ap bio -- unit 2: biochemistry
1/44
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
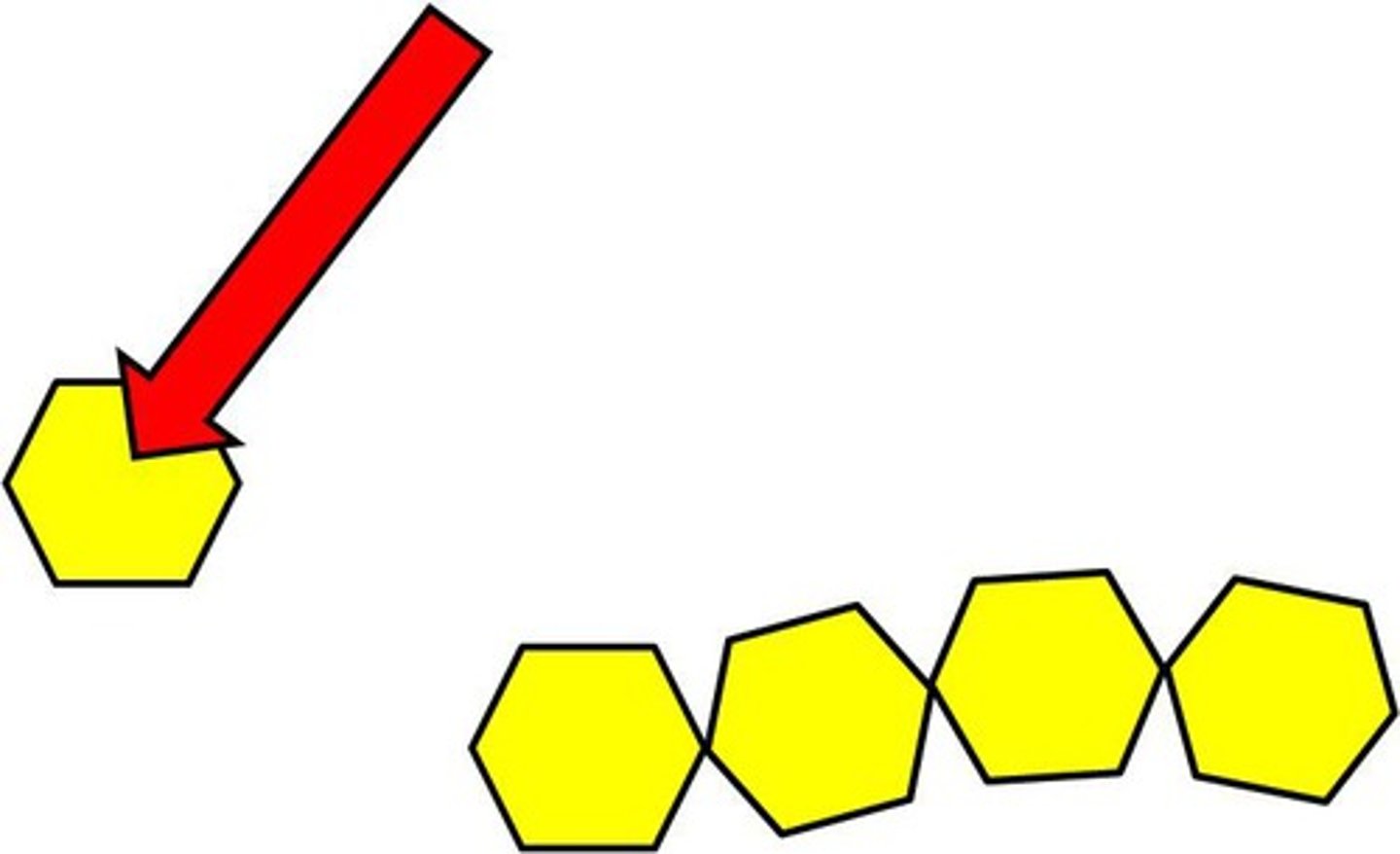
polymer
A large molecule composed of repeating structural units or monomers.
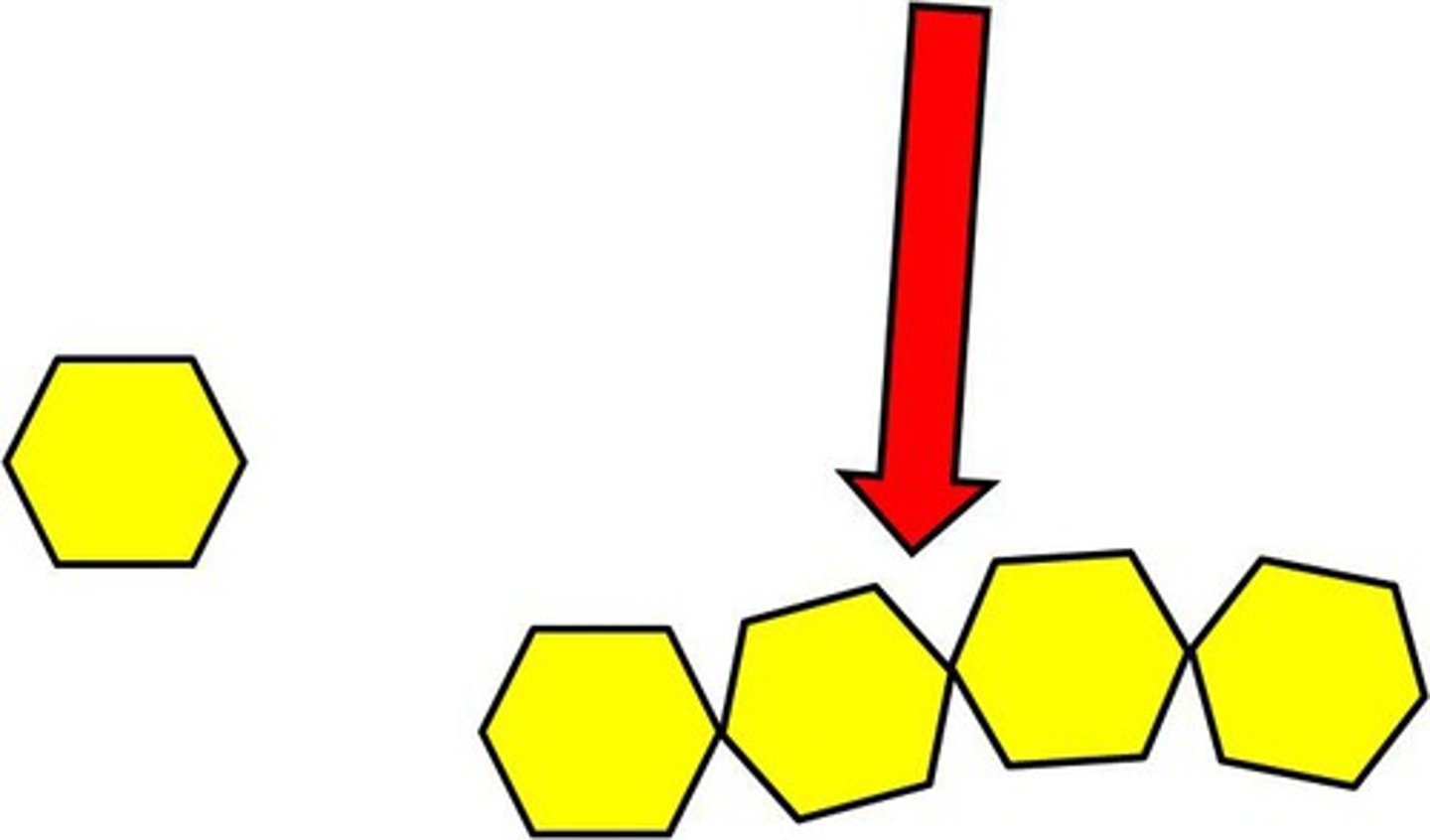
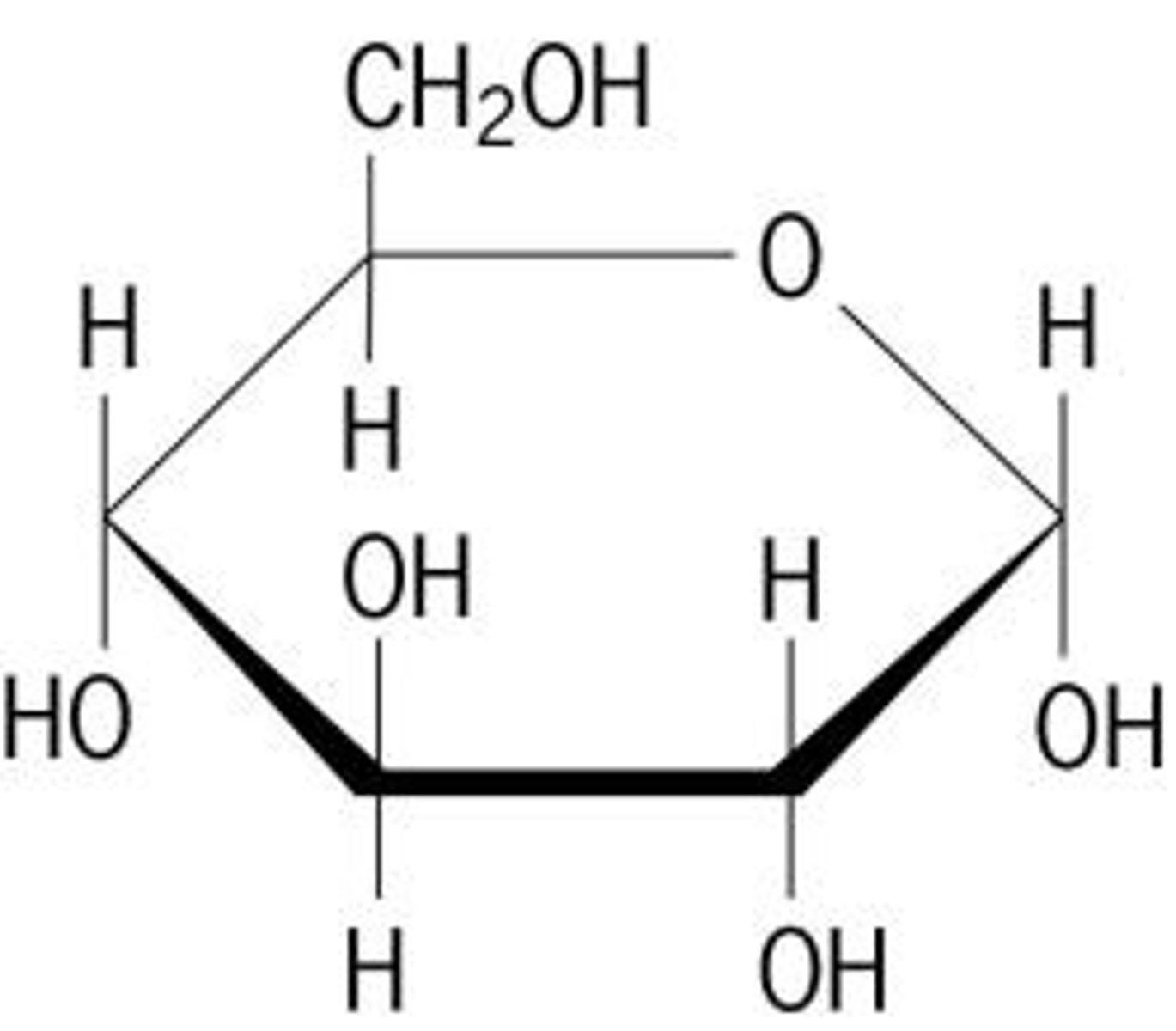
carbohydrate
Compound used for structure and short term energy (e.g., sugars, starches, and cellulose)
protein
Class of nutrients made up of amino acids. They are needed to build and repair body structures, and to regulate almost all processes in the body
lipid
Organic molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and store food energy until needed (fats, oils, waxes)

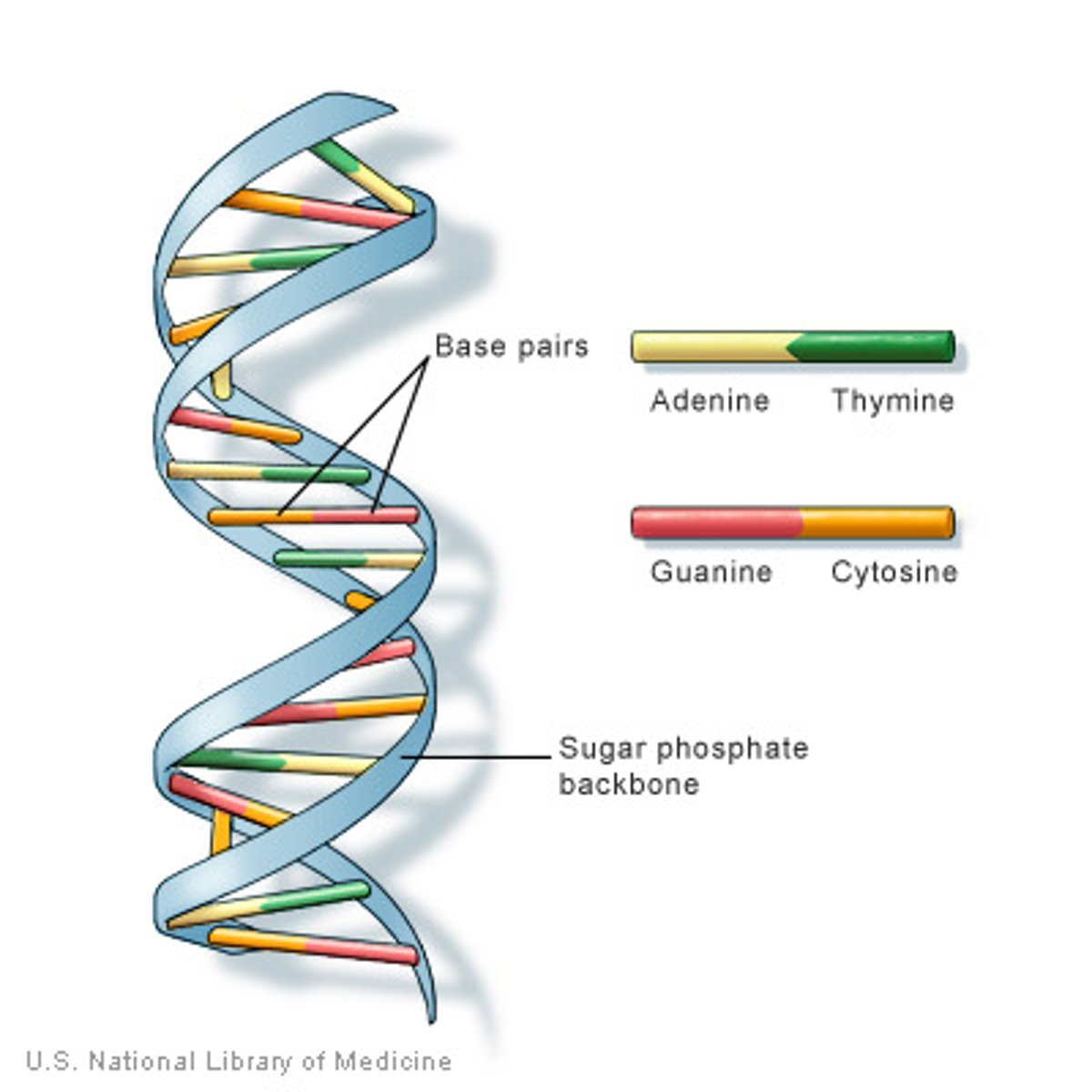
nucleic acid
A biological macromolecule (DNA or RNA) composed of the elements C, H, N, O, and P that carries genetic information. stores the information needed to make proteins.
