Male Reproductive System II
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Excretory Duct of Testis and Epididymis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Identify the cut:
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
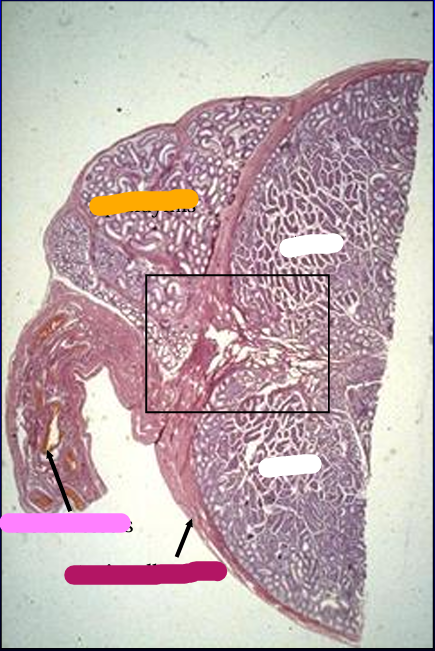
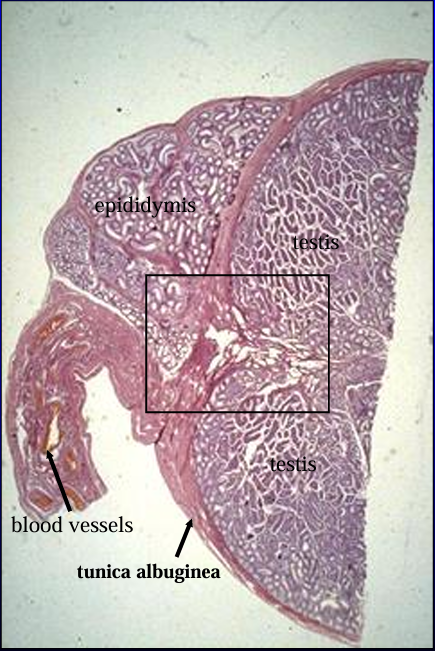
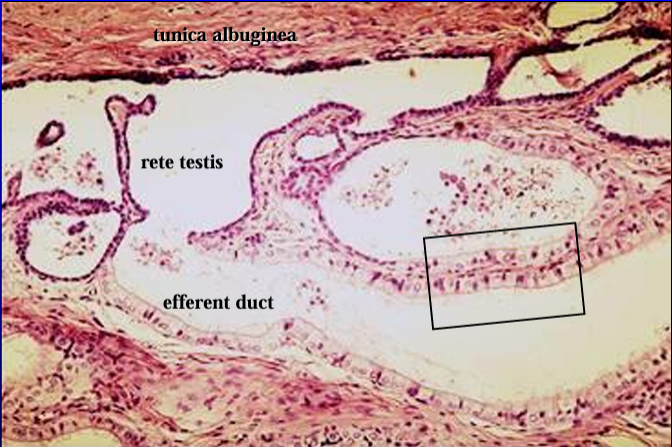
Cross-section of the canine testis (right) and epididymis (top, left), H-E stain.
The section was cut at the level where the head of the epididymis is attached to the testis.
The structure below the epididymis (lower left) contains the blood supply to the testis and epididymis.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Stain used:
Orange:
Pastel Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
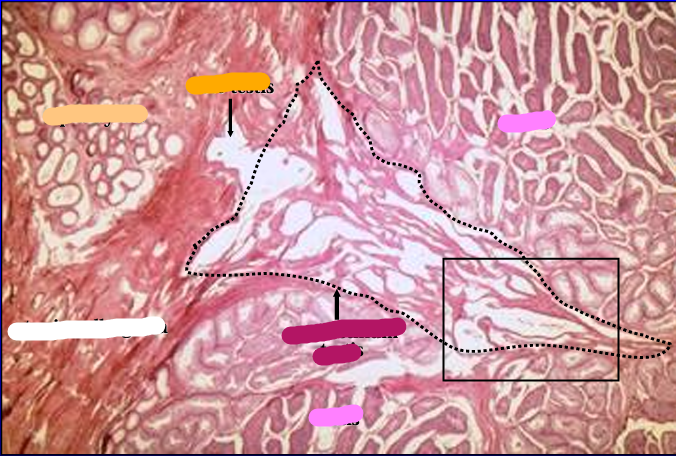
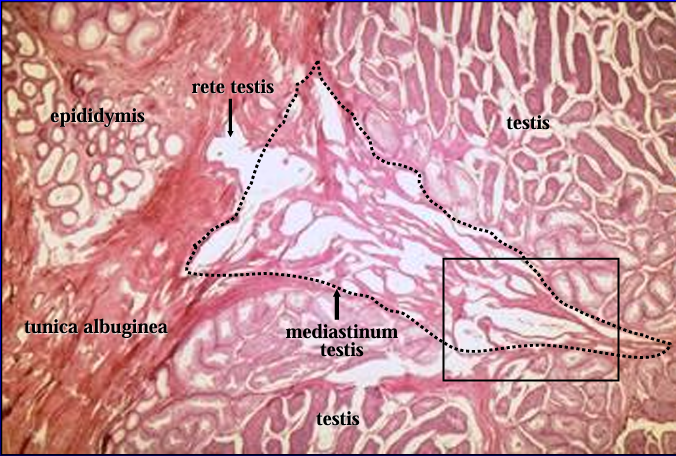
Canine testis and epididymis.
The figure was taken at the region where the seminiferous tubules of the testis connect with the efferent ducts of the epididymis via the rete testis.
In the center of the figure is the mediastinum testis (dotted line), within which are contained the rete testis.
