unit 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
1
New cards
Li +
Lithium ion
2
New cards
Na +
sodium ion
3
New cards
K +
potassium ion
4
New cards
NH4 +
ammonium ion
5
New cards
Ag +
silver ion
6
New cards
Mg 2+
Magnesium ion
7
New cards
Ca 2+
Calcium ion
8
New cards
Ba 2+
barium ion
9
New cards
Cd 2+
Cadmium ion
10
New cards
Zn 2+
Zinc ion
11
New cards
Cu +
copper (I) ion aka cuprous
12
New cards
Cu 2+
copper (II) ion aka cupric
13
New cards
Hg2 1+
mercury (i) ion
14
New cards
Hg2 2+
mercury (II) ion
15
New cards
Mn 2+
Manganese (II) ion
16
New cards
Co 2+
cobalt (II) ion
17
New cards
Ni 2+
nickel (II) ion
18
New cards
Pb 2+
lead (II). ion
19
New cards
Sn 2+
tin (II) ion aka stannous
20
New cards
Sn 4+
tin (IV) ion (stannic)
21
New cards
Fe 2+
ion (II) ion (ferrous)
22
New cards
Fe 3+
iron (III) ion aka ferric
23
New cards
Al 3+
aluminum ion
24
New cards
Cr 3+
chromium (III) ion
25
New cards
F-
fluoride ion
26
New cards
Cl -
Chloride ion
27
New cards
Br -
bromide ion
28
New cards
I -
iodide ion
29
New cards
OH-
hydroxide ion
30
New cards
CN-
cyanide ion
31
New cards
ClO-
hypochlorite ion
32
New cards
ClO2 -
chlorite ion
33
New cards
Cl03 -
chlorate ion
34
New cards
Cl04 -
perchlorate
35
New cards
CH3COO-
acetate ion
36
New cards
C2O4 2-
oxalate ion
37
New cards
MnO4 -
permanganate
38
New cards
NO2 -
nitrite ion
39
New cards
NO3 -
nitrate ion
40
New cards
SCN -
thicyanate
41
New cards
CN -
cyanide
42
New cards
OCN -
cyanate
43
New cards
N 3-
nitride
44
New cards
O 2-
oxide ion
45
New cards
S 2-
sulfide ion
46
New cards
HSO3 -
bisulfite ion
47
New cards
HSO4 -
bisulfate ion
48
New cards
HSO4 -
bisulfate ion
49
New cards
