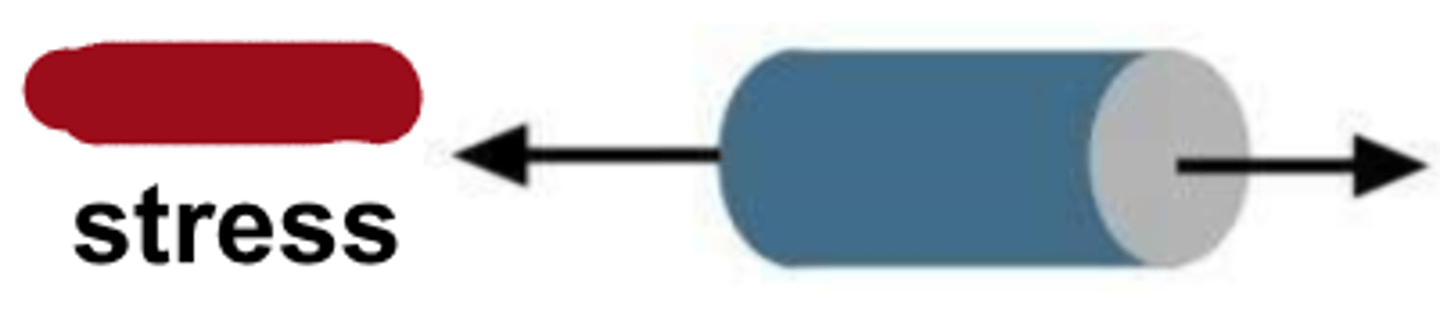
compressive
type of stress?
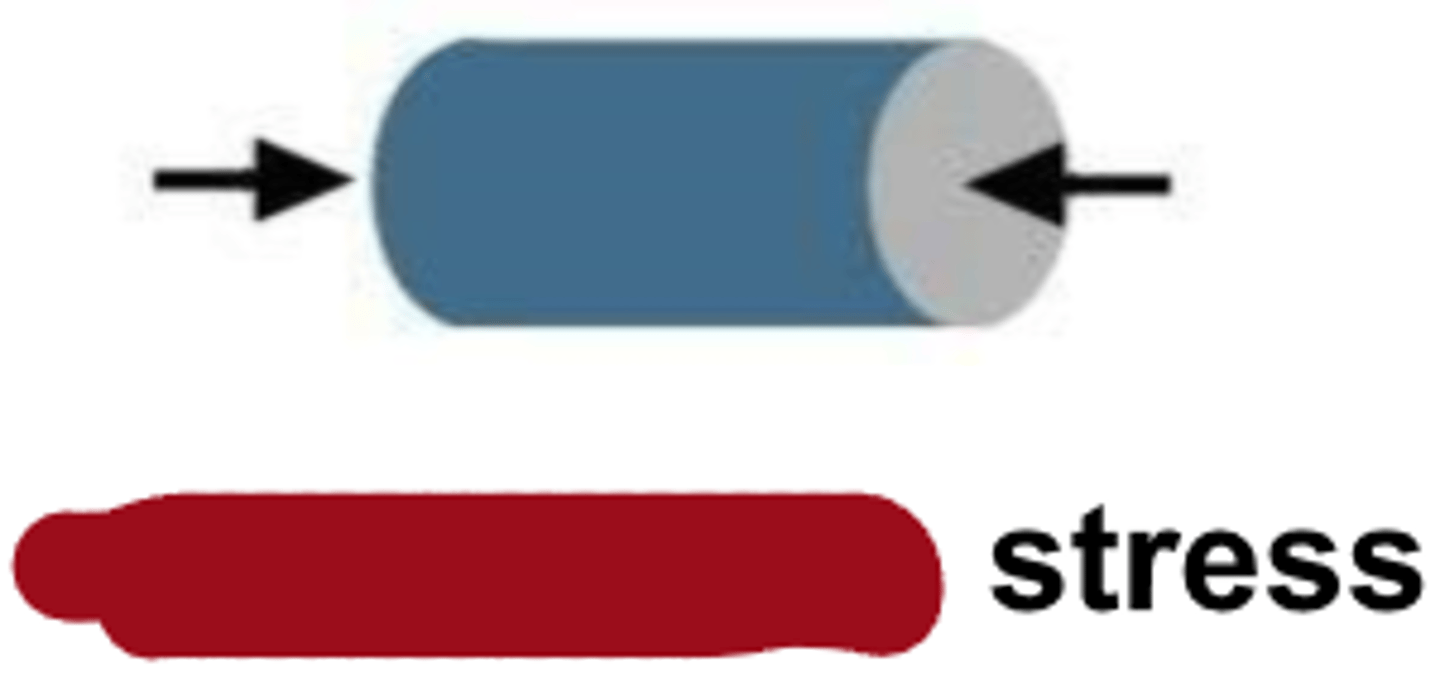
shear
type of stress?
torsional
type of stress?
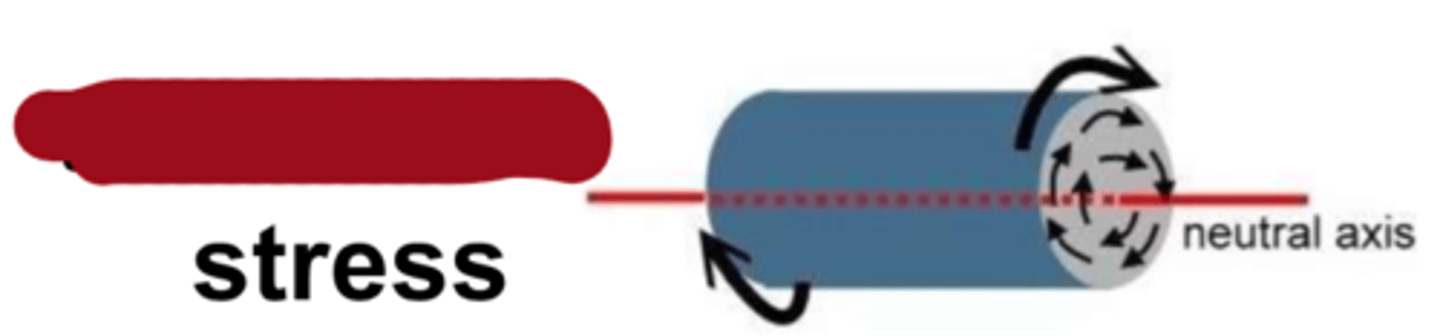
biaxial
type of stress?
bending
type of stress?
strain
mechanical testing basics: extent of deformation relative to its initial condition
normal strain
the ratio of the change in length to the original length
normal strain
equation for what?

shear strain
equation for what?
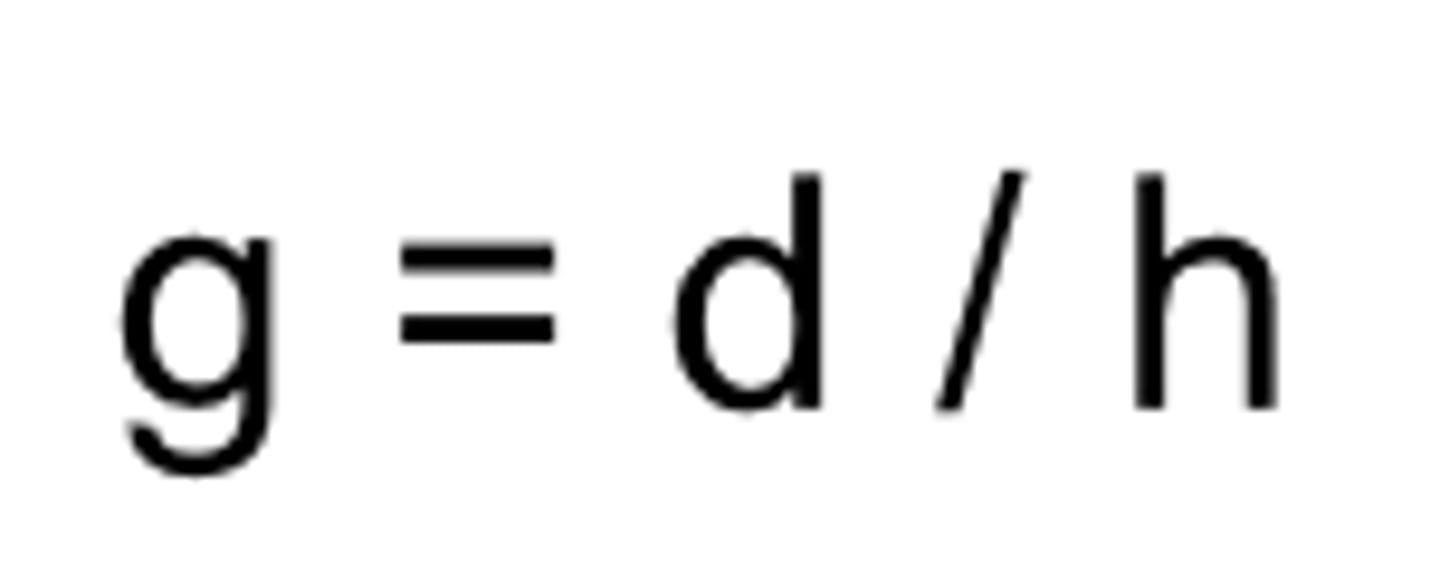
dimensionless
unit for normal stress
radians
unit for shear stress
positive
tensile strain is positive or negative?
