Module 2.3 Data Types
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Strings
A sequence of characters that can be stored in a variable
String Literal
String value specified in the source code of the program
E.g. “class”, “python”, “this is a string!”
input()
gives the user a prompt and then reads in a string from the user
len()
s a built-in function that can be used to find the length of a string (and any other sequence type)
String Concatenation
A program can add new characters to the end of a string
Container
A construct used to group related values together and contains references to other objects instead of data
List
A container created by surrounding a sequence of variables or literals within brackets []
Element
an item in a list
Index
contained elements in a list are ordered by position within the list, starting with 0
are mutable — can be changed
Sequence-type Functions

Tuples
An immutable container, which means the elements within can’t be changed
Sequence type structure that supports sequence functions such as len(), indexing, etc.
Is created using parenthesis
useful to ensure values are not changed when specified
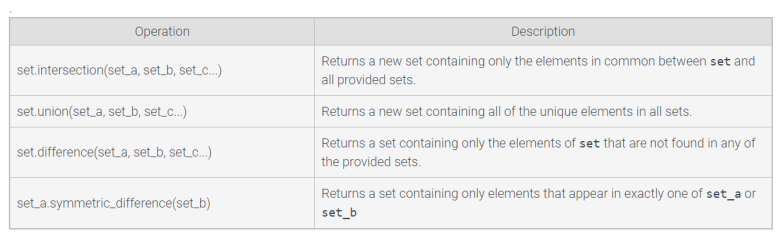
Set
an unordered collection of unique elements
set()
accepts a sequence-type iterable object (list, tuple, string, etc.)
Set literal
written using { } with elements separated by commas
e.g. integers_set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Mutable Sets (add/remove elements)

Set Operations
Dictionary
Python container used to describe associative relationships
Associates keys with values
Key
Term that can be located in a dictionary
Must be unique
Value
describes some data associated with a key and can be duplicated
Key-value pairs
keys need to be immutable types such as numbers, strings, or tuples, while a value can be any type
Dictionary Example
favorite_basketball_playes = {‘Lebron James’: 6, ‘Stephen Curry’: 30}
Keys: ‘Lebron James’ and ‘Stephen Curry’
Values: 6 and 30
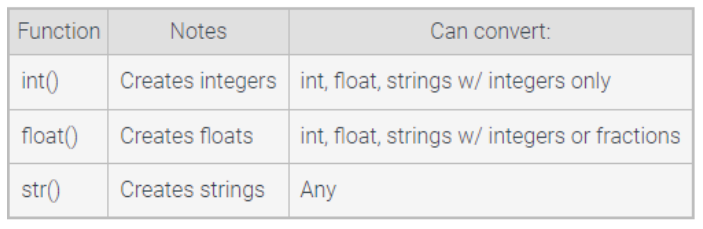
Type Conversions
conversion of one type to another, such as an int to a float
Implicit Conversion
a type conversion automatically made by the interpreter, usually between numeric types
The result of an arithmetic operation like + or * will be a float only if either operand of the operation is a float
Conversion Functions
Binary Number
Each memory location is composed of bits (0s and 1s), a processor stores a number using base 2

Decimal Number
Numbers represented in base 10, where each digit must be 0-9 and each digit’s place is weighed by increasing powers of 10

format()
A function that allows the programmer to create a string with placeholders that are replaced by values or variable values at execution
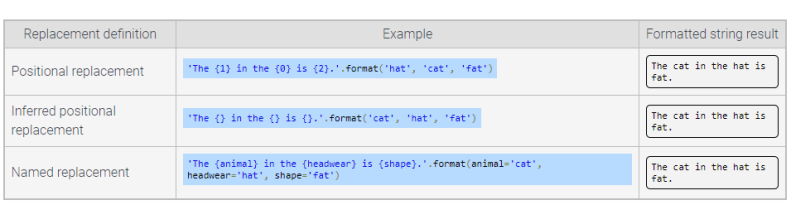
Replacement field
A placeholder surrounded by curly braces
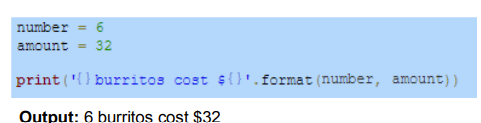
String Formatting Example
Values inside the format() parentheses are inserted into the replacement fields in the string
Formatting Strings
Which of the following are NOT data type names in Python?
Math ; String ; while ; double ; char ; if
Which of the following are data type names in Python?
float ; int ; str ; bool
Match the literal value to its python data type.
1, 1.0, False, “integer”
1 - int
1.0 - float
False - bool
“integer” - str
Match the literal value to its python data type.
123, 22.5, True, “round”
123 - int
22.5 - float
True - bool
“round” - str
Which of the following would be the best data type for a variable to store a friend's name?
str
A chef would like to record the number of guests that visit his restaurant in a day. Which data type would best represents this quantity?
int
Consider the following sequence of instructions:
a = 2 + 2
b = a * 2
a = b - 2
x = a * b
xWhat will the variable x evaluate to on the last line?
48
What will the variable x evaluate to on the last line?
x = 1
y = 8
x = y + 1
y = x - 1
x = x + 1
y = y - 1
x = x - y
x3
What will the variable x evaluate to on the last line?
x = 15
y = 3
x = x + 1
y = y - 1
x = x + y
x18
What will the variable x evaluate to on the last line?
a = 16
x = a + 16
a = 8
x32
Which of the following would be the best data type for a variable to store an alpha-numeric serial number?
str
A physician would like to record the heights of his patients in meters. Which data type would best represents this quantity?
float
Consider the following sequence of instructions:
a = 2 + 3
b = a - 5
a = a + 2
x = a * b
xWhat will the variable x evaluate to on the last line?
0
What will the variable x evaluate to on the last line?
x = 8
y = 11
x = x + 1
y = y - 1
x = x + y
x19
What will the variable x evaluate to on the last line?
x = 4
y = 6
x = y + 1
y = x - 1
x = x + 1
y = y - 1
x = x - y
x3