MKTG 342 EXAM 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
1
New cards
marketing
* activity, set of institutions, and process for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that customers value
* how to meet customer needs, profitably
* how to meet customer needs, profitably
2
New cards
marketing concept
achieving organizational goals requires being more effective than competitors in creating, delivering, and communicating __customer value__ to chosen target markets
3
New cards
what is the difference between marketing research and marketing stretegy?
marketing research
* the process of designing, gathering, analyzing, and reporting information to solve a specific marketing problem
* not continuous, has a beginning and end
marketing strategy
* consists of selecting a target market and designing the proper ‘mix’ of the 4Ps to meet the wants and needs of consumers
good marketing research → good marketing strategy
* the process of designing, gathering, analyzing, and reporting information to solve a specific marketing problem
* not continuous, has a beginning and end
marketing strategy
* consists of selecting a target market and designing the proper ‘mix’ of the 4Ps to meet the wants and needs of consumers
good marketing research → good marketing strategy
4
New cards
when do you use marketing research?
* to help identify marketing opportunities and problems
* __ex____:__ zoom taking the opp. during covid vs. skype
* to help generate, refine, and evaluate potential marketing actions
* used in…
* selecting target markets
* product/pricing/promotion/distribution research
* to monitor marketing performance
* tracking data at the point of sale
* tracking social media
* __ex____:__ zoom taking the opp. during covid vs. skype
* to help generate, refine, and evaluate potential marketing actions
* used in…
* selecting target markets
* product/pricing/promotion/distribution research
* to monitor marketing performance
* tracking data at the point of sale
* tracking social media
5
New cards
strengths + weaknesses (SWOT)
* internal capabilities of the firm’s employees
* company reputation
* customer relationships
* satisfaction, retention, recommendation behavior
* downstream effectiveness
* distribution, pricing, promotion, innovation
* perceptions of quality
* company reputation
* customer relationships
* satisfaction, retention, recommendation behavior
* downstream effectiveness
* distribution, pricing, promotion, innovation
* perceptions of quality
6
New cards
opportunity (SWOT)
buyer needs or interests that has a high probability of profitability satisfying (external)
7
New cards
threat (SWOT)
challenge posed by an unfavorable trend or development that, without counter action, would lead to lower sales or profit
8
New cards
types of research
basic research
* expands general knowledge rather than solving a specific problem
* results often can’t be directly implemented
applied research
* tries to solve specific problems
* most marketing research by companies falls into this category
* expands general knowledge rather than solving a specific problem
* results often can’t be directly implemented
applied research
* tries to solve specific problems
* most marketing research by companies falls into this category
9
New cards
what is marketing information systems (MIS) and what are the 4 components
MIS
* the people, equipment, and procedures used to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute information to marketing decision makers
internal reports system
* gathers information generated __within__ a firm (orders, billings, inventory: accounting related)
* daily transactions information (products purchased, payment methods, etc)
intelligence system
* brings in information generated __outside__ of the firm
* magazines, trade publications, newspapers
decision support system
* data collected that will be __analyzed__ to generate decision-making insights
research system
* gathers information for a __specific__ situation (__ex____:__ what promotion to use or which logo will be more effective)
* information not gathered by the other MIS
* the people, equipment, and procedures used to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate, and distribute information to marketing decision makers
internal reports system
* gathers information generated __within__ a firm (orders, billings, inventory: accounting related)
* daily transactions information (products purchased, payment methods, etc)
intelligence system
* brings in information generated __outside__ of the firm
* magazines, trade publications, newspapers
decision support system
* data collected that will be __analyzed__ to generate decision-making insights
research system
* gathers information for a __specific__ situation (__ex____:__ what promotion to use or which logo will be more effective)
* information not gathered by the other MIS
10
New cards
what are the values of marketing research?
* decrease uncertainty
* increase the likelihood of a correct decision
* improve marketing performance, resulting in higher profits
* increase the likelihood of a correct decision
* improve marketing performance, resulting in higher profits
11
New cards
what are the costs of marketing research?
