Portable - Online Lecture
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Define mobile.
Capable of being moved
When pt’s condition is too critical, or their injuries are too severe, mobile (portable) x-ray machines may be used to take x-rays in the pt’s room
Can be performed on any part of body
Define trauma.
Is an injury that can be caused by an outside force
Define emergency.
A medical condition requiring immediate treatment
Portables all emit _____ ______ during exposure.
ionizing radiation
no led line walls
Describe a C-arm (list 3 types).
All emit ionizing during exposure
Mini C-arm
C-arm
O-arm
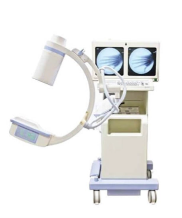
Describe a C-arm.
Must have a technologist immediately present
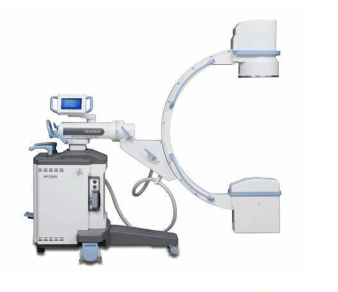
Describe a mini C-Arm.
Can set up and leave it for the doctor to run
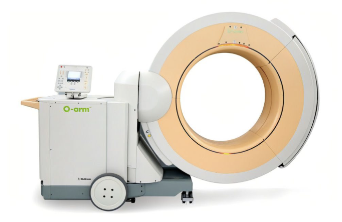
Describe an O-arm.
Must have a technologist immediately present
Most efficient
What are the 5 main features of a portable?
Power source, safety, drive control, IR holder (s), exposure switch with 6-ft cord

What are the features of the power source of the portable?
Battery power (rechargeable battery)
High frequency generator
more consistent kVp @ mAs reading
more affordable
smaller, trending now
allows for lower dose

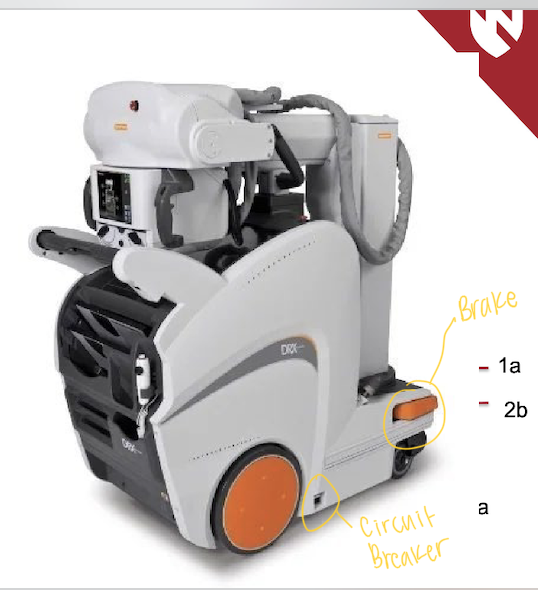
What are the features of safety of the portable?
a. Circuit breaker
b. Break

What are the features of drive control of the portable?
a. Touch sensitive handle

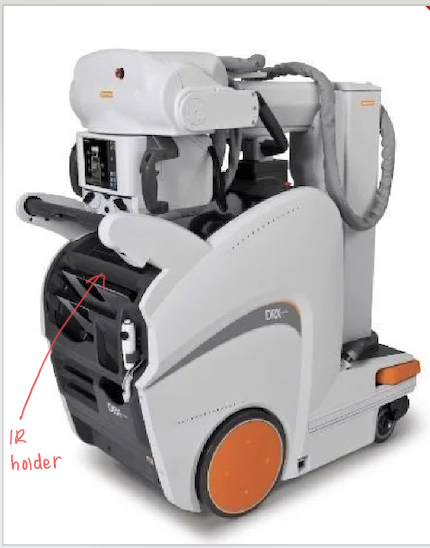
Where is the IR holder?