negative
compressive strain is positive or negative?
stress
apply normal force
-> use area of subject
-> __________
strain
measure deformation
-> based on length change
-> _________
instron
typical mechanical testing device
Instron: interchangeable ______ cells
linear
Instron: very accurate _________ motion
fixtures
Instron: variety of clamps or _________ for many tests
fiducial
biaxial mechanical testing requires __________ markers
tissue
biaxial mechanical testing tracks movement of _________ under load
hooks
biaxial mechanical testing has ________ to immobilize sample
temperature
biaxial mechanical testing may require _______________ control and/or water bath
hydrophobicity
the property of being water-repellent
surface hydrophobicity
__________ _________________ is a crucial regulator of: cell adhesion, protein adsorption, drug delivery, surface degradation
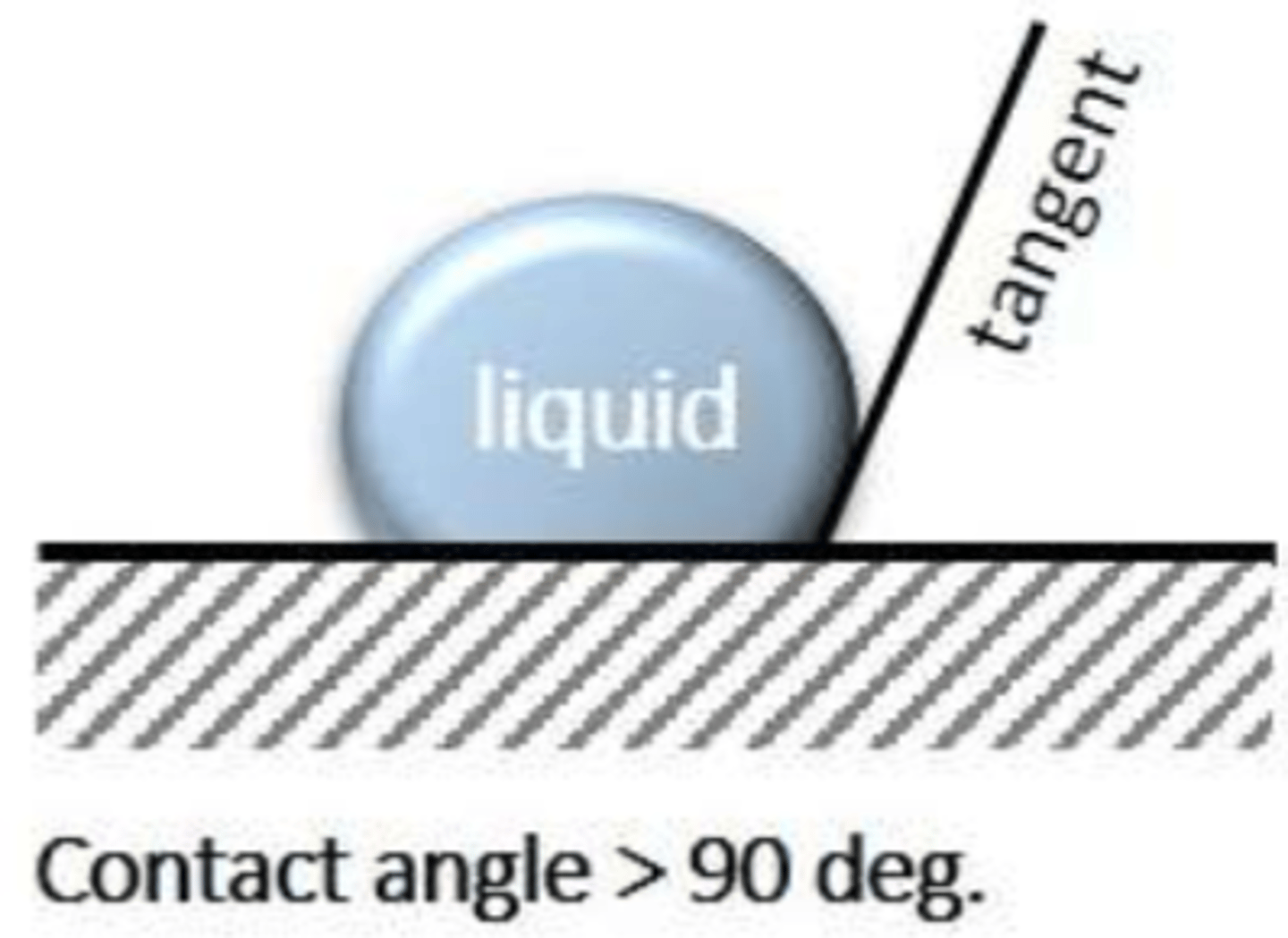
contact angle
interfacial tension present between a solid, a liquid, and a vapor
contact angle
the ___________ __________ is the angle between the tangent line and the solid surface
more
________ hydrophobic -> greater angle
hydrophobic
hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophilic
hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
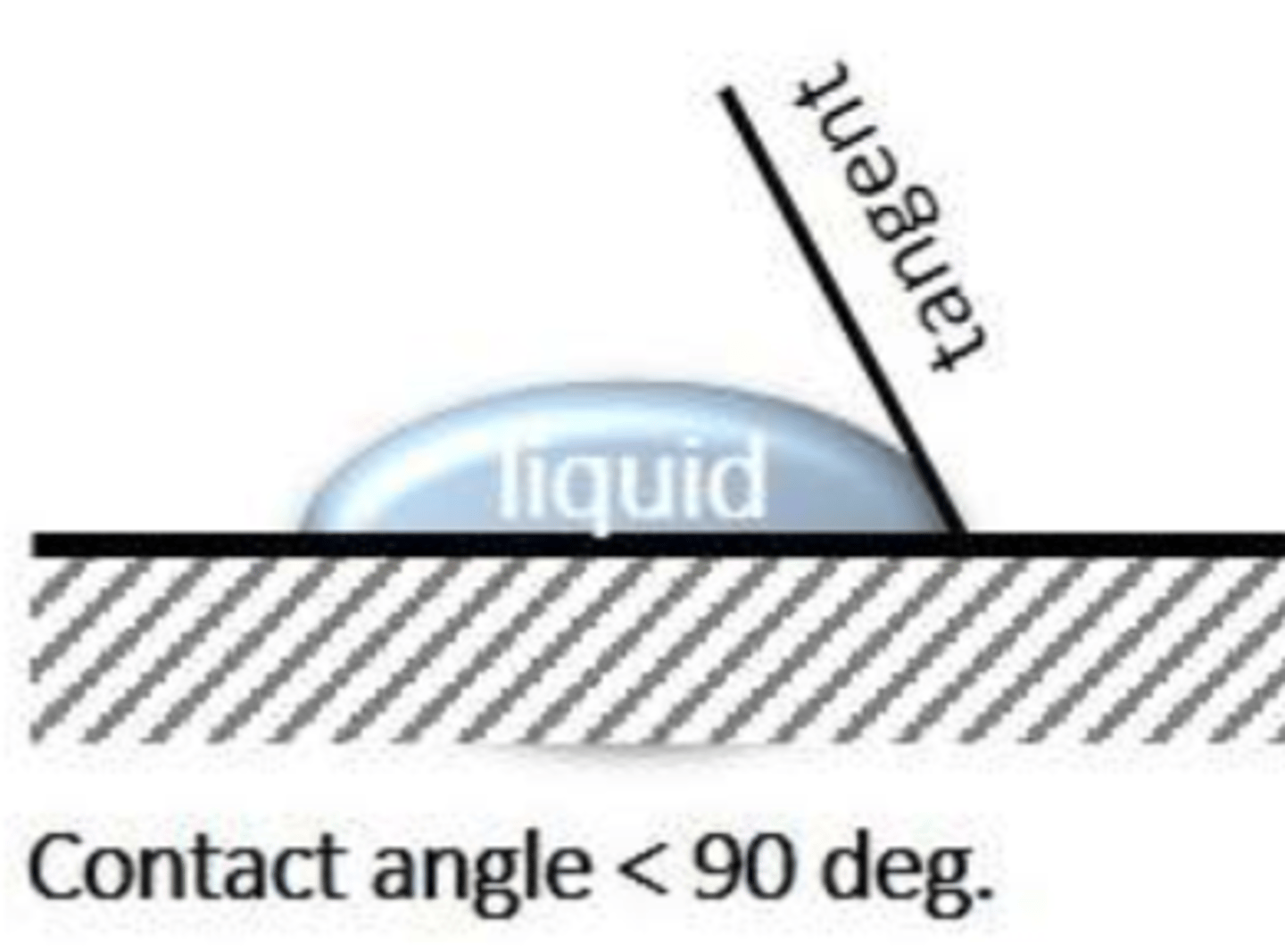
goniometer
hydrophobicity is measured by a contact angle ______________
mechanical, thermal, chemical
degree of crystallinity and the organization of the crystalline regions influence what 3 properties?
