Economics - Protectionism
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are some benefits of free trade? (5) SEECC
S --- benefits from specialisation
E --- increase in efficiency and allocation of world resources (comparative advantage)
E --- economic growth
C --- increased competition
C --- the ability to transfer resources = greater consumer choice
What is the aim of the World Trade Organisation (WTO)?
to help trade be as free as possible, by providing forums for it's member governments to discuss trade agreements and settle disputes, using a set of trade rules
A government may want to impose certain trade barriers in order to tackle the disadvantages of free trade : (DIJBOB - remove hint when acronym is learnt)
D --- to protect against Dumping (companies selling goods abroad at a price lower than the production cost to force domestic companies out of business)
I --- to protect Infant industries (industries just starting out, especially in developing countries, struggle to compete with international companies), but if the industry never truly becomes competitive, domestic consumers will be stuck with low quality and high priced products
J --- may be at risk of many Job losses if foreign firms outcompete domestic firms
B --- may want to Ban certain goods that are bad for society (e.g. firearms, drugs)
O --- specialisation may lead to Overdependence on one industry
B --- to correct imbalances in the Balance of payments (i.e. reduce current account deficit)
What effects do tariffs in the form of taxes on selected imports have? (3)
1) imports more expensive for consumers
2) helps domestic producers can be more competitive
3) raises tax revenue for the government
What are quotas and how do they impact domestic producers?
setting a limit on the quantity of a certain good that can be imported
- any D for a good with a quota on it will be diverted to domestic producers goods'
What are embargoes and what tends to be the reason for them?
basically bans certain products, usually restricted to extreme cases (e.g. drugs, elephant ivory)
- BUT it may also be for political reasons e.g. if two countries are having a disagreement, they might impose embargoes on imports from each other
- so they tend to be more about politics and enforcing laws rather than protecting domestic industries
What would devaluing a currency do to the prices of imports and exports?
- raises the price of foreign imports
- lowers the price of domestic exports
What are the main aims of tight product standard regulation and how are these enforced?
- environmental and consumer protection
