b6
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Photosynthesis Symbol Equation
6 CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Root Hair Cell Adaptation
Large surface area, many mitochondria for active transport
Phloem Function
Structure for sucrose transport in plants
Phloem Structure
Living cells arranged end to end. sieve cells with minimal organelles and companion cells. They have pores
how do plants get the co2 required
diffuses from the air into the leaves via stomata
how does water move up the xylem
transpiration moves one up and then the polarity of water attracts the other molecules up
Photosynthesis Word Equation
Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
Chloroplast Function
Part of plant cell that absorbs light for photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Reaction Type
Endothermic
Xylem Function
Structure for water and mineral transport in plants
Xylem Structure
Lignified dead cells with a thick wall
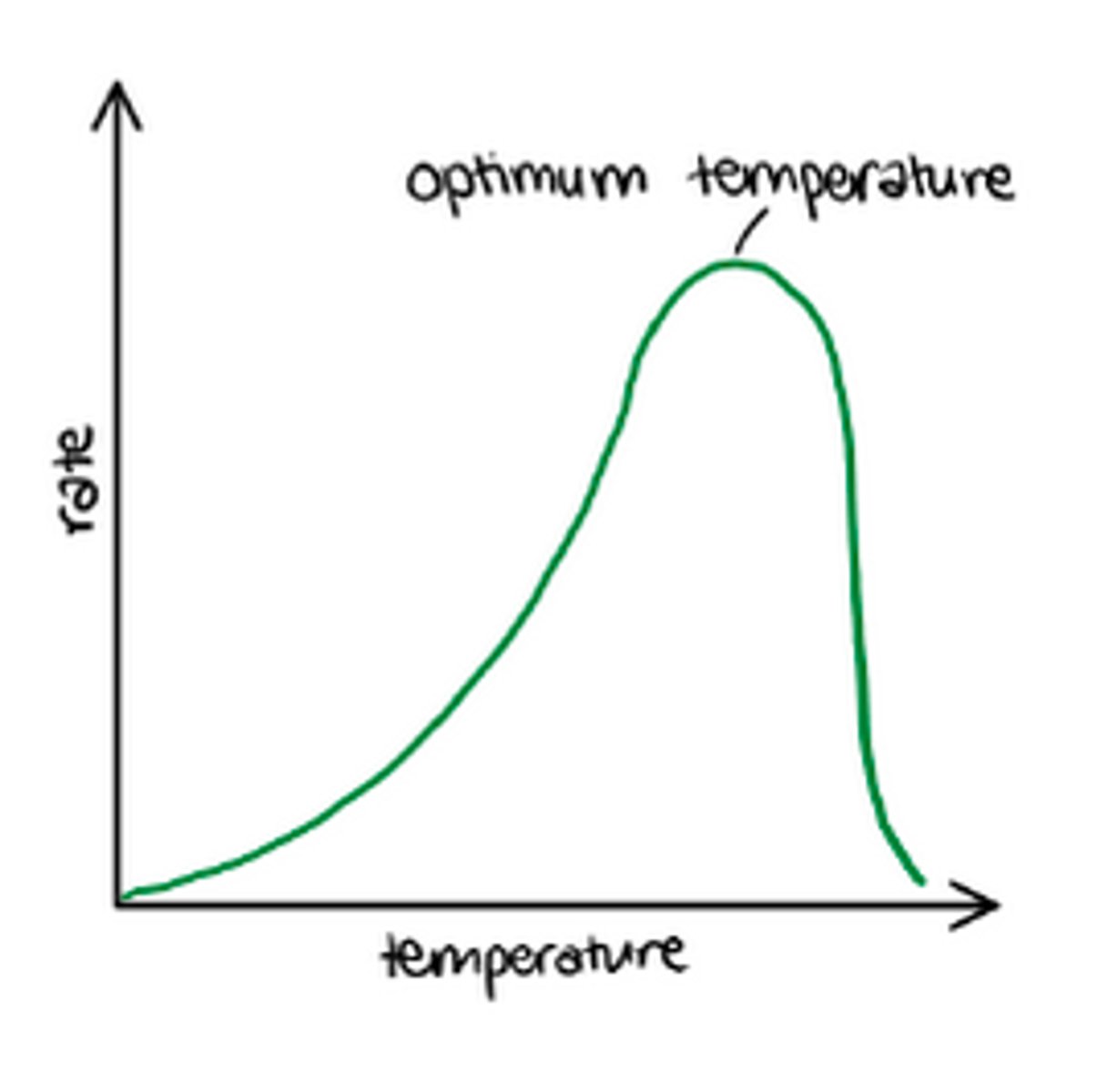
effect of temp on photosynthesis
as temp increases rate of photosynthesis does as well as the enzymes have more KE and are more likely to collide. After the optimum, the enzymes denature and it decreases the rate
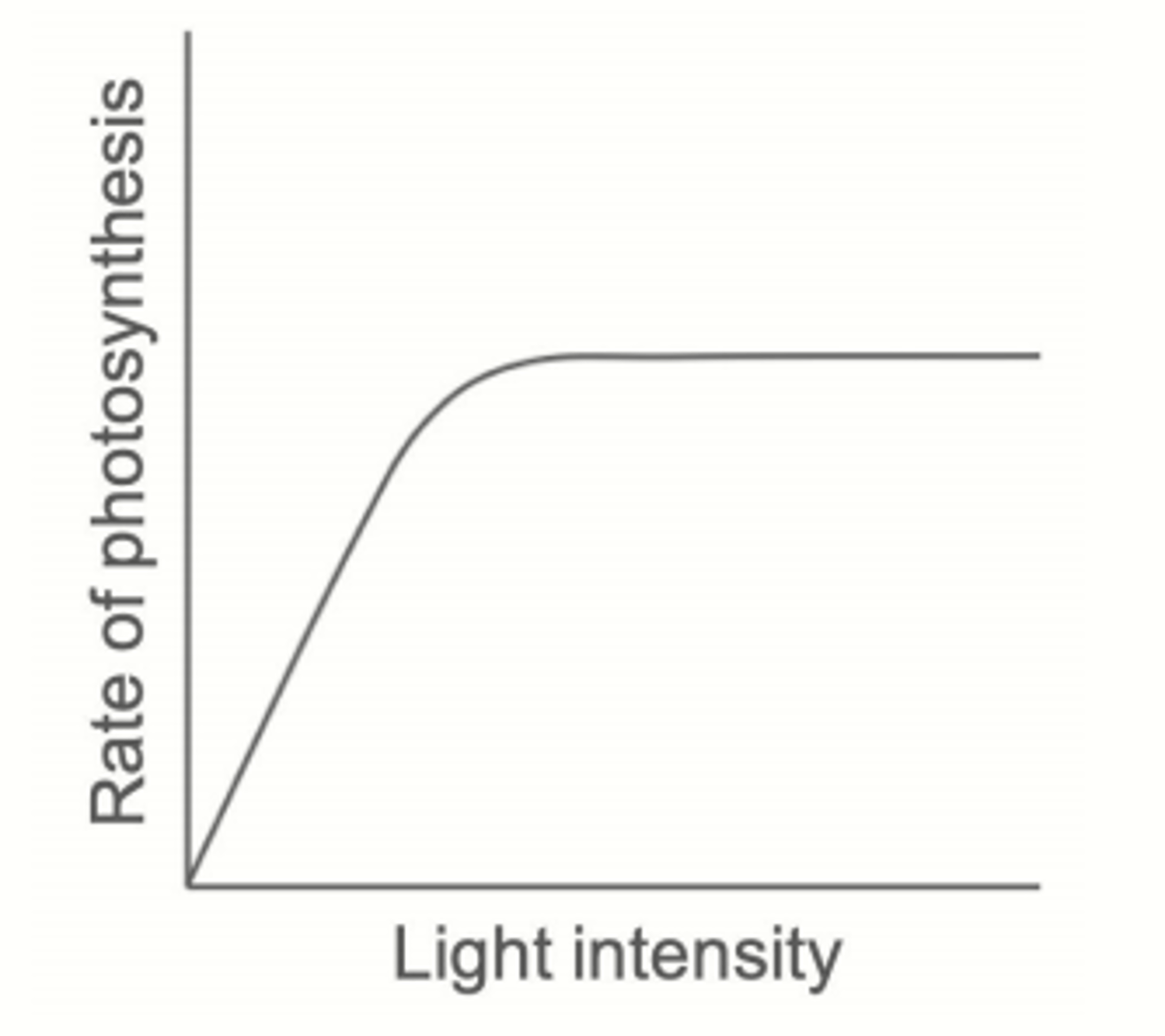
