SEHS UNIT 3 ENERGY SYSTEMS - 3.1 NUTRITION
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
List the macronutrients
Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids (fats) and water
List the micronutrients
Vitamins, minerals
What do macronutrients do?
Provide the energy necessary to maintain bodily functions during rest, and diverse physical activity.
What do micronutrients do?
Facilitate energy transfer and tissue synthesis.
Functions of carbohydrates
Provide fuel for the body.
Acts as an energy storage.
Breaks down fatty acids and prevents ketosis (elevated level of ketone in the blood)
Sources of carbohydrates
Pasta, cereals, quinoa
Functions of proteins
Structure and transport.
Repair and growth of muscles and tissues.
Fuel for the body
Sources of proteins
Meat
Fish
Eggs
Dairy
Nuts
Pulses
Functions of lipids (fats)
Low intensity exercise energy source.
Backup energy in carbohydrates are low.
Protects vital organs (heart, lungs, liver etc.)
Thermal insulation (cold climates)
Sources of lipids (fats)
Meat
Avocados
Dairy
Oils
Eggs
Functions of water
Prevents dehydration
Allows biochemical reactions to occur
Transport
Thermoregulation
Excretion
Lubrication in joints
Sources of water
Beverages (drinks)
Fruit (watermelons)
Vegetables (cucumber)
Functions of vitamins
Energy release from macronutrients
Promotes healthy bones and blood
Increases immune function
Sources of vitamins
Fruits
Vegetables
Fatty fish (salmon)
Functions of minerals
Aids absorption of vitamins
Strengths bones and teeth
Promotes blood oxygen transport
Aids muscle function
Sources of minerals
Fruit
Vegetables (kale)
Fish
Functions of fibre
Helps avoid constipation
Bulk up consumed food
Sources of fibre
Beans
Nuts
Rice
Cereal
Fruit
Vegetables
Chemical composition of a glucose molecule
C = Carbon H = Hydrogen O = Oxygen
1:2:1 ratio
Diagram of basic structure of a glucose molecule
Carbon: 6
Hydrogen: 12
Oxygen: 6
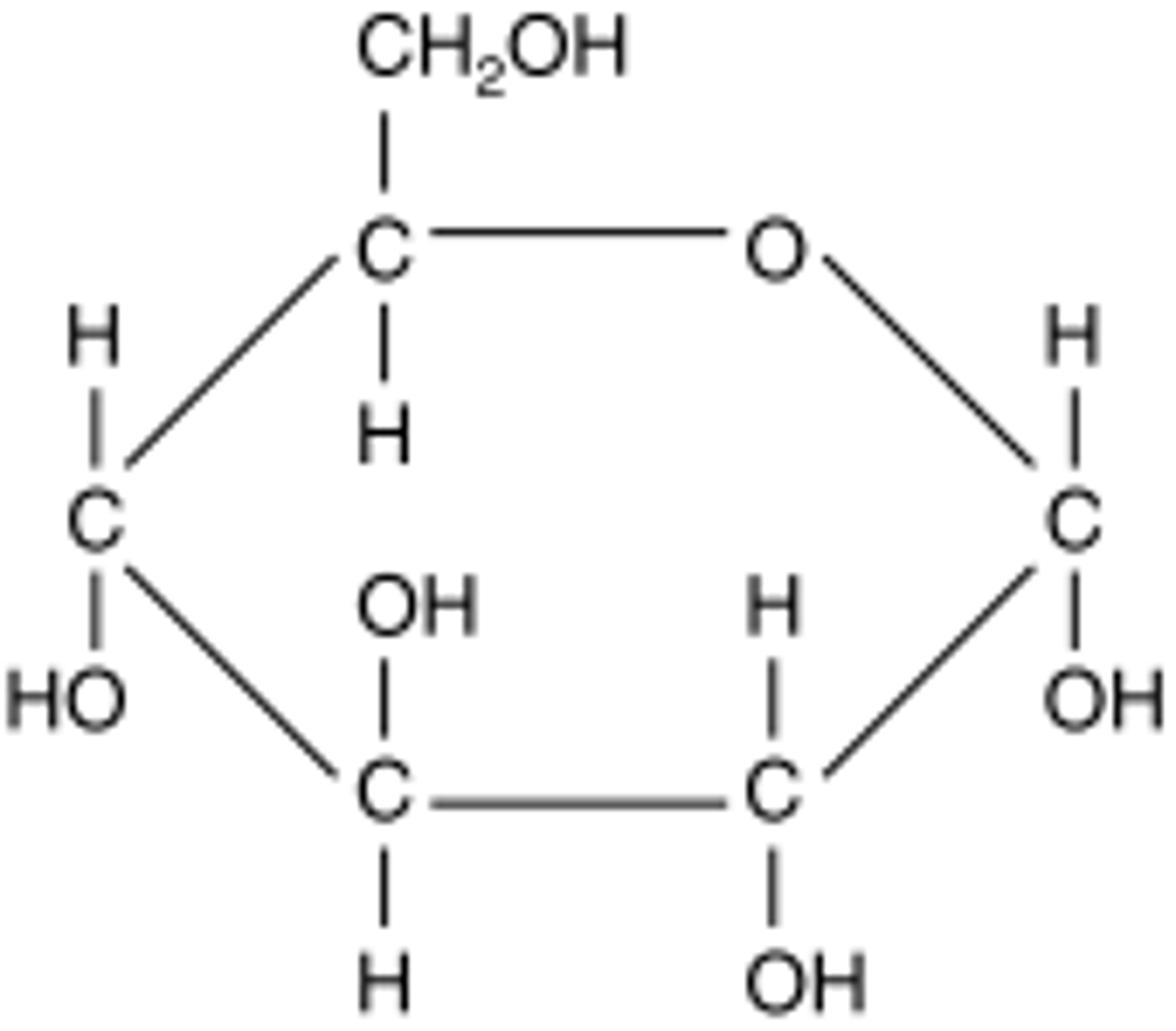
How glucose molecules can combine to form disaccharides and polysaccharides
Condensation reaction: the linking of a glucose molecule to another glucose molecule by losing a water molecule.
One oxygen molecule is left behind and so attaches on to the other glucose molecule (glycosidic bond)
