Unit 2 Building Blocks of Matter: Particles DOVES
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
atom
Smallest particle of an element
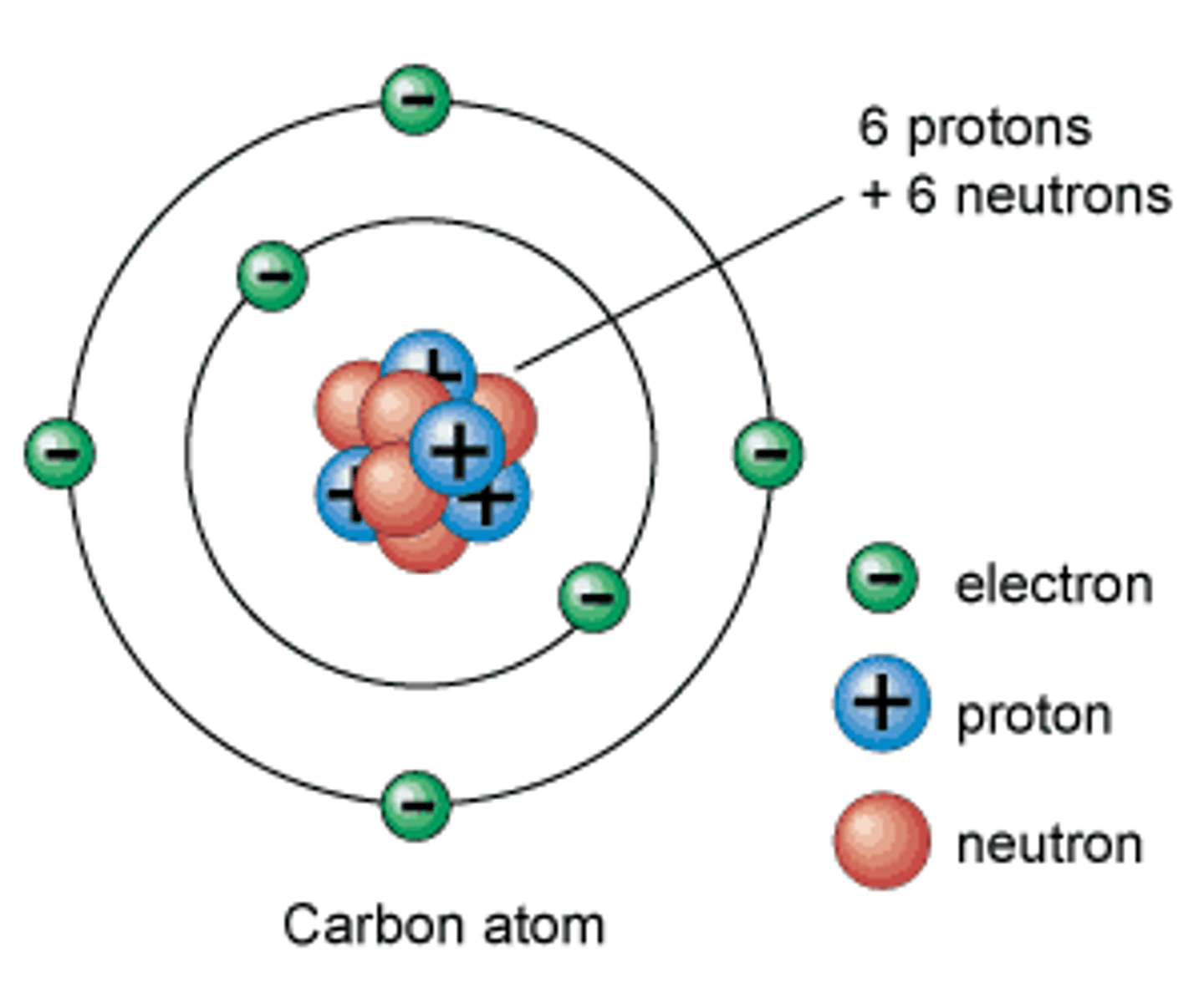
electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
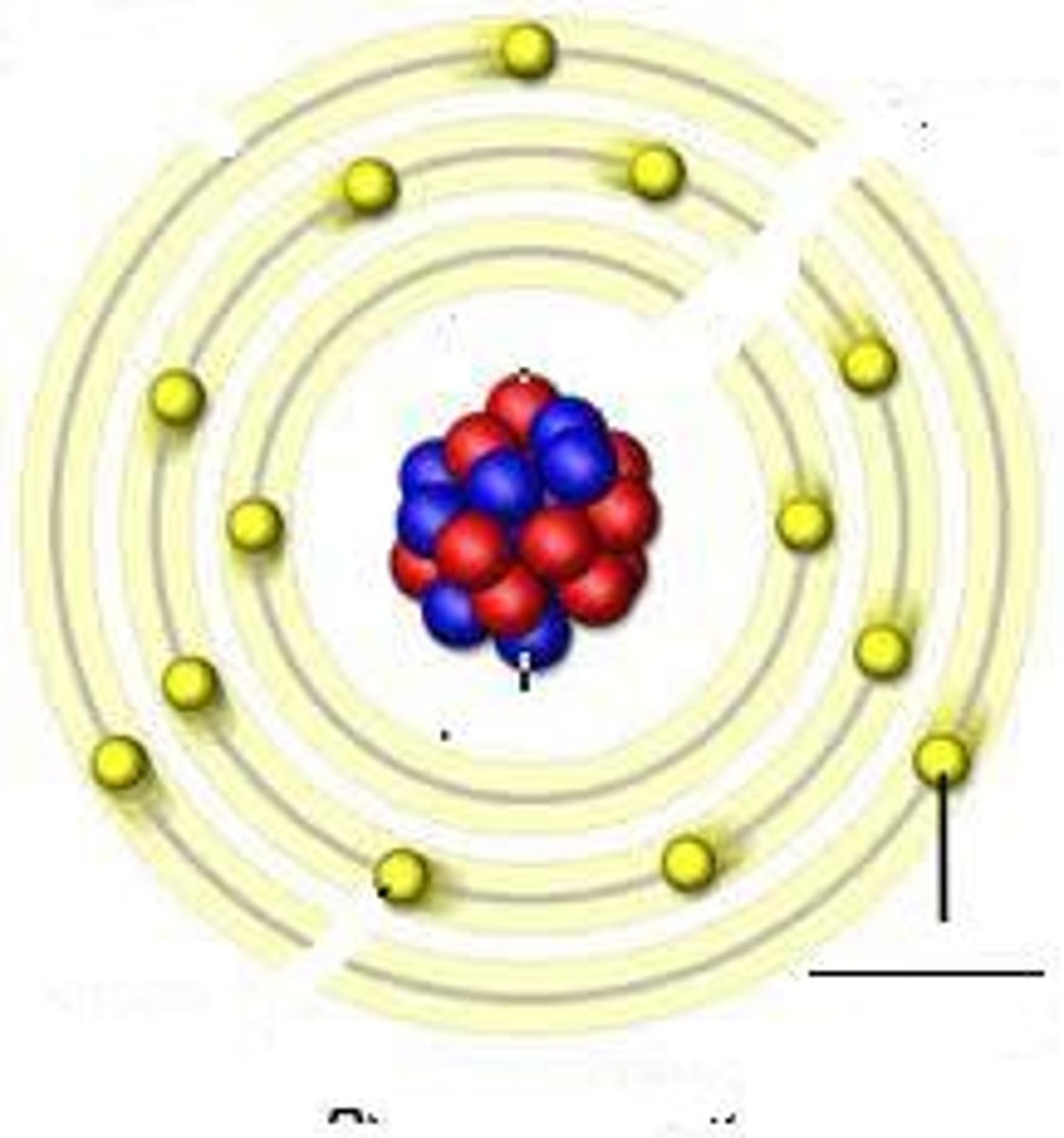
proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
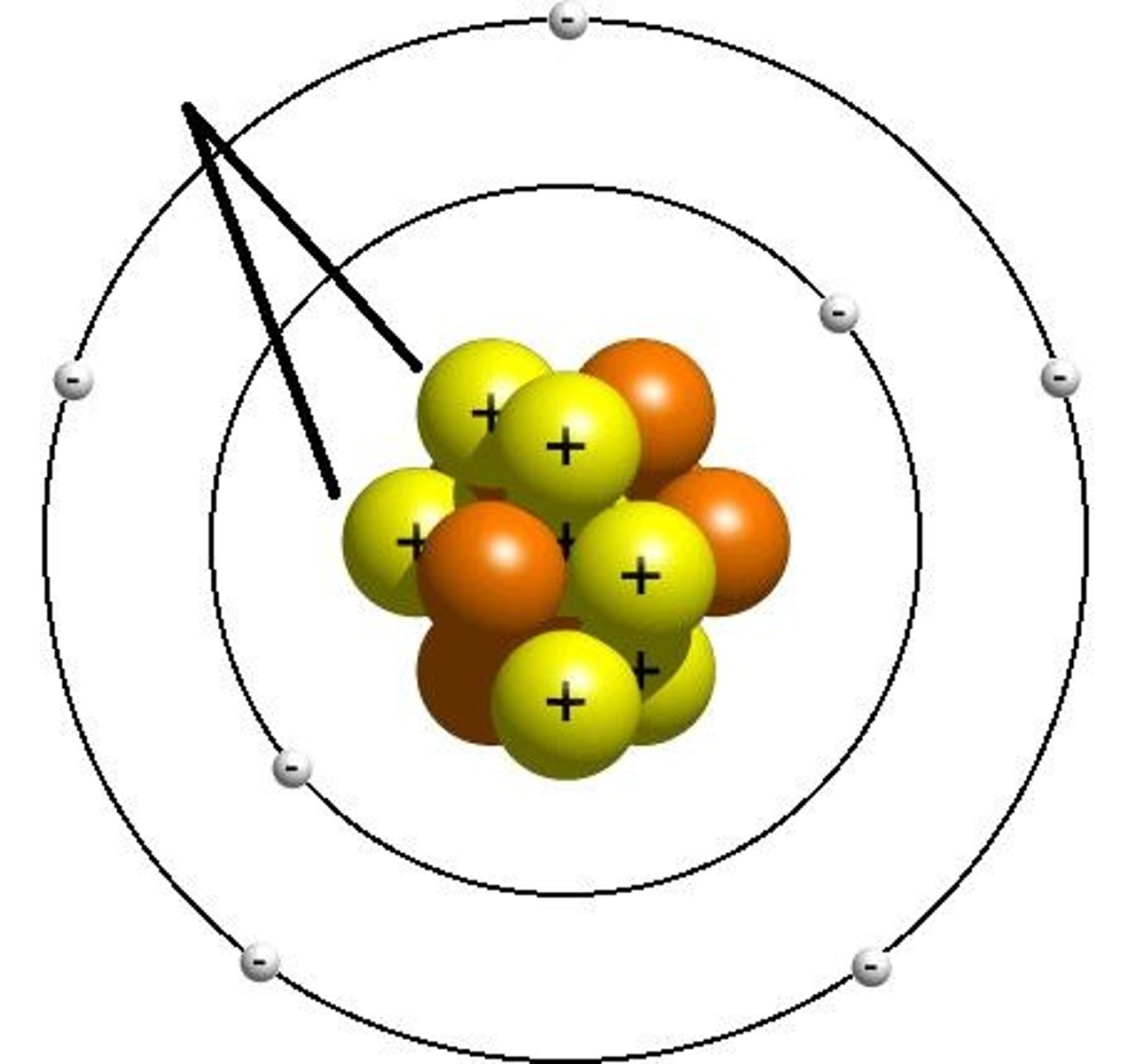
neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
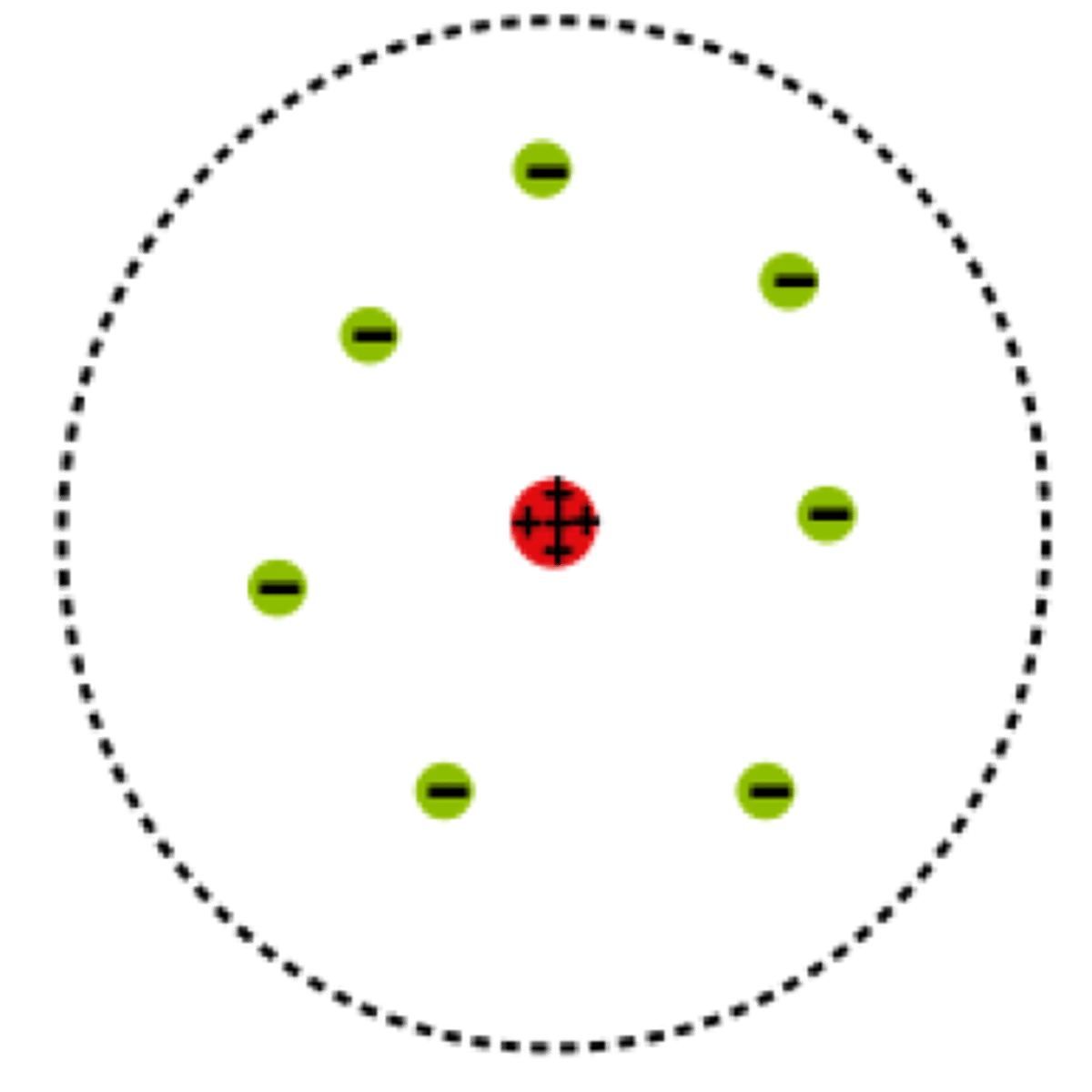
nucleus
Center of an atom
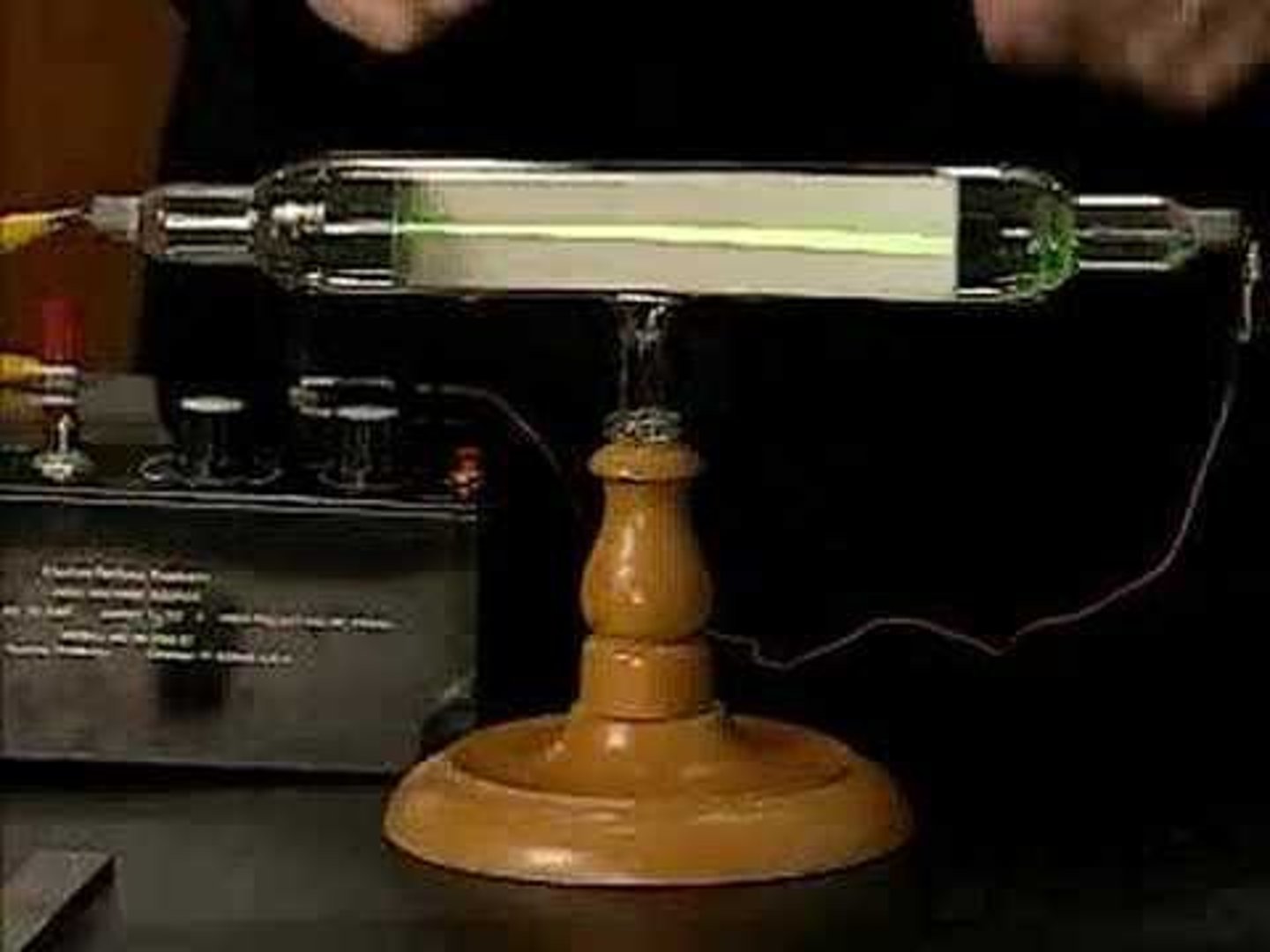