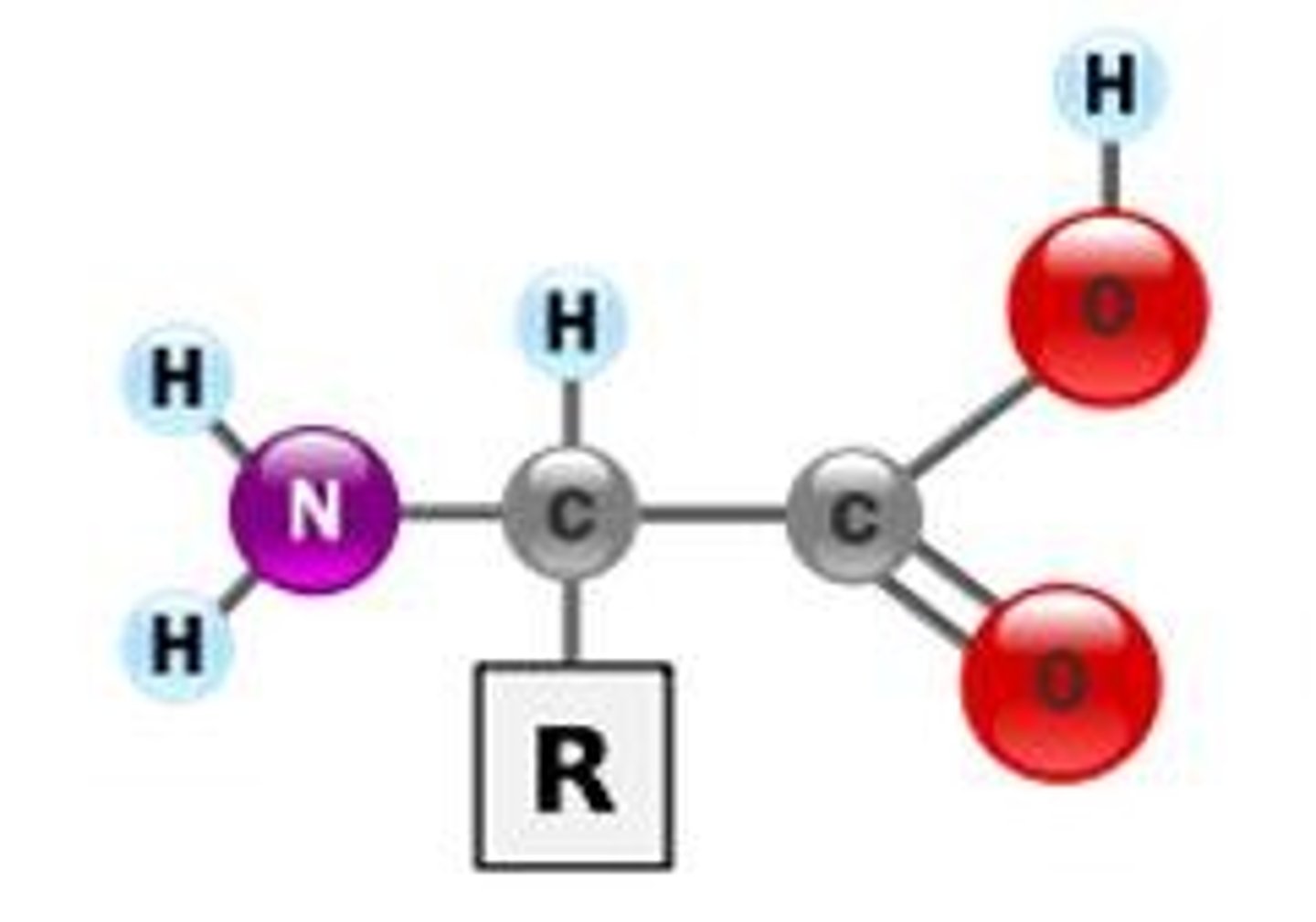
amino acid
Building blocks of protein. there are 20 types
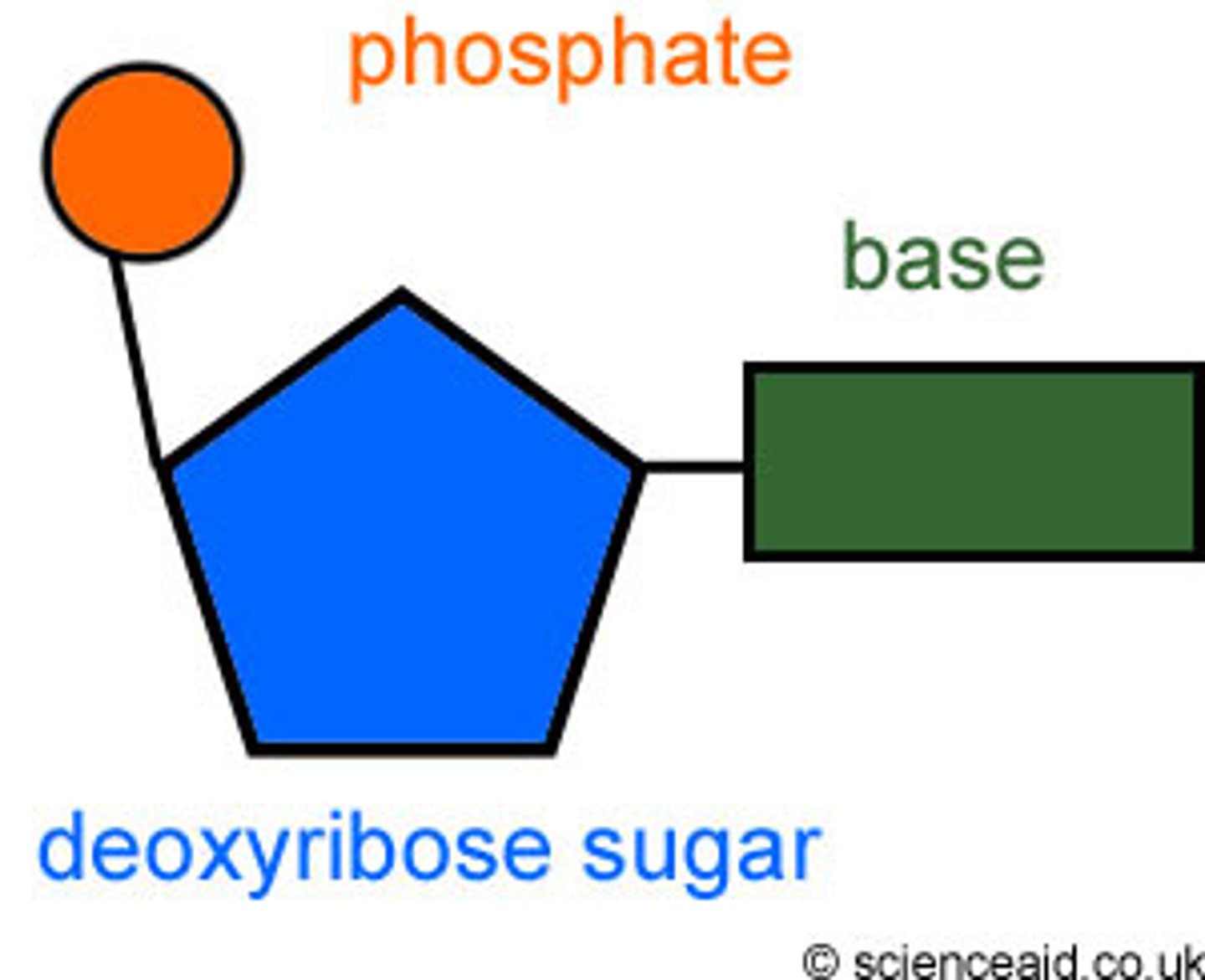
nucleotide
Monomer of nucleic acids made up of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. there are 4 types in DNA
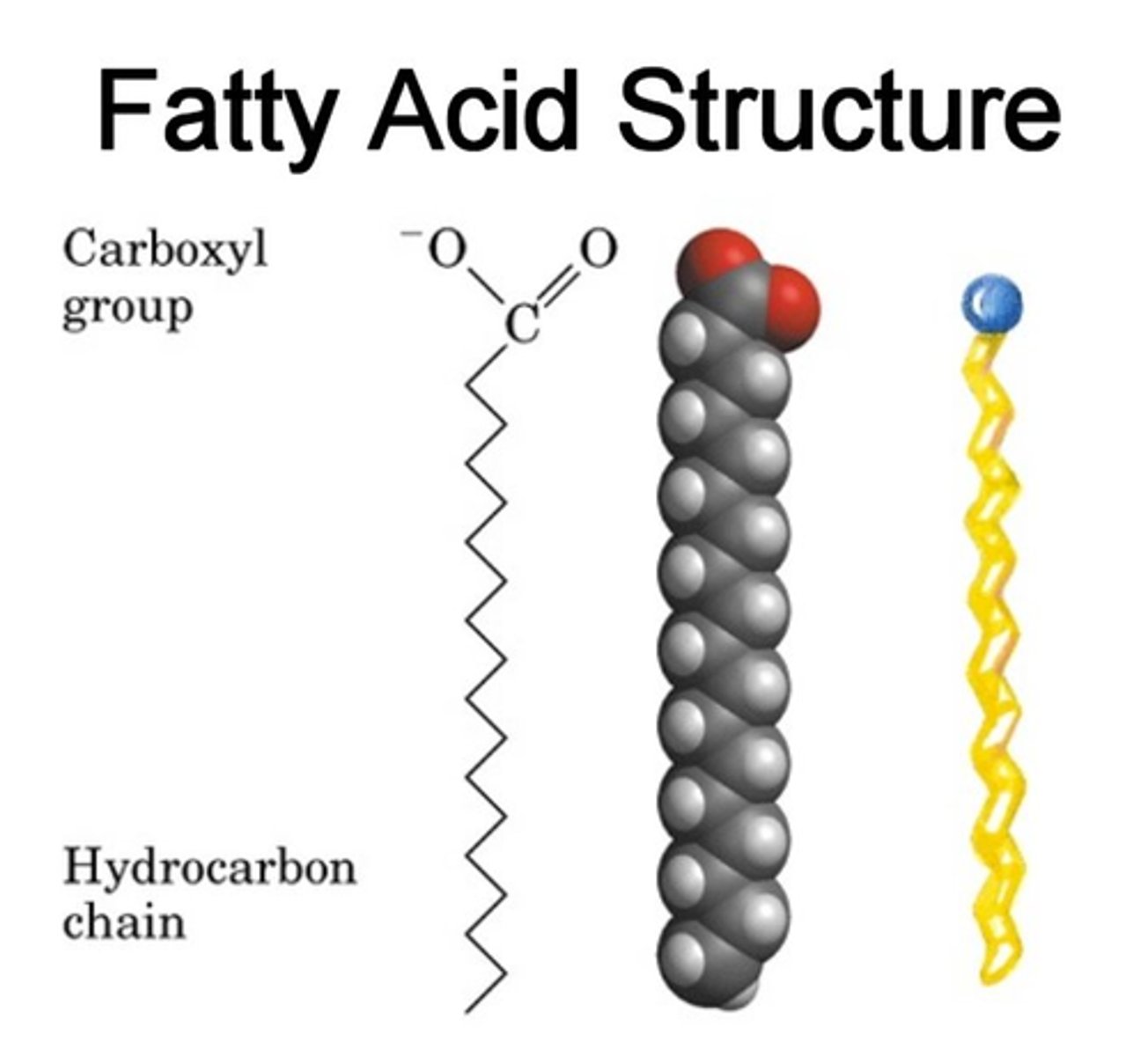
fatty acid
These are hydrophobic and make up the "tails" in the membrane
macromolecule
A very large molecule (as of a protein, nucleic acid, or carbohydrate) built up from smaller chemical structures
enzyme
A protein that makes a reaction happen QUICKER; decreases activation energy of a reaction.