The rete testis can be seen penetrating the tunica albuginea toward the epididymis.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
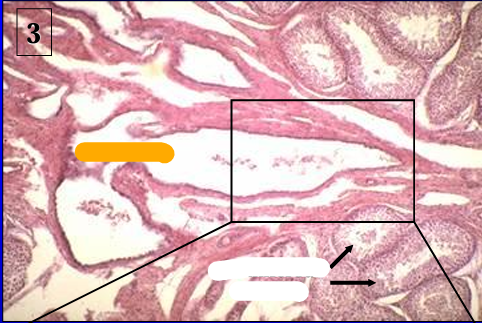
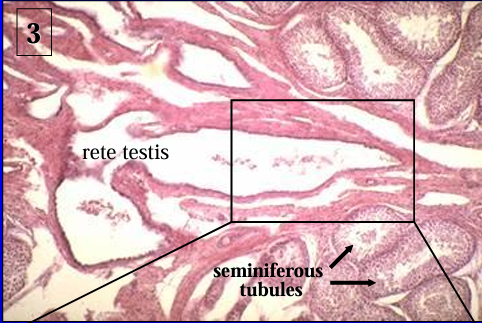
Canine seminiferous tubules and rete testis.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Lined by:
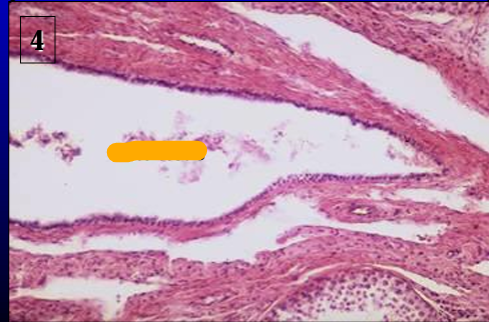
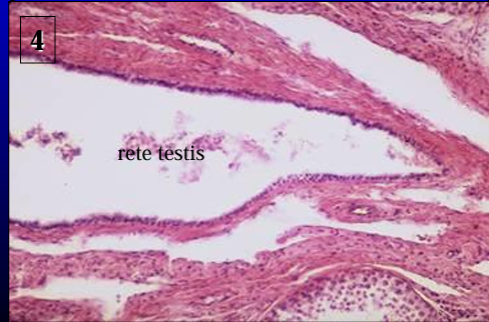
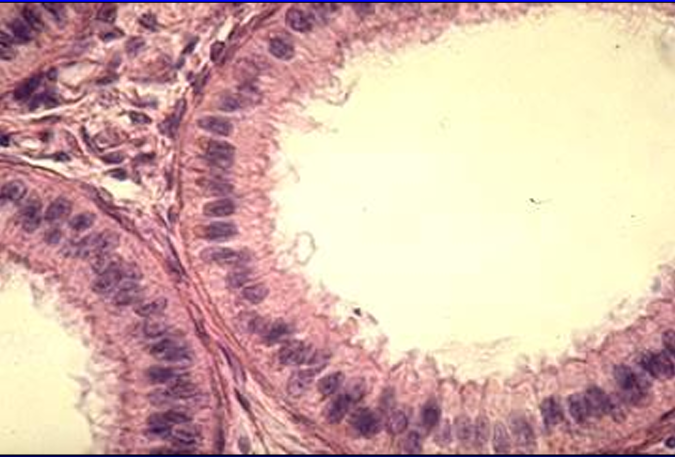
Canine rete testis.
The rete testis is lined by a simple low cuboidal epithelium
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
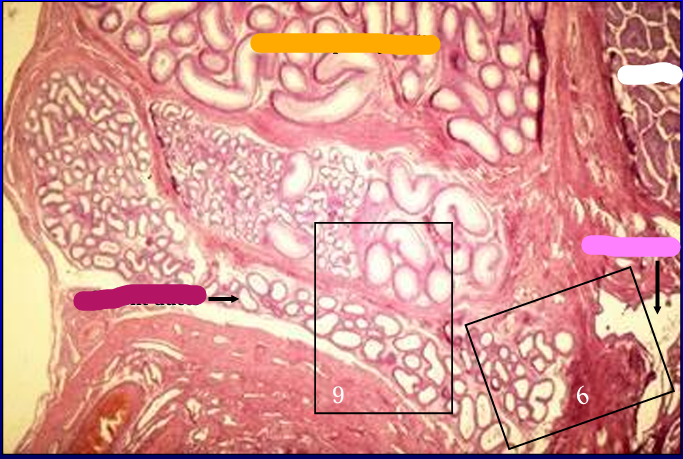
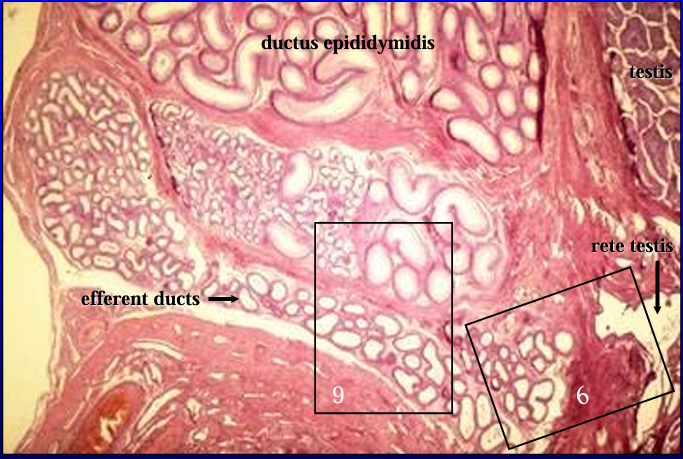
Canine epididymis and rete testis.
This figure was taken just to the left of figure #2 and shows the epididymis and the rete testis (right) penetrating the tunica albuginea and seemingly trying to connect with the epididymis.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
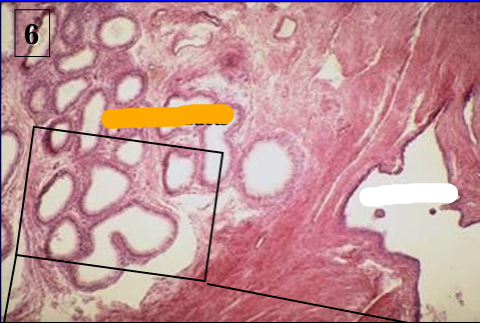
White:
Higher magnification of the rete testis (right side, lined by low cuboidal epithelium) and the efferent ducts of the epididymis (left).
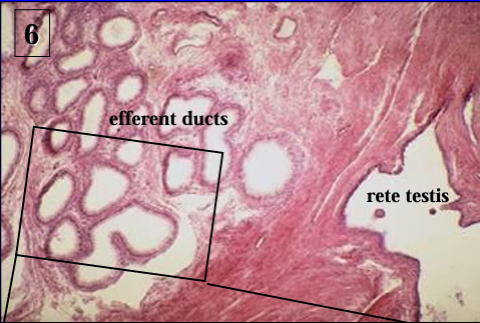
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Lined by:
Efferent ducts of canine epididymis.