cathode ray
a stream of electrons produced at the negative electrode of a tube containing a gas at low pressure

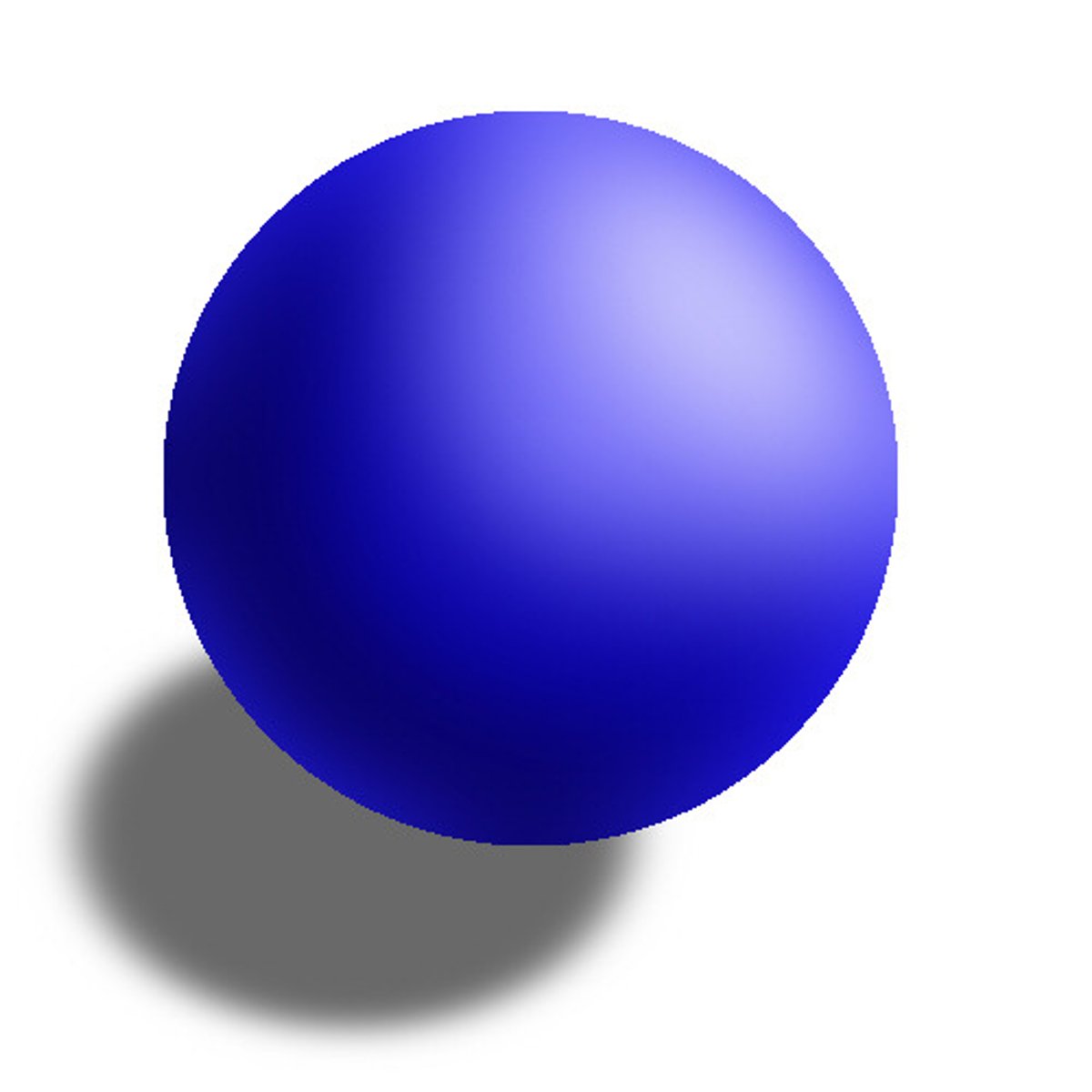
Solid Sphere Model
Dalton- an atom is little more than a singular, solid particle without other components.

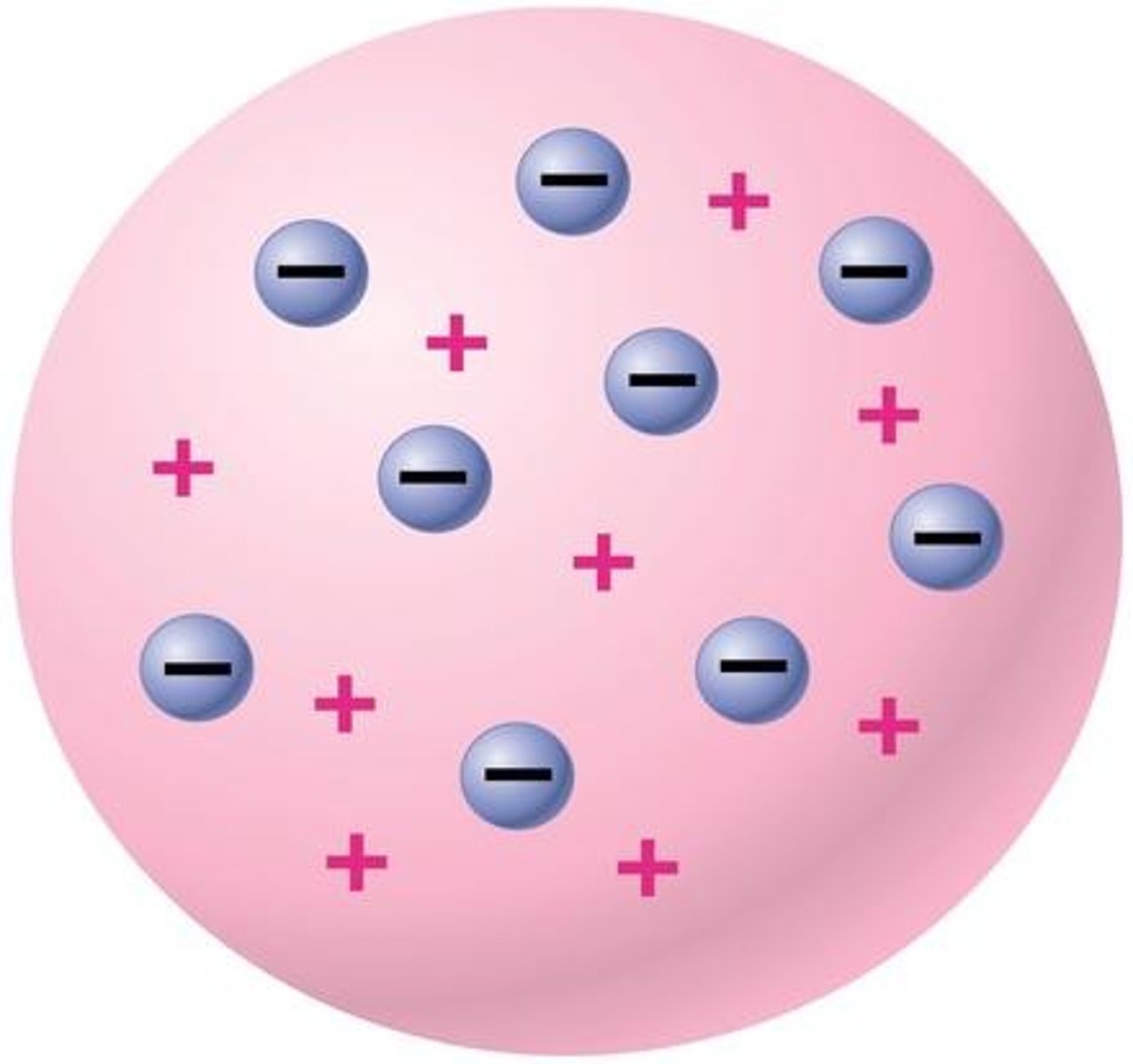
Plum Pudding Model
J.J Thomsons model of an atom, in which he thought electrons were randomly distributed within a positively charged cloud
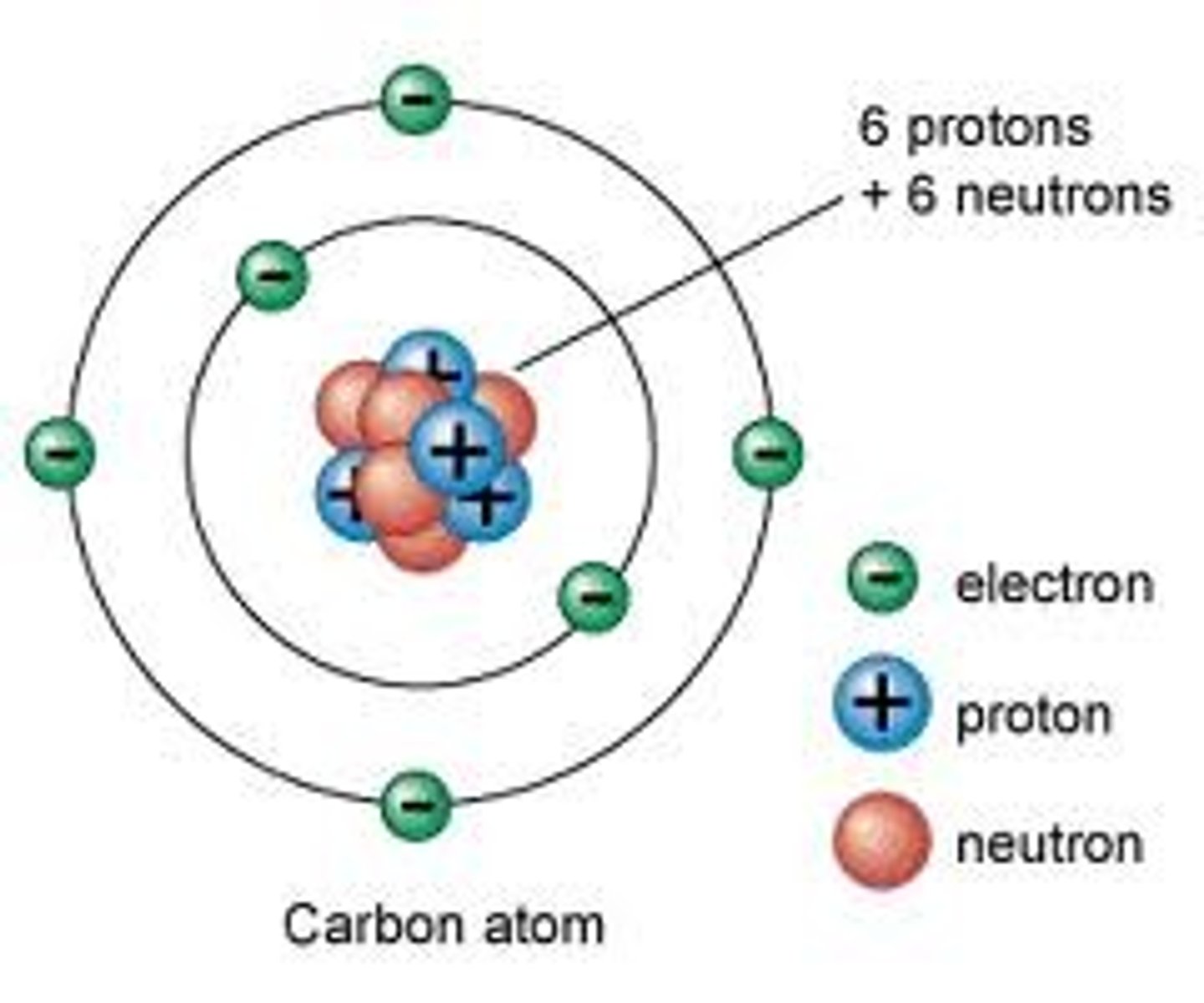
Nuclear Model
