RSP402 Exam 2 Waveforms
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Hemodynamic effects:
High PEEP and excessive airway pressures can reduce venous return
=leading to hypotension and decreased cardiac output. Mechanical ventilation can increase intrathoracic pressure, reducing preload and affecting circulation.
Pressure-time:
Volume-Controlled Ventilation: Pressure increases as the lungs fill due to resistance and compliance.
Pressure-Controlled Ventilation (PCV): A rectangular (square) shape where pressure remains constant, and flow varies
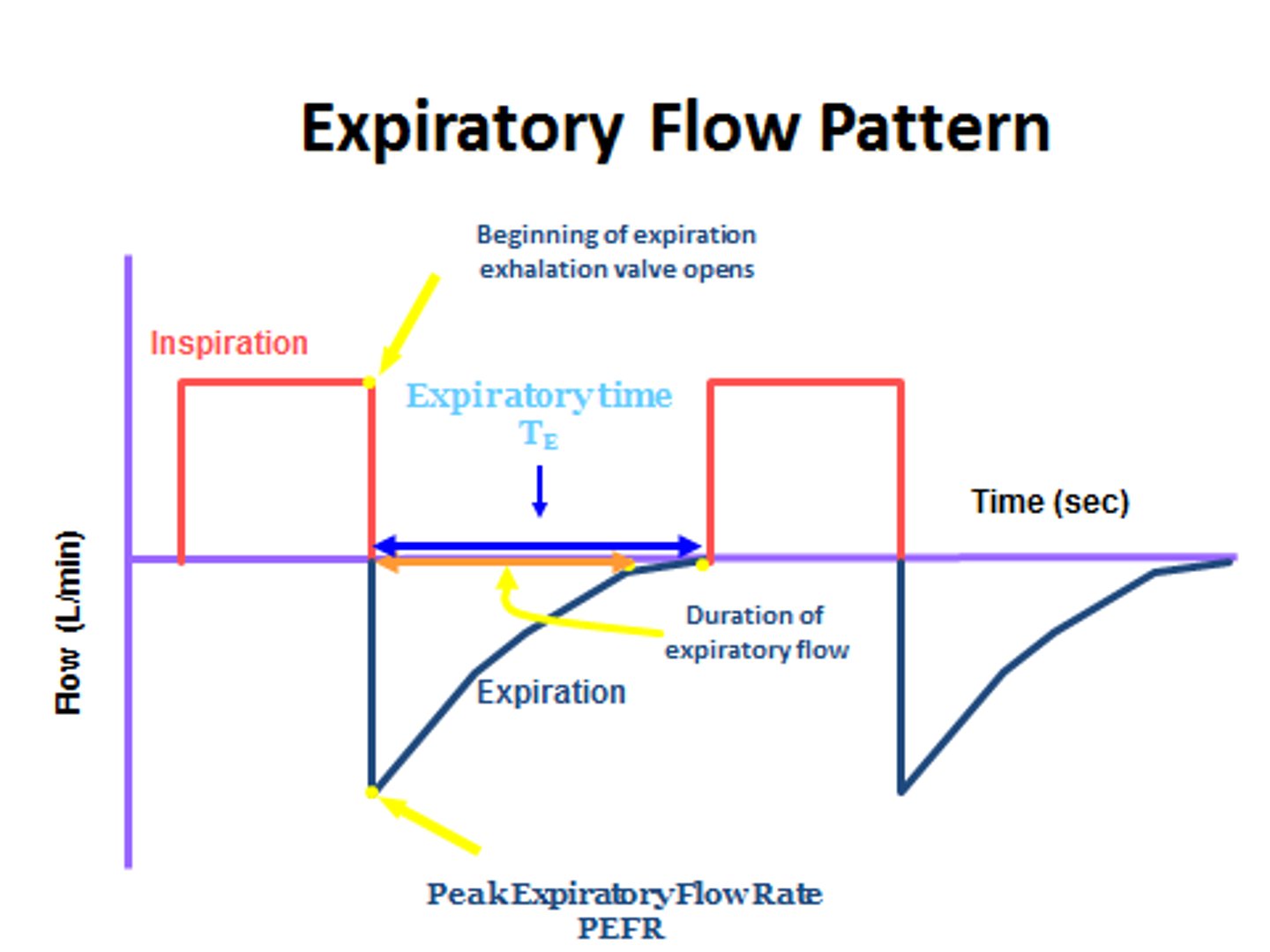
Flow-time
Volume-Controlled Ventilation: Constant or descending flow pattern.
Pressure-Controlled Ventilation: Decelerating flow waveform, which improves gas distribution.
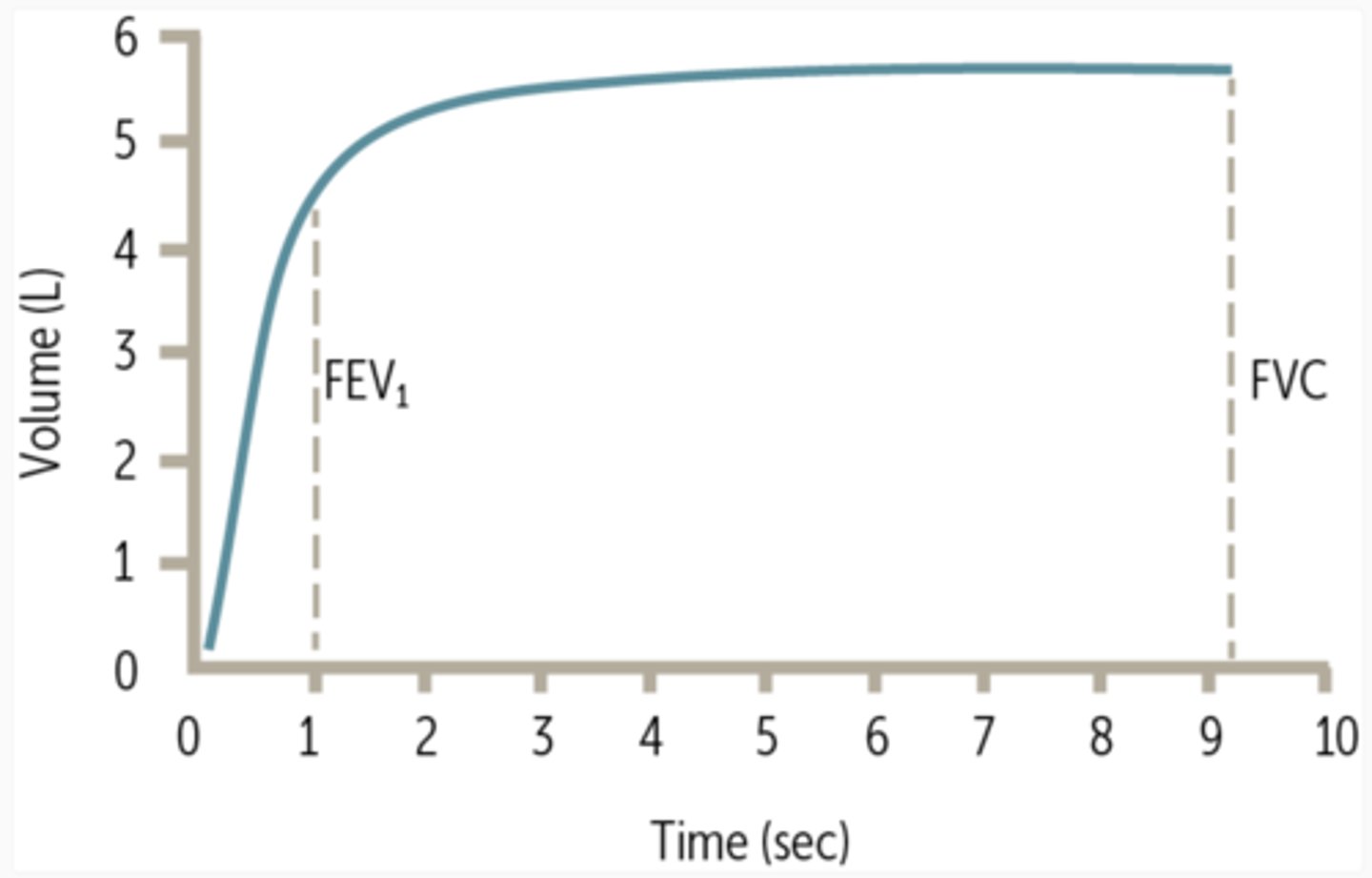
Volume-time curves definition
Shows how much volume is delivered over time.
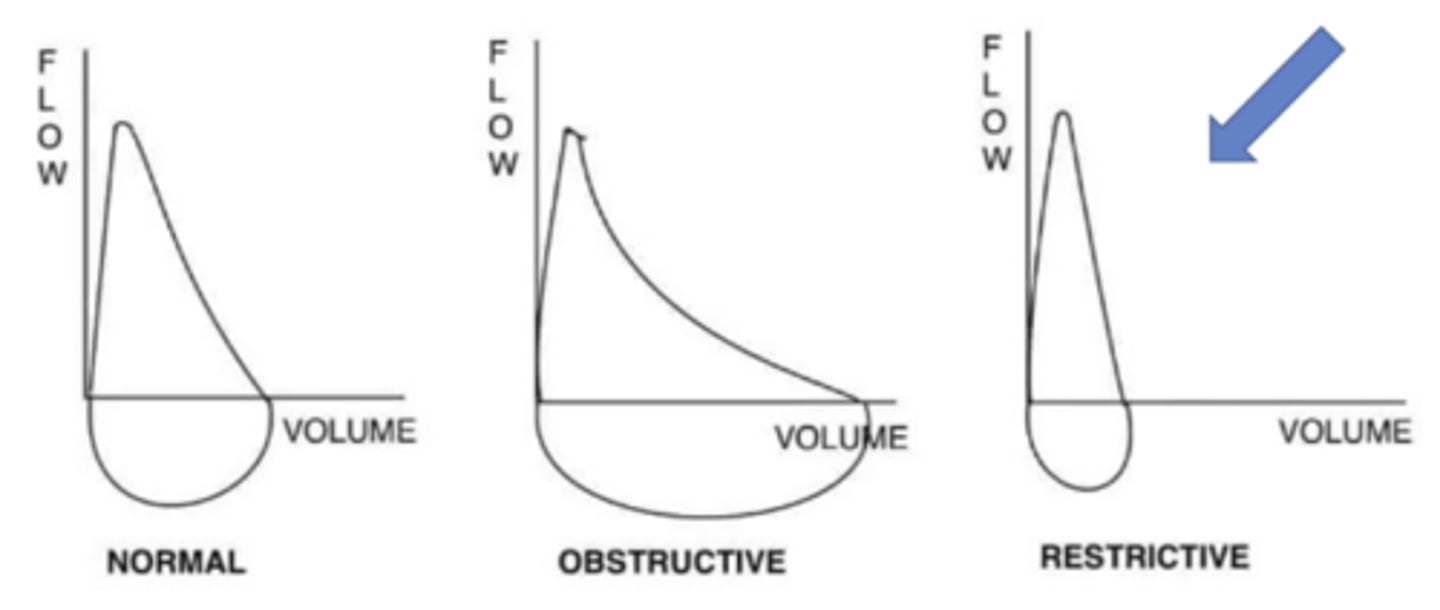
Obstructive patterns:
Scooped-out appearance during expiration, seen in COPD, and asthma due to increased airway resistance.
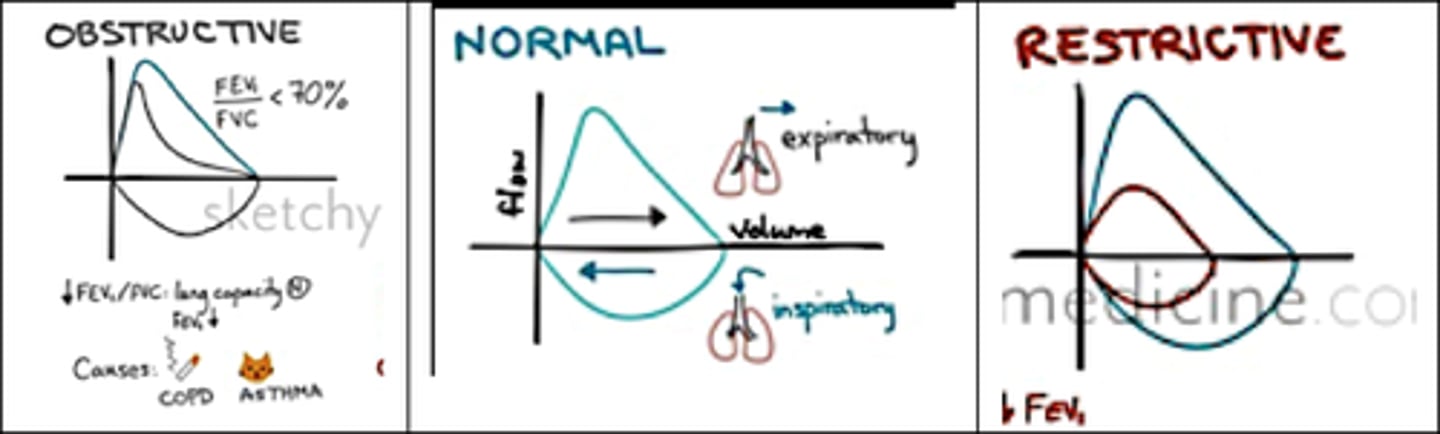
restrictive patterns:
Narrower loop due to reduced lung volumes (e.g., fibrosis, ARDS).
