Part 6 - Strains, Delocalizations, Inductive Effects
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
In order to achieve stability, electrons repel. The more separate the electrons are to each other, the more stable they are.
a. True
b. False
a. True
Stability dictates reactivity. The more stable, the more reactive.
a. True
b. False
b. False
*The more stable, the less reactive.
Unwanted disturbance/deviation from ideal bond angles.
a. Strain
b. Delocalization
c. Resonance
d. Inductive effects
a. Strain
Bond angle of a planar 3-membered cyclic hydrocarbon.
a. 60°
b. 90°
c. 120°
d. 180°
a. 60°
Bond angle of a planar 4-membered cyclic hydrocarbon.
a. 60°
b. 90°
c. 120°
d. 180°
b. 90°
Bond angle of a planar 5-membered cyclic hydrocarbon.
a. 60°
b. 90°
c. 120°
d. 180°
d. 180°
Bond angle of a planar 6-membered cyclic hydrocarbon.
a. 60°
b. 90°
c. 120°
d. 180°
c. 120°
5 and 6 membered rings are relative more table than 3 and 4 membered rings.
a. True
b. False
a. True
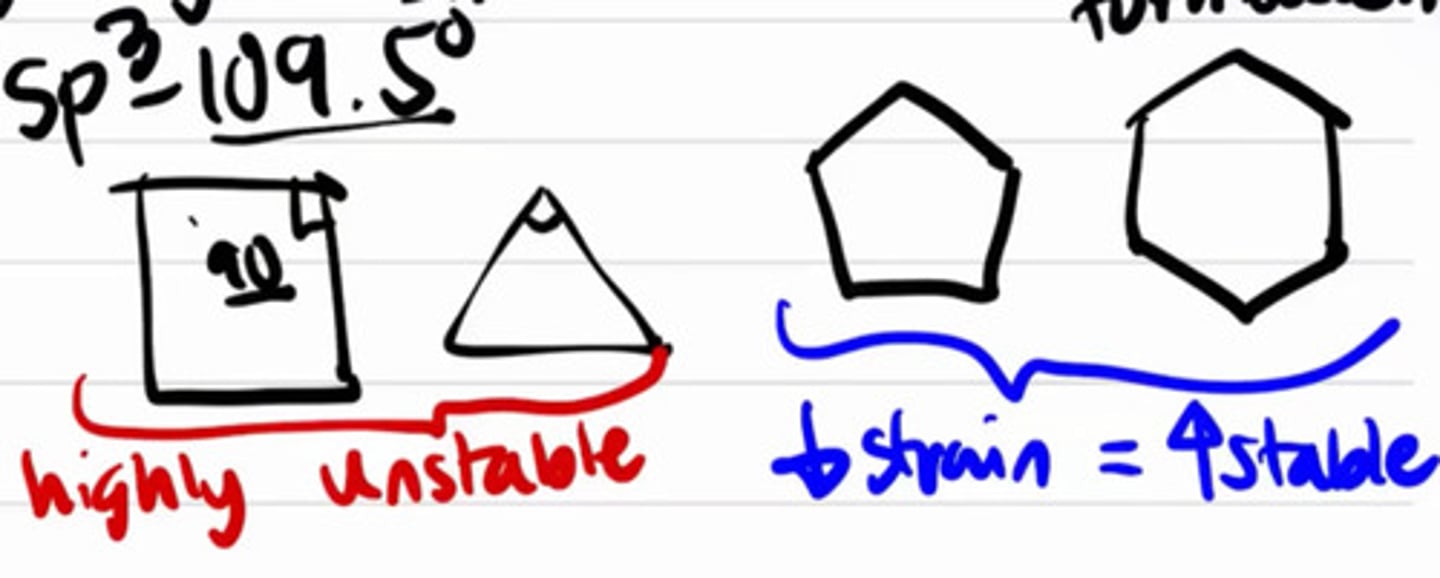
Instability when the molecules are forced to form rings.
a. Angle strain
b. Steric strain
a. Angle strain
Strain when two groups are so close to one another.
a. Angle strain
b. Steric strain
b. Steric strain
Sterio = "space"
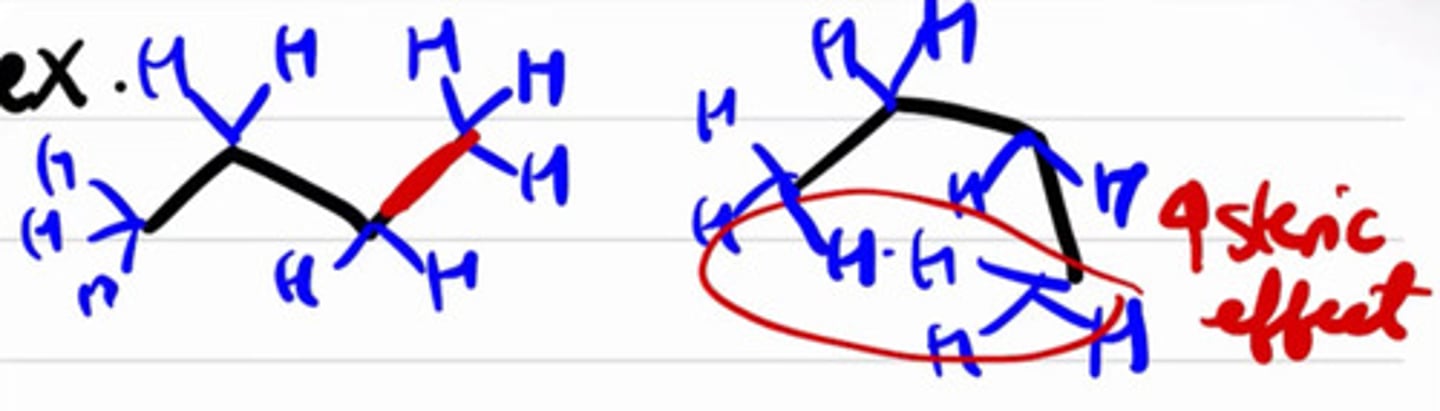
Strain caused by 2 eclipsed CH3 groups.
