working memory model
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what is the working memory model
baddeley and hitch - representation of stm suggesting stm is a dynamic processor of diff types of info using subunits coordinated by a central decision making system
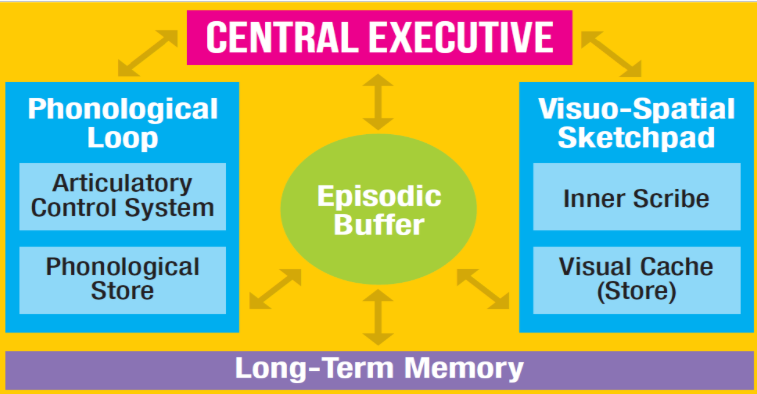
central executive
controls attention and directs information to the two subsystems, draws info from the subsystems and LTM and decides what to focus on, very limited capacity
phonological loop
deals with auditory info in speech based form, 2 components: phonological store/ inner ear - stores acoustic items (speech based sounds) for a short period of time (1-2 seconds), articulatory control process/ inner voice - allows sub-vocal repetition of items in the phonological store/ maintenance rehearsasal
visuo-spatial sketchpad
deals with visual and spatial tasks, 2 sub-components: inner scribe - deals with spatial relationship between objects, visual cache - stores visual info, can also retrieve info from LTM to view and manipulate visually in the working memory
episodic buffer
temporary holding area in working memory, takes info from senses and combines it with things you already know from ltm, allows complete, temporary mental picture of what's happening, you become consciously aware of this combined info when you need to use it - ‘an episode’, sends info to ltm
baddeleys dual task study
when ppts carried a visual and verbal task at the same time, performance was similar to when tasks carried out separately however when both tasks were visual or both were verbal, performance declined as competition for same subsystem
strengths of wmm
research support comes from dual-task studies e.g. baddeley, research support from case studies e.g. KF
limitations of wmm
little research investigating central executive, not clear how central executive works, or what exactly it does, only concerned with stm so not a comprehensive model of memory