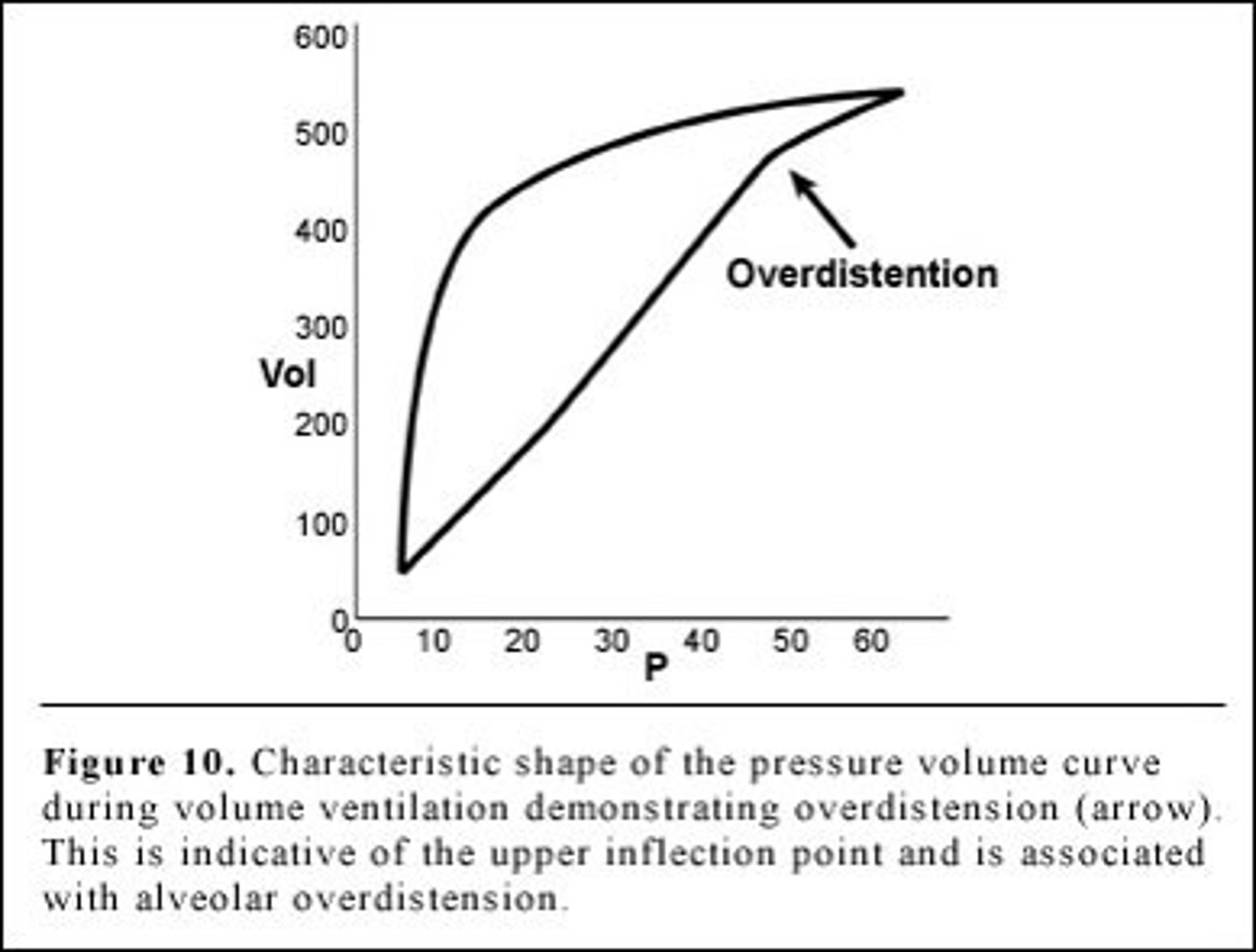
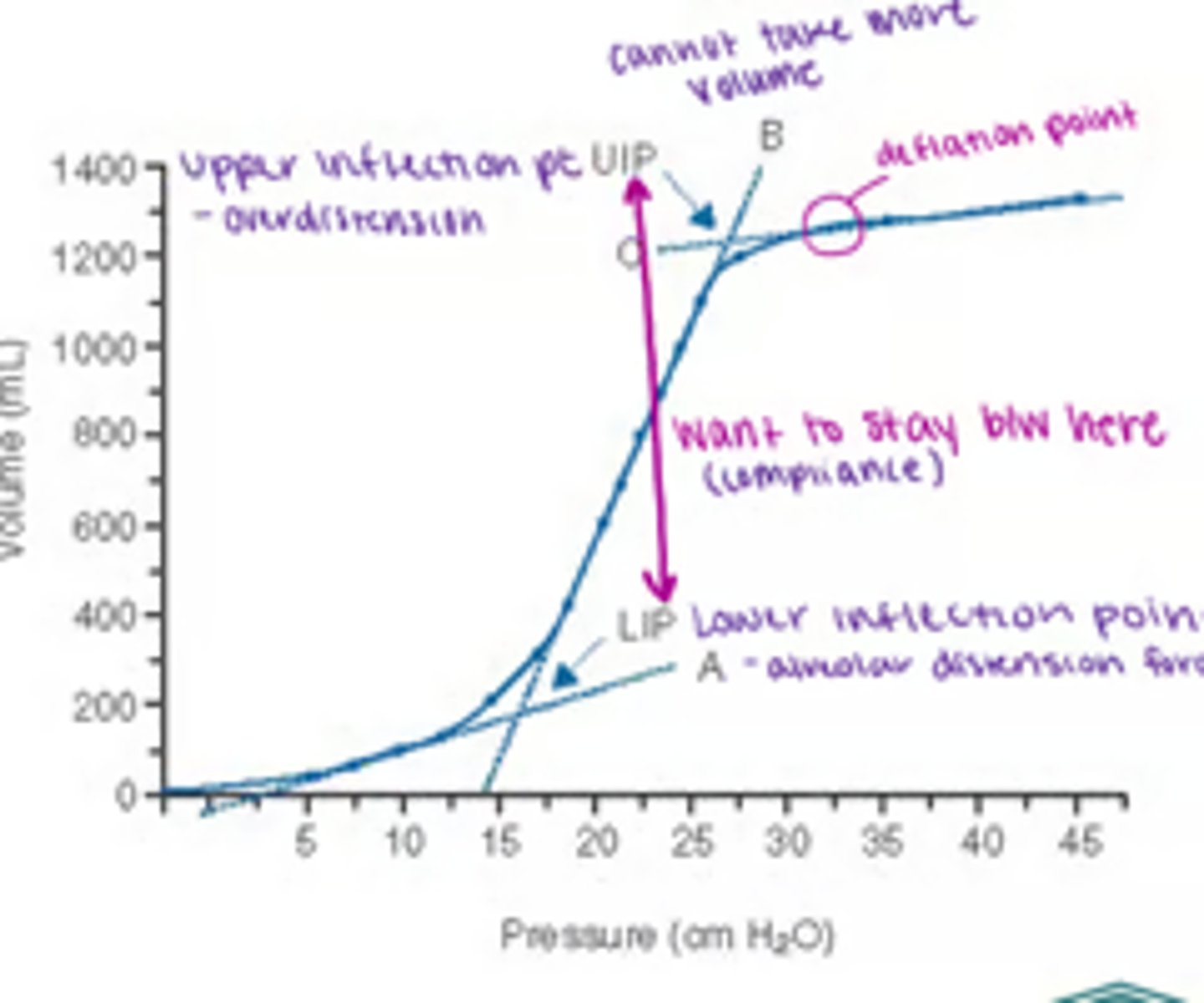
Overdistension:
"Beaking" at the upper inflection point, indicating excessive tidal volume or high pressure.
recruitment needs:
A low-volume loop with a lower inflection point suggests alveolar collapse, requiring higher PEEP to open the lungs.
-You can use F/V loop, P/V loop, or flow-time to find the problem (Obstructive or Restrictive)
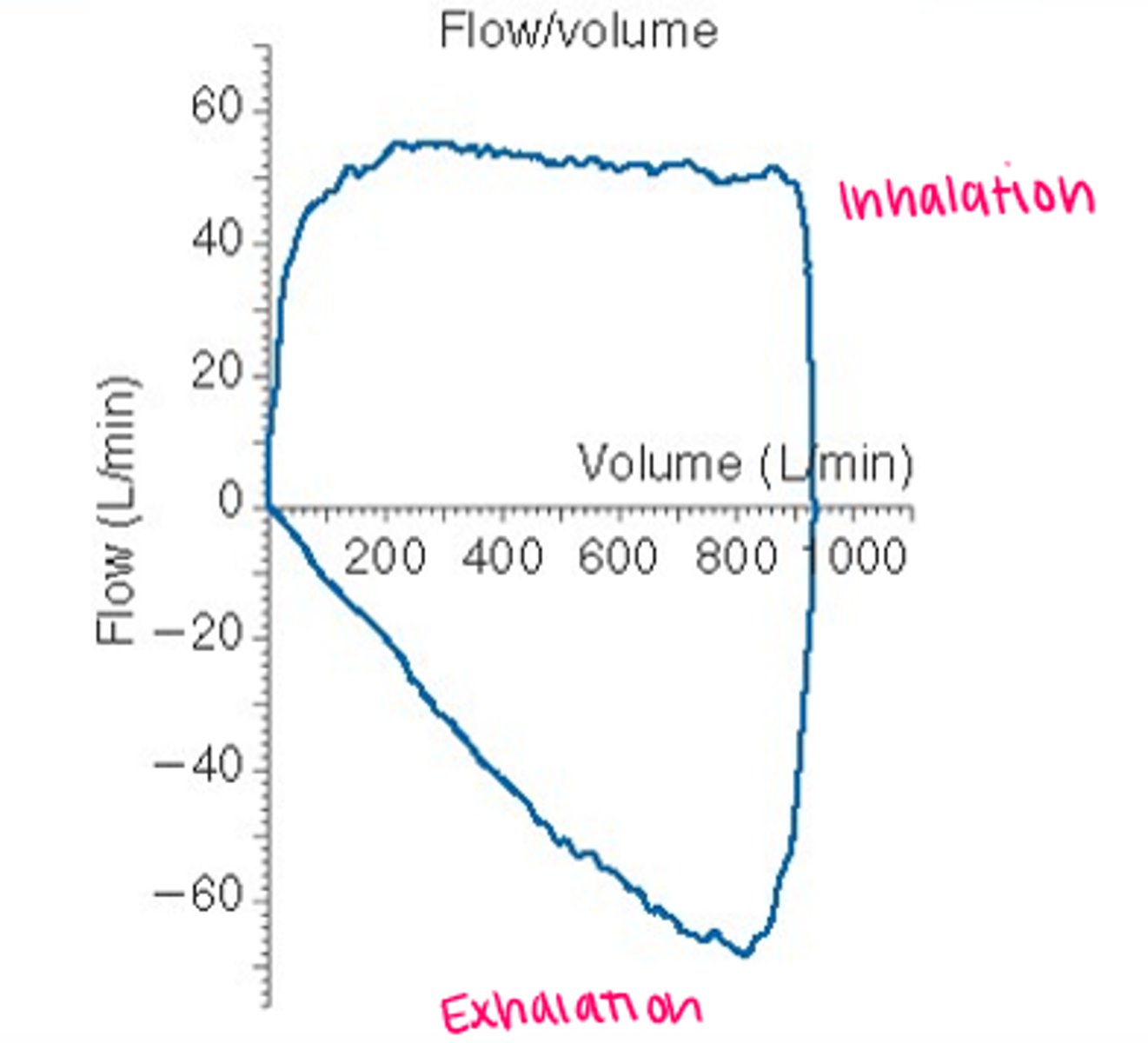
Flow Volume Loop:
Pressure Volume Loop
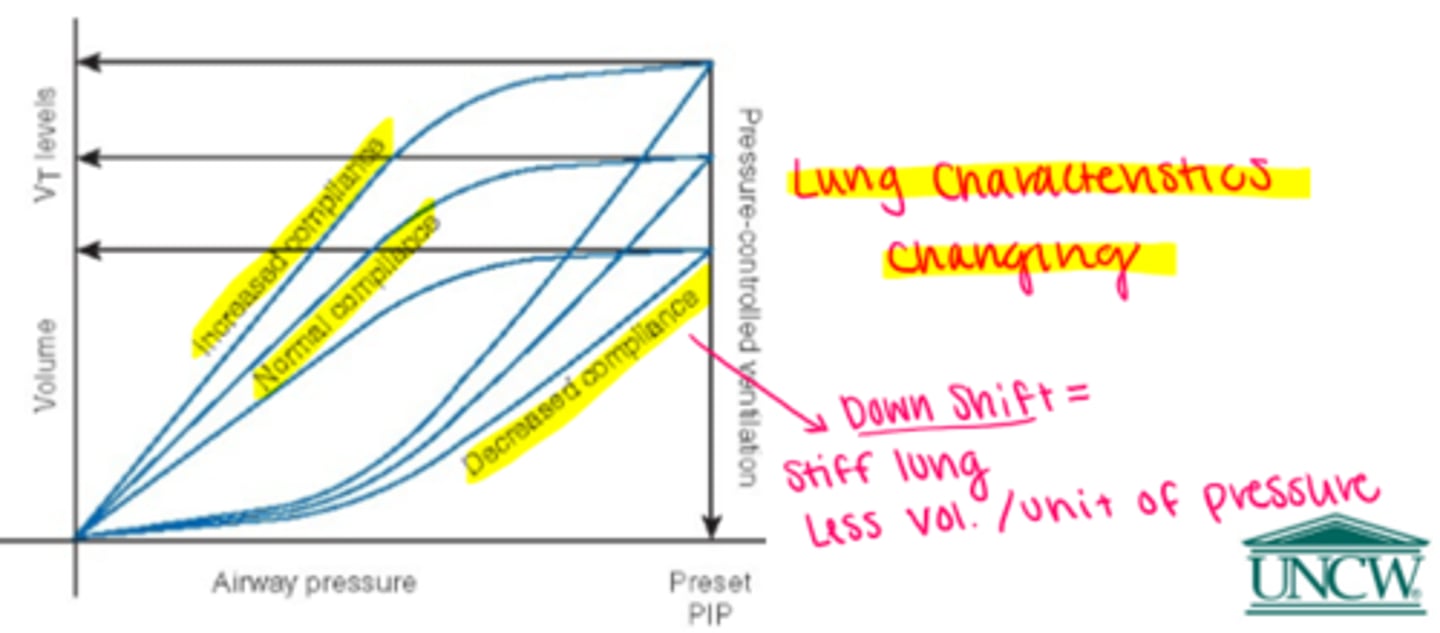
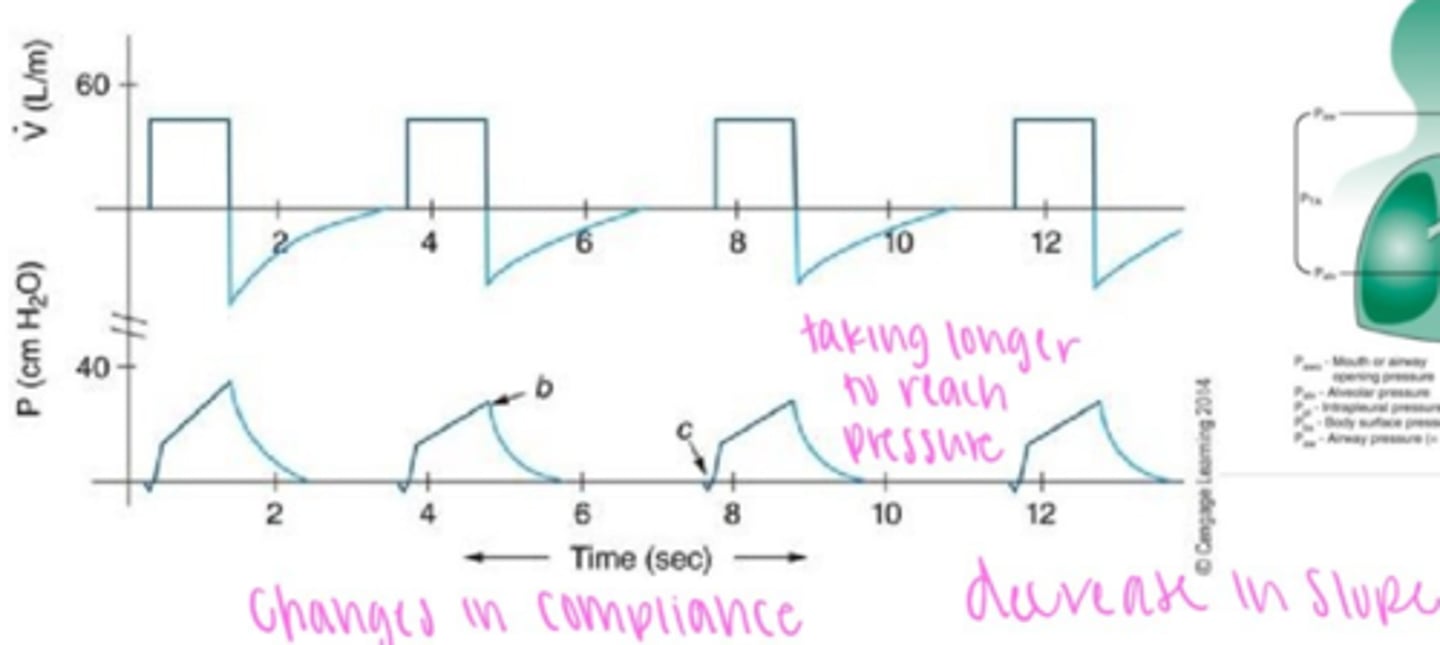
Changes in compliance & resistance
-counterclockwise (mandatory)
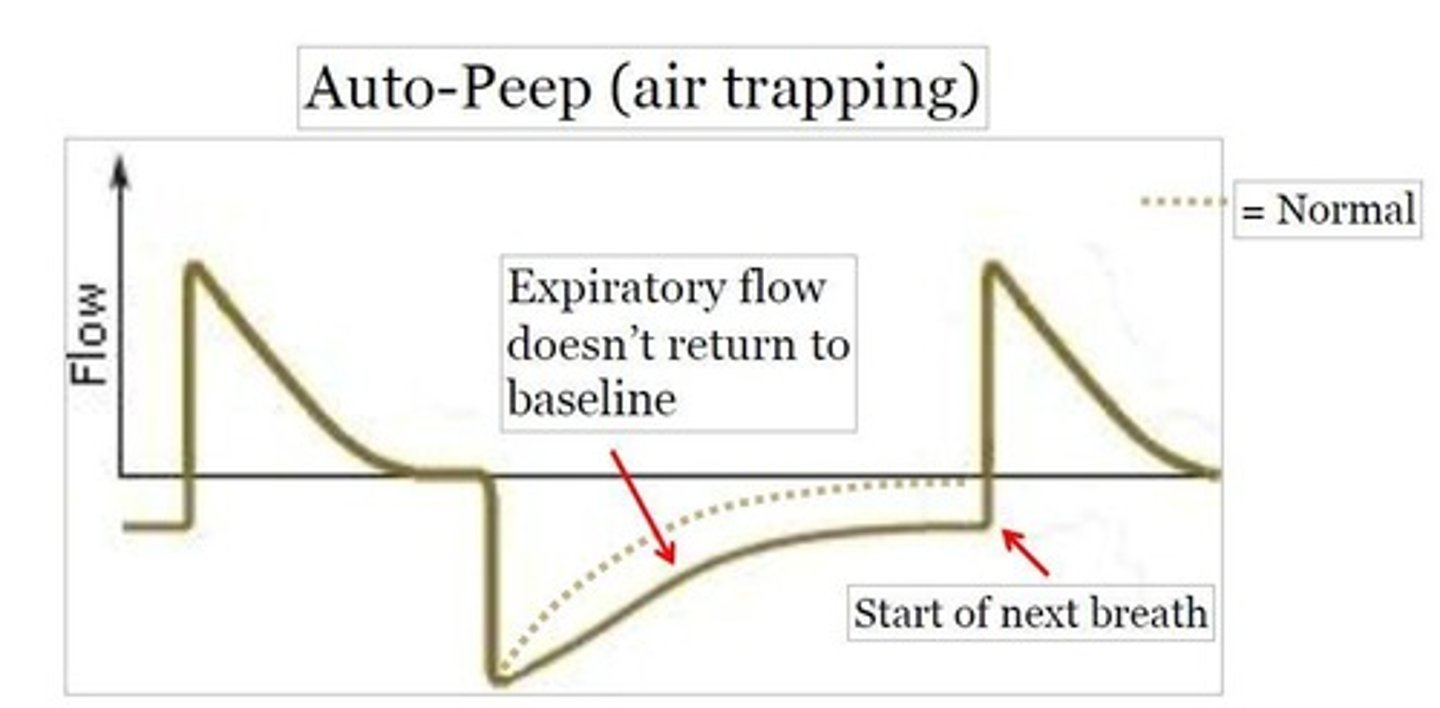
