genetics in medicine
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIOL429
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
modern medical genetics
application of genetic principles to medical practice
medical genetics main aspects
patient symptoms, familial history, molecular basis of disease
gene (genetics definition)
something that encodes a specific trait containing 2 alleles, one from each parent
gene (molecular definition)
unit that encodes a specific protein, carries out gene function, forms outward manifestation of trait
heredity
transmission of trait from parent to offspring
single gene disorder
arise from mutation of one gene that can be tracked through families. phenotype is determined by genetics
multifactorial gene disorder
more than one gene is affected, environmental factors contribute to disease phenotype
chromosomal disorders
part of chromosome is lost or gained, they rearrange or translate, spontaneous and not inherited
mitochondrial disorders
caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA, inherited maternally, easily tracked
infectious diseases
disease that can be contagious, virus, bacteria, can be treated
non-infections diseases
genetic disorders, cannot be transmitted, are inherited
model system
lower organism used for biological study because functions at the cellular level are very similar to humans
mutation
accidental change in gene sequence, can be inherited
allele
variant of gene that has a different nitrogenous base sequence
gene pool
all alleles in a given population for specific gene
Gregor Mendel
determined how traits are inherited using pea plants.
Mendel’s 3 laws
law of segregation, law of independent assortment, concept of dominant
Archibald Garrod
first scientist to study human genetic disease
what did Garrod study
Alkaptoonuria, inborn error in metabolism caused by consanguinity
Thomas hunt
first to discover X-linked inheritance
main concerns of modern medical genetics
transmission of traits, molecular mechanisms that lead to trait expression, disruption of molecular mechanisms that cause disease, genetic counsiling
importance of genetic counsiling
risk and prognosis and treatments available
molecular basis of gene expression
DNA→RNA→Protein
four levels which DNA info is used
molecular, cellular, tissue, organismal
how to genes differ from one another
by the number and order of nitrogenous bases
what effects do mutations have
can lead to changes in phenotype, or disease but most have no affect
how has pediatric mortality changed over last century
has increases 16.5%→50% due to vaccines and treatment for infectious diseases
gene expression
expression of gene that causes phenotype
transcription
using DNA template to produce RNA
Translation
using RNA to protuce protein
nucleotide
building block of RNA and DNA
Nitrogenous bases
parts of DNA and RNA, A C G T U
phosphate groups
bound to 5’ carbon by ester linkage, usually 3 p-groups bound
phosphodiester bond
what bonds nucleotides together
DNA Strand
double stranded helix that is antiparallel, includes base pairings
DNA strand direction
5’→3’
DNA double helix
right handed clockwise turn, very close together 10.5 BP per turn
B-type DNA double helix
predominant confirmation, composed of major and minor grooves
major groove
wide and of moderate depth
minor groove
narrow and of moderate depth
promoter
drives and controls transcription of gene
5’ UTR
5’ mRNA regulation, starts translation, untranslated region
3’ UTR
3’ mRNA regulation, stabilizes mRNA, untranslated region
ORF
open reading frame, part of mRNA that is translated
molecular pathology
takes genotypes and understands how they are expressed on molecular level. determined how phenotypes are affected
loss-of-function allele
mutation that leads to non-functional protein
gain-of-function allele
mutation that leads to over functional protein
dominant negative allele
only one copy is mutated but phenotype is caused by loss of function
null allele
nonfunctional DNA sequence that results in no gene product
coding strand
Watson strand, similar sequence to pre-mRNA
noncoding strand
Crick strand, template for transcription
components of nucleotide
5 carbon sugar, Phosphate groups, nitrogenous bases
how nucleotides are polymerized
phosphodiester bonds formed between phosphate group of 1 nucleotide and 5 carbon sugar of another
purines
G+A
pyridines
T+C
how to nitrogenous bases bind to 5-carbon sugar
bound to 1’ carbon by N-glycosidic linkage
RNA polymerase 2
enzyme that transcribes mRNA
three units in mRNA
5’ UTR, ORF, 3’ UTR
RNA produced by transcription in Eukaryotes
mRNA, rRNA and tRNA
processing of mRNA
5’ capping, splicing of introns, 3’ AAA tail
pre-mRNA splicing
removing of introns and exons come togetehr
diversity of alternative splicing
sometimes coding exons are spliced alongside the introns which causes a variety of different RNA to be formed which causes protein diversity.