The ducts are lined by a simple columnar epithelium
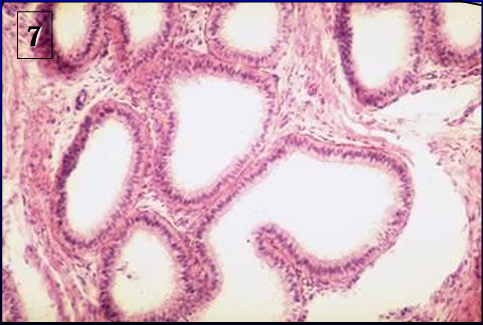
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Lined by:
Efferent ducts.
The efferent ducts are lined by a simple columnar epithelium that contains ciliated and non-ciliated cells
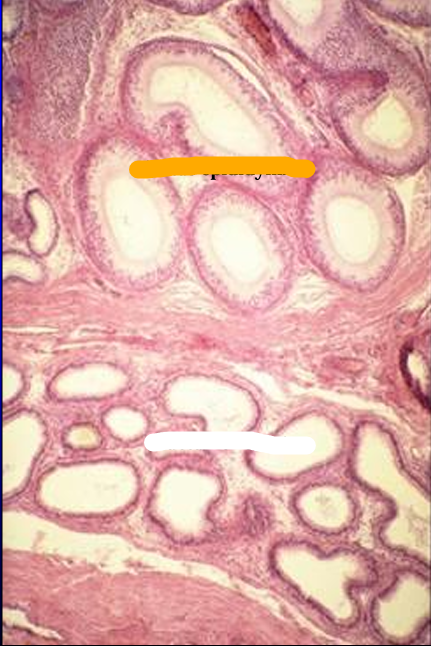
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Another view of a section through the head of the epididymis.
The figure shows the efferent ducts and the duct of the epididymis
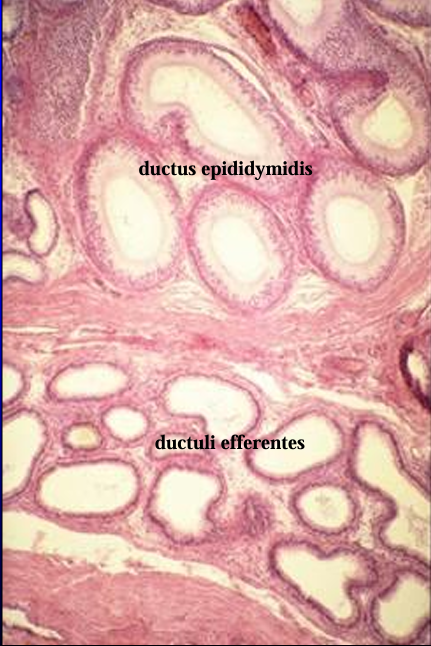
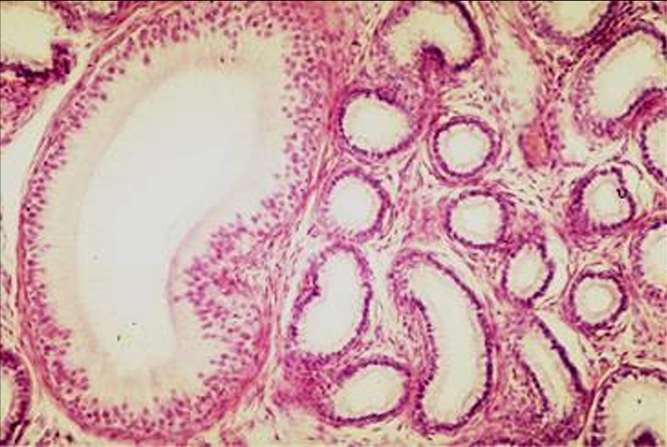
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Lined by:
Head of epididymis.
The efferent ducts (right) will connect with the ductus epididymis (left).
Notice the difference in the size of the ducts and the height of lining epithelium.
The ductus epididymidis is lined by a taller pseudostratified columnar epithelium
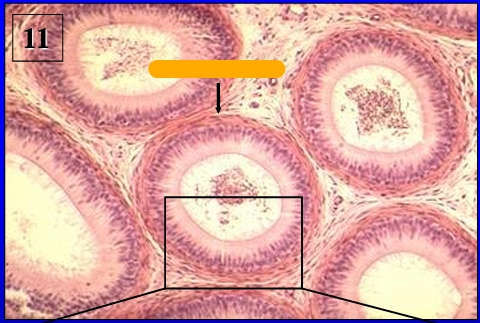
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Another view of the ductus epididymidis.
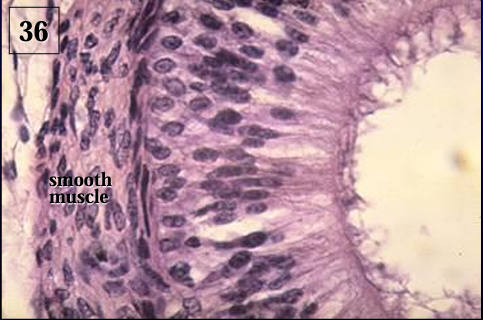
Note the abundance of circularly arranged smooth muscle surrounding the duct.
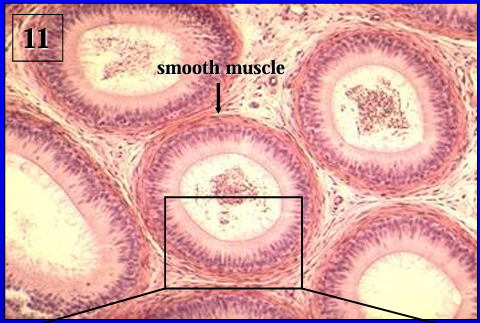
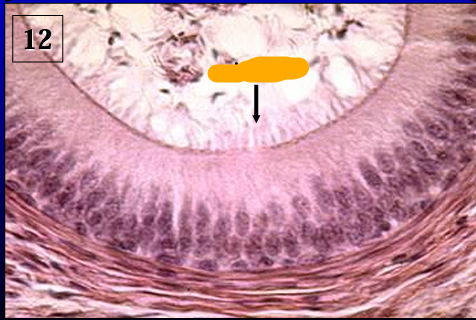
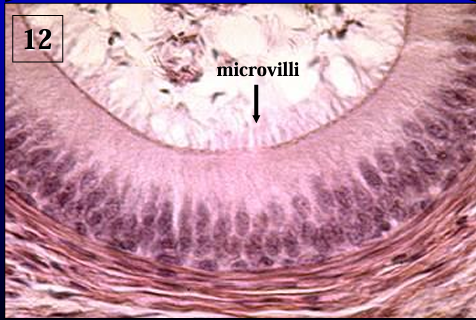
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Lined by:
Ductus epididymidis.
