gb pathologies
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
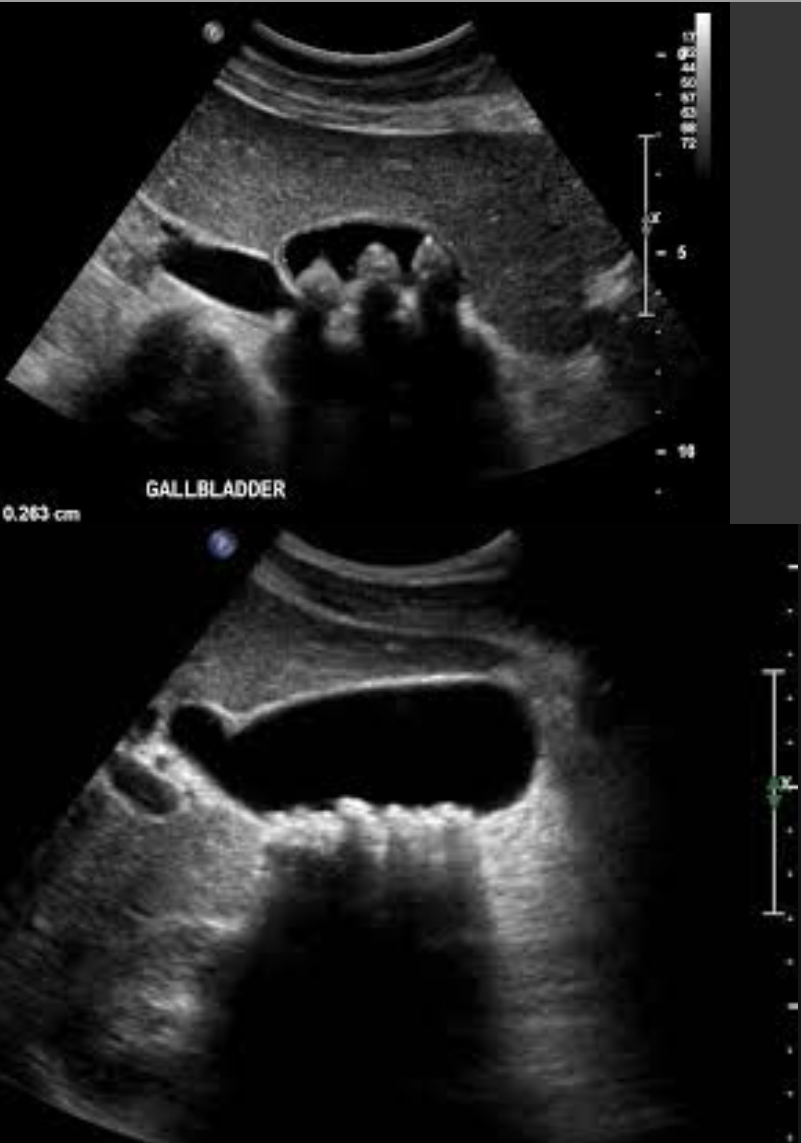
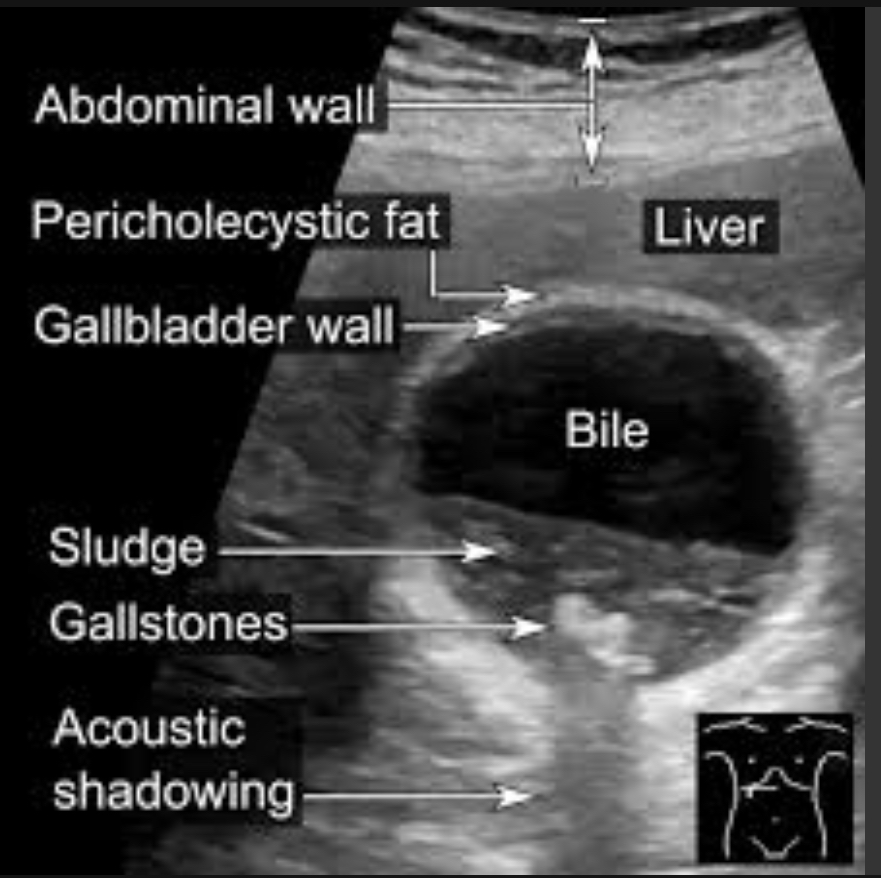
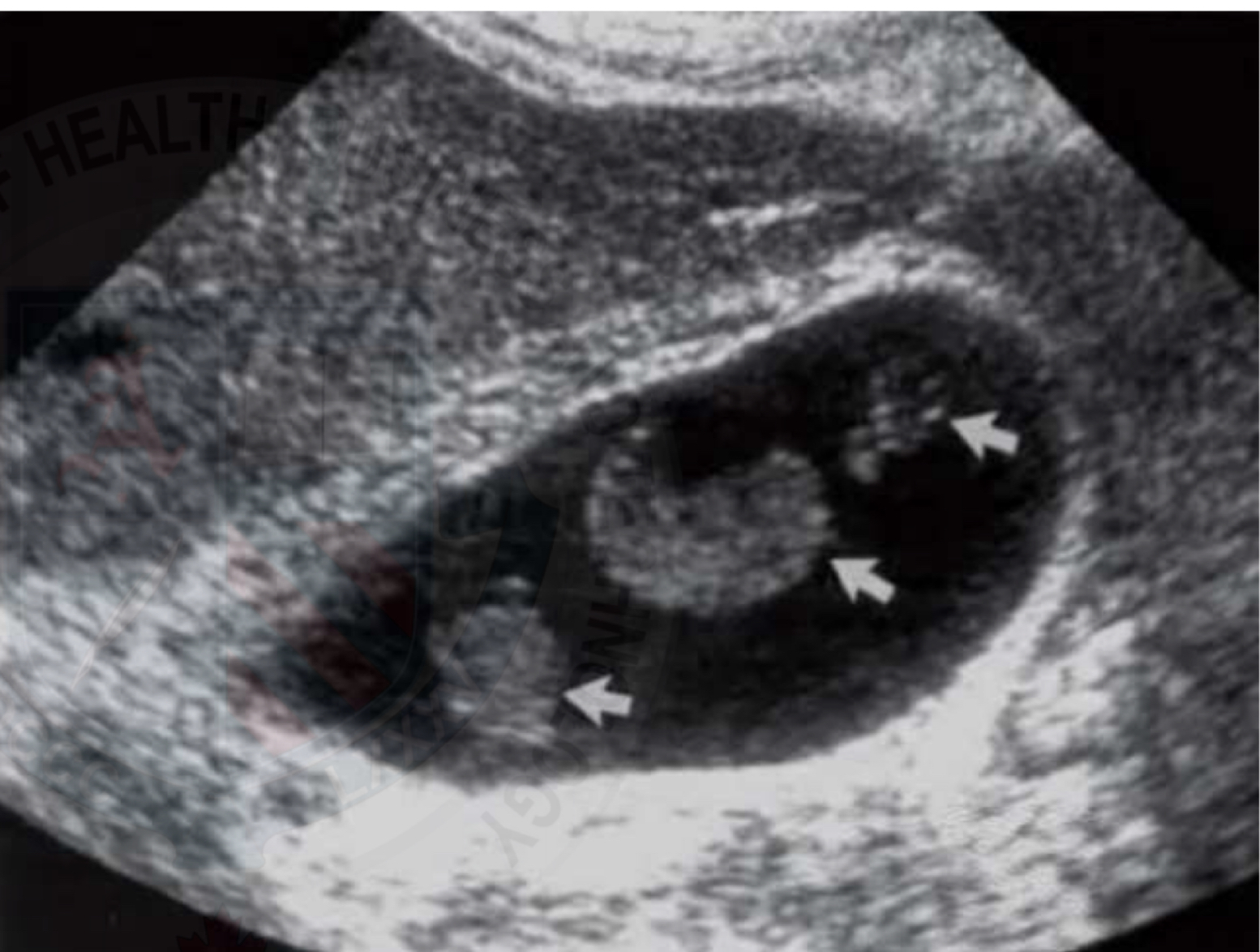
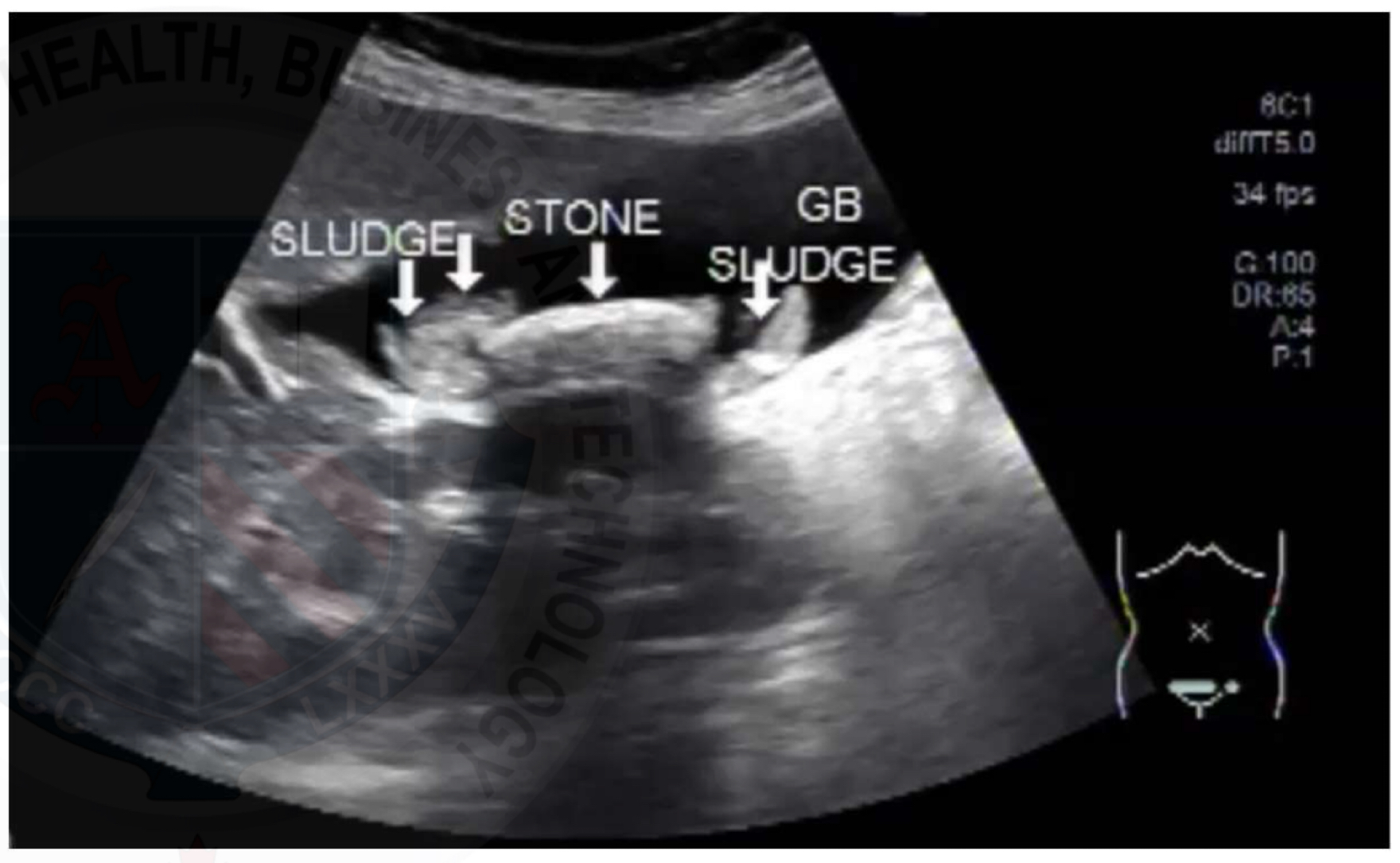
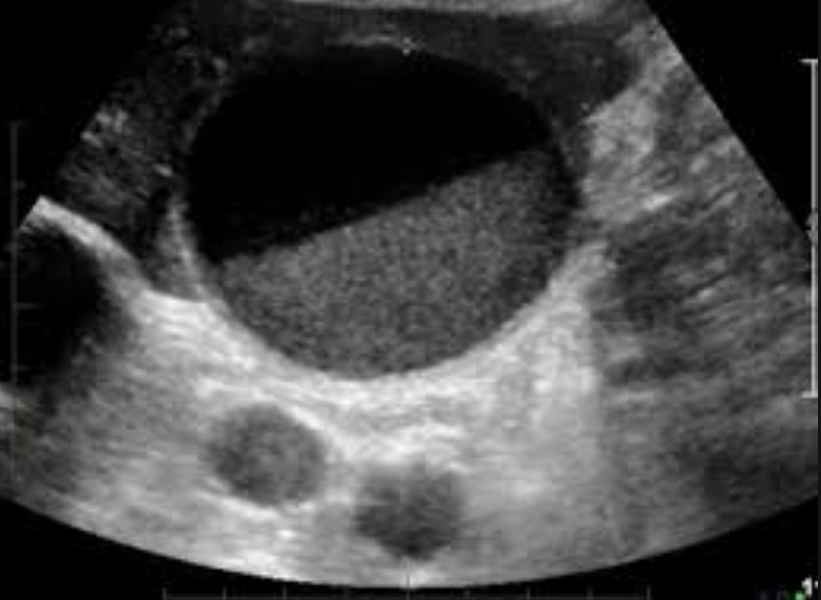
Cholelithiasis
Stones in GB due to bile imbalance; may be associated with sludge
Echogenic foci with posterior shadowing; mobile; WES sign if GB packed
Sludge
Bile stasis; precursor to stone formation; can mimic mass
Low-level echoes layering dependently; no shadowing mobile with position change
Homogeneous Sludge
Uniform low-level echoes
Smooth Echogenic dependent layer
Sludge balls
Round, mobile sludge aggregates
Round, mobile Echogenic foci; no shadowing
Tumefactive sludge
Mass-like sludge; mimics neoplasm
Non-mobile Echogenic mass; no shadowing
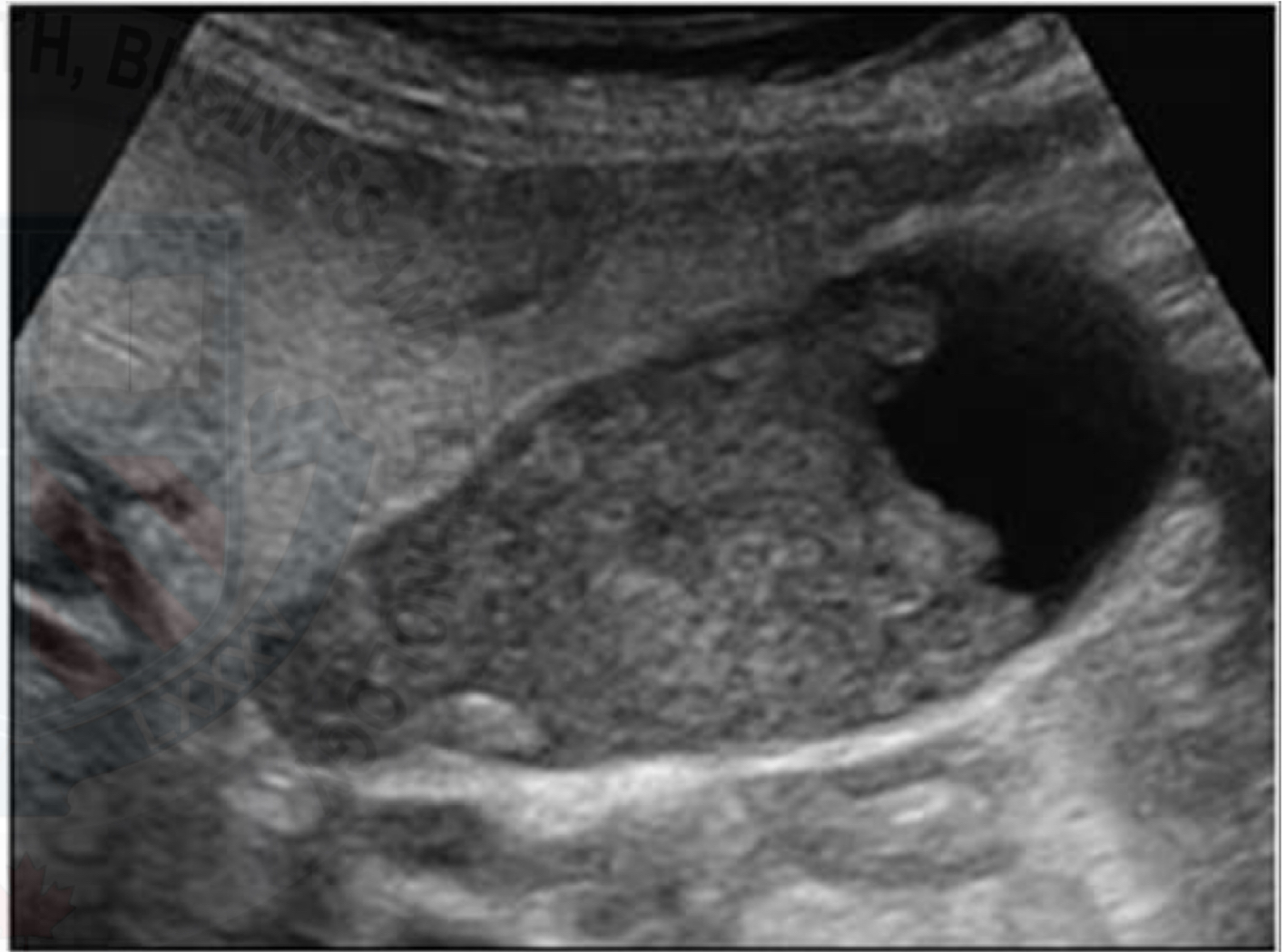
Gallstones VS sludge balls
Feature | Gallstones | Sludge Balls (Tumefactive Sludge) |