* research expenditures
* time needed could delay a marketing decision
* possible wrong research results
* possible disclosure of information to rivals
* time needed could delay a marketing decision
* possible wrong research results
* possible disclosure of information to rivals
12
New cards
when is marketing research not needed?
* information is already available
* past studies
* internal reports in MIS
* timing is wrong
* do we need to act immediately
* is the product at the end of its life cycle
* past studies
* internal reports in MIS
* timing is wrong
* do we need to act immediately
* is the product at the end of its life cycle
13
New cards
what is the difference between symptoms and problems?
symptoms
* __observable__ signs that problems exist
problems
* situations calling for managers to make choices among alternatives
* __observable__ signs that problems exist
problems
* situations calling for managers to make choices among alternatives
14
New cards
problem statements
concise descriptions of problems or opportunities
15
New cards
iceberg principle
* decision maker (top of iceberg) → symptoms
* researcher (under water) → problems
* researcher (under water) → problems
16
New cards
what do KPIs provide?
measures how well a company is performing relative to an objective
17
New cards
situation analysis
gathers background information helpful in defining the problem
18
New cards
how do research objectives relate to hypotheses?
research objectives (RO)
* specified what information is needed to solve the problem
* specifies who to gather information from
* a research study may have multiple ROs
* can be a question or a statement
hypotheses
* statements that are taken as true for the purpose of argument or investigation
* specified what information is needed to solve the problem
* specifies who to gather information from
* a research study may have multiple ROs
* can be a question or a statement
hypotheses
* statements that are taken as true for the purpose of argument or investigation
19
New cards
Unidimensional variables vs. constructs
unidimensional
* height, weight, etc.
constructs
* multidimensional
* abstract concept composed of attitudes or behaviors that are related
* height, weight, etc.
constructs
* multidimensional
* abstract concept composed of attitudes or behaviors that are related
20
New cards
research design
specifies the methods that will be used to collect and analyze information for a research project
21
New cards
what are the objectives of a research design?
* gain background information
* develop hypotheses
* measure a variable of interest
* test hypotheses about relationship between variables
* develop hypotheses
* measure a variable of interest
* test hypotheses about relationship between variables
22
New cards
what are the 3 types of research design?
* exploratory research
* best when there is little known about the problem
* descriptive research
* best when problem is somewhat clear
* causal research
* best when the problem is very clear
* best when there is little known about the problem
* descriptive research
* best when problem is somewhat clear
* causal research
* best when the problem is very clear
23
New cards
exploratory research
unstructured, informal, and often conducted at the beginning of research projects
* used to gain background information
* used to define terms
* used to clarify problems and hypotheses
* used to establish research prioties
* used to gain background information
* used to define terms
* used to clarify problems and hypotheses
* used to establish research prioties
24
New cards
what are the different types of exploratory research methods?
* secondary data analysis
* search for and interpret existing relevant information
* experience surveys
* gather information from those knowledgeable on the relevant issue
* leader-user survey
* case analysis
* viewing information about a past situation that has similarities to the current research problem
* focus groups
* utilize small groups of consumers guided by a moderator through an unstructured discussion to gain information
* search for and interpret existing relevant information
* experience surveys
* gather information from those knowledgeable on the relevant issue
* leader-user survey
* case analysis
* viewing information about a past situation that has similarities to the current research problem
* focus groups
* utilize small groups of consumers guided by a moderator through an unstructured discussion to gain information
25
New cards
what is the purpose of descriptive research studies?