a. Angle strain
b. Steric strain
b. Steric strain

Most relatively stable cyclic hydrocarbon having 0 strain energy.
a. Cyclopropane
b. Cyclobutane
c. Cycloopentane
d. Cyclohexane
d. Cyclohexane

Strain energy of cyclopropane.
a. 0 kcal/mol
b. 6.2 kcal/mol
c. 9.7 kcal/mol
d. 12.6 kcal/mol
e. 26.5 kcal/mol
f. 27.3 kcal/mol
f. 27.3 kcal/mol
Strain energy of cyclobutane.
a. 0 kcal/mol
b. 6.2 kcal/mol
c. 9.7 kcal/mol
d. 12.6 kcal/mol
e. 26.5 kcal/mol
f. 27.3 kcal/mol
e. 26.5 kcal/mol
Strain energy of cyclopentane.
a. 0 kcal/mol
b. 6.2 kcal/mol
c. 9.7 kcal/mol
d. 12.6 kcal/mol
e. 26.5 kcal/mol
f. 27.3 kcal/mol
b. 6.2 kcal/mol
Strain energy of cyclohexane.
a. 0 kcal/mol
b. 6.2 kcal/mol
c. 9.7 kcal/mol
d. 12.6 kcal/mol
e. 26.5 kcal/mol
f. 27.3 kcal/mol
a. 0 kcal/mol
Strain energy of cycloheptane.
a. 0 kcal/mol
b. 6.2 kcal/mol
c. 9.7 kcal/mol
d. 12.6 kcal/mol
e. 26.5 kcal/mol
f. 27.3 kcal/mol
b. 6.2 kcal/mol
Strain energy of cyclooctane.
a. 0 kcal/mol
b. 6.2 kcal/mol
c. 9.7 kcal/mol
d. 12.6 kcal/mol
e. 26.5 kcal/mol
f. 27.3 kcal/mol
c. 9.7 kcal/mol
Strain energy of cyclononane.
a. 0 kcal/mol
b. 6.2 kcal/mol
c. 9.7 kcal/mol
d. 12.6 kcal/mol
e. 26.5 kcal/mol
f. 27.3 kcal/mol
d. 12.6 kcal/mol
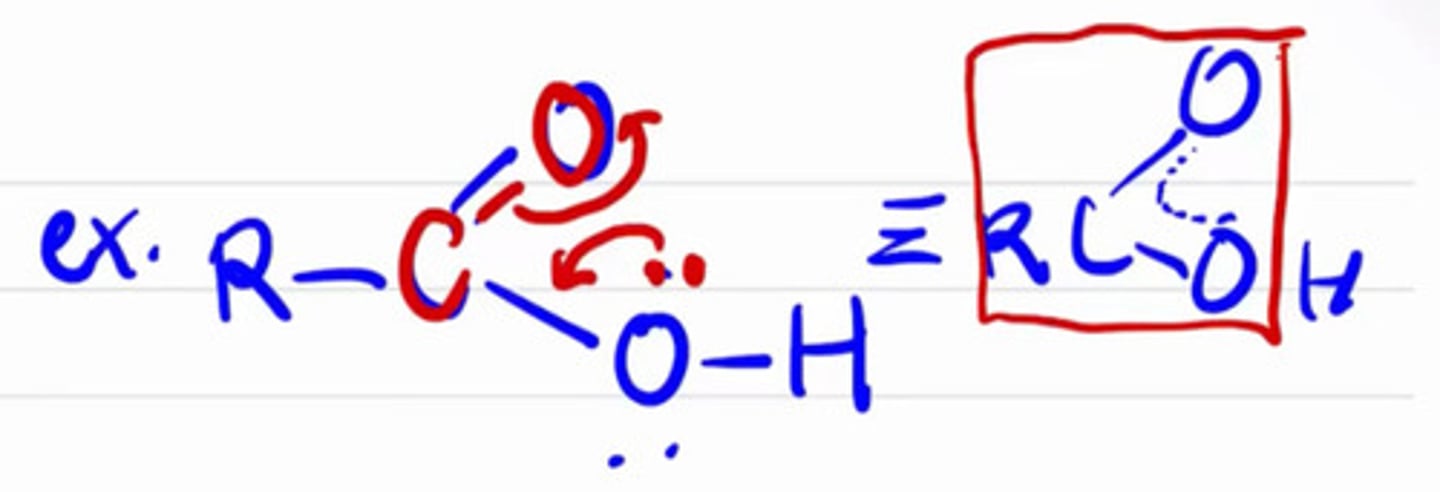
Electrons do not stay in a single space or region.
a. Strain
b. Delocalization
c. Resonance
d. Inductive effects
b. Delocalization

True about conditions for delocalization to occur except:
a. There must have e- source
b. Adjacent to sp2 C
c. e- source can be sigma and pi bond
d. e- source can be lone pair
e. None
e. None
*Conjugation is not a requirement.