The duct of the epididymis is lined by a pseudostratified columnar epithelium with long microvilli called stereocilia (they are not the same as motile cilia). '
Note the presence of spermatozoa in the lumen.
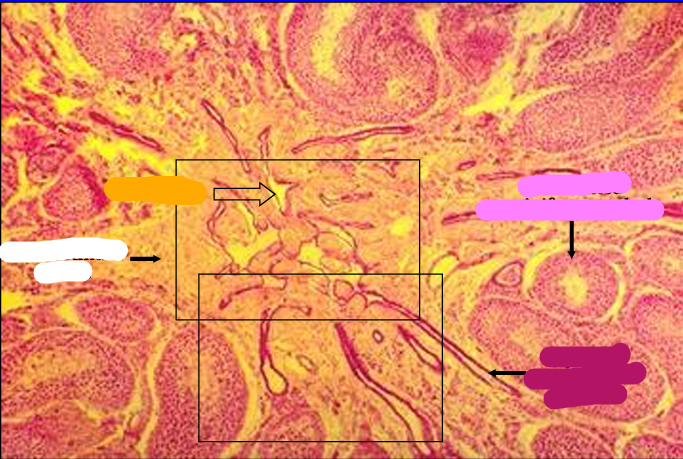
Identify the cut:
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
Cross section of feline testis showing the mediastinum testis.
Within the mediastinum, the straight seminiferous tubules can be seen connecting with the rete testis.
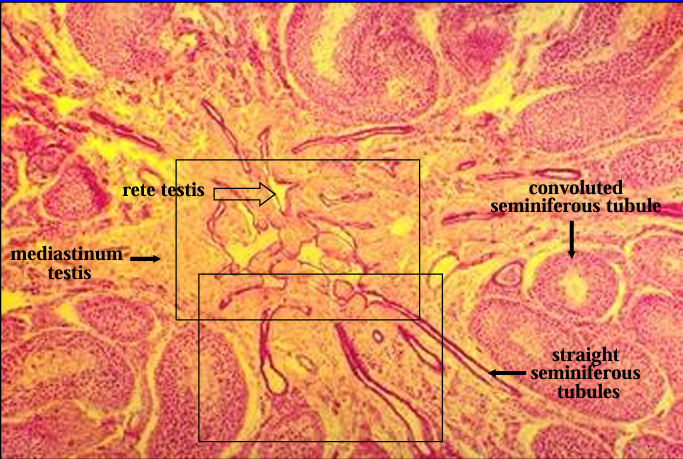
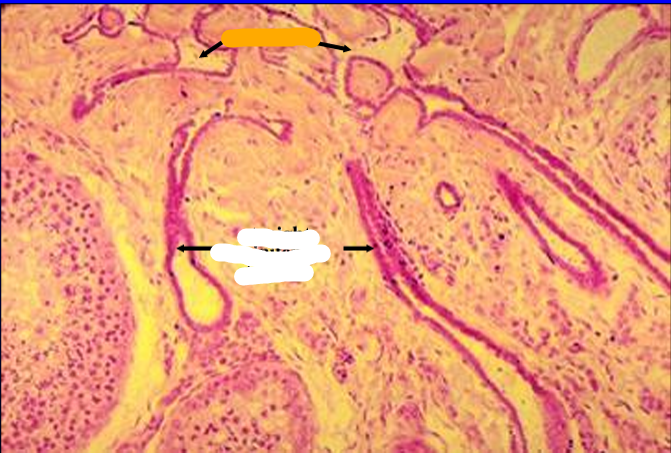
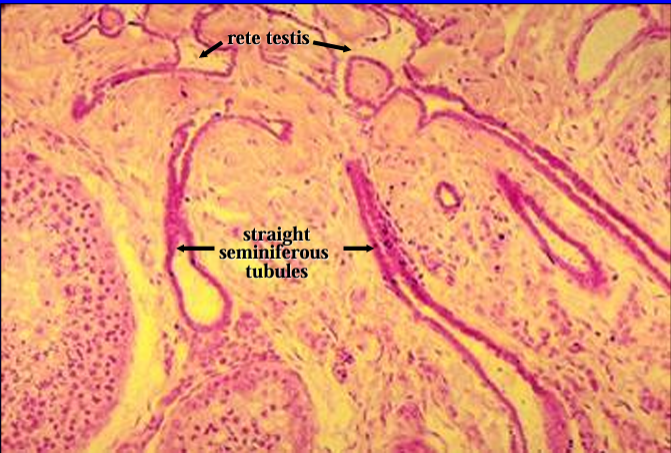
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Mediastinum testis.
Straight seminiferous tubules are seen connecting with the rete testis
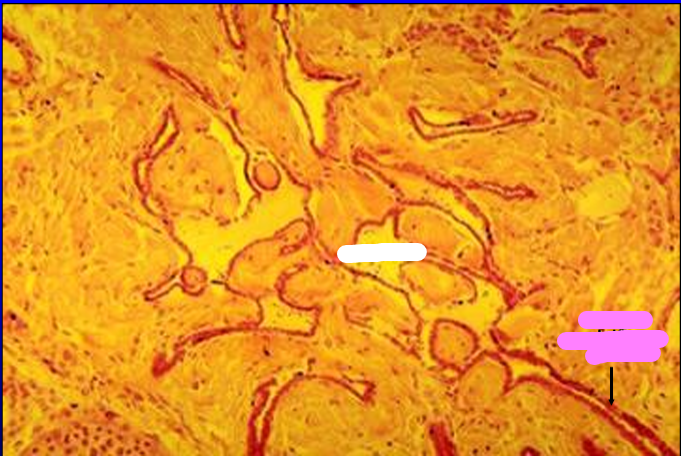
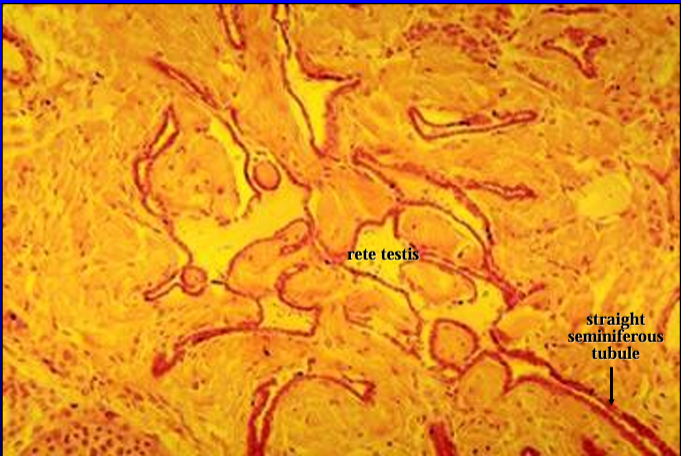
Identify the structure:
Specie:
White:
Pink:
Lined by:
Rete testis.