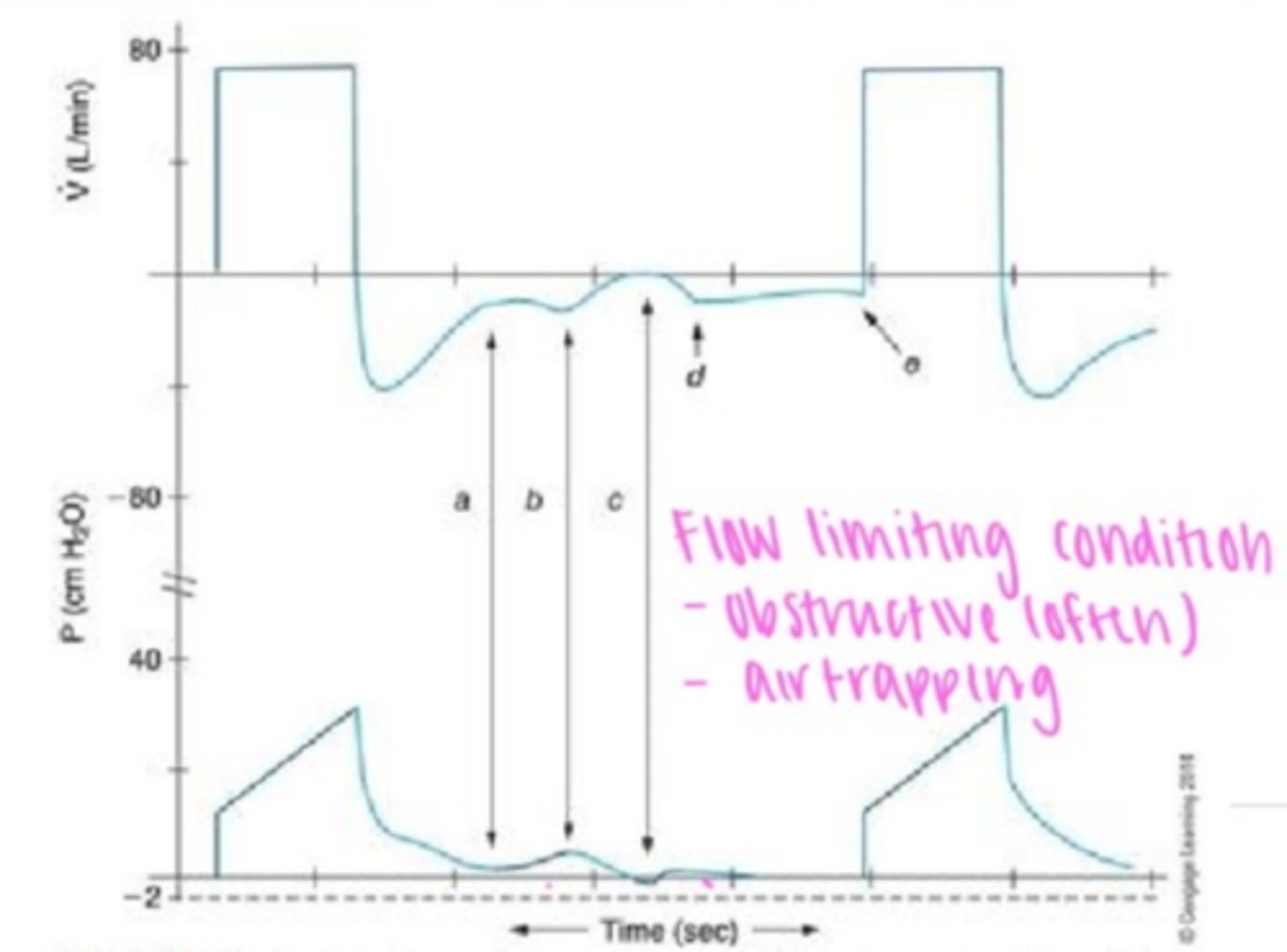
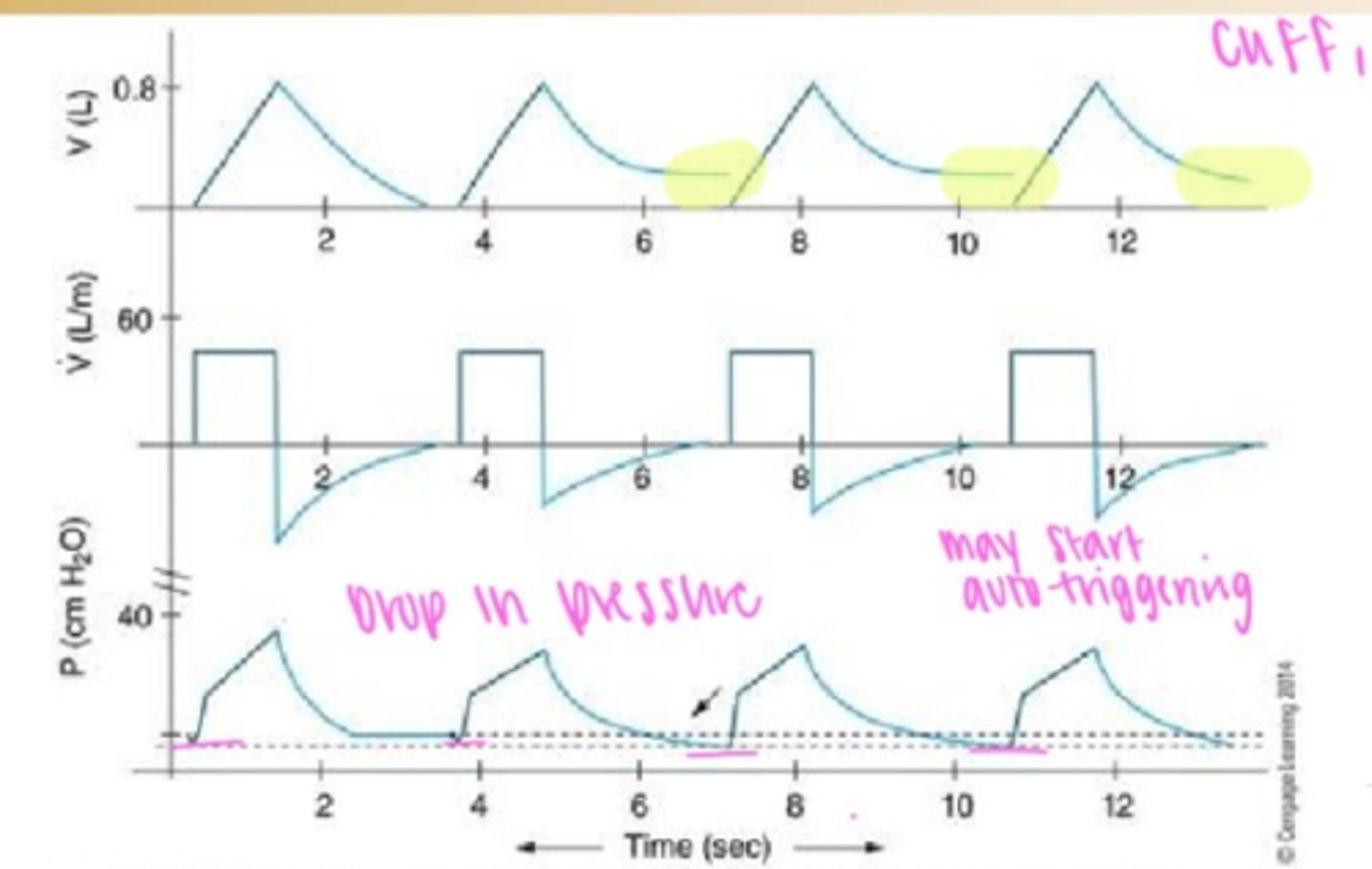
Air trapping
Flow-time curve: Expiratory flow does not return to baseline before the next breath starts.
Fix: Increase expiratory time (reduce RR or decrease I:E ratio), decrease tidal volume, or adjust PEEP.
Breath-stacking
Volume-time curve: Successive breaths increase lung volume without full exhalation.
Fix: Increase expiratory time, reduce respiratory rate, check trigger sensitivity to avoid auto-triggering.
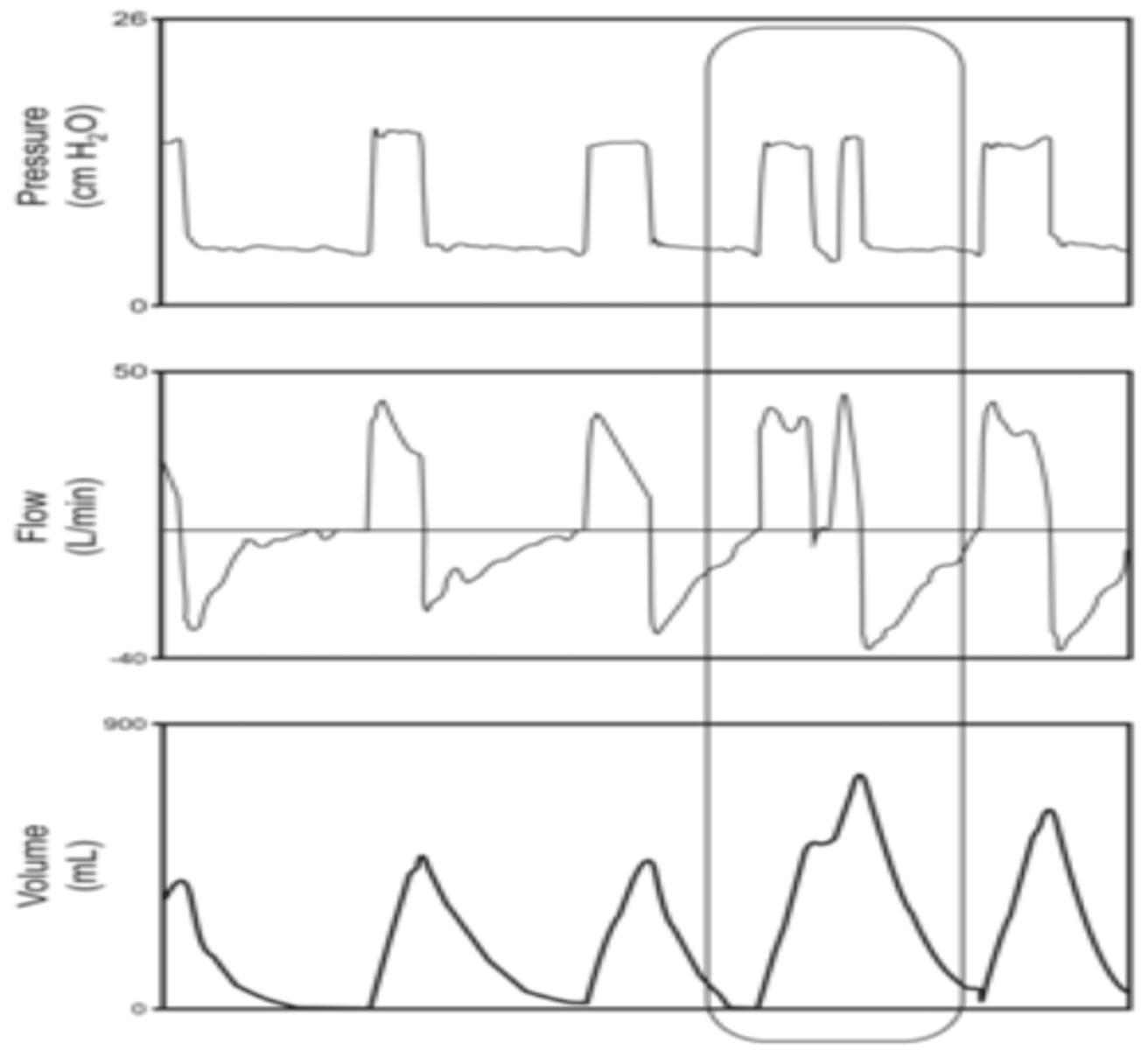
patient-ventilator desynchrony
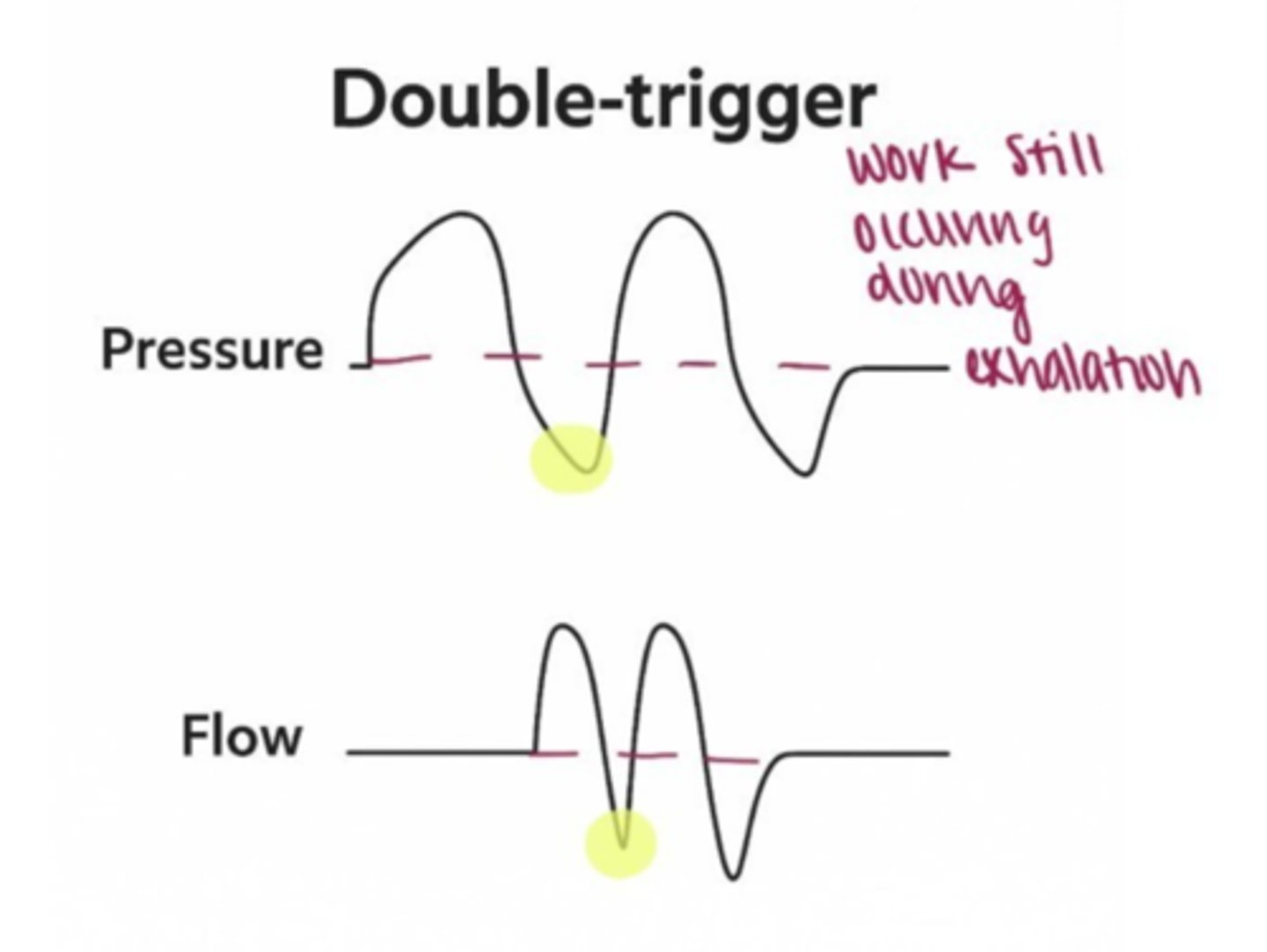
Double Triggering: Two breaths back-to-back suggest that the ventilator cycle is too short.