- not importing any goods that don't comply with the requirements (e.g. high safety standards, low emissions requirements)
What is the main aim of the government giving subsidies to domestic producers?
to reduce the cost of production of domestic products, making them cheaper to buy
- but at a cost to the government
Which types of policies can be used to make a country's products seem more competitive, and how?
tariffs and subsidies
- by making domestically produced products relatively cheaper
Tariffs are a common form of ________. They're a tax that can be a fixed amount per unit or ___ ________ (a % of the value of the good)
protectionism, ad valorem
What does the tariff diagram look like?
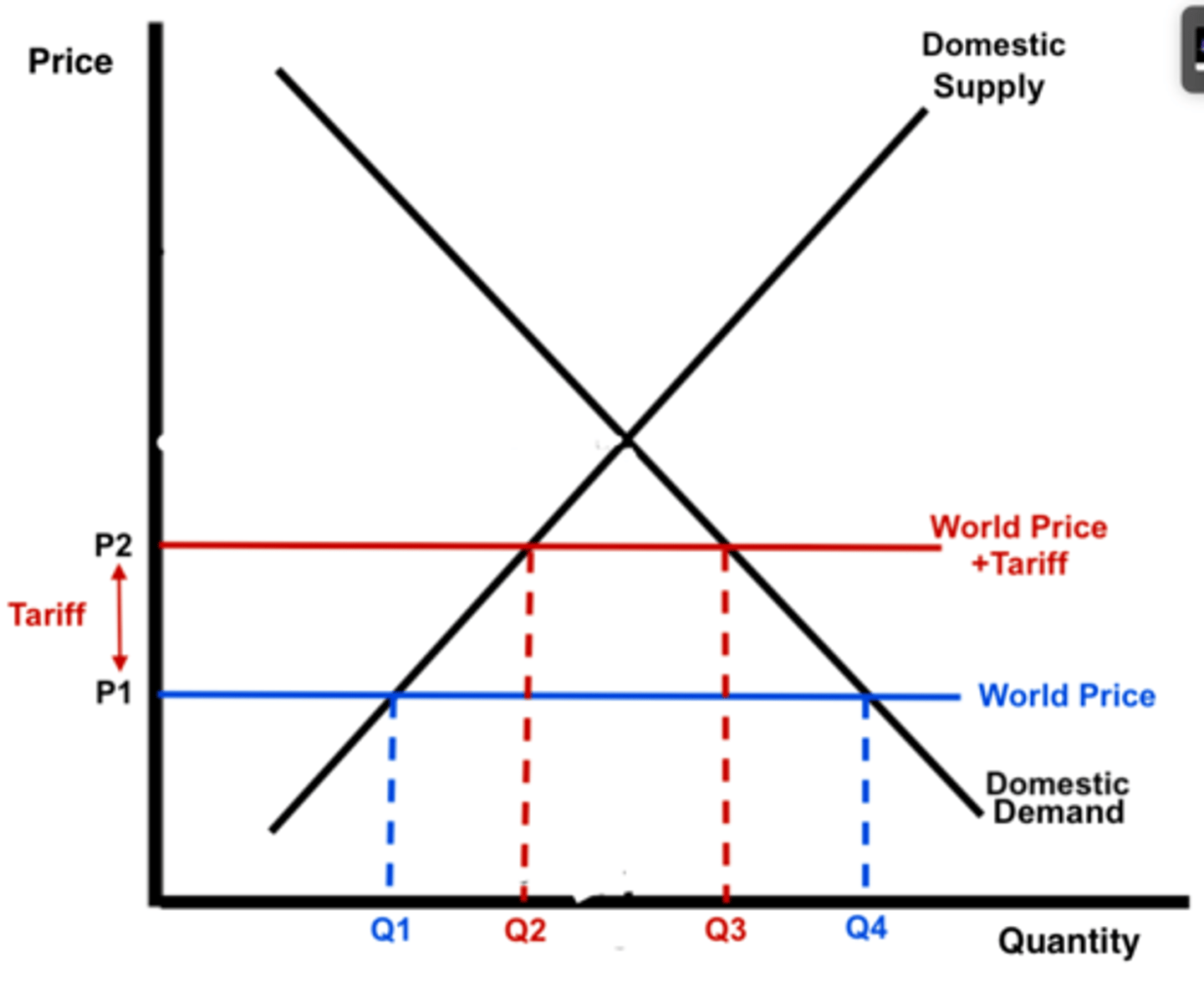
On the tariff diagram :
i) how does domestic demand change?
ii) how does domestic supply change?
i) D falls from Q4 to Q3
ii) S rises from Q1 to Q2
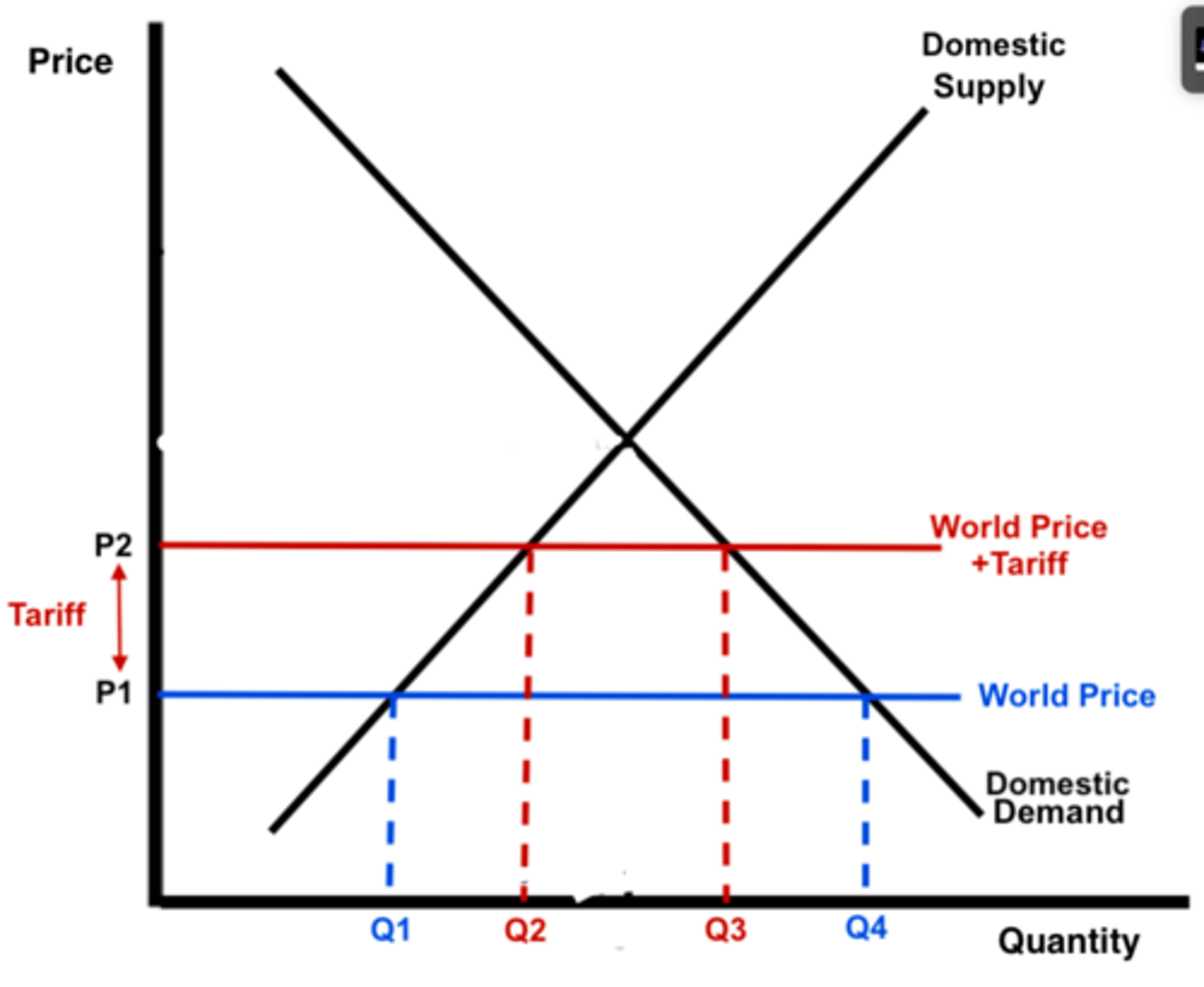
On the tariff diagram :
i) how does consumer surplus change?
ii) how does domestic producer surplus change?
iii) what is the deadweight welfare loss?
iv) what is the total tax revenue gained?
i) falls by CDEF
ii) rises by C
iii) D and F
iv) E
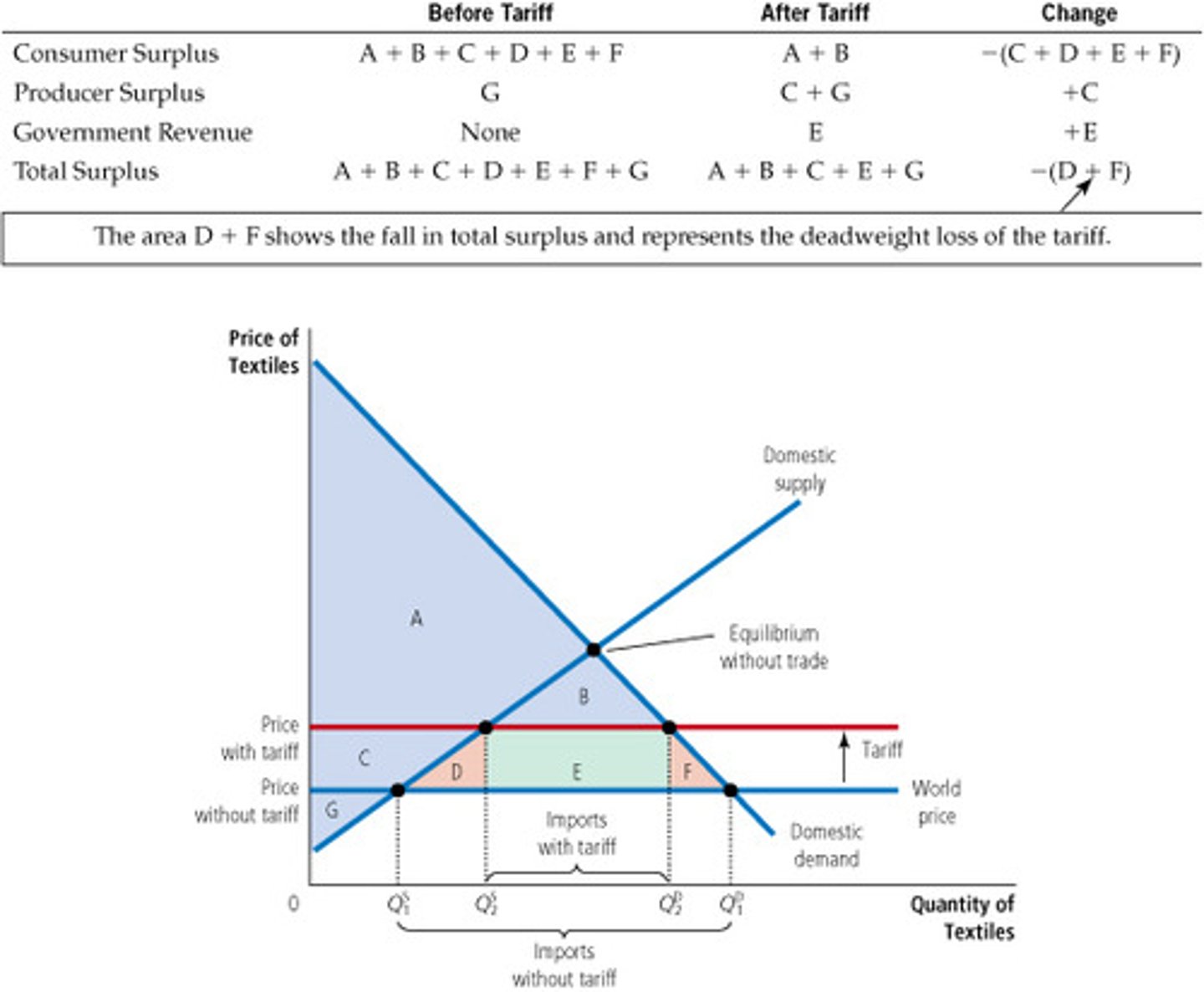
On the tariff diagram :
i) how does the level of imports change?
