Topic 5: R&D and Price Discrimination
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TRIPS agreement and price schemes for patented drugs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Going back to rent-seeking —> Why is it socially valuable?
E.g. for research and development spending (the prospect of increased profits will increase pharmaceutical manufactures’ incentive to develop new drugs)
What tension is there?
Between access (affordable medication, consumer welfare) and innovation incentives (protecting R&D returns)
What does sustainable global access depend on ultimately?
On balancing affordability today with innovation tomorrow
Pharmaceutical patents in Low-Middle Income countries (LMICs)
Under the TRIPS agreement, WTO members are required to enforce product patents for pharmaceuticals —> LMICs argue that enforcing pharmaceutical patents raises medicine prices and limits access to life-saving drugs for their largely poor populations
Art. 31
Countries can use compulsory license (CL) to protect public health (emergency or excessive pricing or insufficient supply by the patent holder) —> CL is a legal authorisation that allows a government to produce (/import) a patented product (usually medicine) without the patent holder’s consent
What effect does domestic producers’ selling copied versions of patented drugs have?
It lowers pharmaceutical prices in LMIC compared to in rich countries
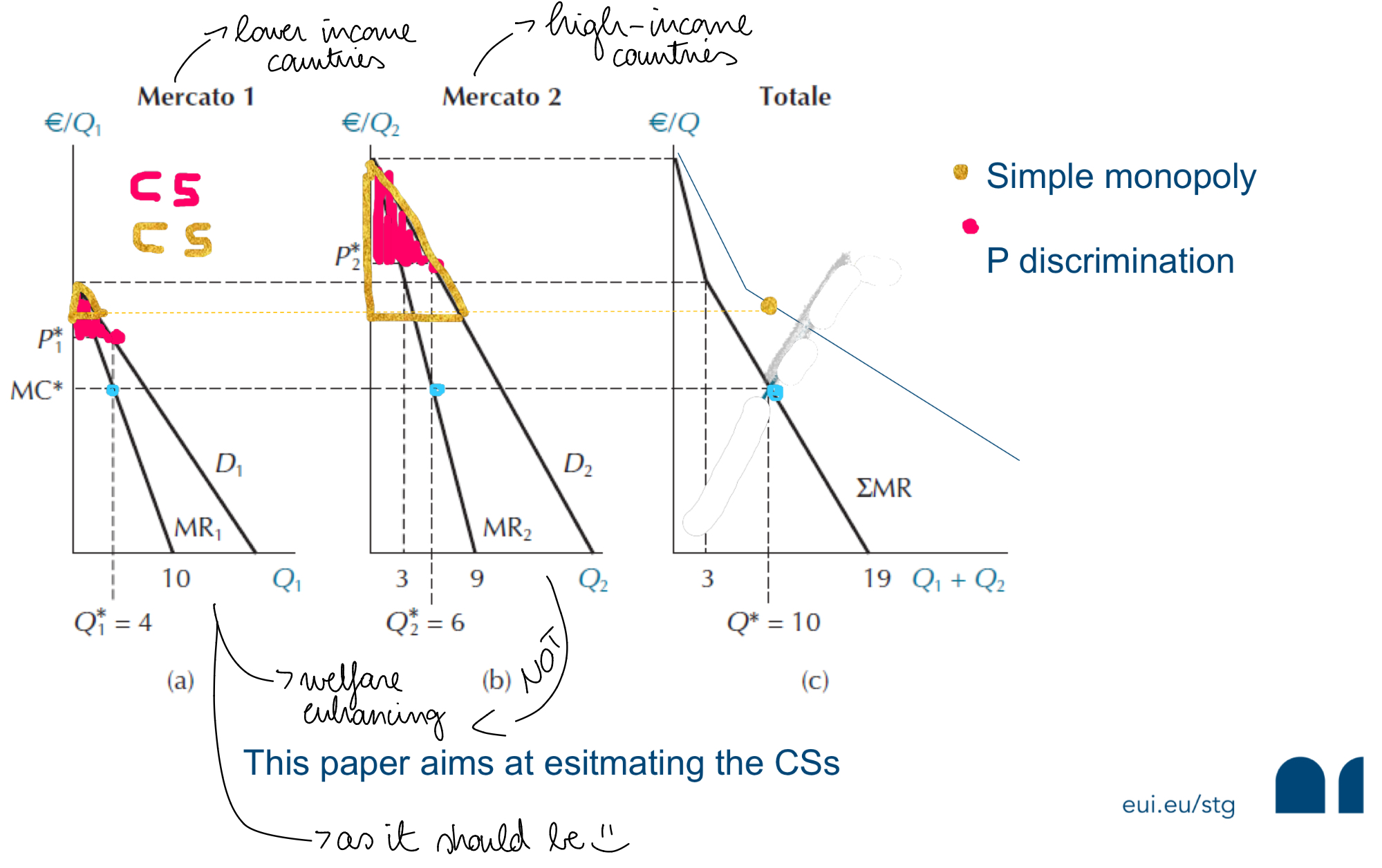
Welfare effects of patent protection - CS changes across pricing schemes

CL versus Differential Pricing
Innovator firms may lower prices in poorer markets, partly to deter CL
Differential pricing can strike a balance: expanding access without eliminating patent value
What is the impact on consumer welfare in LMIC when innovator firms adopt a policy of differential pricing?