Both straight seminiferous tubules and rete testis are lined by a simple low cuboidal epithelium
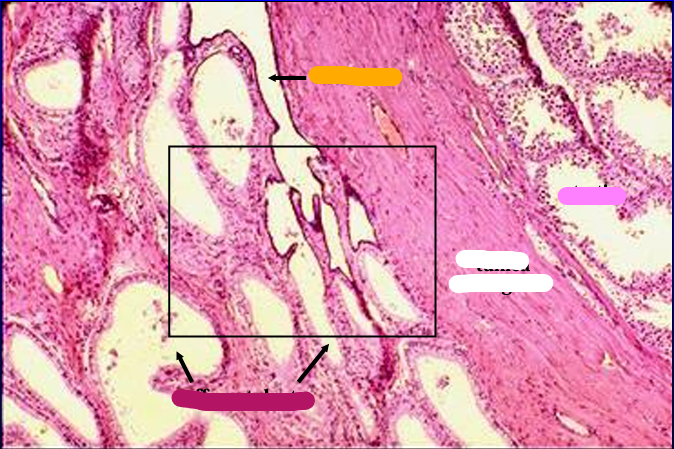
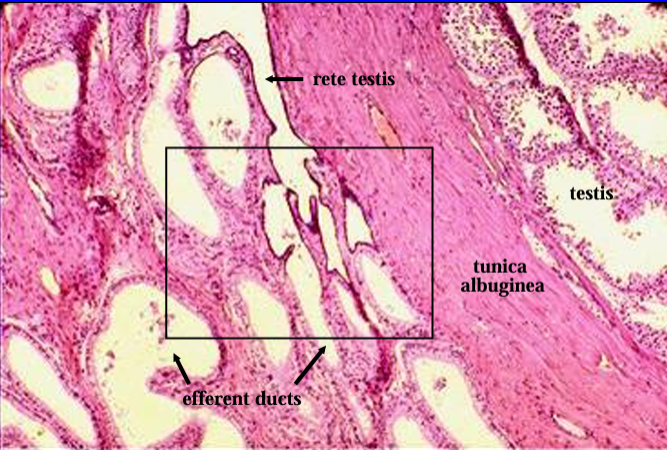
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
Another view of the feline testis (right) and epididymis (left).
The section show the extragonadal part of the rete testis becoming continuous with the efferent ducts.
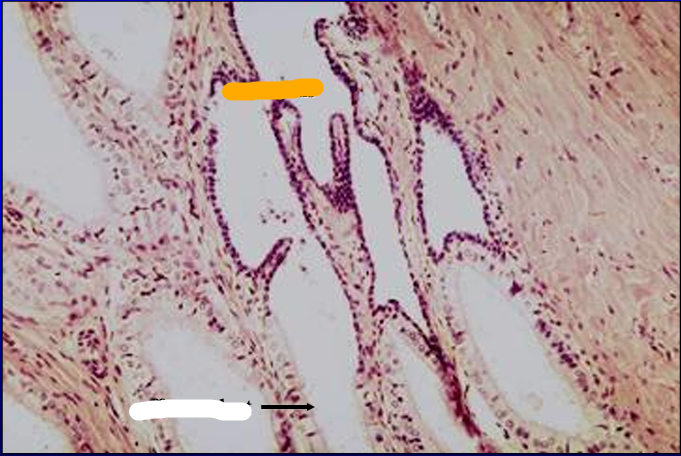
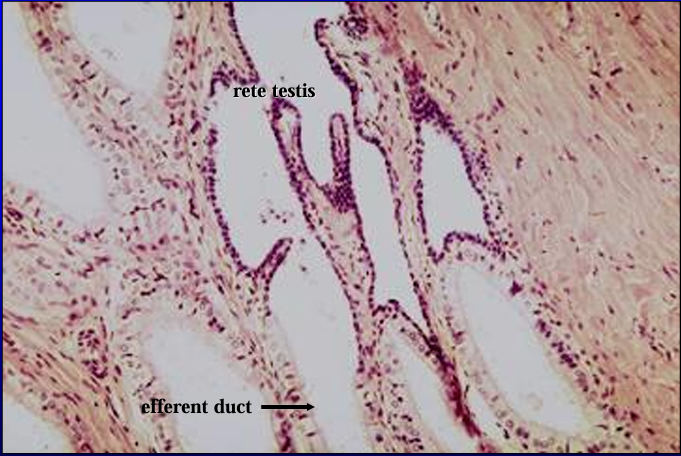
Identify the structure:
Specie:
White:
Orange is lined by:
White is lined by:
Rete testis and efferent duct.
The rete testis is lined by a low simple cuboidal epithelium.
The lining epithelium of the efferent duct is simple columnar
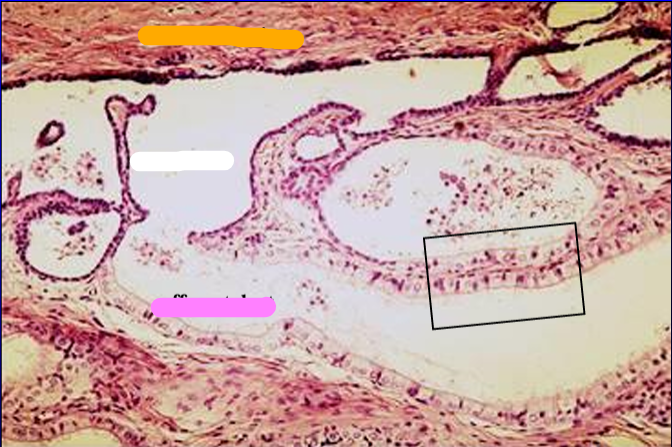
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Another view of the rete testis connecting with the efferent ducts.