Disaccharide: 2 glucose molecules are combined
Polysaccharides: more than 2 glucose molecules are combined
Composition of a triacylglycerol molecule
Glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Glycerol is an alcohol with the formula C3H8O3 - it contains three hydroxyl groups (OH)
Fatty acids are long chain hydrocarbons containing carboxyl (COOH) group at one end
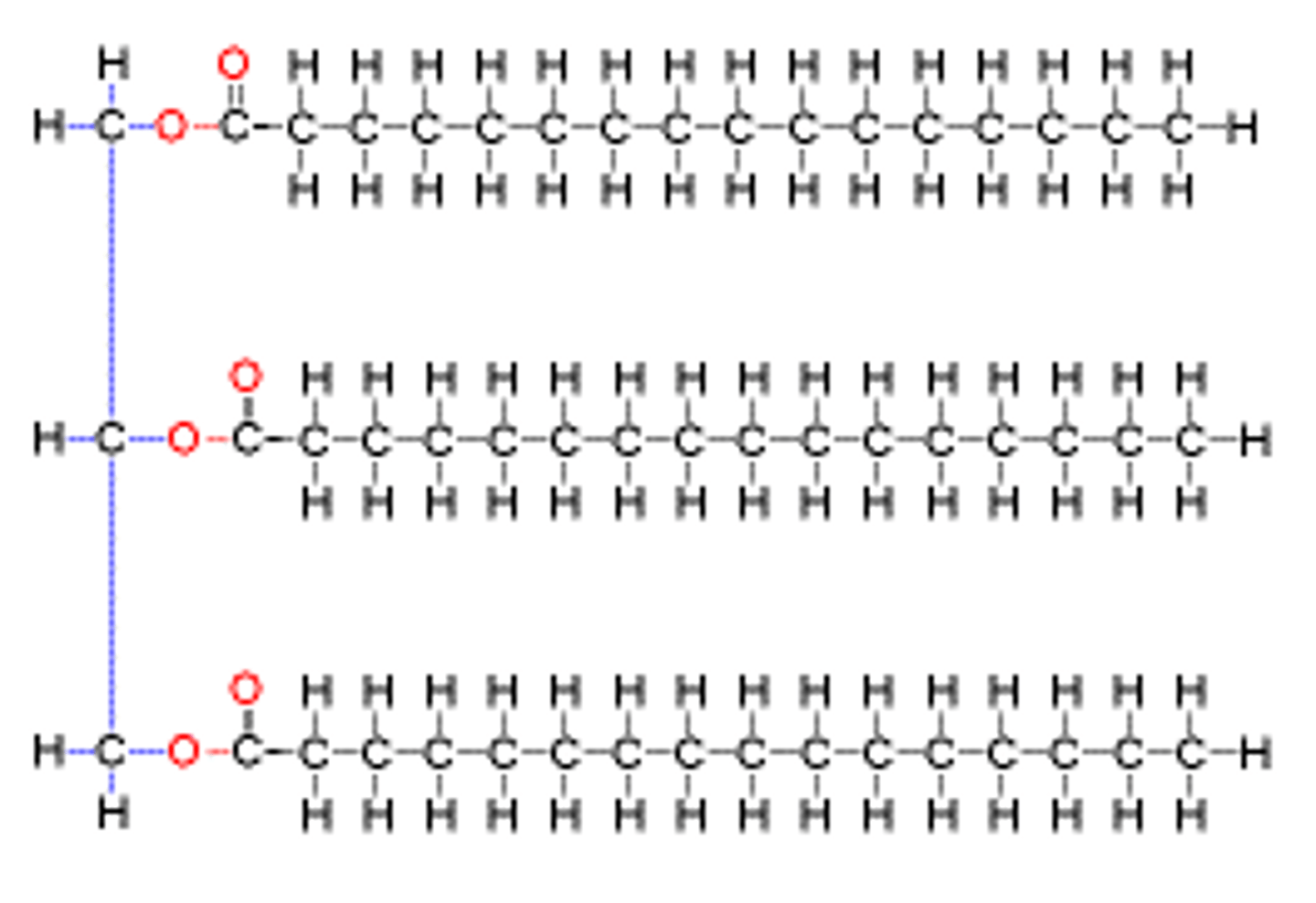
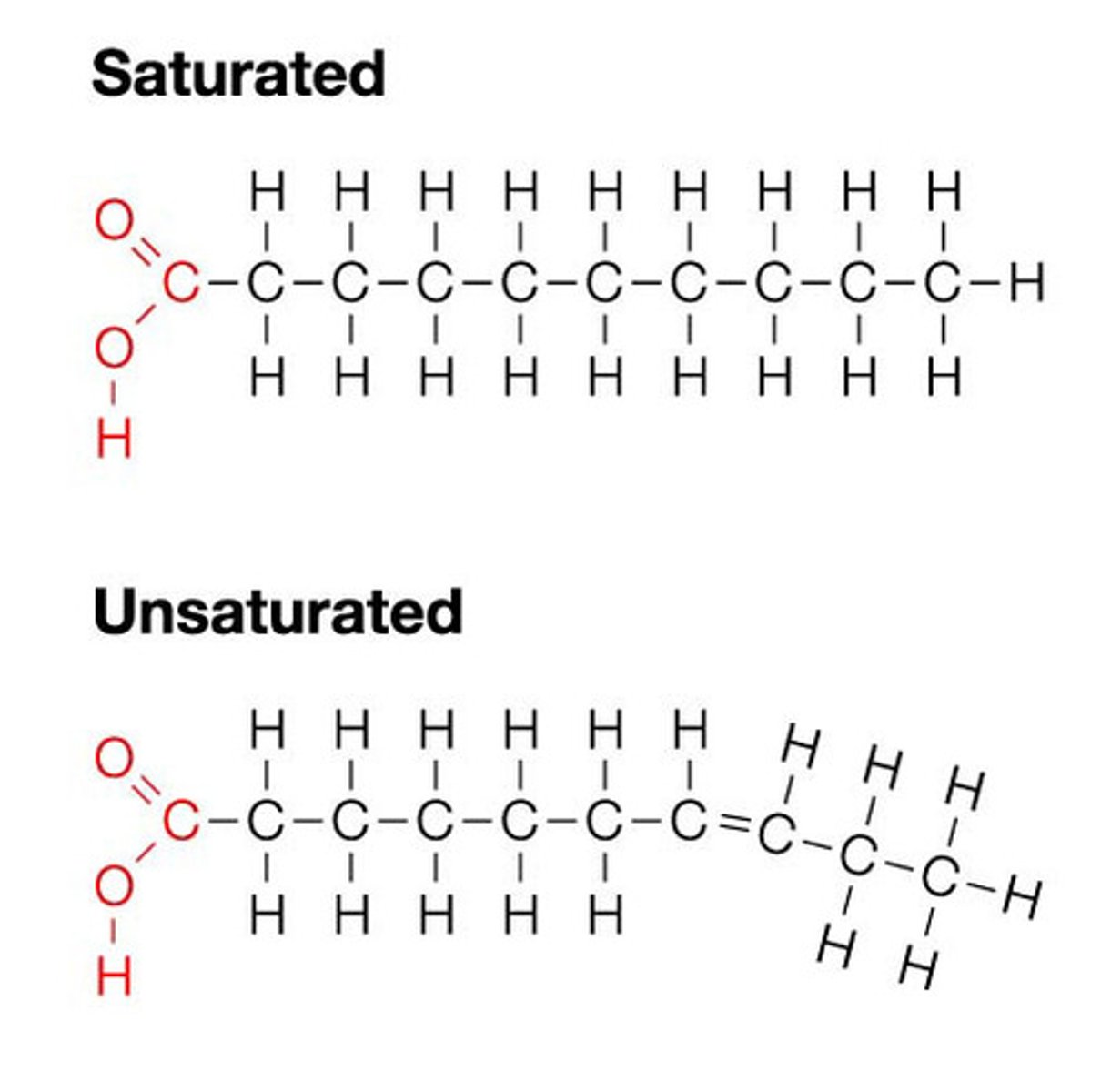
Difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated Fatty Acids:- Have no double bonds between individual carbon atoms of the fatty acid chain
Unsaturated Fatty Acids:- Contain one or more double bonds between carbon atoms within the fatty acid chain
Examples of saturated fats
Meat
Poultry
Full fat dairy
Coconut oils
Examples of unsaturated fats
Olive oil
Olives
Avocados
Canola Oil
Peanuts
Chemical composition of a protein molecule
Carbon: 1
Hydrogen: 1
Oxygen: 1
Nitrogen: 1
Difference between an essential and a non-essential amino acid
Essential amino acids cannot be made by the body. As a result, they must come from food.
Non-essential amino acids are produced by bodily systems.
Current recommendations for a healthy diet
Carbohydrates = 45-55%
Proteins = 10-35%
Lipids = 20-35%
Unsaturated fats = 20-30%
Saturated fats = <10%
Fibre = 3-5%
Salt = < 6g
Water = 3l
What is the main differences between Mediterranean, SE Asian, Western and South Asian diets
Mediterranean: Paella, pies, chorizo, olive oil
SE Asian: Sushi, rice, fish
Western: Roast chicken, pies, hamburgers
South Asian: Rice, curry, naan breads
Approximate energy content per 100g of carbohydrate, lipid and protein
Carbohydrates: 1,760 kJ per 100 g
Proteins: 1,720 kJ per 100 g
Fats: 4,000 kJ per 100 g
Recommended energy distribution of the dietary macronutrients differs between endurance athletes and non-athletes
Calorie difference:
Carbohydrates: Athletes consume significantly more
Proteins: Athletes consume considerably more
Fats: Athletes consume slightly more
Percentage difference:
Carbohydrates: Athletes consume slightly more
Proteins: Athletes consume slightly more
Fats: Athletes consume considerably less