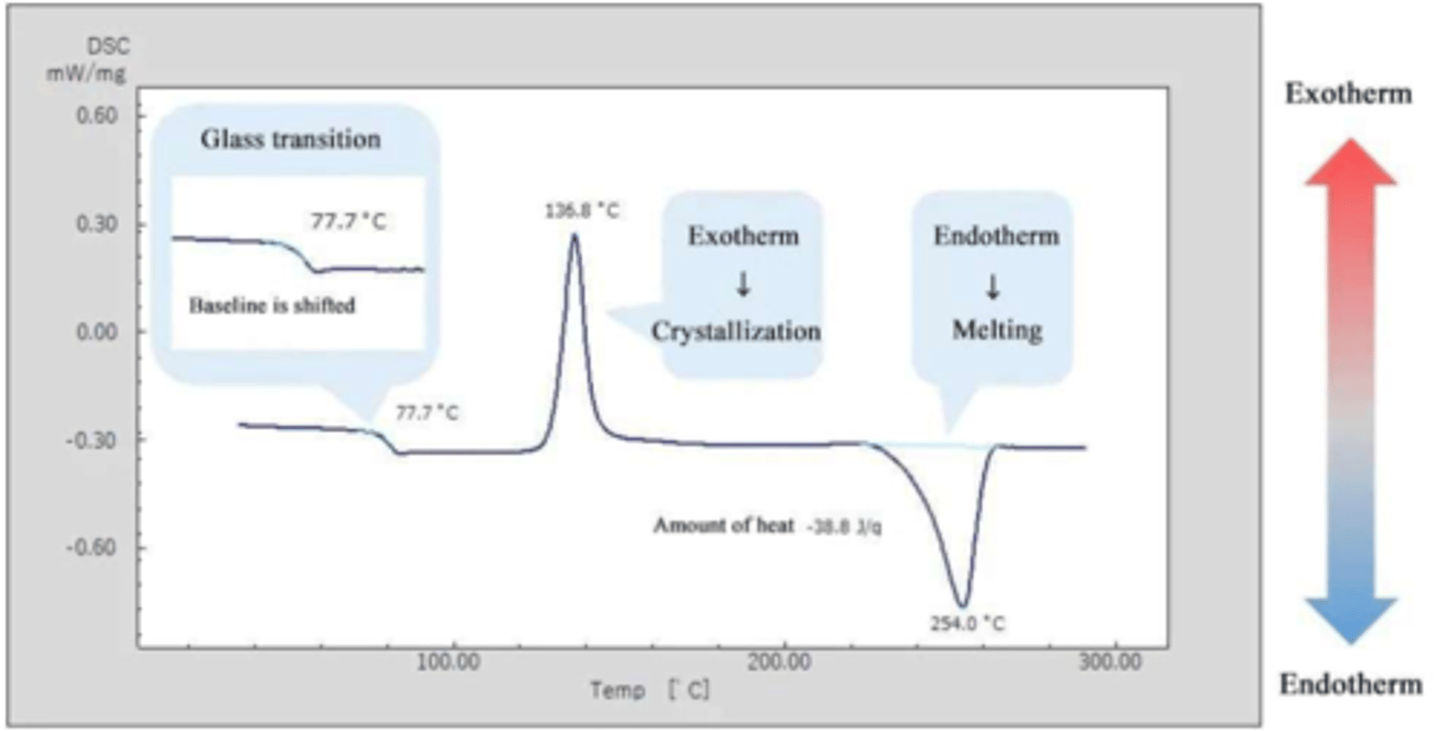
crystallinity
DSC - differential scanning calorimetry (degree of ______________)
Diffraction
XRD - X-Ray _____________ (organization of crystalline region)
order
DSC: crystals give ________ to a substance
heat
______ disrupts order (cause thermal transitions)
DSC
thermo-metric methods such as ______ can measure degree of crystallinity
amorphous
blue
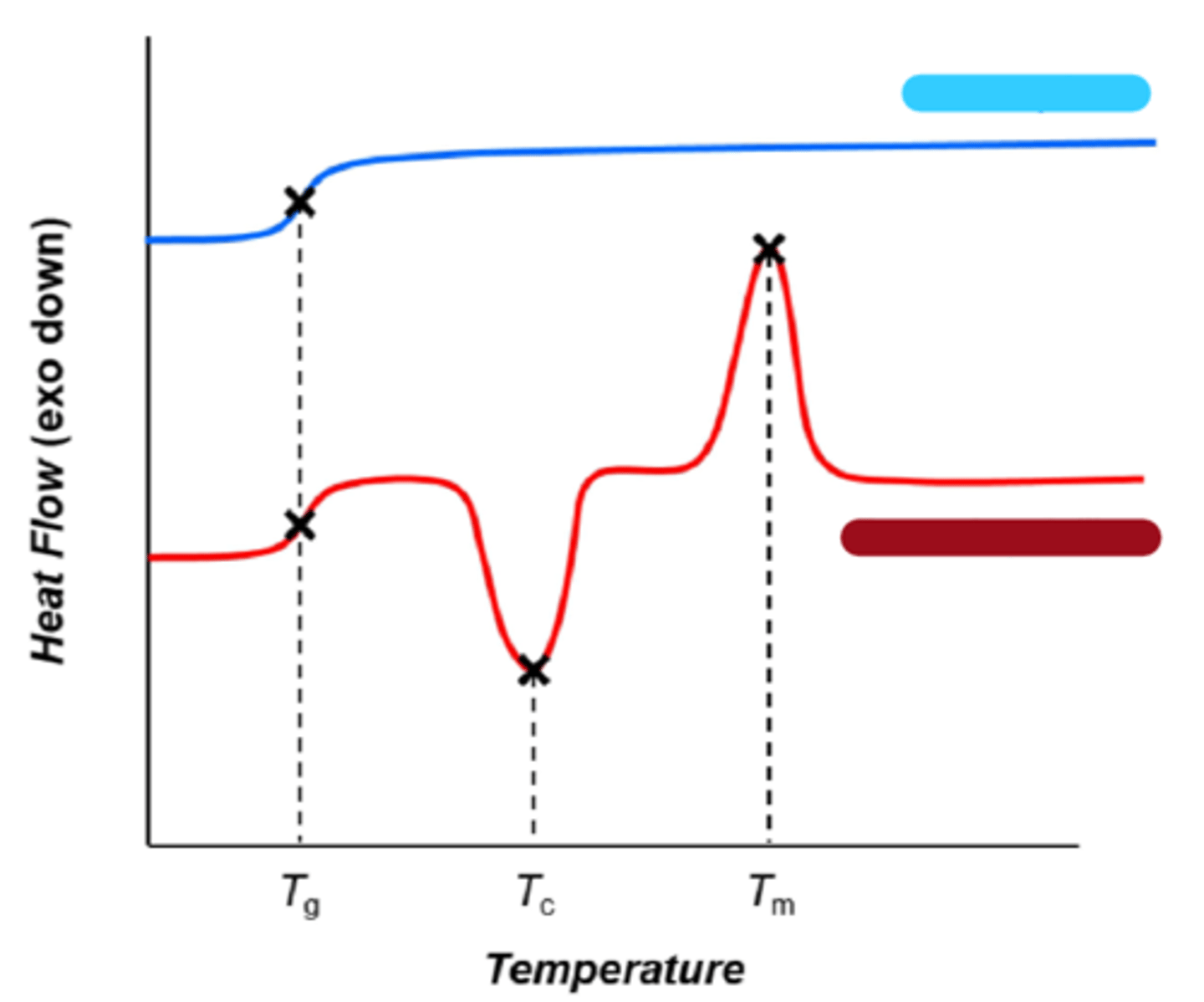
semicrystalline
red
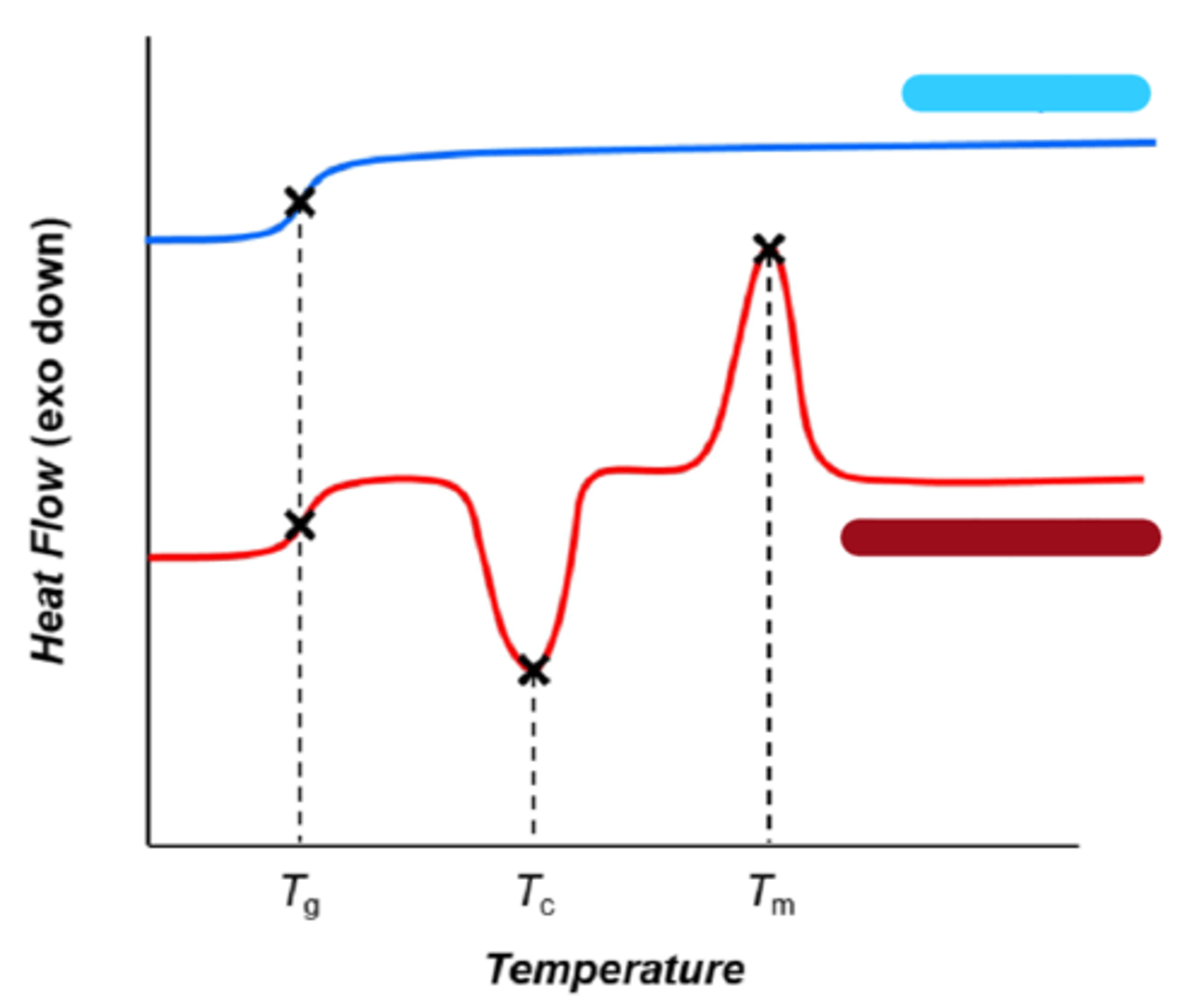
rubbery
at Tg, the sample becomes more __________
freely
polymer chains move around more _________
heat
at Tc crystal forms and releases ______
melted
at Tm crystal is ___________
energy/mass
Area under the curve is _______/______
melting
(deltaHm^o) - reference of ___________ for 100% crystalline material
atoms
XRD - examine show X-rays are diffracted from _______ in a material
structures
XRD - commonly used to determine ____________ of crystals (miller indices and cell size)