Differential pricing is bound to lower prices and improve consumer welfare in LIMCs
Monopolistic firm maximising profit by charging different prices in the two markets
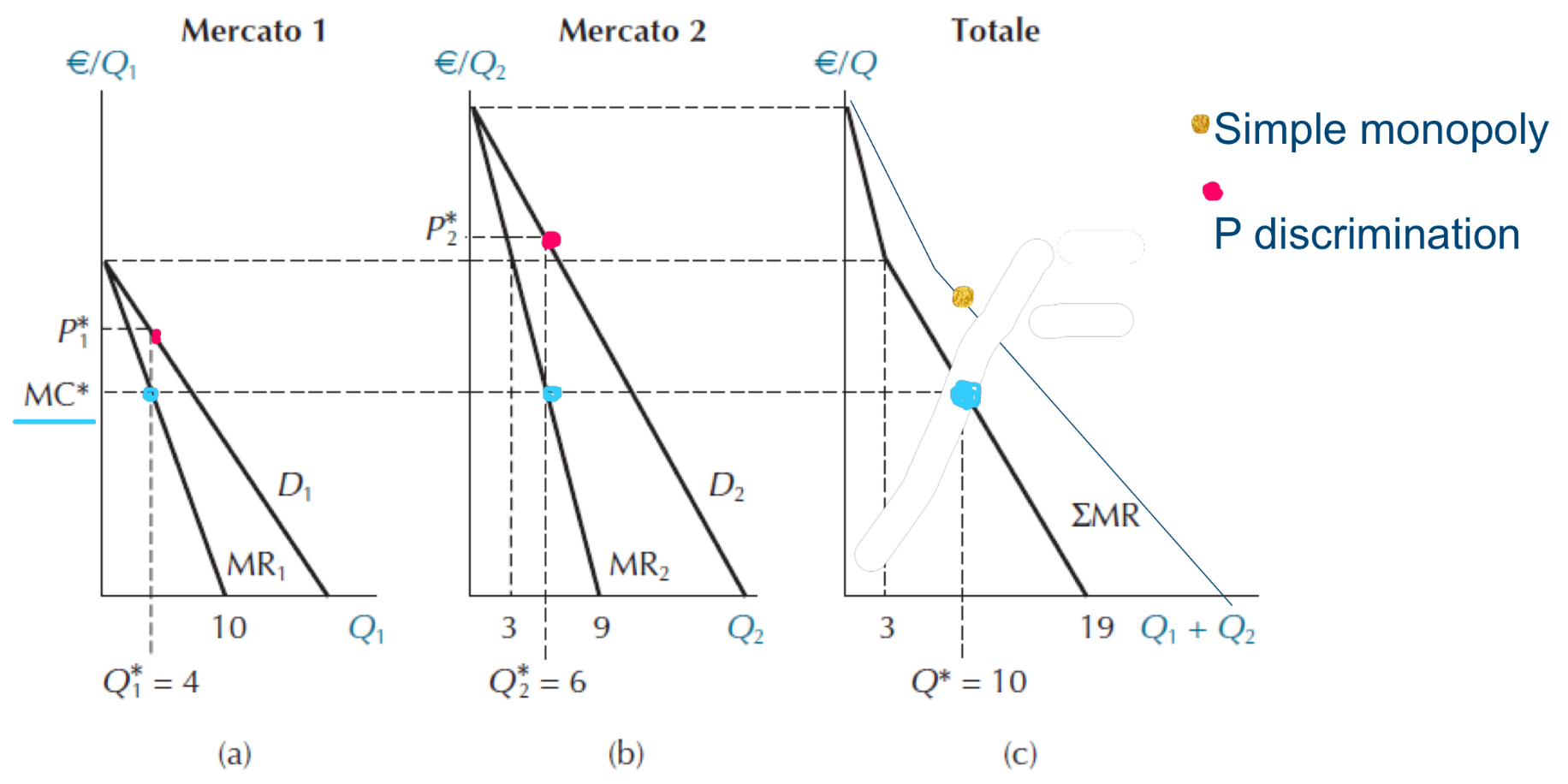
CS with differential pricing (red-shaded area) and simple monopoly (yellow-shaded area)
How common is this in practice?
Partially common, but uneven —> research is limited and uneven especially outside donor-financed markets

Concluding remark
The TRIPS agreement strengthened global patent protection, but its impact highlights a persistent tension: fostering innovation through monopoly rights while risking reduced access and welfare in poorer countries unless flexibilities (e.g. differential pricing or compulsory licensing) are effectively used