SO4 2-
sulfate ion
50
New cards
PO4 3-
phosphate ion
51
New cards
HCO3-
bicarbonate
52
New cards
CO3 2-
carbonate ion
53
New cards
CrO4 2-
chromate ion
54
New cards
Cr2O7 2-
dichromate ion
55
New cards
representative elements
group a; assigned to s or p orbital
56
New cards
d-transition
group b; assigned to a d orbital
57
New cards
f-transition (inner transition orbitals)
assigned to f orbtial
58
New cards
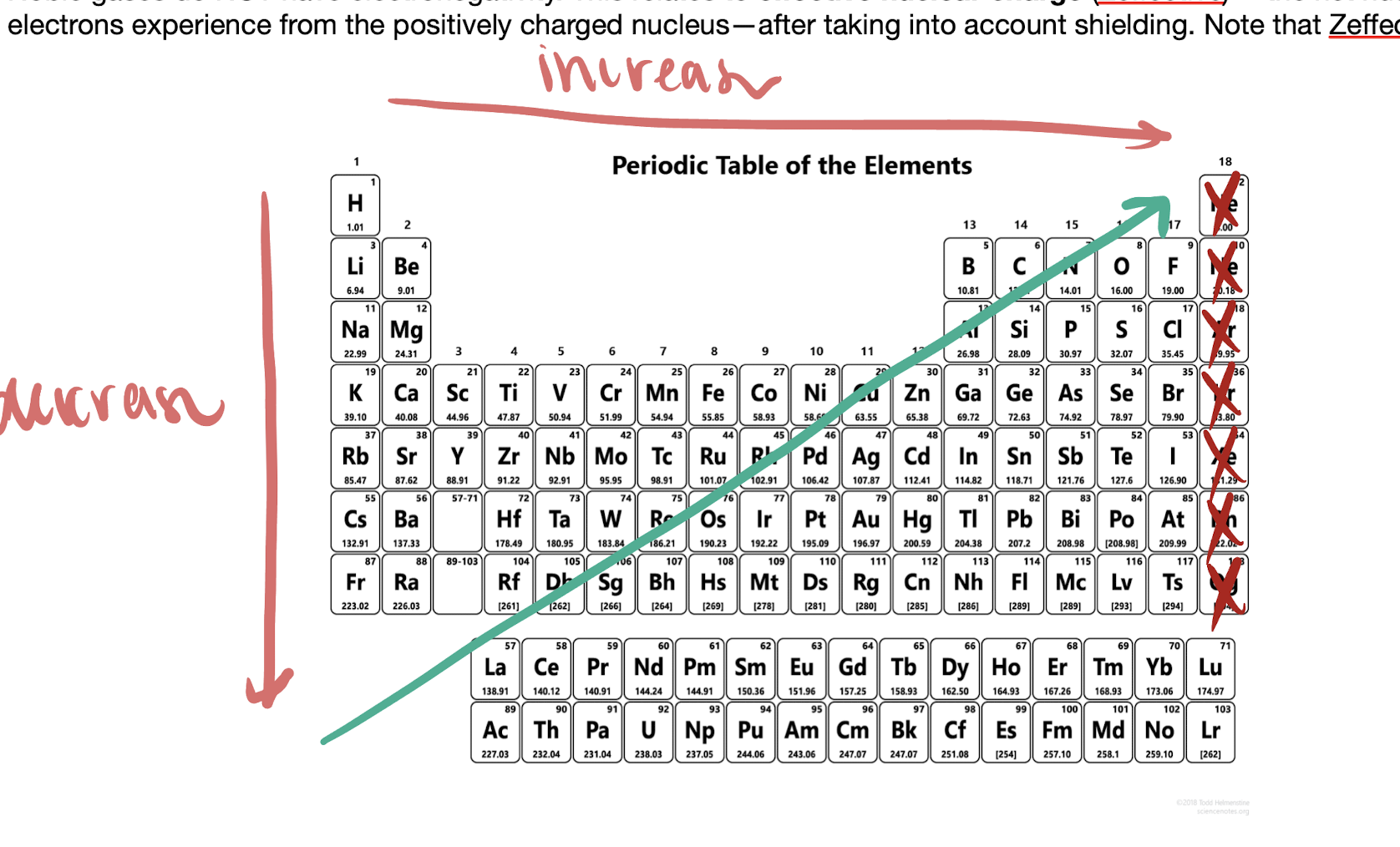
effective nuclear charge
net nuclear charge after taking into consideration shielding
\
always less than Zactual
\
always less than Zactual
59
New cards
atomic radii
size of atom
60
New cards
ionic radius
the size of an atom compared to an ion of the same element
\
smallest to largest is cation → neutral → anion
\
smallest to largest is cation → neutral → anion
61
New cards
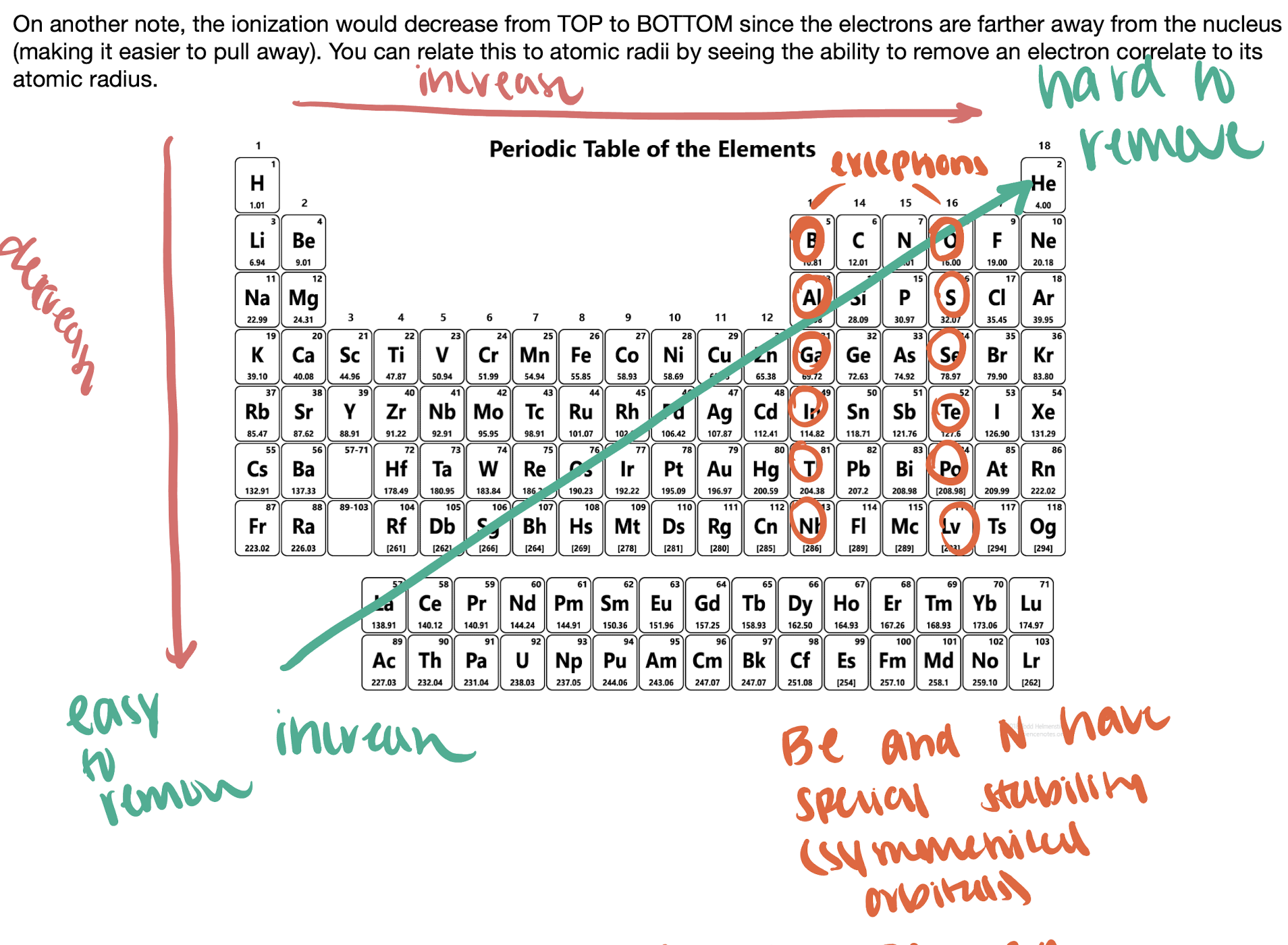
first ionization energy
HINT: nazi wanted to remove jews → niza remove
\
the minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from an isolated atom in the gas phase
\
EXCEPTIONS: group III and IV due to their electron configurations having full pairs except for one
\
the minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from an isolated atom in the gas phase
\
EXCEPTIONS: group III and IV due to their electron configurations having full pairs except for one
62
New cards
second ionization energy
energy required to remove second electron
\
ALWAYS greater than the first ionization energy due to the fact that removing an electron from a cation is considerably more difficult since the electrons are most tightly bounded
\