Fix: Increase i time, and decrease sensitivity.
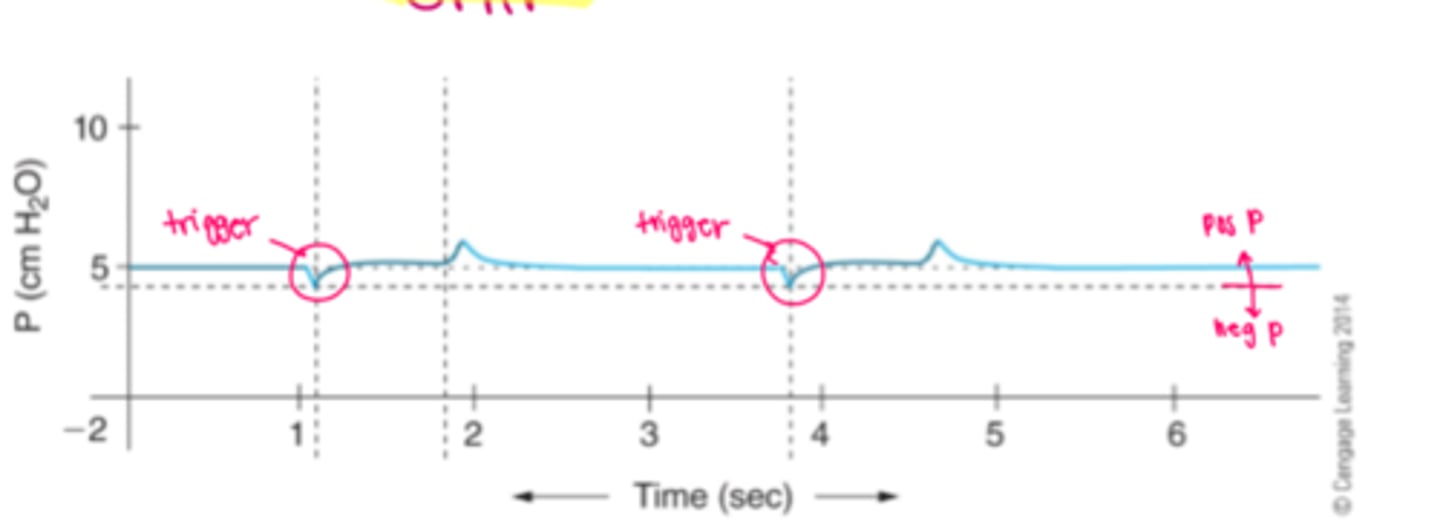
Ineffective Effort (Missed Triggering): attempts a breath, but the ventilator does not respond.
Fix: Adjust trigger sensitivity or reduce PEEP if it's causing auto-PEEP.
Flow Asynchrony: A concave pressure-time curve suggests inadequate inspiratory flow.
Fix: Increase flow rate in volume-controlled modes or adjust inspiratory pressure in pressure-controlled modes.
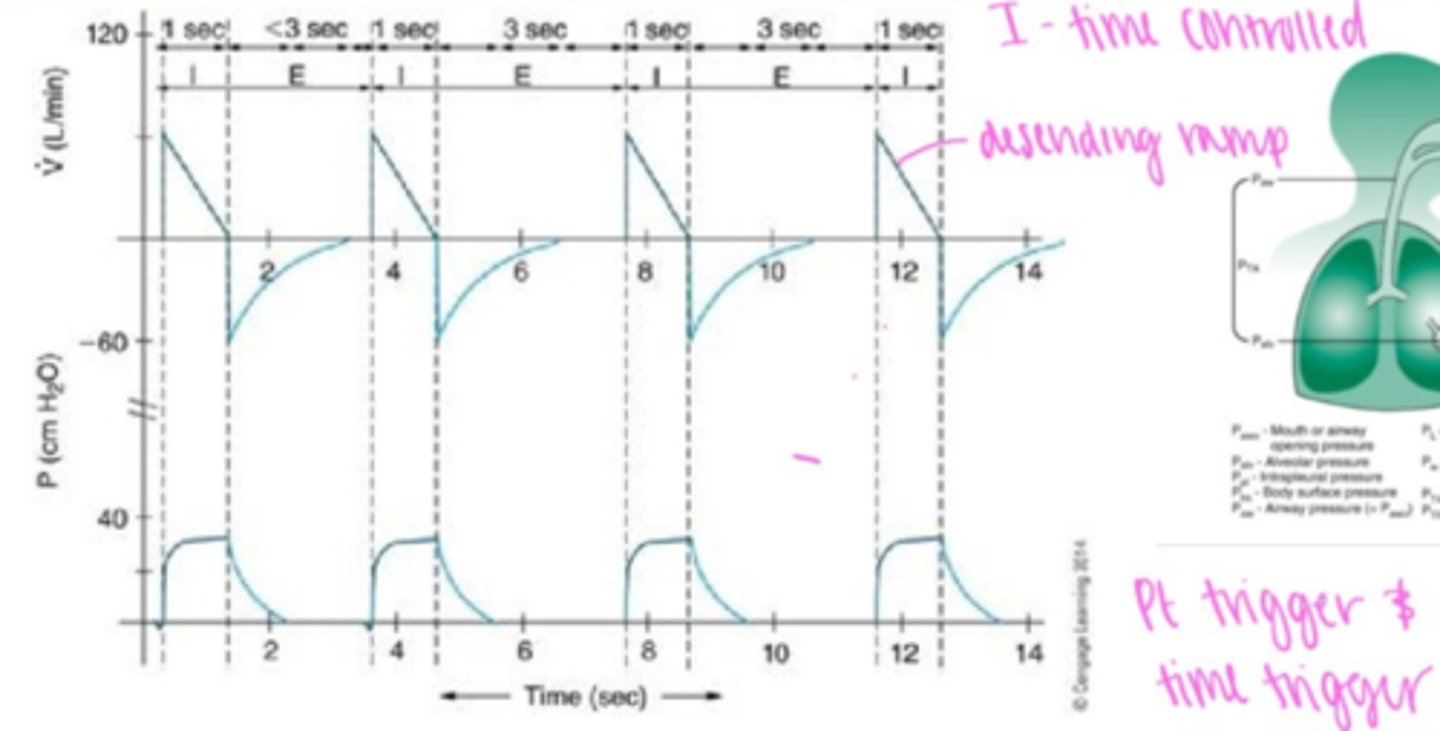
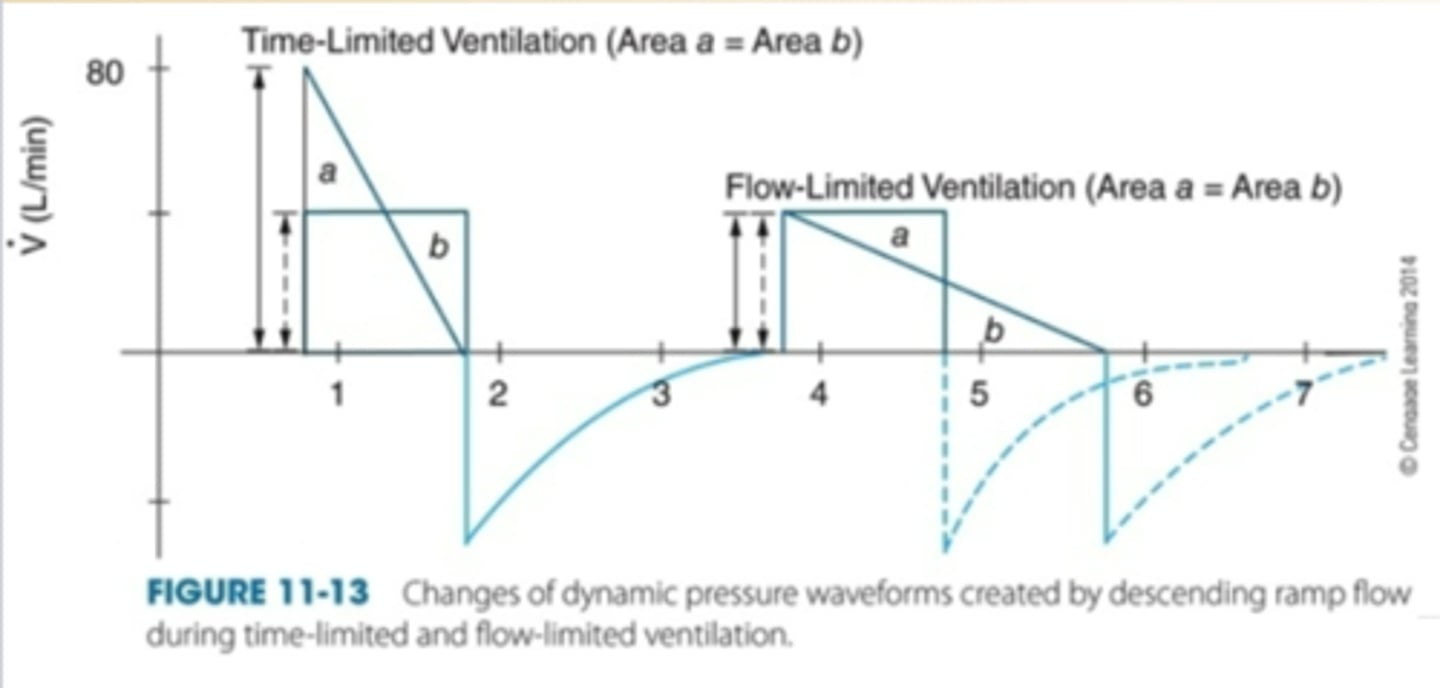
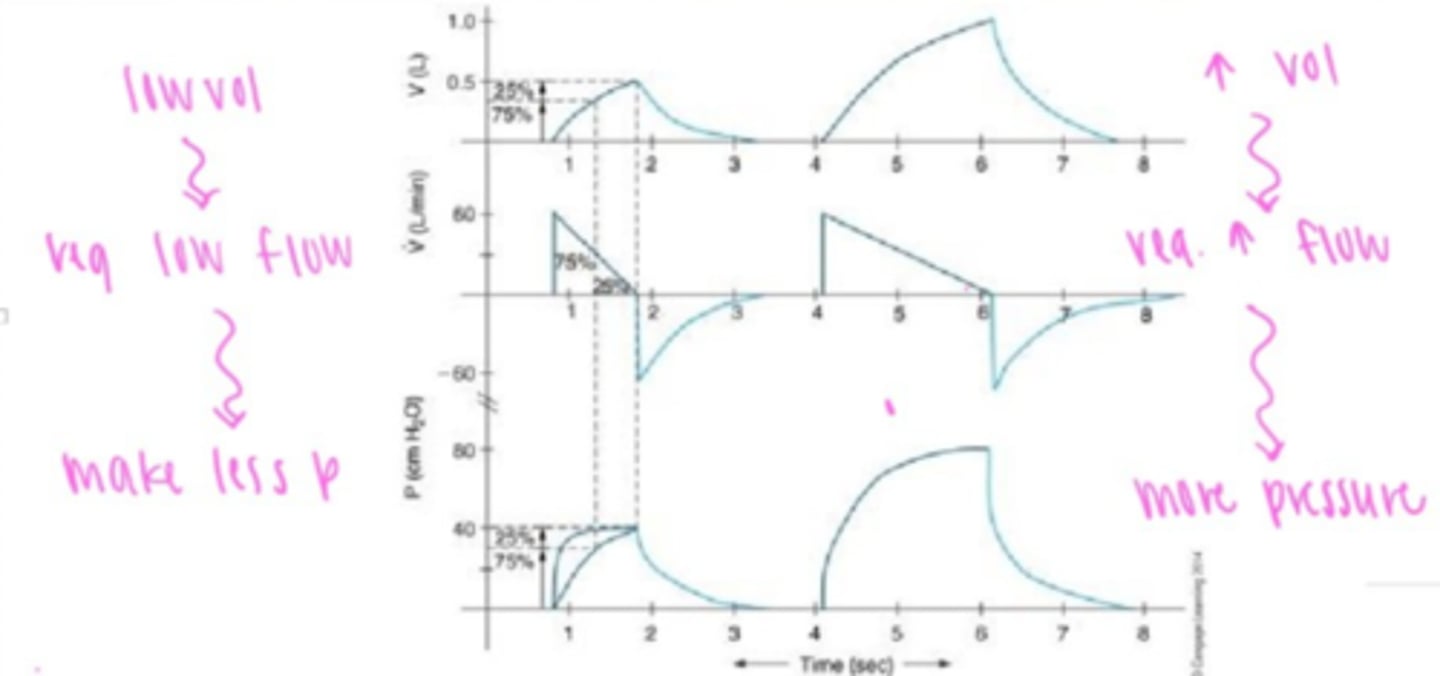
Effects of constant, descending ramp flow on volume-controlled ventilation.