The exposure switch is connect to a ___ foot cord.
6

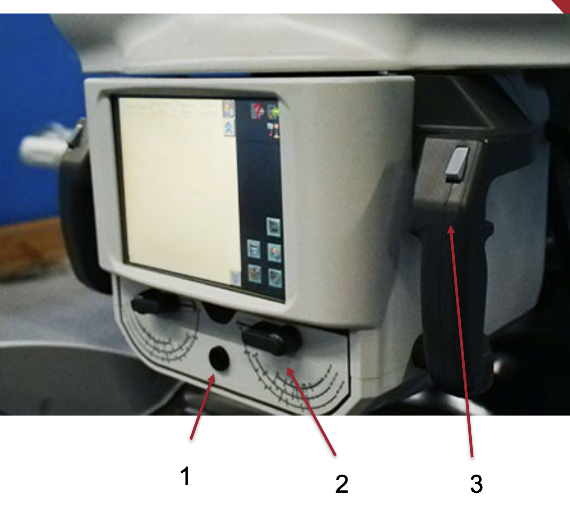
What are the other features of the portable near the screen?
Light button
Collimator controls/knobs
Tower locks/release
What are some positioning aides?
Decubitus board (build off mattress when doing decub), sponges, or medical tape

What are the 3 cardinal rules for radiation protection?
Time, distance, shielding
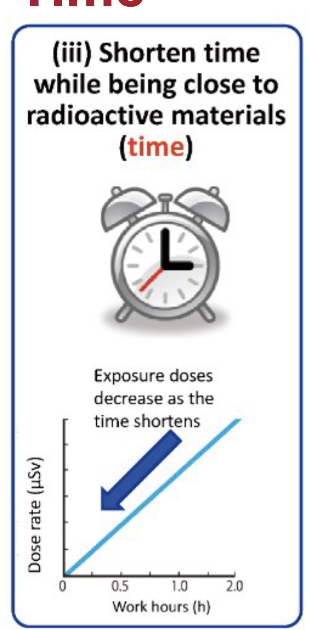
Describe the cardinal principle of time.
Decreasing time near/around radiation reduces your overall dose
Students should NEVER hold pts
Exposure & dose = directly related
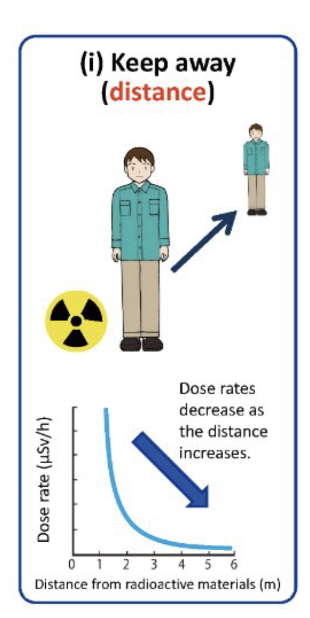
Describe the cardinal principle of distance.
Increasing your distance away from the pt is the MOST EFFECTIVE way to reduce your dose
Inverse square law
Describe the cardinal principle of shielding.
Each portable should have at least one lead apron
Ask visitors & other non-essential staff to leave room during exposure
Shield pt when protocol allows
Always announce your exposure prior to taking the exposure
Lead aprons only work if you use them