Rutherford's model of the atom with a nucleus containing protons and neutrons and with electrons in the space outside the nucleus
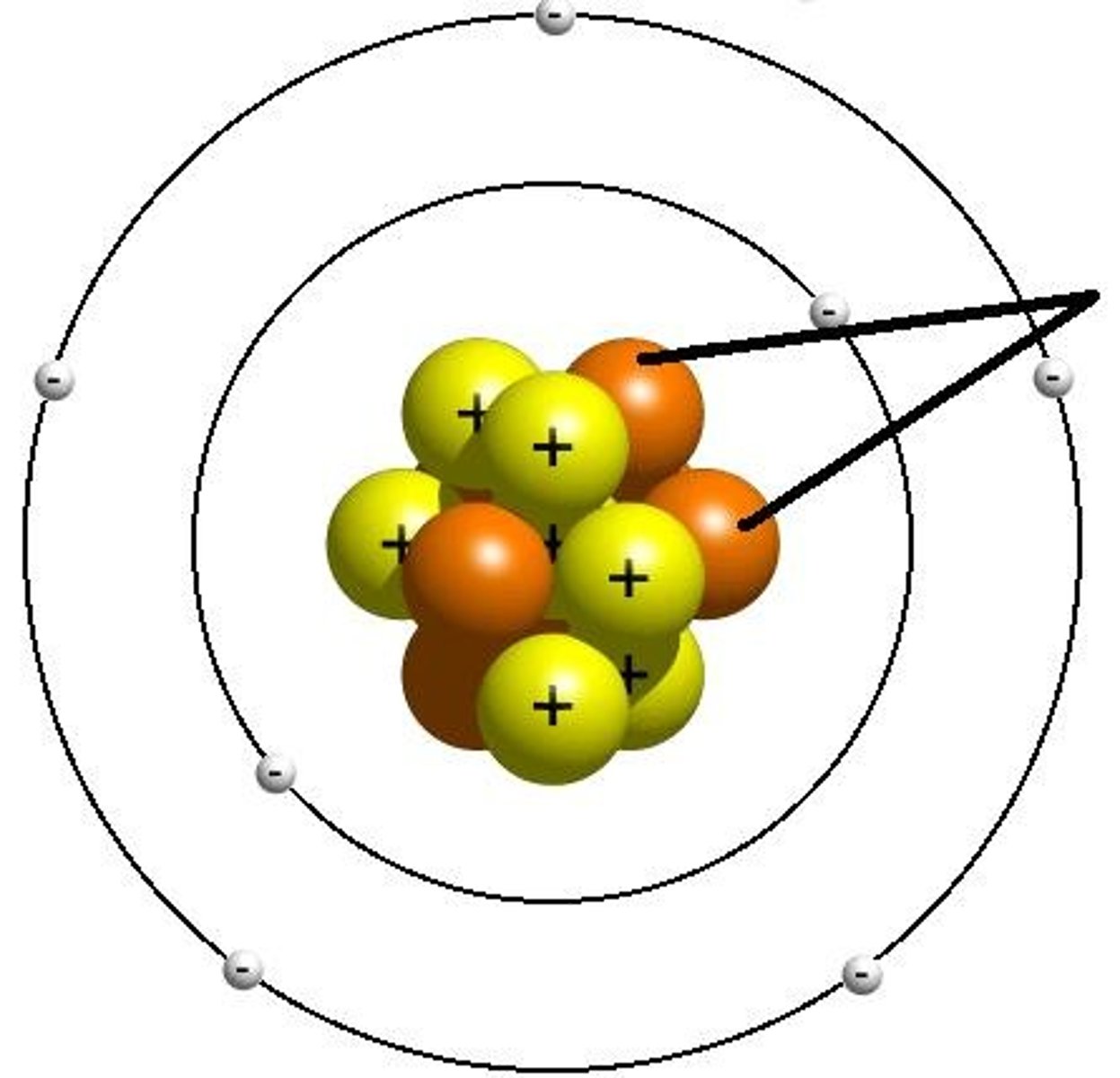
planetary model
Bohr's model - electrons move around the nucleus in fixed, circular orbits
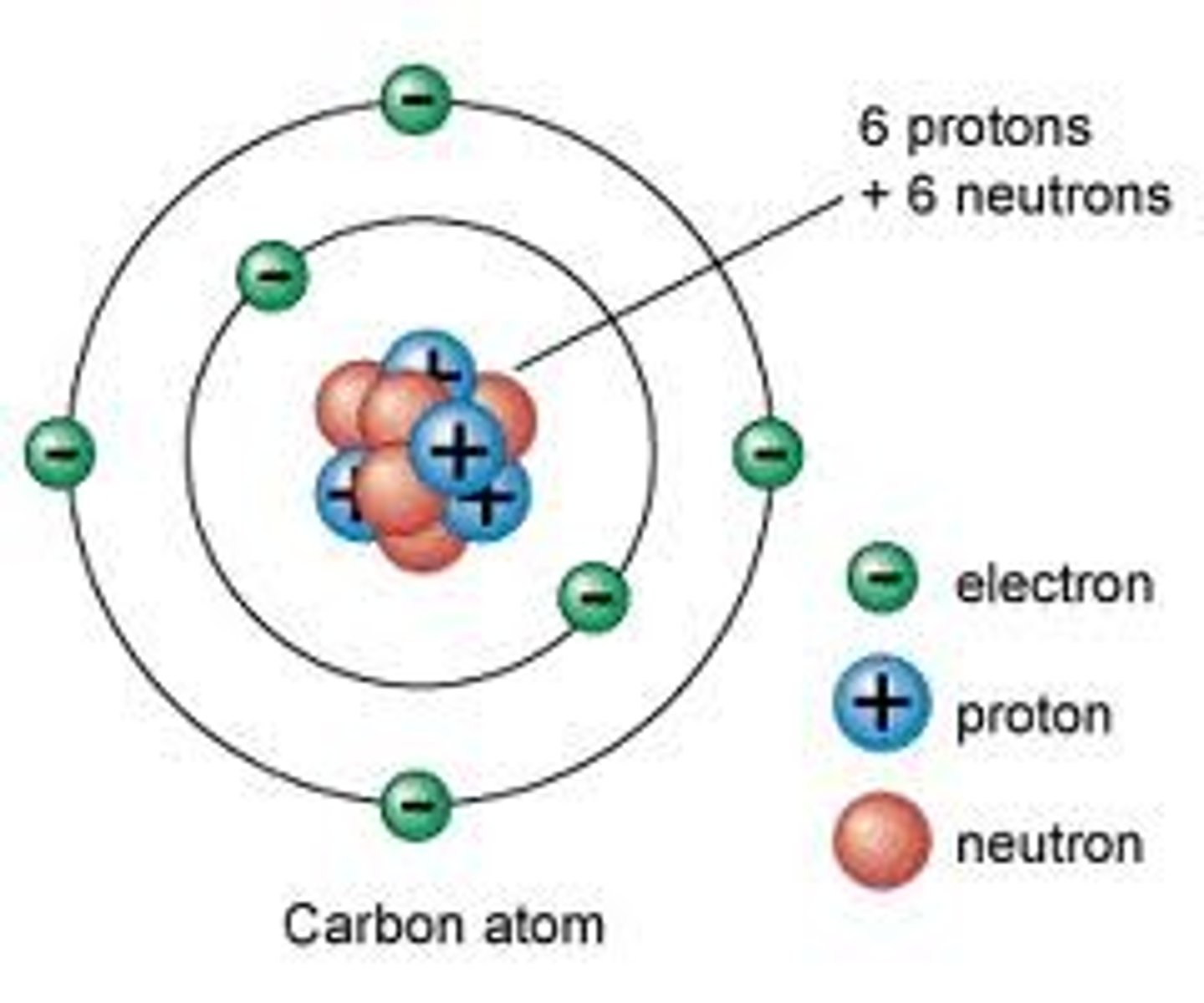
quantum model
Schrodinger's atomic model incorporating the wave aspect of matter and the probability of an electron's location
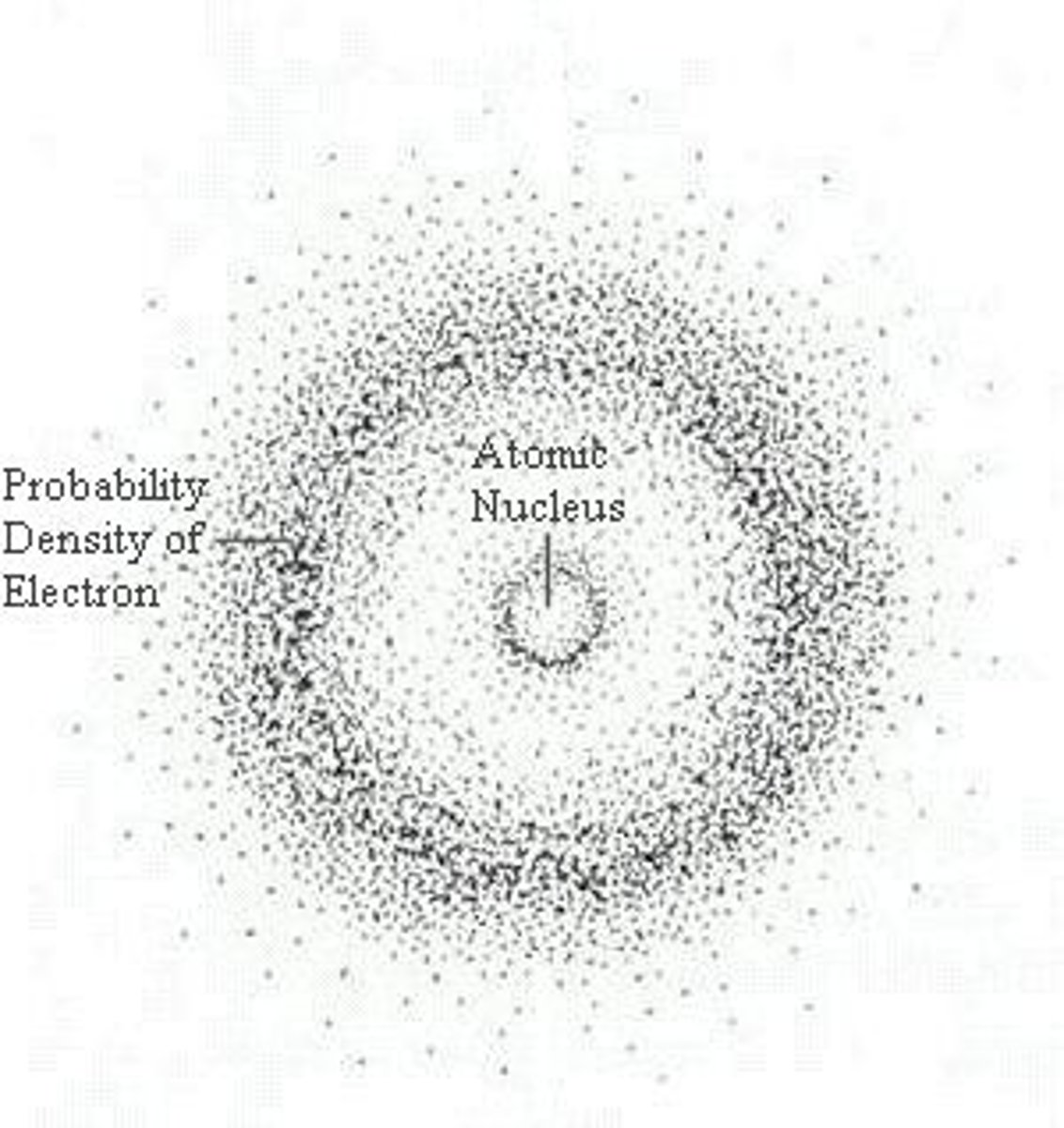
isotope
An atom with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons from other atoms of the same element.