Less I-time= increase in flow
-creates turbulence, high PTA
More I-time= decrease in flow
Increase end-flow effect on pressure descending ramp flow
increase in PTA but not alveolar pressure
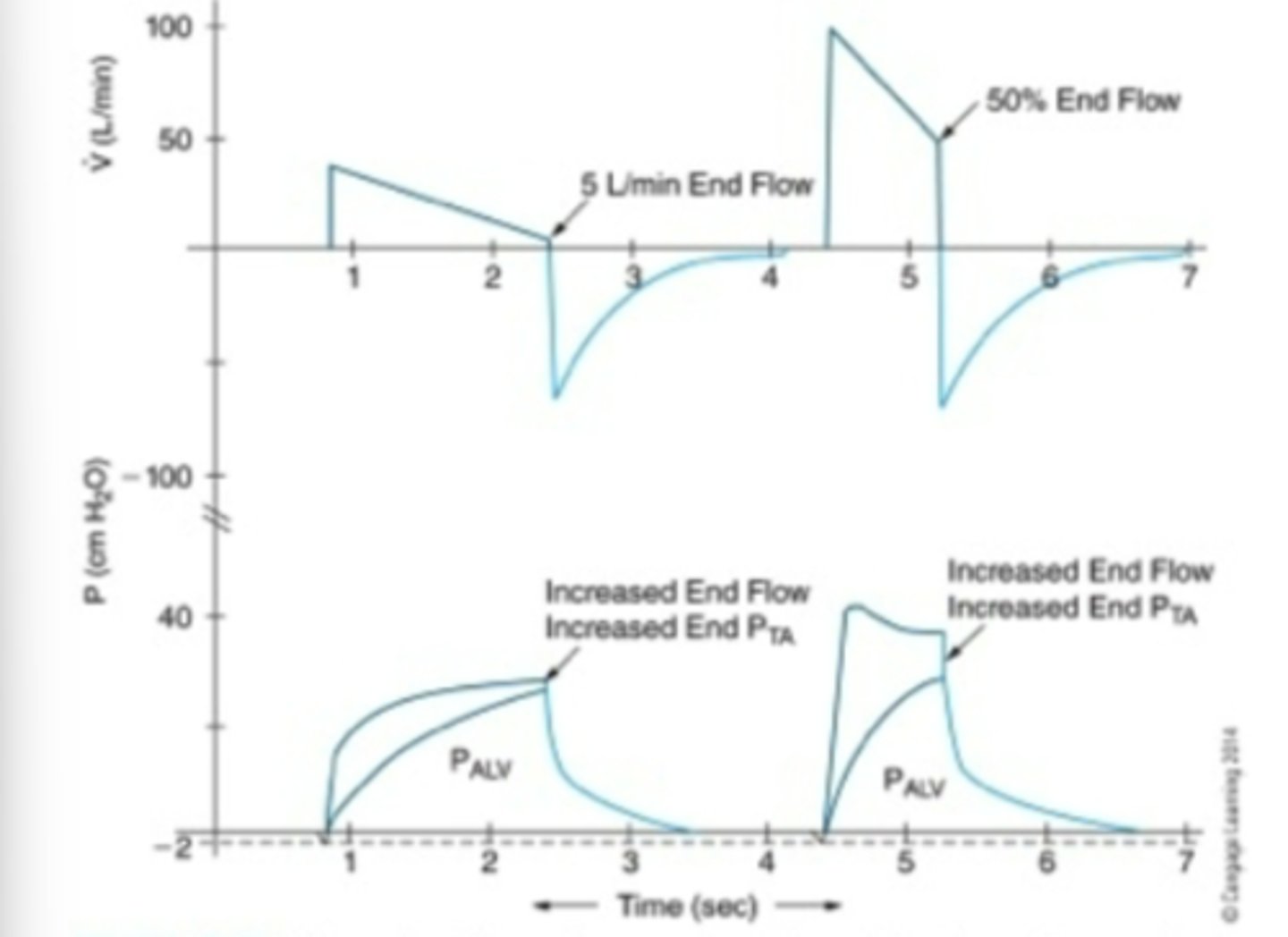
Effect of inspiratory time on descending ramp
Increase I-time= increase VT & PIP
CPAP waveform
SIMV waveform
Pressure Control Waveform
Time trigger, control TCT, consistent
IMV waveform
Flow asynchrony waveform
inadequate inital peak flow
Volume asynchrony
Inadequate VT to meet demand