|---|---|---|
Composition | Solid crystals (cholesterol, bilirubin, etc.) | Thickened bile and mucin |
Appearance | Echogenic foci, well-defined, round/oval | Echogenic clumps, amorphous, may appear mass-like |
Mobility | Highly mobile with position change | May move slowly or be semi-mobile |
Shadowing | ✅ Yes – posterior acoustic shadowing | ❌ No shadowing |
Twinkling artifact | ✅ Often present on color Doppler | ❌ Absent |
Doppler flow | ❌ No blood flow | ❌ No blood flow |
Common Pitfall | May be missed if very small | Can mimic gallbladder tumors |
Mobile debris
Fine, swirling echoes in bile
Cloud-like, non-shadowing Echogenic material
Dependent sludge
Settles in most dependent GB region
Consistently layers in lowest portion
Sludge layering
Horizontal fluid-fluid level
Layered Echogenic line; shifts with patient position
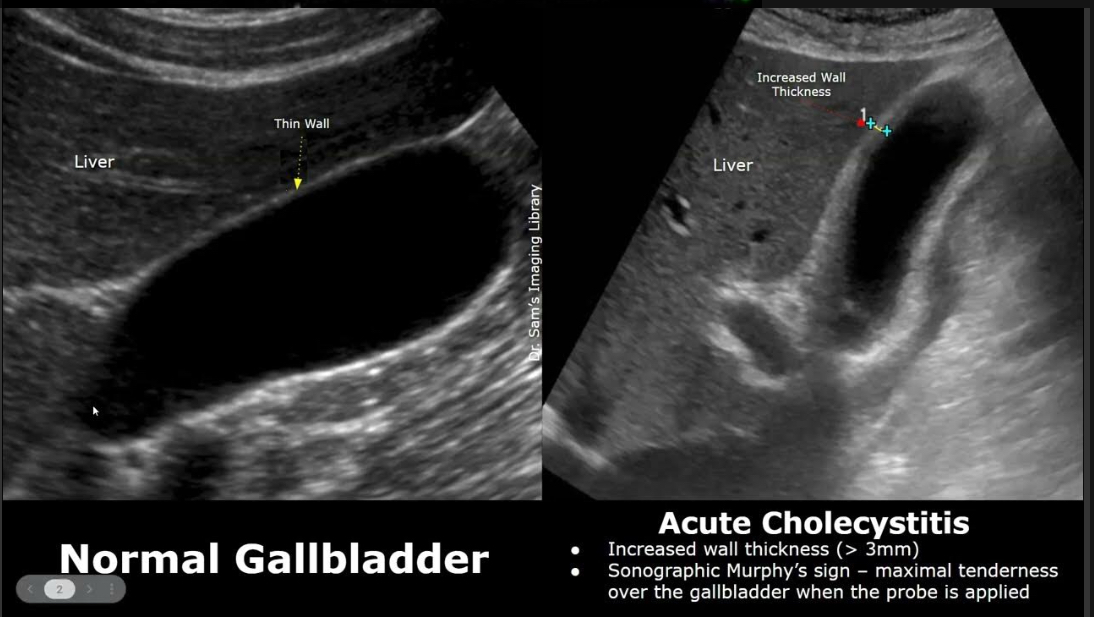
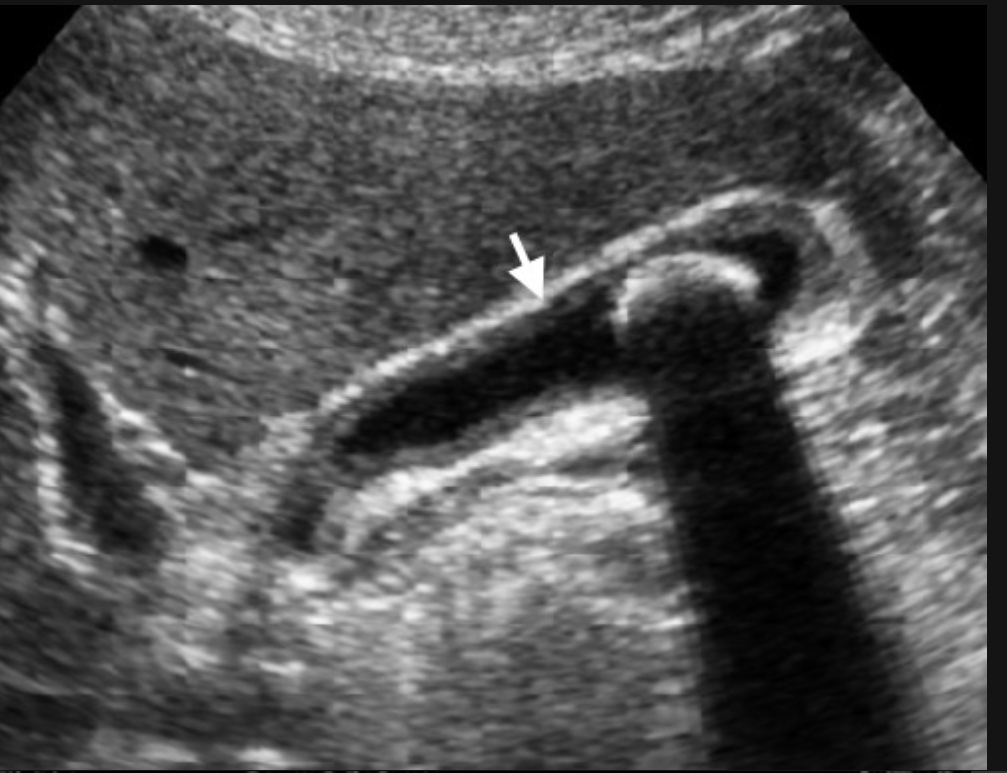
