Unit 7: Biomolecules & Enzymes
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
macromolecule
any molecule that is produced by a living organism; examples are carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids
elements of life
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur
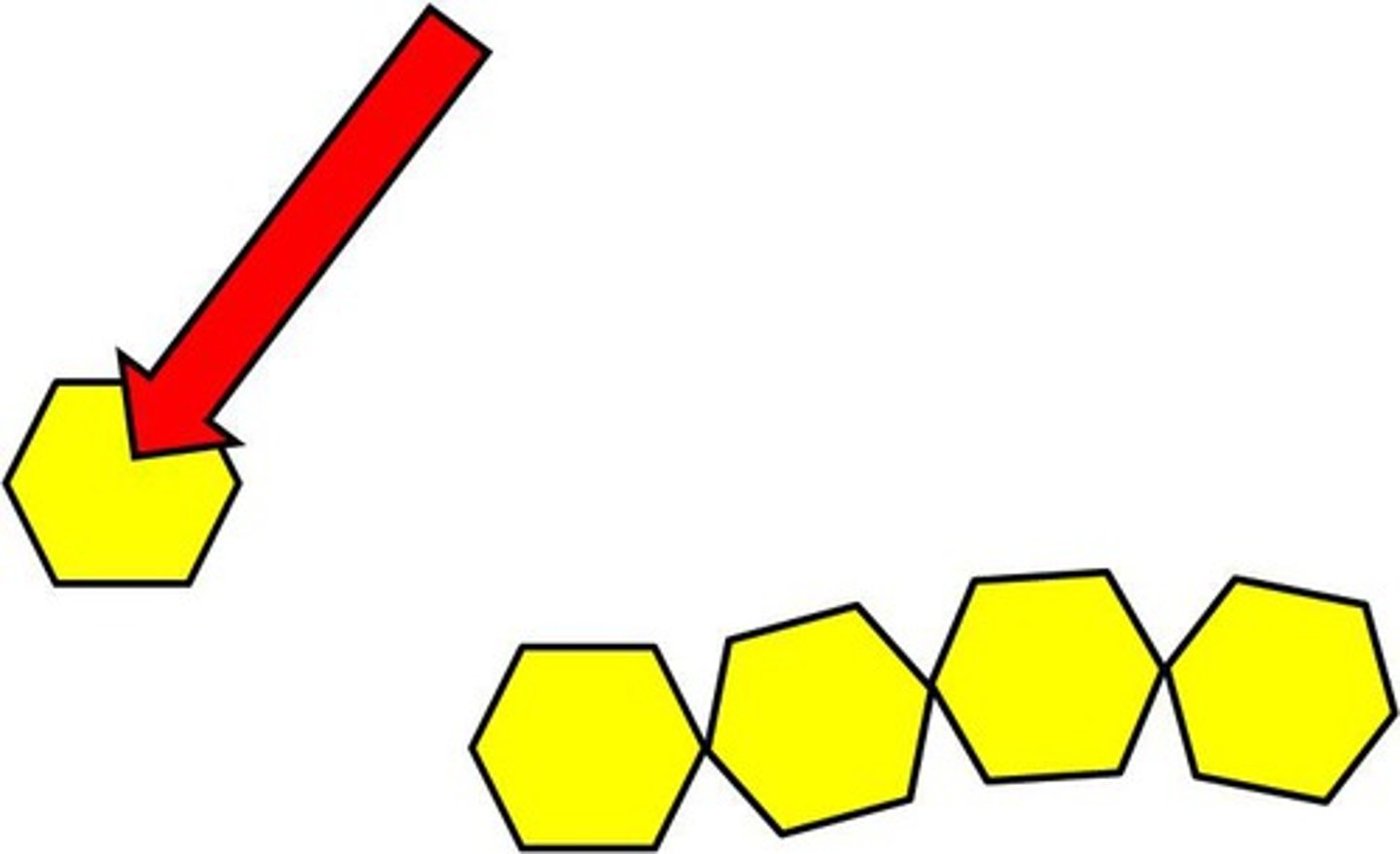
monomer
small units (building blocks) of a bigger molecule
polymer
large molecule formed from combinations of many monomers