helps describe important market/consumer characteristics and function
* process is more formal and well defined
* examines who, what, where, and when
* helps provide answers to broader questions
* necessitates a representative sample
* may be gathered with or without directly interacting with respondents
* process is more formal and well defined
* examines who, what, where, and when
* helps provide answers to broader questions
* necessitates a representative sample
* may be gathered with or without directly interacting with respondents
26
New cards
types of descriptive research studies
* cross sectional studies
* measures units from a sample of the population at only one point in time
* sample surveys
* longitudinal studies
* repeatedly measure the same sample units of a population over time
* measures units from a sample of the population at only one point in time
* sample surveys
* longitudinal studies
* repeatedly measure the same sample units of a population over time
27
New cards
continuous panels
(related to longitudinal studies)
ask panel members the same questions on each measurement occasion
* brand switching studies
* market tracking studies
ask panel members the same questions on each measurement occasion
* brand switching studies
* market tracking studies
28
New cards
discontinuous panels
(related to longitudinal study)
vary questions from one measurement to the next
vary questions from one measurement to the next
29
New cards
causality
a conditional relationship in which a change in a variable(s) affects a change in one or more variables
30
New cards
experiment
(related to causal research)
a study in which one or more IV at a time are manipulated to see how they affect a DV
a study in which one or more IV at a time are manipulated to see how they affect a DV
31
New cards
experimental design
(related to causal research)
provides the setting for us to examine if a change in a DV may be attributed solely to the change in an IV
provides the setting for us to examine if a change in a DV may be attributed solely to the change in an IV
32
New cards
why do we need control and treatment groups?
to tell if the difference in DV is the result of the change in IV or something else
33
New cards
why is random assignment important?
to ensure that we don’t have groups that are fundamentally different
34
New cards
pretest
measures if the 2 groups (that got randomly assigned) are about the same ob an important variable before beginning
35
New cards
before-after testing
the DV is measured in both groups at two time points
**(T2 - T1) - (C2 - C1)**
**(T2 - T1) - (C2 - C1)**
36
New cards
A/B testing
we test 2 alternatives simultaneously to see which is better
* there is no control group
* there is no control group
37
New cards
internal vs. external validity
internal
* the extent to which the change in the DV is actually due to the change in the IV
external
* the extent that the relationship observed between the IV and DV during the experiment is generalizable to the “real world”
* the extent to which the change in the DV is actually due to the change in the IV
external
* the extent that the relationship observed between the IV and DV during the experiment is generalizable to the “real world”
38
New cards
lab vs. field experiments
laboratory
* the IV is manipulated and DV is measured in an __artificial__ setting
* higher internal validity
field
* the IV is manipulated and the DV is measured in its __natural__ setting
* higher external validity
* the IV is manipulated and DV is measured in an __artificial__ setting
* higher internal validity
field
* the IV is manipulated and the DV is measured in its __natural__ setting
* higher external validity
39
New cards
what are the uses of databases?
* identify prospects
* identify customers who requested information and provide them with a personalized sale presentation
* sending customized offers
* send purchasers of a product an offer for a different one 2 weeks later
* reactivate purchases
* automated messages can increase customer awareness (on birthdays, after 6 months, etc.)
* avoid customer mistakes
* identify the most profitable customers can prevent treating them like “any other” customer
* identify customers who requested information and provide them with a personalized sale presentation
* sending customized offers
* send purchasers of a product an offer for a different one 2 weeks later
* reactivate purchases
* automated messages can increase customer awareness (on birthdays, after 6 months, etc.)
* avoid customer mistakes
* identify the most profitable customers can prevent treating them like “any other” customer
40
New cards
advantages and disadvantages of secondary data
advantages
* quickly obtainable
* inexpensive
* readily available
* can enhance primary data insights
disadvantages
* in compatible or unmatched reporting units
* __ex:__ you want city-level data, only state-level is available
* unusable class definitions
* __ex:__ you want data of a city with a population over 80,000, only 60,000+ is available
* may be outdated or not credible
* competition may have access to the same data
* quickly obtainable
* inexpensive
* readily available
* can enhance primary data insights
disadvantages
* in compatible or unmatched reporting units
* __ex:__ you want city-level data, only state-level is available
* unusable class definitions
* __ex:__ you want data of a city with a population over 80,000, only 60,000+ is available
* may be outdated or not credible
* competition may have access to the same data
41
New cards
online user generated content
information created by online users that is and intended to be shared with others
42
New cards
social media monitoring
involves actively gathering, organizing, and analyzing social media data to gain consumer insights
43
New cards
3 main social media data platforms
* online communities/forums
* blogs
* social networks
* blogs
* social networks
44
New cards
how do we analyze social media posts?