(Pressure time scale)
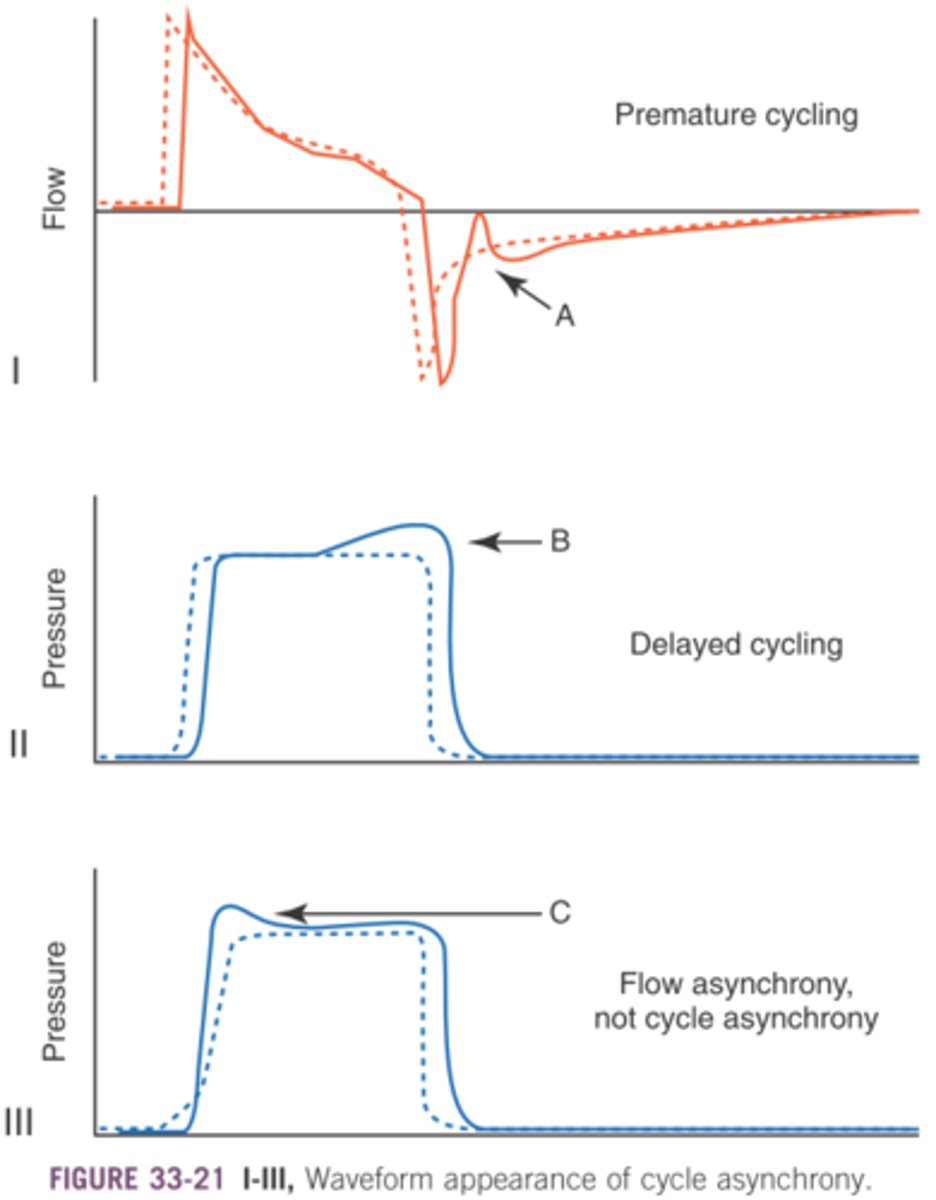
Cycle asynchrony
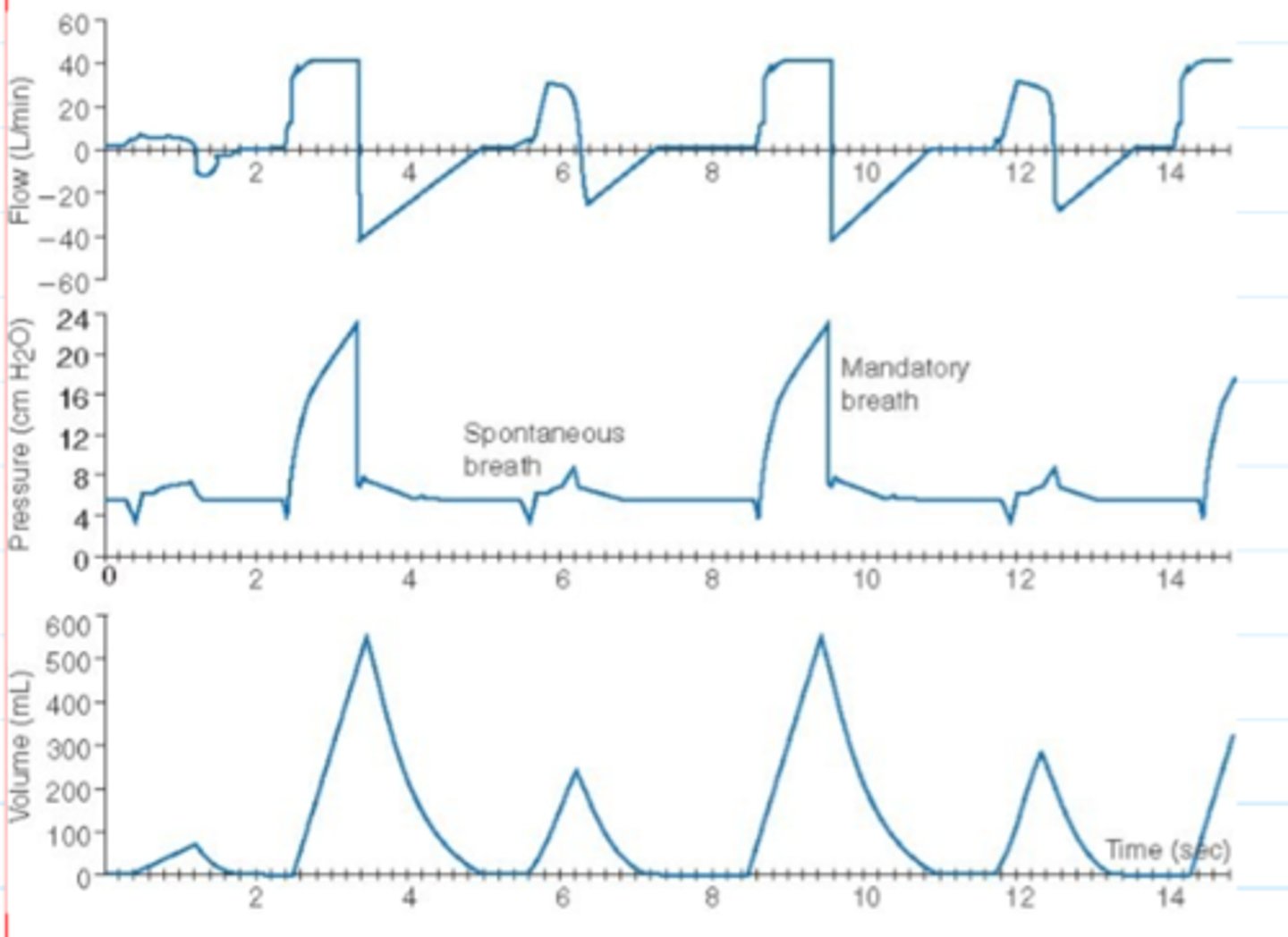
Expiratory flow & pressure waveforms during VC showing airflow obstruction, spontaneous inspiratory efforts, and autopeep during expiratory phase
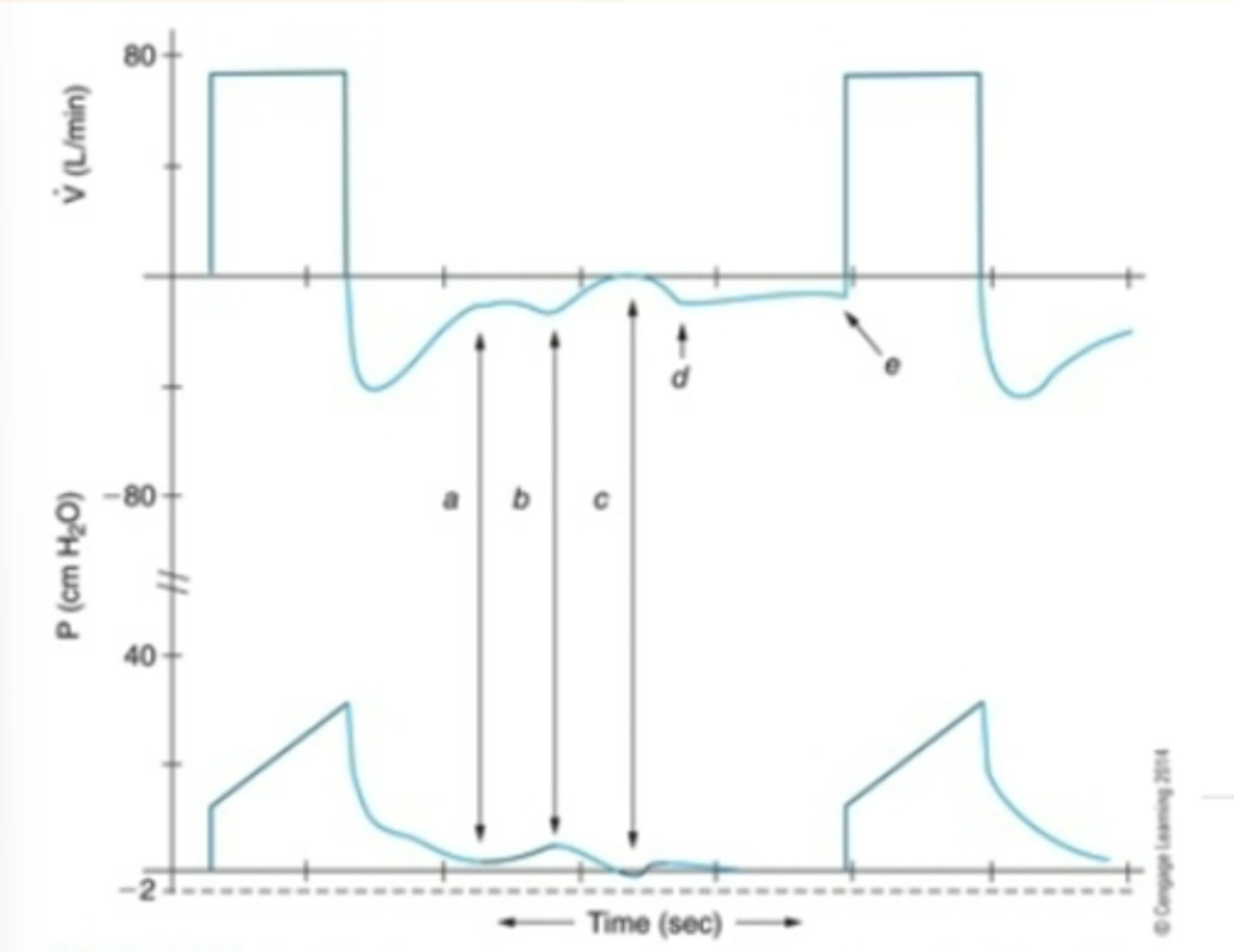
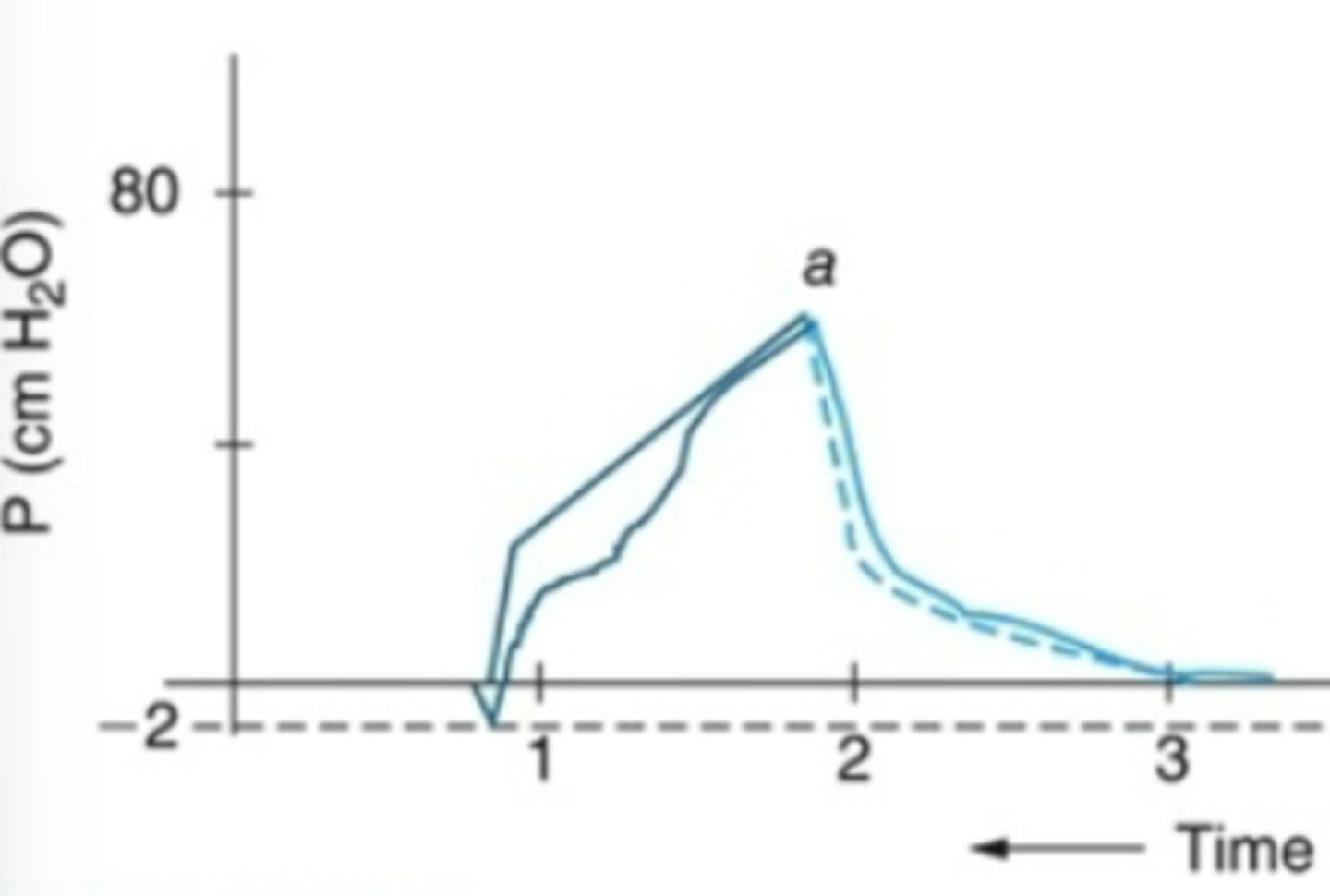
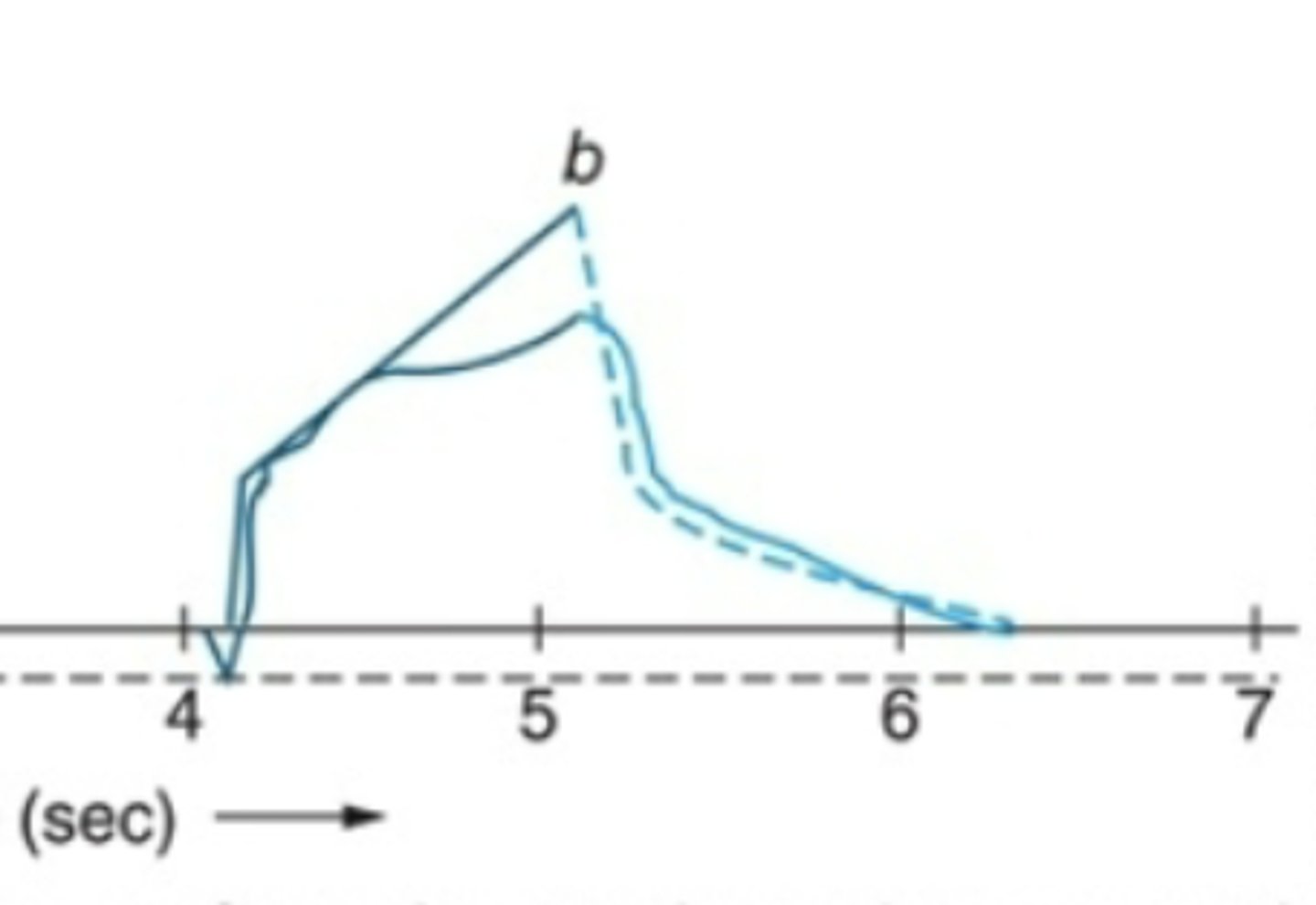
Cstatic waveform analysis
dotted line: normal cstatic
solic line: decreased cstatic
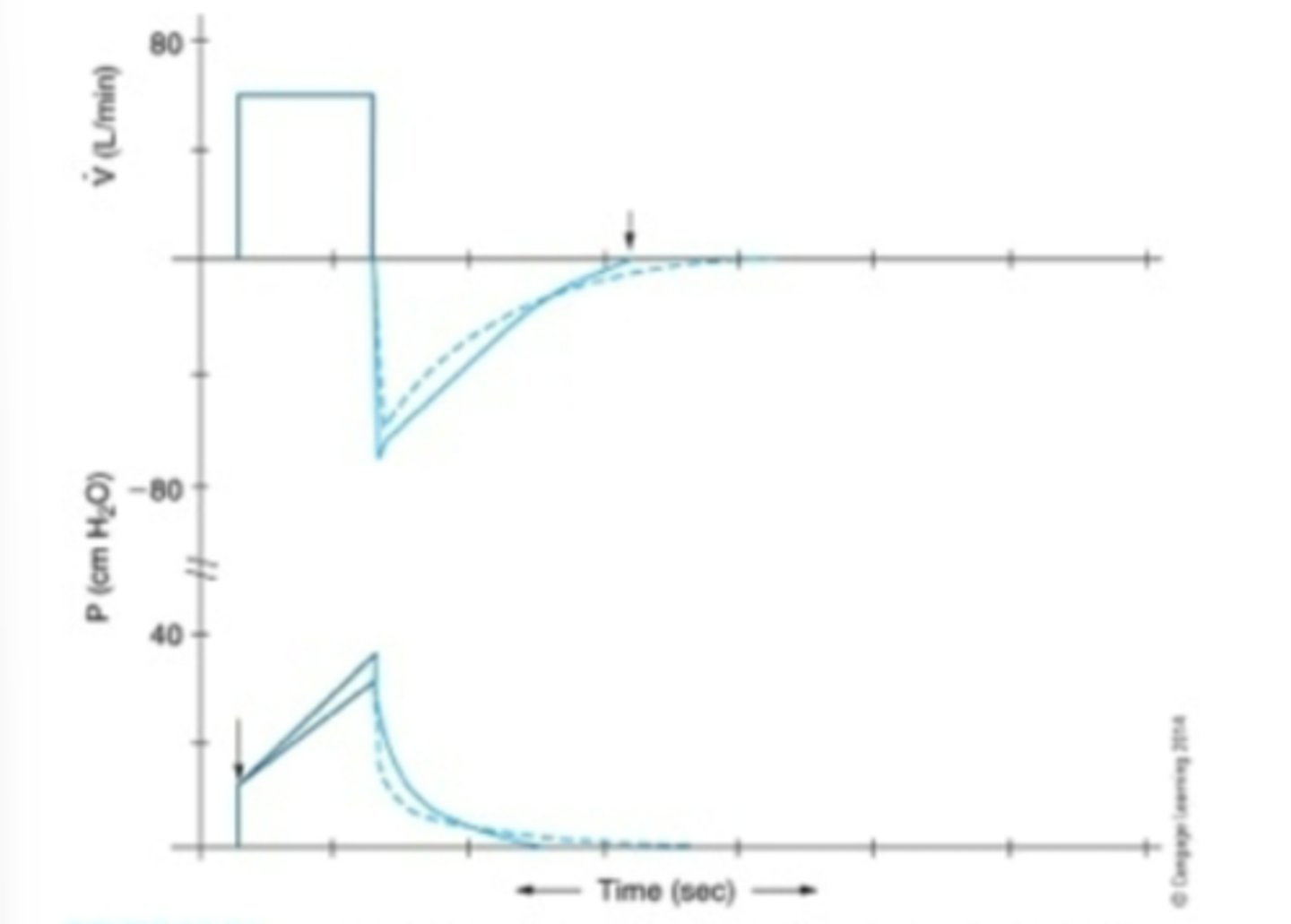
