Unit 2: Oral Anatomy (Cram)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms

Most common headshape
Mesaticephalic

Short and wide headshape. These breeds have crowded, rotated premolar teeth
Brachycephalic

Long and narrow head shape
Dolichocephalic
Which cat breed in known for being brachycephalic?
Persian

Which cat breed is known for being dolichocephalic?
Siamese

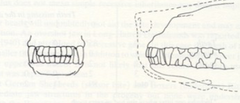
What kind of bite does this mesaticephalic dog have?
Scissor bite
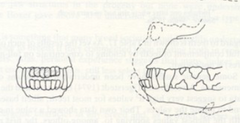
What kind of bite does this brachycephalic dog have?
Undershot bite
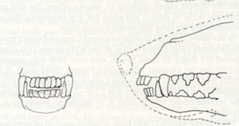
What kind of bite does this dolichocephalic dog have?
Overshot bite
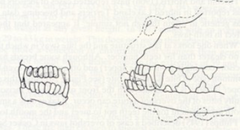
What kind of bite does this brachycephalic dog have?

Upper jaw, made of many bones
Maxilla
Lower jaw
Mandible
The division between the two mandibles
Mandibular symphysis
The portion of the mouth that consists of hard bone covered by mucous membranes
Hard palate

The posterior portion of the roof of the mouth extending down the throat. Does not have bone under it
Soft palate
Irregular ridges on the mucous membrane of the hard palate
Rugae
The space between the cheek/lips and teeth
Vestibule

The area where the two jaws join at the back of the oral cavity
Fauca
Epithelial tissue that is harder and more tightly attached to supportive tissue in the oral cavity
Gingiva
The space between the tooth and surrounding structures other than the tissues in the oral cavity (hint: we measure this with a probe)
Sulcus
The mucous membranes that lines the inside of the mouth
Oral mucosa
Where the upper and lower lips meet (at the corners of the mouth)
Commisure

Where the gingiva meets the mucous membranes. There is a line across the gums
Mucogingival line
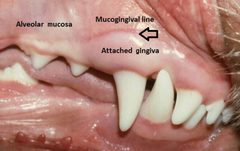
Where the mucous membranes transition to skin
Mucocutaneous junction
Refers to the way the teeth fit together
Occlusion
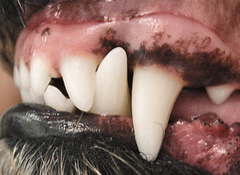
Space or gap between two teeth
Diastema
Tooth surface that faces the lips, only the incisor teeth
Labial
Tooth surface that faces the hard palate, only top teeth
Palatal
Tooth surface that faces the tongue, only bottom teeth
Lingual
Premolar and molar tooth surface that faces the lips (cheeks)
Buccal
Tooth surface at the back of the tooth
Distal
Tooth surface at the front of the tooth
Mesial
Tooth surface in the space between each tooth
Interproximal surface
The very top of the tooth (crown surface)
Note: May be asked "what tooth surface faces the lips"? If the question is not specific about incisors or premolars/molars, the answer is occlusal
Occlusal
Directional term meaning towards the crown of the tooth
Coronal
Directional term meaning towards the apex of the tooth
Apical
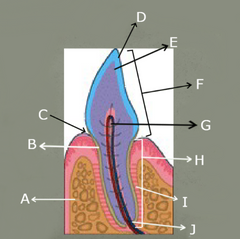
Label A–J on this diagram
A – Alveolar bone
B – Cementum
C – Sulcus
D – Enamel
E – Dentin
F – Crown
G – Pulp cavity
H – Root
I – Periodontal ligament
J – Apical delta
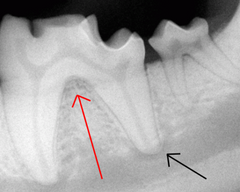
What are the red and black arrows pointing to on the tooth?
Red – Furcation
Black – Apex
Fill in the blank: ______ is the hardest tissue in the body, it is made mostly of mineral crystals, mainly ______.
Enamel, calcium
If enamel is so hard, why wouldn't you want a tooth completely comprised of it?
It is hard but also brittle, an 100% enamel tooth would fracture easily
Cell that forms enamel
Remember: Blast for Build
Ameloblasts
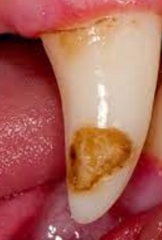
What is this condition of minimal calcification of the enamel?
Enamel hypoplasia
True or false: Dogs and cats have thicker enamel compared to humans. This is why dogs can chew on bones and sticks without enamel damage
False. Dogs and cats have a thinner enamel than humans. Chewing on rocks, sticks, and bones, can easily wear away a dog's enamel, causing permenant damage
Substance that makes up the majority of the tooth structure. It forms the layer just below the enamel of the crown and the cementum of the root
Note: Dentin is also hard, as hard as bone, but not as hard as enamel
Dentin
Cells that make dentin throughout the life of the tooth
Note: Dentin has a regenerative capacity
Odontoblasts
Cells that breakdown dentin and other tooth substances
Note: Hence why lesions involving these cells are called odontoclastic resorptive lesions
Odontoclasts
Substance that covers the outermost surface of the tooth roots. Similar to bone and is the only substance that periodontal ligaments and gingiva will form attachments to
Note: If cementum is damaged deep pockets around the tooth will result
Cementum
True or false: Enamel lacks nerve endings, while dentin and cementum have nerve endings, this is why they are painful when exposed
True
Fill in the blank: Dentin is arranged in _______ which radiate outwards from the _______ chamber towards the enamel
Dentin is arranged in tubules which radiate outwards from the pulp chamber towards the enamel
Note: These tubules are easily colonized by bacteria if dentin is exposed
Type of dentin that is created BEFORE the tooth erupts
Primary (1°) dentin
Type of dentin that is created continuously AFTER the tooth erupts
Secondary (2°) dentin
True or false: The creation of secondary dentin causes an animal's teeth to grow bigger over their lifetime
False. Dentin grows inwards rather than outwards. It makes the pulp chamber smaller as the animal ages
Type of dentin that is produced in areas exposed to injury. It is darker and more irregular than primary or secondary dentin
Tertiary (3°) dentin
The exposure of which tooth structure causes sensitive teeth: enamel, dentin, or pulp?
Dentin
Cells that produce cementum at the root apex throughout the life of the tooth
Cementoblasts
Hardened, keratinized epithelial tissue. Like a callused mucous membrane
Gingiva