polysaccharide
a carbohydrate that is composed of many monosaccharide units joined together
monosaccharide
A simple sugar that is the basic subunit of a carbohydrate
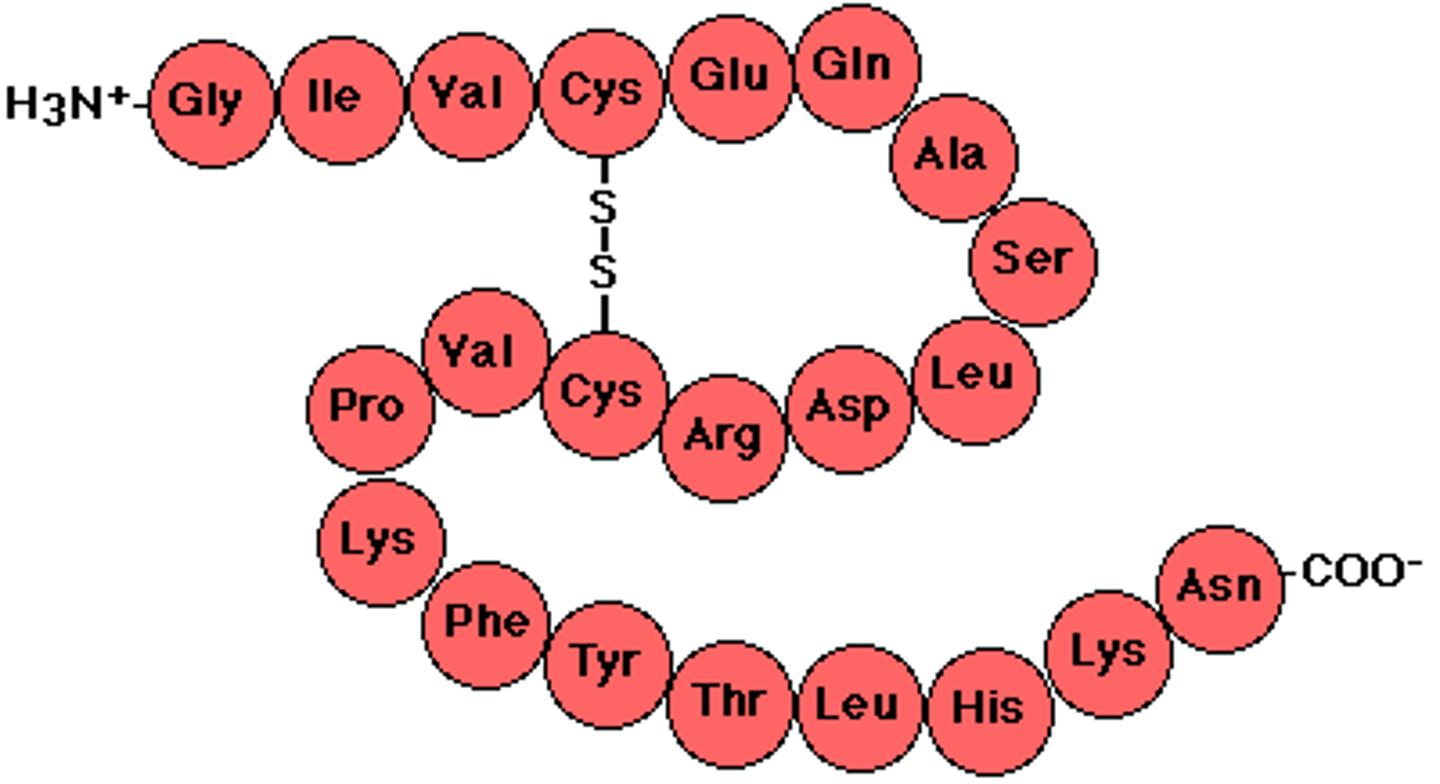
polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. polymer of proteins
Monomer
A simple building block that can join together to form polymers
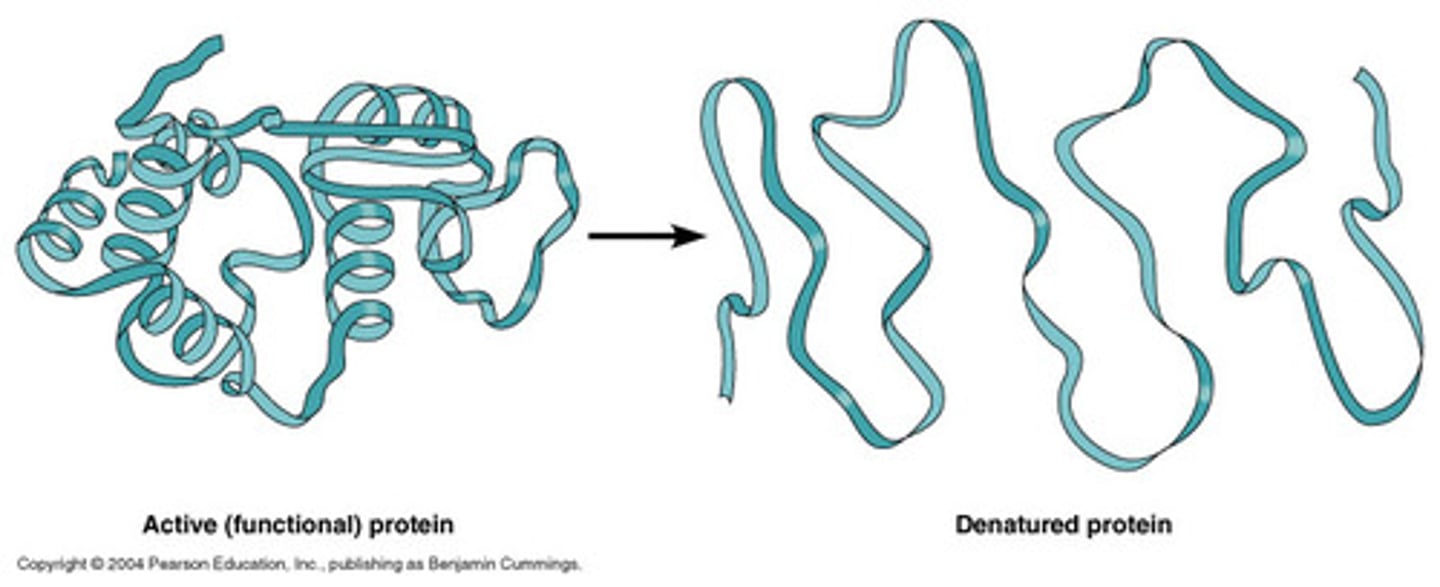
Denature
A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature, salt, or pH .
function of lipids
make up cell membrane and long term energy storage
function of carbs
short term energy storage; structure
function of proteins
essential for the growth, development, and repair of all body tissues. THEY DO EVERYTHING!! enzymes
function of nucliec acids
store genetic information. holds the code for making protiens
pH
hydrogen ion concentration. Range from 0-14. Measures acidity . 0-6 acidic, 8-14 basic
surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid. in water it is really hard to break the surface! due to hydrogen bonding

High specific heat capacity
Water requires a lot of energy to change temperature. Helps maintain homeostasis and a constant temp of water. Due to excessive H-bonds between water molecules.
