A&P II Lab Final Study Guide Overview
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
General senses
Somatic senses such as touch, pain, and temperature.
Special senses
Senses with specialized organs or nerves devoted to them, such as vision, hearing/equilibrium, taste, and smell.
Fibrous tunic
The outer layer of the eye, consisting of the sclera and cornea.
Sclera
The white portion of the eye.
Cornea
The clear, anterior-most portion of the fibrous tunic.
Vascular tunic
The middle layer of the eye, containing structures such as the choroid and ciliary muscles.
Choroid
Prevents light from scattering within the eye.
Ciliary muscles
Control the shape of the lens and produce aqueous humor.
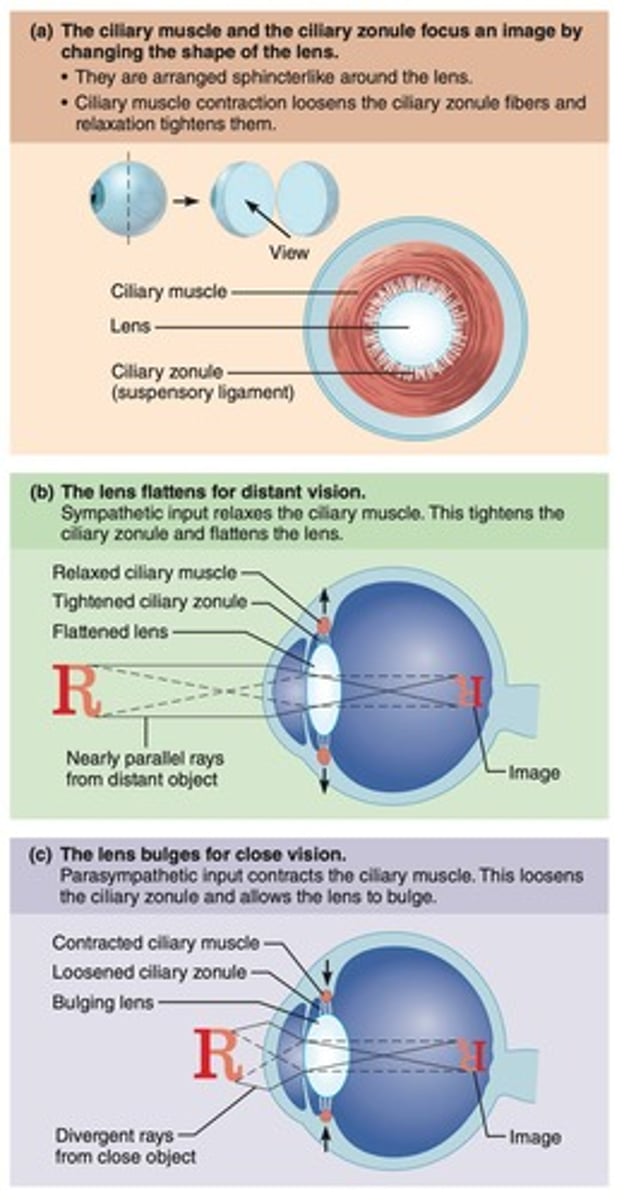
Iris
Muscle fibers around the pupil that divide the anterior cavity.
Retina
Contains photoreceptors for vision.
Rods
Photoreceptors responsible for peripheral vision and functioning in dim light.
Cones
Photoreceptors responsible for color vision and high acuity.
Optic nerve (CN II)
The nerve responsible for transmitting visual information from the retina to the brain.
External Ear
Includes the pinna/auricle and external acoustic meatus.
Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity)
Contains the tympanic membrane and auditory ossicles.
Tympanic membrane
Also known as the eardrum, it separates the external ear from the middle ear.
Auditory ossicles
Three small bones in the middle ear: malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup).
Internal Ear
Contains three bony semicircular canals oriented at right angles to one another.
Superior canal
Responsible for detecting anterior/posterior rotation (nodding).
Posterior canal
Responsible for detecting tilting the head left/right.
Horizontal canal
Responsible for detecting lateral/medial rotation (shaking head for no).
Conductive hearing loss
Dysfunction of the outer and middle ears, typically short term.
Sensorineural hearing loss
Dysfunction of the inner ear, typically long term and irreversible.
Weber Test
A test used to distinguish between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss.
Sensorineural deafness
A type of hearing loss resulting from damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve.