ALWAYS greater than the first ionization energy due to the fact that removing an electron from a cation is considerably more difficult since the electrons are most tightly bounded
63
New cards
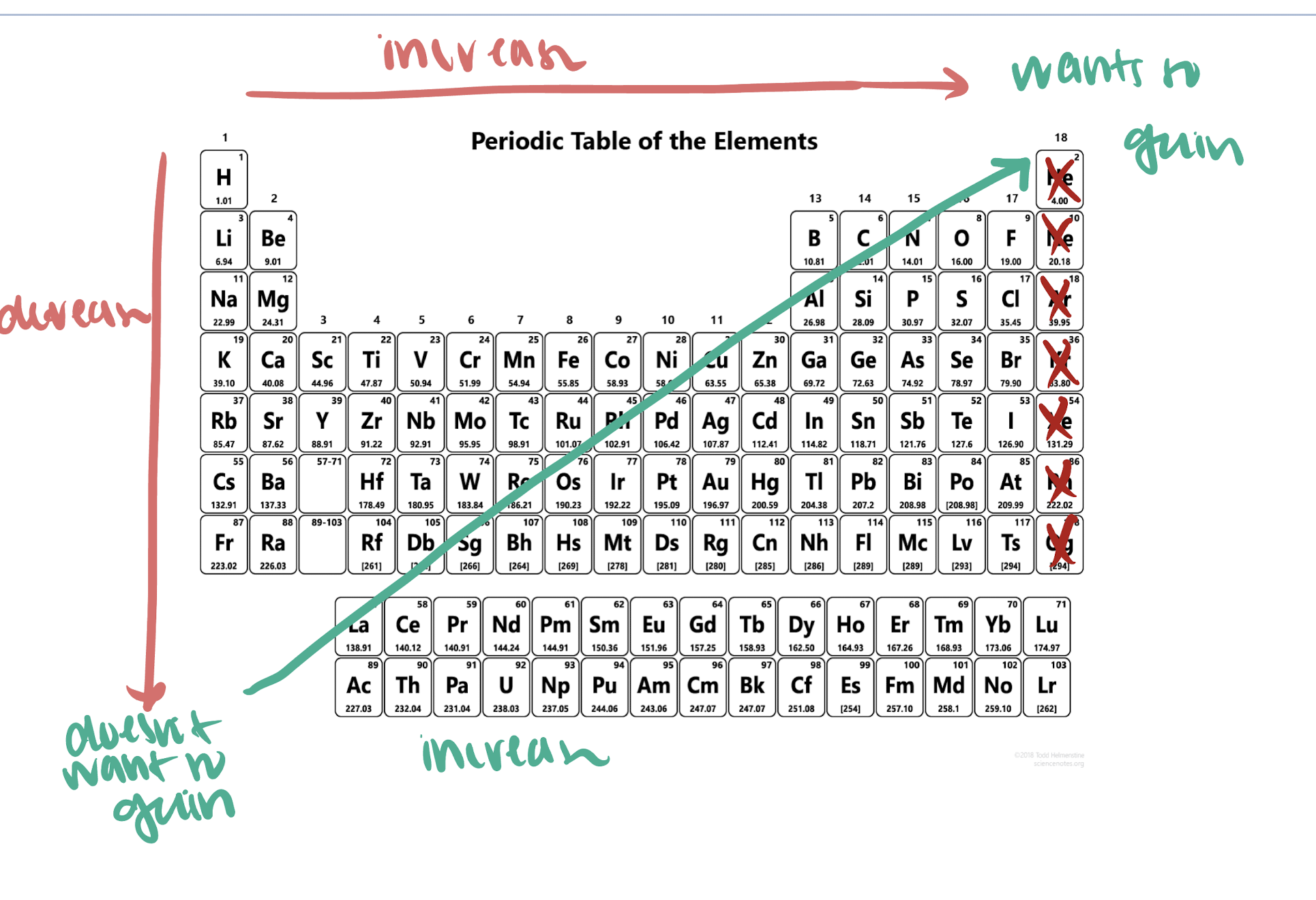
electron affinity
energy associated when an electron is added to an atom in the gas phase
64
New cards
electronegativity
the ability for an atom is hold an electron tightly to the nucleus
65
New cards
isolelectronic
elements and ions that have the same electron configuration and number of electrons
\
size will go from low atomic # → higher atomic #
(higher atomic # will have more protons, therefore holding the electrons tighter to the nucleus)
\
size will go from low atomic # → higher atomic #
(higher atomic # will have more protons, therefore holding the electrons tighter to the nucleus)
66
New cards
exception when losing electrons for transition metals
lose (n-1)d orbitals before ns
67
New cards
forming a bond
energy released
\
exothermic
\
E < 0
\
exothermic
\
E < 0
68
New cards
breaking a bond
energy absorbed
\
endothermic
\
E > 0
\
endothermic
\
E > 0
69
New cards
lattice energy
energy released from the formation of gas phase elements to a crystallic state (a lattice strcture)…REMEMBER FORMING BOND → ENERGY RELEASED
\
uses Coulomb’s law
\
uses Coulomb’s law

70
New cards
heat of formation
energy released from the formation of bond from its NATURAL state
71
New cards
diatomic molecules
**H**ave
**N**o
**F**ear
**O**f
**I**ce
**C**old
__**B**____ee__**r**
**N**o
**F**ear
**O**f
**I**ce
**C**old
__**B**____ee__**r**
72
New cards
melting point
correlates with lattice energy
73
New cards
ionic bond
formed through the electrostatic attraction between ions