Delocalization wherein source of electron is sp3.
a. Hyperconjugation
b. Resonance
c. Lone pair resonance
a. Hyperconjugation
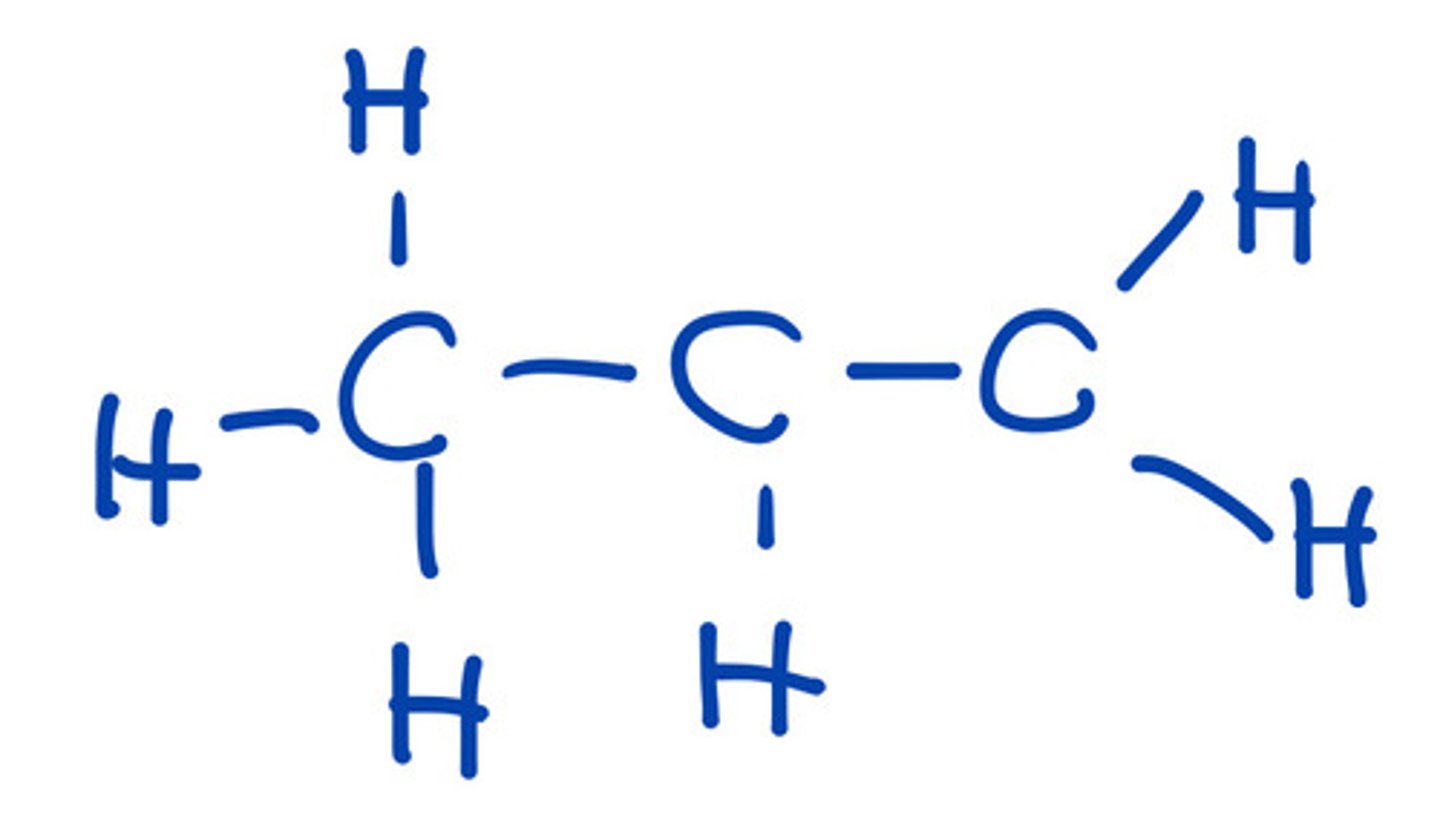
Delocalization wherein source of electron is sp2.
a. Hyperconjugation
b. Resonance
c. Lone pair resonance
b. Resonance

Delocalization present in benzene.
a. Hyperconjugation
b. Resonance
c. Lone pair resonance
b. Resonance
Also known as pi resonance.
a. Hyperconjugation
b. Resonance
c. Lone pair resonance
b. Resonance
Delocalization wherein source of electron is lone pair.
a. Hyperconjugation
b. Resonance
c. Lone pair resonance
c. Lone pair resonance

Delocalization will occur when bond is adjacent to which of the following?
a. sp C
b. sp2 C
c. sp3 C
d. All
b. sp2 C
Both pi and lone pair resonance delocalization is less powerful than hyperconjugation.
a. True
b. False
a. False
Both pi and lone pair resonance delocalization is MORE powerful than hyperconjugation.
