Neuropsychology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
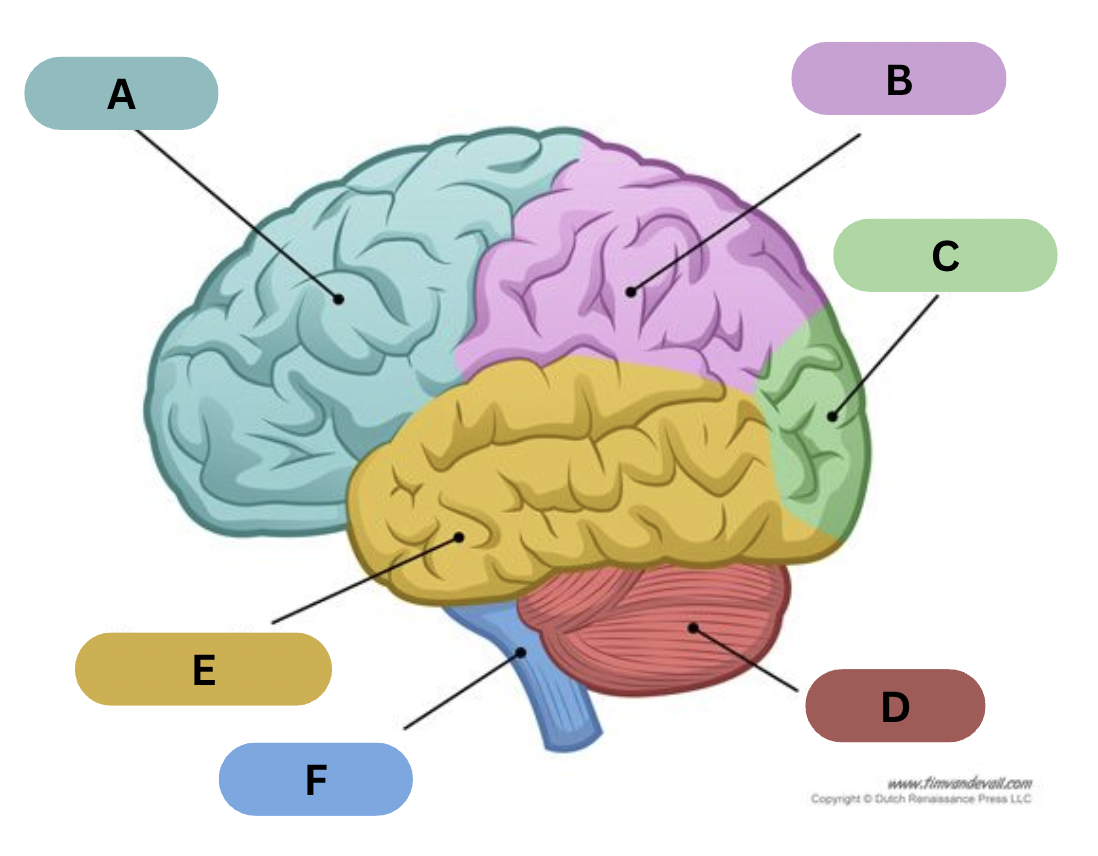
Label A
Frontal lobe
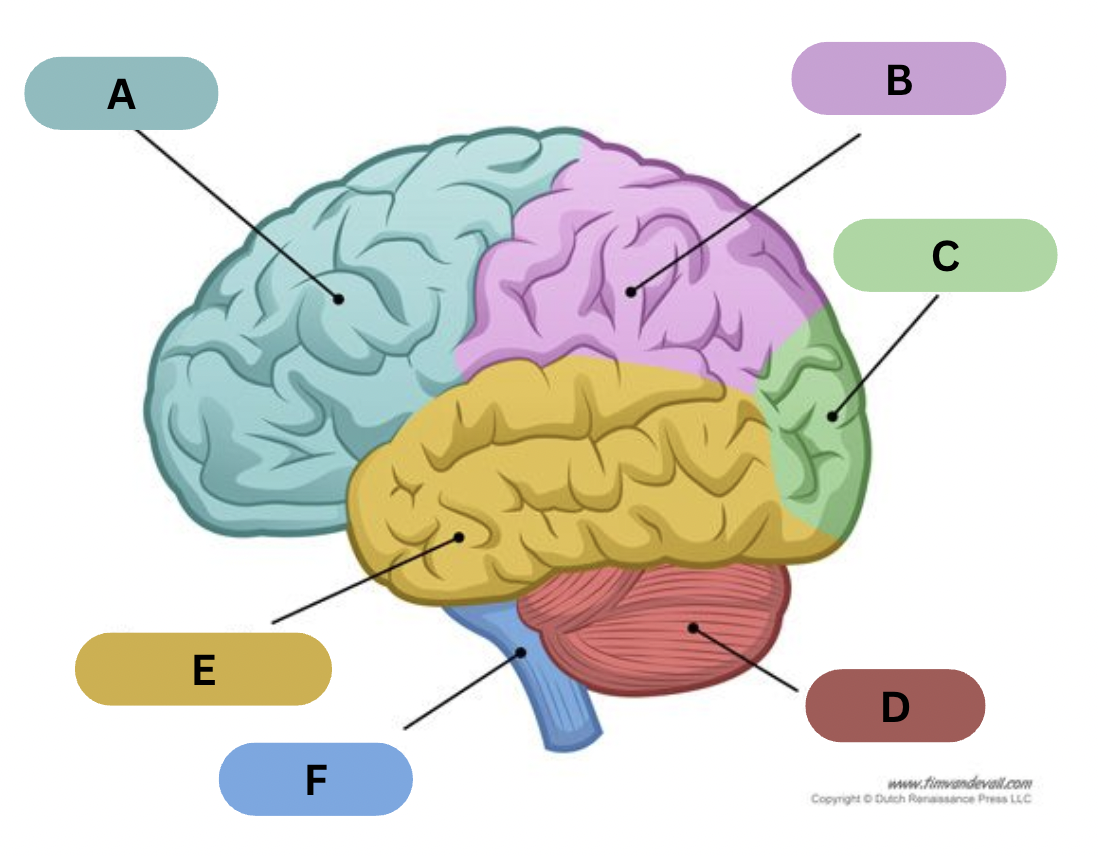
Label B
Parietal lobe
