AP CHEM: Thermochemistry
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Exothermic
Process that releases heat into the surroundings.
Endothermic
Process that absorbs heat from the surroundings.
First law of thermodynamics
Energy is conserved; it can change form, but not be created or destroyed.
q surroundings
q system
ΔHsystem
Heat change of the system at constant pressure.
ΔHsoln
Heat change when a solute dissolves in a solvent
Specific heat
Heat needed to raise 1 g of a substance by 1 °C.
Heat capacity
Heat needed to raise an object’s temperature by 1 °C.
Hess’s Law
Total enthalpy change equals the sum of enthalpy changes for individual steps.
Standard heat of formation
Heat change when 1 mole of a compound forms from its elements in their standard states
Work
Energy transfer when a force moves an object; in chemistry, often pressure–volume work.
Kinetic energy (thermal)
Energy from particle motion; depends on temperature.
Potential energy (Chemical)
Stored energy in chemical bonds and forces.
Bond Energy
Energy required to break 1 mole of a bond in the gas phase.
Molar Heat Capacity
Heat needed to raise 1 mole of a substance by 1 °C.
Heat of Vaporization
Heat needed to convert 1 mole of liquid to gas at constant T and P.
Heat of Fusion
Heat needed to convert 1 mole of solid to liquid at constant T and P.
Calorimeter
Device that measures heat flow in chemical or physical changes.
Low potential energy=
High stability
High potential energy
Less stability
Dilution process=
(Delta H1) + (Delta H2) + (Delta H3) = DELTA H soln
Method of transfer of Energy (DELTA E)
q (heat) and w (work)
q (heat)
q= (mass)(specific heat)(final temp-initial temp)
measured in KJ
w (work)
work DONE on the system
w= -P(final volume-initial volume)
sign indicates endo vs exo work
measured in KJ or J
Heat given off by rxn vs heat absorbed by surroundings?
Heat given off (by rxn/system) = -Heat gained (by surroundings)
Cold to the touch
Endo thermic (+)
Heat evolves
(Heat is produced)
Open Container=
w= 0
No gas produced=
w= 0
Energy changes for element stages
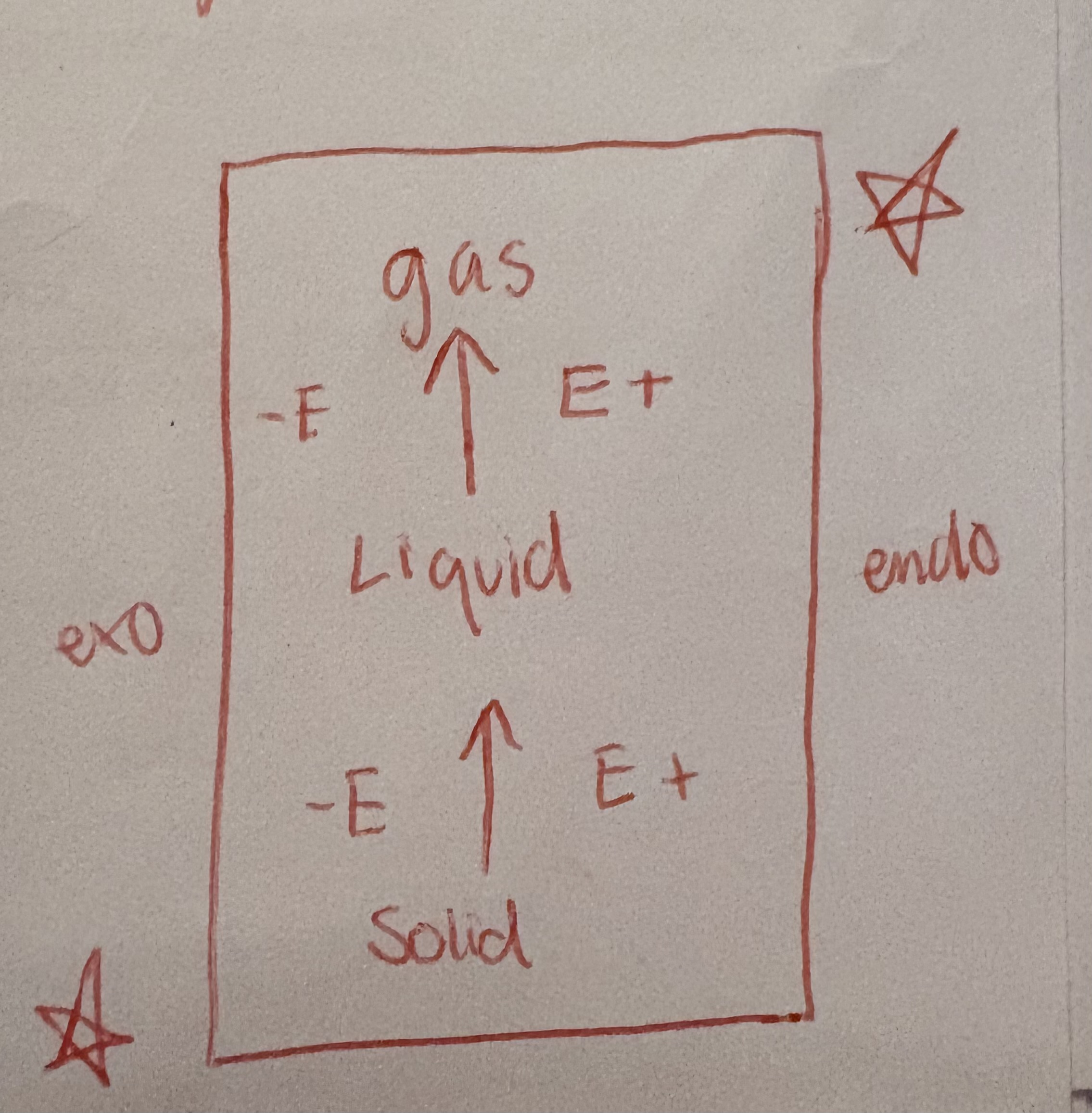
Plateau
Phase change
thermo stoic with delta H vap, fus
Bond Enthalpies
BONDS BROKEN - BONDS FORMED= delta Hrxn
Change in Enthalpy using bond energies
AH = Bond energy of reactants - bond energy of products
Standard Enthalpy of Formation
The heat that is released or absorbed when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states
Increasing/decreasing slope
Temperature change
q is calculated using MCAT
Phase changes
Added E is used to break Intermolecular forces/ attraction forces
Activation Energy