\
TRANSFERRED from one species to another
\
want to achieve noble gas configuration
\
usually formed when the electronegativity difference is large
\
metal + nonmetal (metal more IE and nonmetal more EA)
\
TRANSFERRED from one species to another
\
want to achieve noble gas configuration
\
usually formed when the electronegativity difference is large
\
metal + nonmetal (metal more IE and nonmetal more EA)
74
New cards
formula unit
ionic compound with ions in lowest ratio
75
New cards
covalent bond
compound formed through the sharing of electrons
\
formed between nonmetals (similar EN)
\
formed between nonmetals (similar EN)
76
New cards
ionic compound
solids at room temp
77
New cards
ionic compound
>400 degrees C
78
New cards
ionic compound
insoluble in non-polar solvents
79
New cards
ionic compound
good conductor in molten and aqueous
80
New cards
ionic compound
network of cations and anions held by electrostatic forces
81
New cards
covalent compound
can be solid, liquid, or gases
82
New cards
covalent compound
83
New cards
covalent compound
soluble in non-polar solvents
84
New cards
covalent compound
not good conductors in any state (due to the fact that there are no charges in the compound)
85
New cards
covalent compound
form individual molecules
86
New cards
bond length
distance between the chemical bonds and indicates stability within a compound
87
New cards
hydrogen
needs 2 e- to achieve stable state
88
New cards
beryllium
needs 4 e- to achieve a stable state
89
New cards
boron
needs 6- to achieve a stable state
90
New cards
aluminum
needs 6- to achieve a stable state
91
New cards
formal charge
atomic # - number of assigned electrons