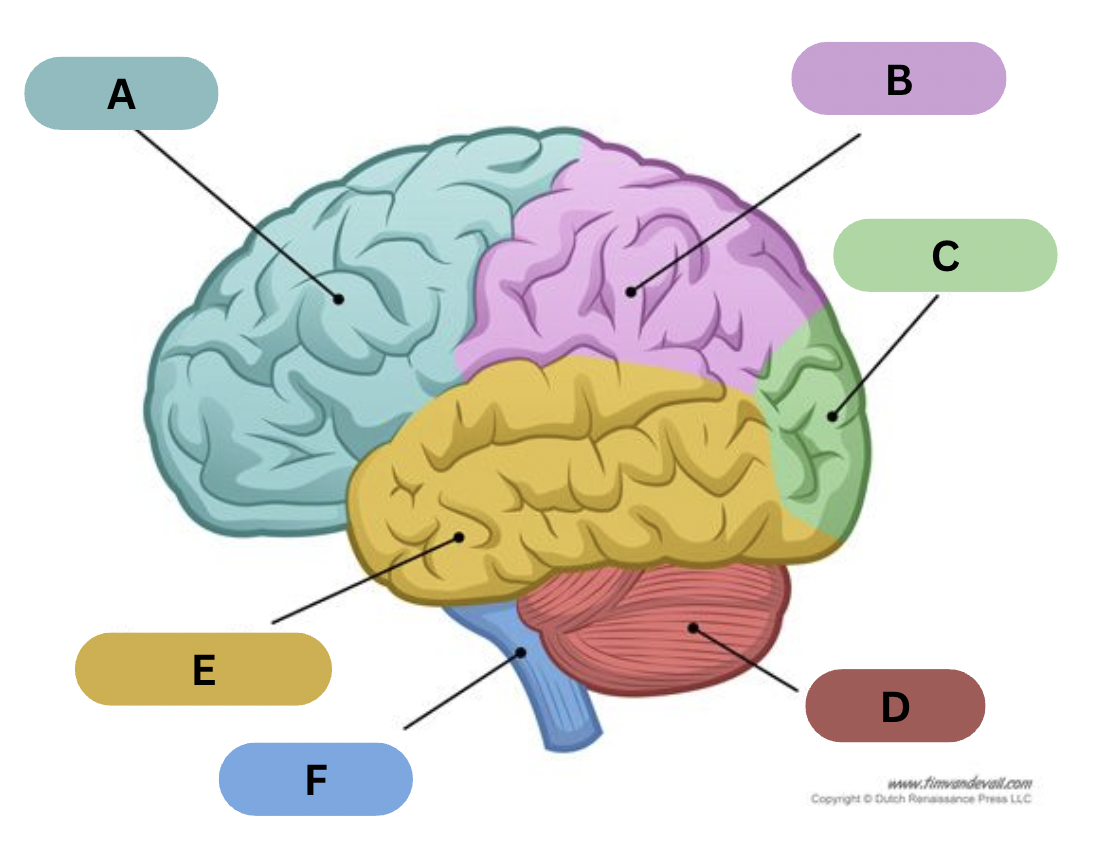
Label C
Occipital lobe
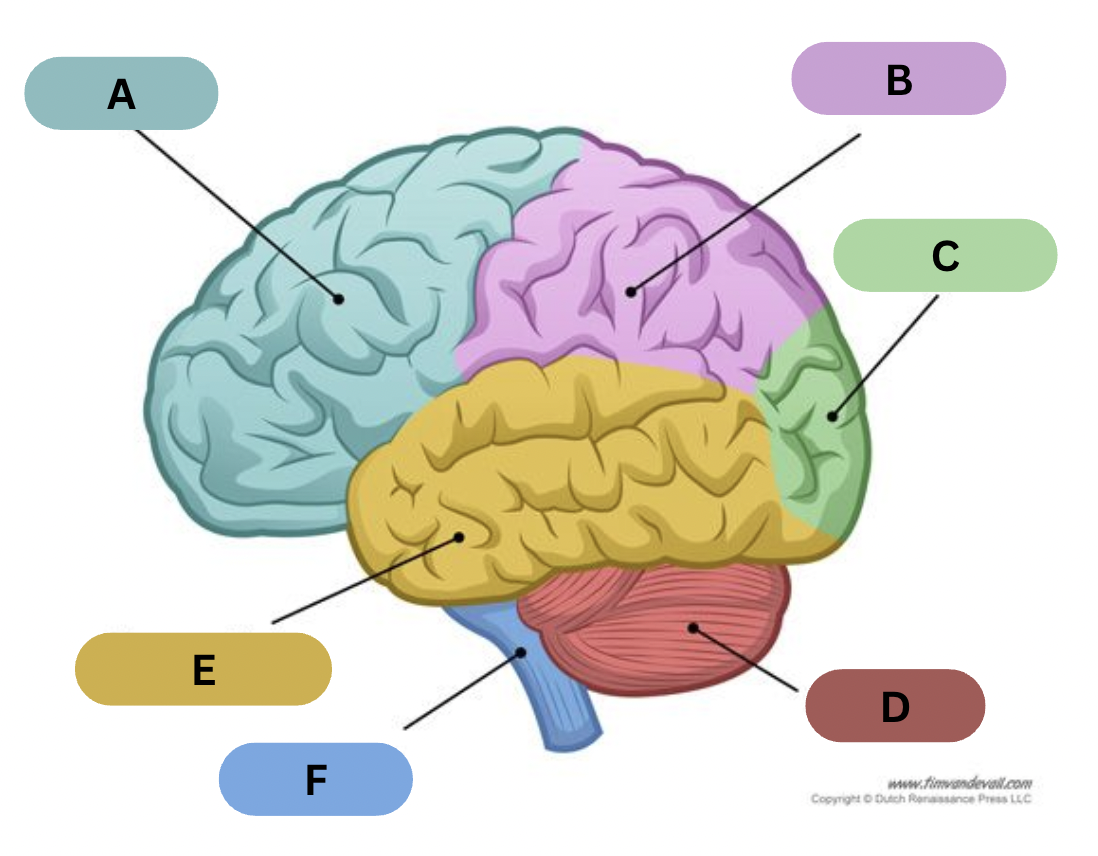
Label D
Cerebellum
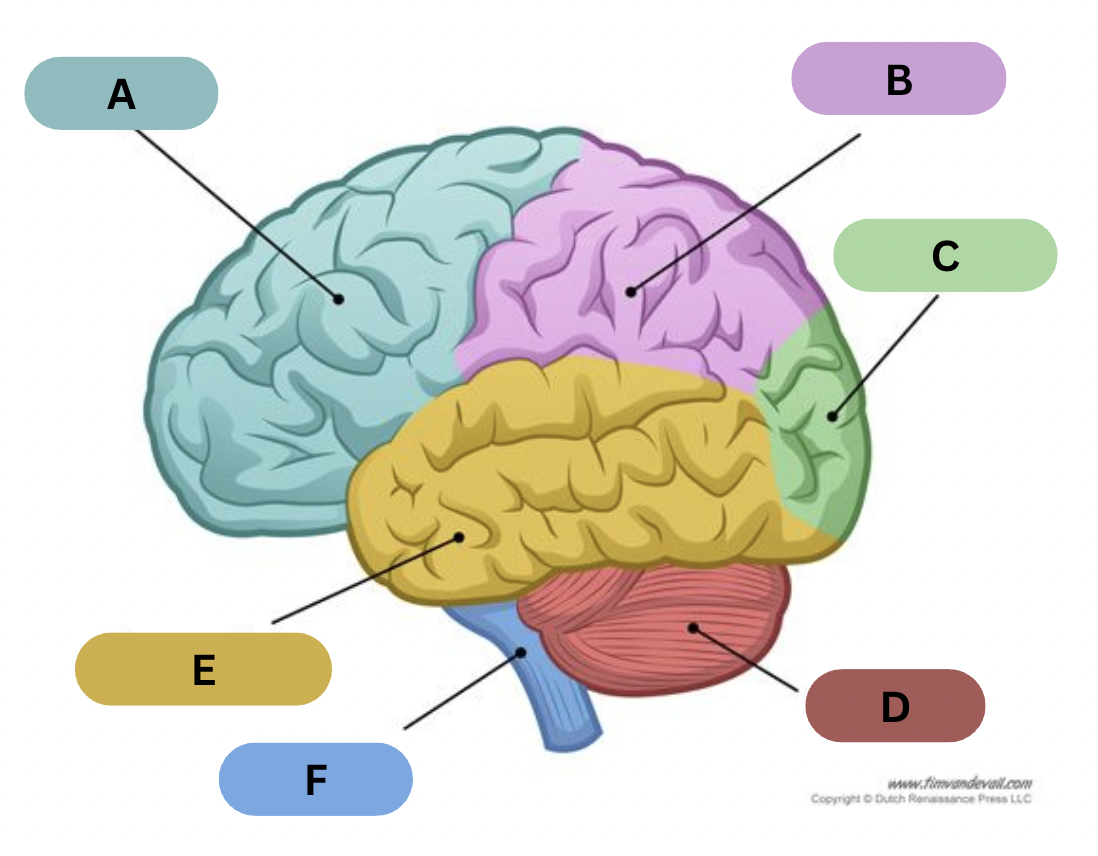
Label E
Temporal lobe
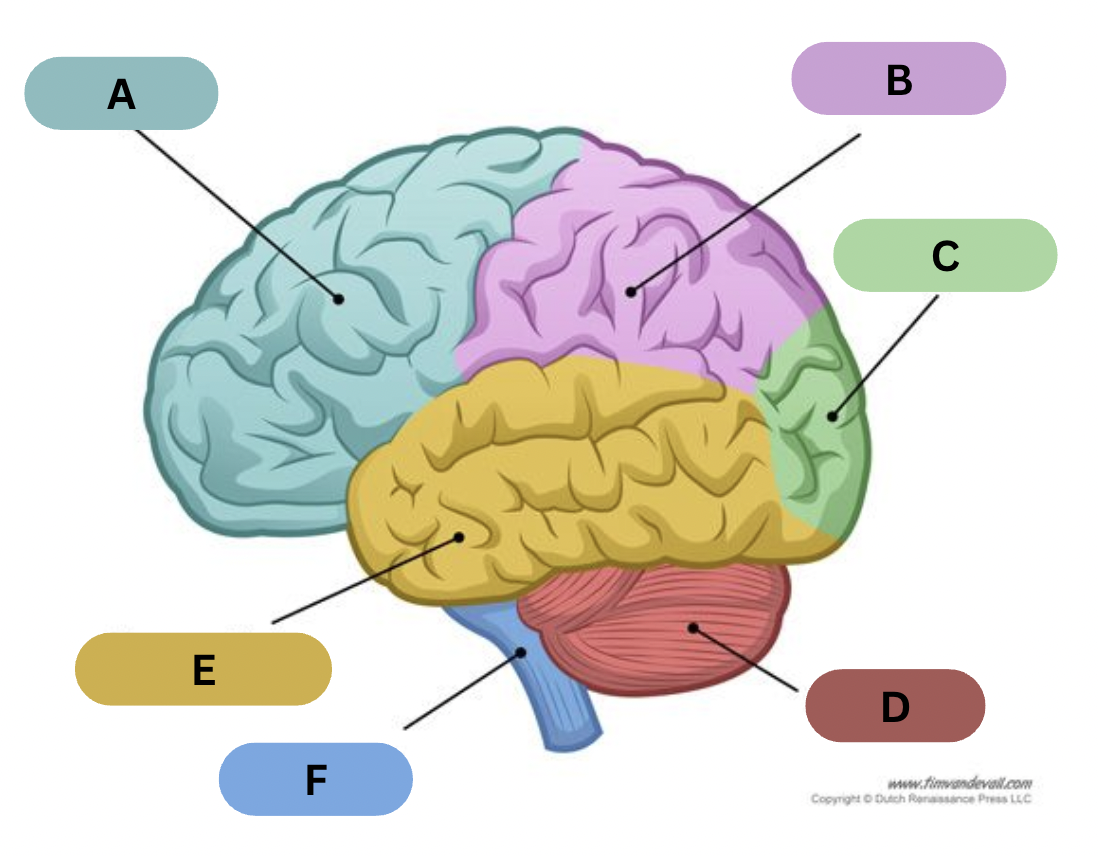
Label F
Brain Stem
What is the function of the Temporal Lobe?
-Hearing
-Emotional behaviours
What is the function of the Occipital Lobe?
Understanding visual information
What are the two important structures in the frontal lobe?
Pre-frontal Cortex and Primary motor cortex.
What is the function of the frontal lobe?
-Movement
-Decision making
-Impulse control
What is the main function of the parietal lobe?
Understanding the world around us (Perception)
What is the cerebellum's function?
Vital role in movement, coordination and balance.
What is asymmetrical function in the brain?
Both sides of the brain are NOT a mirror image of each other.