Acute cholecystitis
Cystic duct obstruction → inflammation
Thick wall >3 mm, +Murphy’s sign, pericholecystic fluid, hyperemia, stones/sludge
Acalculous cholecystitis
Acute inflammation without stones; seen in critically ill, trauma, burns
Wall thickening >3.5mm
Enlarged GB, wall thickening, sludge, pericholecystic fluid, positive Murphy’s sign, no stones
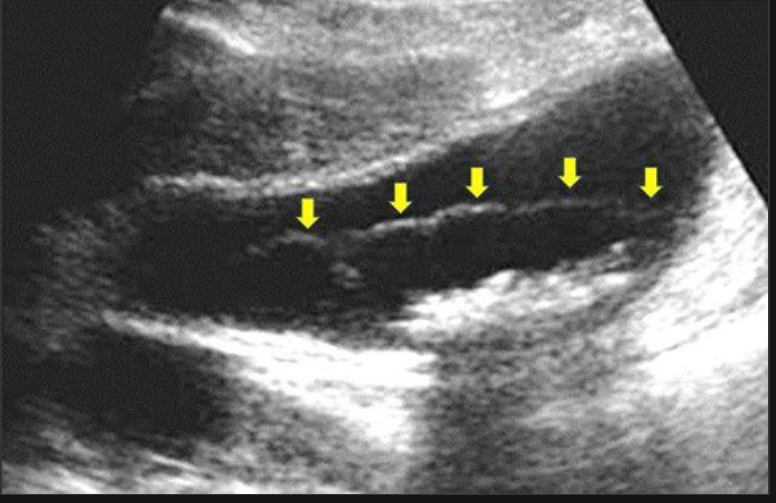
Gangrenous cholecystitis
Necrosis of GB wall due to ischemia; complication of acute cholecystitis
Irregular wall thickening, intraluminal membranes, sloughed mucosa, absence of color flow, possibly gas
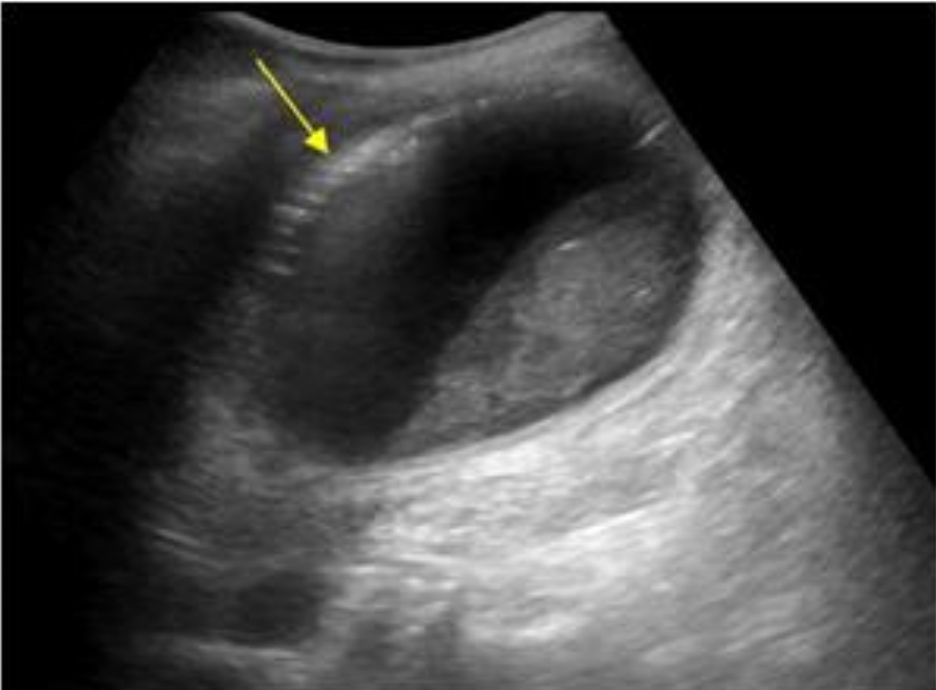
Emphysematous cholecystitis
Infection with gas-forming bacteria; elderly diabetics; surgical emergency
Gas in GB wall/lumen as echogenic foci with dirty shadowing or ring-down artifact; air-fluid levels
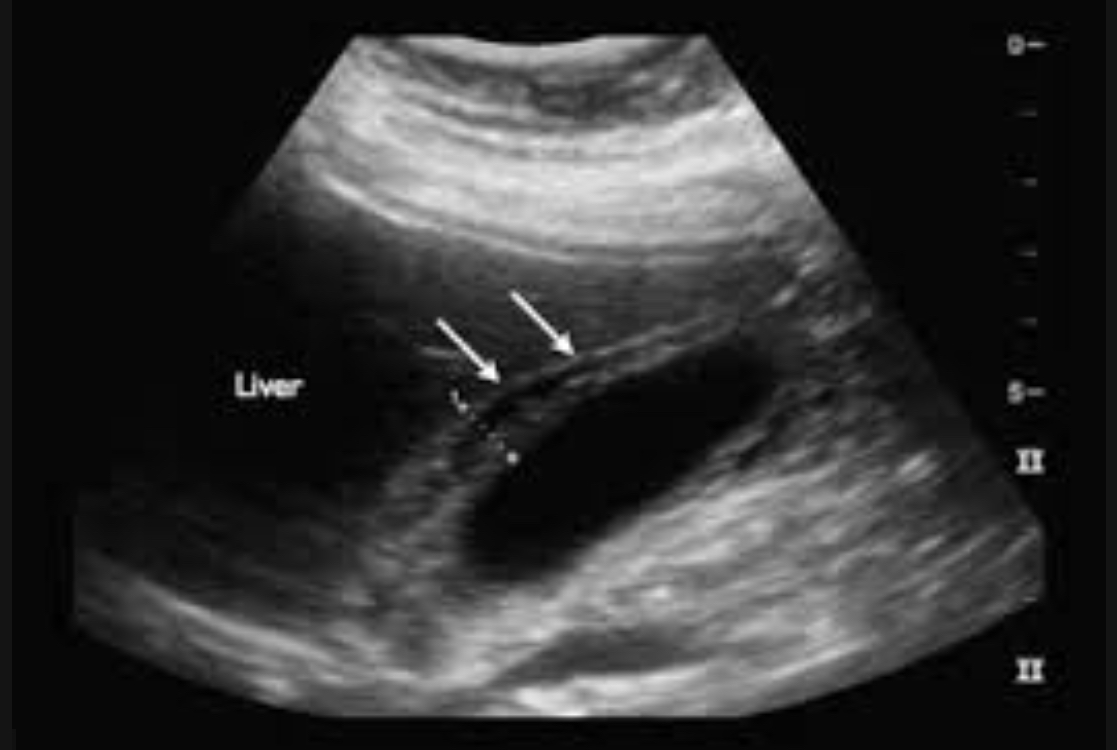
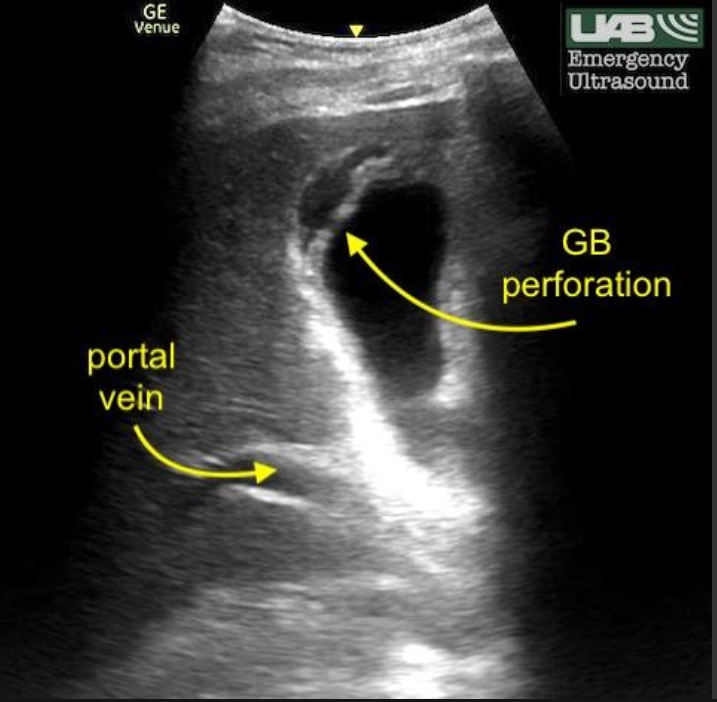
Gallbladder perforation