i) falls from Q1-Q4 to Q2-Q3
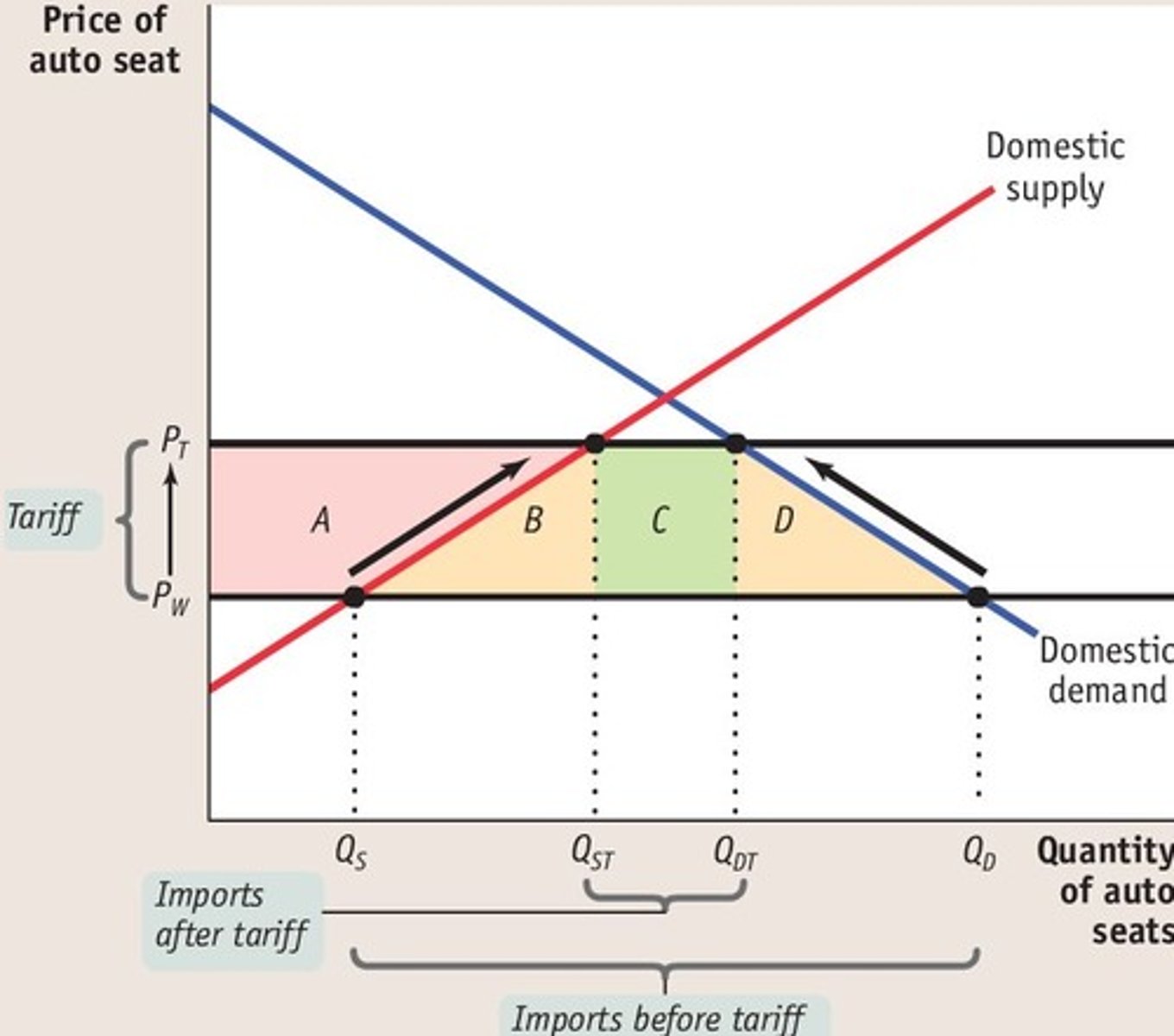
What does the quota diagram look like?