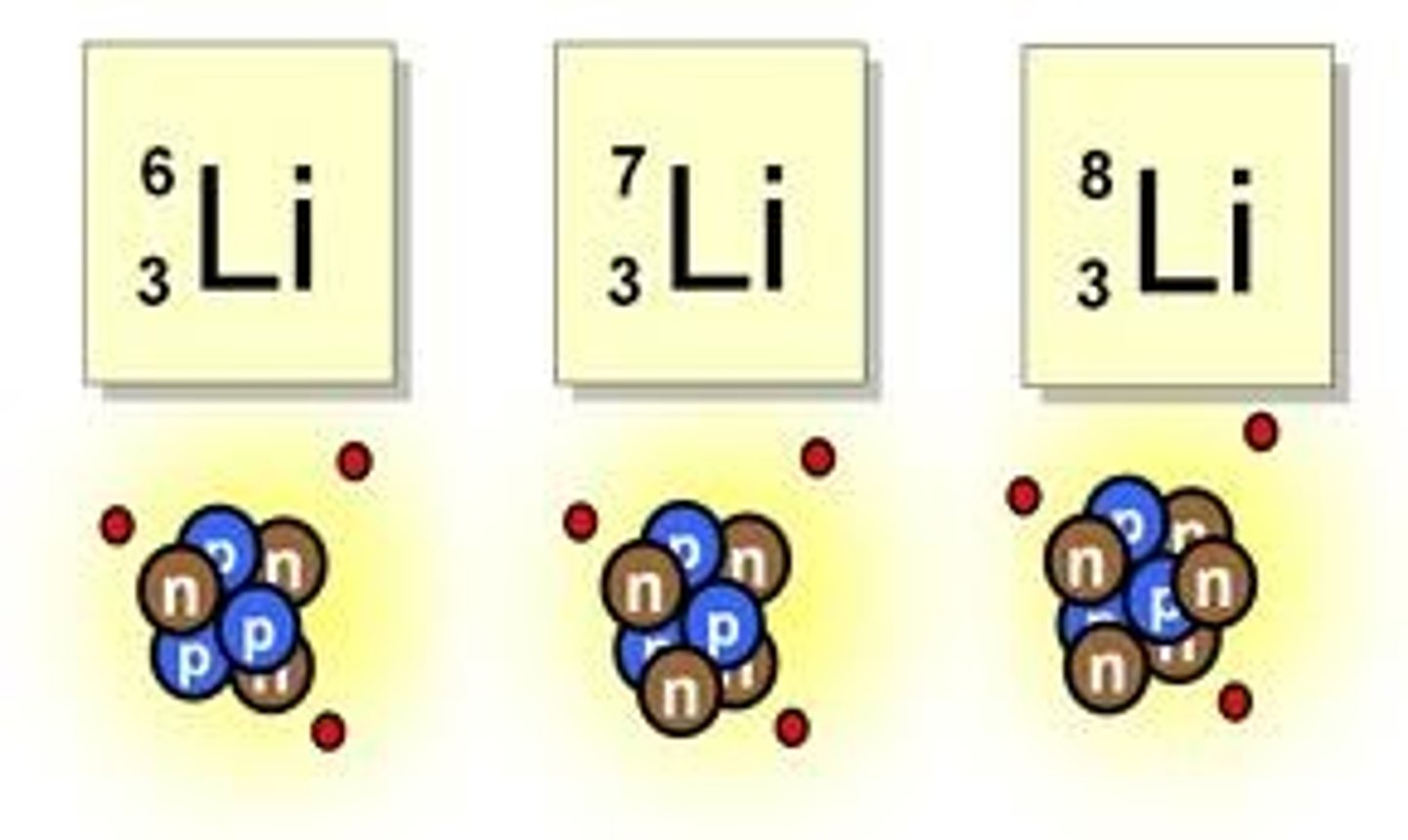
mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
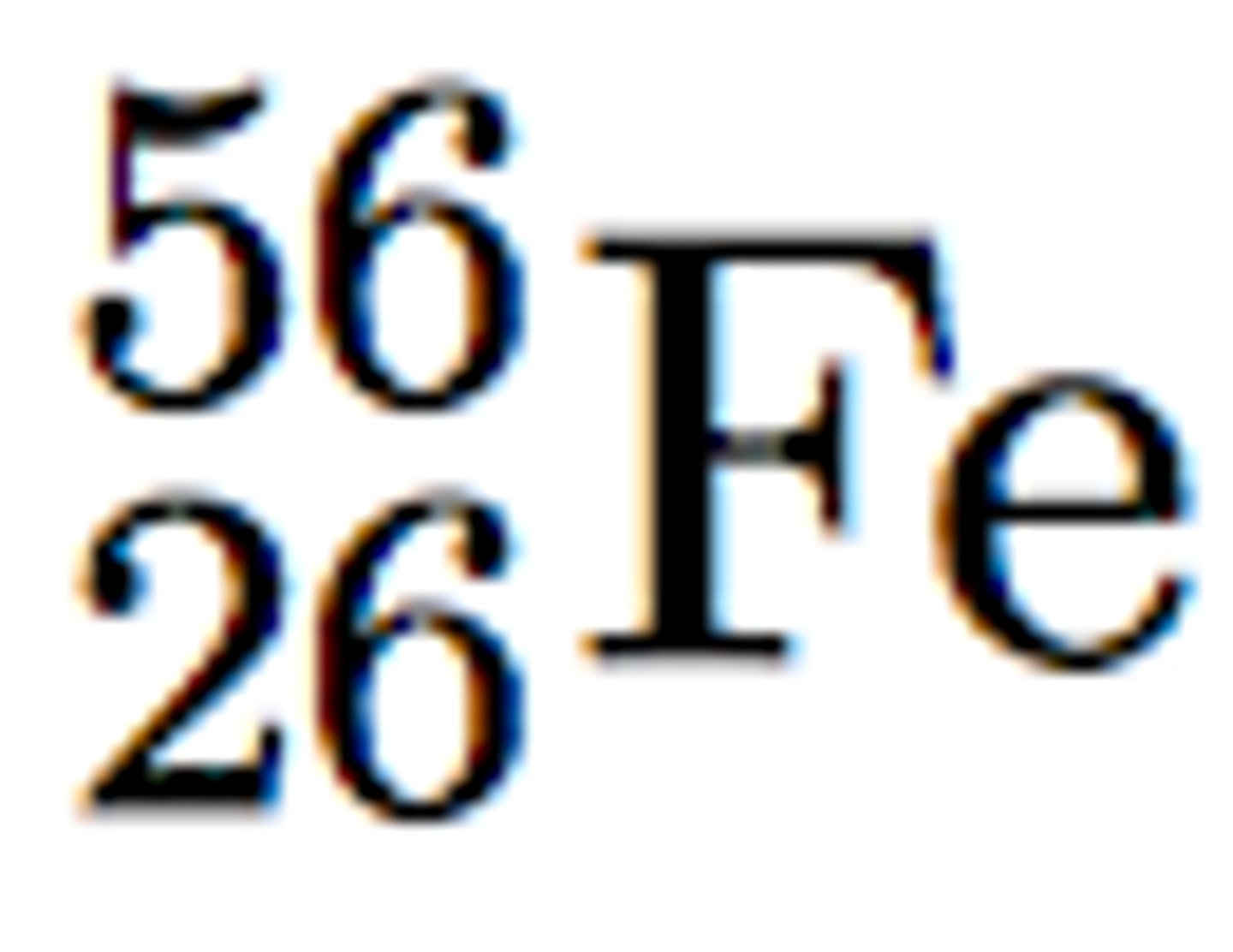
atomic mass unit
a unit of mass that describes the average mass of an atom's isotopes

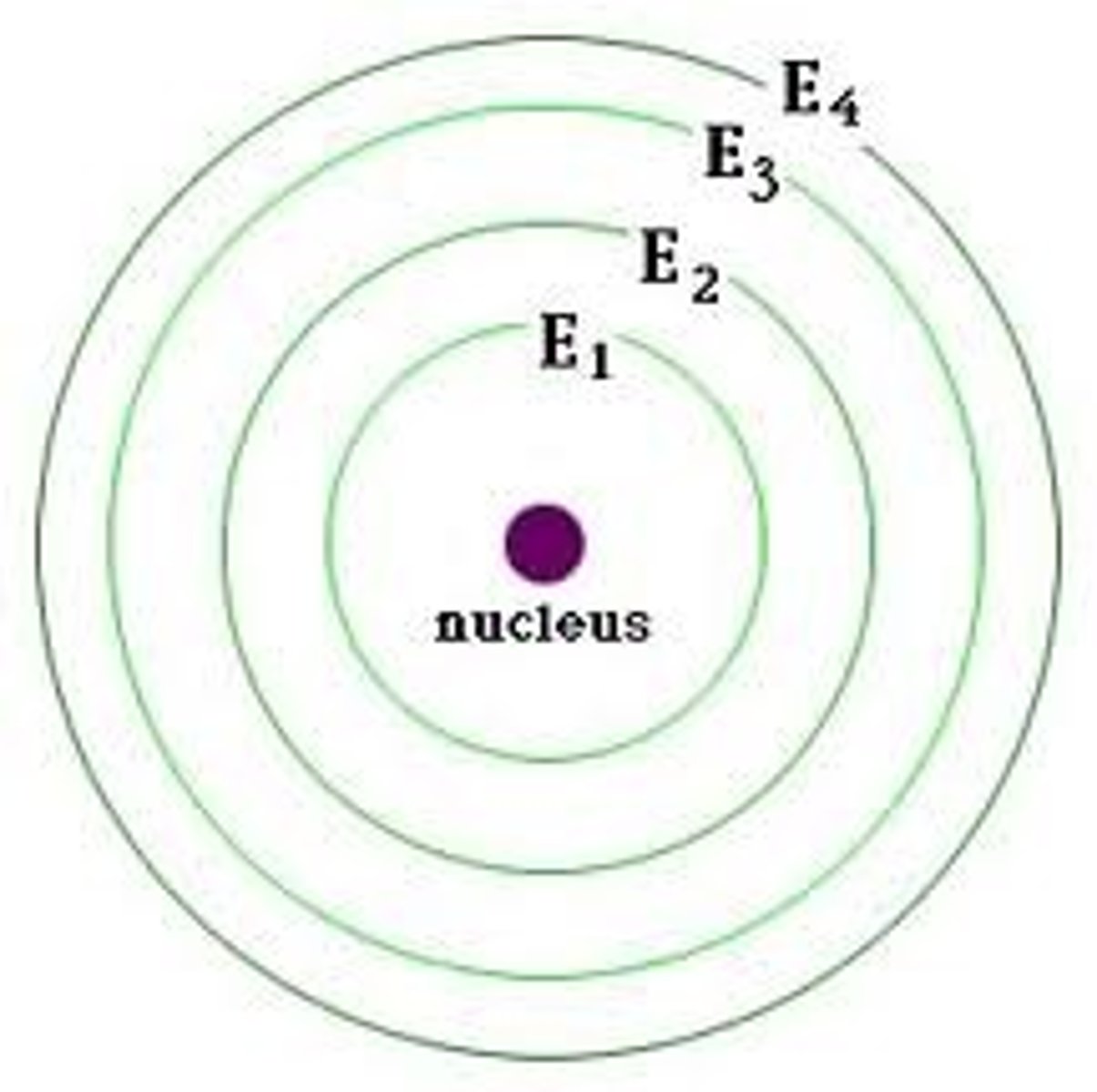
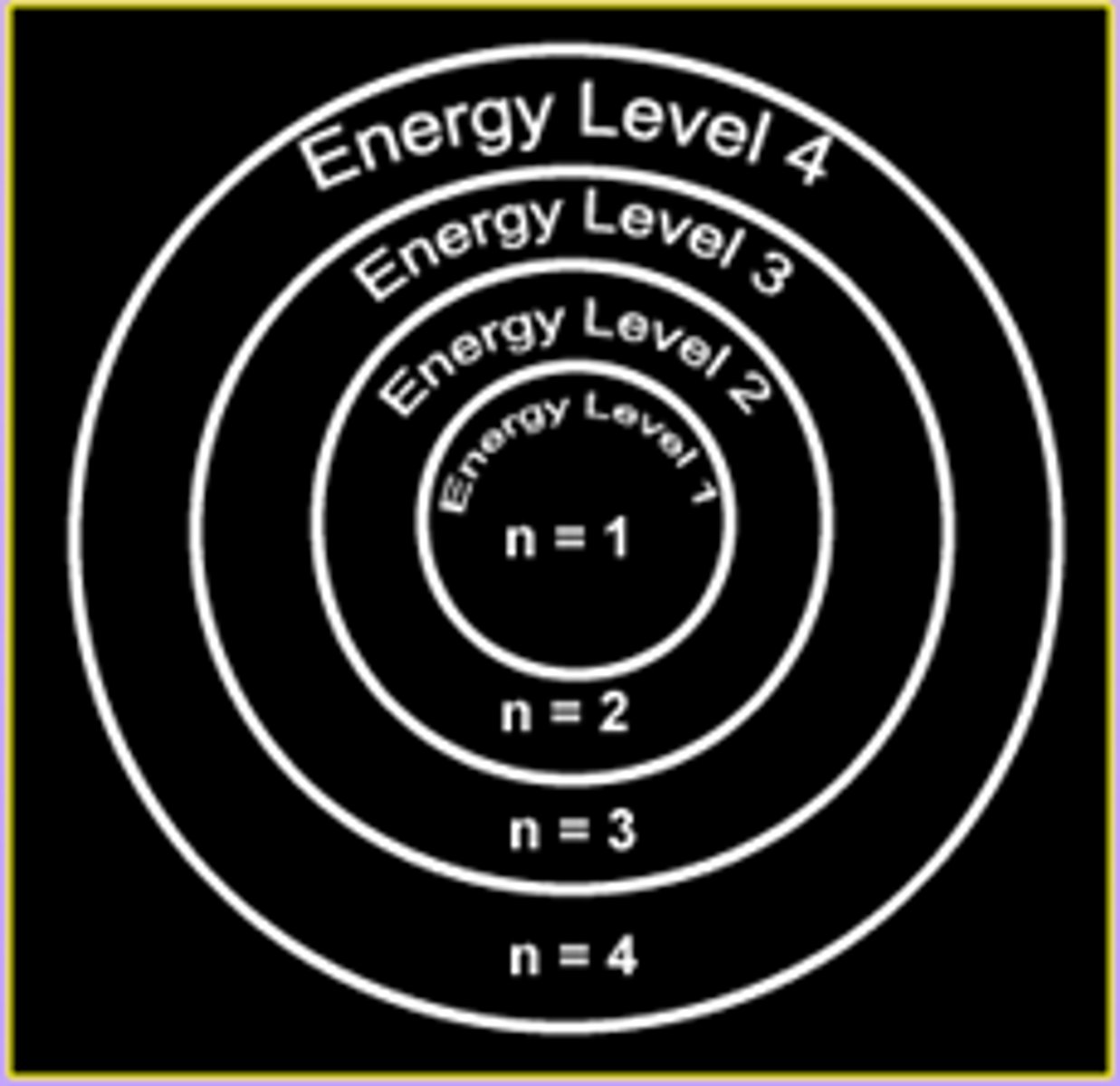
energy levels (shells)
surround the nucleus and contain electrons (nucleus- protons and neutrons, 1st level- 2 electrons, 2nd level- 8 electrons, 3rd level- 8 electrons
Sublevels (s, p, d, f)
a portion of a principal energy level made up of one or more orbitals
orbitals
regions around the nucleus in which given electron or electron pair is likely to be found
principle quantum number
symbolized by n, indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron
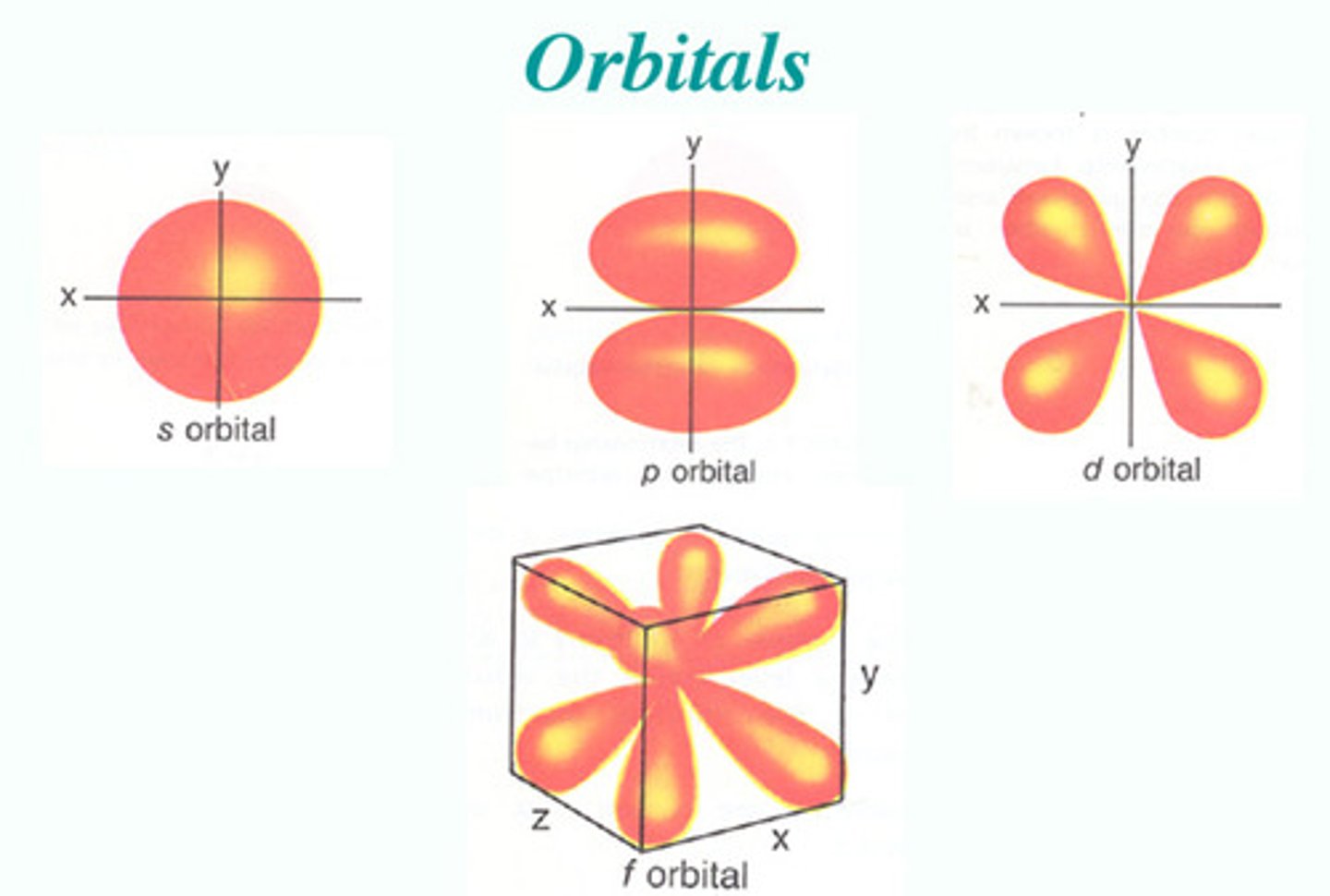
s orbital
Spherical shape and can hold up to 2 electrons
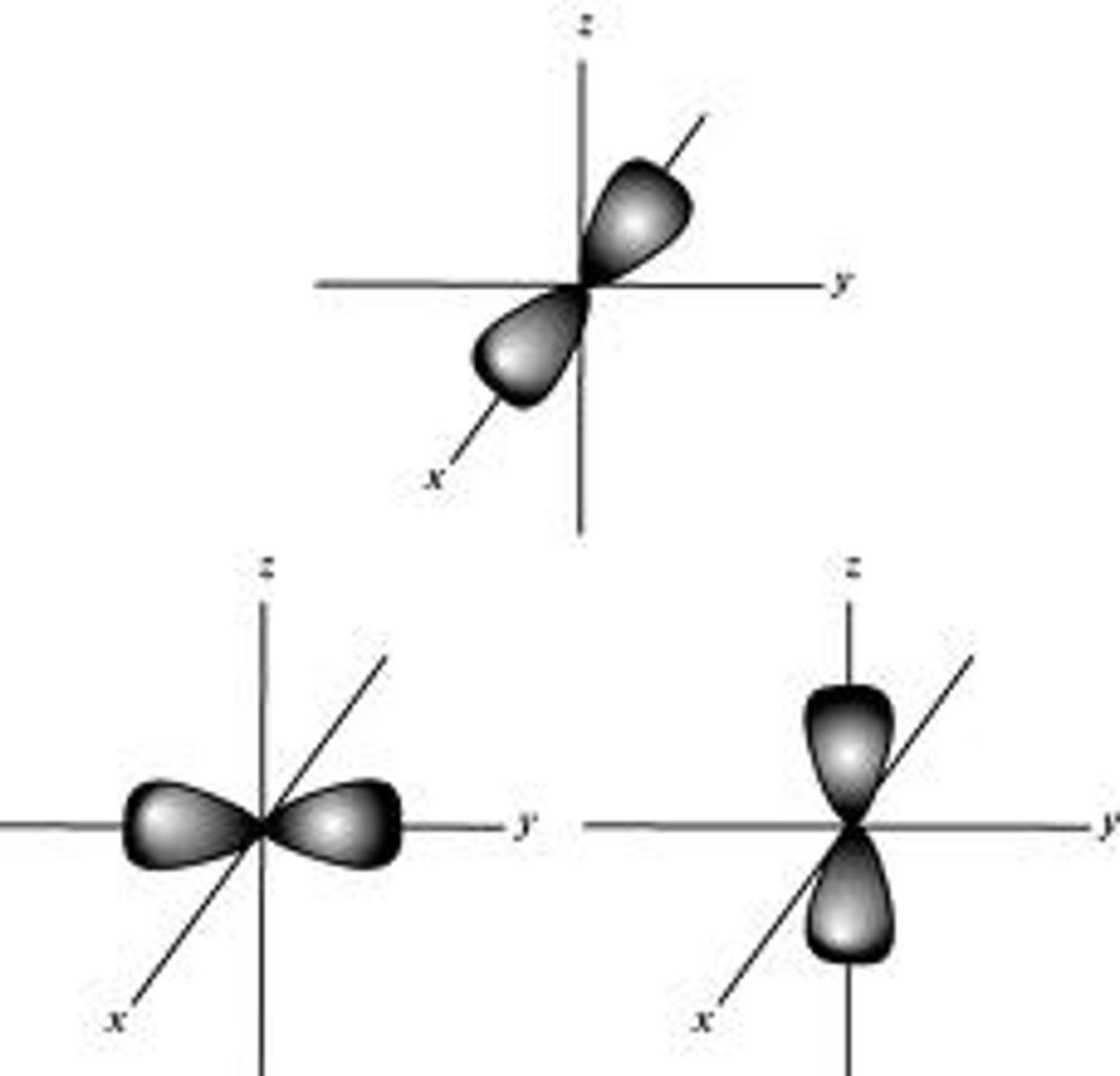
p orbital
peanut shape with 3 orientations and holds a total of 6 electrons
d orbital
daisy shaped has 5 orientations and holds 10 electrons
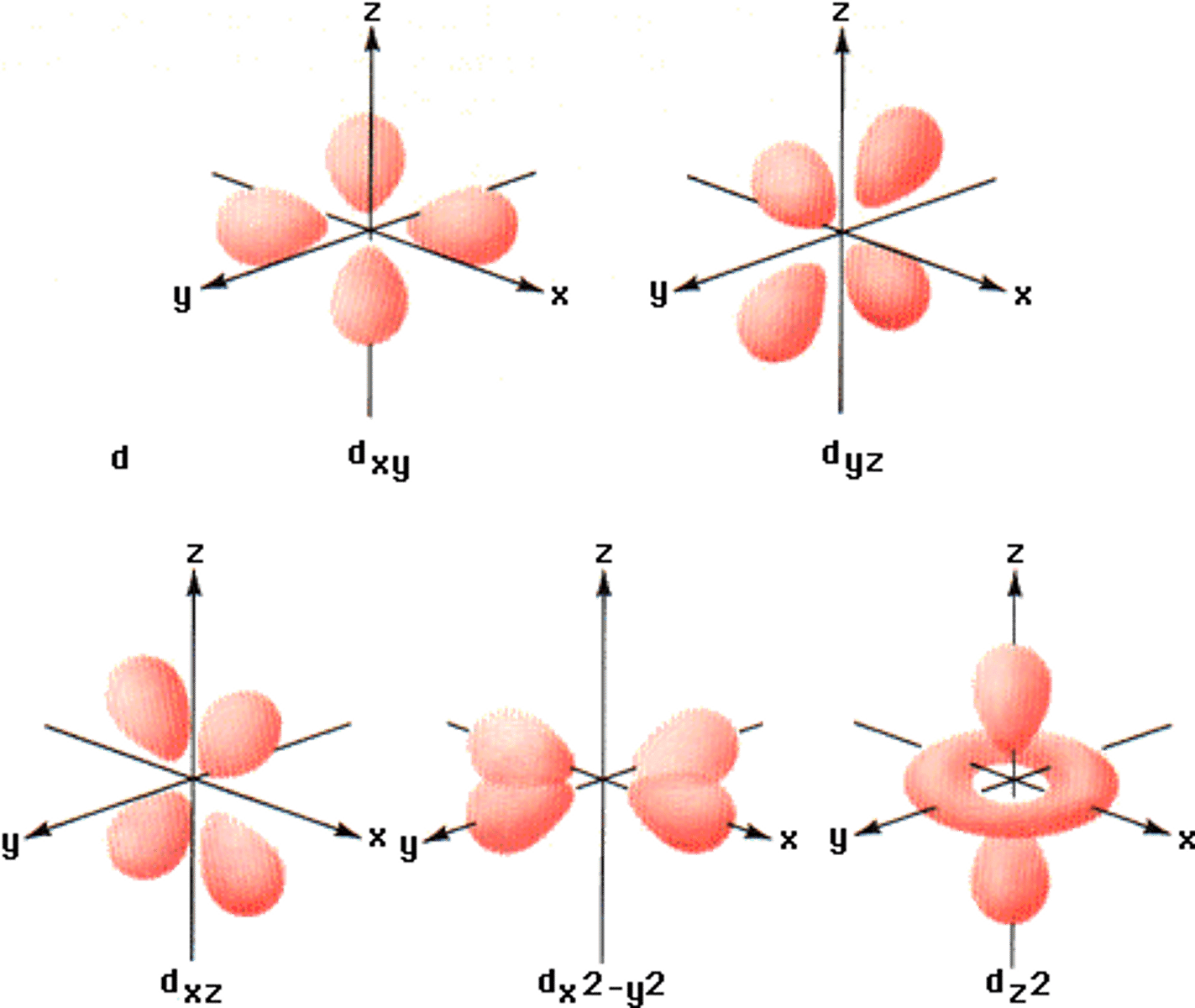
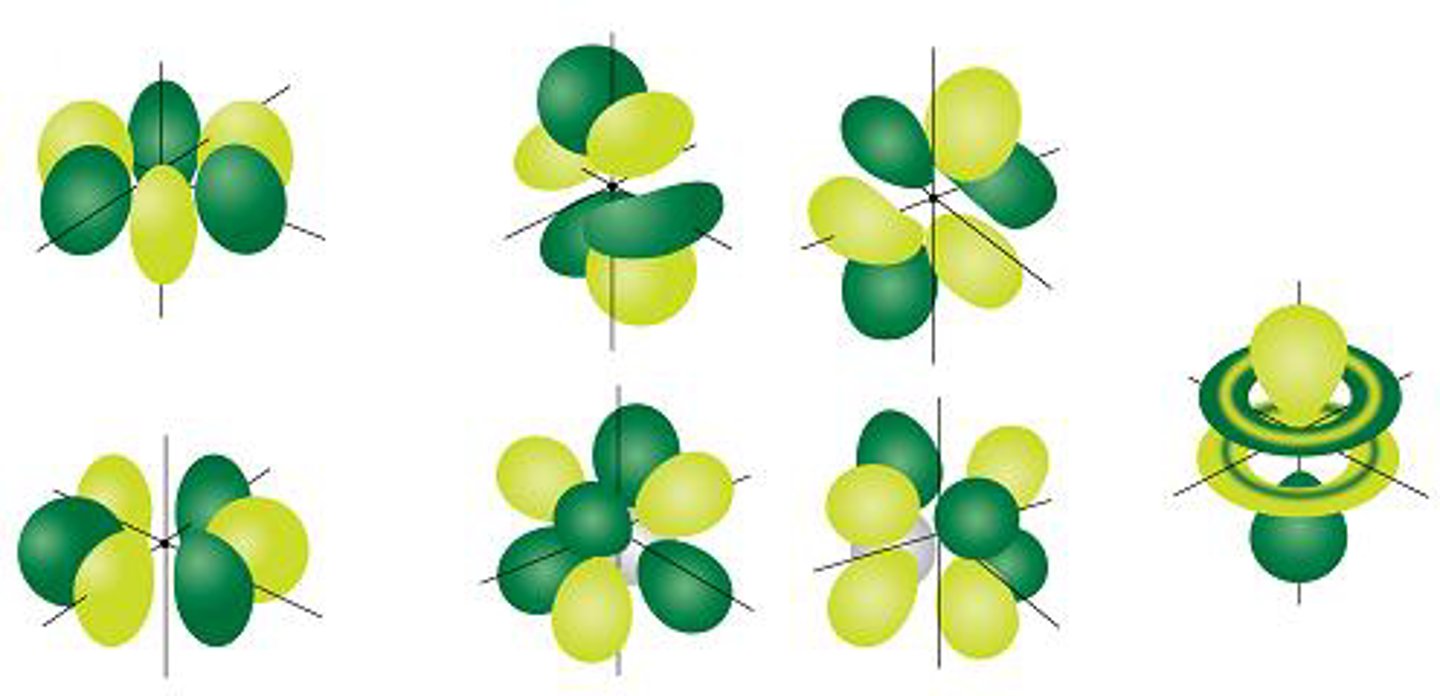
f orbital
large flower shape has 7 orientations and holds 14 electrons
Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it

Pauli Exclusion Principle
An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons, each with opposite spin direction
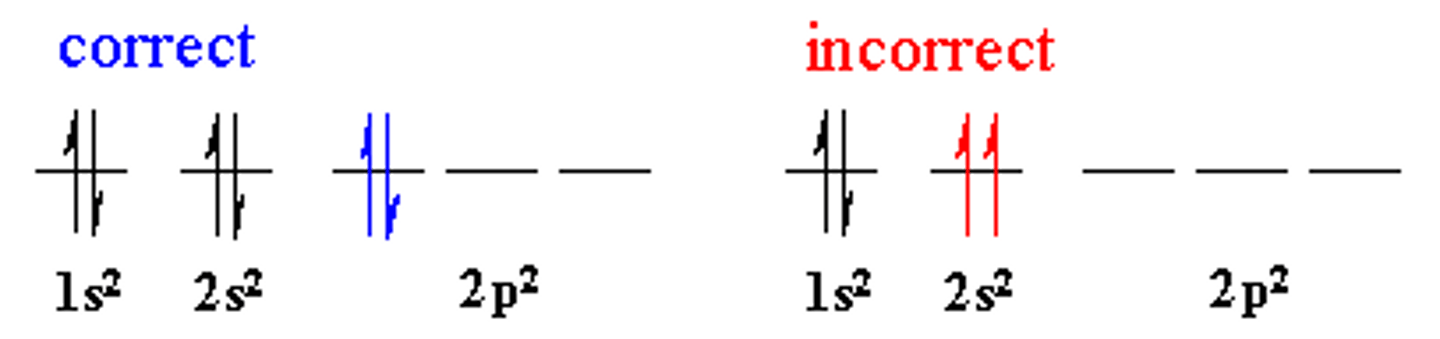
Hund's Rule
orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals must have the same spin