effect of light intensity on photosynthesis
as light intensity increases, so does rate until the optimum when it plateaus as something else is limiting
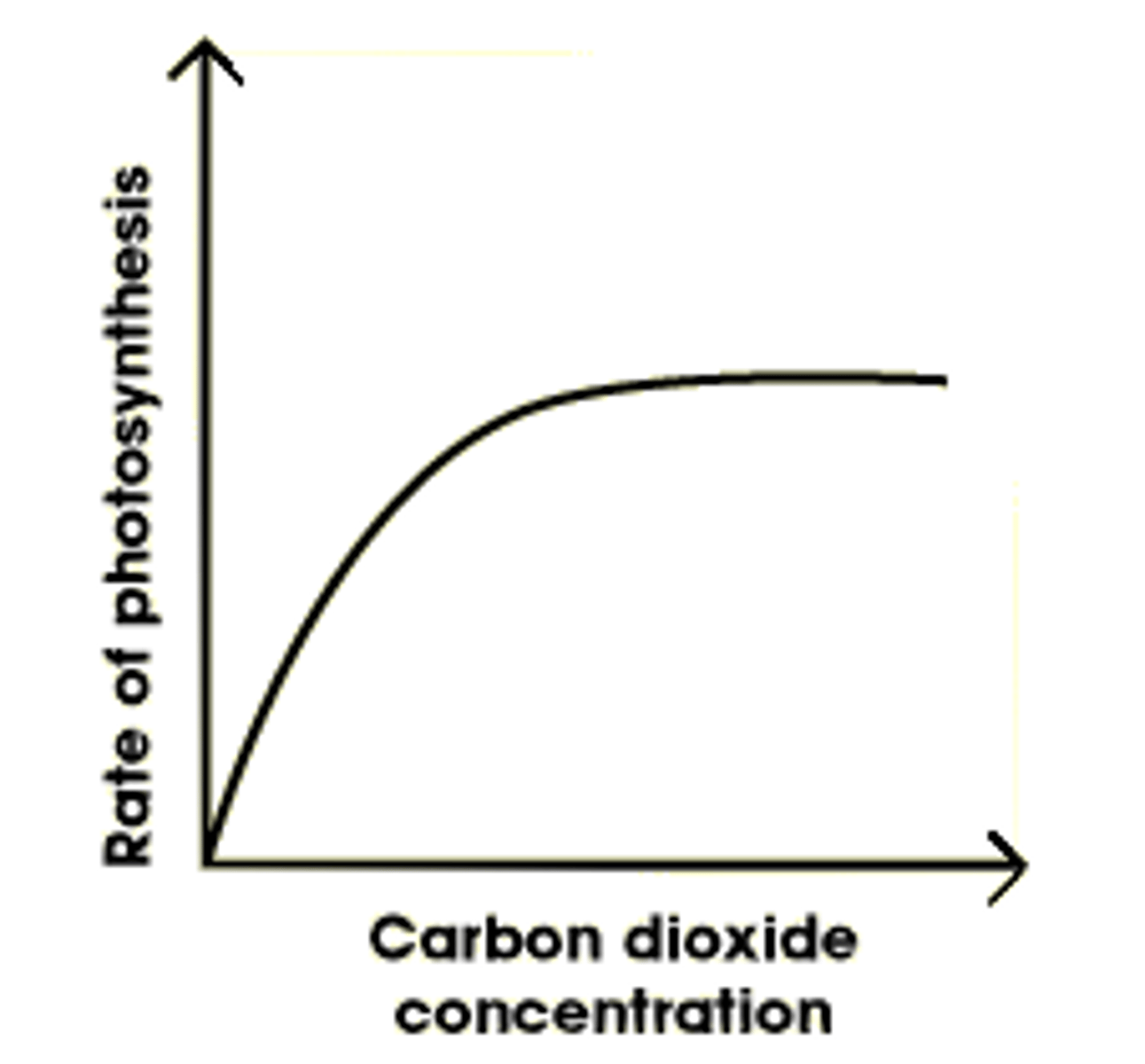
effect of carbon dioxide on photosynthesis
as CO2 increases, so does rate until the optimum when it plateaus as something else is limiting
what makes starch a useful long term storage molecule
can be easily broken down when needed, is compact, insoluble in water
uses of glucose
cellular respiration, make cellulose, make starch to store glucose, make amino acids, make lipids to store energy
why could plants produce insufficient chlorophyll
have a disease like tobacco mosaic virus or lack required nutrients
what does it mean when the guard cells become turgid
they open the stomata
what does it mean when the guard cells become flaccid
they close the stomata
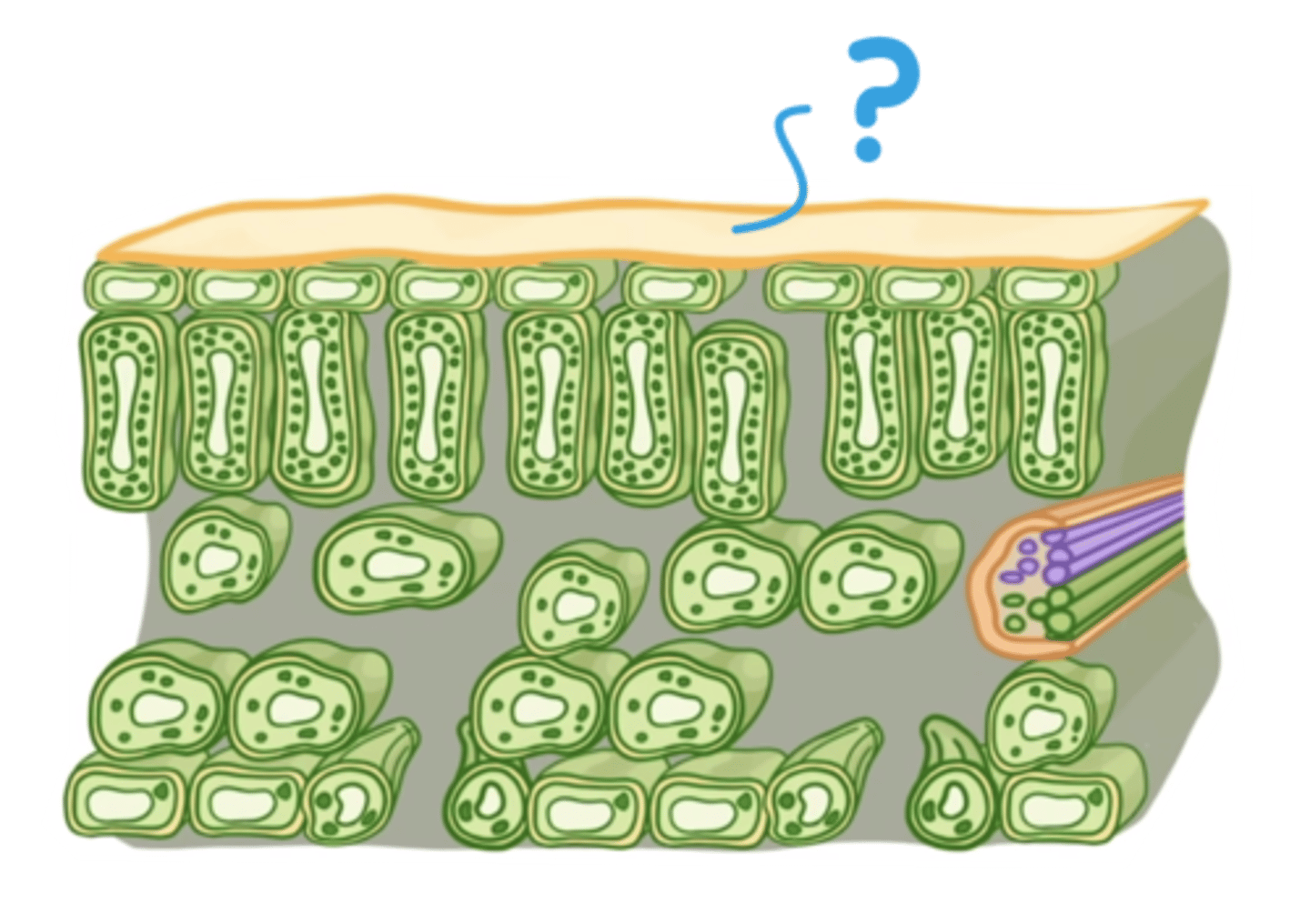
order of leaf structure
waxy cuticle, upper epidermis, palisade mesophyll, spongy mesophyll, lower epidermis
what are the reactants for an experiment testing how light intensity affects photosynthesis rates
pondweed, water, sodium hydrogencarbonate
investigating photosynthesis practical
put pondweed , water and sodium hydrogen carbonate in a test tube with a gas syringe attached