Rinne Test
A hearing test that compares bone conduction to air conduction.
Otitis Media
Inflammation of the middle ear.
Myringotomy
Lancing of the eardrum to relieve pressure.
Olfaction
The sense of smell.
Taste
The ability to perceive flavors through taste buds.
Olfactory epithelium
A tissue that contains bipolar neurons responsible for the sense of smell.
Tongue papillae
Structures on the tongue that contain taste buds; includes filiform, fungiform, foliate, and circumvallate types.
Five basic taste sensations
Umami, salty, sweet, sour, and bitter.
Endocrine System
A diverse group of ductless glands that maintain homeostasis via hormone secretion into the bloodstream.
Hypothalamus
A brain region that releases inhibiting or releasing hormones affecting the anterior pituitary gland.
Pituitary gland
A gland that secretes hormones influencing other glands; divided into anterior and posterior sections.
Tropic hormones
Hormones that stimulate the release of other hormones.
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
A hormone involved in the production and maturation of ovarian follicles and sperm.
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
A hormone that triggers ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum.
Prolactin
A hormone that promotes milk production.
Growth hormone
A hormone that stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
Posterior pituitary gland
NERVOUS TISSUE; not a true endocrine gland; stores oxytocin & ADH produced from the hypothalamus
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
A hormone that influences pigmentation of the skin.
Thyroid
A gland that produces hormones regulating metabolism.
Calcitonin
A hormone produced by the thyroid that helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.
T3 (triiodothyronine)
A thyroid hormone that contains three iodine atoms per molecule.
T4 (thyroxine)
A thyroid hormone that contains four iodine atoms per molecule.
Hyperthyroidism
A condition resulting in faster metabolism, characterized by increased appetite, weight loss, and irregular heartbeat.
Grave's disease
An autoimmune disease that often results in an enlarged thyroid and may cause protruding eyes.
Hypothyroidism
A condition resulting in slower metabolism, characterized by weight gain, cold intolerance, and fatigue.
Goiter
Swelling in the neck due to an enlarged thyroid, typically caused by iodine deficiency.
Hashimoto's Disease
An autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed.
Atria
The two upper chambers of the heart.
Ventricles
The two lower chambers of the heart.
Papillary muscles
Muscles that prevent prolapse of AV valves, connected to chordae tendineae.
Chordae tendineae
Tendons that connect papillary muscles to AV valves.
Angina pectoris
Chest pain caused by hypoxia, typically due to narrowed/blocked coronary arteries.
Myocardial infarction (MI)
Tissue death that may result from severe angina pectoris.
Sinoatrial (SA) node
Located in the right atrial wall, generates impulses ~75x/min, and is the main pacemaker.
Atrioventricular (AV) node
Acts as a backup pacemaker in the cardiac conduction system.
Bundle of His
Part of the cardiac conduction system that transmits impulses from the AV node.
Pulmonary circuit
Pathway: SVC/IVC + coronary sinus → right atrium → tricuspid AV valve → right ventricle → pulmonary SL valve → pulmonary trunk → pulmonary arteries → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium.
