Concept 9.6: Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways
1/5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
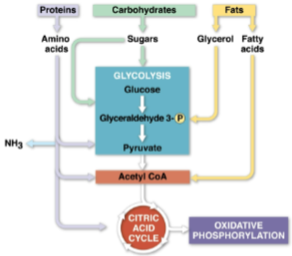
Catabolic pathways
Chains of catabolic reactions that funnel electrons from many kinds of organic molecules into cellular respiration
Seen in glycolysis’ use of many carbohydrates
Deamination
The digestion of proteins used for fuel by breaking them down into their amino acid groups
Nitrogenous waste is excreted as ammonia (NH3), urea, or other products
Nitrogenous waste
Produced as proteins are digested to amino acid groups in the forms of ammonia (NH3), urea, or other products
Glycerol
The substance fats are digested to for glycolysis, broken down in a process known as beta oxidation that produces twice as much ATP as the same mass of carbohydrates
Anabolic pathways
Chains of anabolic reactions to build macromolecules from small molecules in food or from cellular respiration
Seen in protein synthesis from amino acid
Feedback inhibition
The most common mechanism for metabolic control that dictates the level of energy production based on need
Higher ATP demands leads to more respiration
Controlls catabolism by regulating enzymatic activity at strategic points in the pathway