place lamp 20cm away and measure gas produced in 5 minutes
repeat with lamp further away
light intensity formula
1 / d²
what are the units for light intensity
arbitrary units ( a.u )
what do the palisade and spongy mesophyll do
photosynthesis
what does the spongy mesophyll also do
aid gas exchange due to spaces between cells
what are nitrates needed for and what is a deficiency symptom
making proteins, stunted growth
what are magnesium ions needed for and what is a deficiency symptom
making chlorophyll, yellow leave
difference between xylem and phloem for direction of travel
xylem can only transport water upwards. The phloem can travel up and down
what does the waxy cuticle do
reduce water loss by evaporation
translocation
movement of dissolved sugars from the leaves to rest of plant via phloem
transpiration
movement of water up a plant driven by evaporation through stomata
how does water move up the xylem
water evaporates out the leaf via the stomata and the polarity of water molecules drags up the water molecules up the chain.
factors affecting rate of transpiration
air movement, humidity , light intensity, temperature
how does high air movement affect transpiration and why
high air movement means water vapour is removed from the air surrounding the leaf which creates a concentration gradient increasing water loss
how does high humidity affect transpiration and why
high humidity decreases transpiration rate as the concentration gradient is weaker
how does high light intensity affect transpiration and why
high light intensity means guard cells open so more water loss
how does high temperature affect transpiration rate
particles have more kinetic energy to evaporate and diffuse away faster
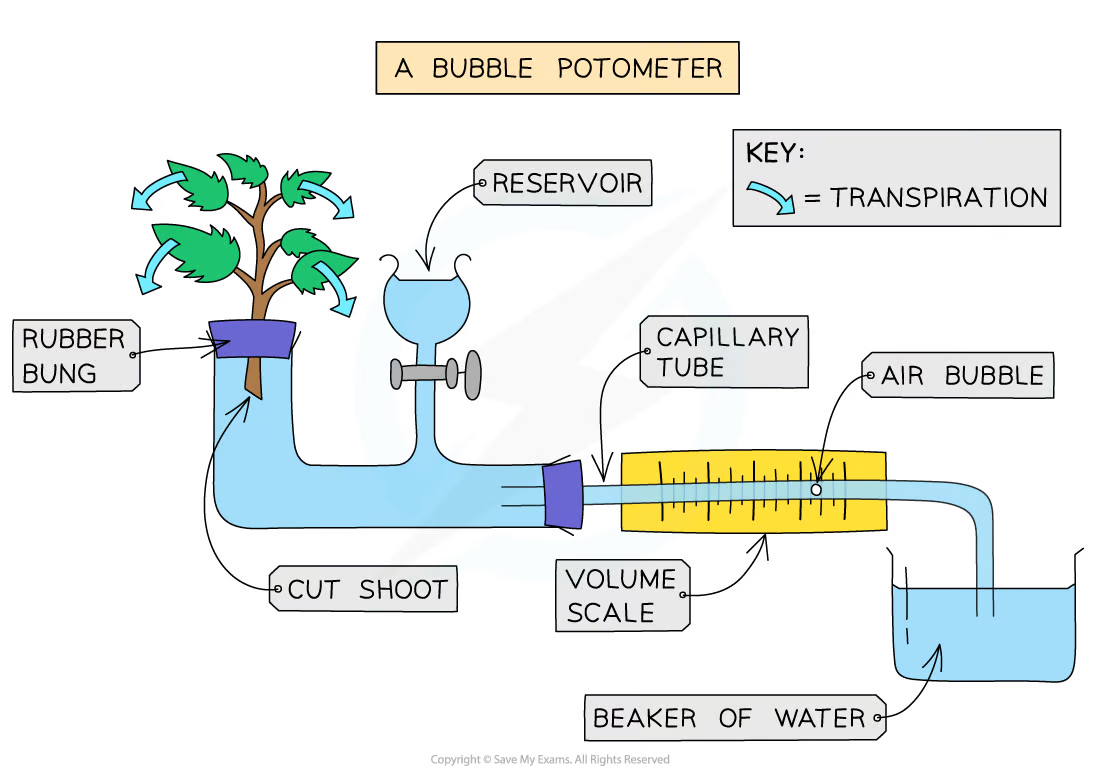
investigating transpiration experiment
set up potomoter
remove tube and insert it into beaker to create a bubble
measure how far the bubble travels in 10 minutes
what Is used to measure transpiration
potometer
formula for transpiration rate
distance travelled by bubble / time
Ficks law for diffusion
surface area x concentration gradient / diffusion distance
xerophytic plant adaptations to prevent water loss
thick waxy cuticle , small leaves with smaller surface area, less stomata that only open at night , sunken stomata, curled leaves
how do sunken stomata prevent water loss
reduce air flow
how are plants adapted for gas exchange
waxy cuticle, stomata, thin and flat leaves, spongy mesophyll
how do thin and flat leaves aid gas exchange
short diffusion distance for CO2