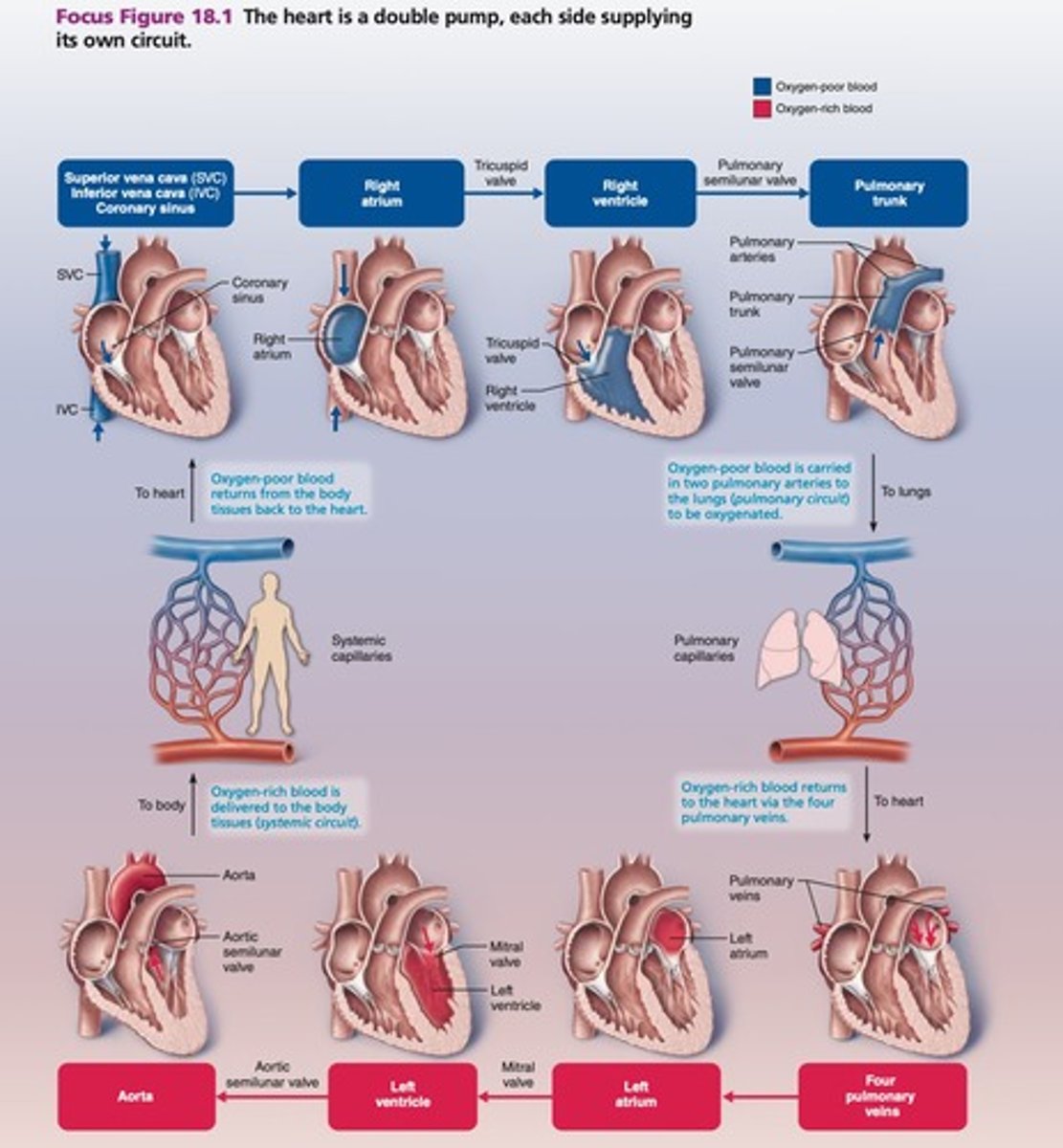
Systemic circuit
Pathway: left atrium → bicuspid/mitral AV valve → left ventricle → aortic SL valve → aorta → body's tissues.
Plasma
Nonliving fluid matrix (~55% of blood) mainly composed of water.
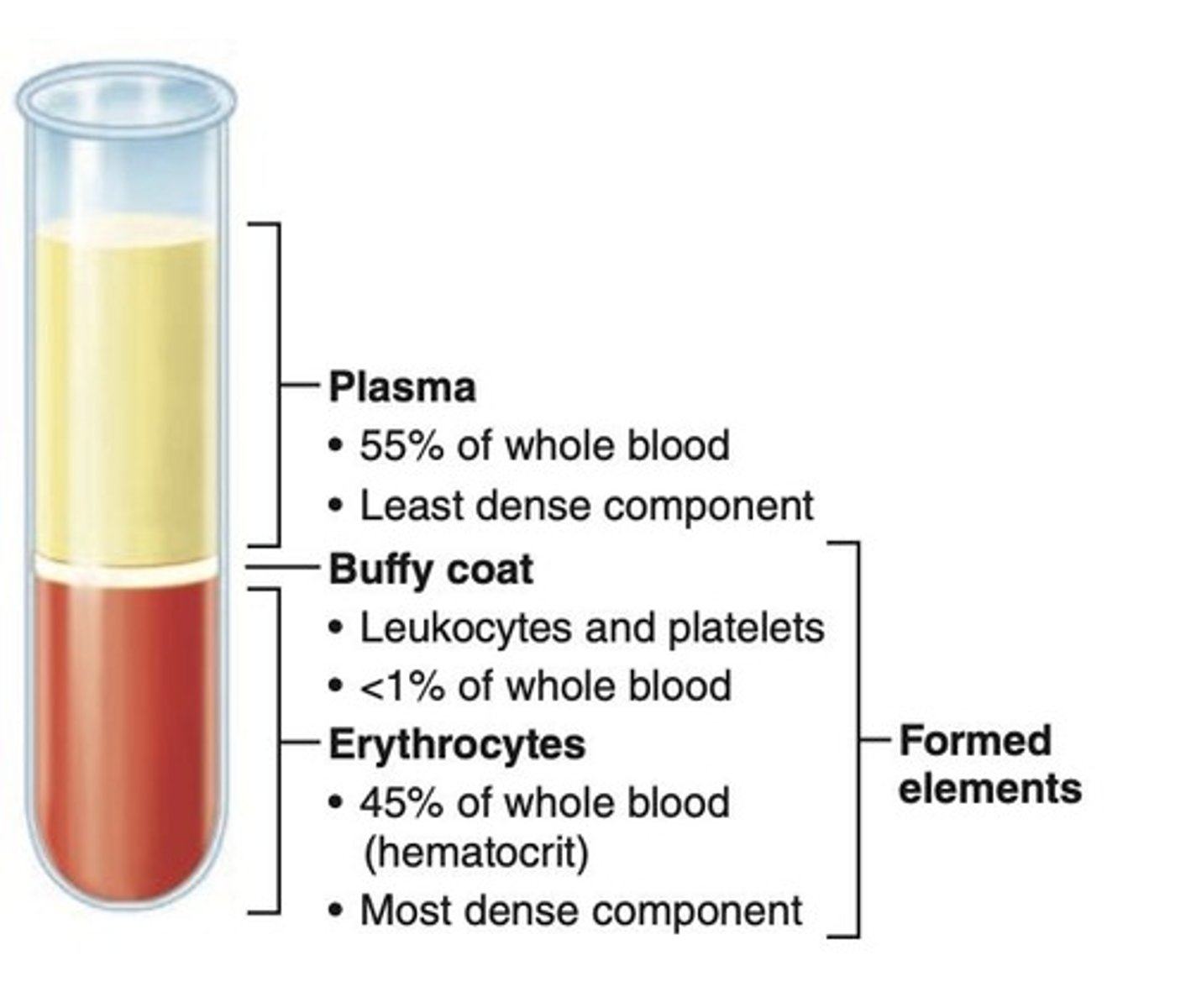
Formed elements
Cellular components of blood.
Platelets
Derived from megakaryocytes; functions in hemostasis.
Erythrocytes (RBCs)
Biconcave, anucleate cells with a lifespan of ~100-120 days; each hemoglobin (Hb) molecule carries 4 O2 molecules.
Leukocytes (WBCs)
Nucleated cells crucial to defense; "Never let monkeys eat bananas"
Granulocytes
WBCs characterized by granules; includes neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. "B.E.N"
Neutrophils
50-70% of WBCs; have 3-7 lobes; respond to acute infections (e.g. colds).
Eosinophils
2-4% of WBCs; bi-lobed; involved in allergies and parasitic infections.
Basophils
0.5-1% of WBCs; release histamine and heparin; involved in inflammatory response.
Agranulocytes
WBCs without granules; includes lymphocytes and monocytes.
Lymphocytes
~25% of WBCs; smallest WBCs; include B-cells and T-cells.
B-cells
Give rise to plasma cells which produce antibodies released into the blood.
T-cells
Direct response against tumor and virus-infected cells.
Monocytes
3-8% of WBCs; actively phagocytic; involved in chronic infections (e.g. tuberculosis).
Conducting Zone
Pathway for air: nasal cavity → pharynx → larynx → trachea → primary bronchi → terminal bronchioles.