codon
sequence of three nucleotides that form genetic codes
start codon
AUG, starts translation
stop codon
UAA, stops translation
b-confirmation of DNA
forms in dilute salt concentration, major and minor groove, 10.5 BP per turn, clockwise twist
where to sequence specific DNA proteins bind
they bind on the major groove
A-T H bond acceptors and donors
ADAM
G-C H bond acceptors
AADH
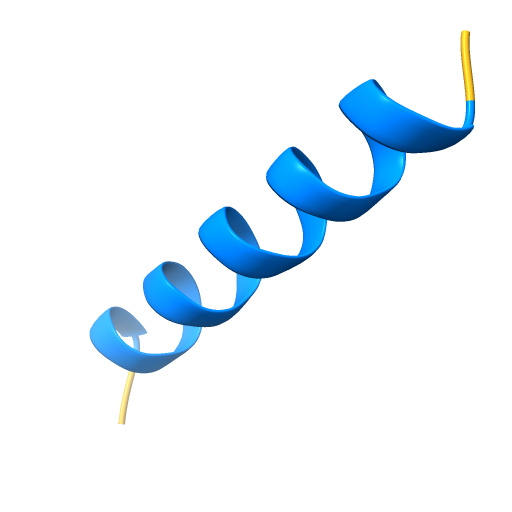
alpha helix
parallel beta sheets