how are leaves adapted for photosynthesis
broad leaves for large surface area for light, transparent upper epidermis to let in light , xylem and phloem, stomata
auxins
plant hormones that are released at roots or shoots and affect growth
phototropism
growth in response to light
gravitropism / geotropism
growth in response to gravity
Auxins effect on growth at roots and shoots
inhibits growth at roots, stimulates growth at shoots
shoots are -
positively phototropic and negatively geotropic
roots are -
negatively phototropic, positively geotropic
investigating phototropism
set up seeds in a Petri dish . Control light intensity, temp, water and CO2. Position light at different directions. Plants will grow towards the light
how do plants grow towards light
auxins are released at the darker side of the shoot. it stimulates growth of that side so the plant bends towards the light
how do roots grow in gravity direction
auxins are released in lower side of root. It inhibits growth on the lower side so the top grows more. The root will grow downwards
auxins use commercially
rooting powder to grow cuttings, selective weedkiller
how can auxins be used as selective weed killer
they are absorbed by broad leaved plants due to large surface area. They cause excess growth so the plant dies
gibberellins function
seed germination
gibberellins use commercially
induce fruit and flower formation , make seedless fruit grow but not the seeds
ethene function and use
ethene ripens fruit
how do smaller leaves help prevent water loss for plants in dry arid conditions
few and sunken stomata , thick waxy cuticle , needle shaped or small leaves , hairs around stomata
how can curled leaves prevent water loss
it reduces exposure to wind and sunlight to decrease transpiration
algal balls experiment
place algal balls in a bottle with water and hydrogen carbonate indicator. Place bottle at different distances from the lamp. As light intensity increases , the rate of photosynthesis also increases meaning there is less carbon dioxide meaning the solution is more alkaline .
how does translocation transport sugars. steps
source cell turns glucose produced from photosynthesis into sucrose
it enters the companion cell via active transport
it diffuses into the sieve tube element as water diffuses in via osmosis
sucrose dissolves in water and the solution moves down the phloem
sucrose diffuses into companion cell and then into sink cell to be stored as glucose
water diffuses back by osmosis
source cell
where glucose is made
sink cell
where glucose is stored