Recording Final
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
3 Stages of Multitrack Recording
Tracking
Mixing
Mastering
What mastering is and where it occurs
happens after mixing where someone optimizes a finished product for consistent playback across all systems
Comping
the process of combining the best parts from multiple takes into a single, composite track
Threshold of Hearing
0 dB
Threshold of Feeling
118 dB
Threshold of Pain
140 dB
What frequencies are percieved as harsh?
odd harmonics
Inverse Square Law
sound intensity diminishes with distance, each time you double the distance, its sound pressure becomes 6 dB less
Range of Human Hearing
20 Hz-20 kHz
First Step in Human Hearing
sound waves enter the ear canal and make the ear drum vibrate
Second Step in Human Hearing
ear drum moving makes a tiny chain of bones in the middle ear
Tiny Chain of bones
malleus, incus and stapes
Third Step in Human Hearing
last bone knocks on the membrane window of cochlea and makes fluid in cochlea move
Fourth Step in Human Hearing
fluid movement triggers response in Auditory Nerve
RT60
amount of time it takes for a sound to decay 60 dB once source is turned off
Why non-parallel walls are used
because parallel walls reflect sound back and forth (flutterecho) and even leads to the destructive interface of the sound waves
Primary Acoustic Factors
Acoustic Isolation
Symmetry
Frequency Balance
Absorption
Reflection
Reverb
Purpose of Gobos
to control sound by isolating instruments/vocals, managing reflections, reducing bleed, and shaping room acoustics
Speaker Placement Guidelines
should be placed 1 to 2 feet away from the nearest wall/corner to avoid bass build up
equilateral triangle for listening position
rectangular room→long dimension
3 Types of Microphones
Dynamic
Ribbon
Condenser
3 Types of Transducer
Moving Coil Dynamic
Ribbon Dynamic
Capacitor
Phantom Power
48 V
3:1 Rule
for every distance between a mic and its source, a nearby mic(s) should be separated by at least 3x the distance
In Phase
sound is doubled
Out of Phase
cancelled
Partially Aligned
half cancelled
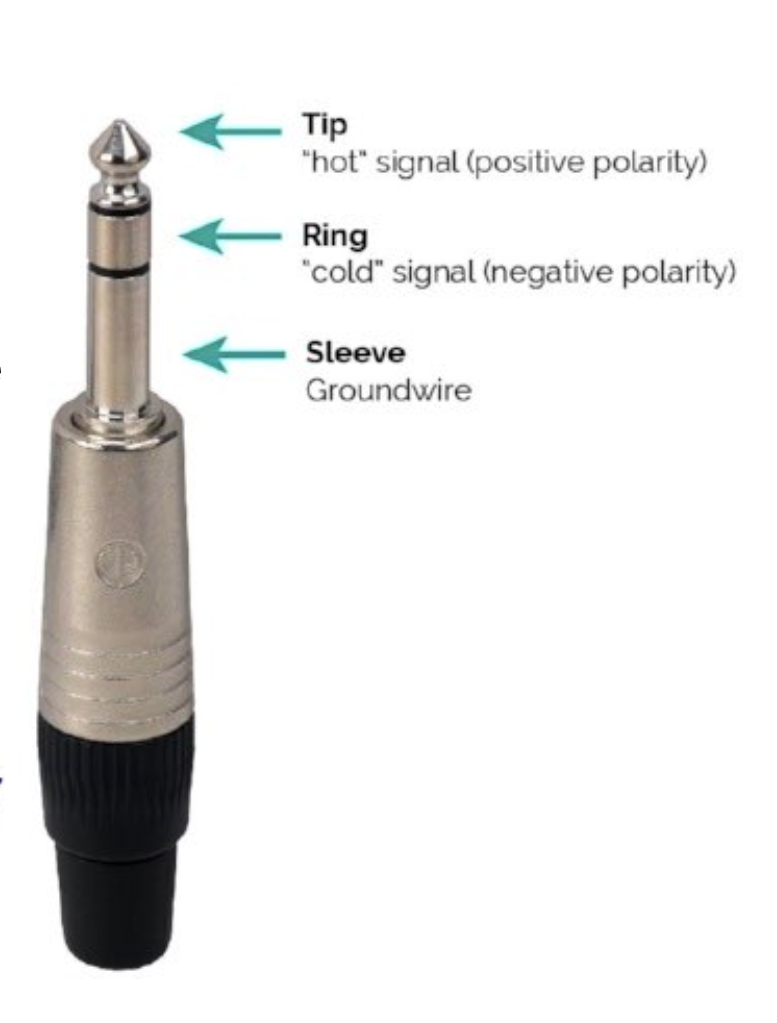

Balanced Cables
3 wires
A signal wire (tip)
Another signal wire that is identical, except for the fact that it’s polarity is inverted
Grounding Wire (sleeve)
These are better at eliminating noise. This is due to the face that the wires have opposite polarity. It gets inverted at the preamp, cancelling outside noise
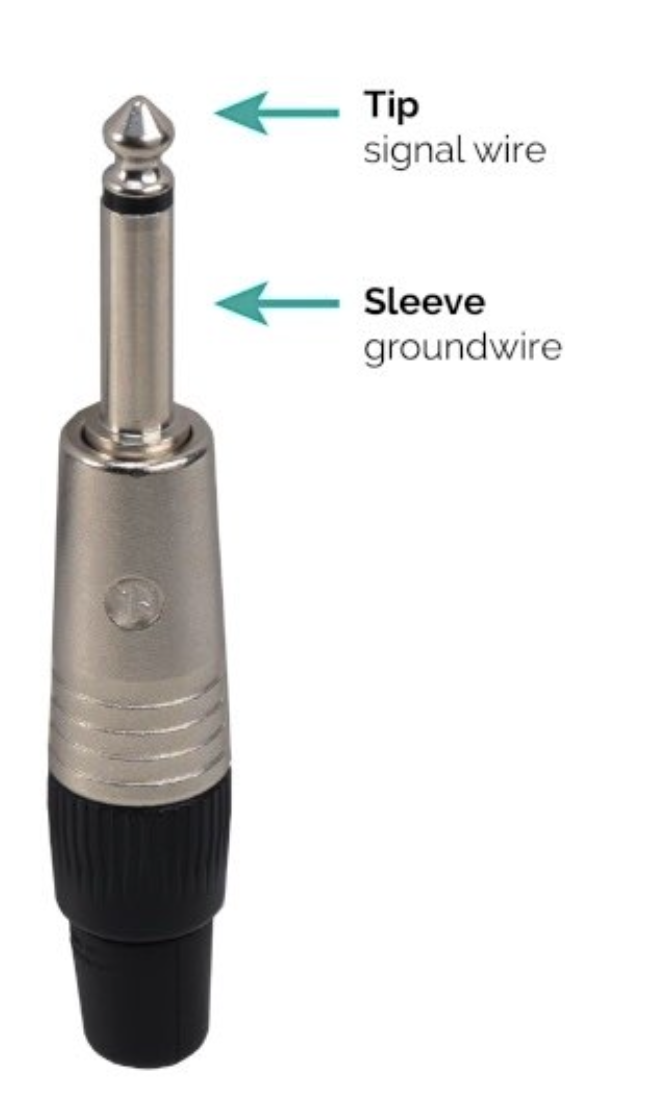

Unbalanced Cables
2 wires
A signal wire (tip)
A ground wire
Patchbay Details
outputs are on top and inputs are on the bottom
Full Normal
a patch cable inserted into the input (bottom) breaks the normaled connection
best for scenarios where you need to completely isolate a signal from its normal destination when patching it elsewhere