antiparallel beta sheets
unstructured turns
COOH-COOH bond or NH2-COOH bond between beta sheets
pedigree
chart of family
autosome
relating to any of the chromosomes
autosomal dominant
only one copy of gene needed to inherit disease
autosomal recessive
2 copies of gene needed to have disease
x-linked dominant
1 copy of gene on x-chromosome needed to have disease
x-linked recessive
all x chromosomes contain allele for diease
y-linked
copy of disease allele on y chromosome
mitochondrial inheritance
inherited from mother, very rare
penetrance
individuals that have a genotype for disease but do not show it
expressitivity
rate at which phenotype of disease is expressed
age-related penetrance
patient seems healthy but symptoms dont appear until later in life
first degree relatives
parents, siblings, offspring
second degree relatives
grandparents, grandchildren, aunts, uncles, nieces, nephews, half-siblings
third degree relatives
first cousins
proband
affected individual in pedigree
consultand
unaffected individual in pedigree
normal distrubution
±2 std dev from mean, more than likely individual is healthy
quantitative trait
trait that can be measured
qualitative trait
whether or not phenotype appears
autosomal dominant pedigree
both sexes have equal frequency, affected individual=affected parent
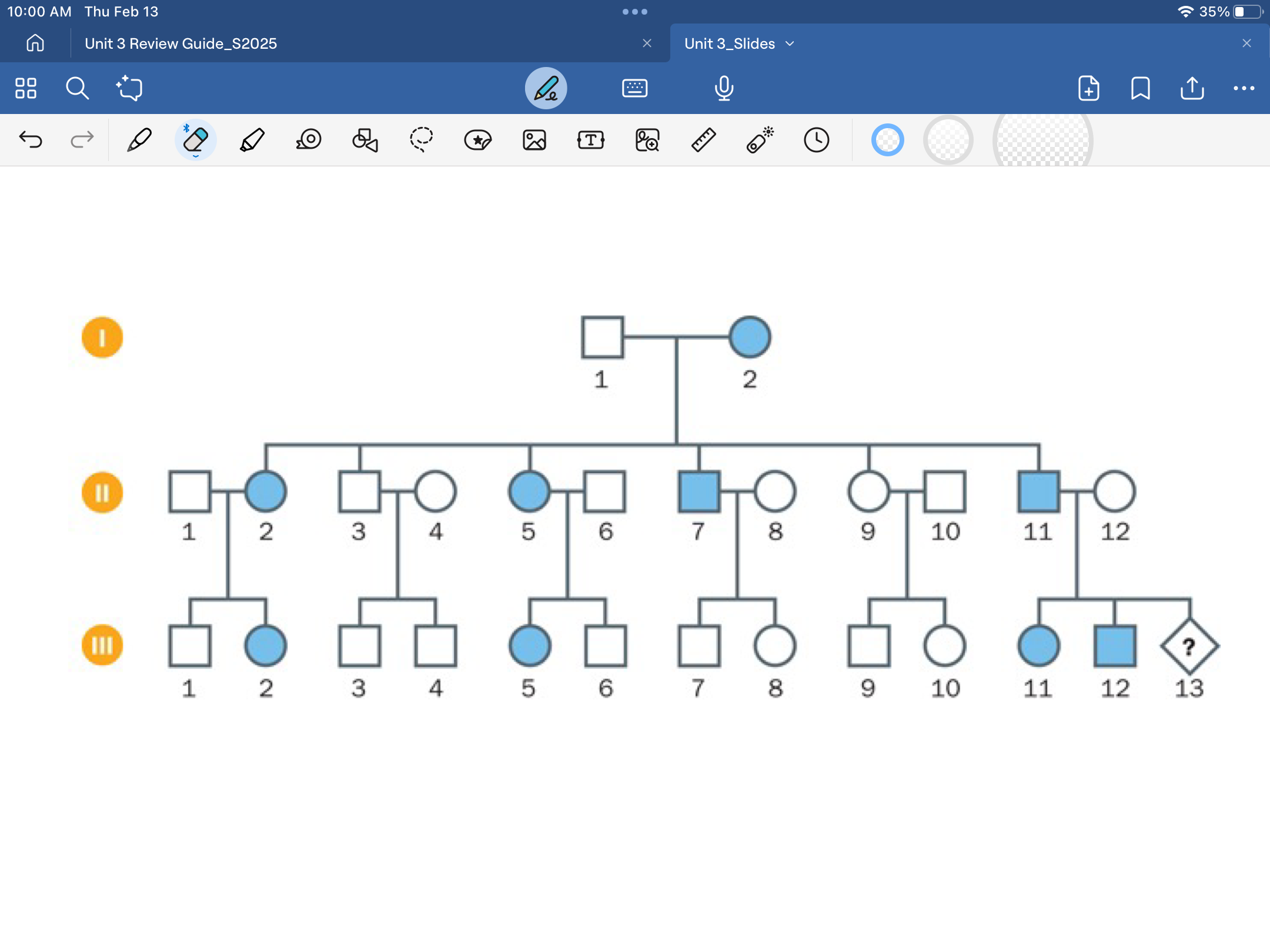
autosomal recessive pedigree