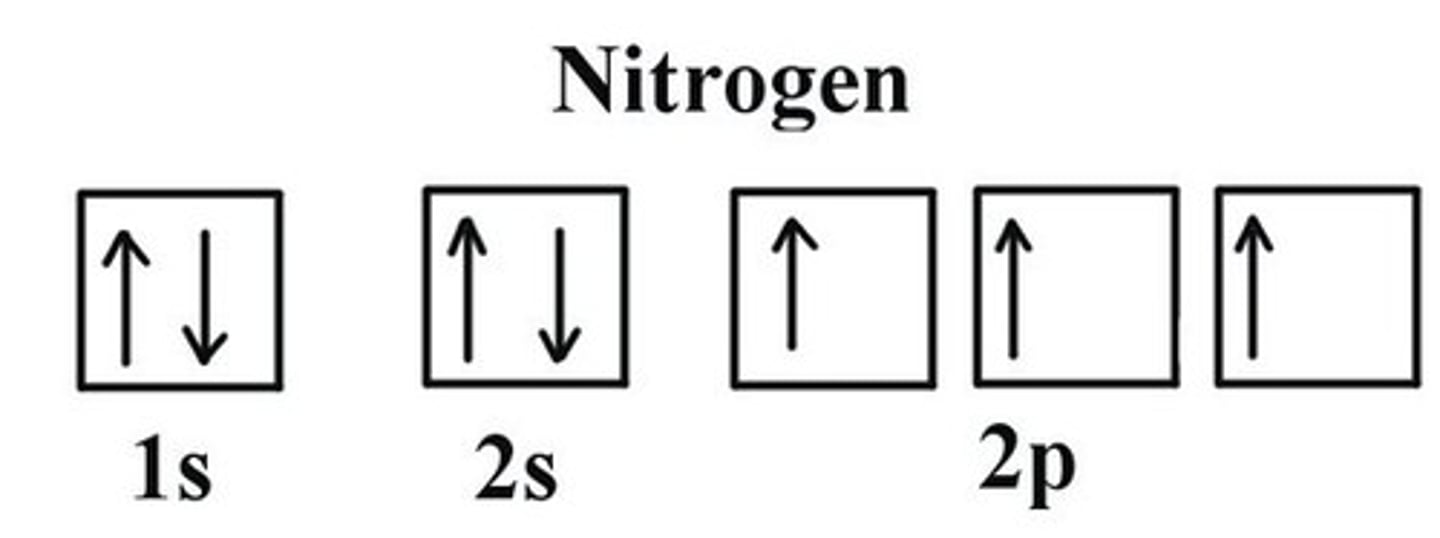
electron configuration
the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom
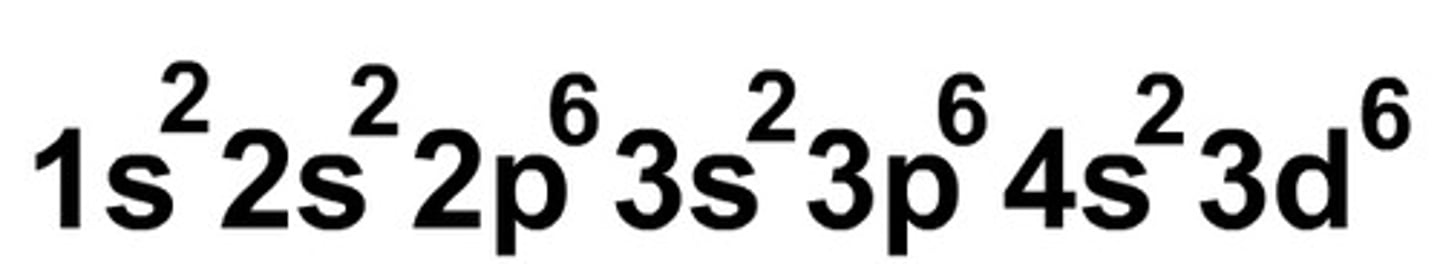
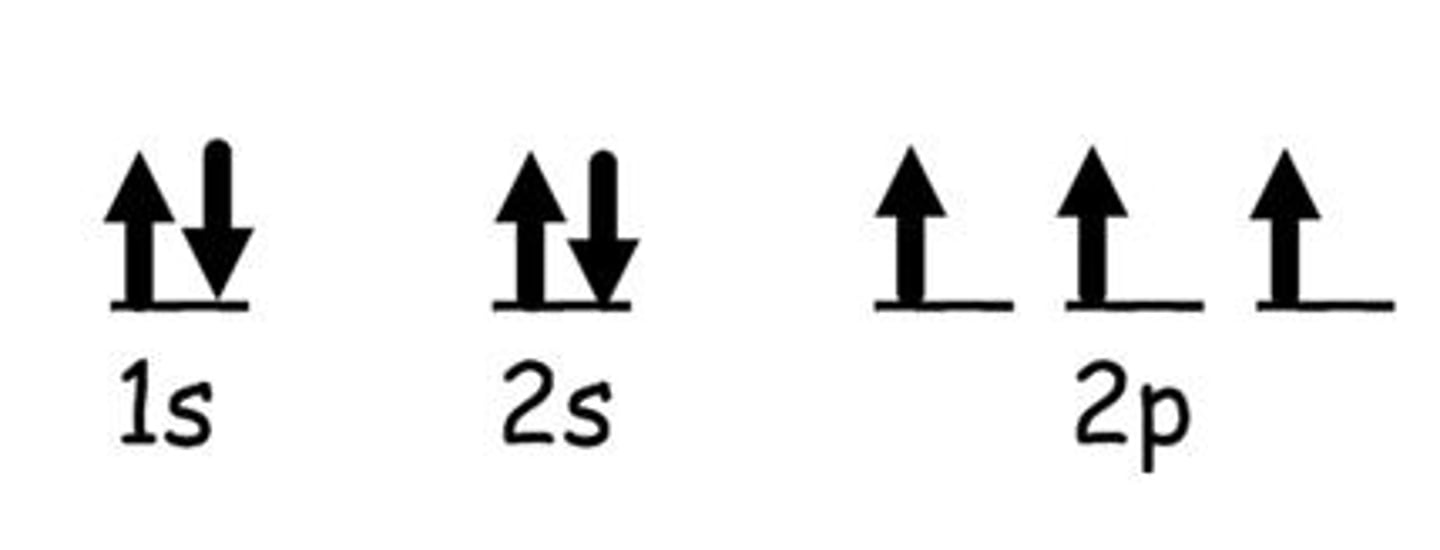
orbital notation
uses arrows pointing up or down to represent the electrons
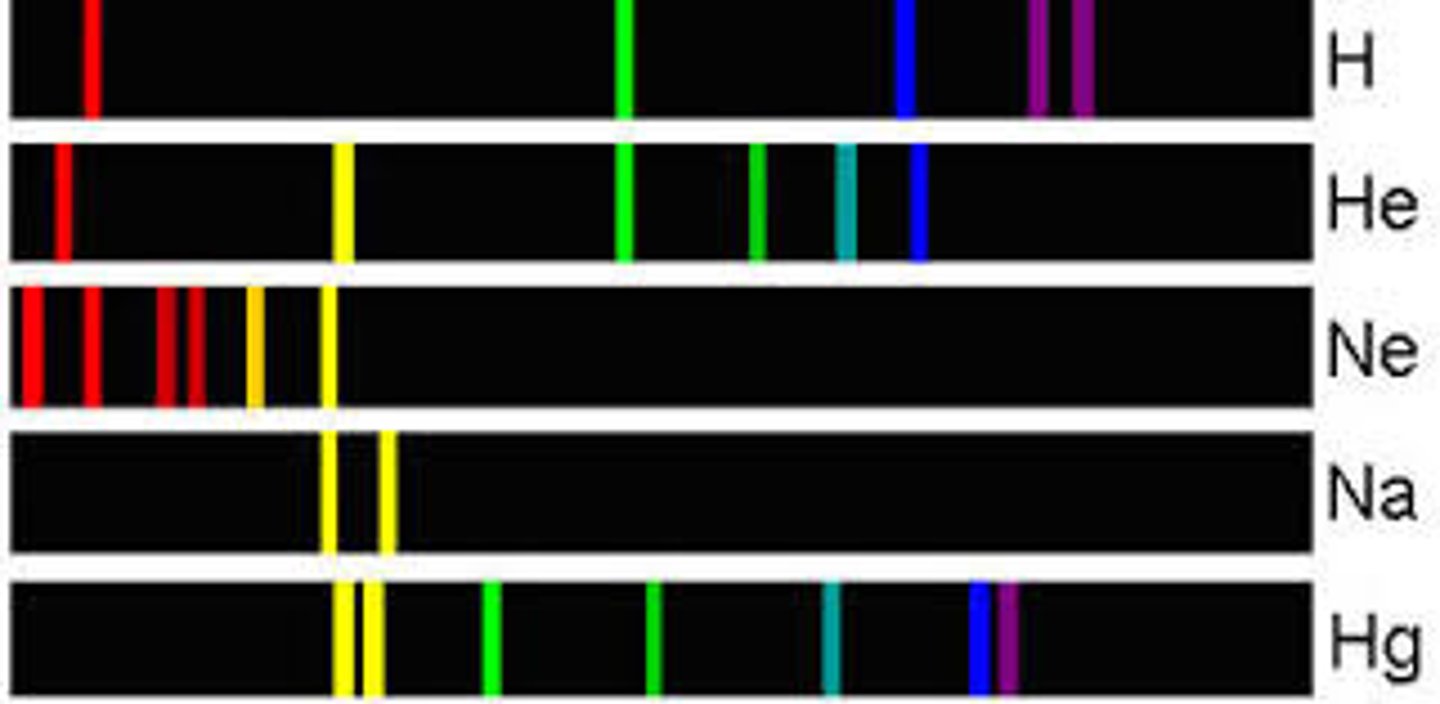
atomic emission spectrum
the set of frequencies of the electromagnetic waves emitted by atoms of the element
Mendeleev
Russian chemist who developed a periodic table of the chemical elements and predicted the discovery of several new elements

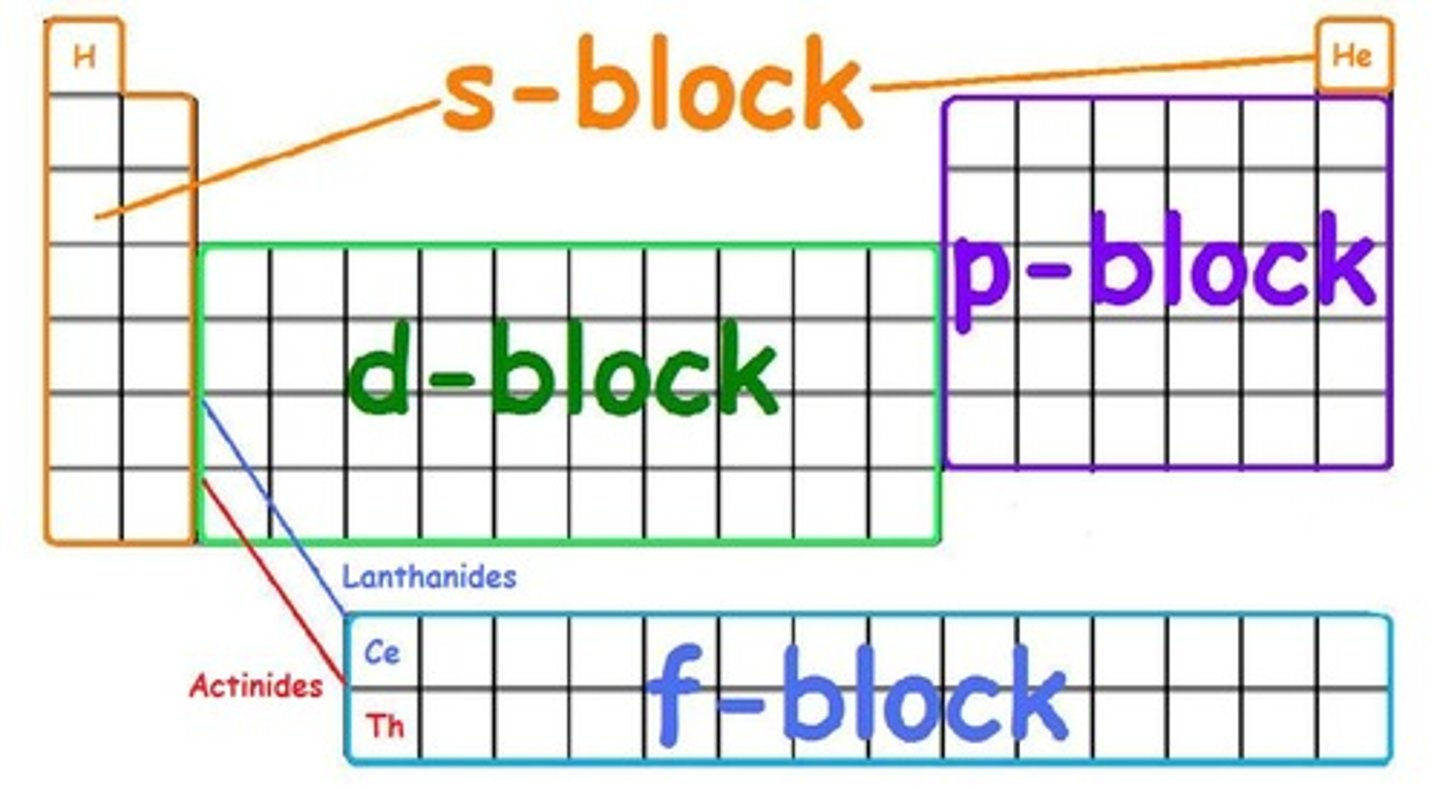
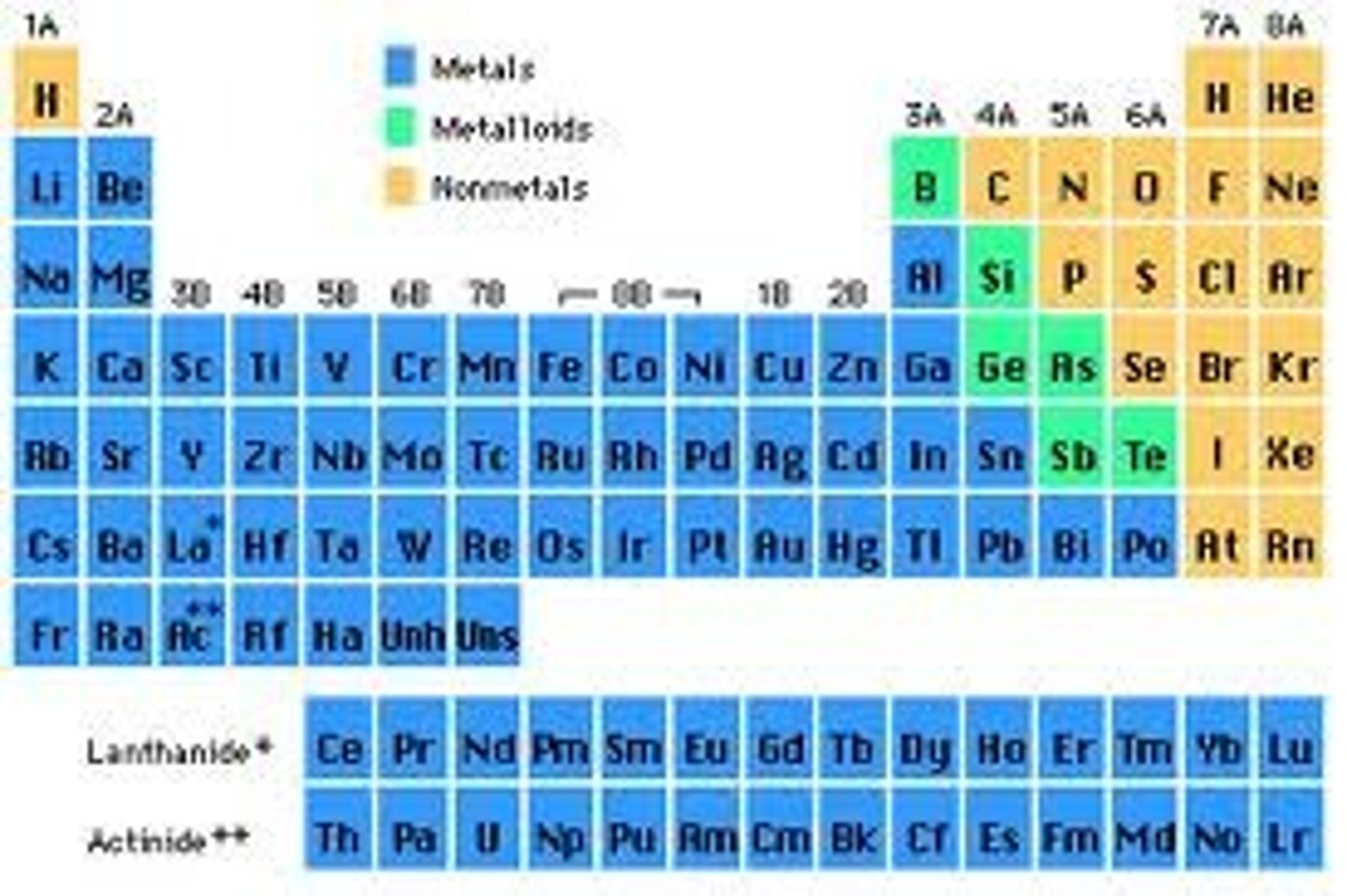
periodic table
A chart of the elements showing the repeating pattern of their properties
groups/families
Vertical columns on the periodic table