Presence of delocalization can be an indication of stability.
a. True
b. False
a. True
Benzene has resonance thus is very stable.
a. True
b. False
a. True
Push and pull of electron by a group.
a. Strain
b. Delocalization
c. Resonance
d. Inductive effects
d. Inductive effects
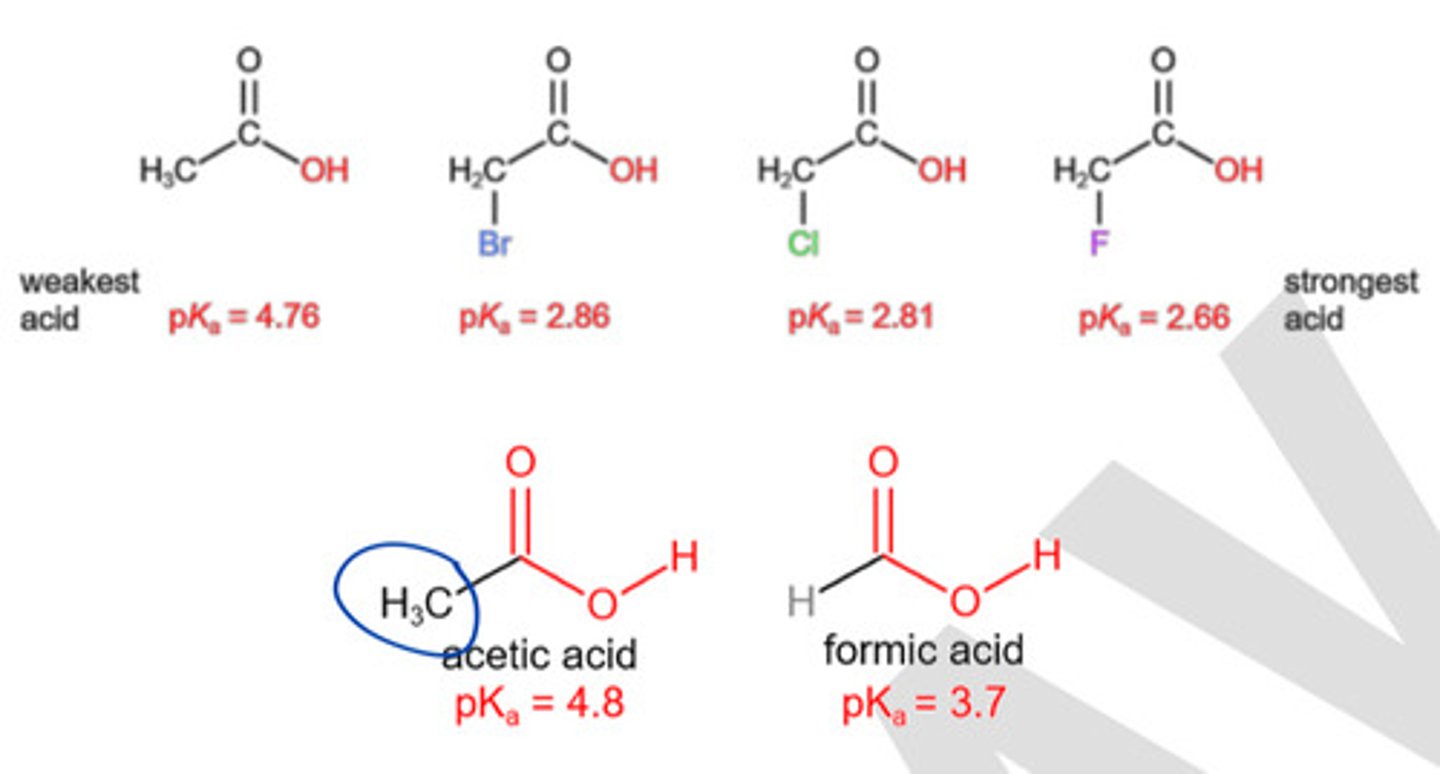
Which of the following has electron donating effect?
a. F
b. Cl
c. Br
d. I
e. O
f. None
f. None
All are electronegative atoms which like to pull electrons thus have electron WITHDRAWING effect not electron DONATING.
Which of the following has electron donating effect?
a. C
b. Atoms with available lone pairs.
c. O
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
C and atoms with available lone pairs are non- electronegative atoms that tend to push electrons thus has electron donating inductive effects.
O is electronegative, thus electron withdrawing.
How does strain affect the stability of molecules?
a) Strain increases the stability of molecules
b) Strain has no effect on the stability of molecules
c) Strain decreases the stability of molecules
d) Strain stabilizes some molecules but destabilizes others
c) Strain decreases the stability of molecules.
Strain in molecules arises when bond angles or bond lengths deviate significantly from their ideal values. This leads to higher energy and decreased stability, as the strained molecule is under additional strain energy.
What effect does electron delocalization have on the stability of molecules?
a) Electron delocalization decreases the stability of molecules
b) Electron delocalization has no effect on the stability of molecules
c) Electron delocalization increases the stability of molecules
d) Electron delocalization stabilizes some molecules but destabilizes others
c) Electron delocalization increases the stability of molecules.
Electron delocalization, as seen in resonance structures or conjugated systems, spreads the electron density over a larger area, leading to greater stability. This phenomenon lowers the energy of the molecule and contributes to its overall stability.