wavelength
X-ray _____________: 0.5-50 angstroms, similar to distance between atoms in a solid
diffraction
_____________ occurs when incident rays are scattered by atoms in a way to reinforce the wave
constructive, destructive
two types of diffraction that occurs during XRD
directions
XRD single particle: incident beams scattered uniformly in all ____________
constructively
XRD solid: scattered beams interfere _________________ in some directions, producing diffracted beams
pattern
XRD solid: random arrangements cause beams to randomly interfere, and no distinctive __________ is produced
regular
XRD crystalline material: regular pattern of crystalline atoms produces __________ diffraction pattern
crystal
XRD crystalline material: diffraction pattern gives information on ___________ structure
constructive
what type of interference?
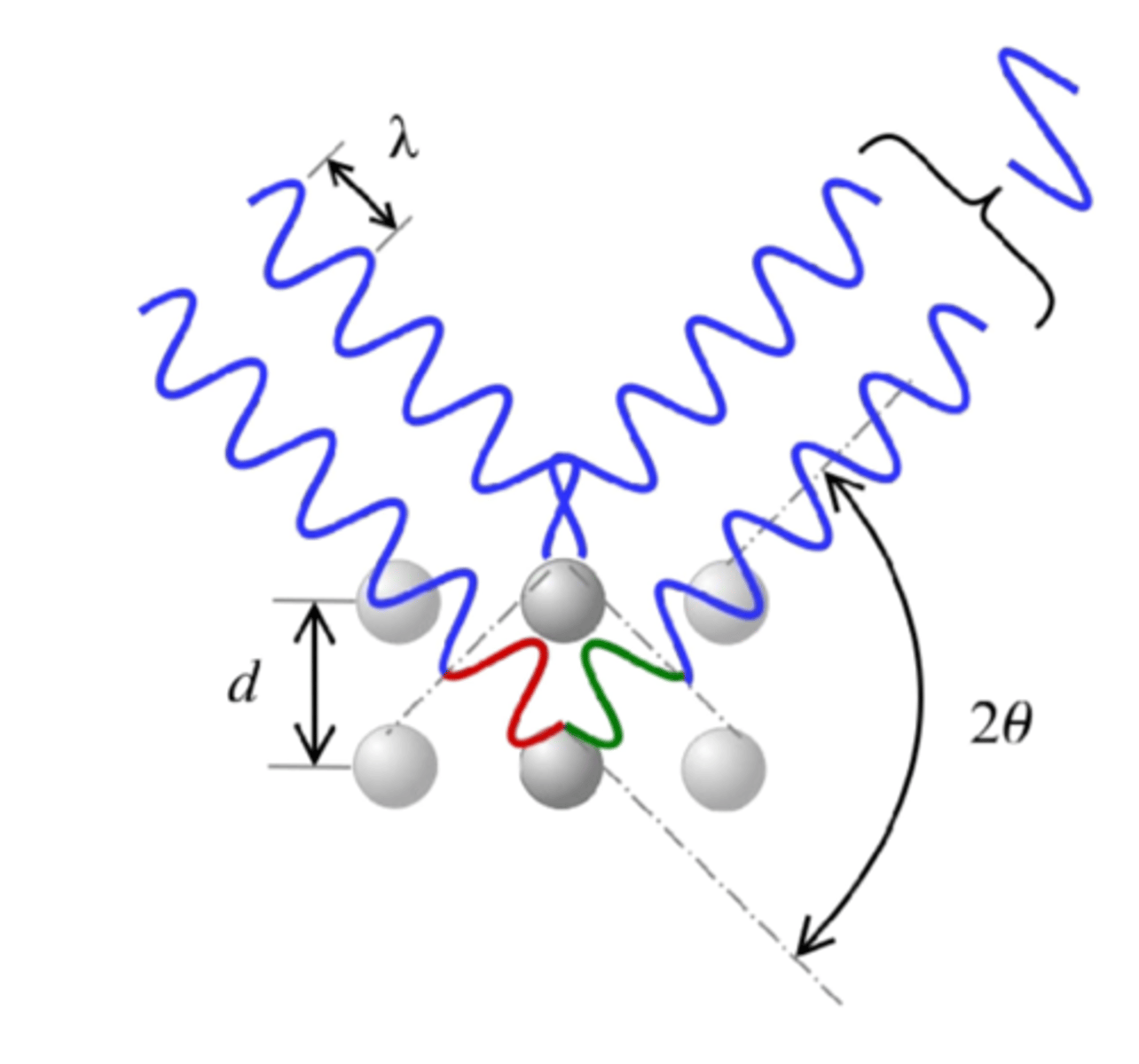
destructive
what type of interference?