several dimensions of __posts__
* post sentiment (positivity/negativity of post)
* post emotions
* post length
also…
* mean post characteristics
* number of comments
* post sentiment (positivity/negativity of post)
* post emotions
* post length
also…
* mean post characteristics
* number of comments
45
New cards
3 categories of research
* quantitative research
* qualitative research
* mixed methods research
* qualitative research
* mixed methods research
46
New cards
quantitative research
uses structured questions with predetermined response options, response is 'quantified’
47
New cards
qualitative research
involves collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data that is in the form of words or text
48
New cards
mixed methods research
integrates both quantitative and qualitative research methods
* qualitative before quantitative
* quantitative before qualitative
* both at the same time
* qualitative before quantitative
* quantitative before qualitative
* both at the same time
49
New cards
observation methods
techniques in which phenomena of interest involving people, objects, and/or activities are systematically __observed__ and __documented__
50
New cards
types of observation methods
* direct vs. indirect
* overt vs. covert
* structured vs. unstructured
* in situ vs. invented
* overt vs. covert
* structured vs. unstructured
* in situ vs. invented
51
New cards
direct vs. indirect observation
direct
* observes behaviors as it occurs in real time
indirect
* observes the effects/results of behavior
* archives
* physical traces (like popcorn in movie theatre)
* observes behaviors as it occurs in real time
indirect
* observes the effects/results of behavior
* archives
* physical traces (like popcorn in movie theatre)
52
New cards
covert vs. overt observation
covert
* subjects are unaware that they are being observed
overt
* subjects are aware that they are being observed
* subjects are unaware that they are being observed
overt
* subjects are aware that they are being observed
53
New cards
structured vs. unstructured observation
structured
* the behaviors to be observed (and recorded) are determined beforehand
unstructured
* all behavior is observed and recorded
* the behaviors to be observed (and recorded) are determined beforehand
unstructured
* all behavior is observed and recorded
54
New cards
in situ vs. invented observation
in situ
* approaches observe subjects in natural settings (higher external validity)
invented
* uses a ‘simulated’ environment (higher internal validity)
* approaches observe subjects in natural settings (higher external validity)
invented
* uses a ‘simulated’ environment (higher internal validity)
55
New cards
advantages and disadvantages of observational techniques
advantages:
* insight into actual consumer behavior, not just what they say they do
* no chance of recall errors by consumers
* applicable to most settings
disadvantages:
* behavior observed needs to be relatively short
* interpretations are more subjective than analyzing secondary data
* does not examine causality
* insight into actual consumer behavior, not just what they say they do
* no chance of recall errors by consumers
* applicable to most settings
disadvantages:
* behavior observed needs to be relatively short
* interpretations are more subjective than analyzing secondary data
* does not examine causality
56
New cards
Purpose and objective of focus groups
* generate new ideas
* understand the vocabulary of consumers
* reveal motives, perceptions, and attitudes
* deepen understanding of quantitative studies (we see the “why”)
* describe (not predict) a phenomenon
* understand the vocabulary of consumers
* reveal motives, perceptions, and attitudes
* deepen understanding of quantitative studies (we see the “why”)
* describe (not predict) a phenomenon
57
New cards
advantages and disadvantages of focus groups
advantages:
* great for generating new ideas
* can be used to understand a wide variety of issues
* allow fairly easy access to special respondent groups
disadvantages:
* representativeness of target market may be low
* depend on moderator’s skill
* interpretation of information sometimes is difficult
* great for generating new ideas
* can be used to understand a wide variety of issues
* allow fairly easy access to special respondent groups
disadvantages:
* representativeness of target market may be low
* depend on moderator’s skill
* interpretation of information sometimes is difficult
58
New cards
ethnographic research
descriptive study of a group and their behavior, characteristics, and culture
* shopalongs
* mobile ethnography
* netnography
* shopalongs
* mobile ethnography
* netnography
59
New cards
thematic analysis
* thematic analysis
* examines qualitative data to uncover themes (patterns that relate to the objective of research)
* researchers look for substantiating examples from what participants said/wrote that provide evidence of a theme
* word cloud
* examines qualitative data to uncover themes (patterns that relate to the objective of research)
* researchers look for substantiating examples from what participants said/wrote that provide evidence of a theme
* word cloud
60
New cards
eye tracking
measures eye positions and movement
61
New cards
facial coding
measures expressions of emotions by facial appearances
62
New cards
why not just sample the entire populaion?