both sexes have equal frequency, skips generations, both parents have to be heterozygous for offspring to have diease
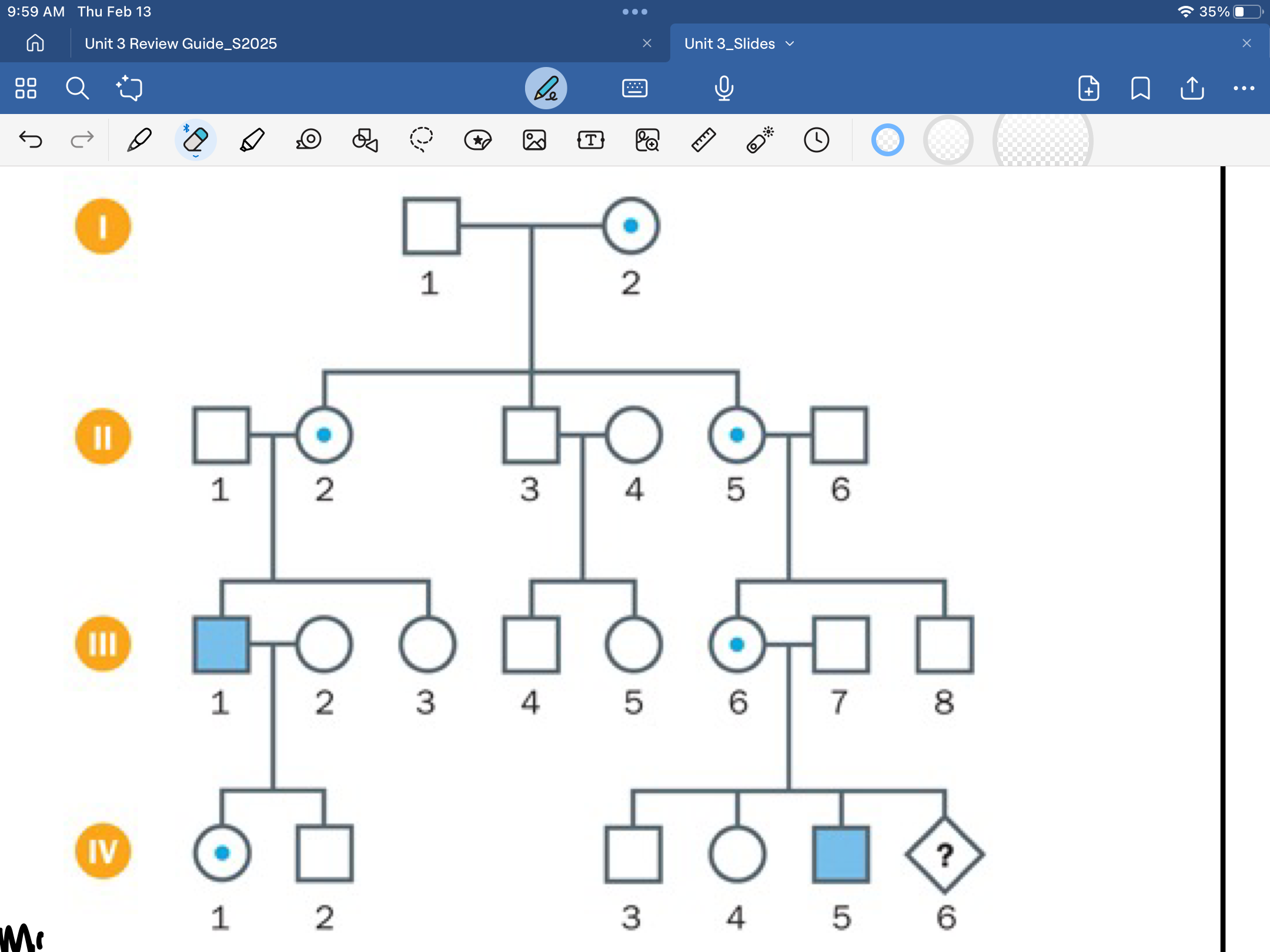
x-linked dominant pedigree
both sexes affected, doest skip generations, affected father=all daughters will be affected
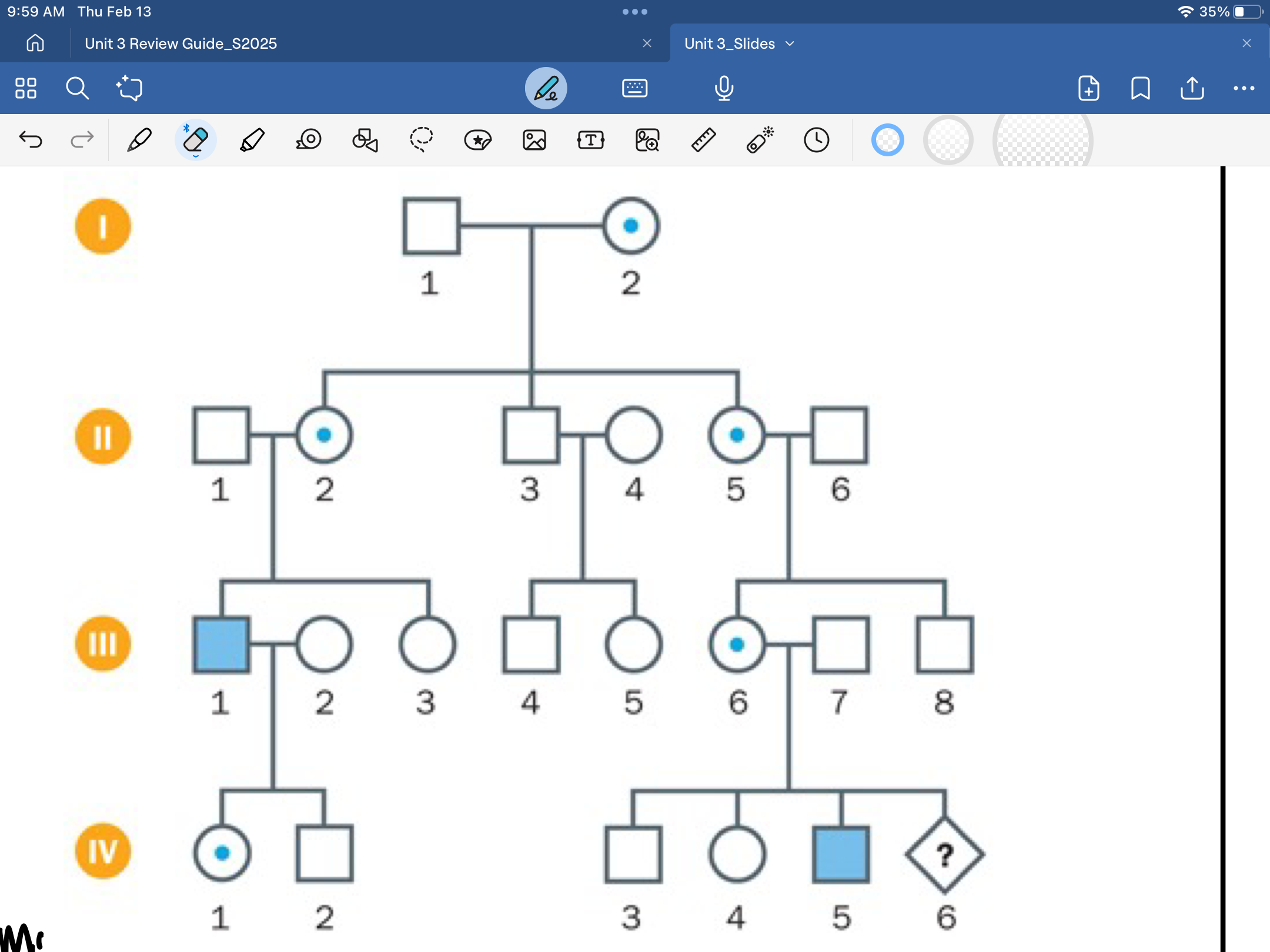
x-linked recessive pedigree
males affected more often than females, skips generations, mothers must be carriers for male to be affected, affected dad+carrier mom=affected daughter