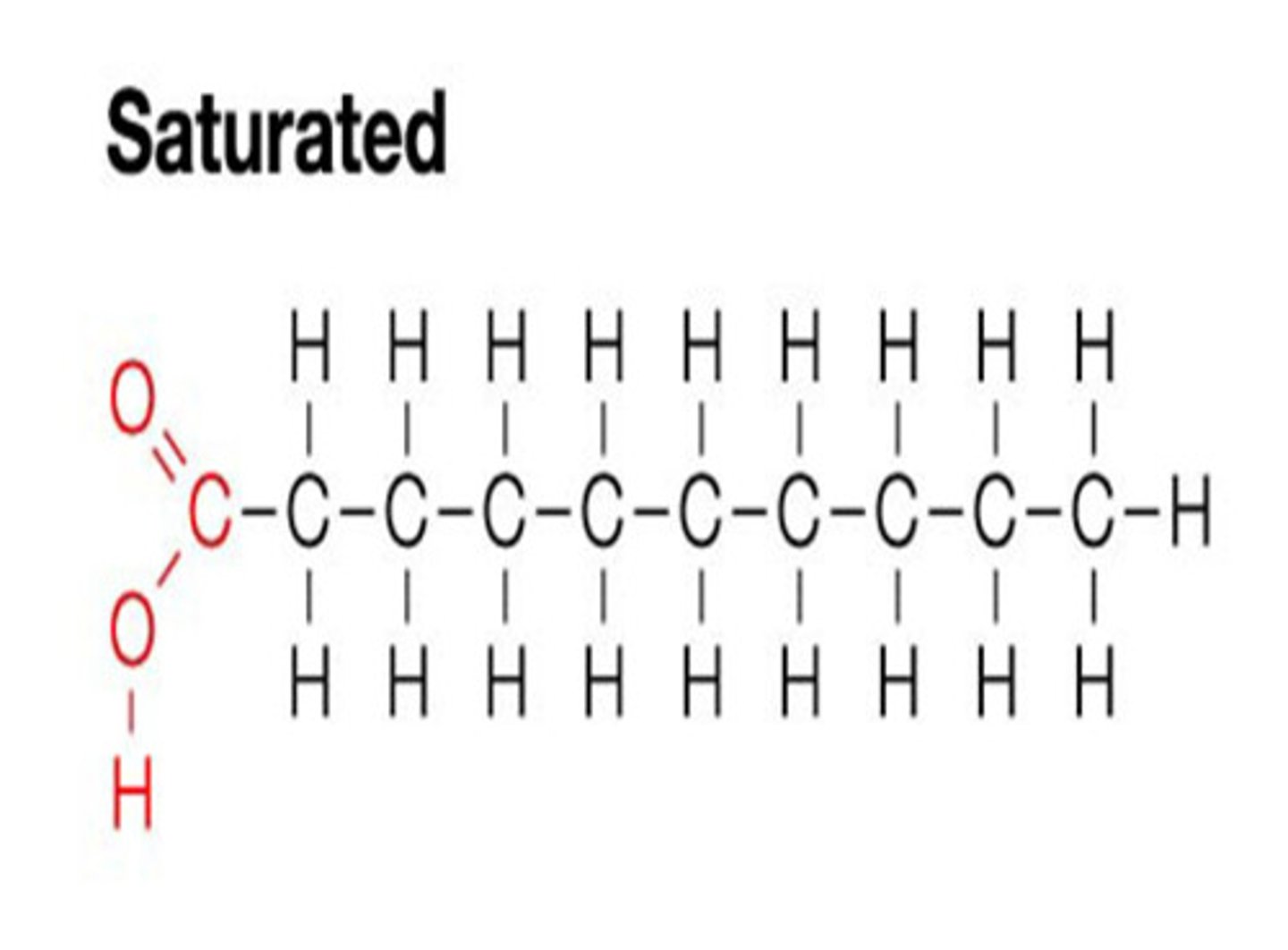
saturated fats
single bonds between carbons in a lipid molecule. packs closely together, solid at room temp
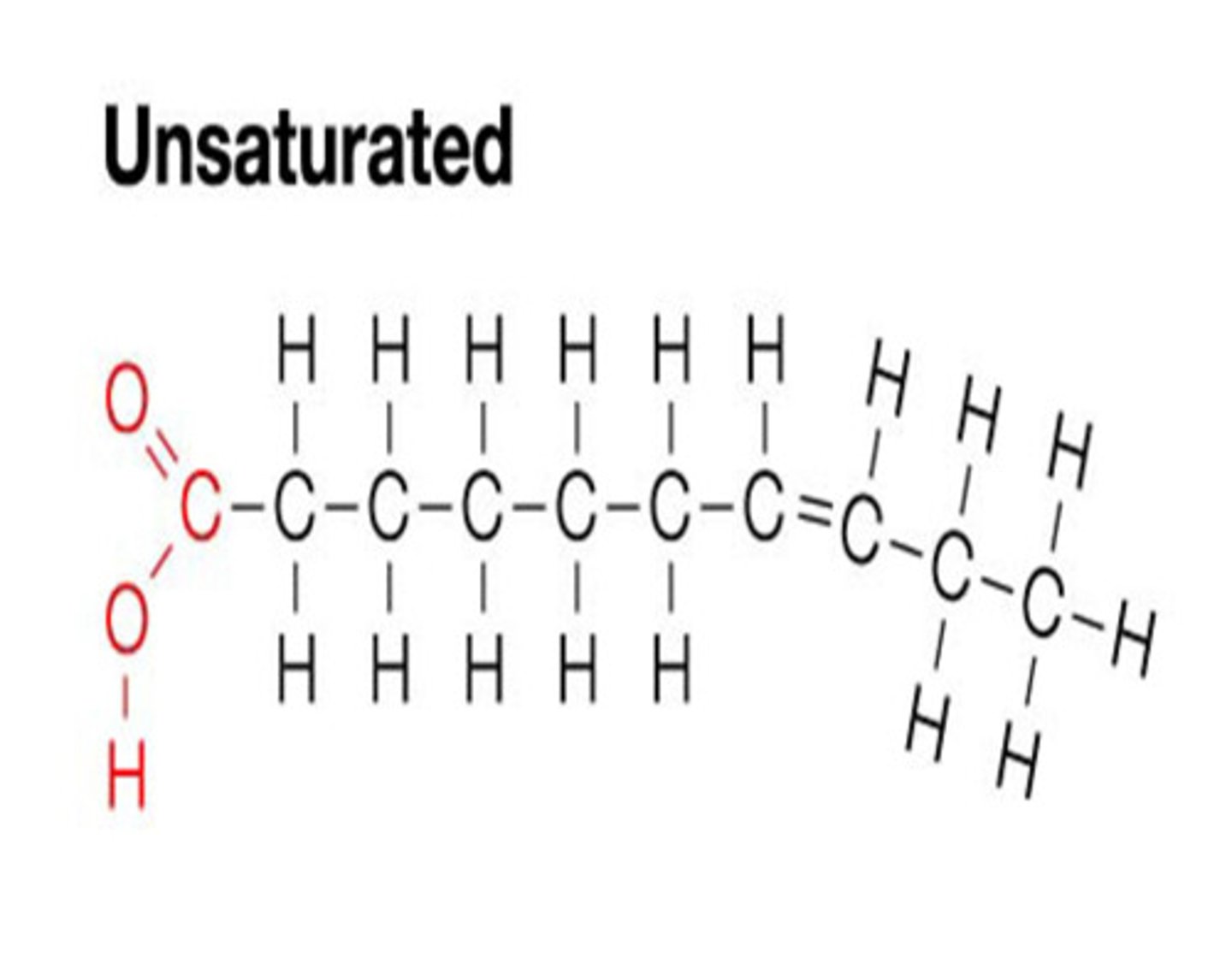
unsaturated fats
double bonds between carbon in a lipid molecule. DOES NOT pack closely together, liquid at room temp
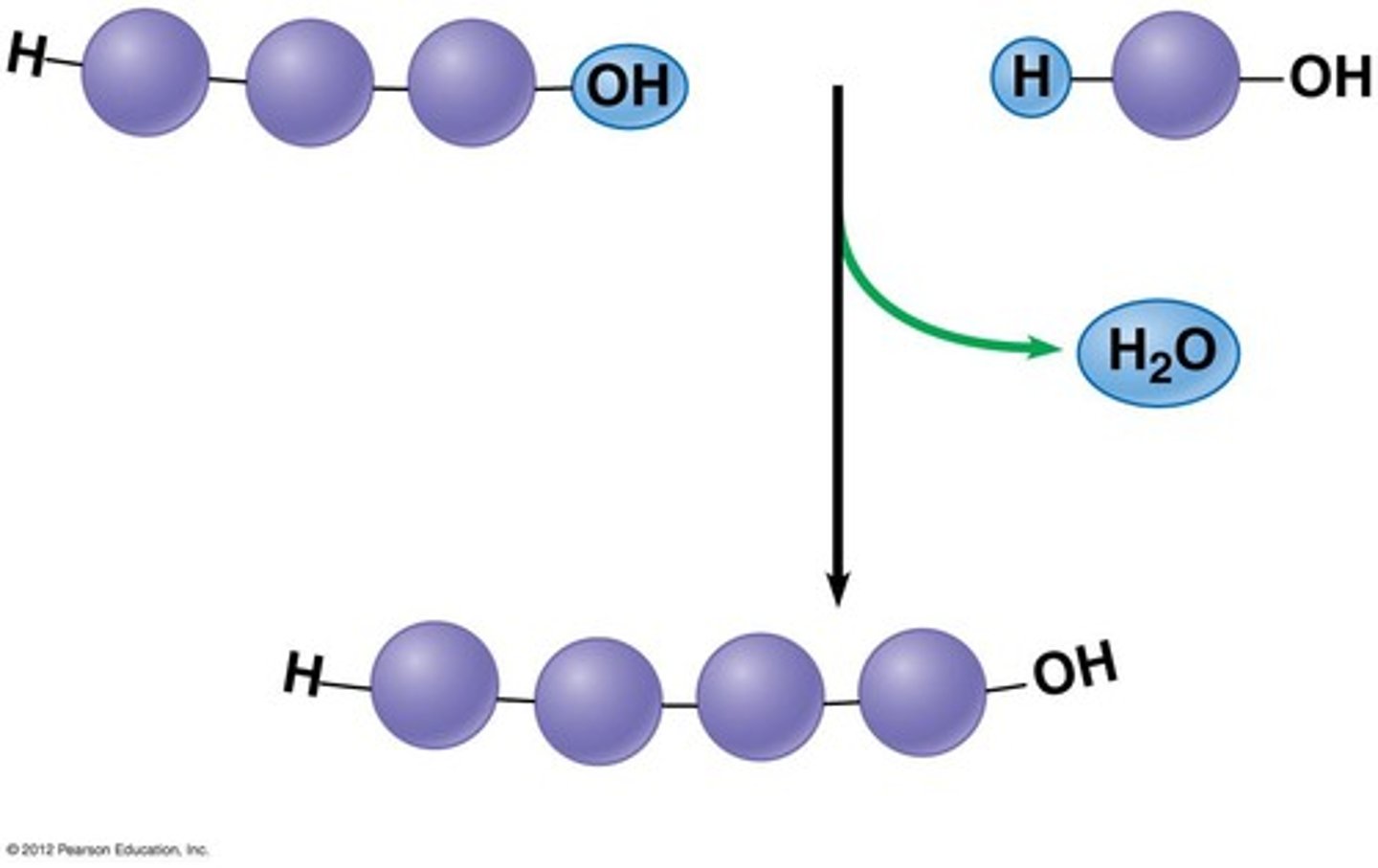
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
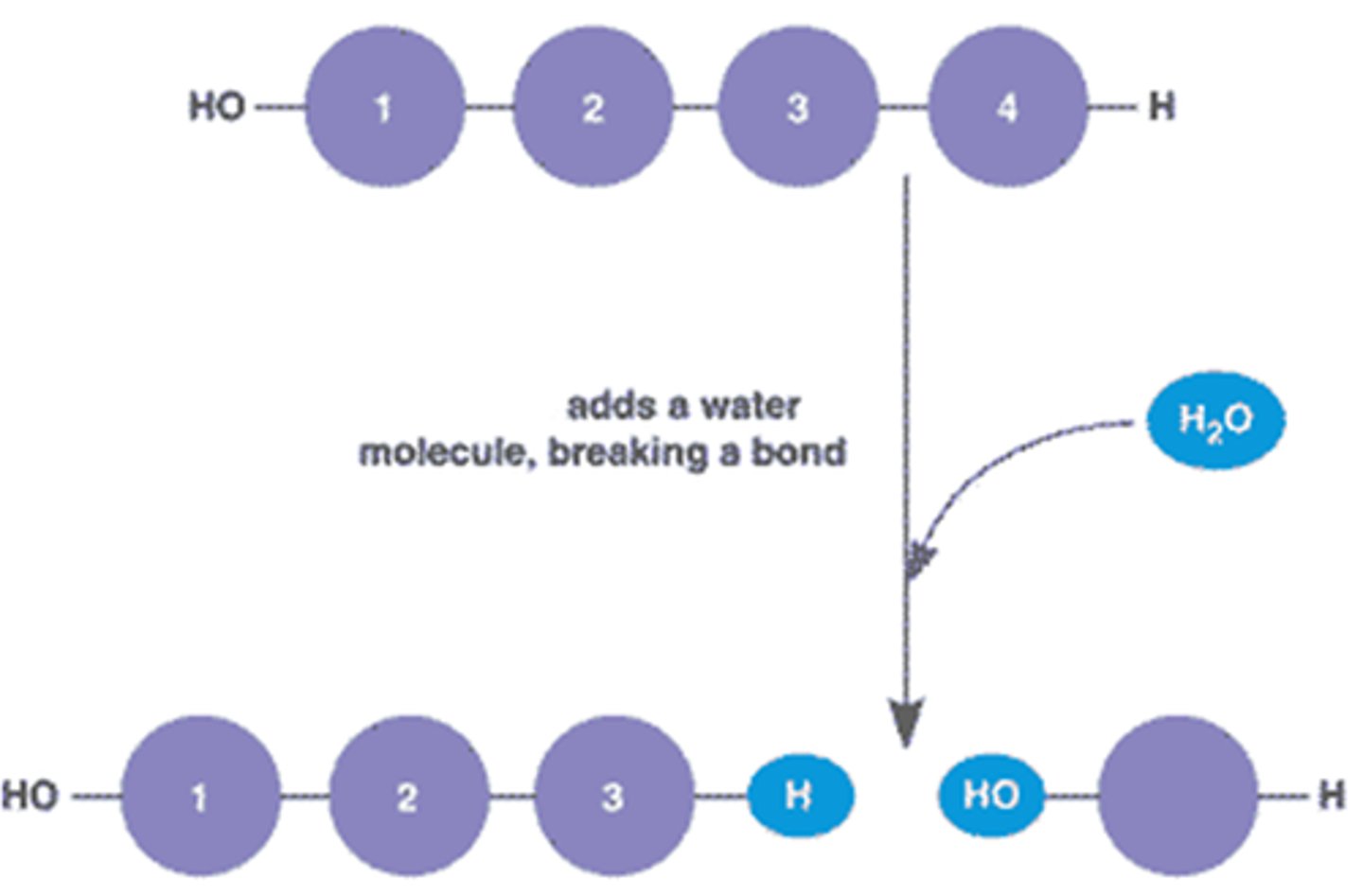
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