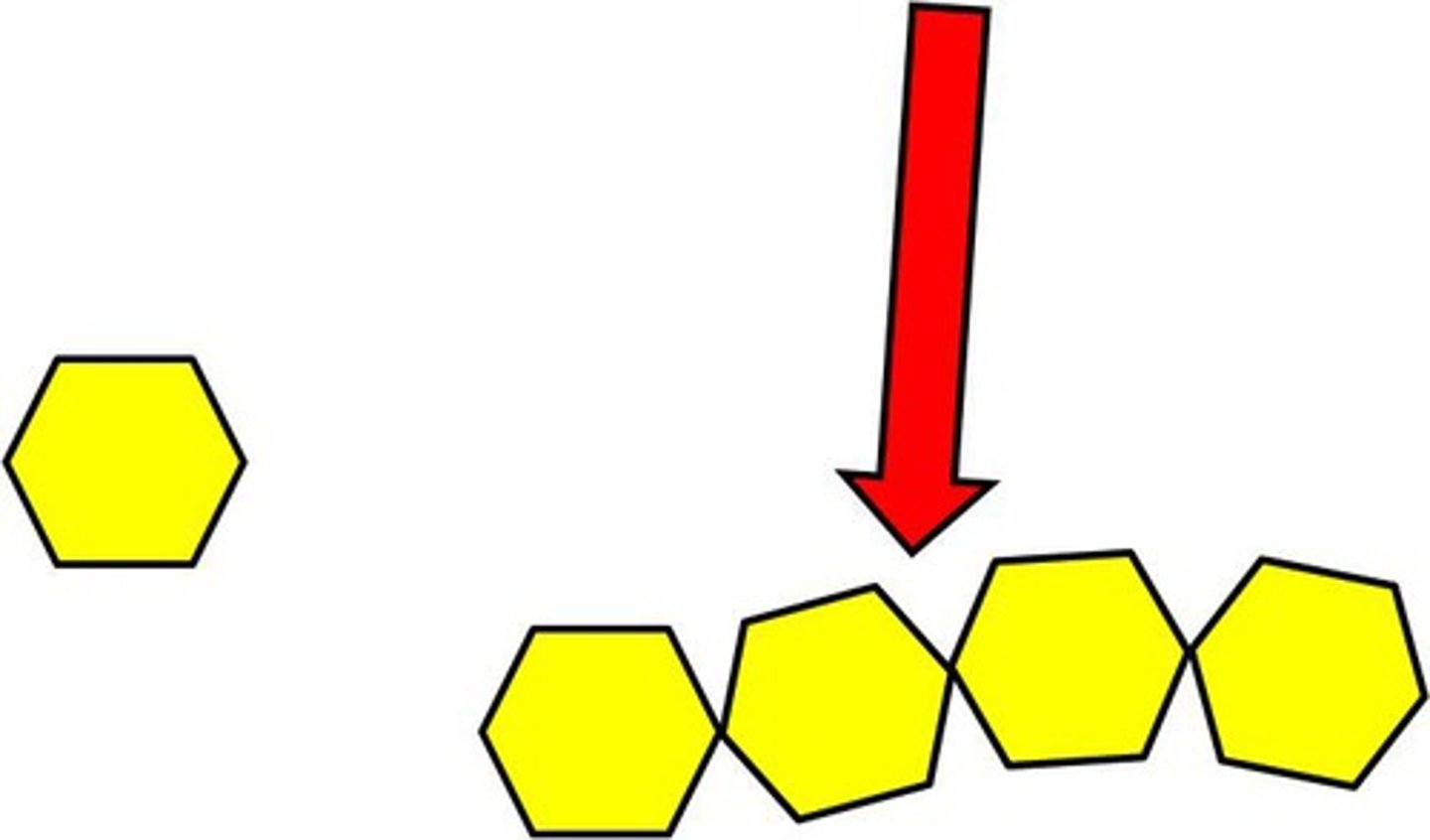
dehydration synthesis
a chemical reaction that removes water from two small molecules to build a larger molecule
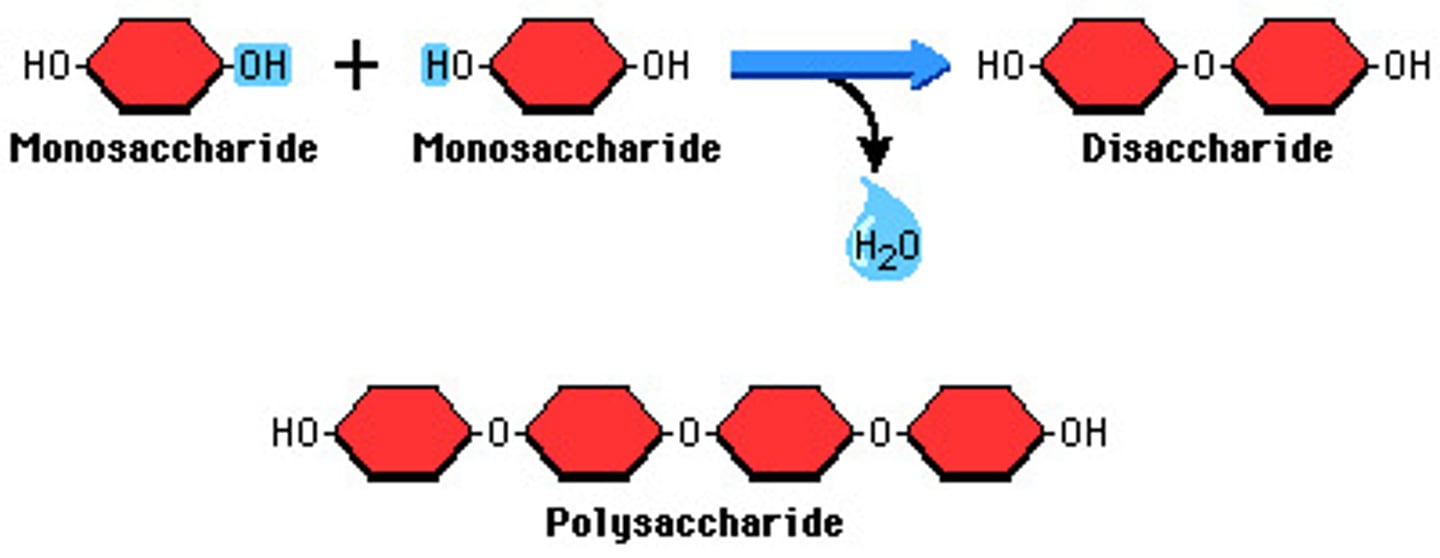
hydrolysis
a chemical reaction that breaks molecules apart by adding a water molecule
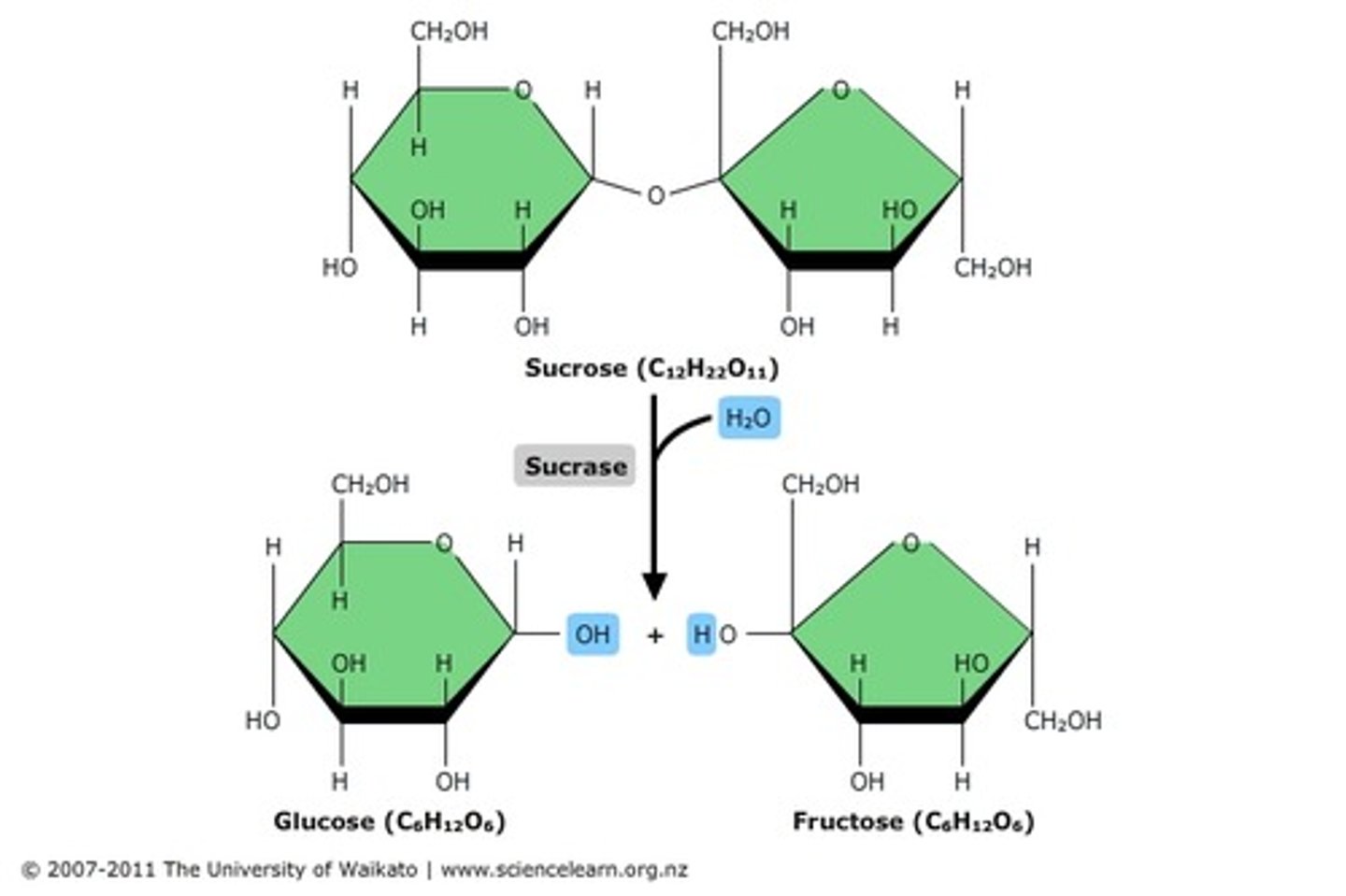
carbohydrate
utilized as a primary energy source for living things
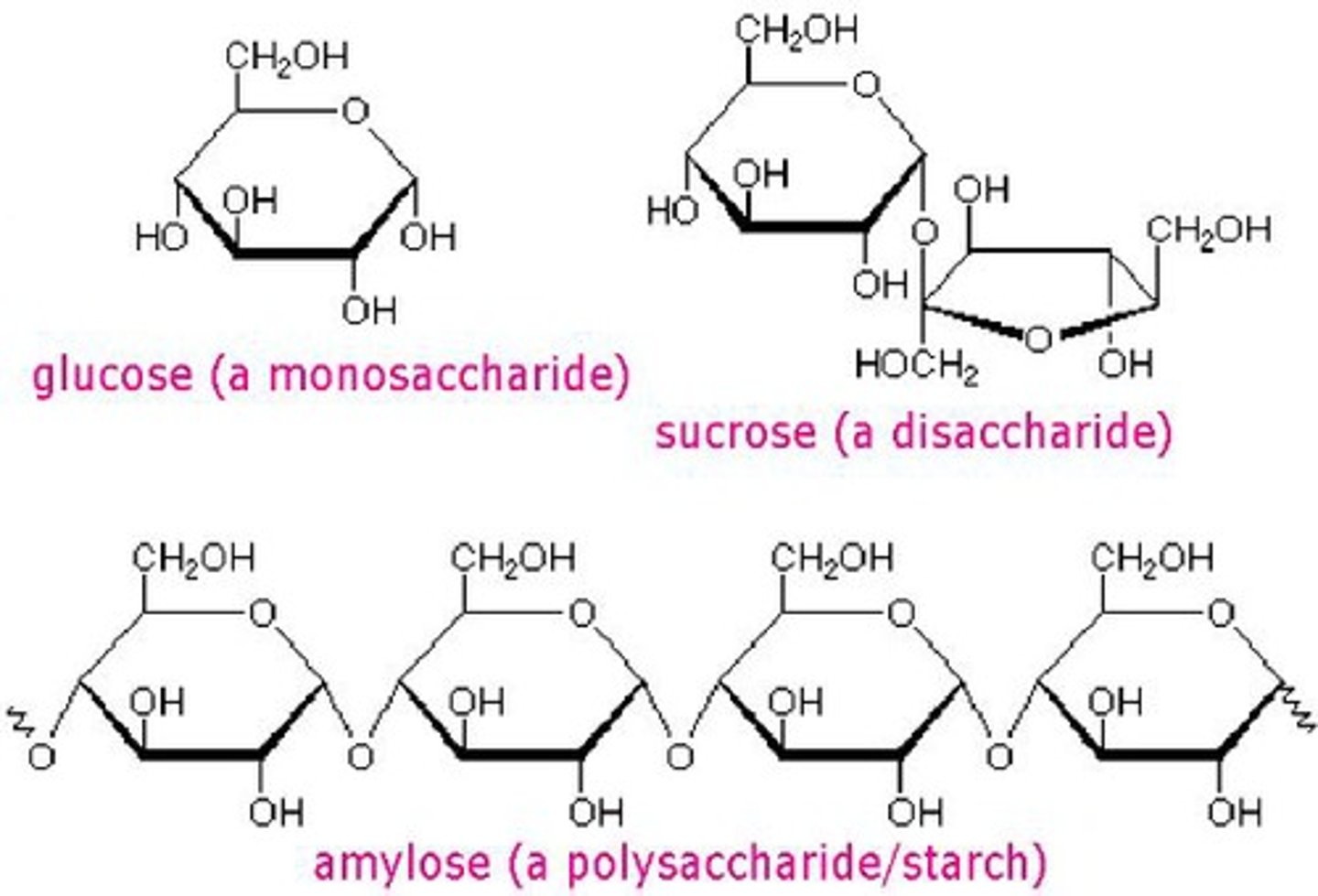
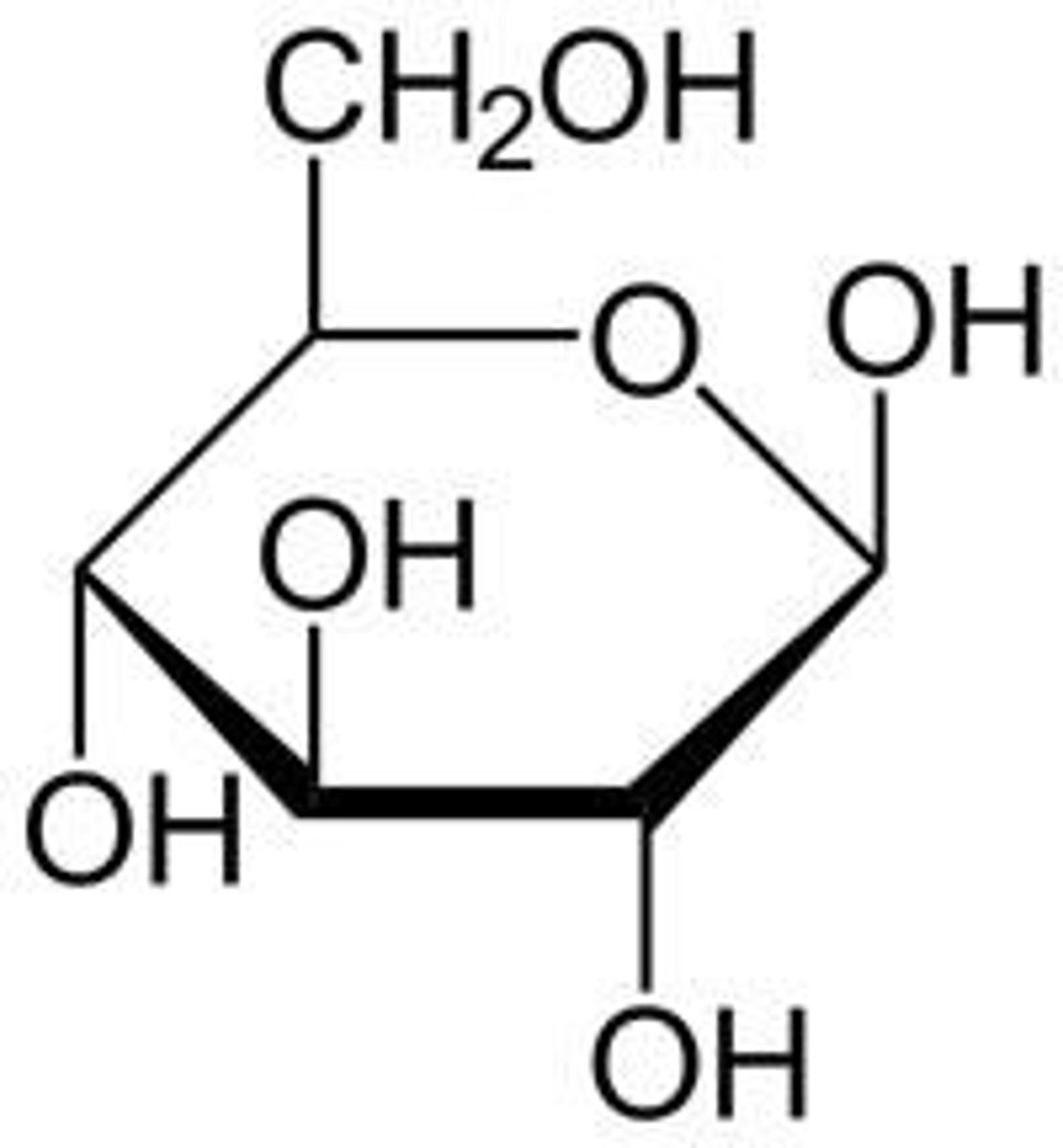
monosaccharide