Wall rupture due to untreated acute cholecystitis
Wall defect, adjacent abscess/fluid, complex pericholecystic area, possible stones/debris outside GB
Chronic cholecystitis
Long-standing inflammation, fibrosis; often associated with stones
Thick fibrotic wall, contracted GB, stones, no hyperemia; WES sign
Types of cholecystitis
Type | Definition | Cause | Symptoms | Ultrasound Findings | Key Differentiator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Acute Cholecystitis | Sudden inflammation of GB | Cystic duct obstruction by gallstone (most common) | RUQ pain, fever, +Murphy’s sign, nausea | Thick GB wall (>3mm), distended GB, pericholecystic fluid, gallstones, +Sonographic Murphy’s sign | Gallstones with signs of acute inflammation |
Acalculous Cholecystitis | Acute GB inflammation without stones | Critically ill patients (trauma, burns, sepsis, TPN) | Often vague or absent in non-verbal or ICU patients | GB wall thickening, distention, pericholecystic fluid, no stones | Critically ill + same findings as acute cholecystitis but no stones |
Chronic Cholecystitis | Repeated or long-term inflammation | Recurrent gallstones or chronic irritation | Intermittent RUQ pain, intolerance to fatty meals | Thickened fibrotic GB wall, small/contracted GB, stones, WES sign | Shrunken GB with stones and no acute symptoms |
Emphysematous Cholecystitis | Severe form with gas-forming bacteria | Clostridium, E. coli (diabetics at risk) | RUQ pain, fever, very ill, sepsis risk | Air in GB wall/lumen, ring-down artifact, dirty shadowing | Gas in wall or lumen; surgical emergency |
Gangrenous Cholecystitis | Complication of untreated acute cholecystitis leading to necrosis | Prolonged inflammation & ischemia | Severe pain, fever, unstable vitals | Irregular GB wall, sloughed membranes, intraluminal debris, no Murphy’s sign | Necrosis with absent Murphy's sign, debris inside GB |