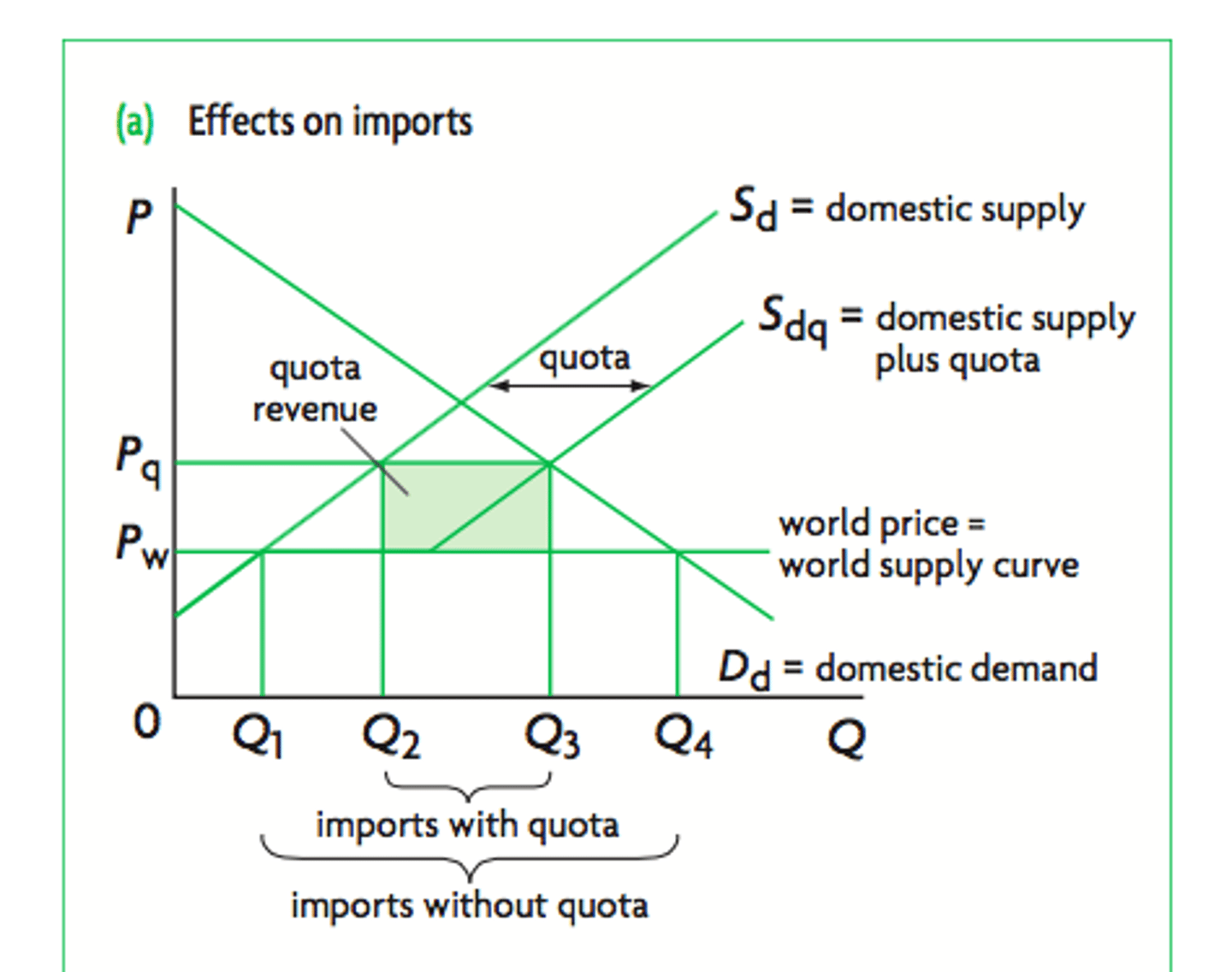
On the quota diagram :
i) how does price change?
ii) how does domestic demand change?
ii) how does domestic supply change?