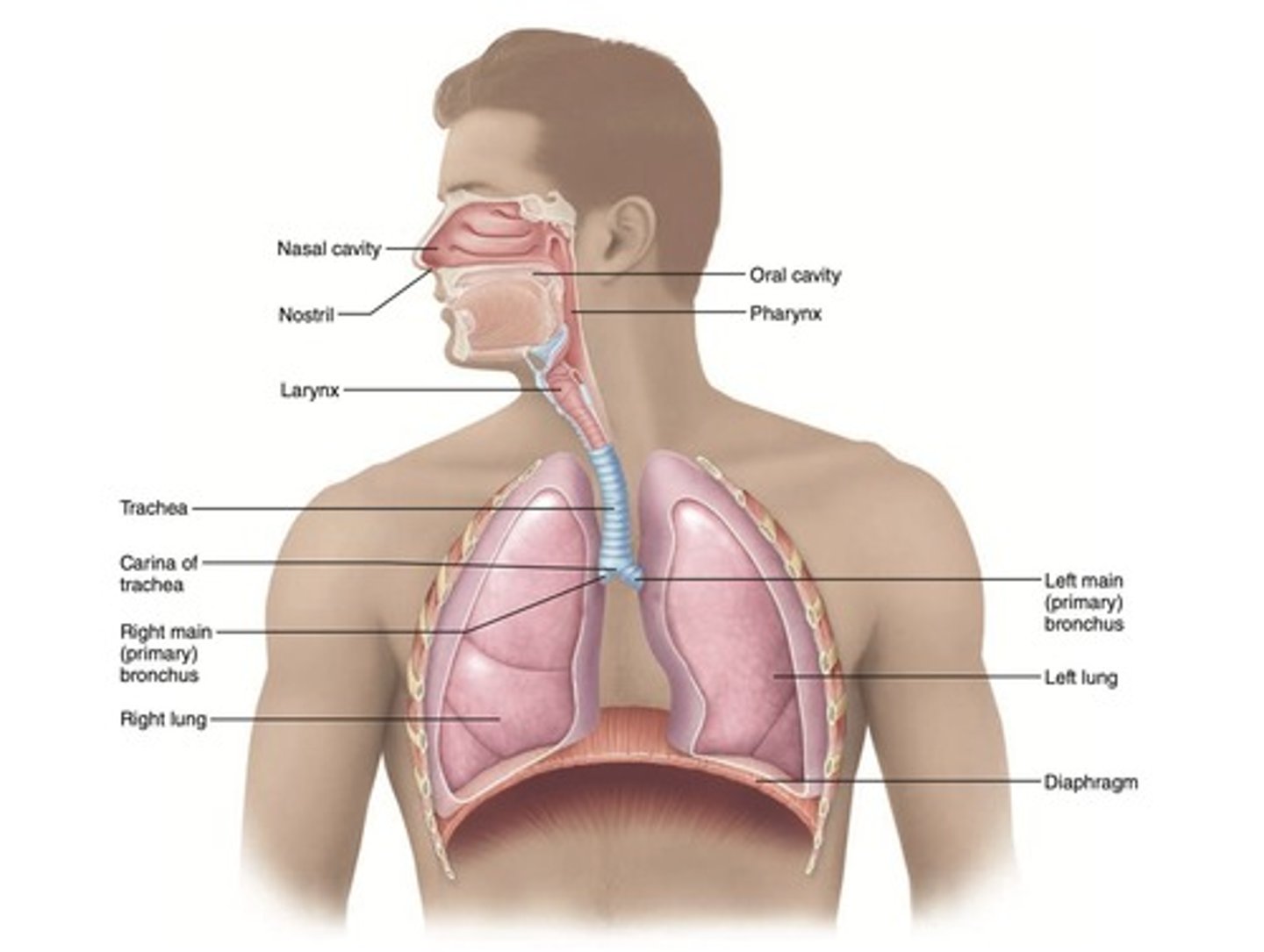
Respiratory Zone
Pathway for gas exchange: respiratory bronchioles → alveoli.
Pulmonary ventilation
Movement of air into and out of the lungs (breathing).
External respiration
Gas exchange across the lungs.
Circulation
Transport of gases through blood.
Internal respiration
Gas exchange across capillaries with tissues.
Alimentary canal (GI tract)
Four tunics: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa/adventitia.
Mouth
Food enters the GI tract through the oral cavity; leaves it as bolus.
Esophagus
Passageway from the pharynx to the stomach; has NO digestive function.
Stomach
Parietal & chief cells produce HCl & pepsinogen; foodstuff leaves as chyme.
Small intestine
Includes duodenum, jejunum, ileum; has deep folds (plicae circulares) for absorption.
Large intestine
Stores and concentrates fecal matter.
Liver
Creates bile (fat emulsifier).
Gallbladder
Stores and secretes bile.
Pancreas
Has endocrine & exocrine functions; produces alkaline pancreatic juice to neutralize chyme.