single sugar molecule; monomer of a carbohydrate
polysaccharide
polymer of a carbohydrate
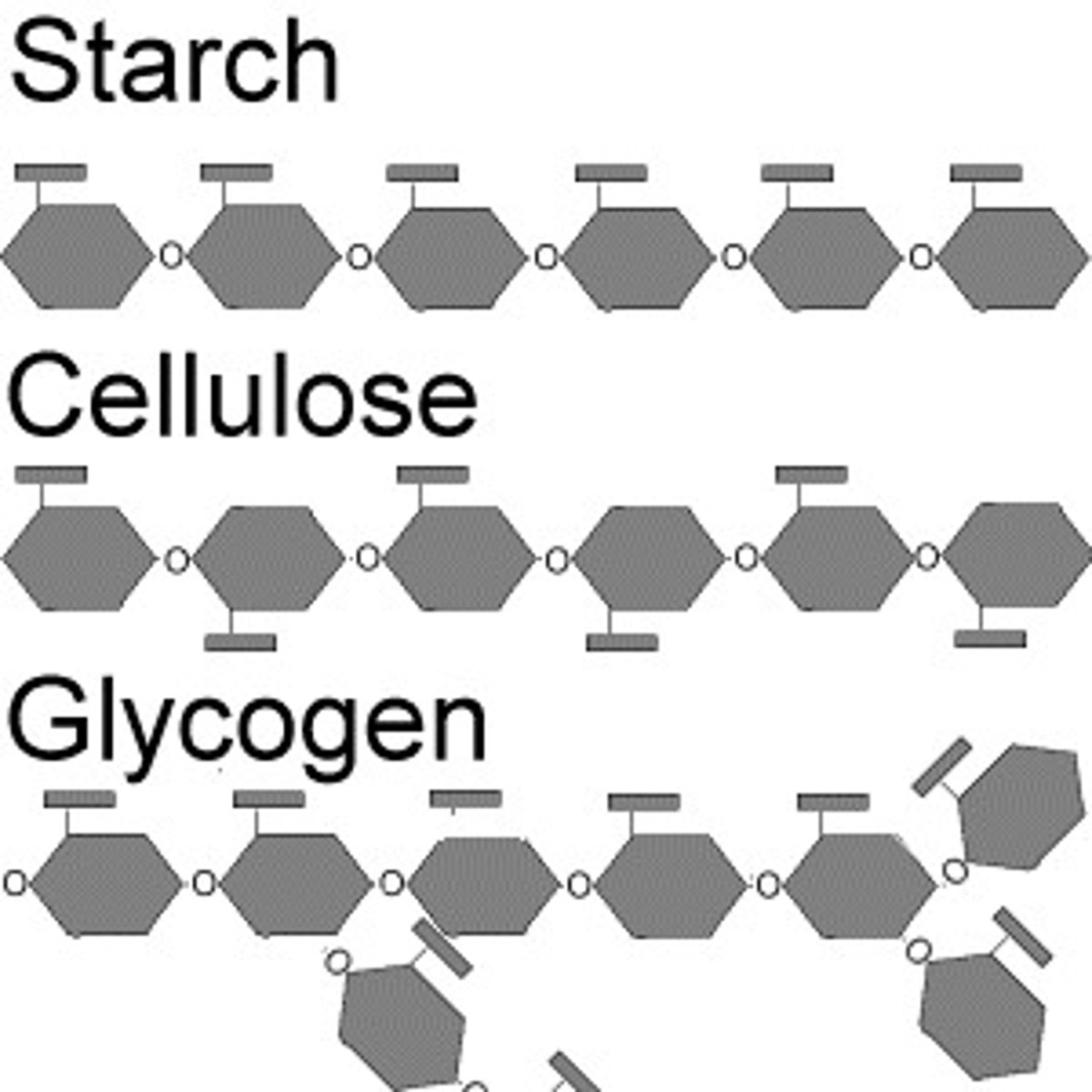
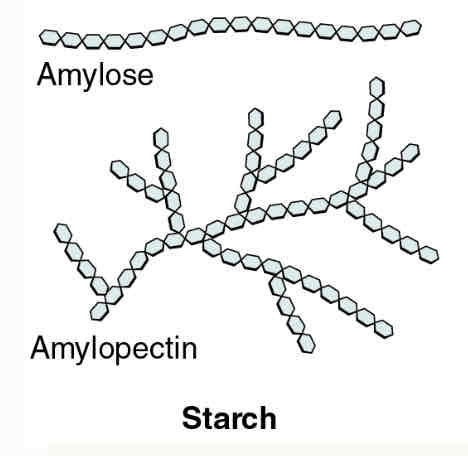
starch
plant glucose storage
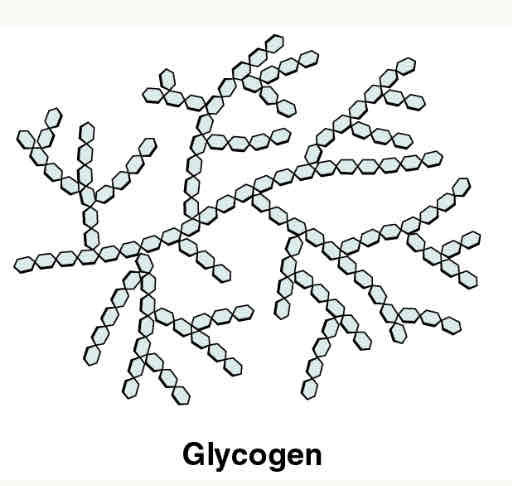
glycogen
animal glucose storage
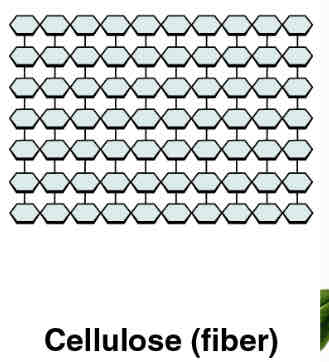
cellulose
carbohydrate that reinforces plant cell walls
chitin
carbohydrate that reinforces fungi cell walls and composes exoskeletons
lipid