Half Normal
a patch cable inserted into the output jack (top) does not break normalled connection, allowing signal to be sent to both the normal destination and patched desitation (Y cable)
generally preferred due to its flexibity. it’s useful for occasional signal spitting and introduces minimal risk
Preamp
boosts weak audio signals from mics to line level, making them usable for recording
Channel Strip Order
Channel Input
Dynamics
EQ and Filter
Cue and FX Outputs
Channel Output Pan
Channel Faders
individual audio sources
Subgroups
multiple channels
Digital File Formats
.Wav
Broadcast Wave (can add text strings)
AIFF
Latency Causes
Buffer Size
Audio Drivers
Computer Power
Connection Type
Reducing Latency
Lower the input buffer size
Use zero latency monitoring
Avoid plug ins
Buffer Size
to balance CPU load and latencyt in digital audio processing, acting as temporary storage for audio data
Nyquist Theorem
in order to accurately reproduce a signal, it should be periodically sampled at a rate at least twice the highest frequency recorded
Bit Depth
the number of bits used to represent the amplitude of each digital audio sample, determining the resolution and dynamic range
Amplitude
Bobby Owsinski’s Mix Elements
Balance
Frequency Range
Pan
Dimension
Dynamics
Interest
Improving Recordings via Mic Placement
Move mic closer to sound source
Move mic further from interfering sound and reflective surfaces
Peak
highest level of each individual sound wave and used to to determine whether a signal will start clipping
1.414 x rms voltage
RMS
measures the average amplitude of all of the sample
.707 x peak voltage
closest to human hearing
Ground Noise
unwanted electrical interference (hum or buzz) caused by multiple paths to the electrical ground in interconnected equipment
EQ in Context
applying it to audio elements within the full mix, not in isolation to ensure instruments sit well together
Tape Heads
made from rings of ferromagnetic material with a gap where the tape contacts it so the magnetic field can fringe out to magnetize the emulsion on the tape
Tape Saturation
when the incoming audio signal exceeds the point where the tape’s magnetic particles can accurately track the converted voltage swings, then this results in gradual clipping of the positive and negative peaks of the wave that’s being imprinted on the tape
has a unique warmth and edge
Compression
reduces an audio signal’s dynamic range by automatically turning down loud peaks and bringing up quiet sounds
Fastest connection types
Thunderbolt 3
USB-C vs Thunderbolt
Thunderbolt has a higher bandwidth and is more compatible with more transmission protocolsm meaning it can connect with more types of devices
Thunderbolt is also more expensive