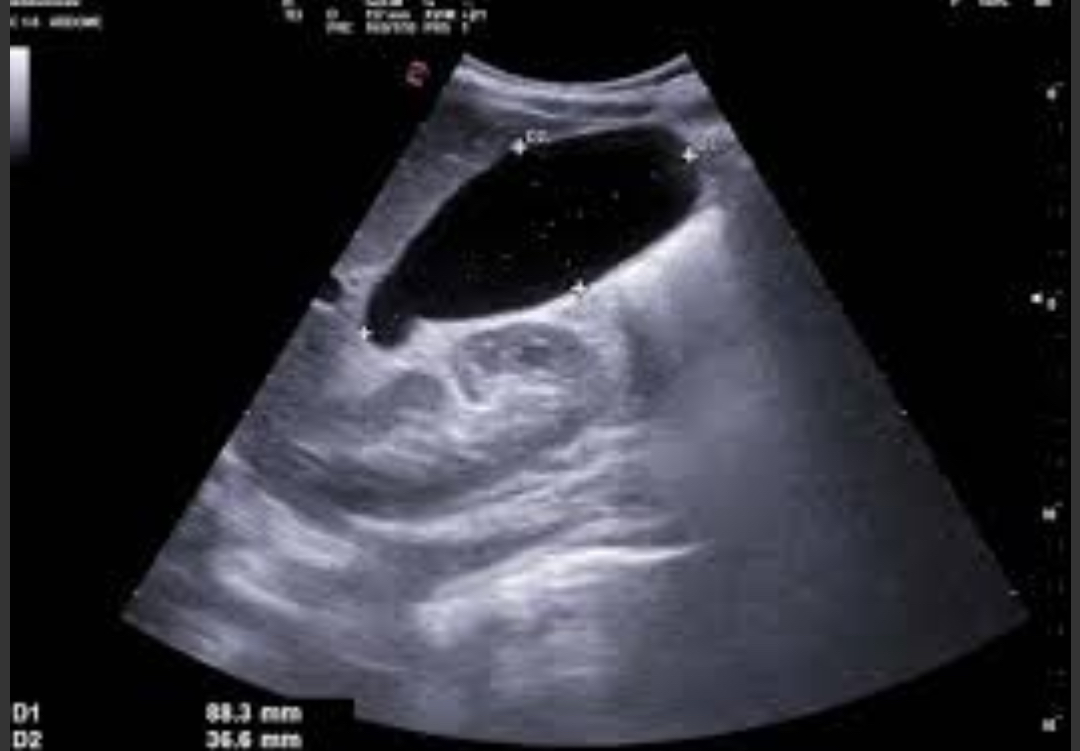
Hydropic GB / Mucocele
GB distension from prolonged cystic duct obstruction; filled with mucus
GB >5 cm transverse, anechoic content, thin wall; often with obstructing stone in neck
Torsion of Gallbladder
GB twists on mesentery; elderly or congenital; surgical emergency
Enlarged, floating GB; whirlpool sign; hyperemic early, avascular later; abnormal orientation
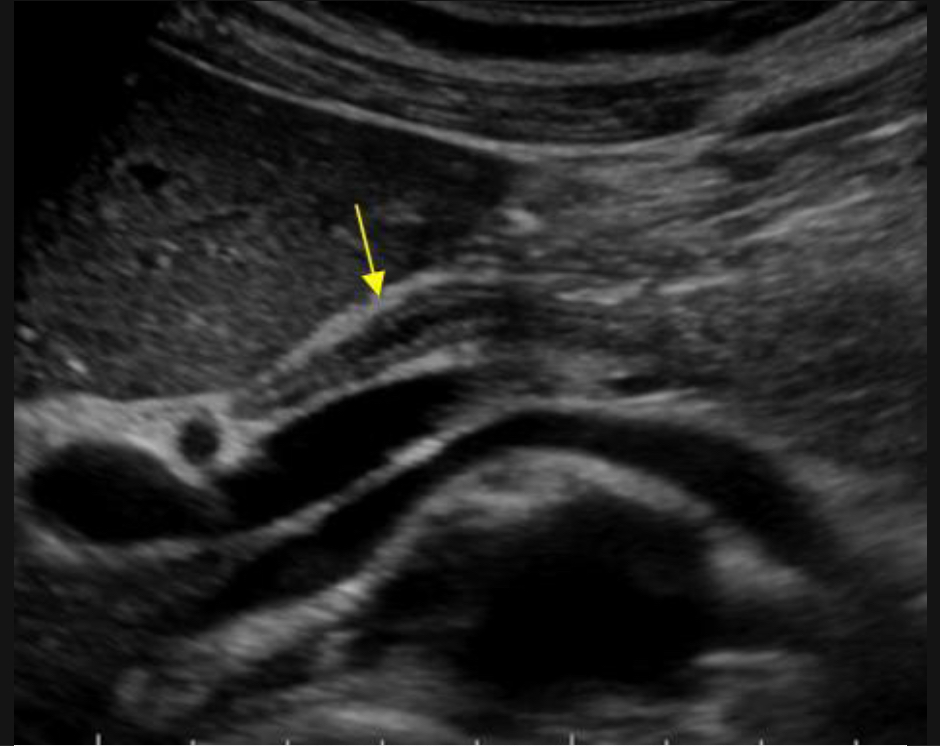
Choledocholithiasis
Stones in CBD; may cause cholangitis or pancreatitis
Echogenic shadowing foci in CBD; dilated ducts; sludge or debris may be present
Cholangitis
Biliary duct infection, often due to obstruction
Duct wall thickening, dirty echoes in bile ducts, dilated intrahepatic ducts, possible abscess
Biliary atresia
Neonatal absence of biliary ducts; fatal if untreated
Absent GB; triangular cord sign; hepatomegaly; minimal/absent intrahepatic duct dilation
