Brain and Behaviour (10): Schizophrenia
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Schizophrenia (SZ)
A syndrome involving losing touch from reality, affects ~1% of the population.
What are positive symptoms of schizophrenia?
Symptoms that add behaviors:
Delusions
Hallucinations
Thought disorders
What are hallucinations?
Sensory experiences without actual stimuli, commonly auditory or olfactory.
What are negative symptoms of schizophrenia?
Symptoms that reduce normal behaviours:
Flattened emotion
poverty of speech (alogia)
anhedonia
social withdrawal
lack of initiative.
What are cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia?
Poor attention
memory deficits
poor problem-solving
low psychomotor speed
abstract thinking.
Associated with the Dorsolateral Prefrontal cortex
Which symptoms appear first and last?
Negative symptoms appear first, followed by cognitive, then positive symptoms.
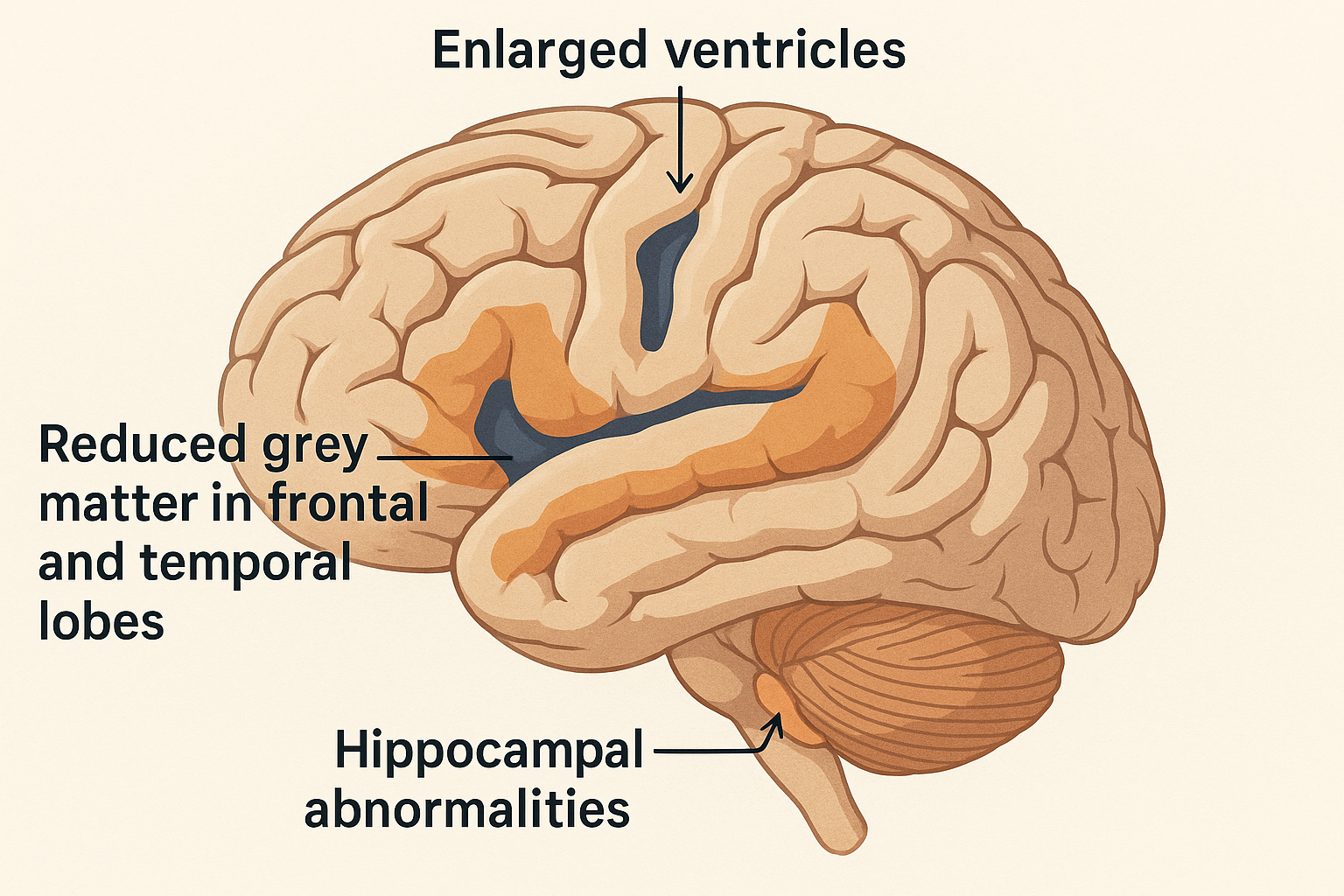
What structural brain differences are found in schizophrenia?
Enlarged ventricles
Reduced grey matter in frontal and temporal lobes
Hippocampal abnormalities.
Is Schizophrenia Genetic?
Yes, highly heritable but polygenic.
What is DISC1?
A gene linked to neuronal development; once thought to be a major risk factor for SZ but now disputed.
How does paternal age affect risk?
Having older fathers increase risk of SZ due to sperm mutations. (Brown et al., 2002)
What does twin research show about heritability of SZ?
Monozygotic twins show higher concordance, especially if monochorionic (shared placenta).
What is the "two-hit" model of schizophrenia?
Early brain disruption + Adolescent synaptic pruning abnormalities = schizophrenia.
What does the dopamine hypothesis propose?
Overactive mesolimbic dopamine (DA) pathway = positive symptoms
Underactive mesocortical dopamine (DA) pathway = negative/cognitive symptoms.
What drugs supports the dopamine hypothesis? (treatment)
Dopamine agonists (e.g., amphetamines) induce psychosis
Dopamine antagonists (e.g., chlorpromazine) treat symptoms.
What are typical antipsychotics?
D2 antagonists (e.g. chlorpromazine) reduce positive symptoms but cause Parkinson-like side effects and tardive dyskinesia.
What are atypical antipsychotics?
Drugs (e.g. clozapine) that treat both positive and negative symptoms with fewer motor side effects.
What is the Glutamate Hypothesis?
Schizophrenia is due to decreased NMDA receptor functioning (where glutamate binds)
Evidence for Glutamate Hypothesis
NMDA antagonists (PCP, ketamine) mimic all schizophrenia symptoms
Glutamate agonists help treat them.
How does NMDA dysfunction explain symptoms?
↓NMDA =
↑Mesolimbic Dopamine (→ positive symptoms)
↓Prefrontal Dopamine (→ negative/cognitive symptoms).
What role do microglia play in schizophrenia?
Overactive microglia may cause:
Neuroinflammation
Pruning deficits
Altered synaptic circuitry
What environmental factors contribute to SZ?
Prenatal infections
Early-life inflammation
Immune gene variants (e.g., MHC on chromosome 6).
How might estrogen protect against schizophrenia?
It has neuroprotective effects:
Women have later onset
Milder symptoms
Better treatment response.
What causes schizophrenia?
A combination of:
Genetic vulnerability
Neurodevelopmental disruptions
Neurotransmitter dysfunctions
Immune involvement.