periods
Horizontal rows on the periodic table
metals
Elements that are good conductors of electric current and heat.

nonmetals
Elements that are poor conductors of heat and electric current

metalloids
Elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals.

alkali metals
Group 1, 1 electron in outer level, very reactive, soft, silver, shiny, low density; Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, Cesium, Francium
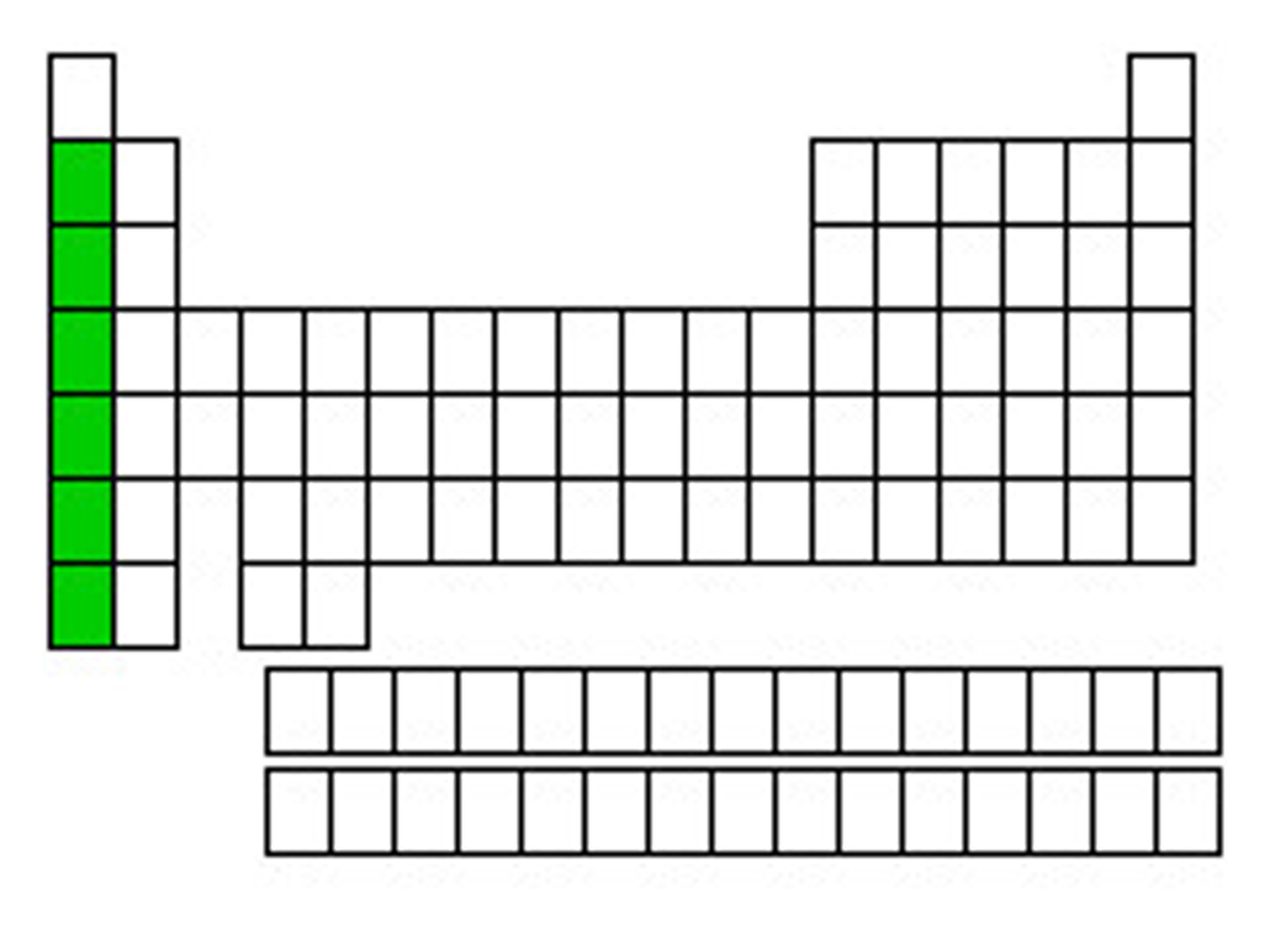
alkaline earth metals
metallic elements in group 2 of the periodic table which are harder than the alkali metals and are also less reactive
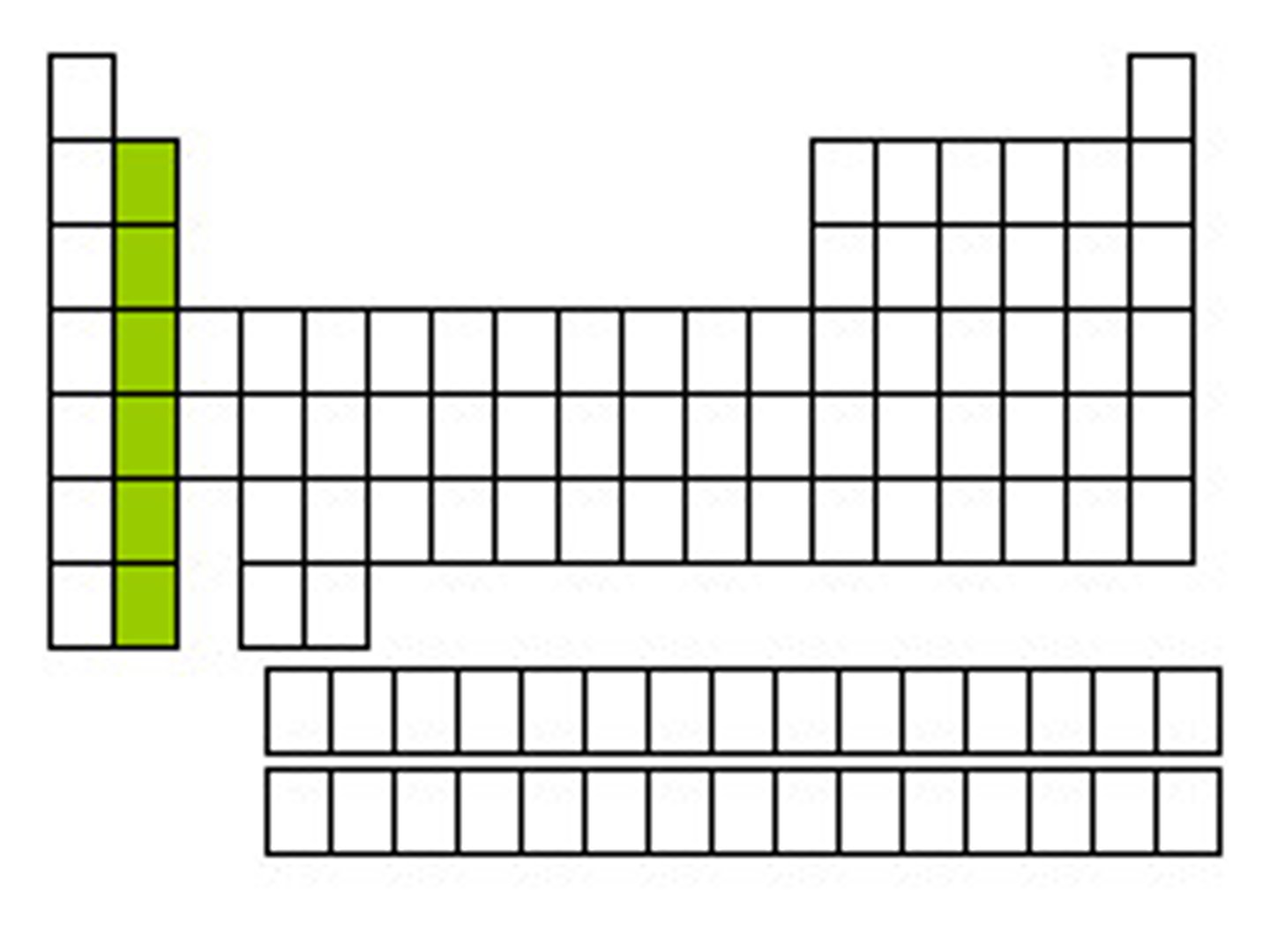
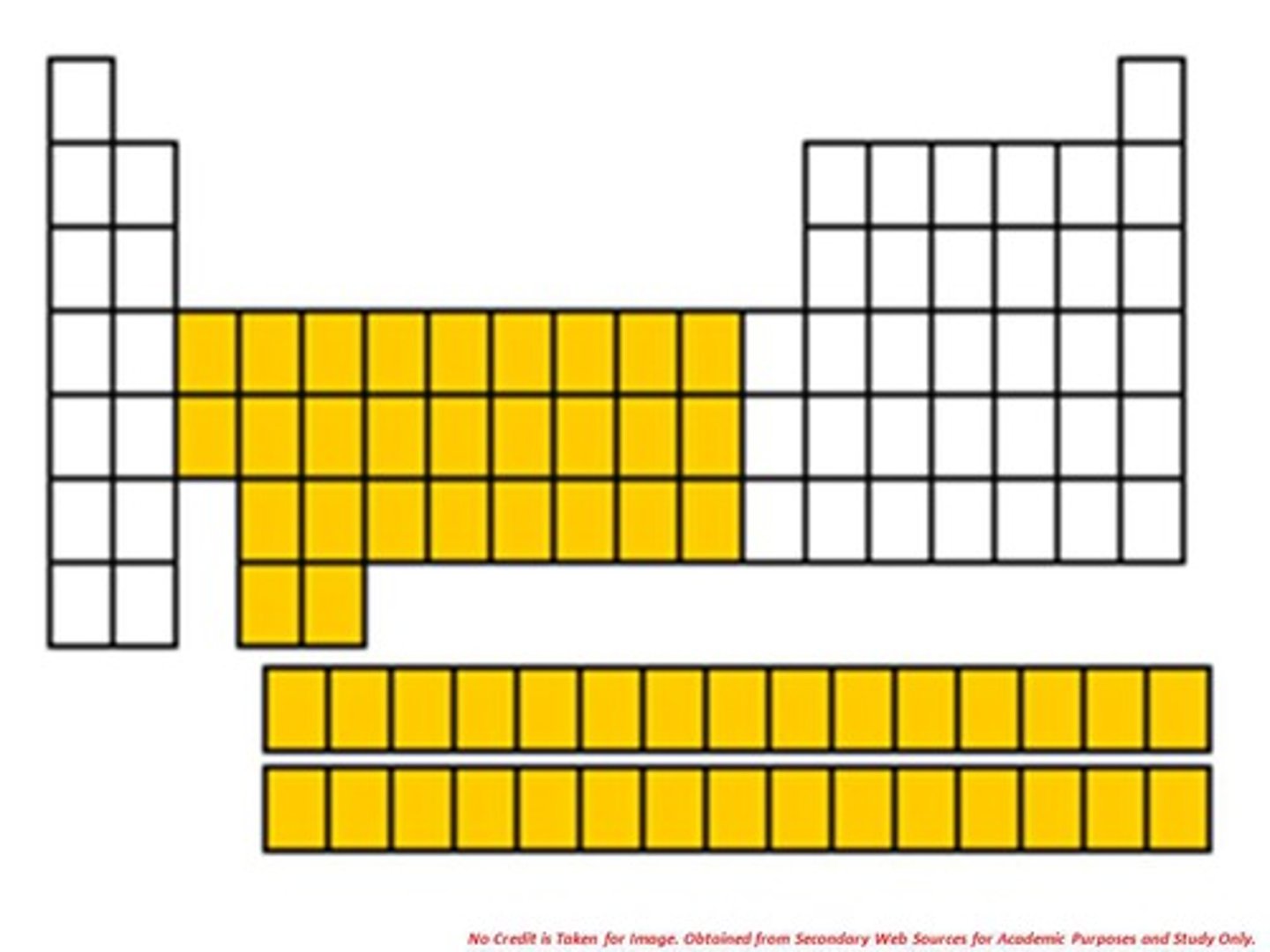
transition metals