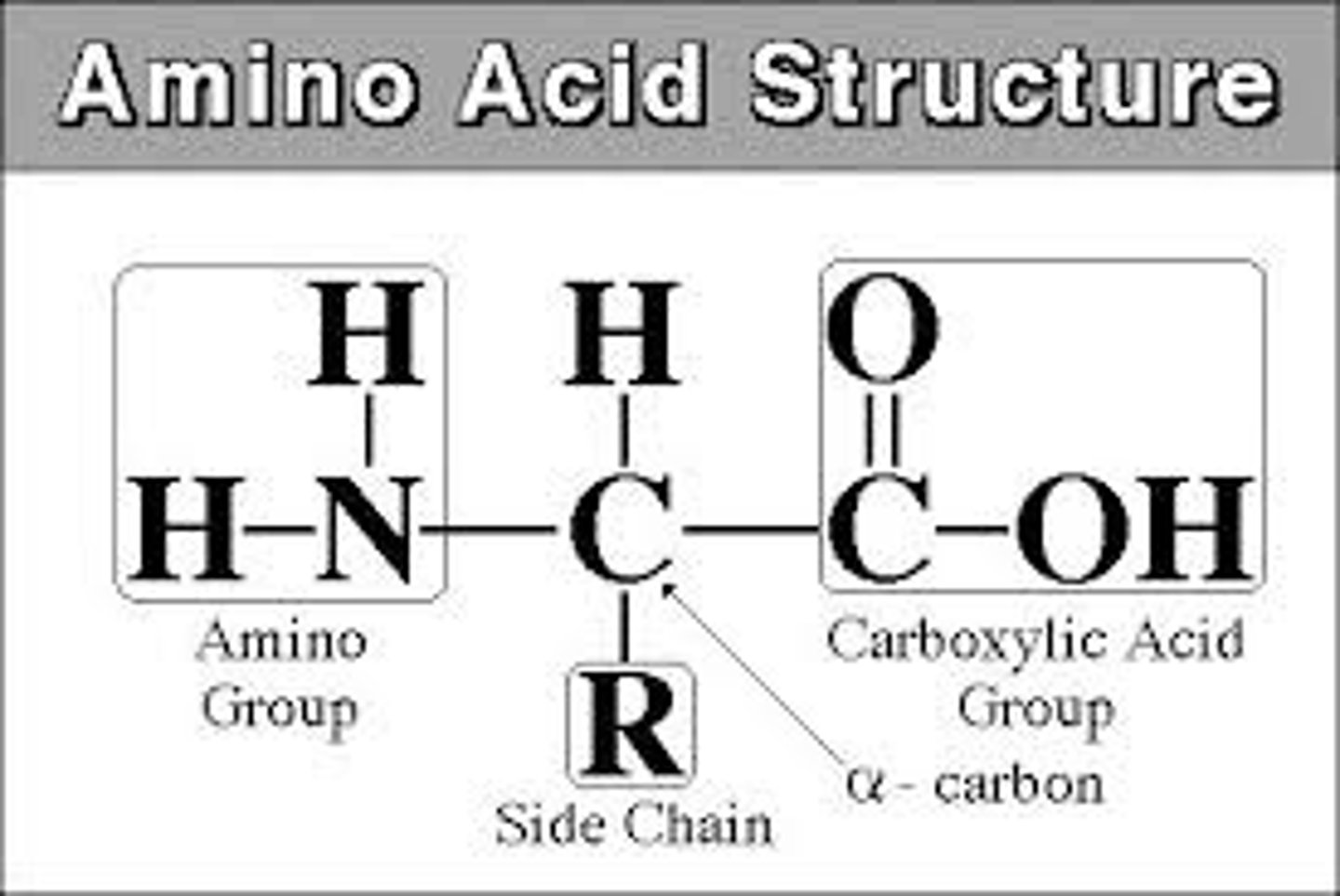
R group (side chain)
part of amino acid that determines the molecule's physical and chemical properties; determines folding
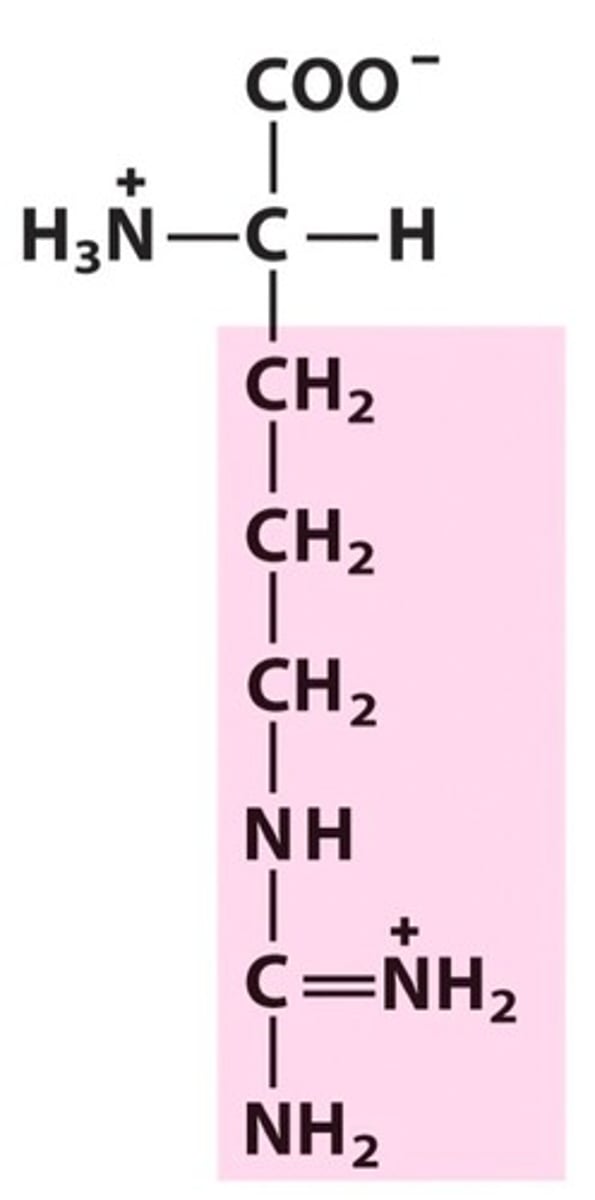
parts of an amino acid
hydrogen atom, a carboxyl group (−COOH), an amino group (−NH2), and a R-group.
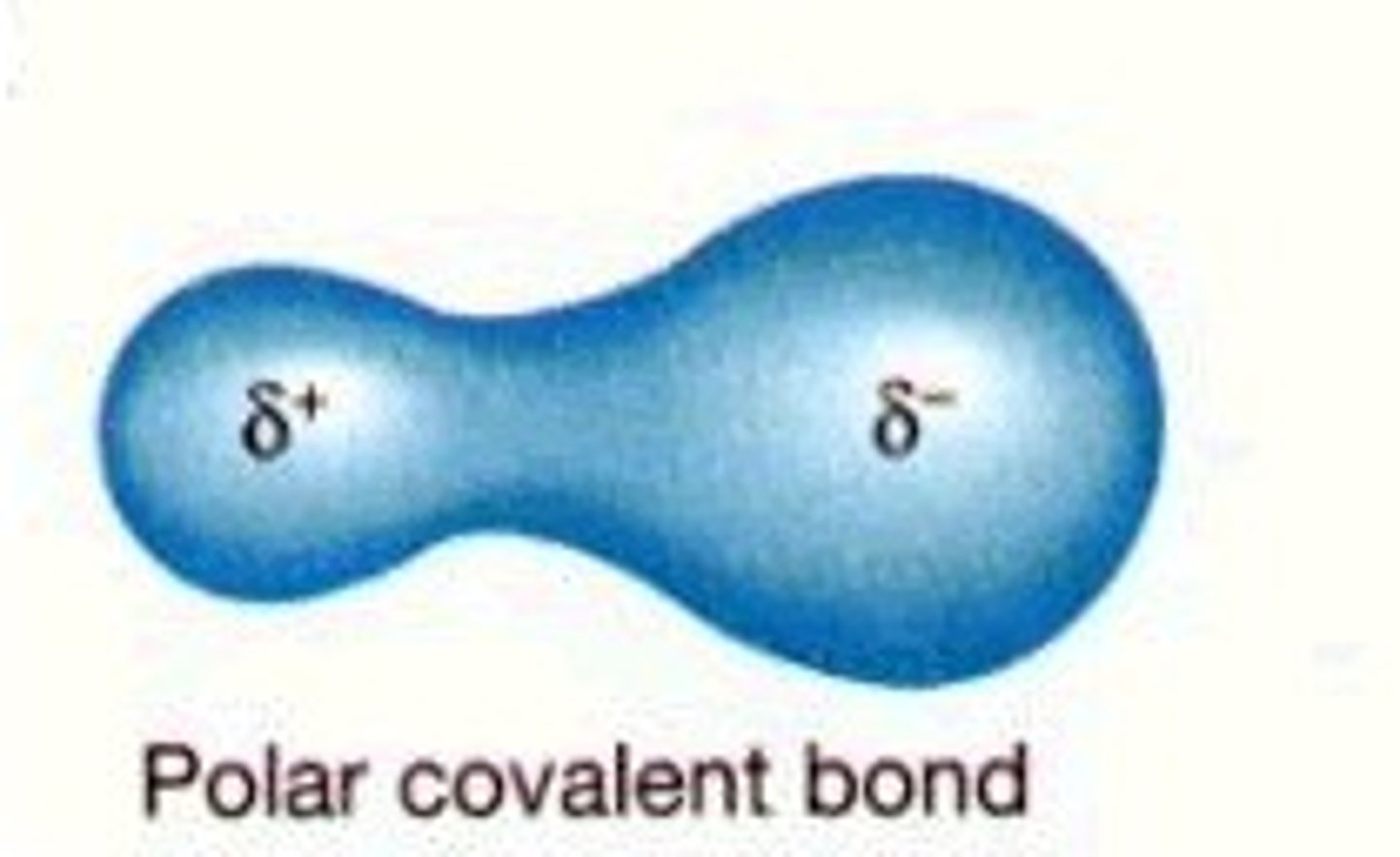
polar
Molecule with partial charges. Mixes with water.
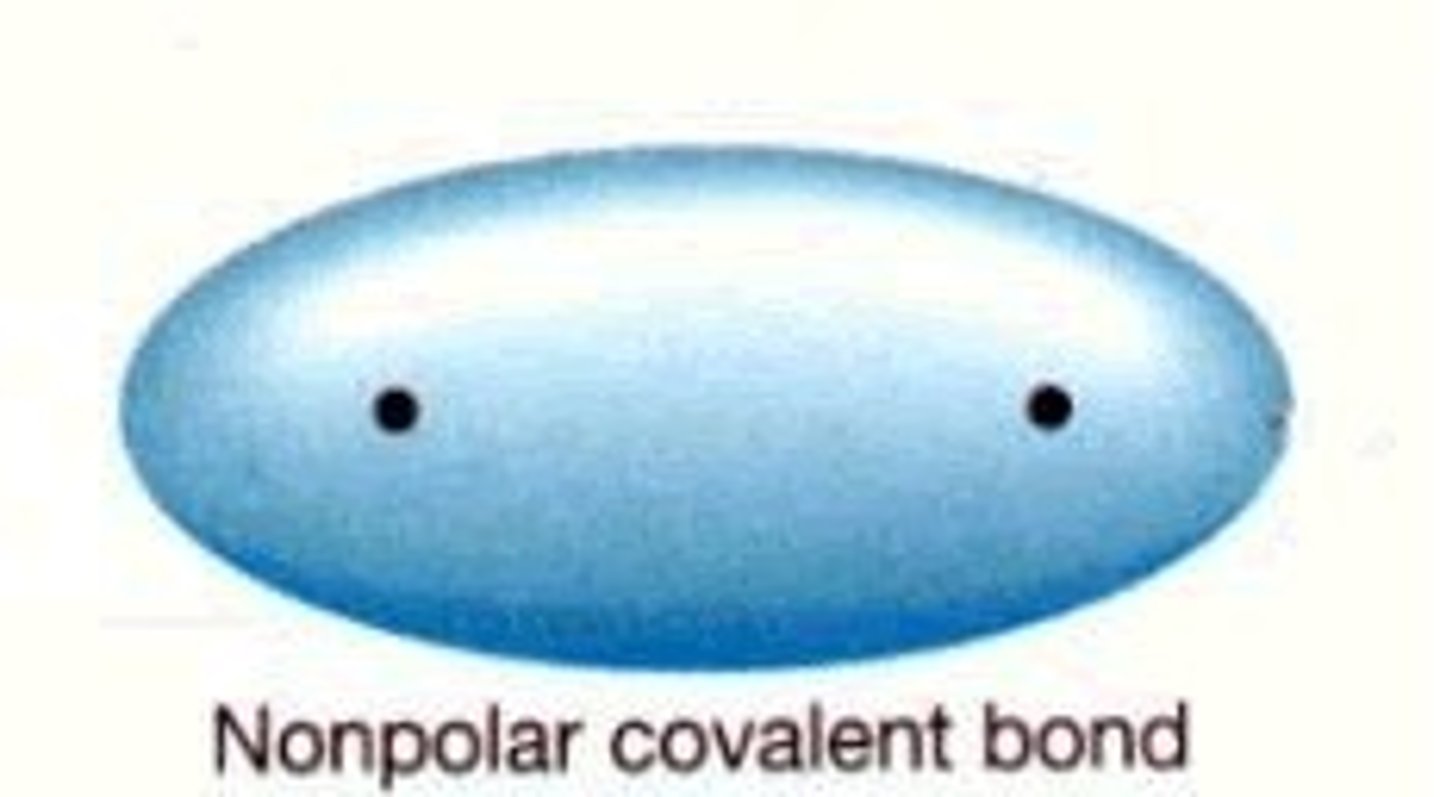
nonpolar
No partial charges. Do not mix with water.