Notice the change in the height of the epithelium which lines the rete testis (low cuboidal) to that which lines the efferent ducts (columnar).
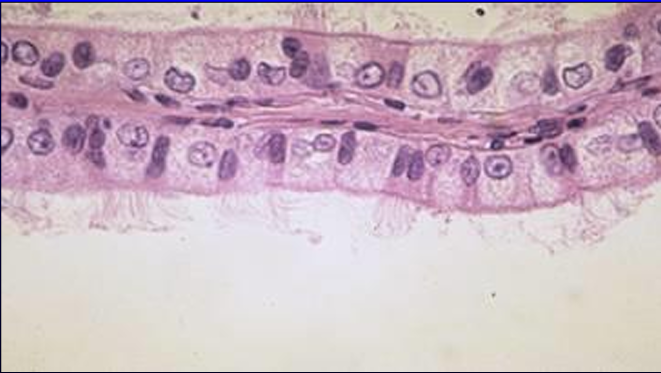
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Lining epithelium is composed by:
Efferent duct, feline epididymis.
The lining epithelium of the efferent duct is composed of ciliated and non-ciliated cells.
Ciliary motion helps move the spermatozoa along the efferent ducts.
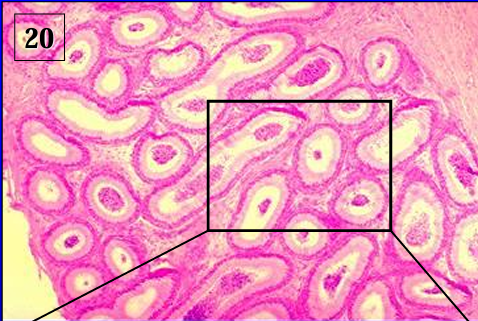
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Ductus epididymidis, feline.
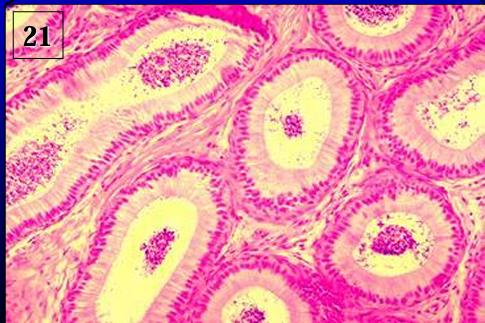
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Lined by:
Ductus epididymidis.
The duct is lined by a pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
Observe also the circularly oriented smooth muscle fibers around the duct.
The amount of smooth muscle fibers increases toward the tail of the epididymis.
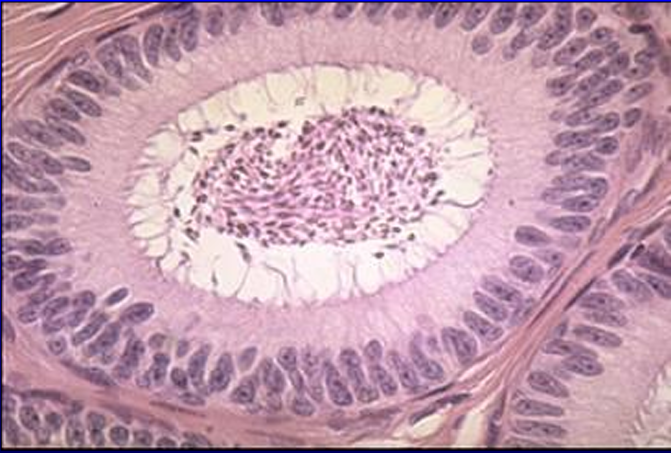
Identify the structure:
Lining epithelium is provided with:
Lumen contains:
Ductus epididymidis.
The lining epithelium is provided with stereocilia (long microvilli).
The lumen of the duct contains spermatozoa which undergo a period of maturation in the epididymis
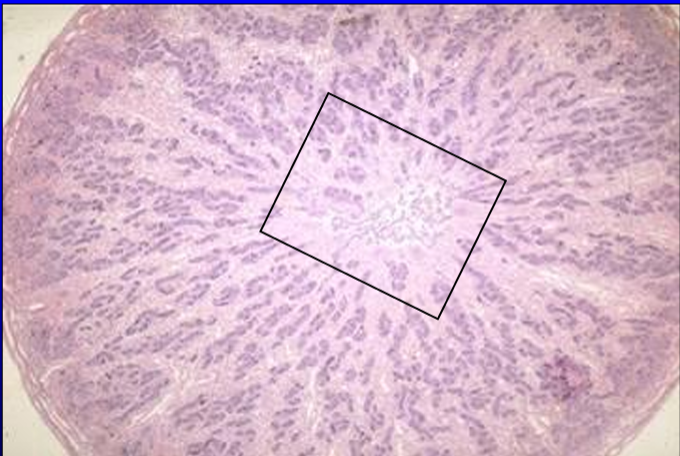
Identify the cut:
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Cross section of testis of 1-day-old pig.
This section is shown for orientation.
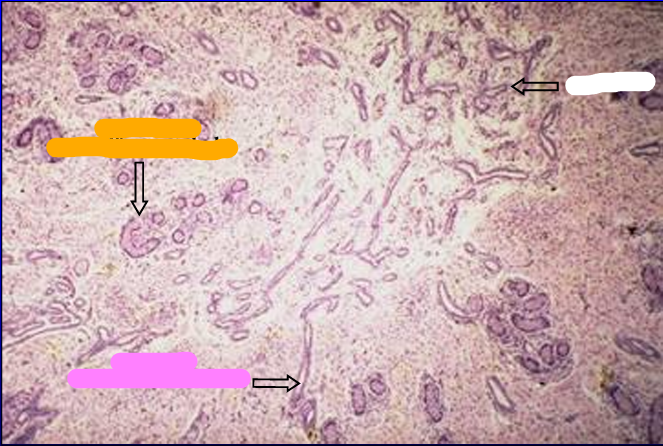
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Mediastinum testis, 1-day-old pig testis.
The area of the mediastinum contains straight seminiferous tubules and the rete testis.