What are the technical factors for a portable chest (AP & decub)?
72” SID
Grid recommended
14×17 portrait or landscape
CR: 90-95 kVp @ 4-6.5 mAs (no grid) & 125 kVp @ 5-12.5 mAs (Grid)
DR: 90 kVp @ 2-3 mAs (no grid) & 117 kVp @ 3-8 mAs (Grid)
What is the pt position for an AP portable chest?
Supine/semi-erect on cart
Roll pt’s shoulders forward if condition allows
What is the pt position for a decub portable chest?
Cart or bed is locked
Cardiac board/radiolucent pad/sponge directly under pt’s side
Lying on side indicated RLD = lie on R side, LLD = lie on left side
Chin extended
Both arms raised above head
Coronal plane parallel to IR
AP: back against IR
PA: Chest against IR
What is the part position for an AP portable chest?
IR behind pt, align center of IR to CR (top of IR about 1.5 inches above shoulders
Center pt to CR & IR
Roll pt’s shoulder’s forward if condition allows
What is the part position for a decub?
IR height centered to thorax
Adjust pt and cart to midsagittal plane & level of T7
Top of IR approximately 1 inch above vertebra prominens
Pts must lie on their side for 5 mins before exposure
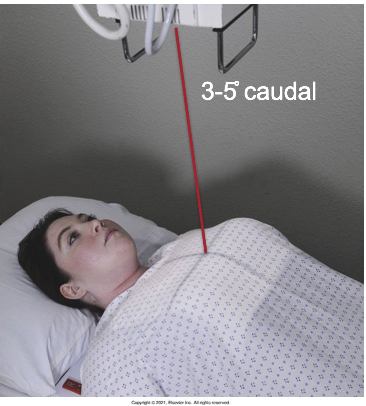
Where is the CR for an AP portable chest?
CR is perpendicular to long axis of sternum directed to T7 (3-4” below jugular notch) perpendicular to IR
Supine pt: angle CR 3-5 degrees caudal
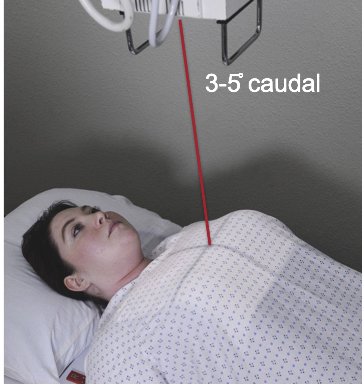
Where is the CR for a decub portable chest?
CR is horizontal directed to center of IR at level of T7 (3-4”) inferior to level of jugular notch
Top of border of light at vertebra prominens
What is the collimation for an AP & decub portable chest?
Tight collimation 4 sides to area of lung fields
Use BB marker or supine marker (if supine) or upright marker (semi-erect)
Mark the side up for a decub
What is the respiration for an AP & decub portable chest?
Make exposure at end of second full inspiration
What are the technical factors for an AP Supine & LLD abdomen?
40” SID
Grid
14×17 portrait or landscape
CR: 80 kVp @ 50-100mAs
DR: 80 kVp @ 8-40mAs
Include decub and upside markers, mark side up
What is the pt position for an AP portable Supine Abdomen?
Supine on cart
Arms abducted from body
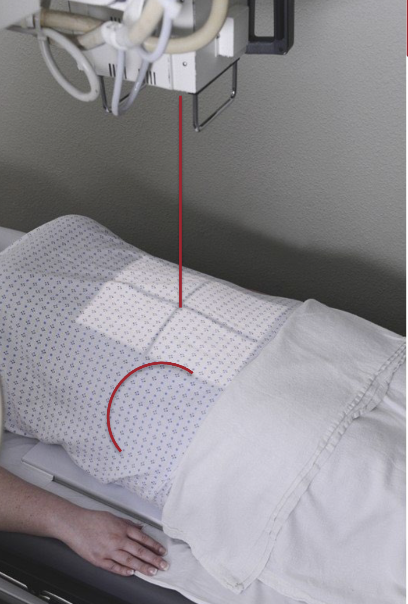
What is the pt position for a LLD portable abdomen?
Cart or bed is locked
Cardiac board/radiolucent pad/sponge directly under pt’s L side
Pt lying on L side
Both arms raised above head
Coronal plane parallel to IR
AP: back against IR
PA: Chest against IR
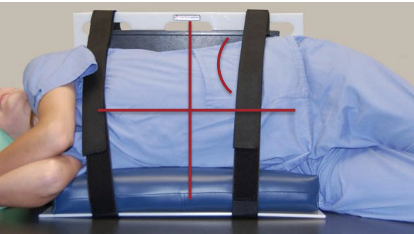
What is the part position for an AP portable Supine Abdomen?
Center IR at level of iliac crests
Ensure both sides of abdomen are equal distances from edge of IR
May need to place something under parts of IR to ensure IR is perpendicular to CR
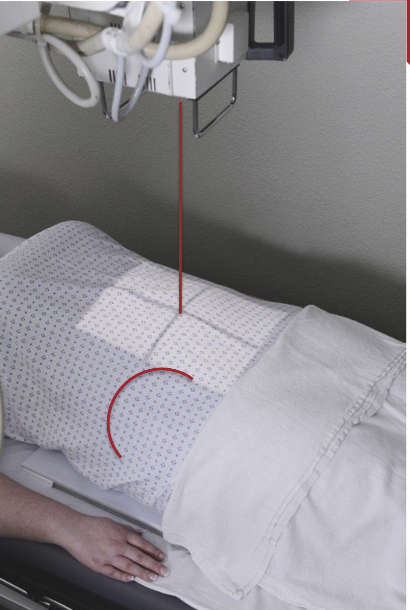
What is the part position for a LLD portable abdomen?
IR height centered to the abdomen
Adjust pt and cart to midsagittal plane at approximately 2” above the level of the iliac crests
Top of IR approximately axilla
Ensure the diaphragm and upper abdomen are included
Ensure IR is perpendicular to CR
Pt must like on side for 5 mins before exposure
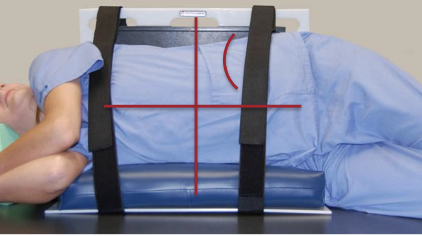
Where is the CR for an AP portable Supine Abdomen?
CR is perpendicular to level of iliac crests and to center of IR
Check for IR tilt (autofirm button)
Where is the CR for a LLD portable Abdomen?
CR horizontal directed to center of IR
Center of CR should be 1-2” above iliac crests
Ensure no rotation
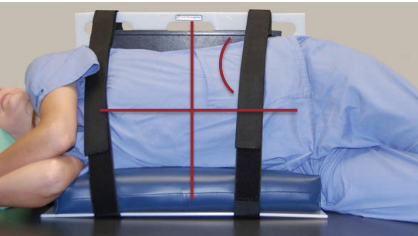
What is the collimation for an AP Supine portable abdomen?
Collimate to field of view or collimated on all 4 sides to anatomy of interest
Must include symphysis pubis
Use marker with BB’s or supine marker