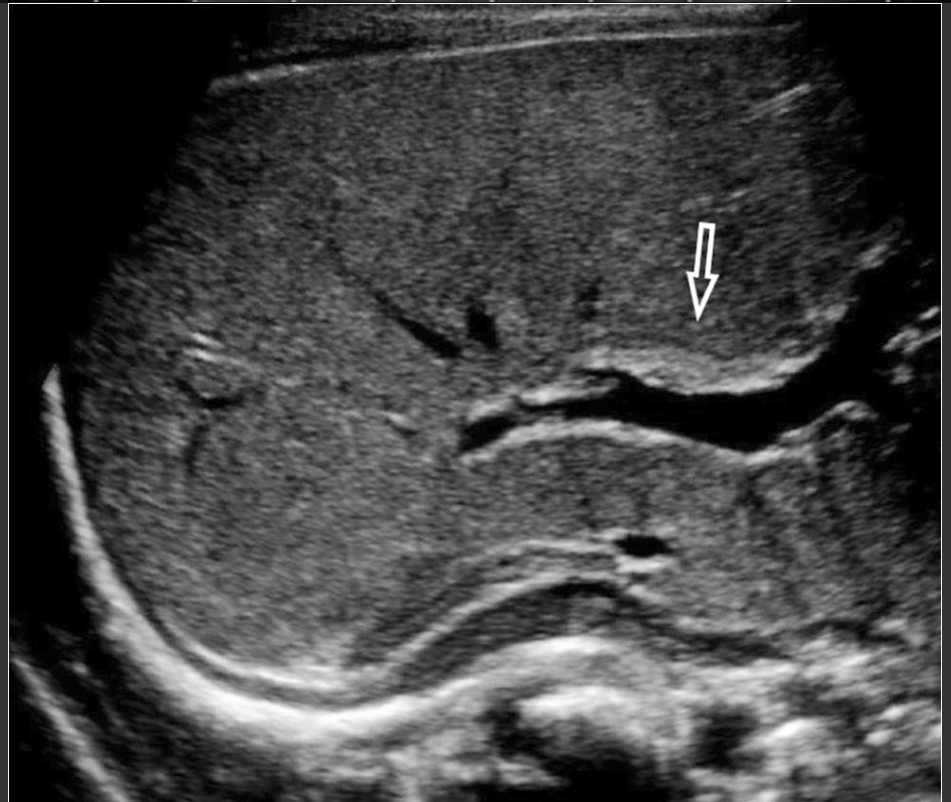
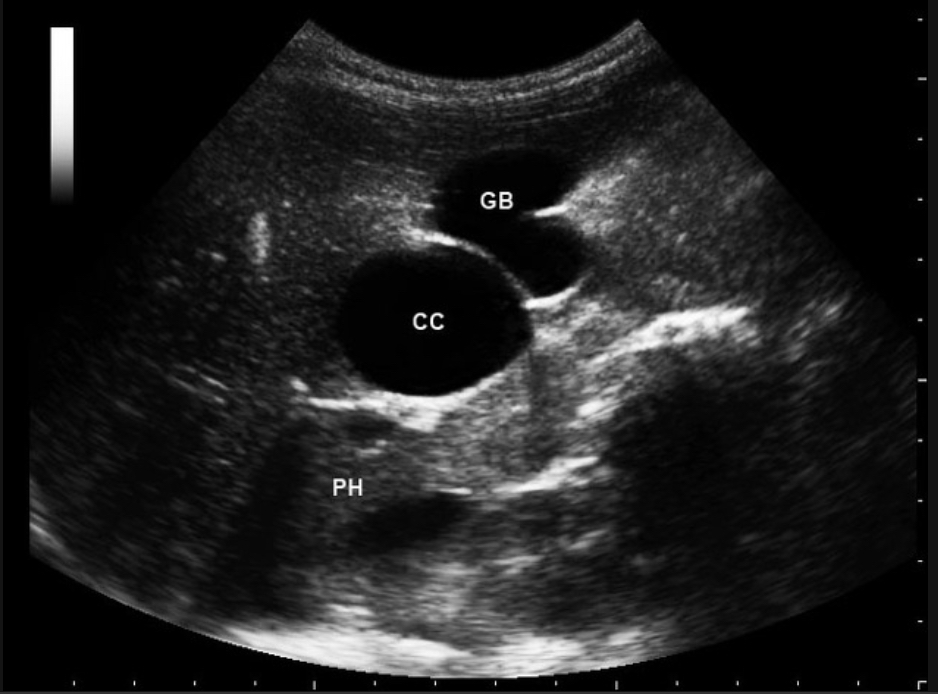
Choledochal cyst
Congenital cystic dilation of biliary ducts
Anechoic mass near porta hepatis; fusiform or saccular dilation of CBD
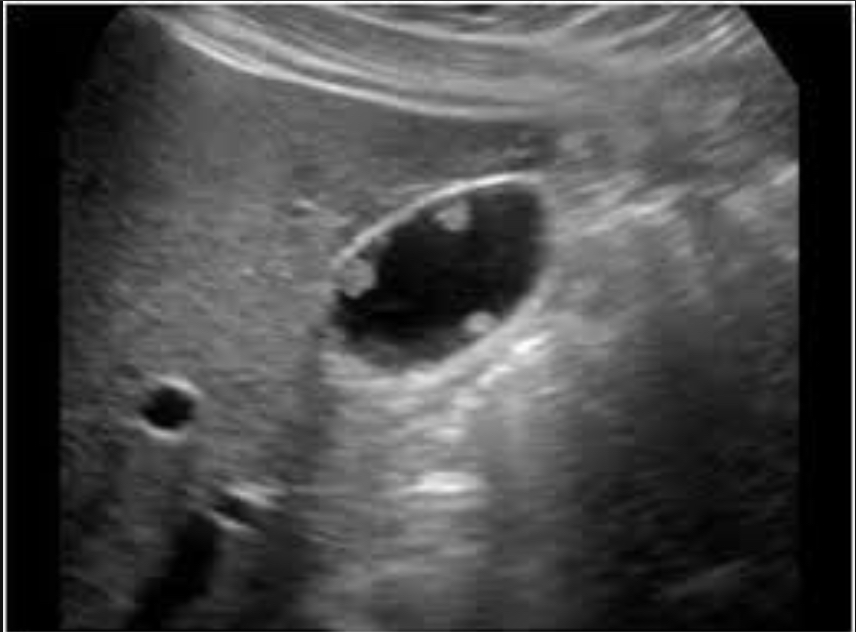
Gallbladder polyps
Benign mucosal projections ; usually <10mm
Non-mobile, non-shadowing Echogenic lesions
Types of gallbladder polyps
Type | Description | Common? | Malignant Risk? |
|---|---|---|---|
Cholesterol polyps | Accumulation of cholesterol-laden macrophages | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
Adenomas | True epithelial tumors | ⚠ Less common | ⚠ Yes, potential for cancer |
Inflammatory polyps | Related to chronic inflammation | 🚫 Rare | ❌ No |
Adenomyomatosis | Thickening with intramural diverticula | Moderate | ❌ No (usually) |
Gallbladder carcinoma | Malignant mass/polyploid lesion | ❗ Rare | ✅ Yes |
Benign vs malignant polyps
Feature | Benign | Suspicious for Malignancy |