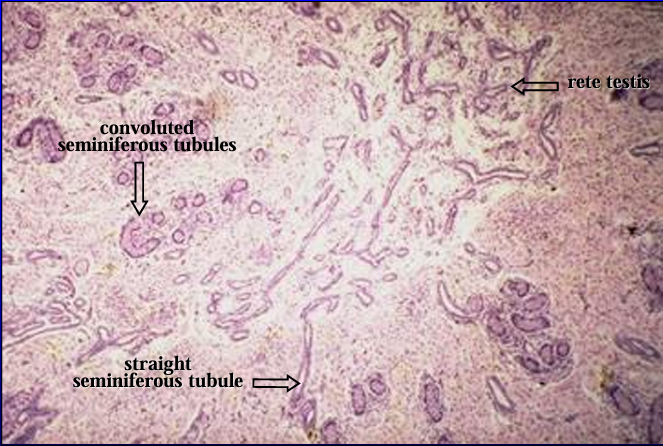
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Pink:
Magenta:
Mediastinum testis, 1-day-old pig testis.
A convoluted seminiferous tubule is seen connecting with the straight seminiferous tubule and the rete testis.
The latter two structures are lined by a low cuboidal epithelium.

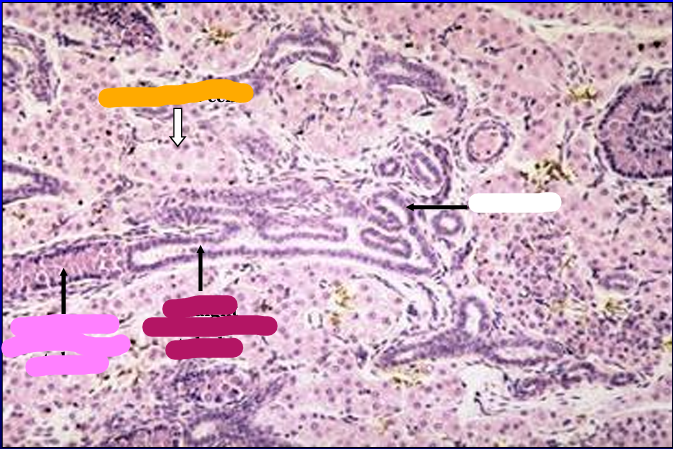
Identify the structure:
Specie:
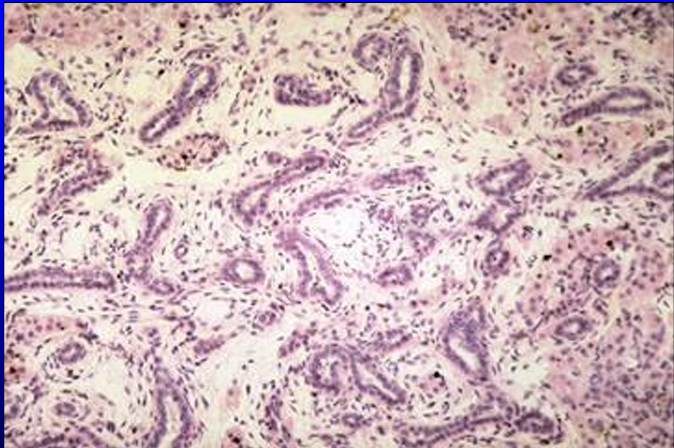
Rete testis, 1-day-old pig testis.
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Equine epididymis.
The section was taken through the head of the epididymis and shows the efferent ducts and the duct of the epididymis.
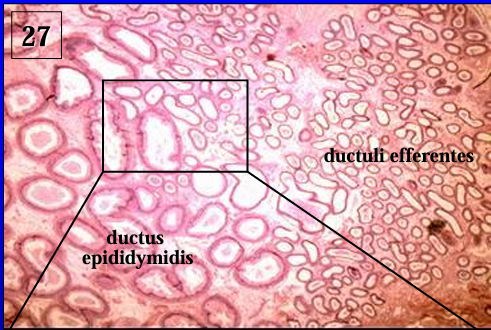
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Efferent ducts (right) and epididymal duct (left).
Equine
Observe the difference in the size of the tubules and the height of the epithelium
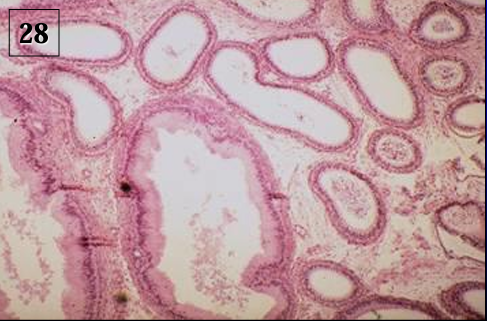
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Lined by:
Structure present in the lumen:
Efferent duct, equine epididymis.
The pseudostratified columnar epithelium contains ciliated and non-ciliated cells.
Spermatozoa are present in the lumen of the ducts
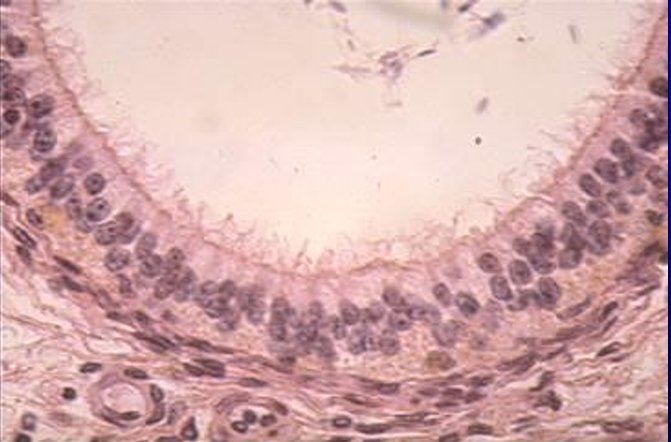
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Ductus epididymidis, equine epididymis.
Note the taller pseudostratified columnar epithelium (vs. the epithelium of the ductuli efferentes).