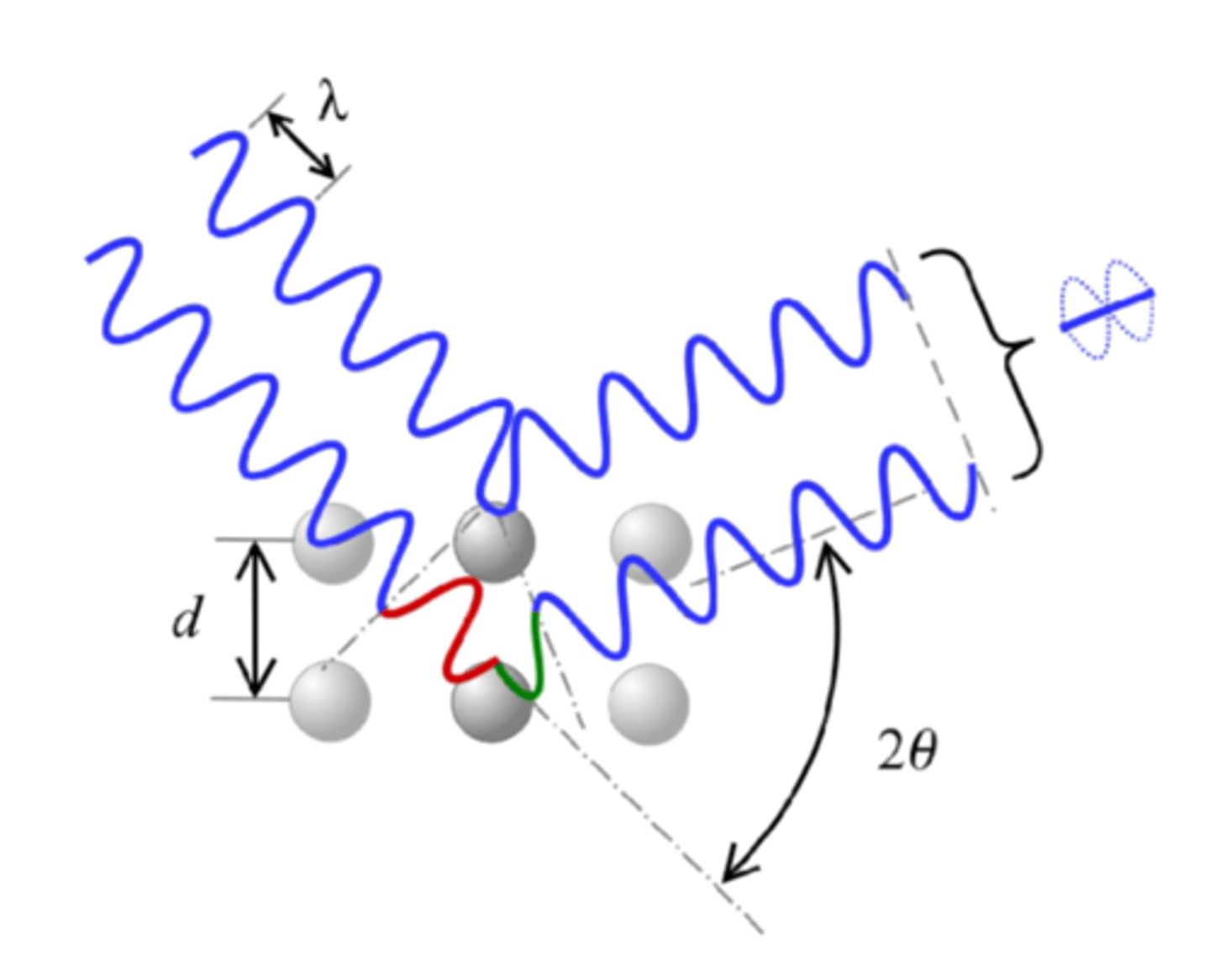
bragg's law
equation name?

d
lattice interplanar spacing of the crystal

theta
x-ray incidence angle (bragg angle)

lambda
wavelength of the characteristic x-rays

surface topography
affects host/implant interactions,
surface topography
can affect biocompatibility
surface topography
can influence functionalization
surface probe microscopy
surface topography: SPM meaning
scanning tunneling microscopy
surface topography: STM meaning
atomic force microscopy
surface topography: AFM meaning
scanning electron microcopy