Kidneys
Filters/removes nitrogenous waste products from blood.
Nephron
Urinary unit of the kidney.
Micturition
Another term for urination.
Incontinence
Inability to voluntarily control urination (or defecation).
Fertilization
Sperm (male gamete) + egg/oocyte (female gamete) = zygote (diploid cell).
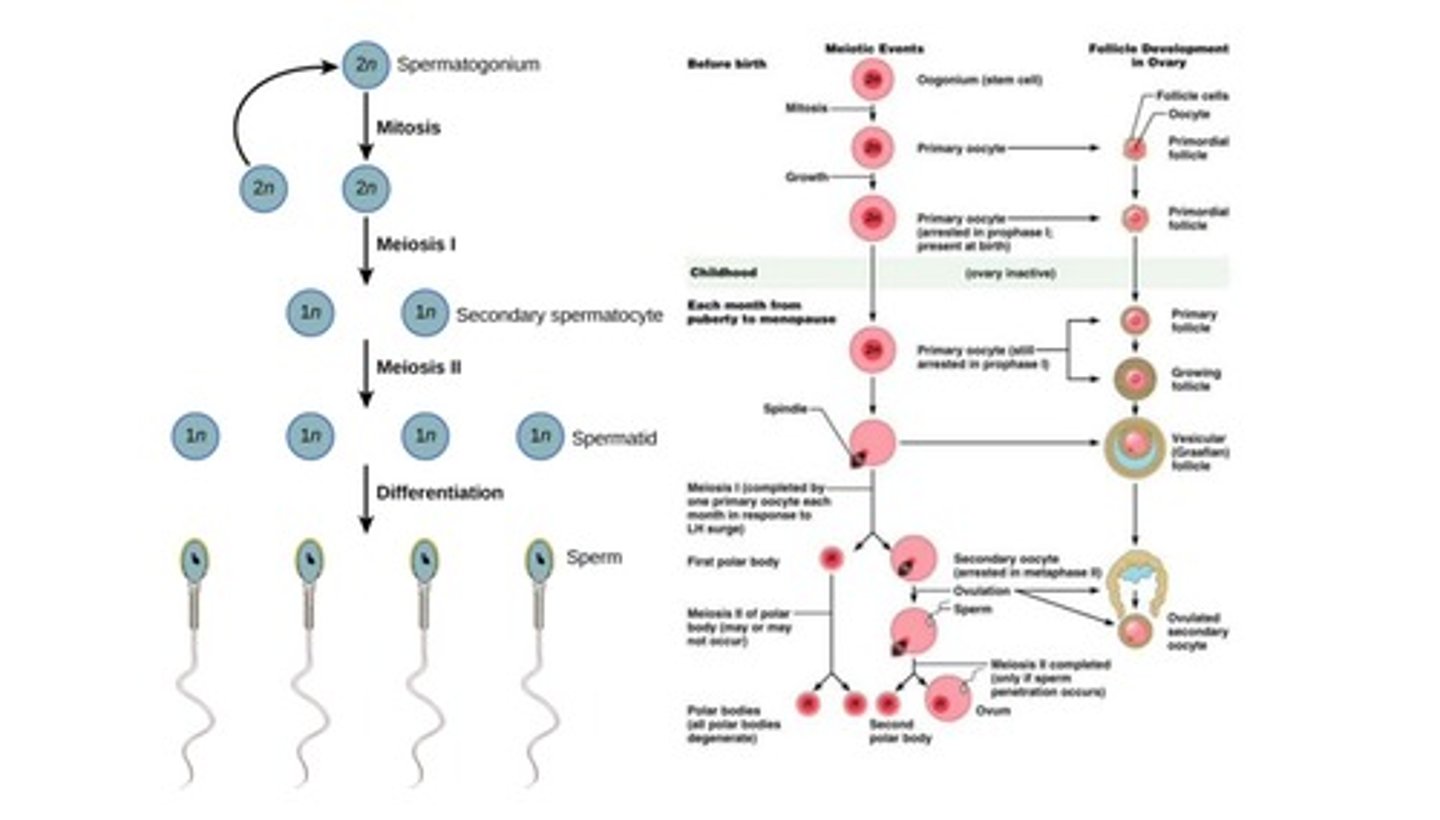
Negative feedback loop
A process that counteracts a change to maintain homeostasis.
Positive feedback loop
A process that amplifies a change, leading to an even greater change.