‘fats’ used to store energy long term and provide insulation; important part of the cell membrane; hydrophobic, no momomers
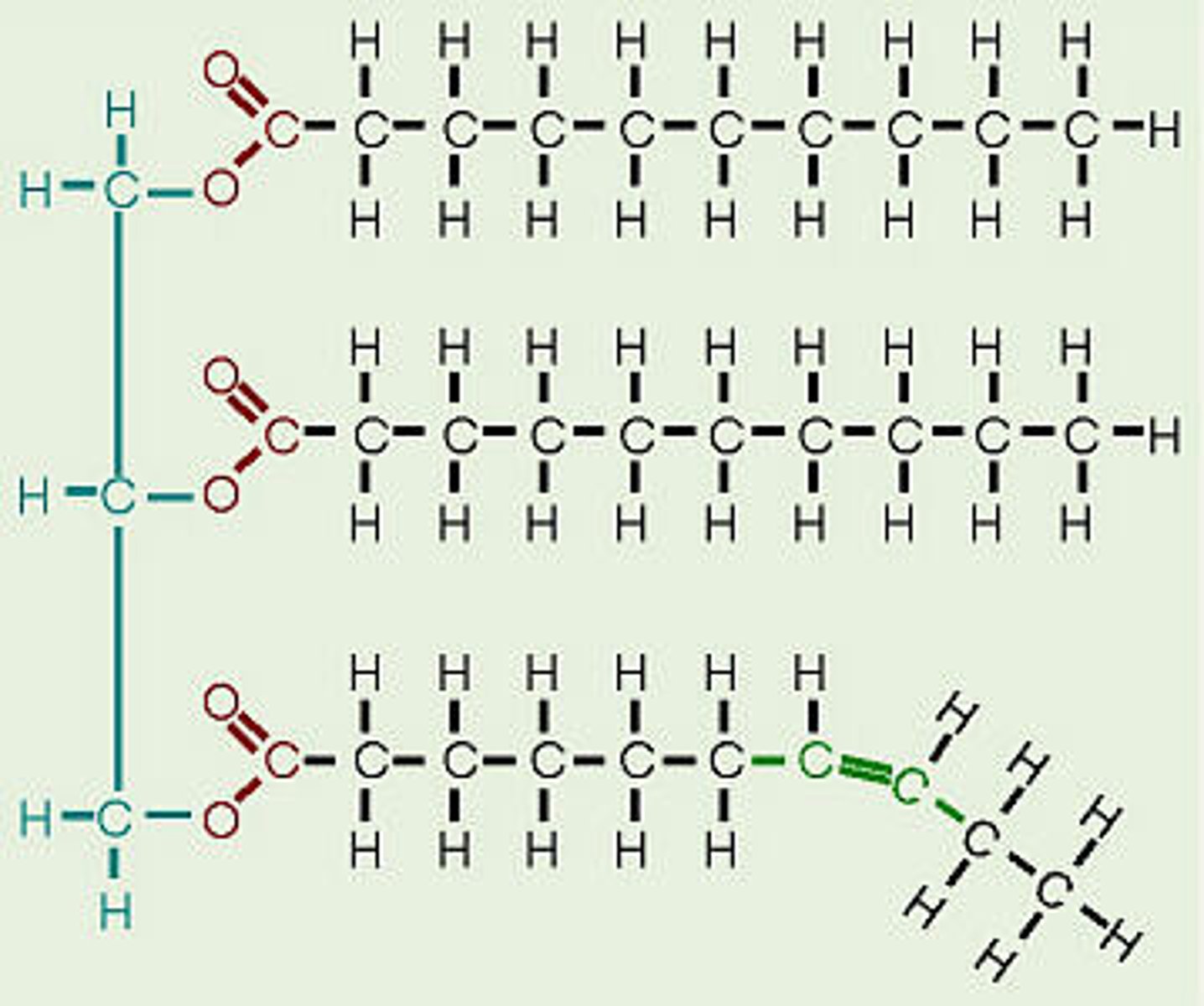
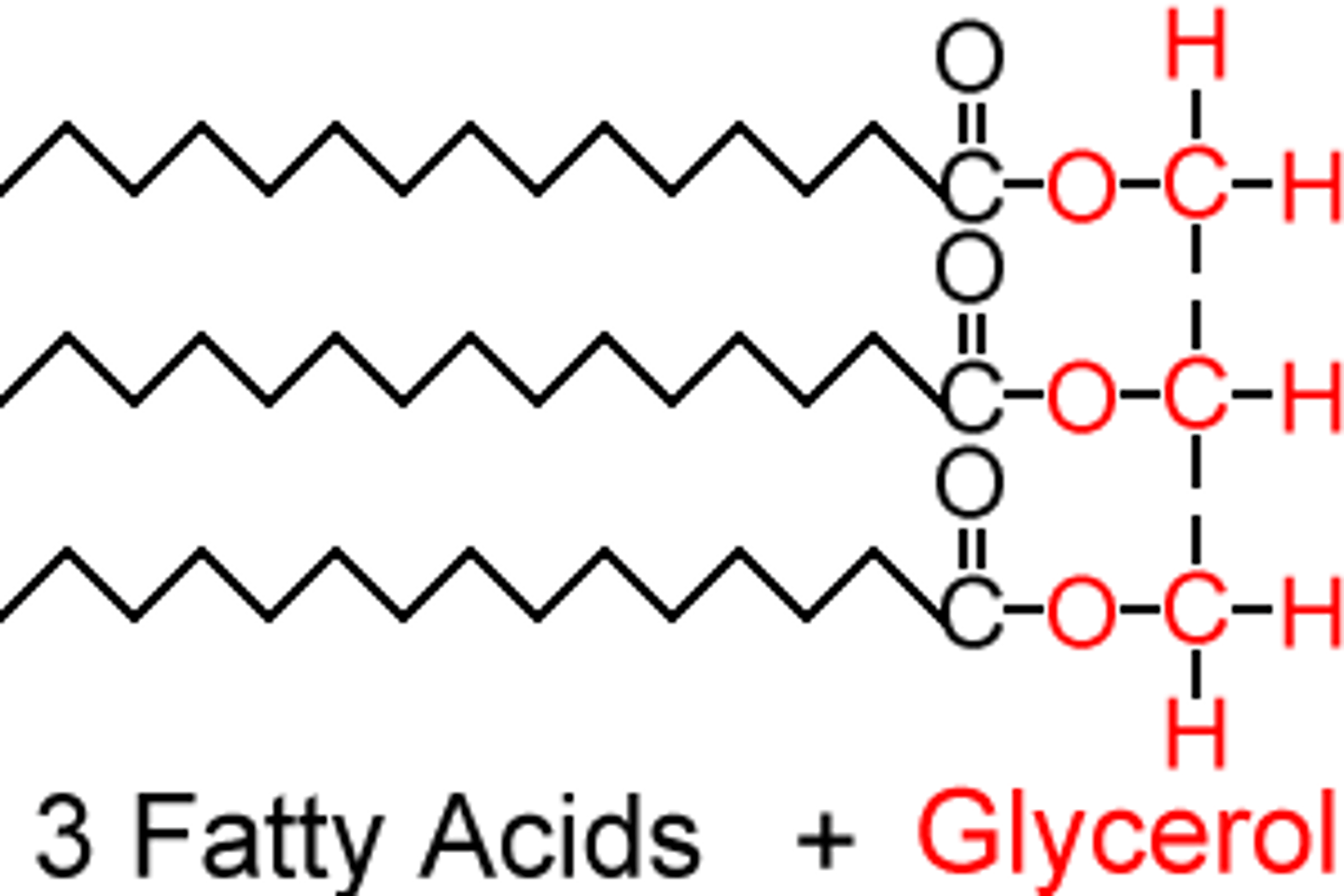
triglyceride
lipid used for long term energy storage; insulate against heat loss
wax
lipid that functions to repel water and protect surfaces
steroid
lipids that function as chemical messengers
phospholipid
lipid that composes cell membranes and surrounds organelles
protein