* expensive
* too many people
* analyzing that much data is difficult
* too many people
* analyzing that much data is difficult
63
New cards
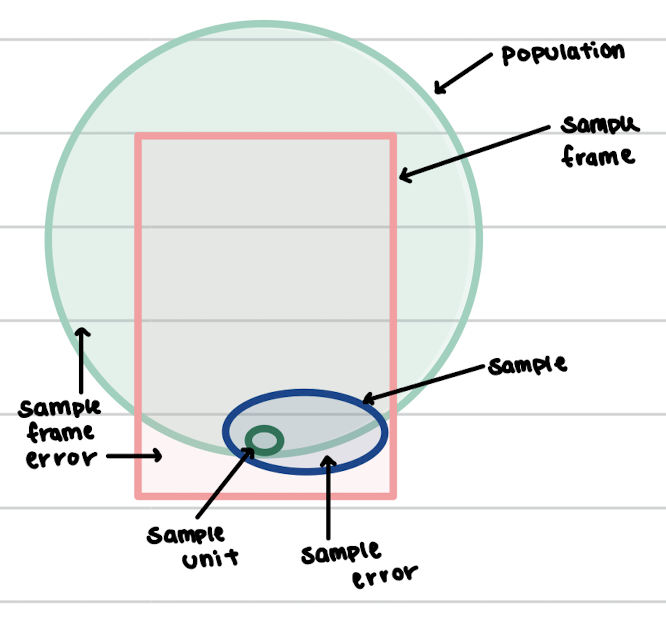
sampling error, sampling unit, sample, population, sampling frame, sampling frame error -- how are they related?
sample unit
* the basic level of investigation
sample frame
* a master source of sample units in the population (hopefully)
sampling frame error
* the sample frame fails to account for all of the population
sampling error
* any error in a survey that occurs because a sample is used
* could be due to sample selection method
* could be due to sampling size
* the basic level of investigation
sample frame
* a master source of sample units in the population (hopefully)
sampling frame error
* the sample frame fails to account for all of the population
sampling error
* any error in a survey that occurs because a sample is used
* could be due to sample selection method
* could be due to sampling size
64
New cards
probability vs. non probability sampling
probability sampling
* members have a known probability of being selected for the sample
* using an objective method to select sample units
nonprobability sampling
* probability of selecting members from the population into the sample is unknown
* subjective way of selecting samples and based on the knowledge of researcher
* members have a known probability of being selected for the sample
* using an objective method to select sample units
nonprobability sampling
* probability of selecting members from the population into the sample is unknown
* subjective way of selecting samples and based on the knowledge of researcher
65
New cards
what are the 4 probability sampling methods
* simple random sampling
* systematic sampling
* cluster sampling
* stratified sampling
* systematic sampling
* cluster sampling
* stratified sampling
66
New cards
simple random sampling
the probability of being selected into the sample is equal for all members of the population
* sample size / population size
**advantage**:
* every population member has an equal chance to be selected, so representative
**disadvantages:**
* creating a population list and randomly selecting from it may be time consuming
* there still may be sample error if the population is listed incompletely or inaccurately
* sample size / population size
**advantage**:
* every population member has an equal chance to be selected, so representative
**disadvantages:**
* creating a population list and randomly selecting from it may be time consuming
* there still may be sample error if the population is listed incompletely or inaccurately
67
New cards
systematic sampling
a sample is selected systematically from a list using skip interval
* population list size / sample size
**advantages:**
* easy and quick way to draw samples
* less costly
**disadvantage:**
* if the sample frame doesn’t include all members of the population, then they cannot be included in the sample
