1.2 Amine Neurotransmitters
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Briski
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
what was the first NT identified
ACh
ACh activates which receptors
nicotinic and muscarinic
ACh activates receptors in which nervous system(s)
CNS and PNS
most cholinergic neurons reside in the ____ but some occur in the ____
subcortical areas; cerebral cortex
explain the synthesis of ACh
Acetyl CoA + Choline —> ACh + CoA (enzyme: Choline Acetyltransferase)
is the synthesis of ACh reversible or irreversible
irreversible
muscarinic receptors are ____ while nicotinic receptors are ____
GPCRs; ionotropic
what are the muscarinic receptor subtypes
M1-M5
what are the functional roles of cholinergic neurons in the CNS
memory, motivation, perception, cognition, attention, and fine motor functions
what are some examples of monoamine neurotransmitters
dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine
what are the methods of inactivation for monoamine neurotransmitters
reuptake, metabolism, and drifting
explain how to make the main three catecholamines
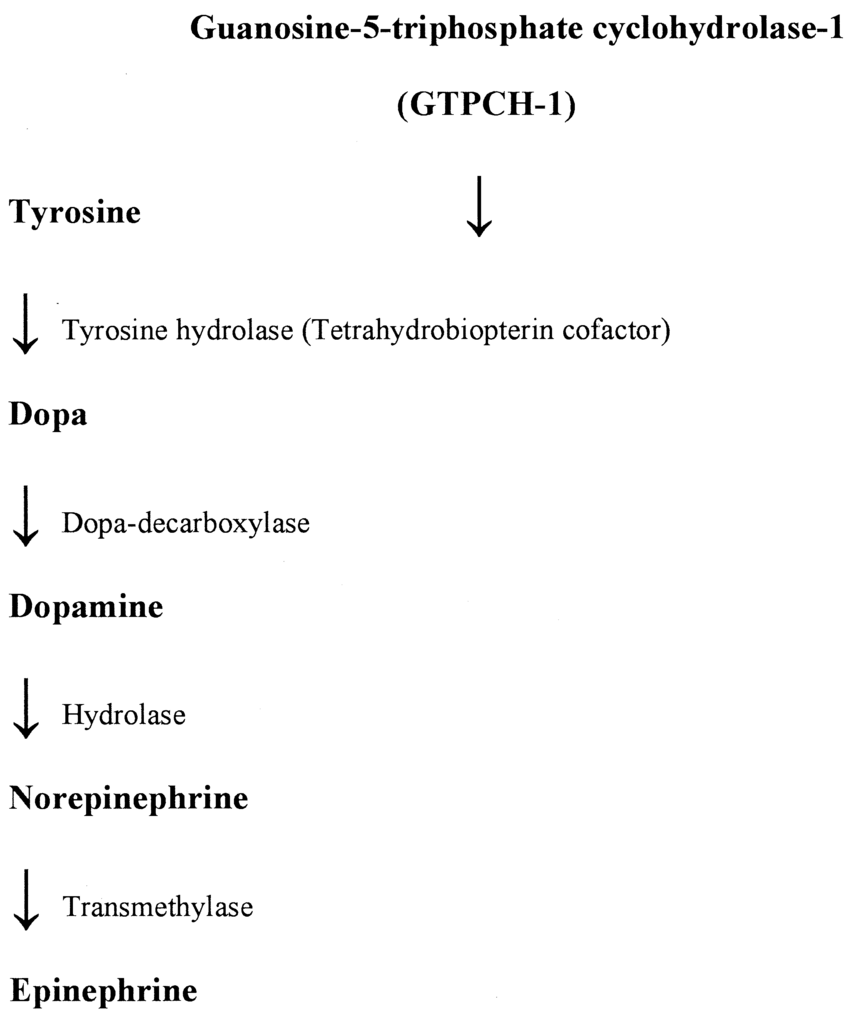
which enzymes are responsible for the metabolism of catecholamine monoamine neurotransmitters
MAO and COMT
what are the subtypes of the MAO receptor
MAOa and MAOb
MAOa is responsible for metabolizing which catecholamines (monoamine NTs)
NE, EPI, and 5HT
MAOb is responsible for metabolizing which catecholamines (monoamine NTs)
DA
COMT is responsible for metabolizing which catecholamines (monoamine NTs)
DA, NE, EPI
dopamine receptor subtypes
D1-D5
catecholamine receptors are _____
GPCRs
Catecholamine receptor subtypes can induce…
postsynaptic membrane depolarization or hyperpolarization
the nigrostriatal pathway is an example of a ____ pathway
CNS dopamine
explain the nigrostriatal pathway
substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons project to the caudate nucleus-putamen (extrapyramidal system)
degeneration of the nigrostriatal pathway is associated with which disease
parkinsons
degeneration of the ____ pathway is associated with parkinsons disease
nigrostriatal
the mesolimbic forebrain system is an example of a(n) _____ pathway
CNS dopamine
explain the mesolimbic forebrain system
midbrain ventral tegmentum dopamine neurons project to the limbic system
the mesolimbic forebrain system is associated with…
emotional behavior and schizophrenia
which CNS Dopamine pathway is associated with emotional behavior and schizophrenia?