Waveform Analysis: Disconnection
Inflection points
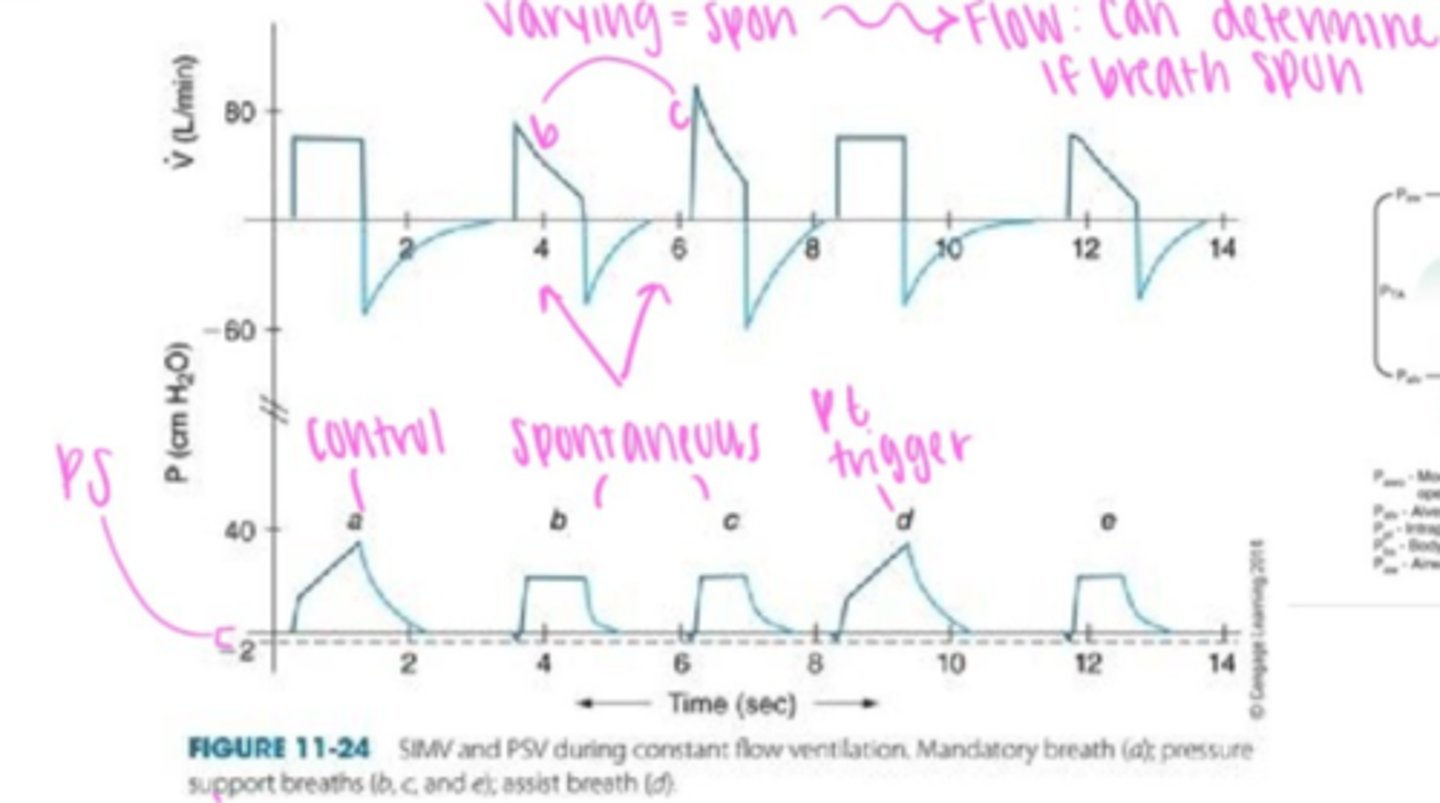
Pressure Support Waveform
varying flow & I-time
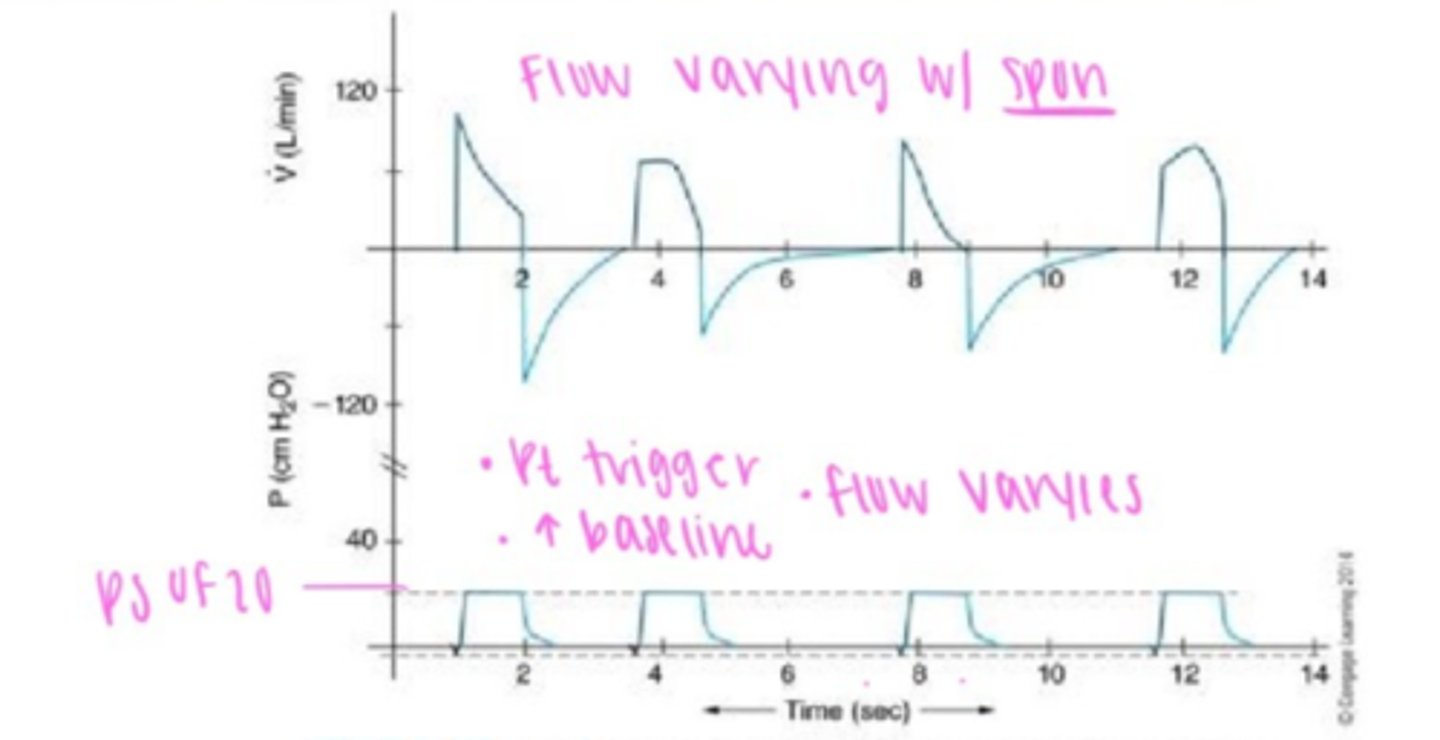
Asynchrony basic waveform PSV example
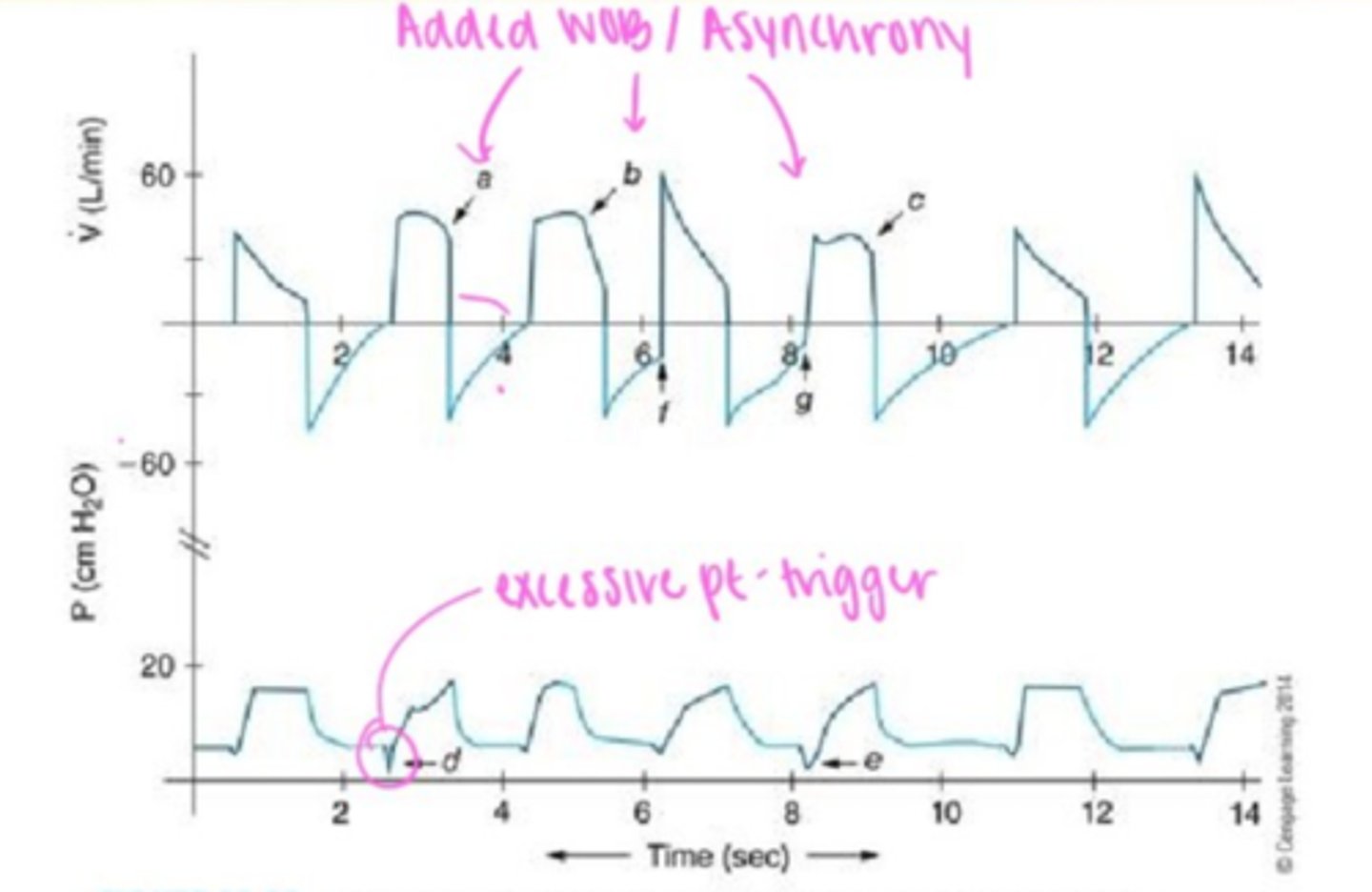
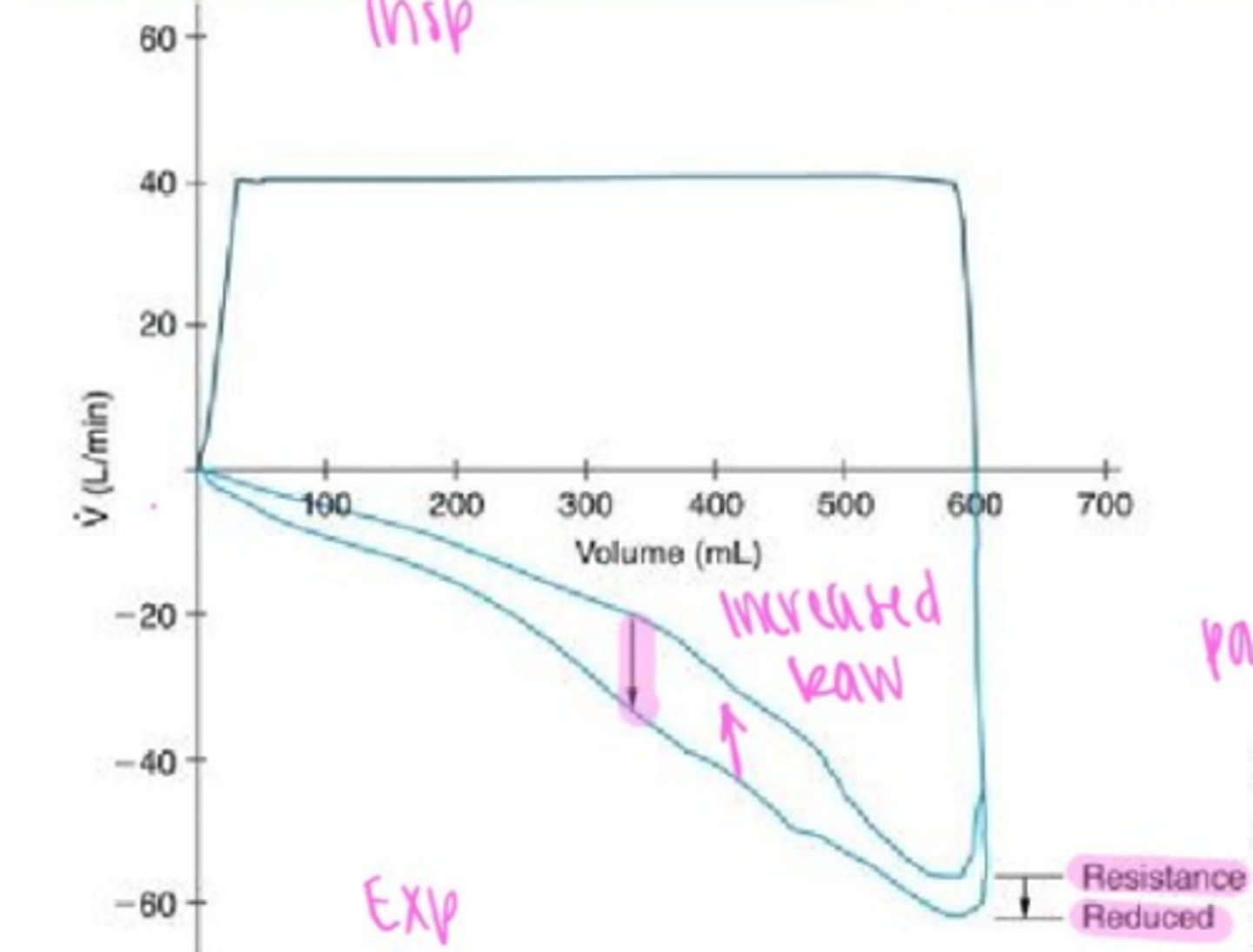
Raw Waveform
Compliance waveform
Air leak waveform
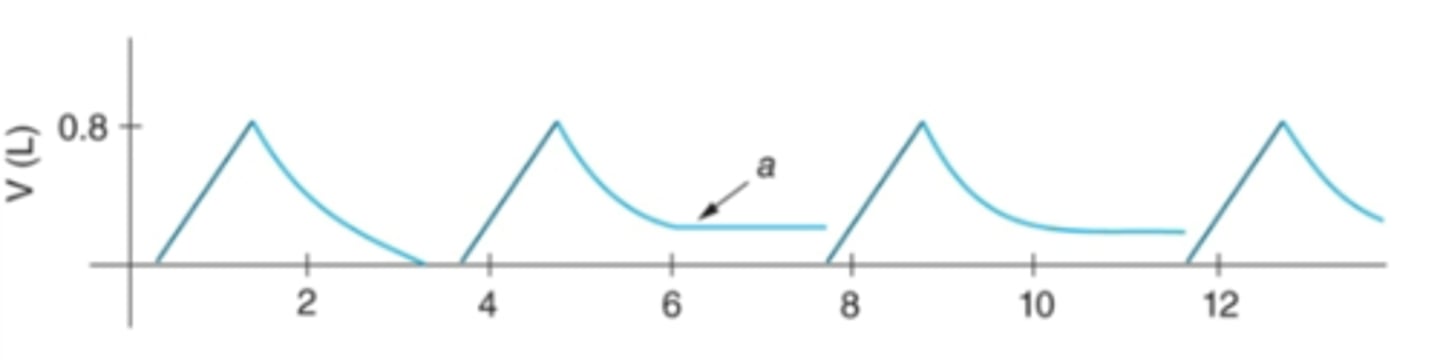
Flow volume loop: Raw analysis
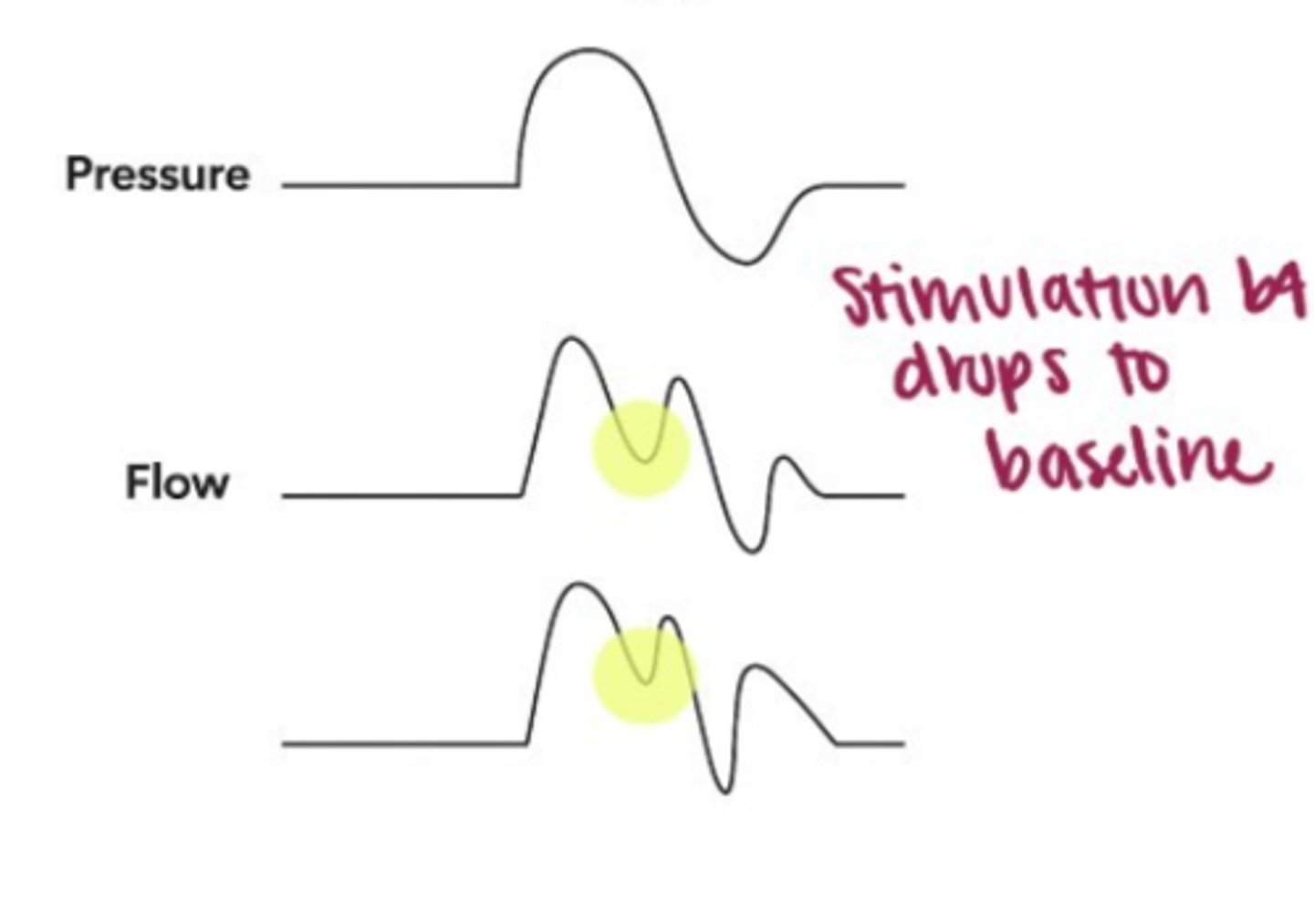
Reverse Trigger
double-trigger option