AoIP
allows you to transmit multiple uncompressed digital audio signals over ethernet (Cat 5/6) cables with minimal latency
Wavelength Equation
λ=V/f
V=1130 ft/sec at 68 F
Speed increases 1.1 ft/sec for each F increase
Problems with Voice Recording
Excessive Dynamic Range
Sibilance and Plosives
Proximity Effect
Direct Sound
the sound that travels in a straight line from a source to a listener without bouncing off any surfaces
Early Reflections
sound waves that bounce off nearby surfaces and reach listener’s ears just ms after direct sound
Reverb
creates distance, depth, and spaciousness in recordings
Active Listening
listening as the primary activity
Close Mic Issues
Proximity Effect
Plosives
Sibilance
Distortion
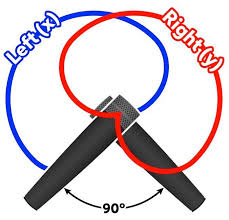
XY Mic
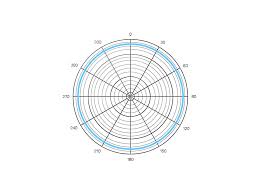
Omni
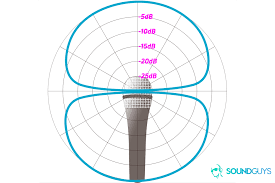
Bidirectional
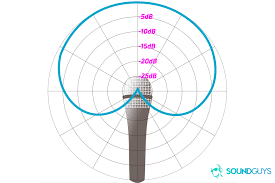
Cardioid
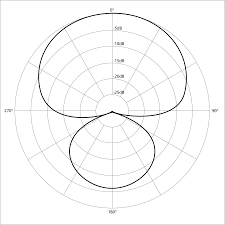
Hypercardioid
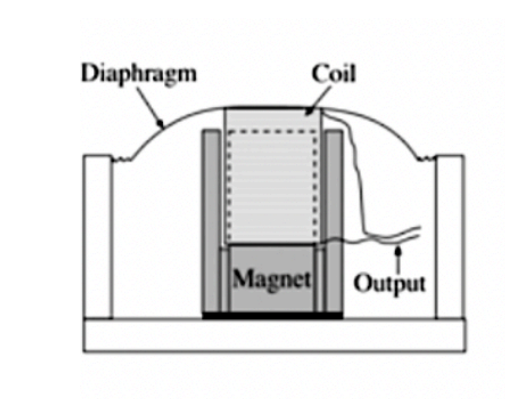
Moving Coil Dynamic

Ribbon Dynamic
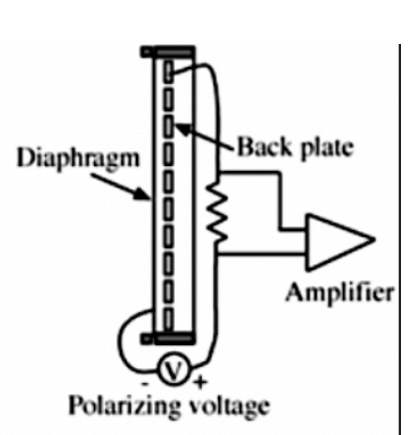
Capacitor
Frequency
Sample Rate
Time-based errors in a digital audio system are commonly referred to as:
Jitter
Which of the following audio formats is known for its lossless compression?
FLAC
Which one of the following is NOT a digital audio transmission specification?
mLAN
Tails Out
Refers to the tape being fast forwarded to the end
Gain
A level adjustment designed to optimize each signal coming into the console
Insert Loop
A patch point for connecting outboard gear, such as a compressor or effects unit
HPF
A circuit which sharply decreases low frequencies, reducing mic handling noise, stage rumble, and plosives (p-pops)
Aux Mix
A separate mix of each channel which has its own output, which can be used to feed stage monitors, a recording mix, sends to a reverb unit, or other uses.
Pre/Post
An indication of where the Aux mix splits off from the main signal. If it
is labeled as as “Pre” or “PreFade” mix, then its level is completely
independent of the channel’s fader. If it is labeled as a “Post” or
“PostFade” mix, then the aux’s level will also be affected by the channel
fader as it is adjusted
Pad
If you turn the gain all the way to the left and the signal is still too hot,
then you should engage the pad, which will reduce the incoming signal
by a preset amount (usually 20 dB or so)
Direct Out
An individual channel output after the gain stage, but before EQ or
fader involvement
PFL
Pre Fade Listen. Works as a “solo” button for the engineer’s headphones
Clipping
~Since the clipping was caused by the gain boost in the compressor plug-in, the
signal needs to be attenuated either in the plug-in or before it, which
would require a region-based level adjustment