What does lateralisation of function mean?
Each hemisphere in the brain has different jobs and roles.
What is the function of the left hemisphere?
-Broca's area: Language and speech
-Logic
What is the function of the right hemisphere?
-Creativity
-Spatial awareness
What is the function of the corpus callosum?
Joins together the two hemispheres of the brain
How are female lateralisation different from males?
-Females use both hemispheres more than males.
-Males tend to be dominant to one hemisphere only.
What are some strengths to the theory of gender differences in lateralisation?
-Lots of scientific research to increase reliability
What are some weaknesses to the theory of gender differences in lateralisation?
-It is not always accurate
-Although research has been conducted, no valid conclusion has been made.
What does dopamine do?
Influences learning and attention
What happens if there isn't enough dopamine?
Difficulty concentrating
What does serotonin do?
Plays a large role in our mood
What happens if there isn't enough serotonin?
Can cause depressive emotions
What does GABA do?
Responsible for calming us down
What happens if there isn't enough GABA?
We become over-stressed.
How does synaptic transmission work?
1.Neurotransmitter vesicles arrive at terminal button.
2. Vesicles release neurotransmitters across synaptic gap
3. Receptors on the next nerve cell absorbs the neurotransmitters and pass the message along
What is the role of CNS?
Sends messages around the body, initally from the spinal cord and through PNS around the body.
What is visual agnosia?
Inability to recognize things that can be seen
Symptoms of visual agnosia
Can’t recognize colours, name objects or recognize places.
Where is the brain damaged if someone has visual agnosia?
Parietal Lobe
What is Prosopagnosia?
Face blindness
Symptoms of Prosopagnosia
inability to recognize faces and assume all faces are the same
Where is the brain damaged if someone has prosopagnosia?
FFA- Fusiform face area in the temporal lobe.
What is the function of the pre-frontal cortex?
Controls aggression
What happens if the pre-frontal cortex is damaged?
More aggression and impulsiveness.
What happened to Phineas Gage?
Railway line work had brain damage to the pre-frontal cortex resulting in more aggression and rudeness.
Later died due to epilepsy.
What was Damasio et al (1994) 's Aim?
Investigate the brain damage of Phineas Gage and determine functions of the frontal lobe
What was Damasio's procedure?
-Built a 3D model of Gage's brain
-Looked at where the iron rod had damaged the brain
What was the results to Damasio's study?
-Extreme damage to frontal lobe
-Affected both hemispheres
-Damage to white matter
What did Damasio conclude?
That the frontal lobe (ventromedial region) was responsible for emotion which is why Gage became so agressive.
Strengths to Damasio et al.
-Scientific procedure helped modernized their understanding.
-Helps us understand what damage to frontal lobes ensues.
-Real life scenario increases validity
Weaknesses to Damasio et al.
-Old case (over 150 years)
-Hard to generalize due to high uniqueness of the case.
What was Spery (1968)'s Aim?
To find out the cognitive functions that are linked to each hemisphere in the brain
What was Sperry's choice of participants like?
11 participants from USA who had just undergone surgery for severe epilepsy. They had a "split brain"
How did Sperry test hemispheric functions (The 6 tasks)?
Task 1: Language, visual and sensory interpretation
Task 2:Sensory
Task 3:Matching visual with actions
Task 4: Math
Task 5: Reaction testing
Task 6: Spatial task
What was significant about the way Sperry tested his aim?
Tested with both the right visual field and left visual field, to see the functions of both hemispheres.
What did Sperry conclude from his experiment?
-The left hemisphere has the main role of language
-The right hemisphere was mainly focused on spatial awareness, emotions, reading and math.
Strengths to Sperry (1968)
-A lot of info to support the reliability of the study
-Standardized procedure for each participant.
-Helps the understanding of lateralisation
Weaknesses to Sperry (1968)
-Lacks generalisability due to small sample
-Split brains don't represent normal brains
-Lab experiment reduce ecological validity