Pt tries to breathe longer or deeper than vent setting
-cycles to expiratory phase while pt makes insp effort
To fix: increase i-time or switch mode (PSV,assist)
Reverse trigger
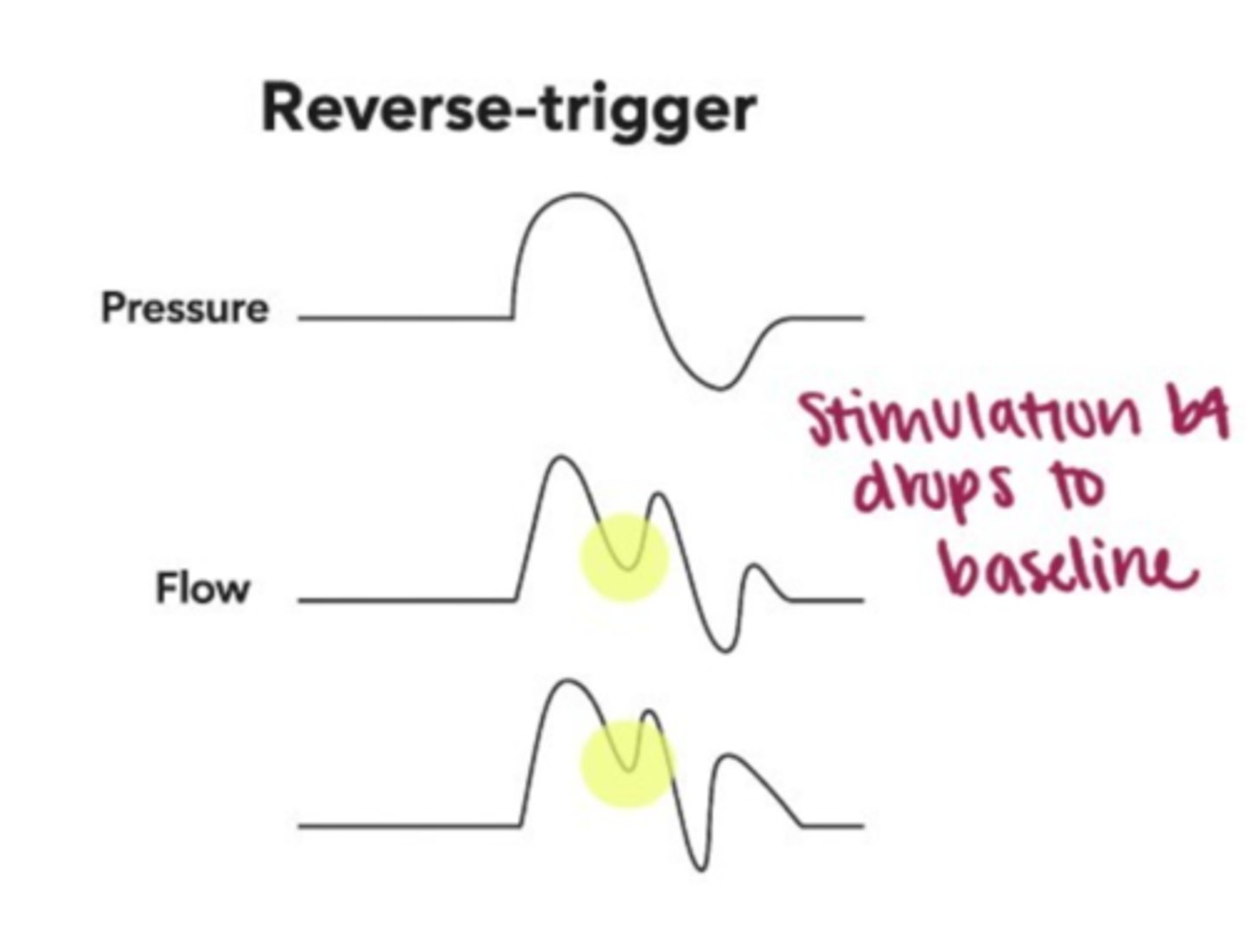
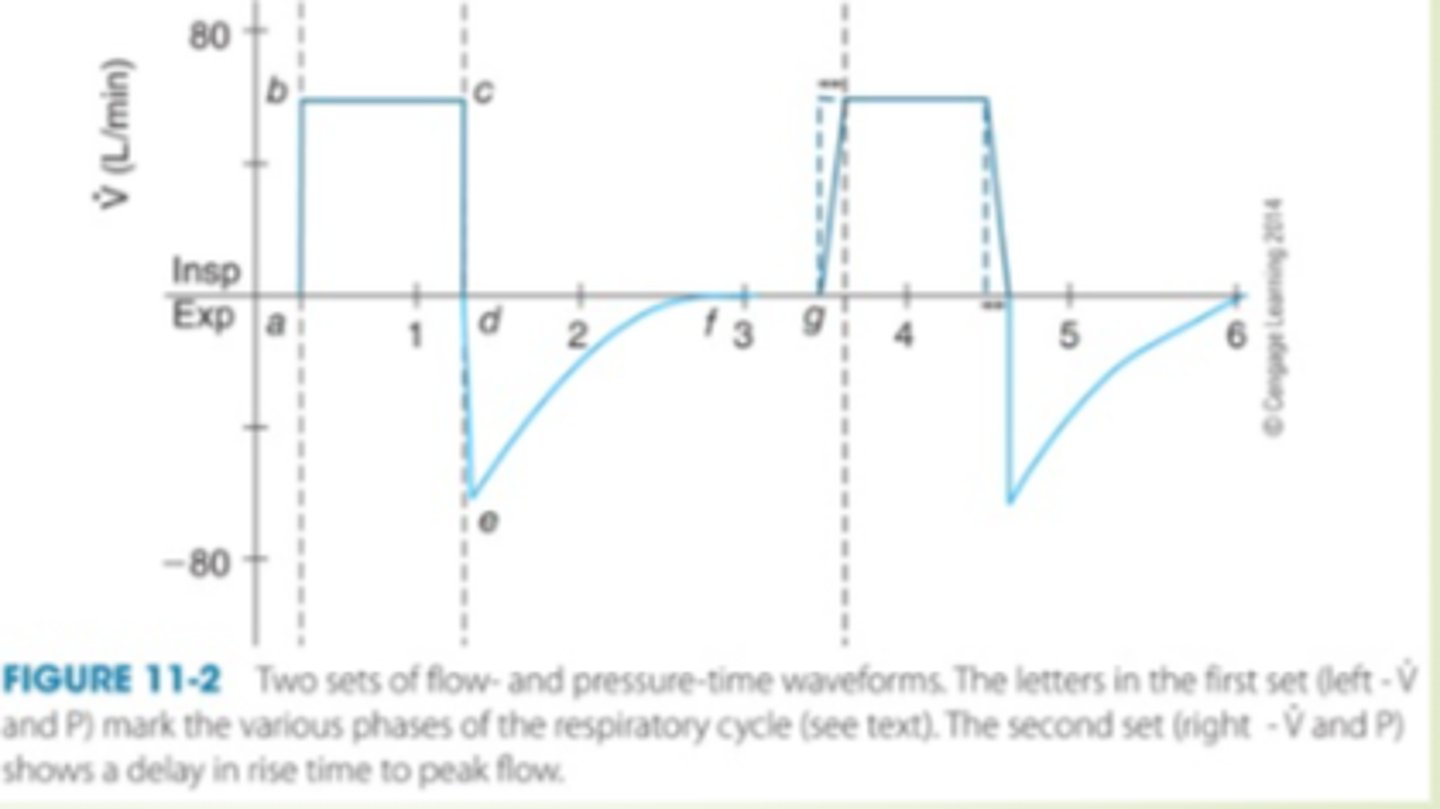
Flow asynchrony: graph details
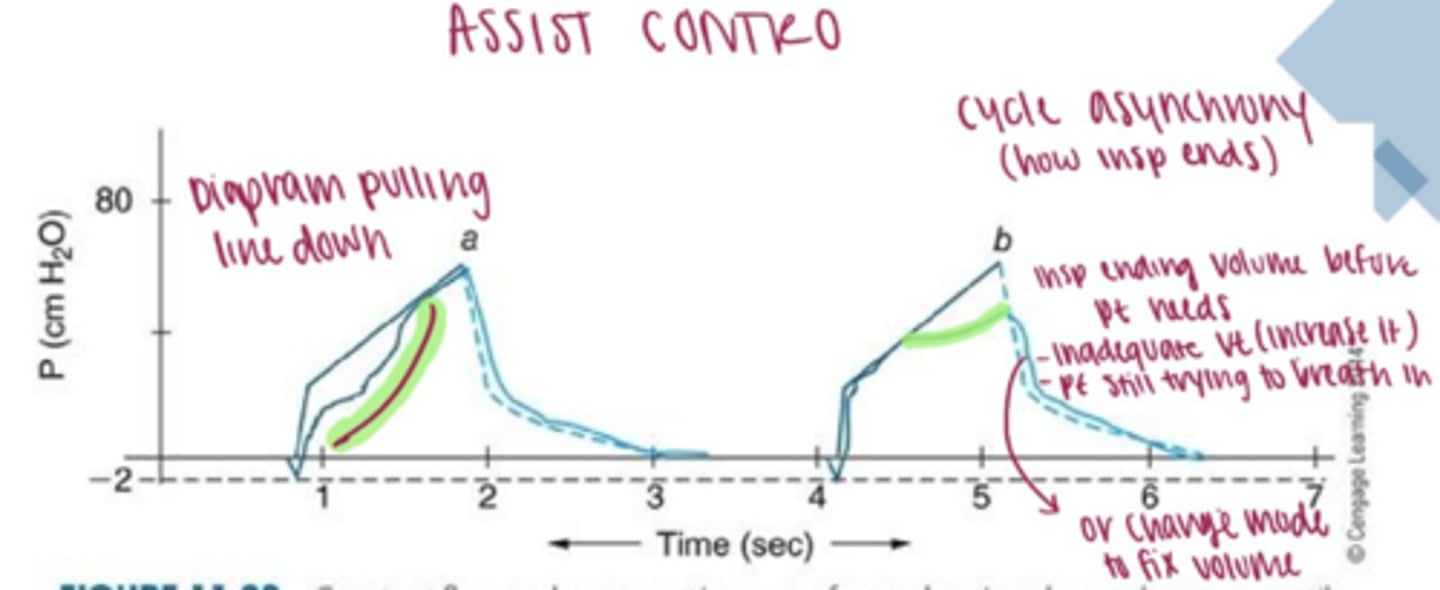
Flow patterns types
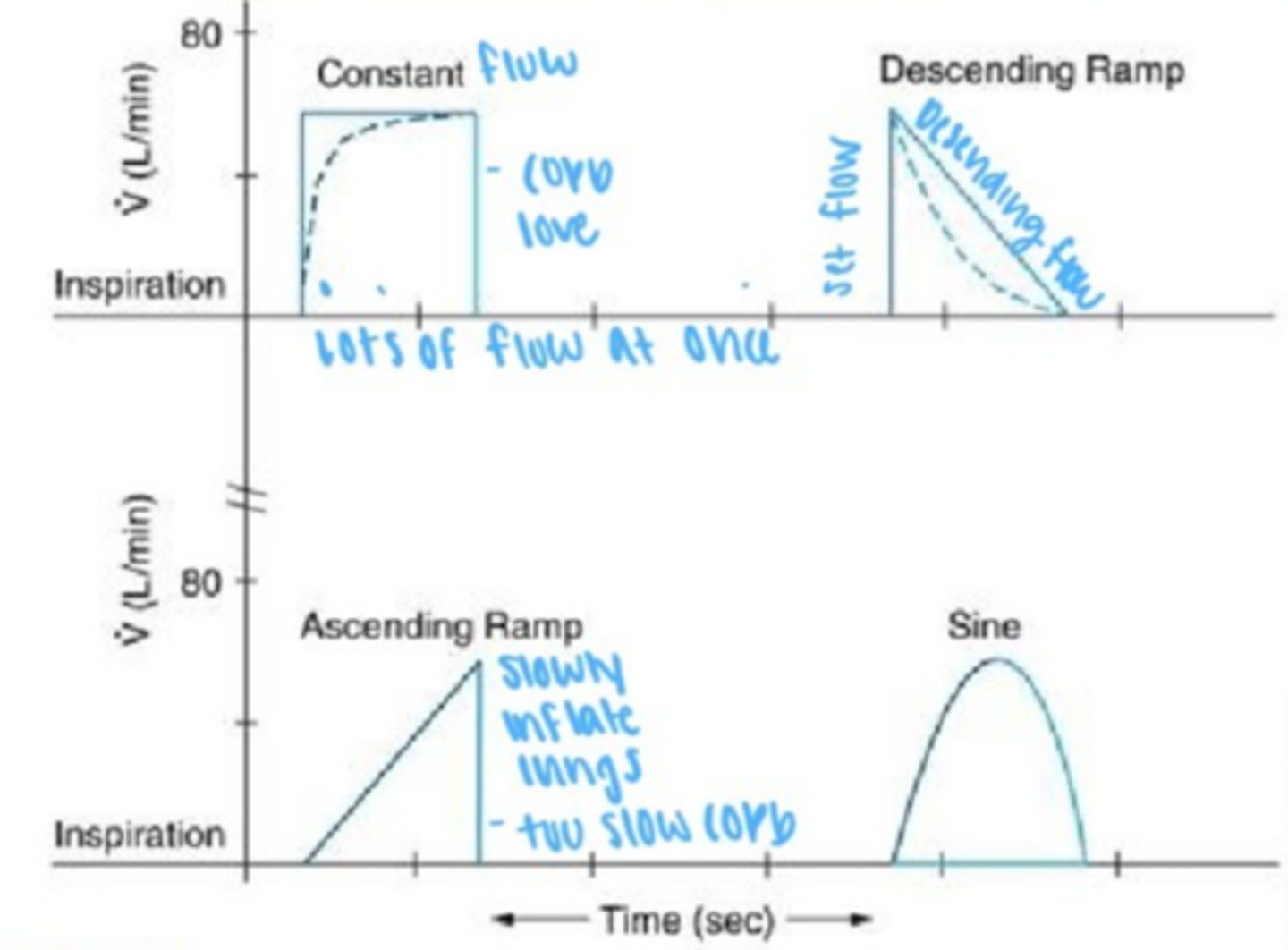
Constant Flow wave- lag in rise time
2nd waveform
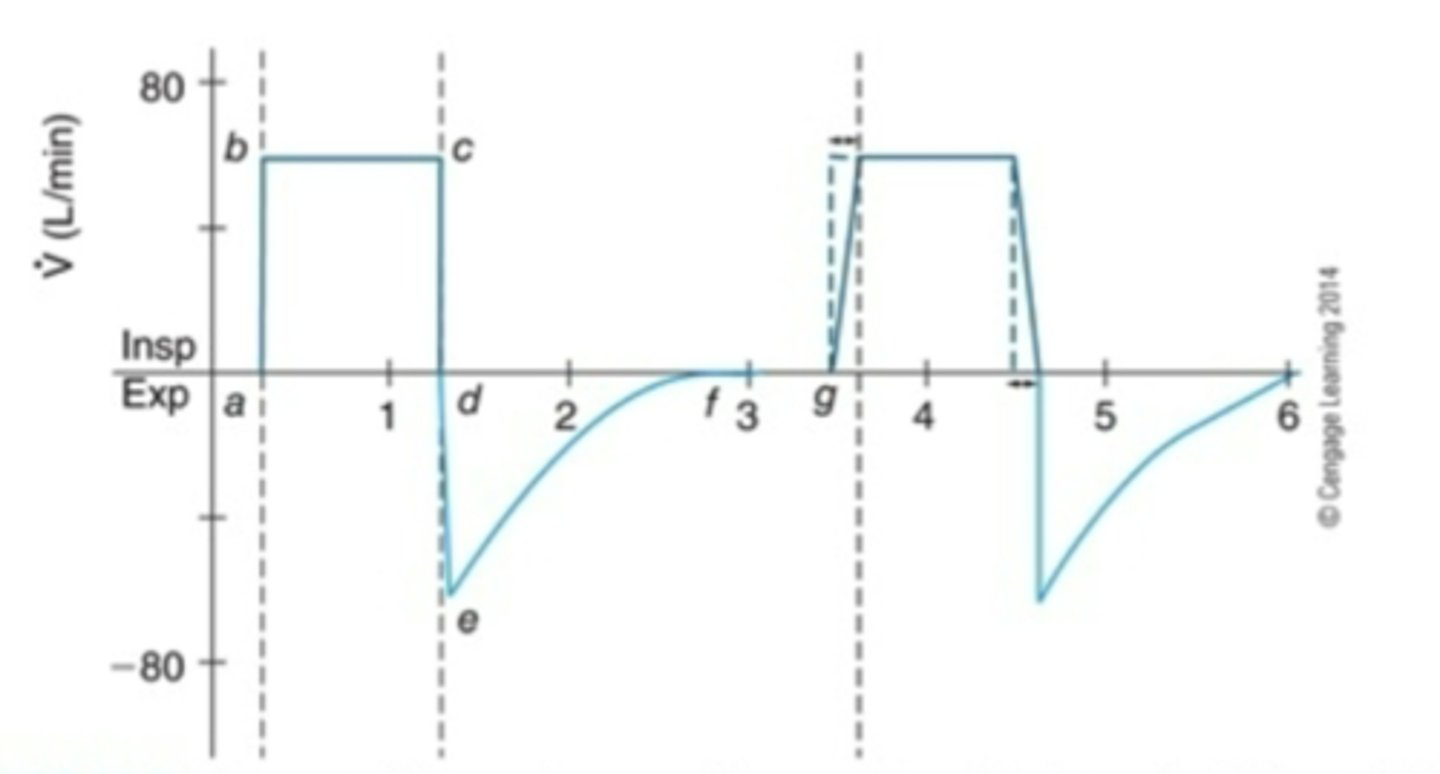
Assist control waveform