mesolimbic forebrain system
the mesocortical pathway is an example of a(n) ____ pathway
CNS dopamine
explain the mesocortical pathway
midbrain dopamine neurons project to cerebral cortex
the mesocortical pathway is associated with…
logical reasoning, perception
the _____ pathway is associated with logical reasoning and perception
mesocrotical
dysfunction associated with the mesocortical pathway is associated with…
psychosis
dysfunction in the ____ pathway is associated with psychosis
mesocoritcal
the tuberoinfundibular system is an example of a _____ pathway
CNS dopamine
explain the tuberoinfundibular system
hypothalamic arcuate nucleus dopamine neurons terminate in the median eminence and release the neurotransmitter for vascular transport to the anterior pituitary gland
which area of the CNS has the highest concentration of EPI
brainstem
NE neuronal cell bodies are located in the…via…
brainstem locus coeruleus project rostra via the medial forebrain bundle
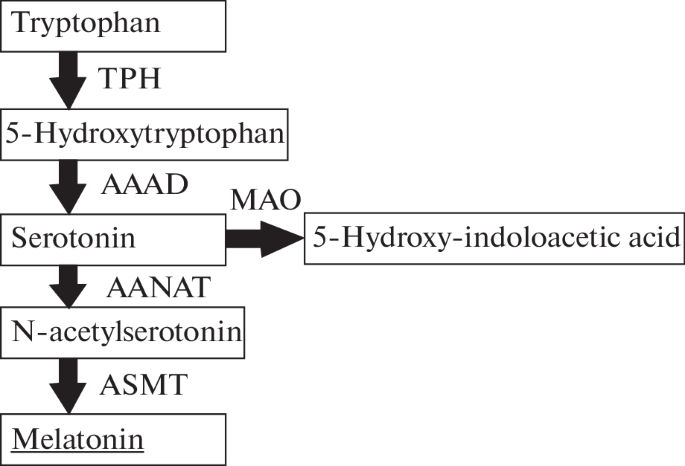
explain the synthesis of 5HT(serotonin)
how many 5HT receptors are GPCRs
12
5HT receptors elicit which types of responses (IPSP or EPSP)
both!
what are the 5HT receptor subtypes
5HT1a-f
5HT2a-c
5HT3
5HT4
5HT5
5HT6
5HT7
how is 5HT inactivated
MAOa metabolizes 5HT to form 5HIA which is then metabolized to 5HIAA OR it can be reuptaked to the presynaptic terminal
which enzyme is responsible for inactivating serotonin
MAOa
where do 5HT neurons reside in the CNS
midline region of the upper brainstem/pons; raphe nuclei
5HT1 is coupled to…
inhibitory G proteions
5HT2, 5HT4, 5HT6, and 5HT7 are all coupled to…
stimulatory (excitatory) G proteins
5HT3 receptors are linked to…
ion channels (ionotropic)
other amine neurotransmitters include
octopamine
tyramine
melatonin
histamine
posterior hypothalamic histamine neurons are associated with…
body temp regulation , vascular dynamics, retinal arousal
posterior hypothalamic _____ neurons are associated with body temp regulation , vascular dynamics, retinal arousal
histamine
histamine receptors are which type of receptors
GPCRs
what are the histamine receptor subtypes
H1-H4
H1 receptors location
glial cells, blood vessels
H1 receptor function
mobilize Ca
H1 receptor antagonists (antihistamines) cause…
sedation
where are H2 receptors located
nerve cells
H2 receptor function
stimulates adenyl cyclase and increases cAMP
most H2 antagonists do not…
cross the BBB
H2 antagonists are used as…
antacids (due to their role in gastric acid secretion)
H3 receptor function
nerve cell calcium influx
where are H4 receptors found
hematopoietic cells (mast cells, WBCs, and dendritic cells)
H4 receptor antagonists lead to
alertness
how do peptide NT’s differ from classical NT’s
synthesis takes place on ribosomes in the cell bodies and is directed by mRNA
neuropeptide transmitter examples
orexin, opioids, gastrin etc
orexin is also called
hypocretin
what are the Orexin receptor subtypes
OX1 and OX2
OX1 and OX2 are which type of receptor
GPCRs
Orexin receptors are involved in…
activating monoamine and ACh neurons to maintain awake state and energy, balance, and metabolism
lack of oxrexin produces which disease
narcolepsy
narcolepsy is caused by…
lack of orexin
true or false:
many neurotransmitters coexist in neurons and can be released at the same time into the synapse
true
what are some atypical neurotransmitters
CO, NO, purines (adenosine and ATP), cannabinoids
why are atypical neurotransmitters hella weird
not usually stored in the synaptic vesicles or released via exocytosis
purine receptor classes
P1 and P2
P1 receptors bind to…
adenosine receptors
what are the adenosine receptors
A1 and A2
A1 antagonists act as…
cognition enhancers
A1 ____ act as cognition enhancers
antagonists
example of an A1 antagonist
caffiene
caffeine is an example of an…
A1 antagonist
caffeine acts as a ___ at low doses but at high doses it acts as a ____
stimulant ; irritant
A2 receptors have an inverse relationship with _____
dopamine
A2 receptors have an _____ relationship with dopamine
inverse
A2 antagonists have potential to be used as…
anti-parkinsons agents
P2 receptors bind to…
ATP
P2 receptors that bind to ATP are involved in…
pain perception, inflammation
P2 antagonists may be effective in treating…
chronic pain
_____ receptor antagonists may be effective in treating chronic pain
P2
what are the cannabinoids
anandamide and 2-arachidonylglycerol
cannabinoid receptors
CB1 and CB2
the cannabinoid receptors are which type of receptor
GPCR
cannabinoid receptor agonists are used for
stimulation of appetite in anorexic, HIV, and cancer patients
chronic pain relief
depression
cannabinoid receptor antagonists can potentially treat
nausea, vomiting, and obesity
how is NO (nitric oxide) made
nitric oxide synthase (NOS)
excessive NO can be ______
neurotoxic
how can NO excess be neurotoxic
contributes to neural damage caused by stroke
CO is highly toxic at ____ concentrations
high
CO may play a role in
circadian rhythm