macromolecule that serves multiple functions in the body, such as - storage, transport, regulation, movement, structure, enzyme activity, and immunity
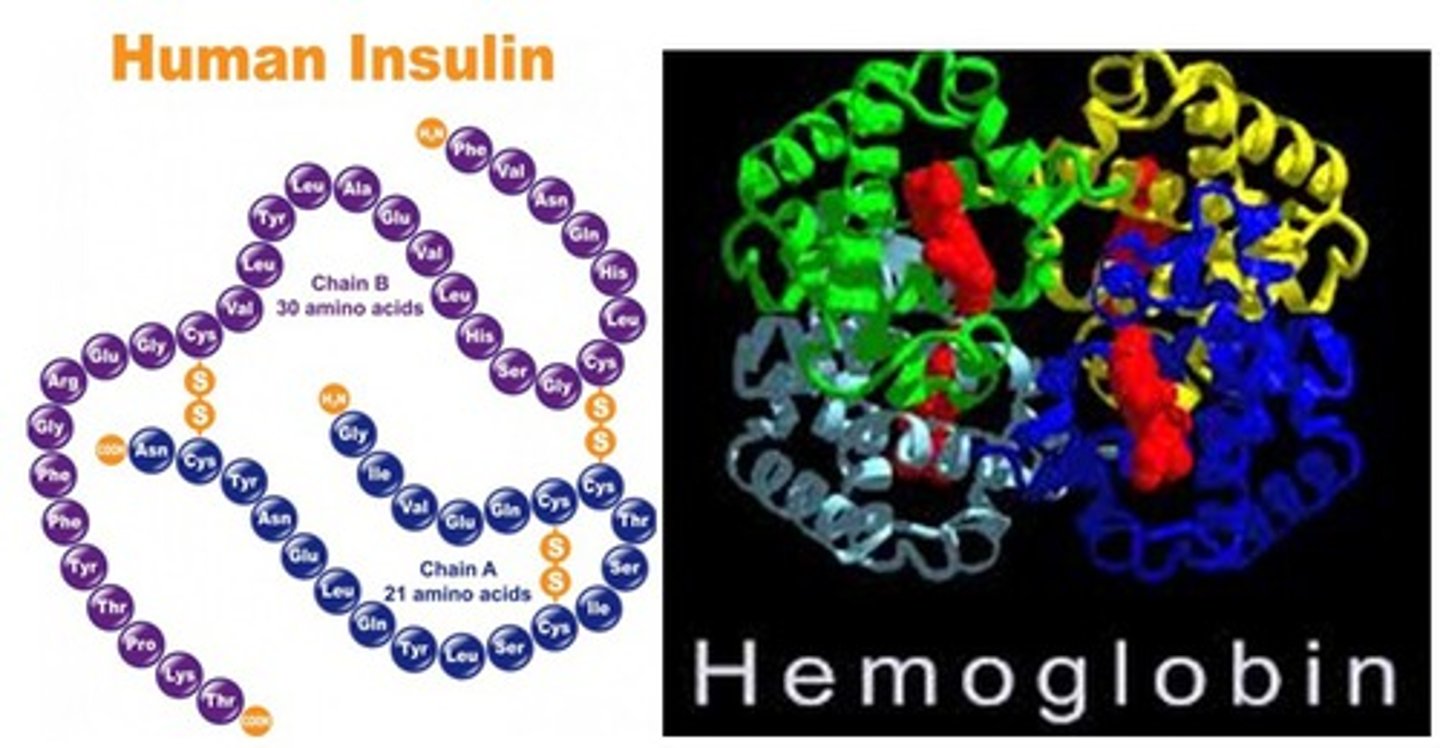
amino acids
monomer of proteins
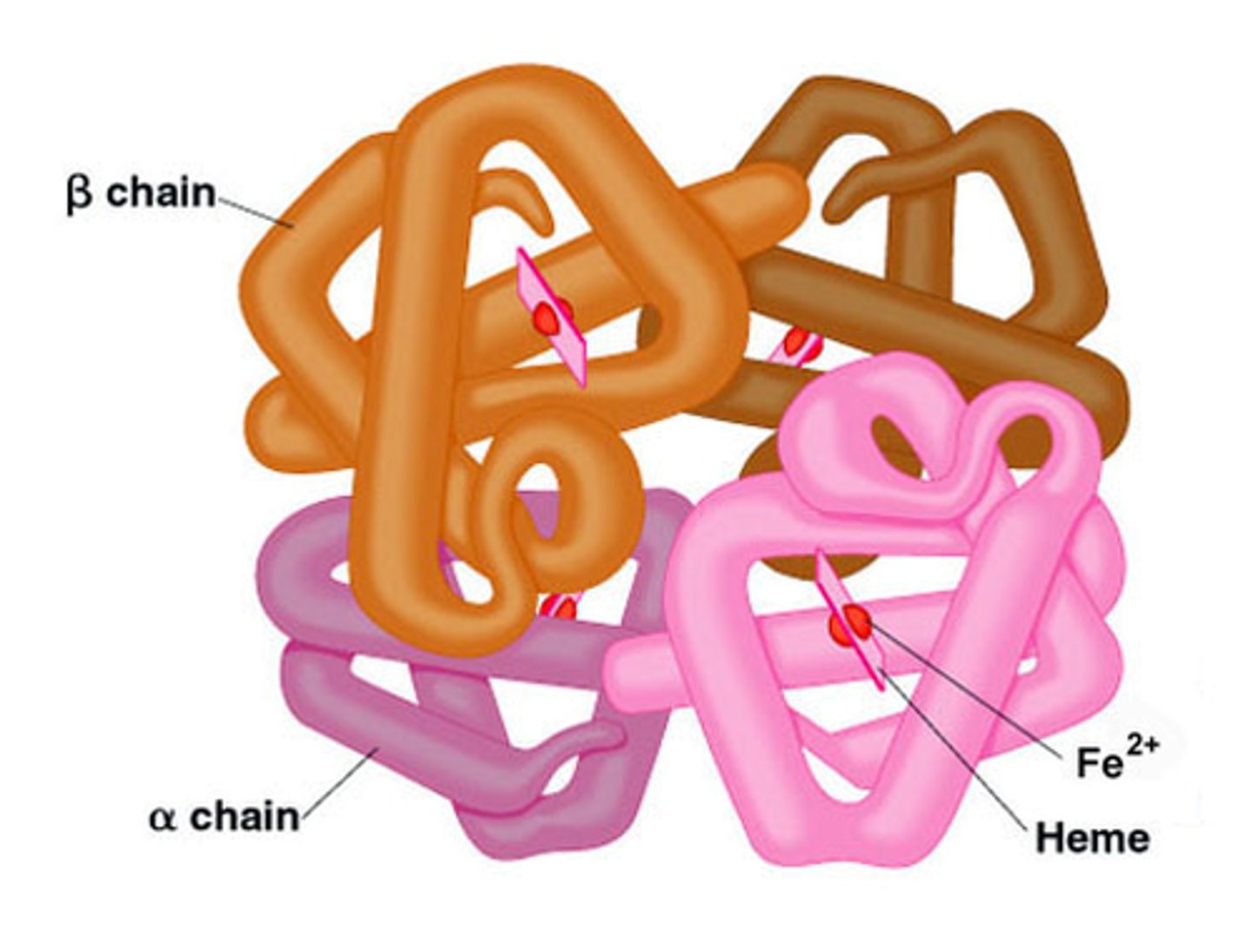
hemoglobin
protein that functions on red blood cells to transport oxygen
collagen
protein that reinforces the structure of the skin
pepsin
protein in the stomach that acts as a digestive enzyme
insulin
protein that regulates blood sugar