i) rises from Pw to Pq
ii) falls from Q4 to Q3
iii) increases from Q1 to Q2
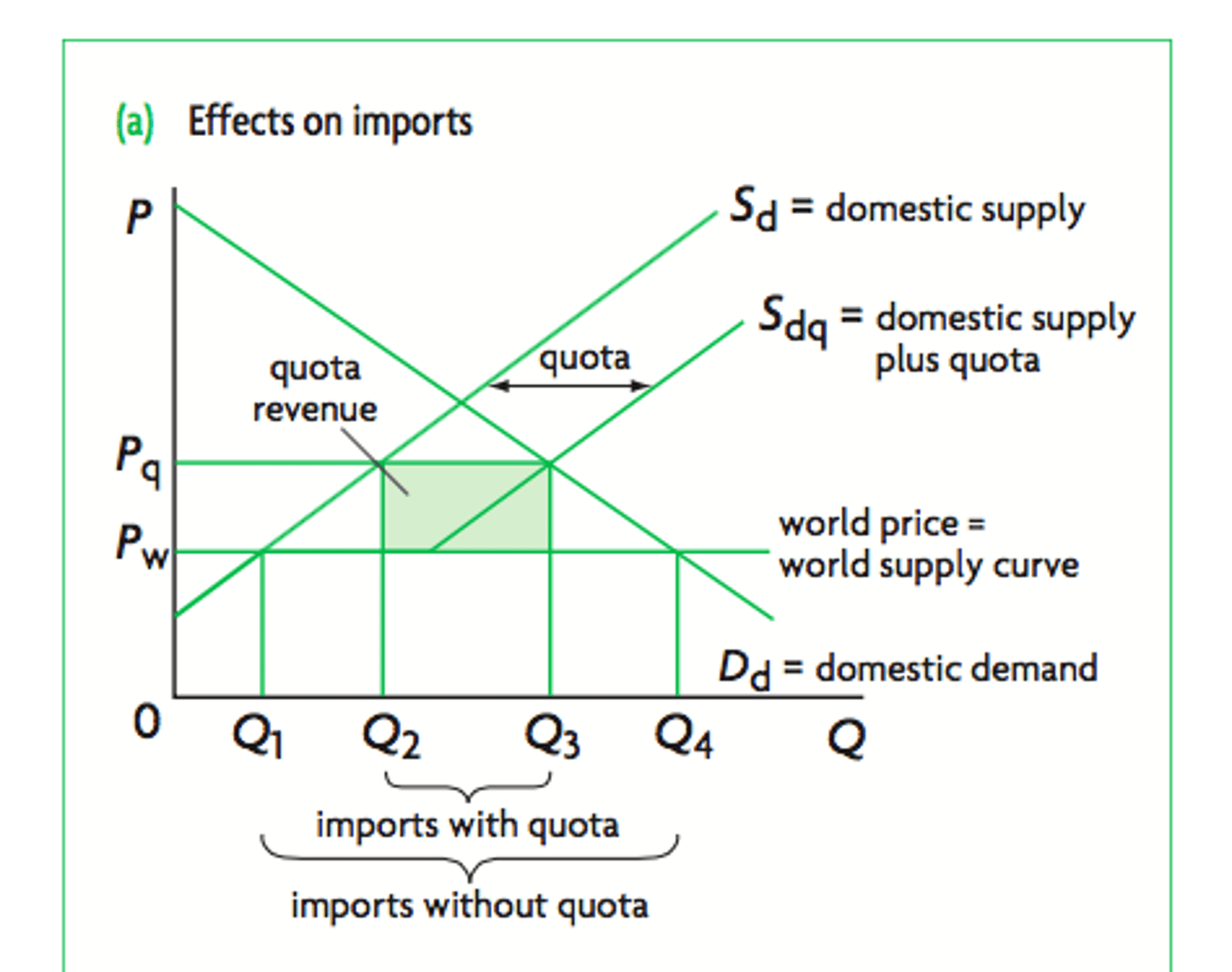
On the quota diagram :
i) how does the level of imports change?
ii) what is the deadweight welfare loss?