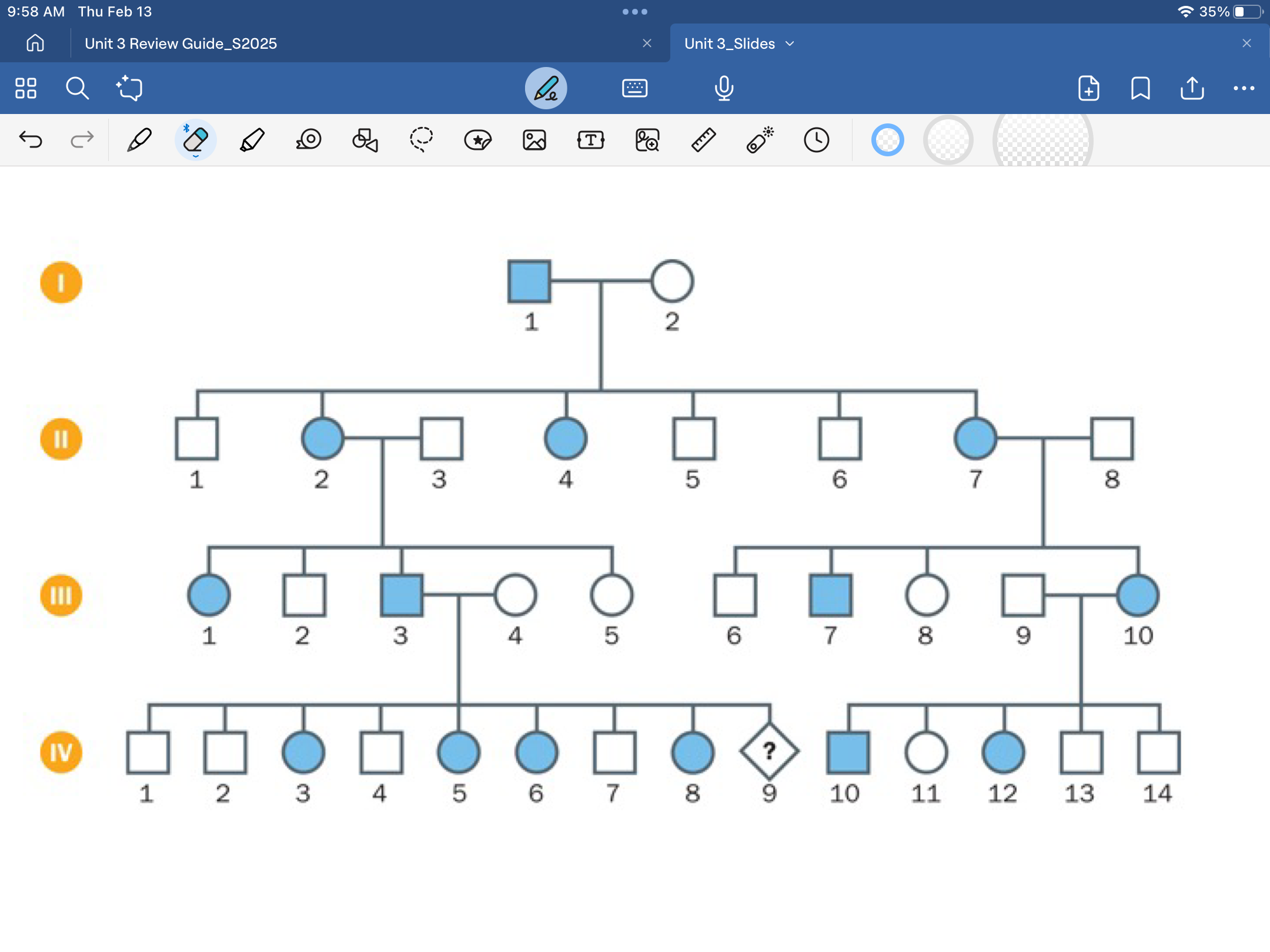
y-linked pedigree
only males will be affected, doesnt skip generations
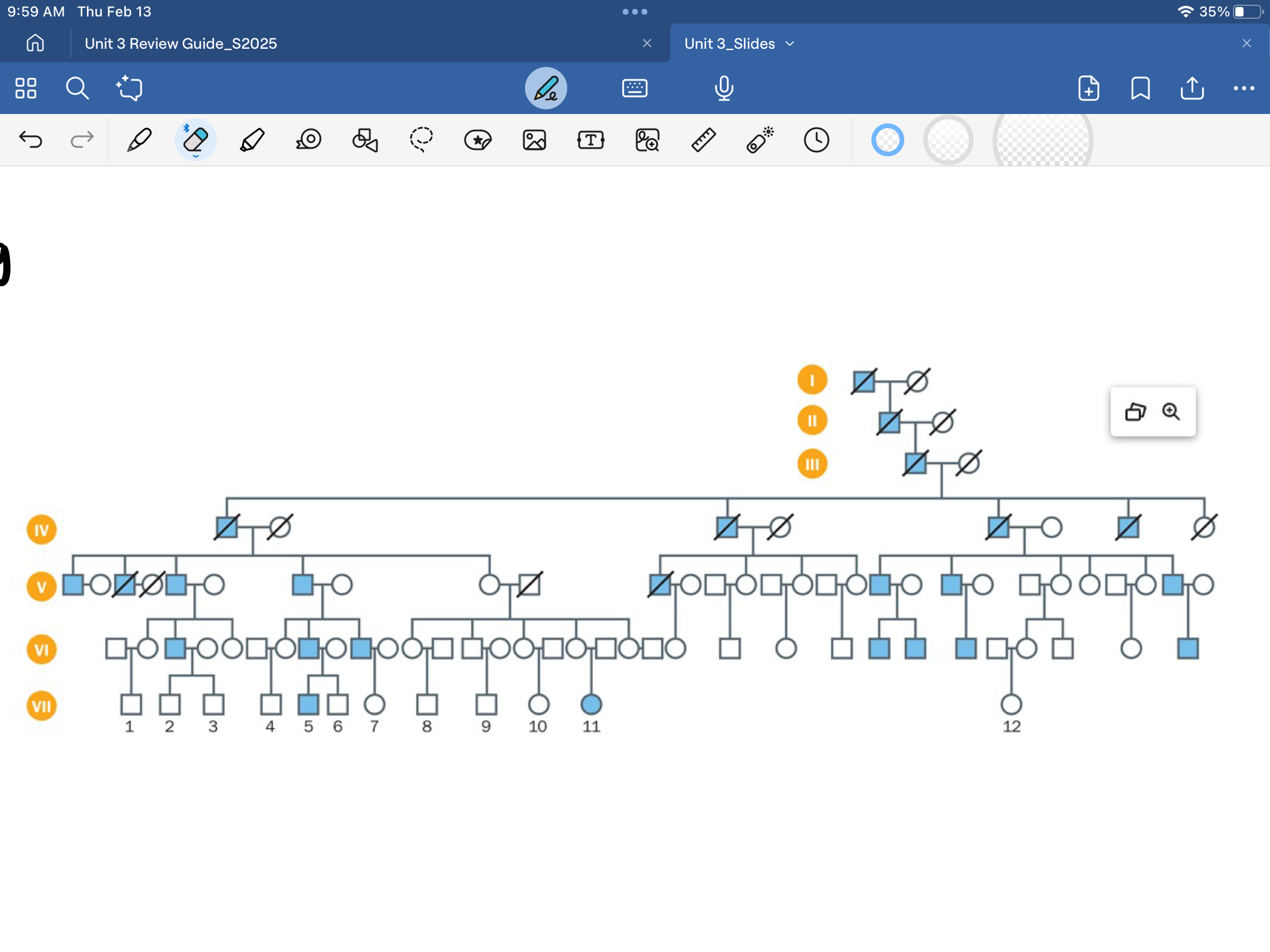
problems of age-related penetrance and single gene disorders
disease phenotype not expressed until older, has time to reproduce offspring before knowing disease exists
male lethality in x-linked disorders
males often die before birth
mosaisism
phenotype is only shown in certain areas