surface topography: SEM meaning
weak
STM: based on quantum mechanics - _______ electric current between tip and sample
voltage
STM: current created by ___________ potential between sample and tip
heigh, current
STM: scanning maintains constant _______ or constant __________ to determine topography
attractive, repulsive
AFM: operates through _____________ and _____________ forces between tip and samples
laser
AFM: based on a _______ feedback system
resolution
AFM: tip size and shape, as well as scan speed determines _____________
ligand
AFM in biological application: coat tip with __________
binding
AFM in biological applications: interrogate surface to look for ___________ events
protein, antibody
AFM in biological applications: __________ interactions, _____________ binding events
integrins
AFM in biological applications: ligand binding to ____________ (force measurements of biochemical processes)
F
AFM for micromechanical testing: force
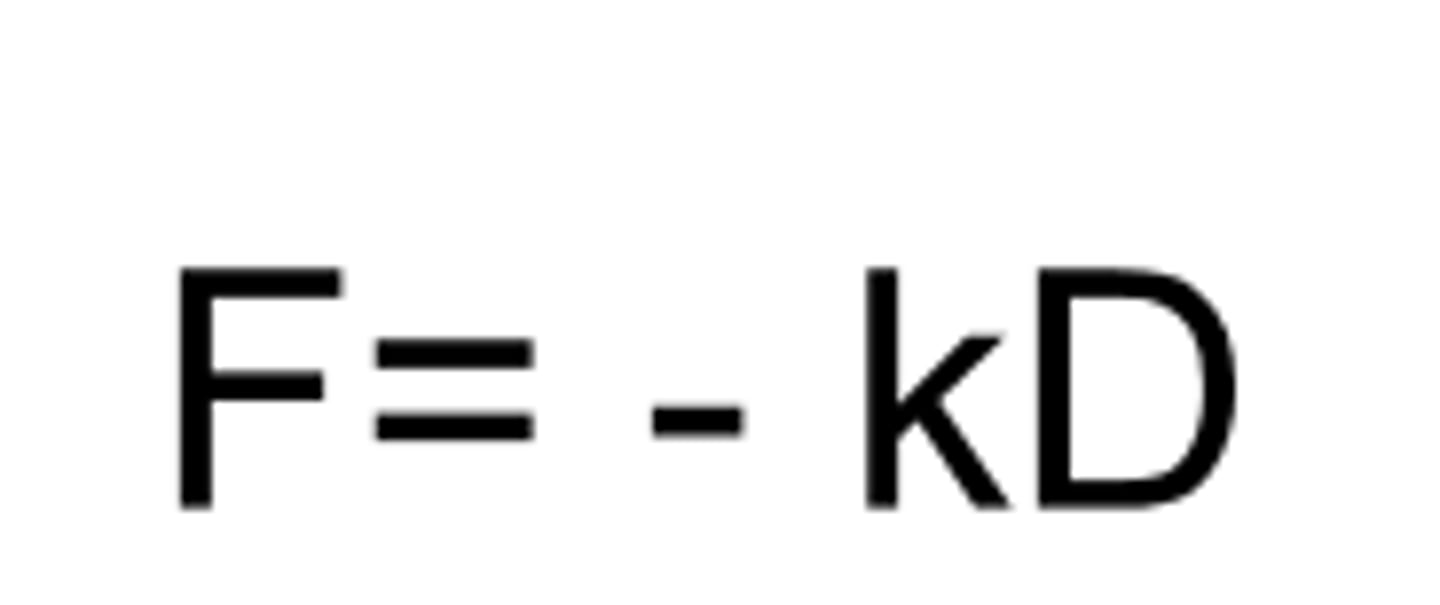
k
AFM for micromechanical testing: spring constant
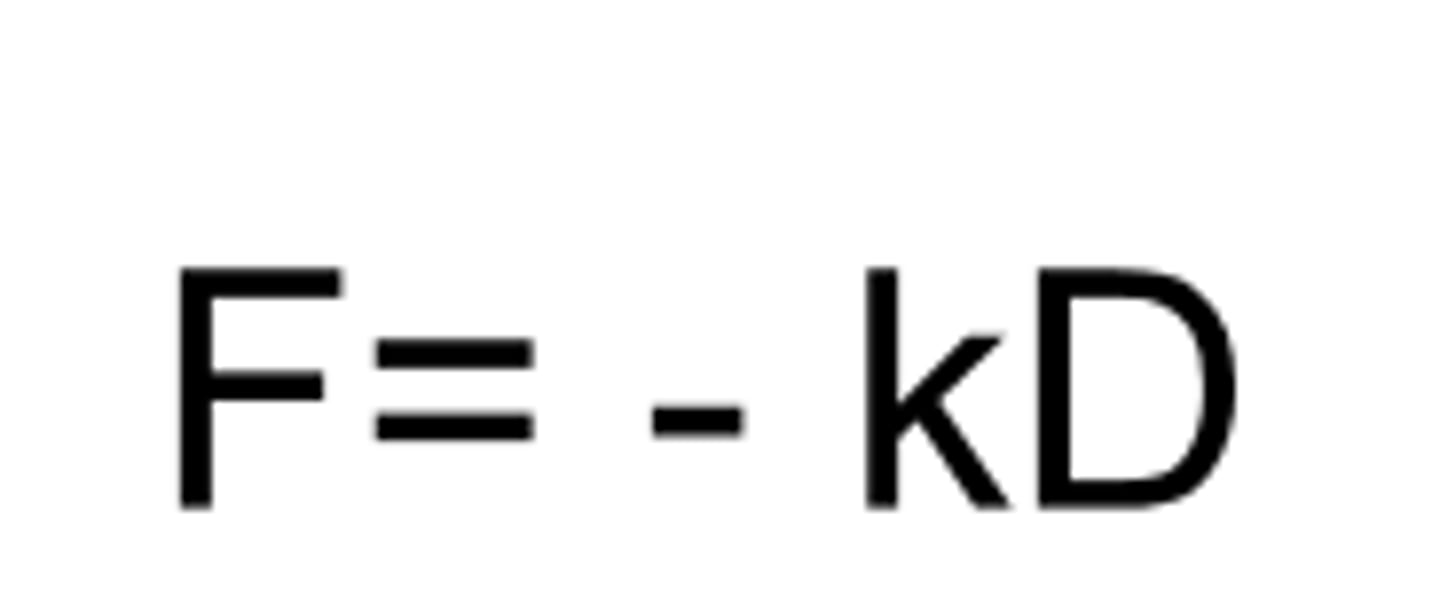
D
AFM for micromechanical testing: distance