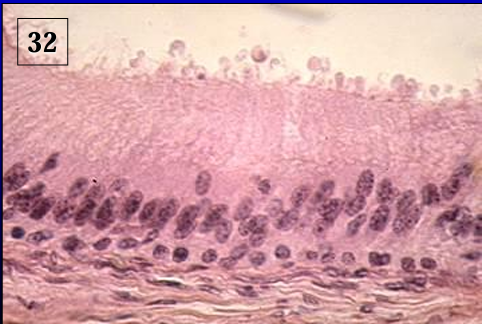
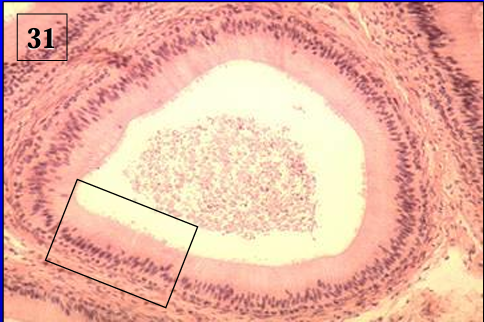
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Ductus epididymidis, equine epididymis.
The epithelium shows cytoplasmic blebs at the apical border of the cells.
The epididymis furnishes an environment that is conducive to sperm cell maturation
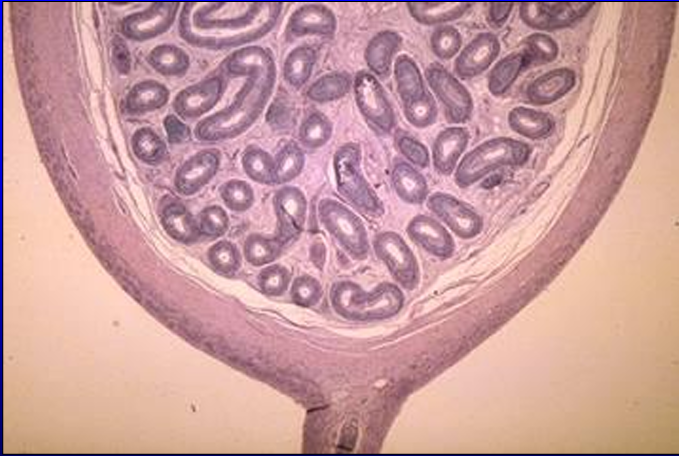
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Section through the body of the epididymis, equine.
The epididymis is surrounded by a connective tissue capsule (tunica albuginea).
The ductus epididymidis is a single duct that has a very tortuous course; it is, thus, cut in different planes in this section
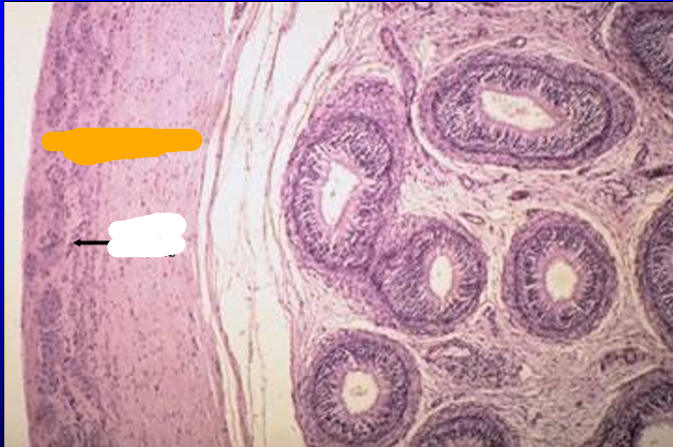
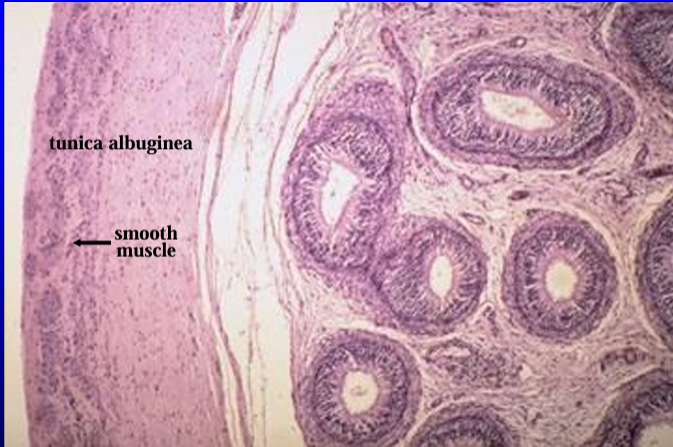
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
White:
Equine epididymis.
The tunica albuginea and the ductus epididymidis are shown at a higher magnification.
Note the presence of smooth muscle fibers in the tunica albuginea
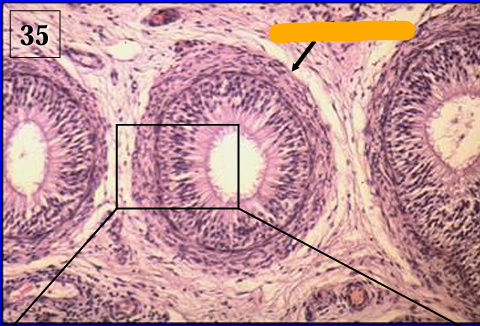
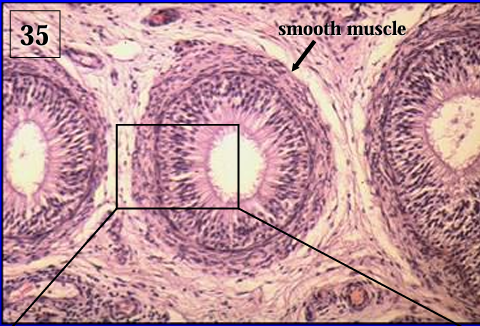
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Ductus epididymidis, equine.
Notice the circularly arranged smooth muscle fibers surrounding the duct; this layer is thicker than the smooth muscle layer surrounding the duct in the head of the epididymis.
Smooth muscle contraction helps move the spermatozoa along the duct system.
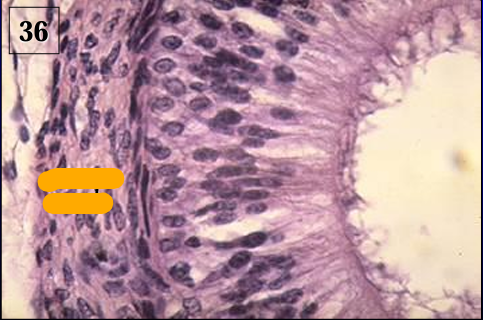
Identify the structure:
Specie:
Orange:
Lined by:
Ductus epididymidis, equine.
The duct is lined by a tall pseudostratified columnar epithelium with long microvilli.