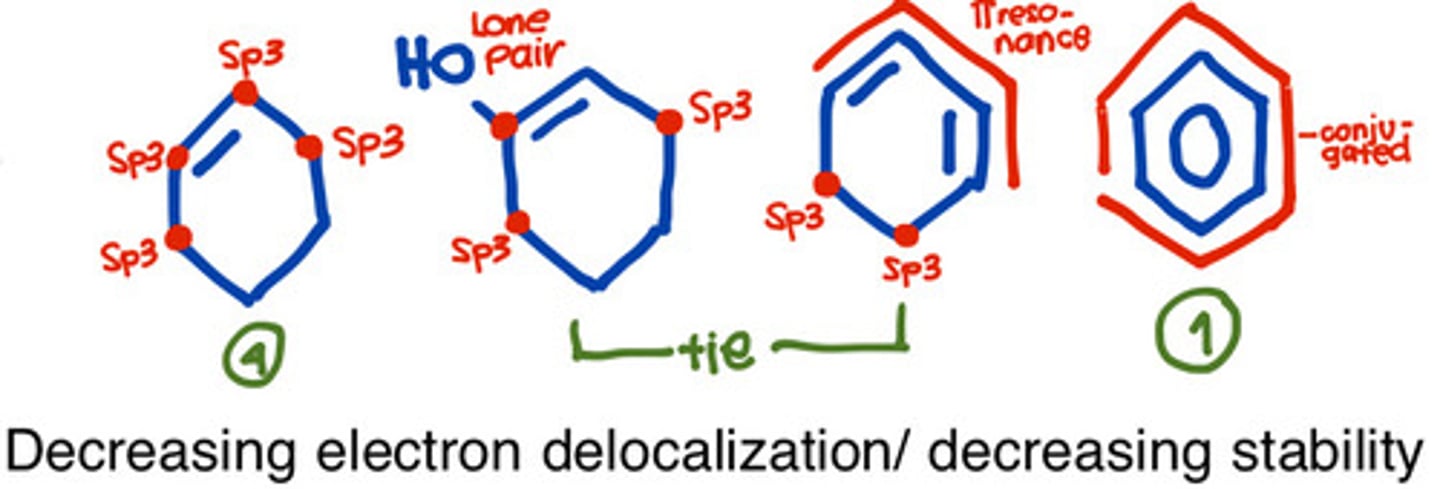
How does the electron withdrawing effect impact the stability of molecules?
a) Electron withdrawing effect decreases the stability of molecules
b) Electron withdrawing effect has no effect on the stability of molecules
c) Electron withdrawing effect increases the stability of molecules
d) Electron withdrawing effect destabilizes some molecules but stabilizes others
a) Electron withdrawing effect decreases the stability of molecules.
Electron withdrawing groups tend to pull electron density away from the rest of the molecule, creating regions of partial positive charges. This can lead to instability and higher energy states in the molecule.
What is the impact of the electron donating effect on the stability of molecules?
a) Electron donating effect decreases the stability of molecules
b) Electron donating effect has no effect on the stability of molecules
c) Electron donating effect increases the stability of molecules
d) Electron donating effect destabilizes some molecules but stabilizes others
c) Electron donating effect increases the stability of molecules.
Electron donating groups tend to release electron density into the rest of the molecule, creating regions of partial negative charges
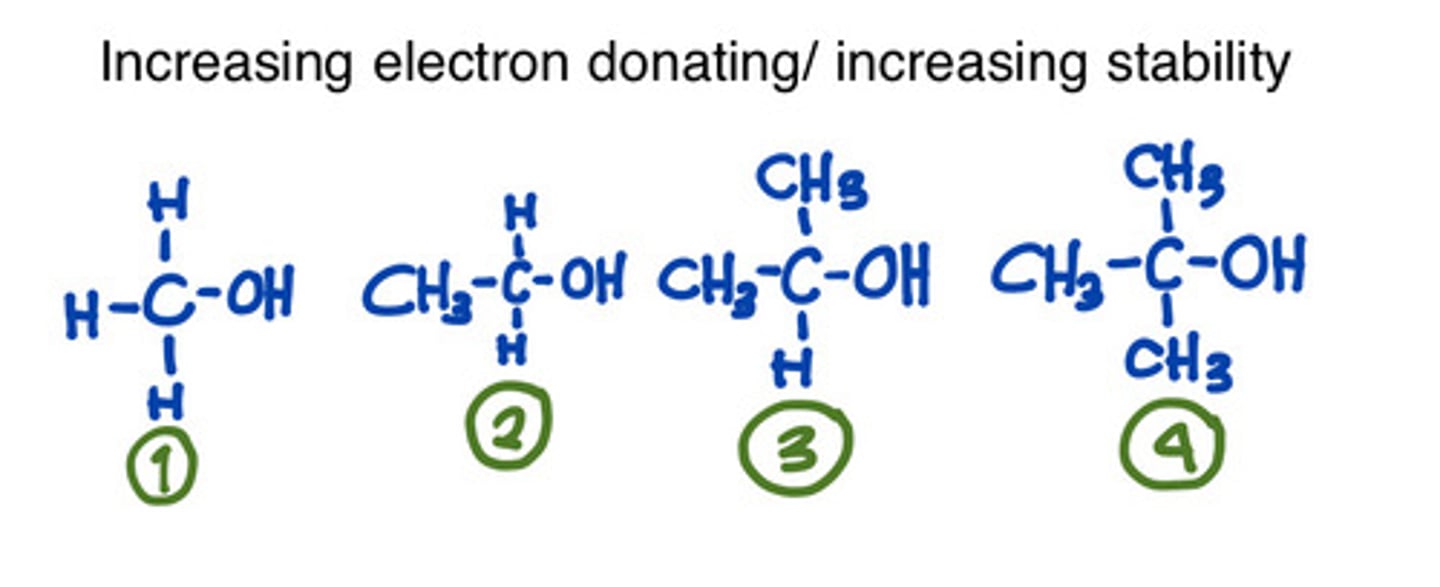
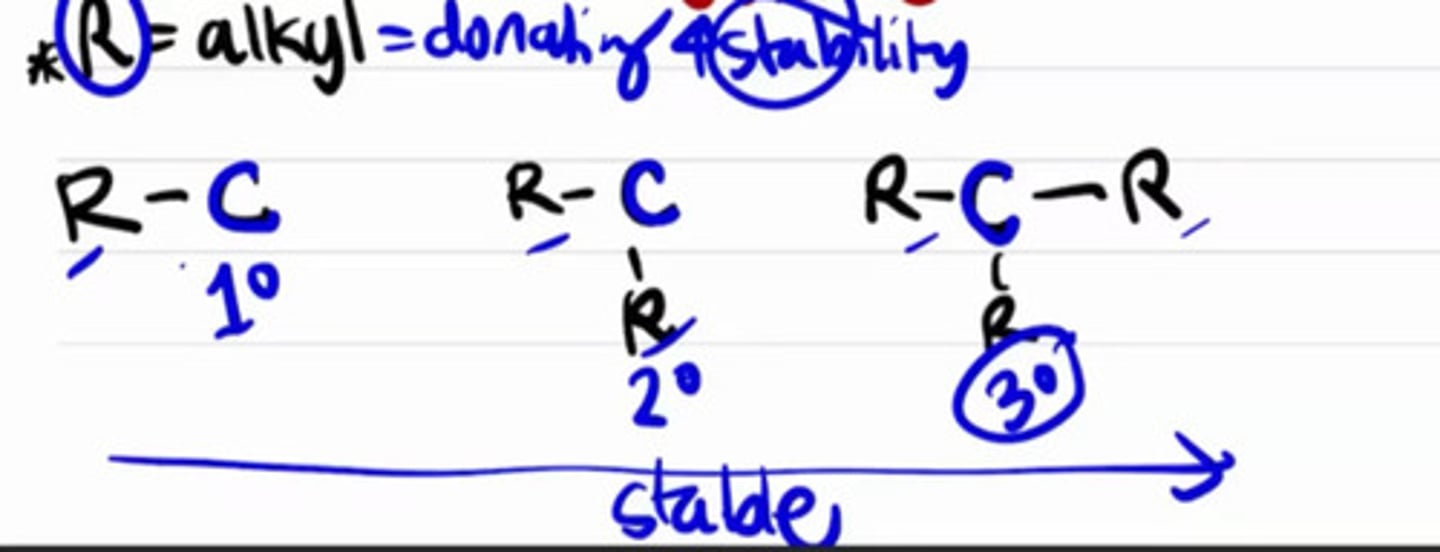
Type carbon that is the most stable.
a. Primary
b. Secondary
c. Tertiary
d. All are equal
c. Tertiary
Arrange the following structures in increasing order of delocalization of electrons:
1- CH3CH2CH2CH3
2- CH2=CHCH=CH2
3- CH3CH=CHCH2
4- CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
a. 4132
b. 4123
c. 1432
d. 1423
c. 1432
Delocalization of electrons occurs when electrons are distributed over multiple atoms or bonds in a molecule. In option 1, CH3CH2CH2CH3, the electrons are localized within the carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds, showing little to no delocalization. In option 4, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, the hydroxyl group introduces some delocalization through the oxygen atom. Option 3, CH3CH=CHCH2, has a double bond that allows some delocalization of electrons within the pi bond. Finally, option 2, CH2=CHCH=CH2, has two conjugated double bonds, leading to the highest degree of delocalization among the given structures.
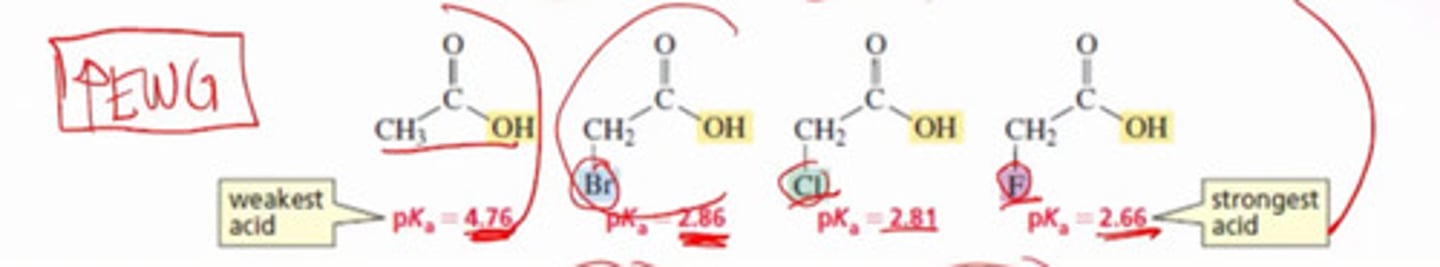
*How does electron delocalization impact the acidity of molecules?
a) Electron delocalization increases acidity
b) Electron delocalization decreases acidity
c) Electron delocalization has no impact on the acidity of molecules.
d) The effect of electron delocalization on acidity varies depending on the specific functional groups involved.
a) Electron delocalization increases acidity

How does the electron withdrawing effect impact the acidity of molecules?
a) Electron withdrawing effect increases acidity.
b) Electron withdrawing effect decreases acidity.
c) Electron withdrawing effect has no impact on the acidity of molecules.
d) The effect of electron withdrawing effect on acidity depends on the specific functional groups involved.
a) Electron withdrawing effect increases acidity.