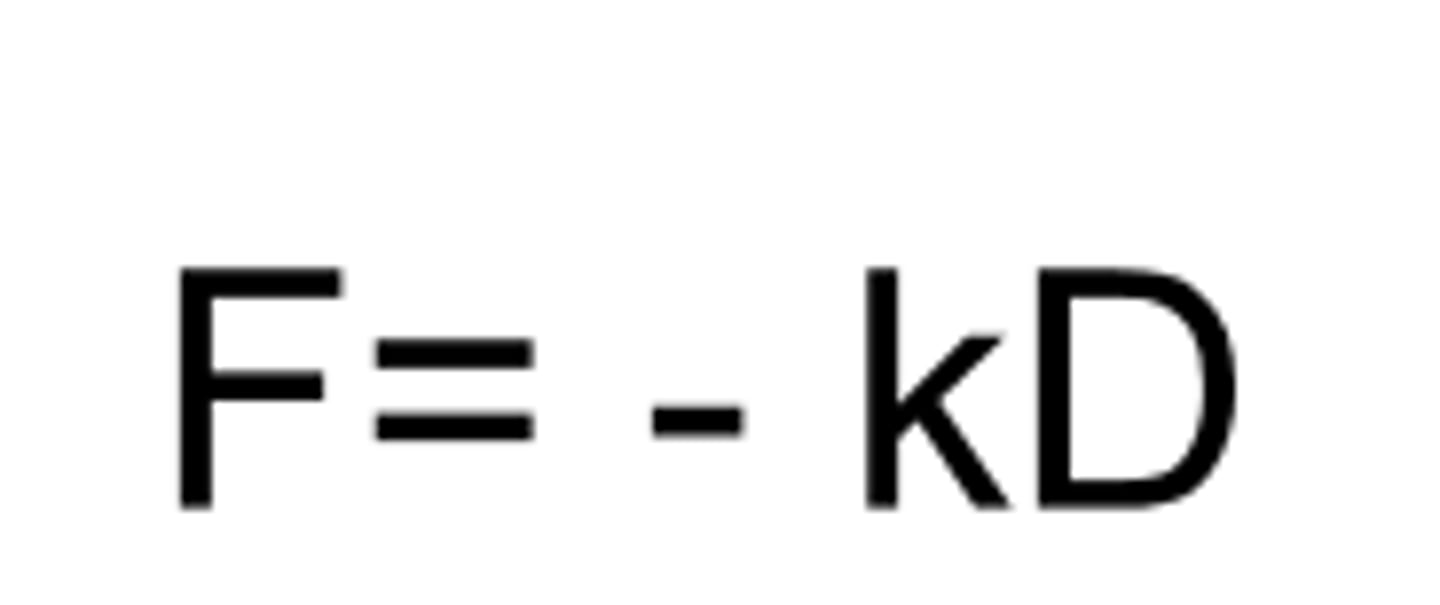
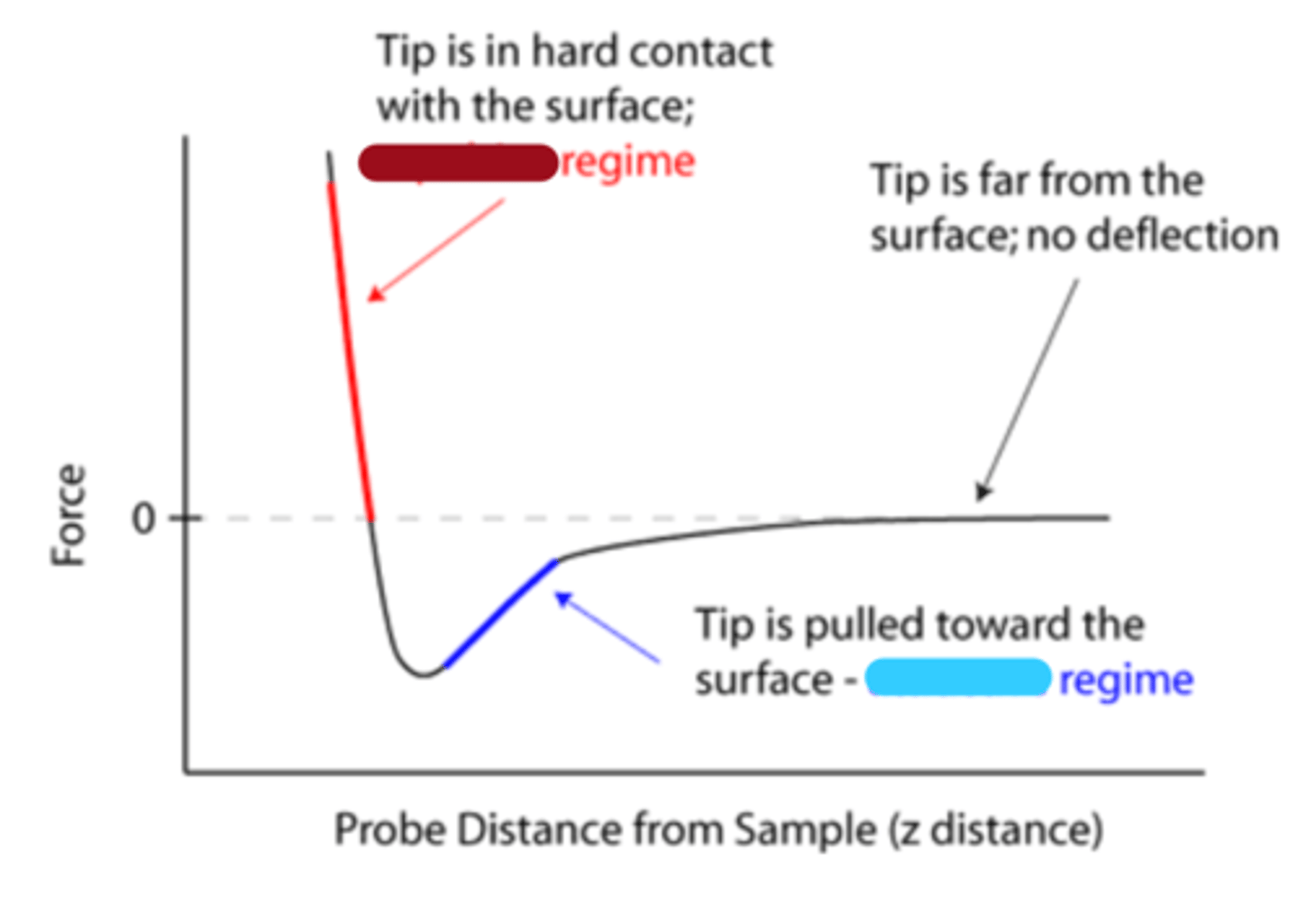
repulsive
AFM for micromechanical testing: red
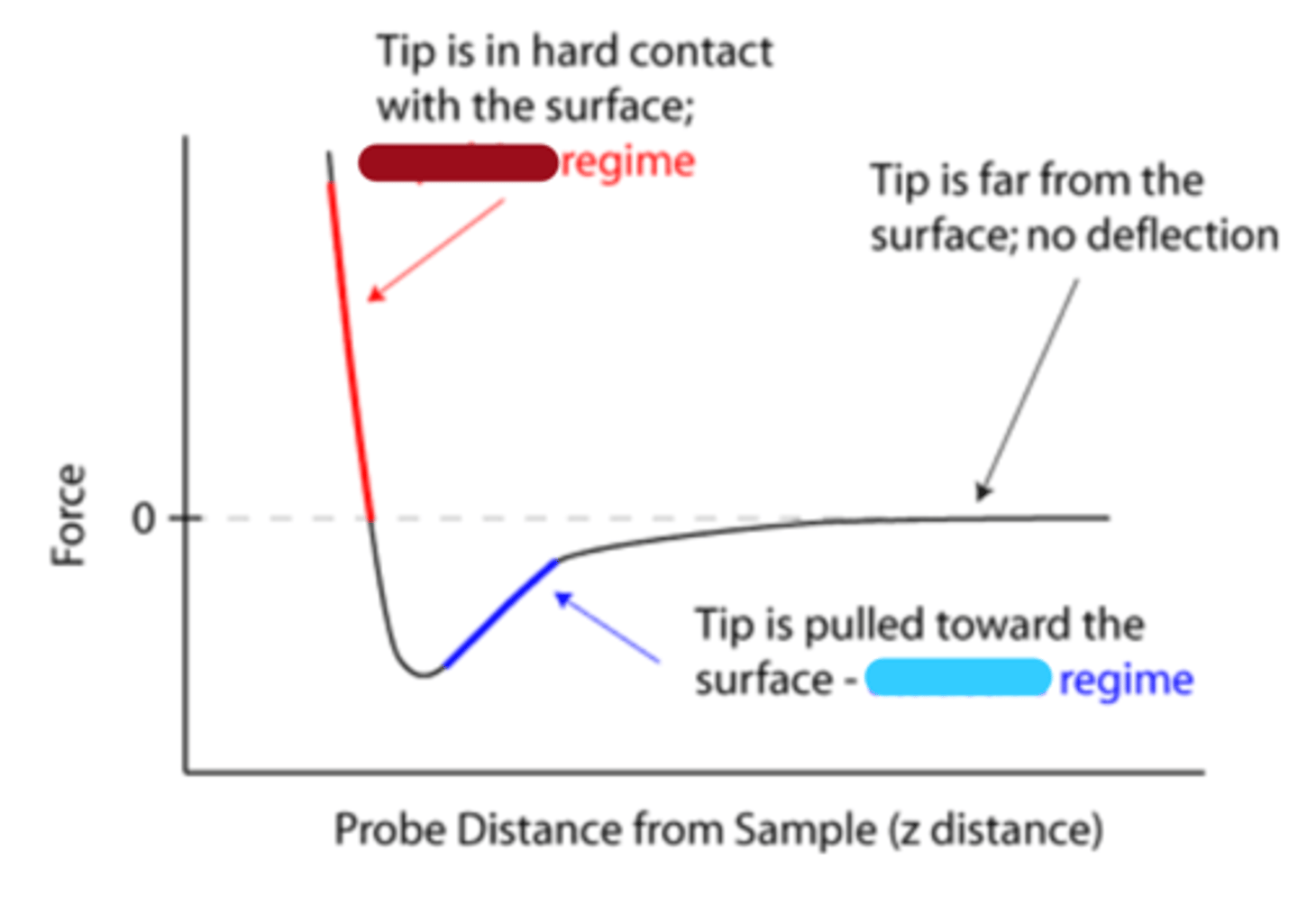
attractive
AFM for micromechanical testing: blue
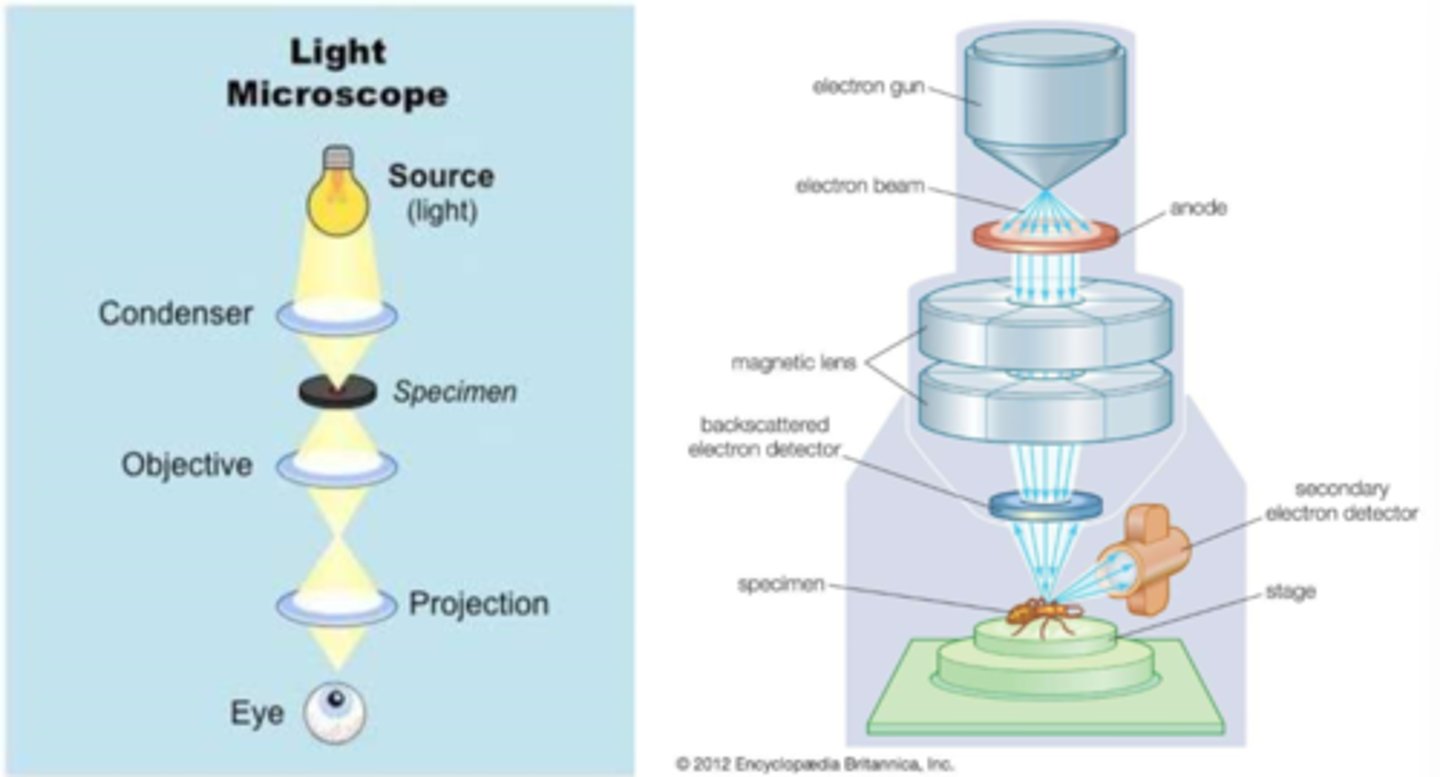
electrons
SEM: anode draws in ___________
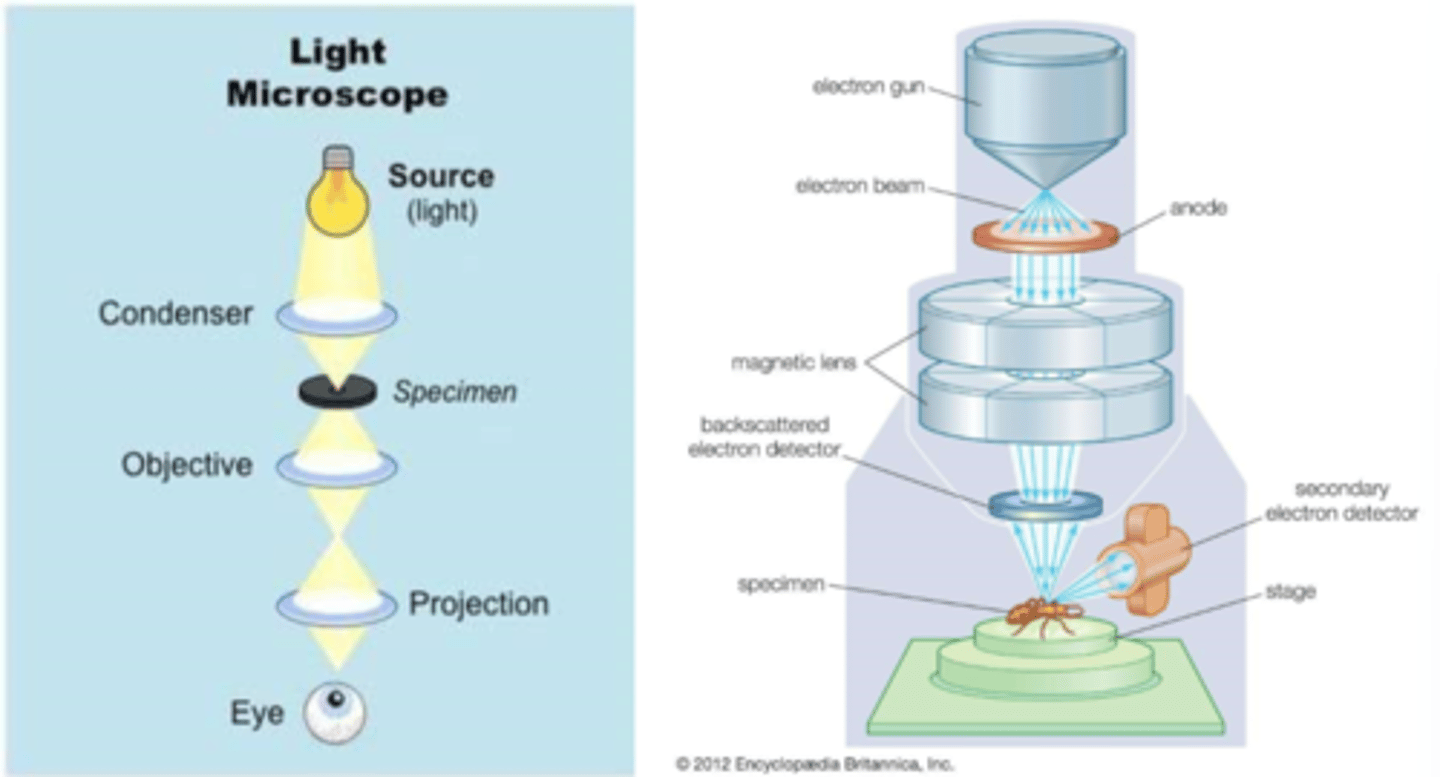
specimen
SEM: magnetic lens as a condenser to focus the electrons through the detector onto the ______________
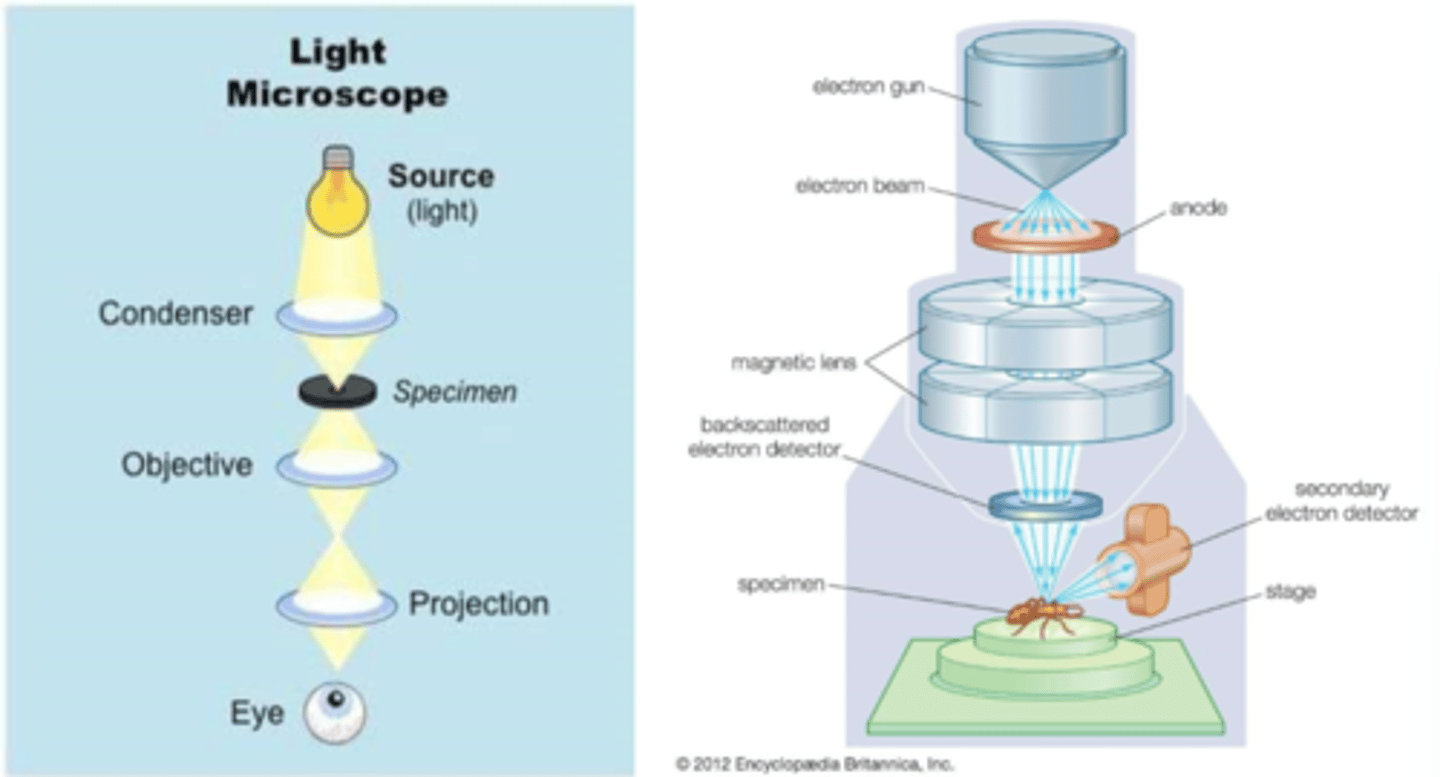
scan
SEM: stage moves to raster over _____ region