antibodies
proteins that serve in the immune system
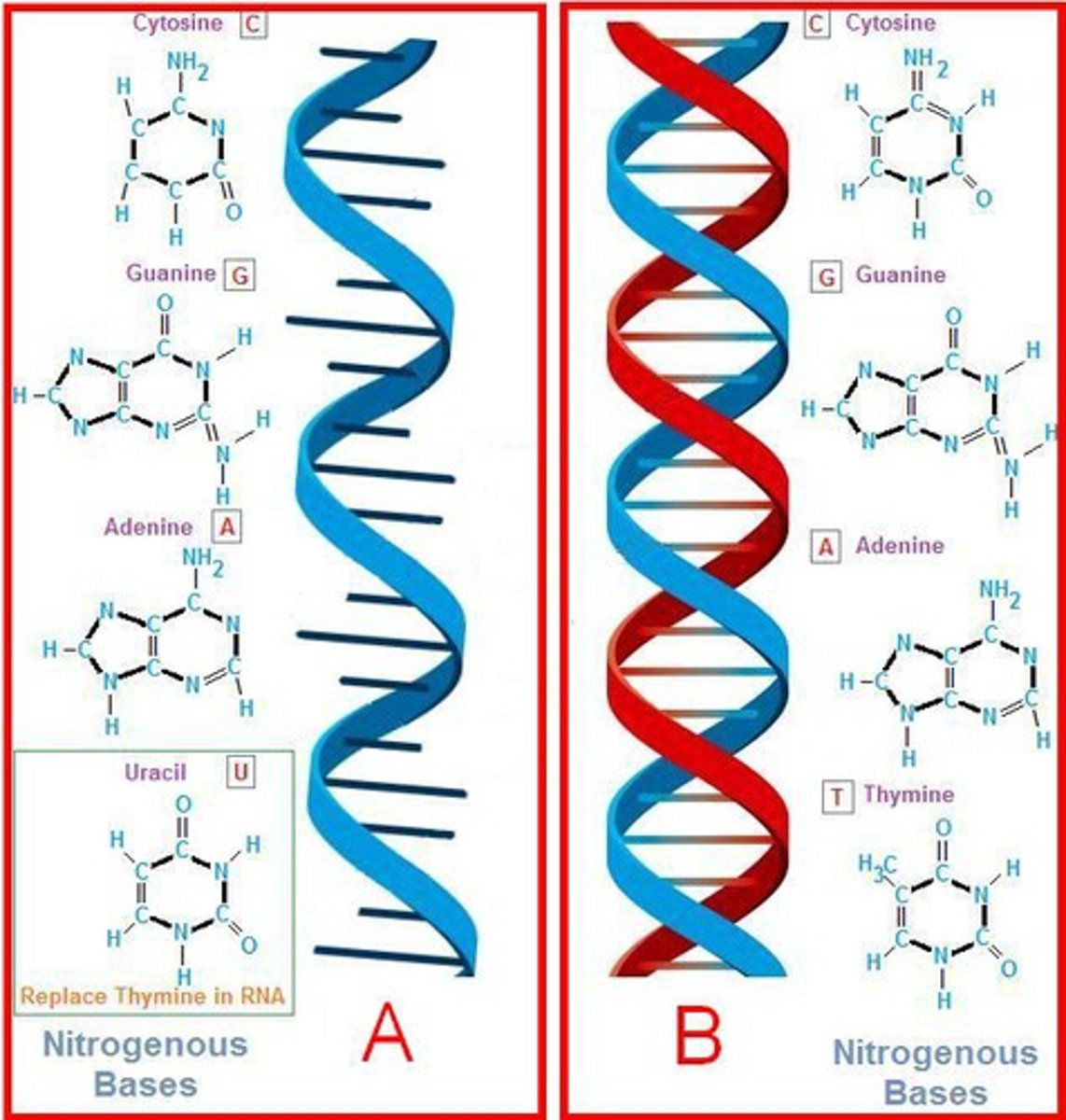
nucleic acid
function to store and transmit genetic information
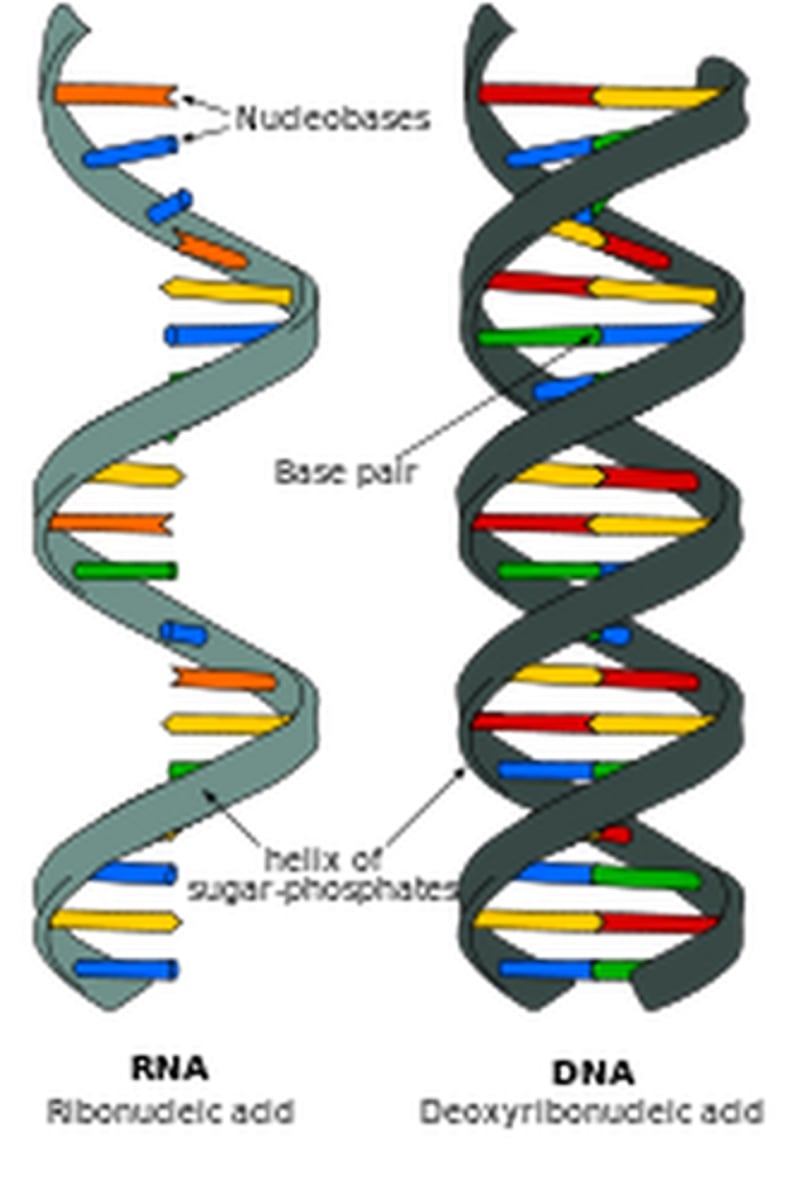
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acid
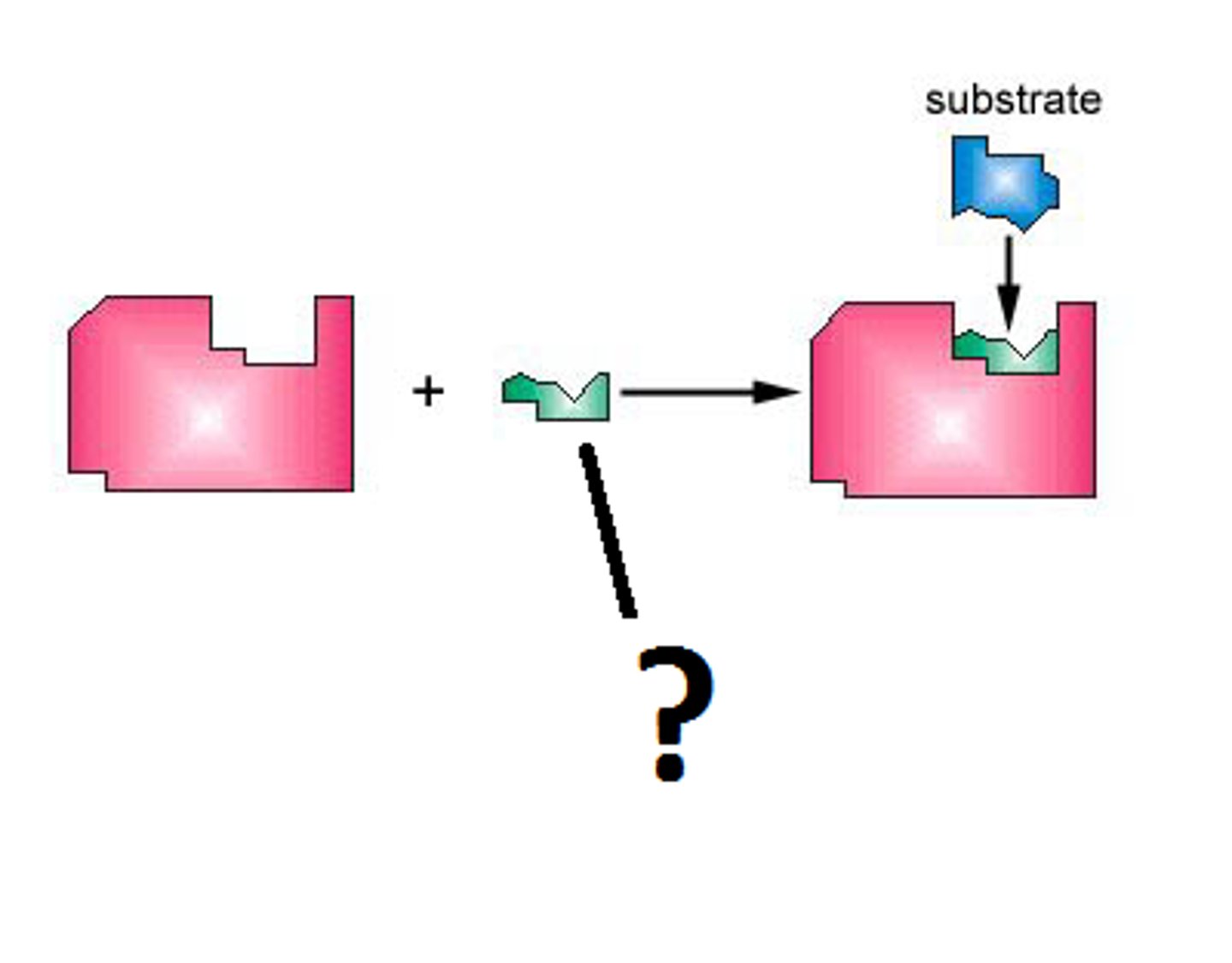
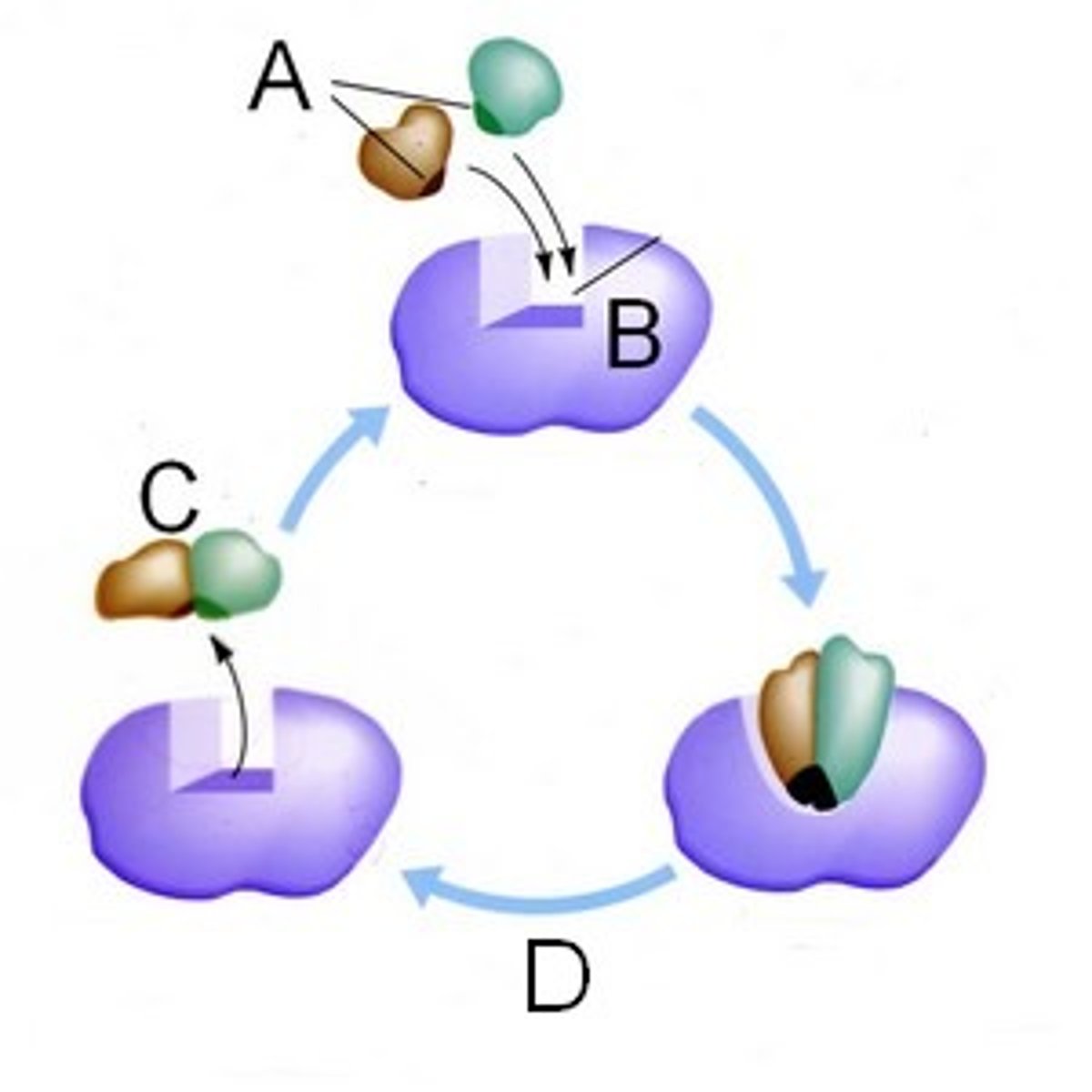
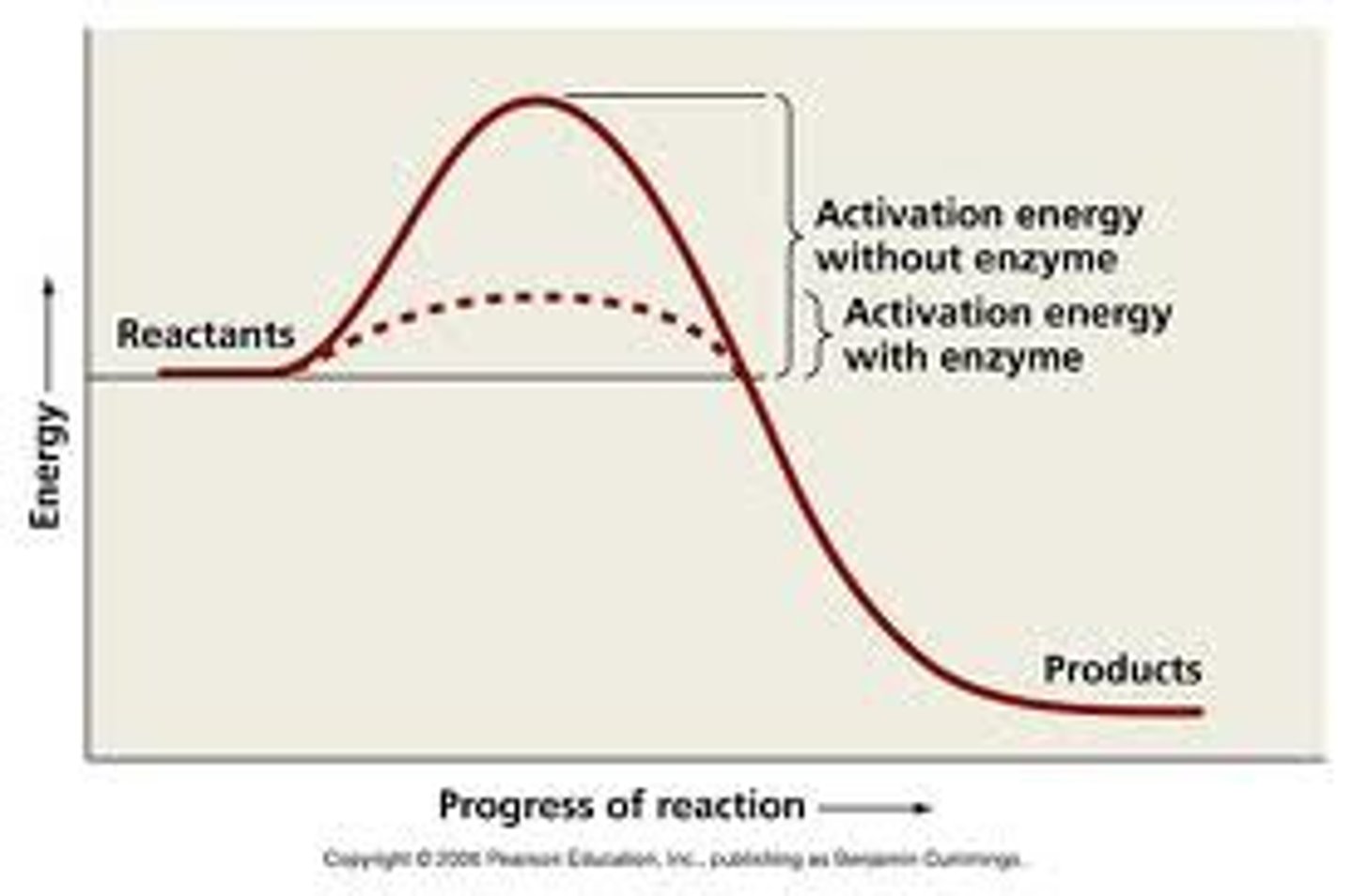
enzyme
protein that speeds up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy
activation energy
energy needed to get a chemical reaction started
substrate
reactant in a chemical reaction using an enzyme
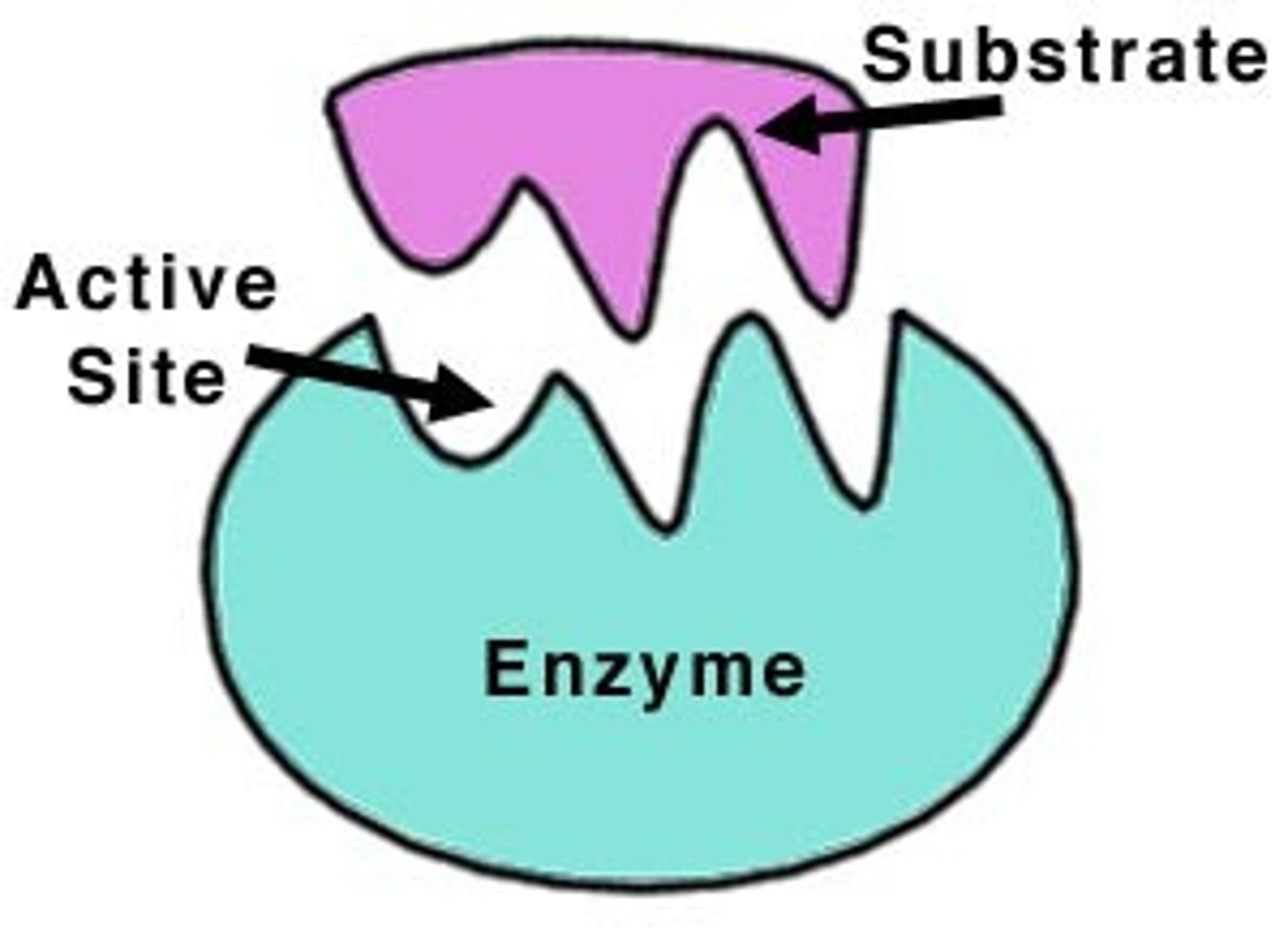
active site
the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind
carbohydrate examples
sugars, starches, glycogen, cellulose

protein examples
hemoglobin, enzymes (like amylase), insulin
lipid examples
fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, steroids

nucleic acid examples
DNA, RNA, ATP