* population list size / sample size
**advantages:**
* easy and quick way to draw samples
* less costly
**disadvantage:**
* if the sample frame doesn’t include all members of the population, then they cannot be included in the sample
68
New cards
cluster sampling
the population is divided into naturally existing clusters (subgroups), each of which could represent the entire population
* each cluster is assumed to be representative of the population
* we take a subsample of a cluster
* clusters can be created based on a variety of identifiers
* *area sampling* divides demographic areas into clusters
**advantages:**
* cost effective
* easy to implement
* the clusters are often readily available
**disadvantage:**
* cluster specification error
* when clusters are NOT homogeneous
* each cluster is assumed to be representative of the population
* we take a subsample of a cluster
* clusters can be created based on a variety of identifiers
* *area sampling* divides demographic areas into clusters
**advantages:**
* cost effective
* easy to implement
* the clusters are often readily available
**disadvantage:**
* cluster specification error
* when clusters are NOT homogeneous
69
New cards
stratified sampling
population is divided into different subgroups (called strata) and all subgroups are sampled
* useful when we think that the units within each stratum are not ‘balanced’
* must consider the sizes of the strata relative to the population size to calculate a weighted mean
* (data %) + (data \* %) …
* proportionate stratified sample
* sample size scaled to population size
* useful when we think that the units within each stratum are not ‘balanced’
* must consider the sizes of the strata relative to the population size to calculate a weighted mean
* (data %) + (data \* %) …
* proportionate stratified sample
* sample size scaled to population size
70
New cards
what are the 4 nonprobability sampling approaches
* convenience sample
* chain referral “snowball” sample
* purposive “judgment” sample
* quota sampling
* chain referral “snowball” sample
* purposive “judgment” sample
* quota sampling
71
New cards
convenience sampling
draw at the convenience of the researcher
* the selection of time, place, and situation is subjective
**advantages:**
* can interview a high number of respondents quickly
* good in early stages of research to pretest a questionnaire
**disadvantages:**
* difficult to determine if the sample is representative
* results are often not generalizable
* often times not much variation in the sample
* the selection of time, place, and situation is subjective
**advantages:**
* can interview a high number of respondents quickly
* good in early stages of research to pretest a questionnaire
**disadvantages:**
* difficult to determine if the sample is representative
* results are often not generalizable
* often times not much variation in the sample
72
New cards
chain referral “snowball” sampling