What is the collimation for a LLD portable abdomen?
Collimate to field of view or collimate on all 4 sides to anatomy of interest
Must include elevated side of abdomen
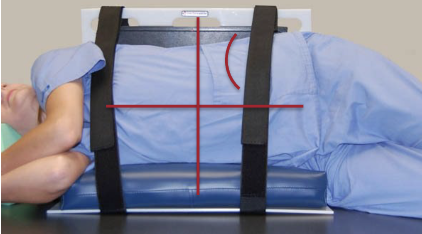
What is the respiration for an AP Supine/LLD portable abdomen?
Make exposure at end of expiration
What are the technical factors for a portable AP pelvis?
40” SID
Grid Recommended
17×14 light field
CR: 80kVp @ 20-32mAs
Dr: 80-85kVp @ 25mAs
What is the pt position for a portable AP pelvis?
Supine with arms abducted from body
CR perpendicular to center of IR and pelvis
MSP center to bucky or IR
What is the part position for a portable AP pelvis?
Top of IR should be 1” above iliac crests
Ensure no rotation — both ASIS should be same distance from IR
Rotate lower limbs internally 15 degrees if possible
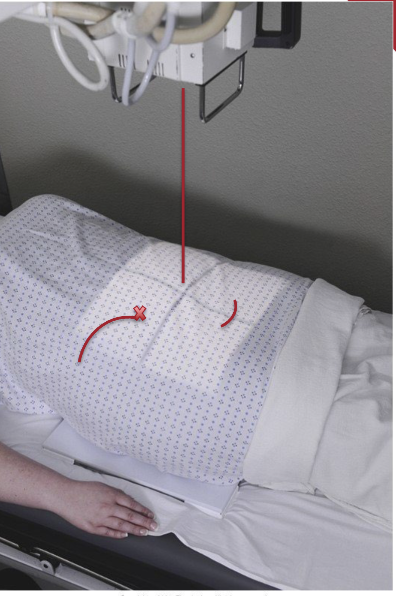
What is the CR for an AP portable pelvis?
Cr perpendicular to IR, centered midway between level of ASIS and the symphysis pubis (this will be approximately 2 inches inferior to level of ASIS)
Top of light field 1 inch above iliac crests
What is the collimation for a portable AP pelvis?
Tight collimation 4 sides to area of pelvis
What is the respiration for an AP portable pelvis?
Suspend respiration during exposure
Trauma examples slides 29-31