Groups 3-12, 1-2 electrons in the outer energy level, less reactive than alkali-earth metals, shiny, good conductor of thermal energy and electrical current, high density
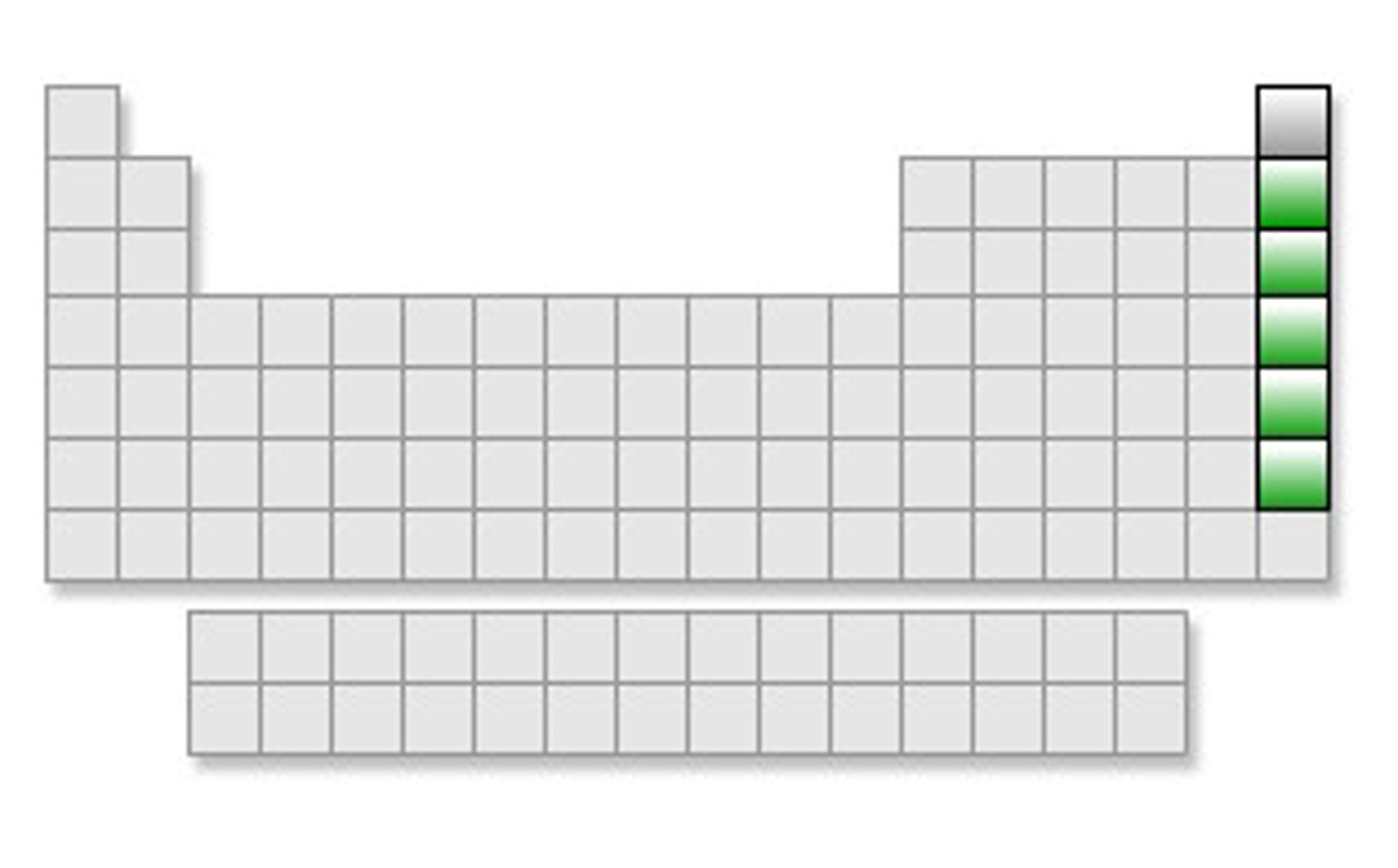
noble gases
the elements in Group 8A of the periodic table
atomic radius
one-half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element when the atoms are joined, trend increases down a group & decreases across a period
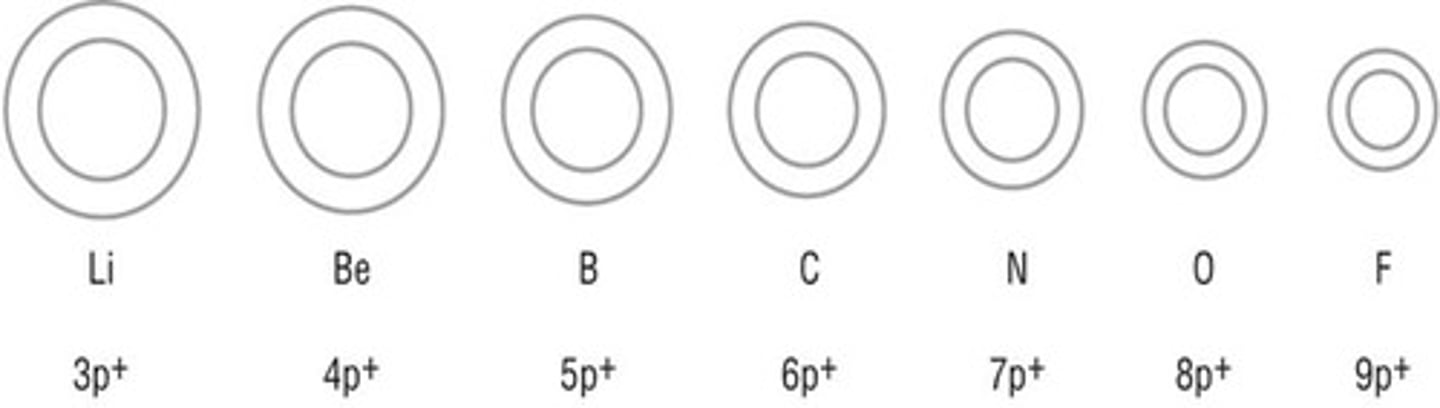
electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound, trend increases across a period & decreases down a group
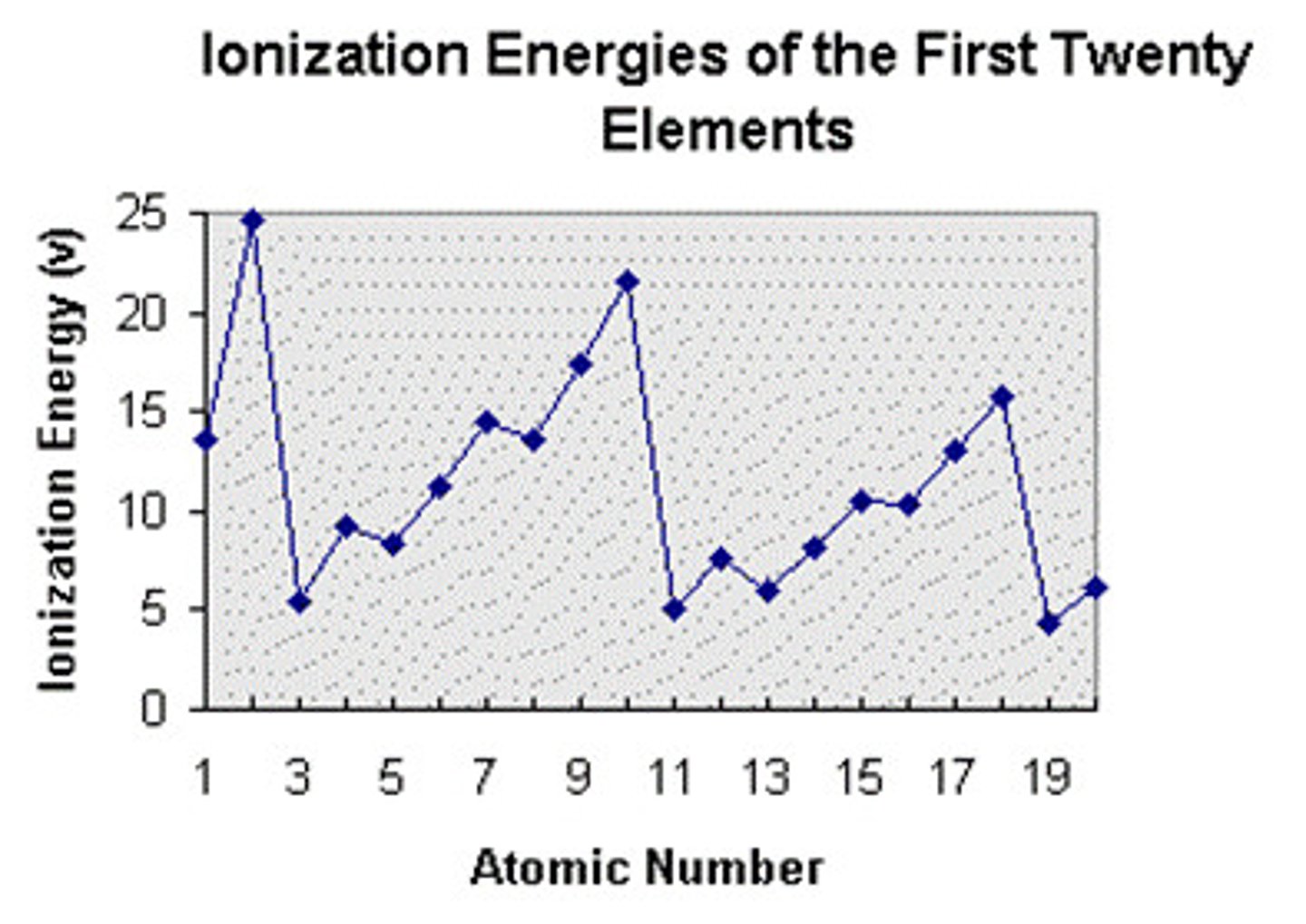
ionization energy
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom, decreases from top to bottom in a group; increases from left to right in a period