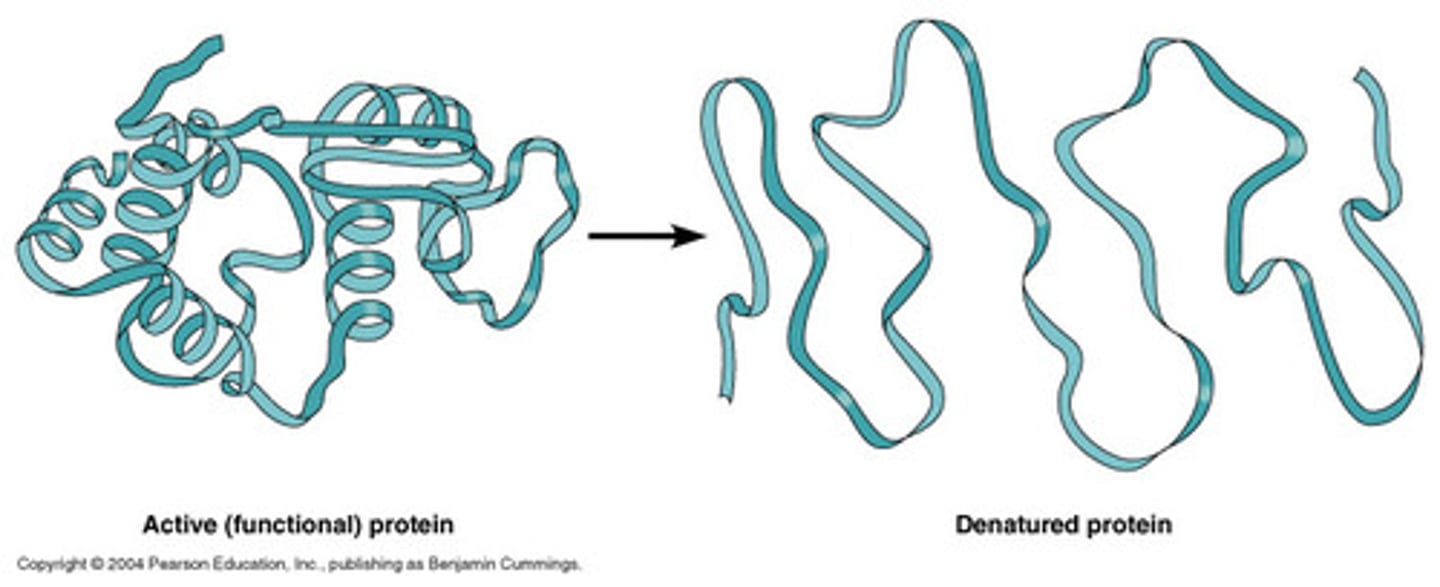
denaturation
Change in shape of an enzyme caused by high temperature or other conditions; prevents it from functioning
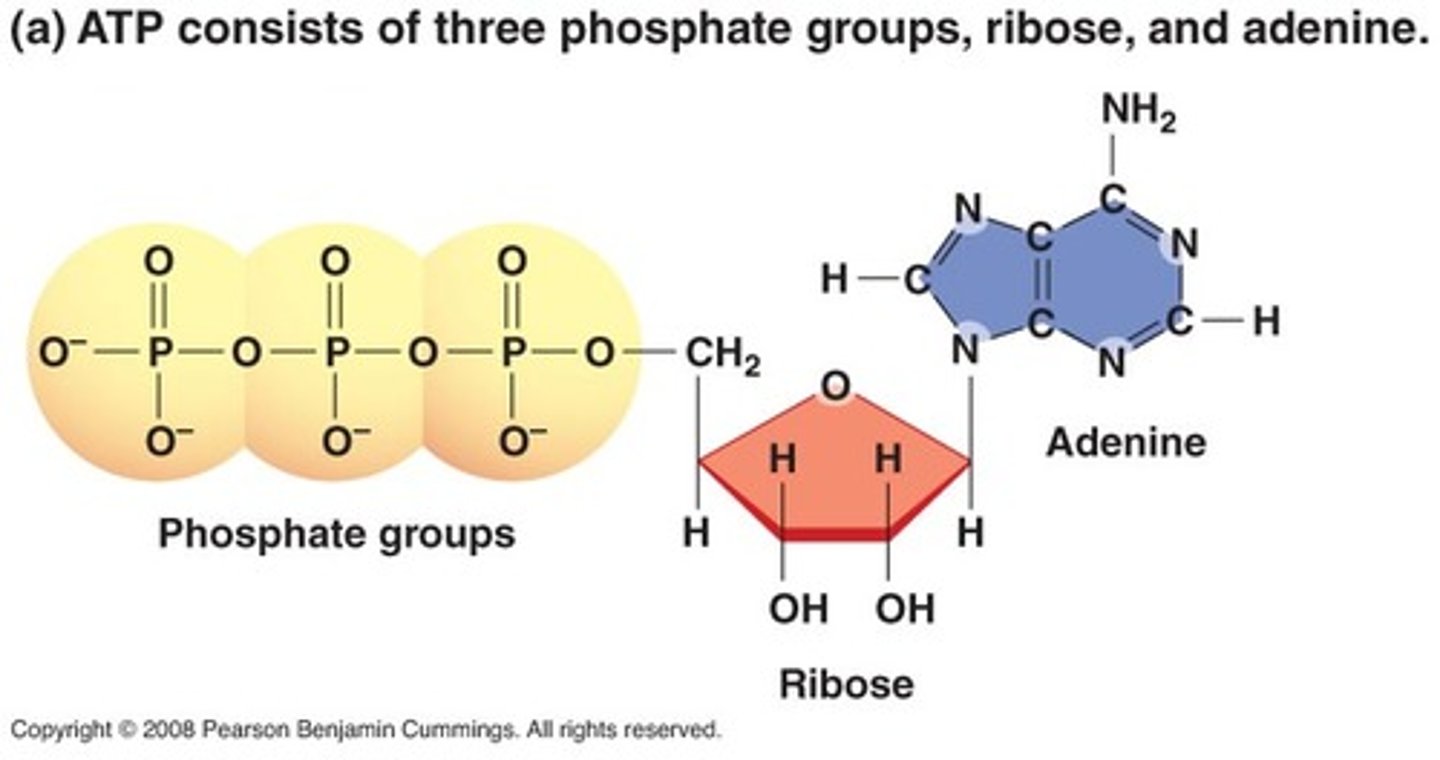
ATP
example of a nucleic acid that serves as the energy molecule for the cell
Biomolecule
binds to active site to prevent enzyme from working correctly
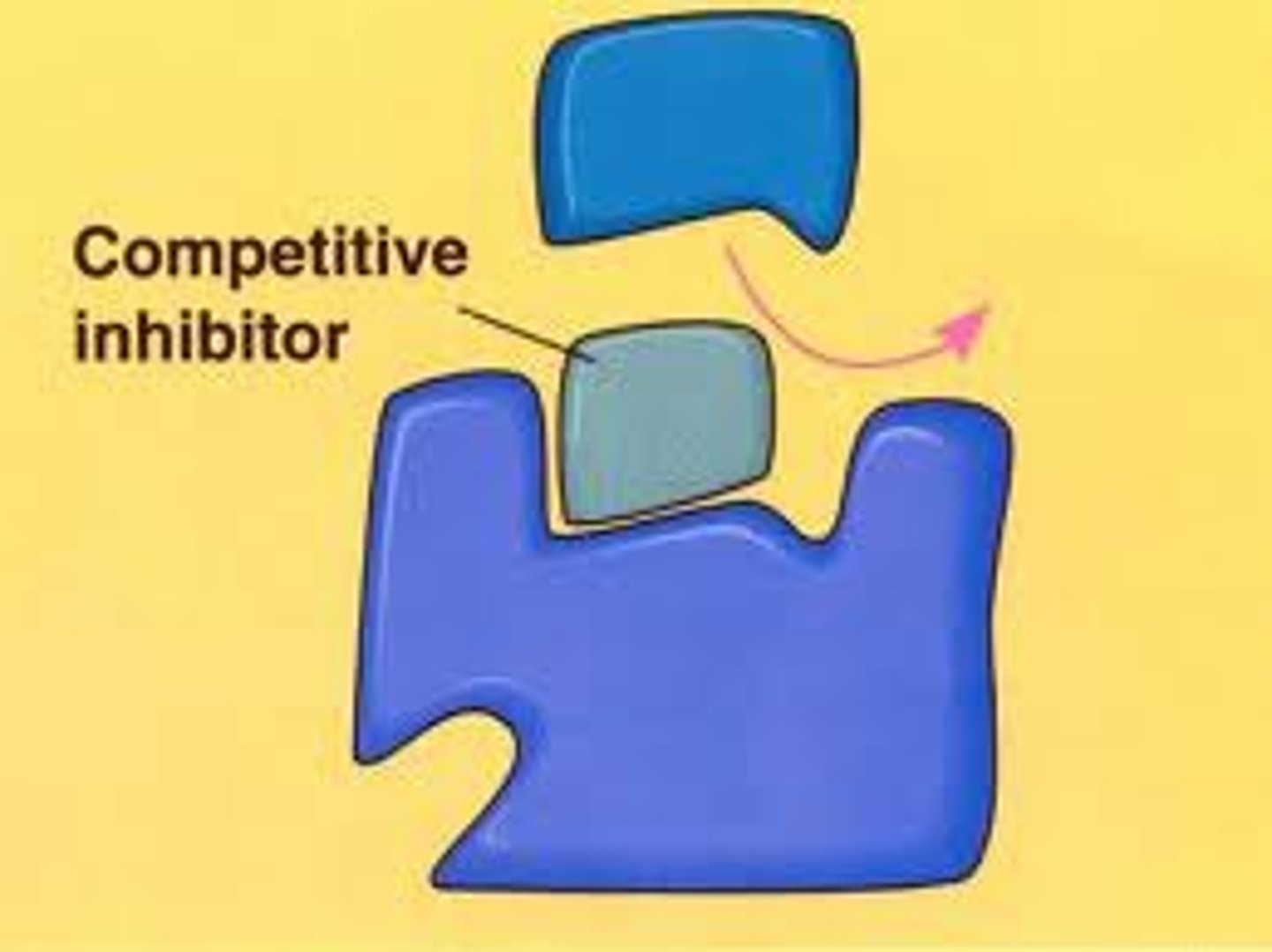

coenzyme
substance needed for the enzyme to work which can slow the rate of a reaction