the initial respondents provide names of other prospective respondents
**advantages:**
* effective when the population is small or unique
* helpful when conducting qualitative research
**disadvantages:**
* the generalizability of the results will likely be limited
* recommendations are based on the sample unit
**advantages:**
* effective when the population is small or unique
* helpful when conducting qualitative research
**disadvantages:**
* the generalizability of the results will likely be limited
* recommendations are based on the sample unit
73
New cards
purposive “judgment” sampling
requires an “educated guess” made by an experienced researcher as to who should represent the population (__ex:__ focus group)
**advantage:**
* can help gather insights from key respondents who may have important insights about larger groups
**disadvantages:**
* the sample likely won’t be representative
* depends on the expertise (and possible bias) of the researcher
**advantage:**
* can help gather insights from key respondents who may have important insights about larger groups
**disadvantages:**
* the sample likely won’t be representative
* depends on the expertise (and possible bias) of the researcher
74
New cards
quota sampling
ensures that specified percentages of the total sample come from various types of individuals or subgroups and selects them in a non-random way
**advantages:**
* can improve the representativeness of a sample, but it is still not random
* useful when researchers have a detailed demographic profile of the respondents
**disadvantages:**
* results may not be generalizable
* the study’s sample depends on subjective decisions by researchers
**advantages:**
* can improve the representativeness of a sample, but it is still not random
* useful when researchers have a detailed demographic profile of the respondents
**disadvantages:**
* results may not be generalizable
* the study’s sample depends on subjective decisions by researchers
75
New cards
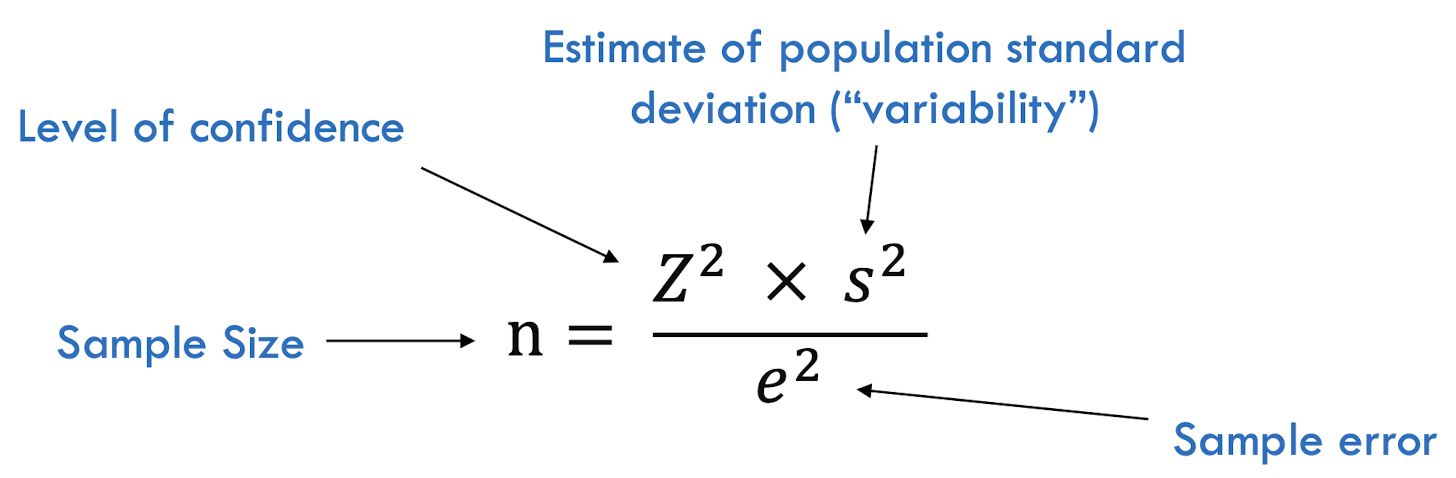
sample size general formula
76
New cards
margin of error
sample accuracy
* how close a random sample’s characteristics of interests (i.e., mean) is to the true population’s value it represents
as our acceptable margin of error decreases (more precise), the sample size we need increases
* the ‘e’ in the equation (denominator)
* how close a random sample’s characteristics of interests (i.e., mean) is to the true population’s value it represents
as our acceptable margin of error decreases (more precise), the sample size we need increases
* the ‘e’ in the equation (denominator)
77
New cards
variability
refers to how similar or dissimilar responses are to a given question
* as variability in the population increases, the sample size we need also increases
* the “s” in the equation (numerator)
* as variability in the population increases, the sample size we need also increases
* the “s” in the equation (numerator)
78
New cards
how do we estimate variability? what are our options?