92
New cards
resonance
same arrangement of atoms but different arrangement of electrons
\
involves delocalized electrons
\
involves delocalized electrons
93
New cards
below 3
can have expanded octet rule
94
New cards
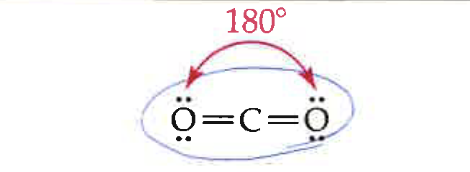
2
0
linear
linear
180 degrees
0
linear
linear
180 degrees
\# of rhed ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
95
New cards
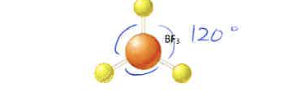
3
0
trigonal planar
trigonal planar
120 degrees
0
trigonal planar
trigonal planar
120 degrees
\# of rhed ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
96
New cards
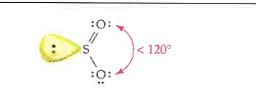
3
1
trigonal planar
bent
1
trigonal planar
bent
\# of rhed ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
97
New cards
4
0
tetrahedral
tetrahedral
109\.5 degree
0
tetrahedral
tetrahedral
109\.5 degree
\# of rhed ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
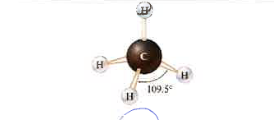
98
New cards
4
1
tetrahedral
trigonal pyramidal
109\.5 degrees
1
tetrahedral
trigonal pyramidal
109\.5 degrees
\# of rhed ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
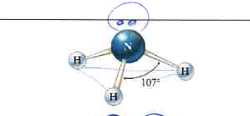
99
New cards
4
2
tetrahedral
bent
2
tetrahedral
bent
\# of rhed ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
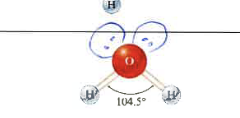
100
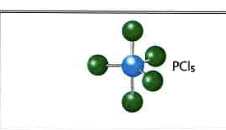
New cards
5
0
trigonal bipryamidal
90 degrees, 120 degrees
0
trigonal bipryamidal
90 degrees, 120 degrees
\# of rhed ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???
\# of lone pairs ???
electronic geometry ???
molecular geometry ???
bond angle ???