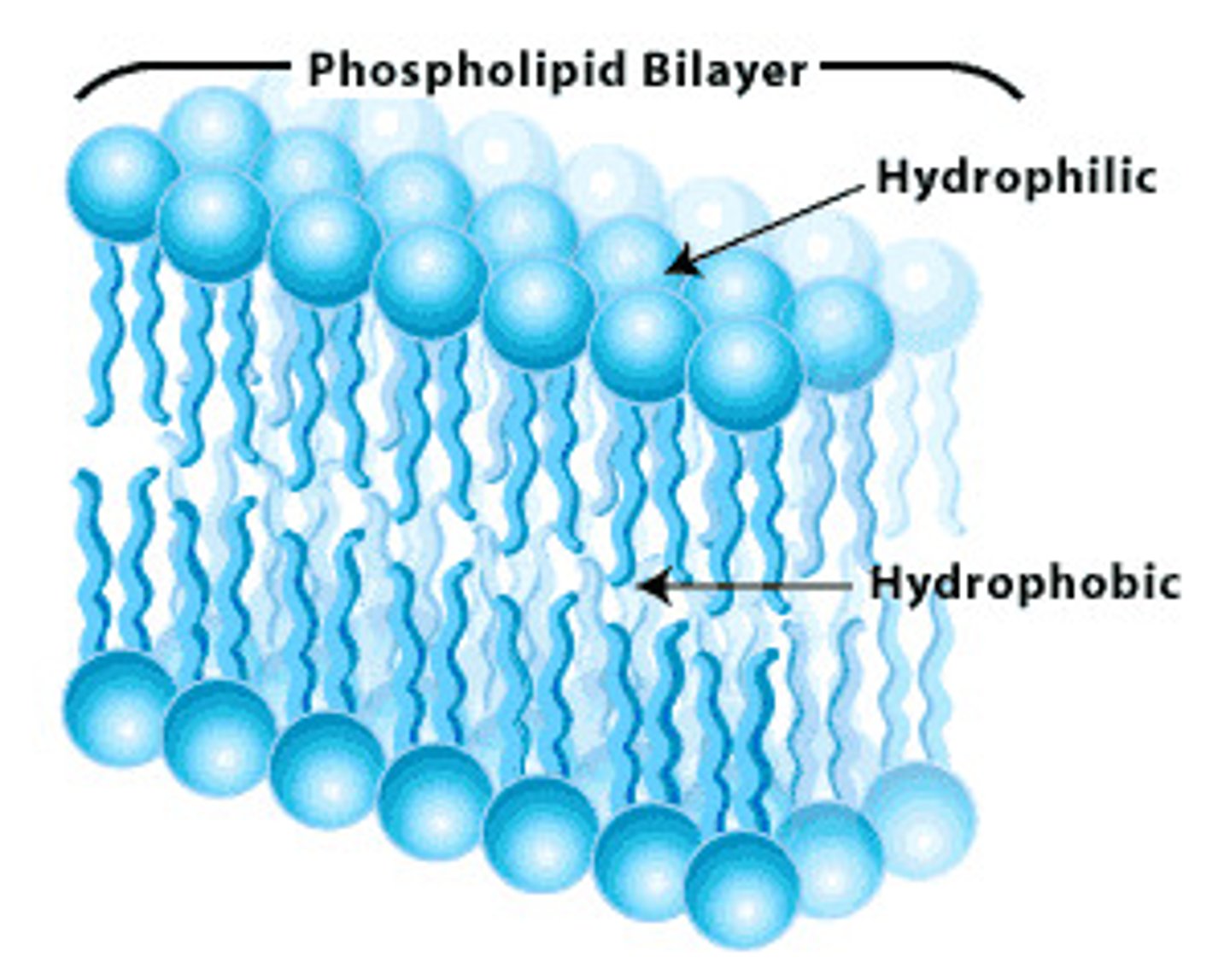
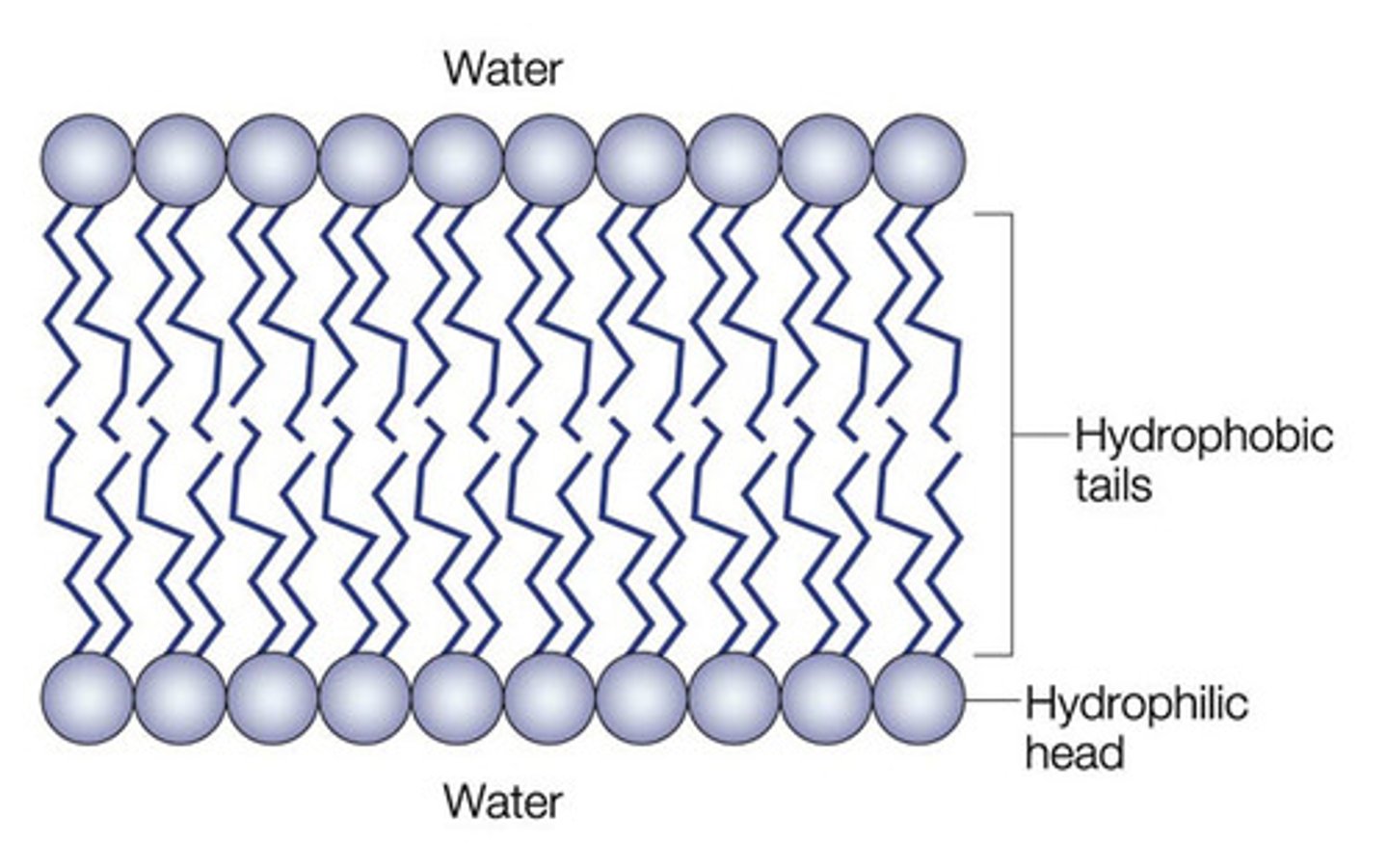
phospholipid bilayer
Plasma membrane layers composed of phospholipid molecules arranged with polar heads facing the outside and nonpolar tails facing the inside.
primary structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain.
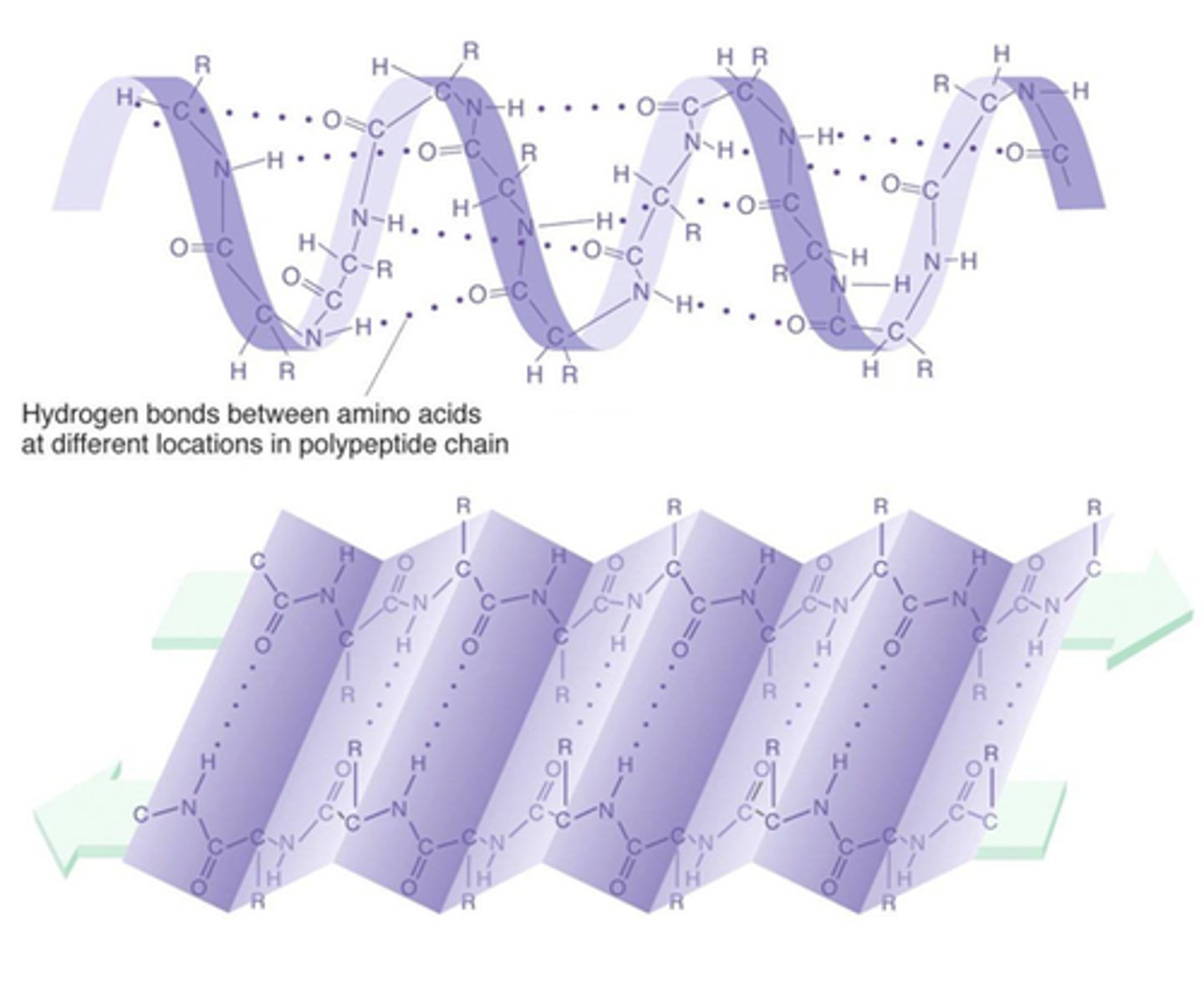
secondary structure
The second level of protein structure; the regular local patterns of coils (alpha helix) or folds (beta sheets) of a polypeptide chain. occurs between interactions of the polypeptide backbone.