* we can use data from a previous study on the same population that measured the population characteristic of interest
* we can conduct a pilot study of the population
* (1/4) \* range
* we can conduct a pilot study of the population
* (1/4) \* range
79
New cards
confidence level
how confident we want to be that the sample mean will contain the population mean
* “z” in the equation (numerator)
* “z” in the equation (numerator)
80
New cards
two types of major erros
nonsampling error
* all sources of error other than sample selection method and sample size
* the wrong problem is specified
* the questions are biased
* data is recorded incorrectly
* the data analysis is wrong
sampling error
* any error that occurs because a sample is used
* could be due to sample selection method
* could be due to sample size
* all sources of error other than sample selection method and sample size
* the wrong problem is specified
* the questions are biased
* data is recorded incorrectly
* the data analysis is wrong
sampling error
* any error that occurs because a sample is used
* could be due to sample selection method
* could be due to sample size
81
New cards
the normal distribution
* it is continuous
* it is symmetrical
* the distribution on each side of the mean is 0.5 (50%)
* it is symmetrical
* the distribution on each side of the mean is 0.5 (50%)
82
New cards
central limit theorem (CLT)
a sampling distribution derived from a random sample will be normally distributed
83
New cards
68-95-99.7 rule
* 68.27% of the data is within 1 SD of the mean
* 95.45% of the data is within 2SD of the mean
* 99.73% of the data is within 3 SD of the mean
* 95.45% of the data is within 2SD of the mean
* 99.73% of the data is within 3 SD of the mean
84
New cards
what is the z score?
the number of SD that a value, *x*, is away from the mean
* the z score for 95% is 1.96 because 95% of the area under the standard normal curve is within z scores of -1.96 and 1.96
* 95% of our data will be greater than or equal to z=-1.96 and less than or equal to z=1.96
* the z score for 95% is 1.96 because 95% of the area under the standard normal curve is within z scores of -1.96 and 1.96
* 95% of our data will be greater than or equal to z=-1.96 and less than or equal to z=1.96
85
New cards
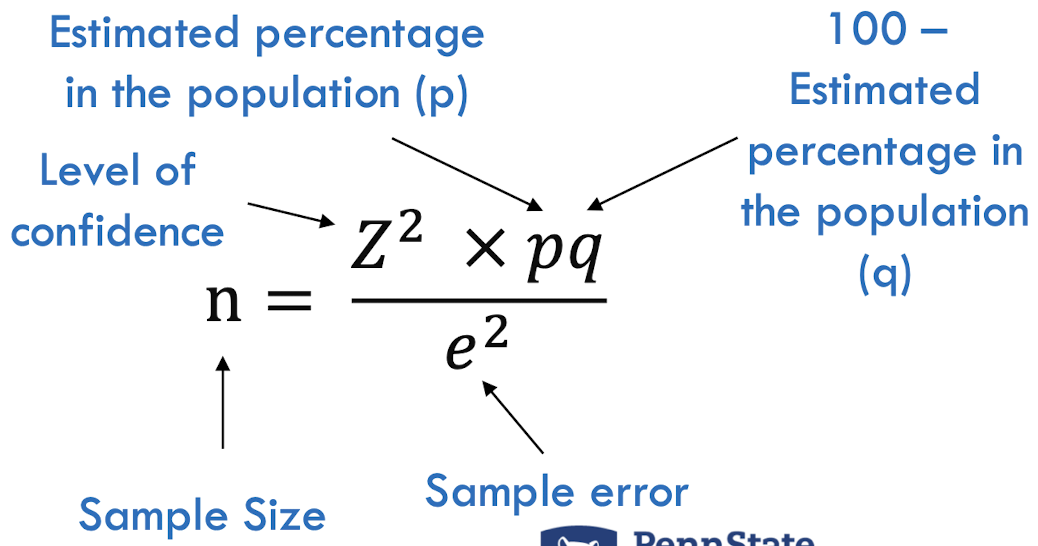
calculating sample size with proportions
* 50 X 50 is a “safe estimate”
* p = estimated % in a population
* q = 100 - p
* p = estimated % in a population
* q = 100 - p
86
New cards
what are the 5 dimensions of service quality?
* reliability
* responsiveness
* tangibles
* empathy
* assurance
* responsiveness
* tangibles
* empathy
* assurance