How does the electron donating effect impact the acidity of molecules?
a) Electron donating effect increases acidity.
b) Electron donating effect decreases acidity.
c) Electron donating effect has no impact on the acidity of molecules.
d) The effect of electron donating effect on acidity varies depending on the specific functional groups involved.
b) Electron donating effect decreases acidity.
Requirements for aromaticity
a. It must be cyclic
b. It must be planar
c. Must follow Huckel's rule
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Planar - all atoms are sp2
Huckle's rule
a. 4n + 2 = # of pi electrons where n should be whole number
b. 4n + 4 = # of pi electrons where n should be whole number
c. 2n + 2 = # of pi electrons where n should be whole number
d. 2n + 4 = # of pi electrons where n should be whole number
a. 4n + 2 = # of pi electrons where n should be whole number
All conjugated rings are aromatic.
a. True
b. False
b. False
How many pi electrons does benzene contain?
a. 2
b. 3
c. 4
d. 6
d. 6 - every pi bond, there is 2 pi electrons
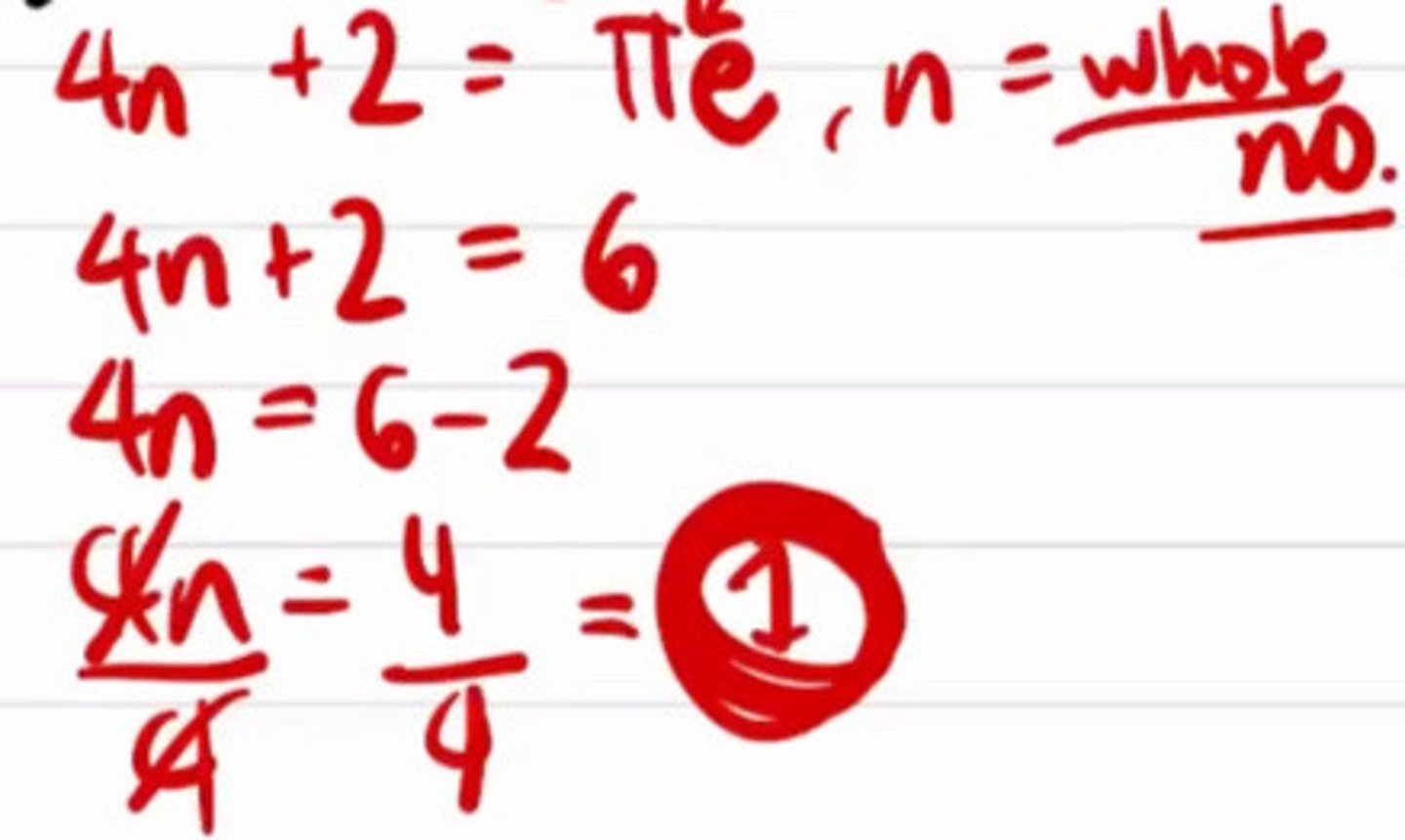
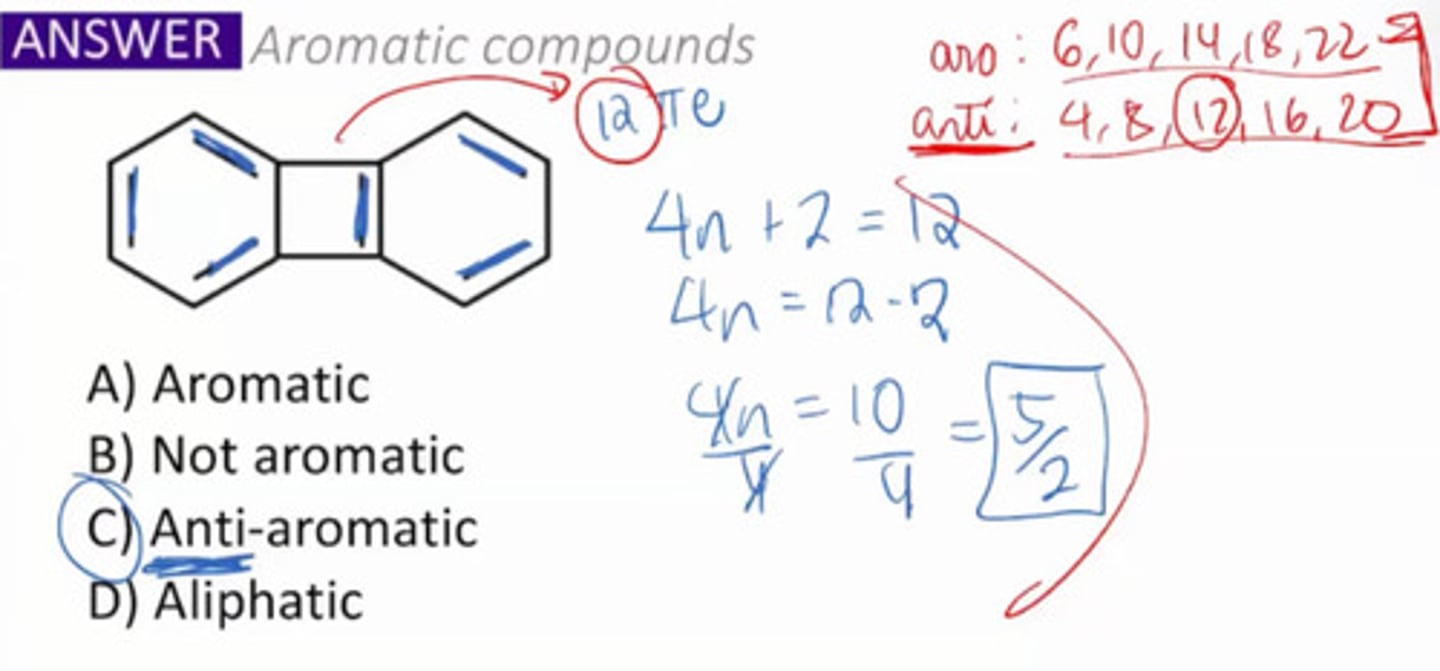
Compounds that are cyclic and planar but do not follow the Huckle's rule.
a. Nonaromatic
b. Antiaromatic
c. Pseudoaromatic
d. Anaromatic
b. Antiaromatic
Aromatic compounds are homocyclic only.
a. True
b. False
b. False - Heterocyclic compounds can be aromatic also.
Multiple rings can be aromatic.
a. True
b. False
a. True
How does resonance affects acidity?
a. Increase
b. Decrease
c. No effect
a. Increase

How do electron withdrawing groups affect acidity?
a. Increase
b. Decrease
c. No effect
a. Increase
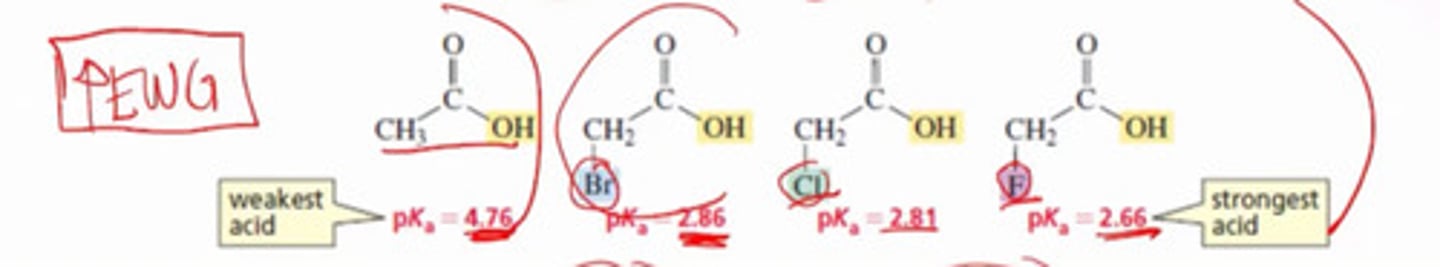
How do electron donating groups affect acidity?
a. Increase
b. Decrease
c. No effect
b. Decrease