i) from Q1-Q4 to Q2-Q3
ii) d and f
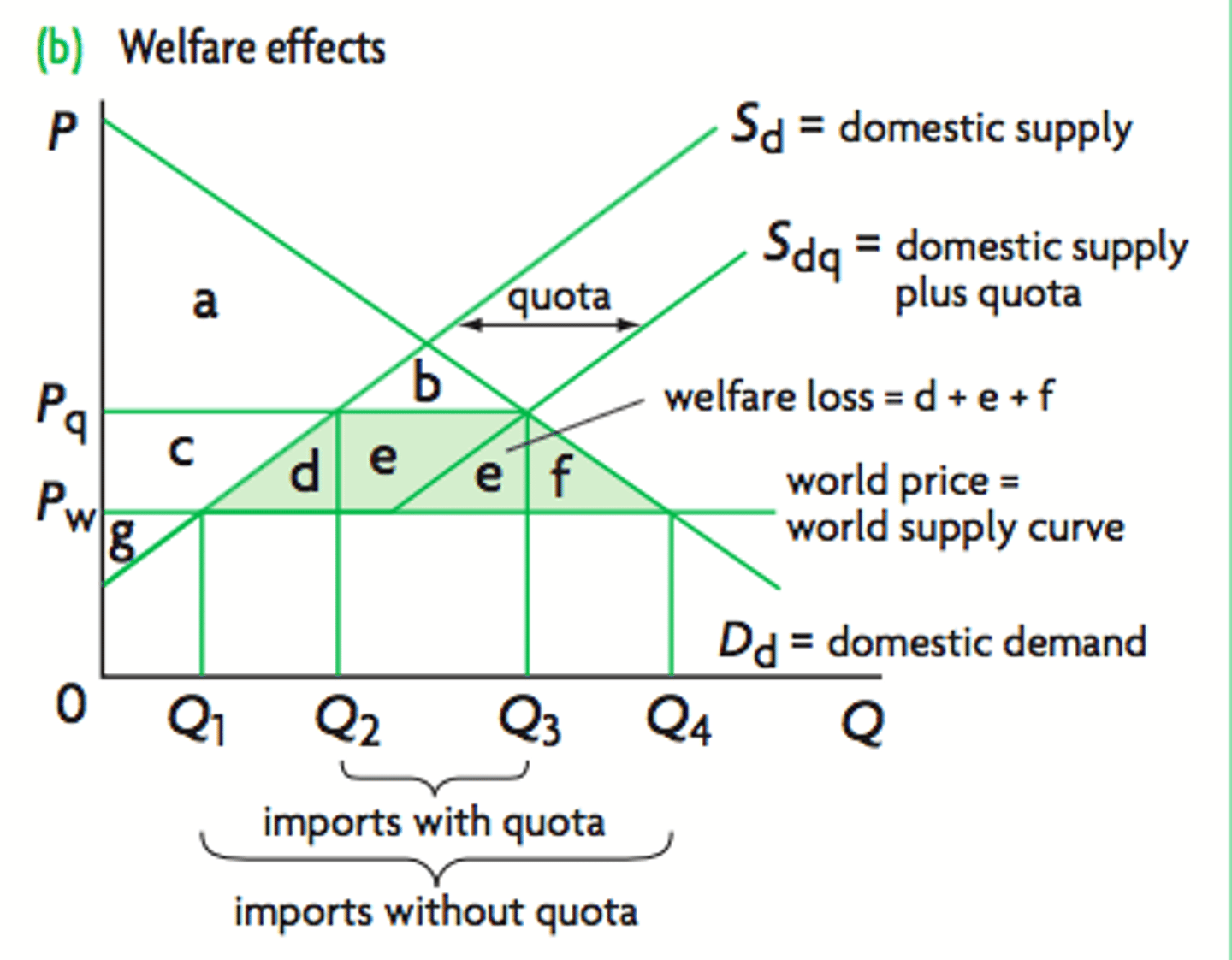
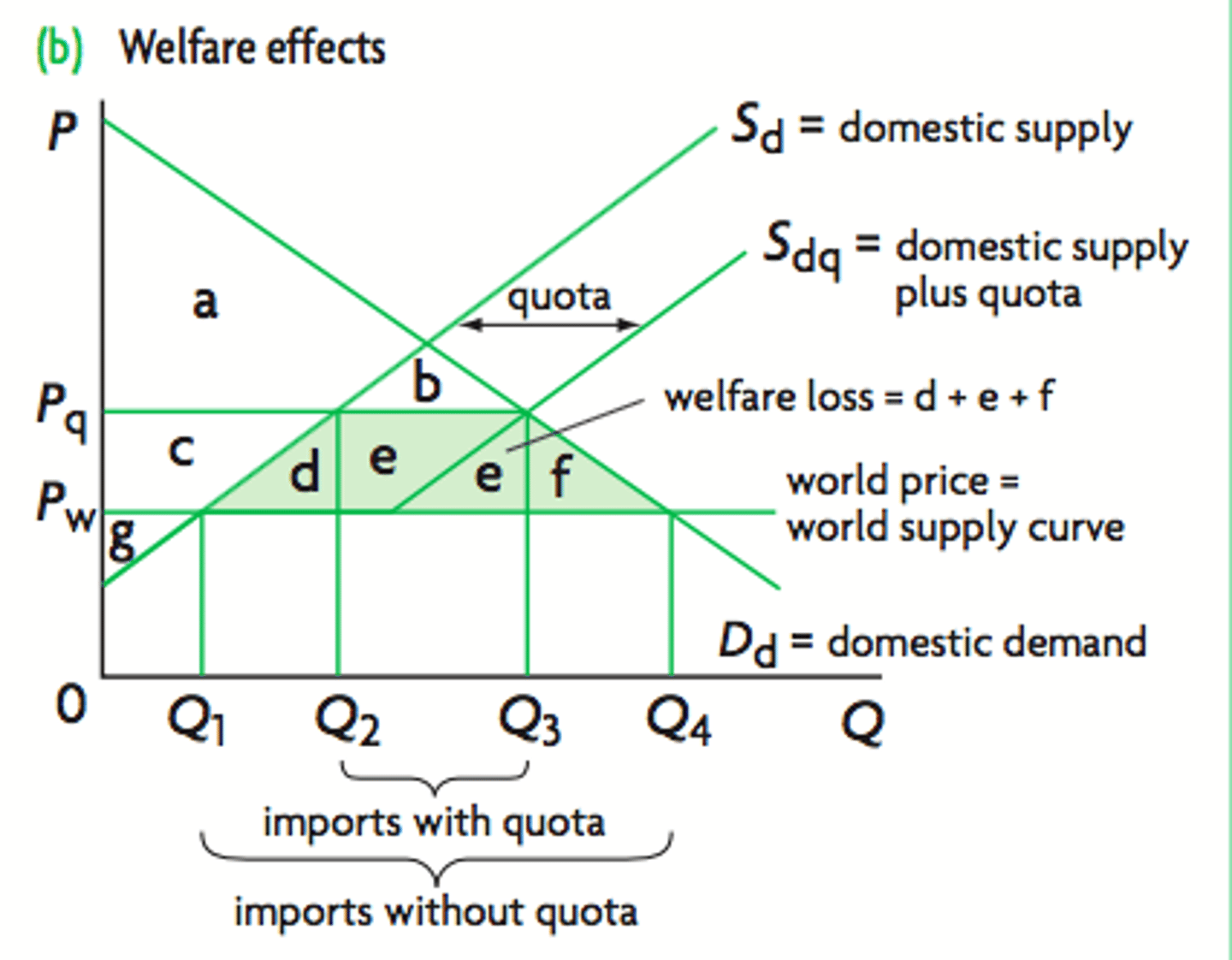
On the quota diagram :
i) how does consumer surplus change?
ii) how does domestic producer surplus change?
iii) how does foreign producer surplus change?
i) falls by cdef (is ab now)
ii) increases by c (is cg now)
iii) increases by e
Why does implementing protectionist policies increase government revenue?
- tariffs are a tax on imports = govt collects more tax revenue
- imports fall = domestic Q produced increases = govt collects more tax revenue (corporation, income, VAT)
Why does implementing protectionist policies reduce the current account deficit?
it is an expenditure switching policy :
- make imports more expensive = reduces the amount of money leaving the country's current account
What are the overall effects of protectionist policies (such as taxes and quotas) on domestic consumers? (1x analysed point, 1x surplus)
worse off overall
- pay increased P for goods = cannot afford good/can afford less of other goods = lower SOL
- loss in consumer surplus
What are the overall effects of protectionist policies (such as taxes and quotas) on domestic producers? (2x analysed points + 1x surplus)
better off overall
- costs for foreign firms rise = they raise their P = foreign competitors are less competitive in the domestic market
- increase in the market price = increased production = increased revenue + profits & increased EoS
- gain in producer surplus
What are the overall effects of protectionist policies (such as taxes and quotas) on the domestic government? (3x briefly analysed points)
better off overall
- fall in the current account deficit
- increased domestic production = more tax revenue (from tariff itself too) & employment & output (GDP)
- domestic producers protected = may develop comparative advantage over foreign producers = may see a boost in exports
What are some drawbacks of protectionist policies (such as taxes and quotas)? (hint : SECWI)
S --- lack of specialisation and competition = increased prices = increase in inequality = fall in SOL
E --- reduces specialisation and diverts resources away from most efficient use = reduces allocative and productive Efficiency
C --- reduces consumer Choice
W --- if a country retaliates to trade barriers = reduces world trade & worsens other problems (e.g. efficiencies) = trade War
I --- if the P of raw materials rises = cost-push Inflation