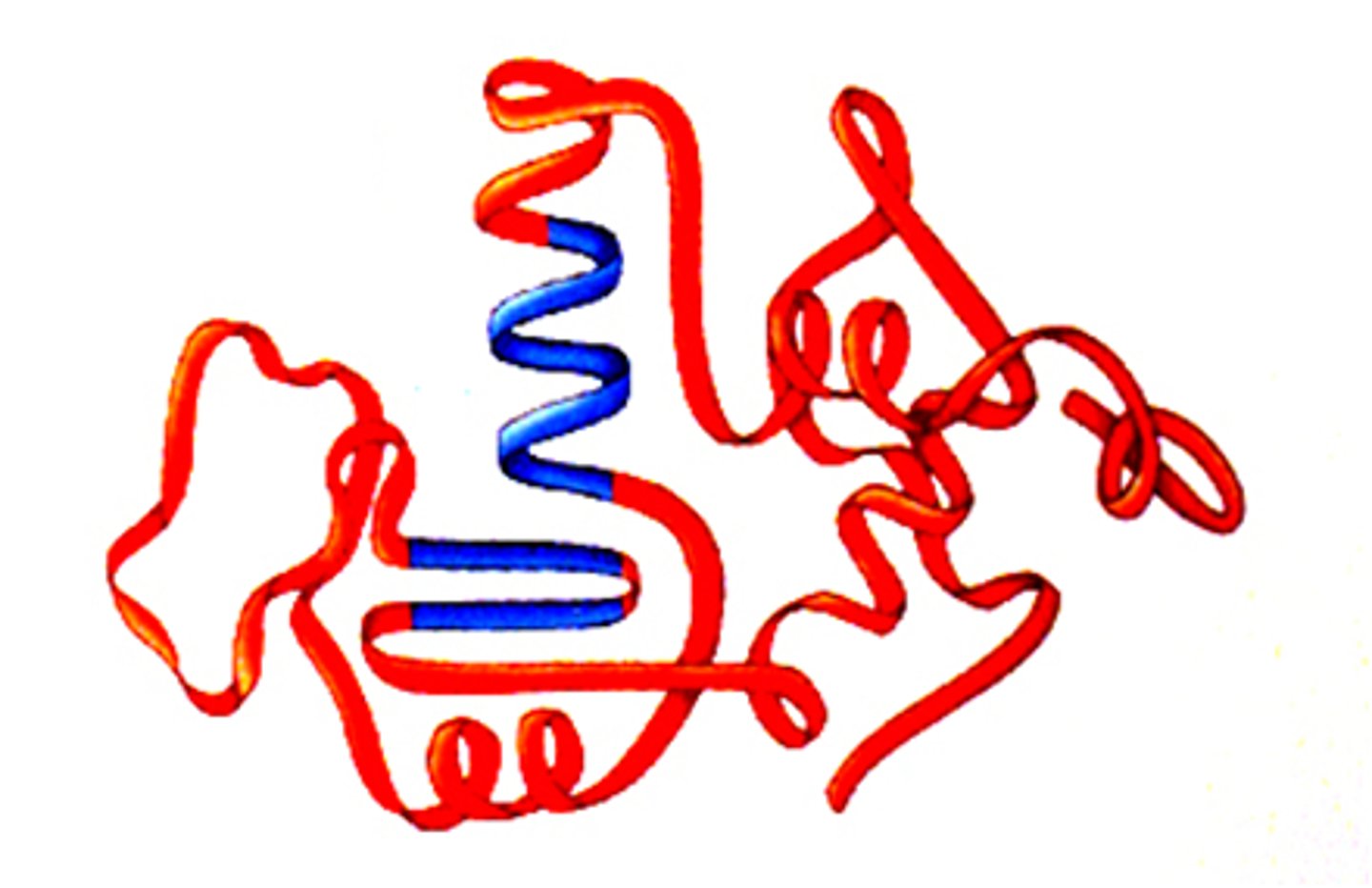
tertiary structure
is the result of folding due to interactions among R groups along the polypeptide chain. includes ionic interactions, disulfide bridges, hydrophobic/philic interactions.
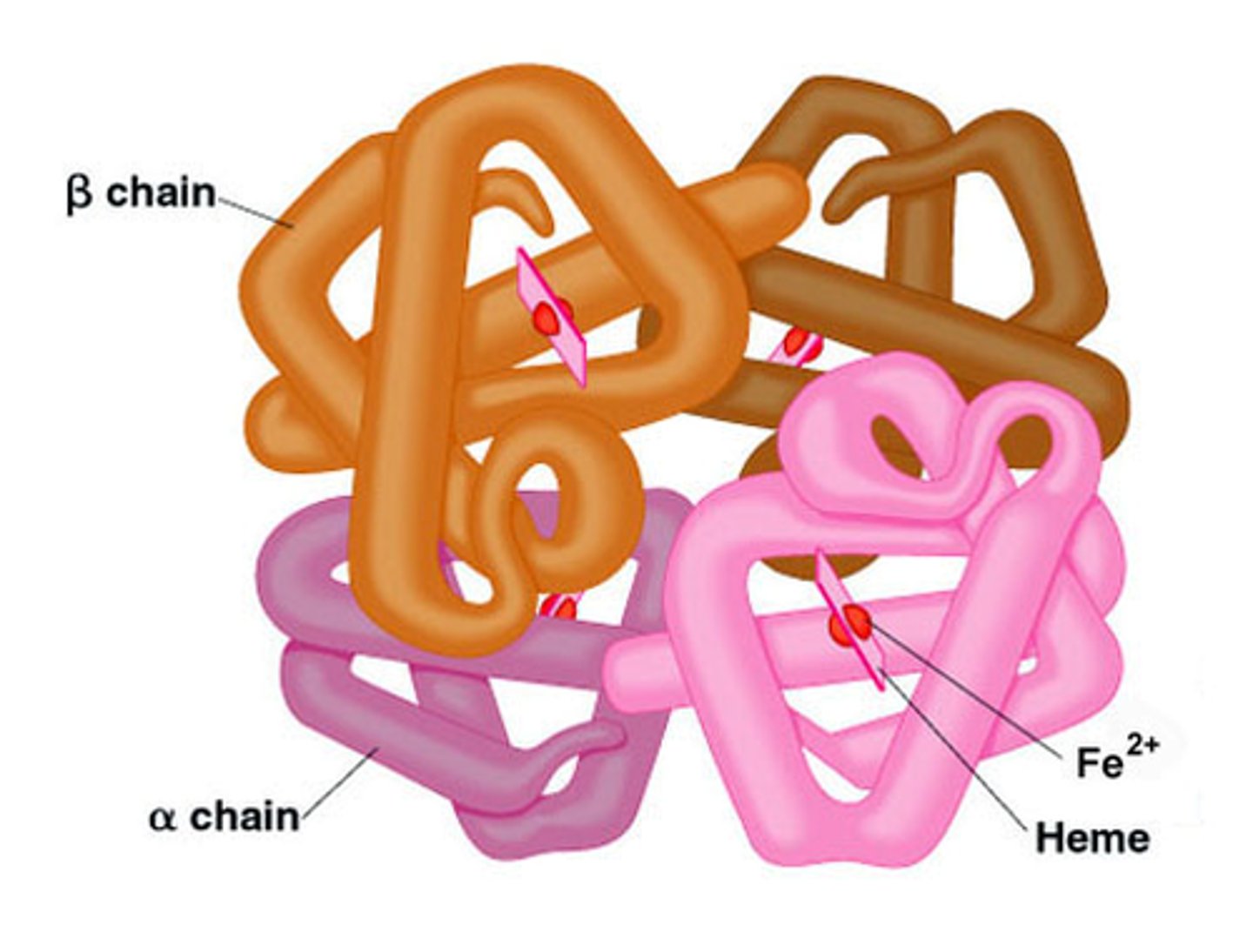
Quaternary Structure
the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
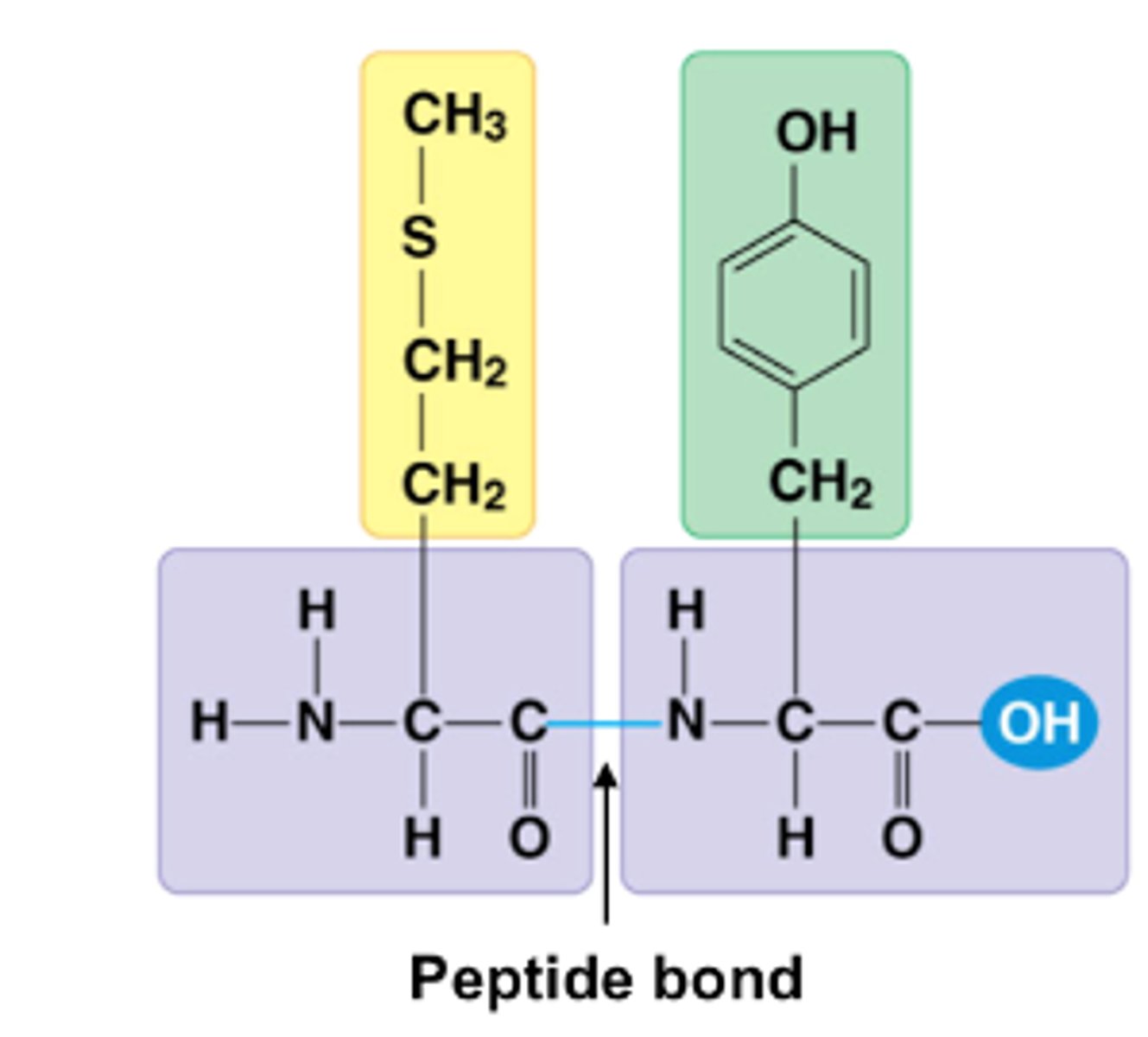
peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
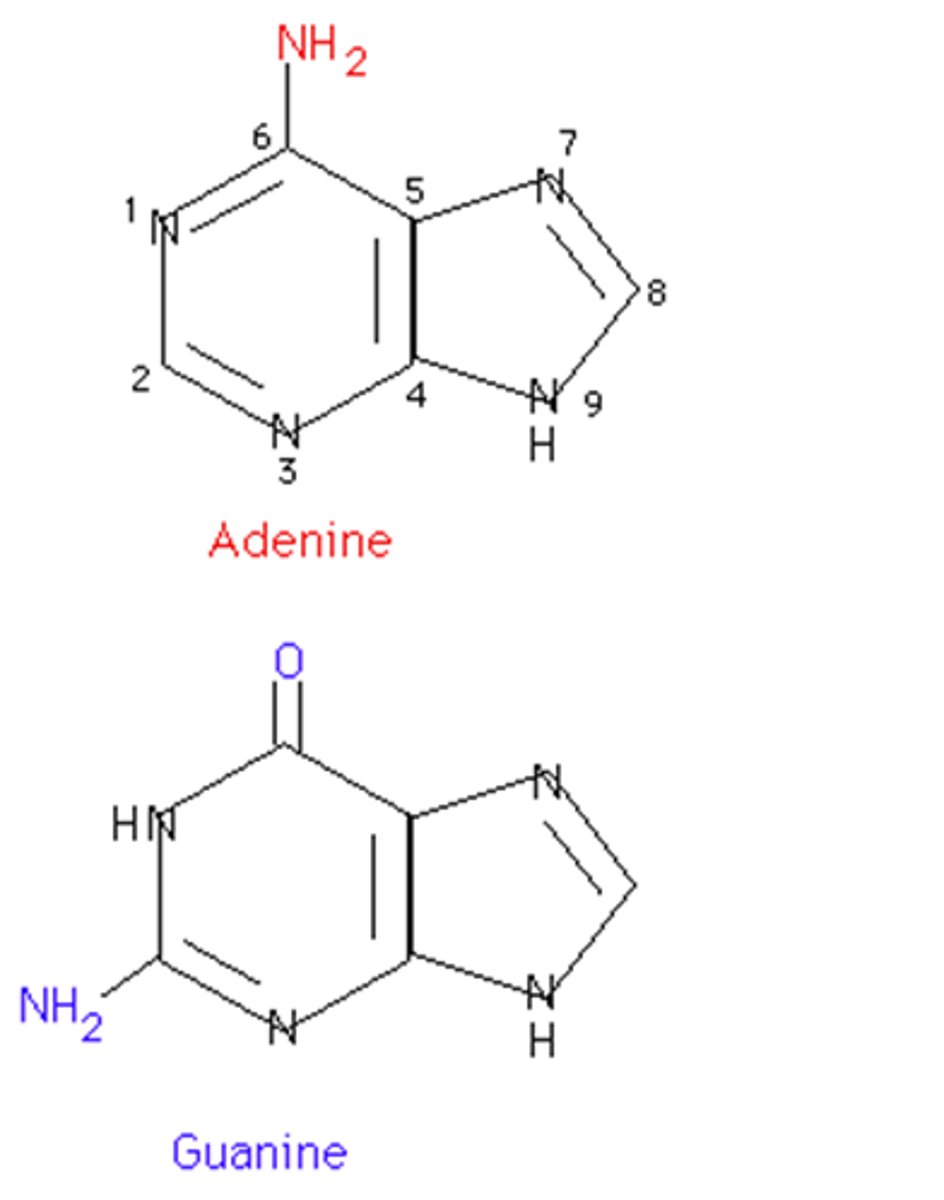
Purines
Bases with a double-ring structure.
Adenine and Guanine
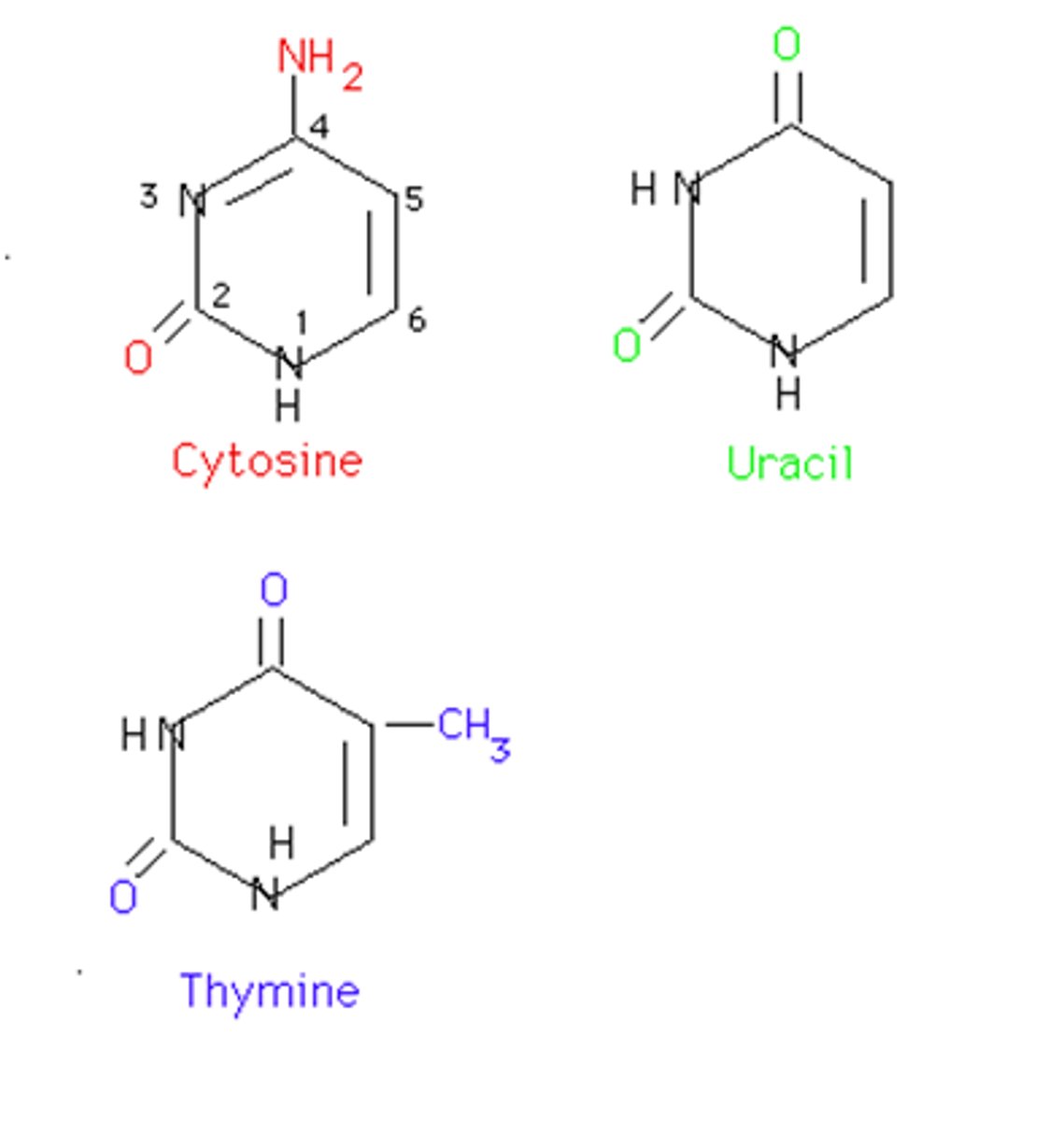
Pyrimidines
Bases with a single ring structure— cytosine, thymine, uracil
complementary base pairing rules
A always pairs with T
G always pairs with C
number of bonds between A & T
2 hydrogen bonds
number of bonds between G & C
3 hydrogen bonds
Starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose.
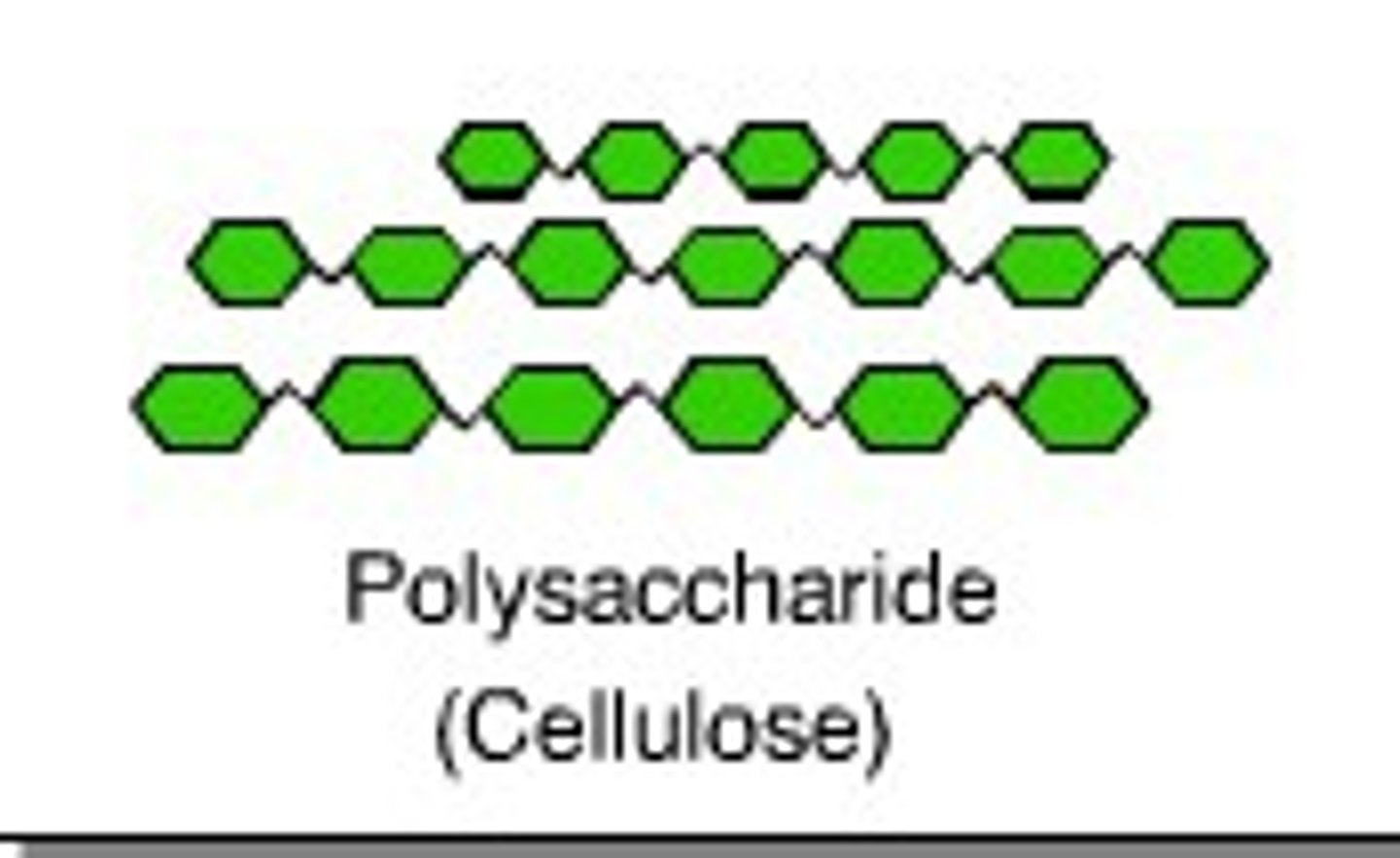
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms
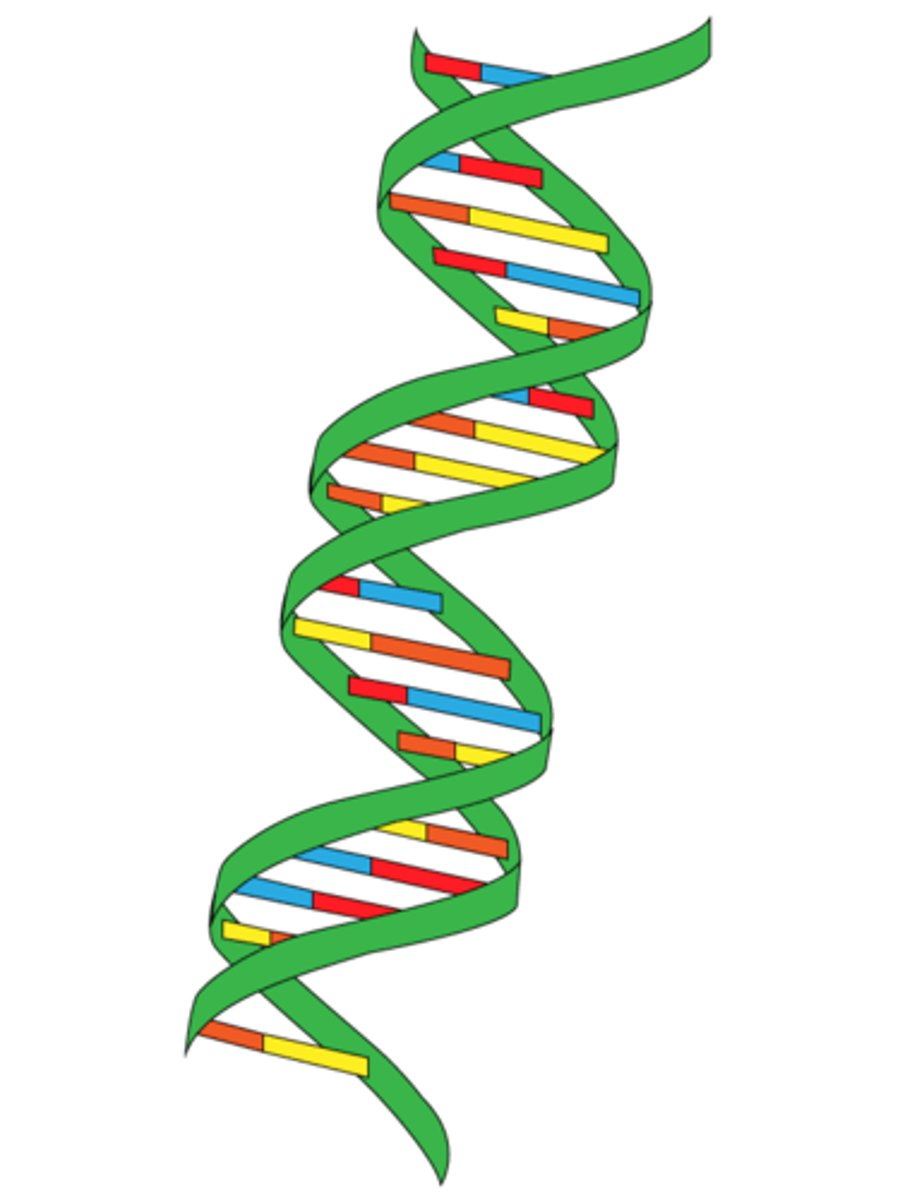
double helix
The form of DNA, referring to its two adjacent strands wound into a spiral shape.
DNA backbone
Made of deoxyribose SUGAR and Phosphate. held together by covalent bonds