|---|---|---|
Size | <10 mm | >10 mm |
Shape | Round, smooth | Irregular, sessile |
Mobility | Fixed (unlike stones) | Fixed |
Shadowing | No | No |
Growth rate | Stable | Rapidly growing over time |
Cholesterol polyps
Most common GB polyp type; lipid-laden macrophages
Small, multiple Echogenic polyps; non-shadowing, non-mobile; often <10mm
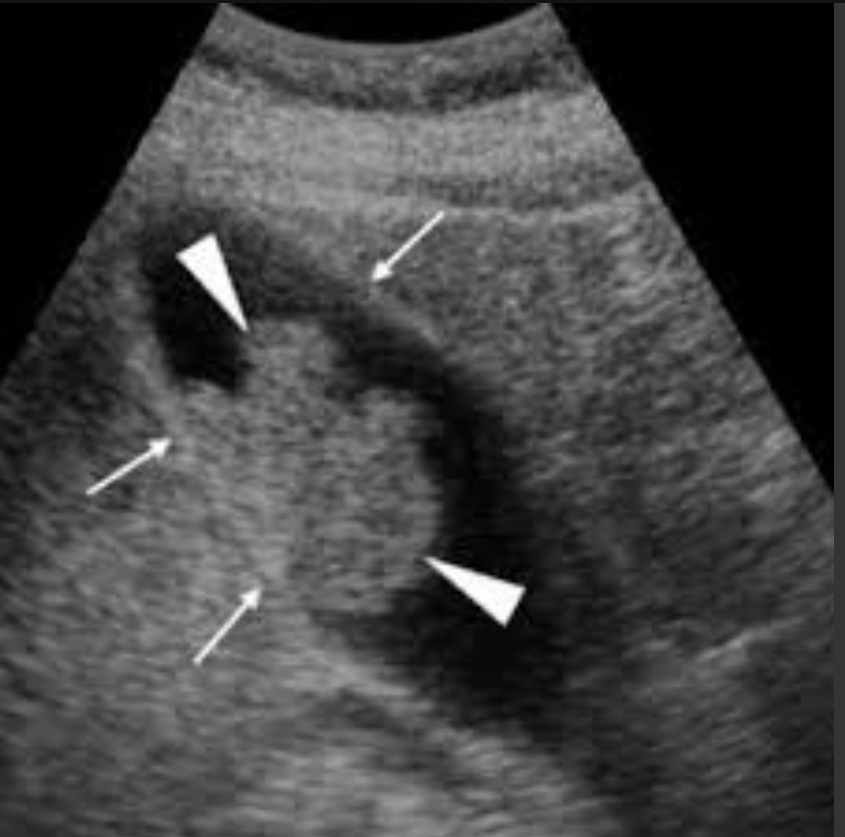
Gallbladder adenoma
Benign epithelial tumor; <1cm usually; pre malignant if >1cm
Non-mobile, non-shadowing Echogenic polyploid lesion; smooth contours; color Doppler may show flow
Gallbladder carcinoma
Rare, aggressive malignancy; associated with stones or porcelain GB
Irregular, heterogeneous mass; wall thickening; polypod lesion>1cm; may invade liver
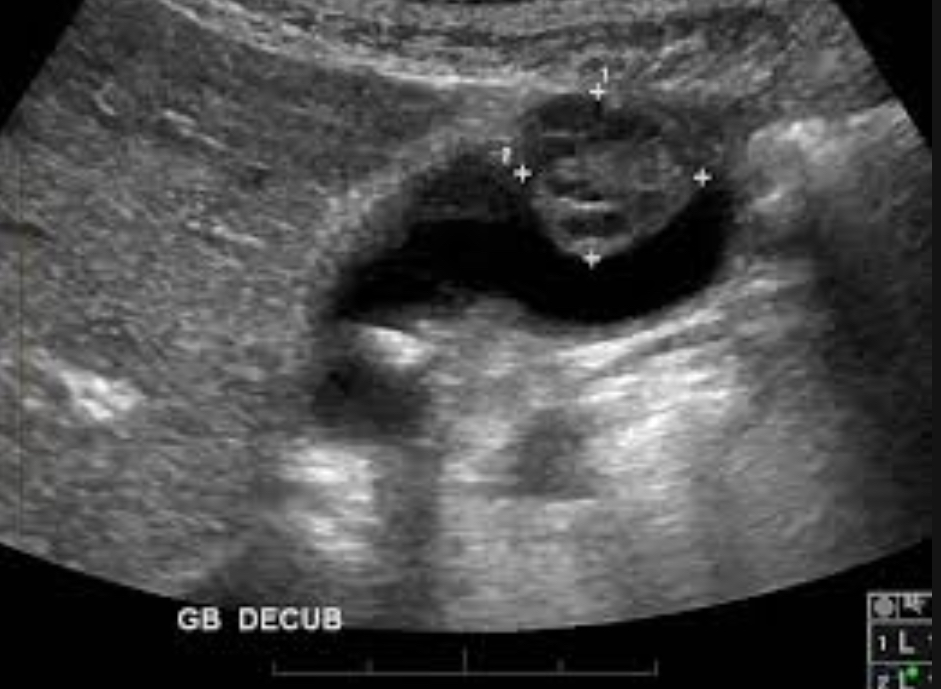
Porcelain gallbladder
Calcified GB wall; strongly associated with carcinoma
Echogenic wall with shadowing; complete or partial calcification pattern
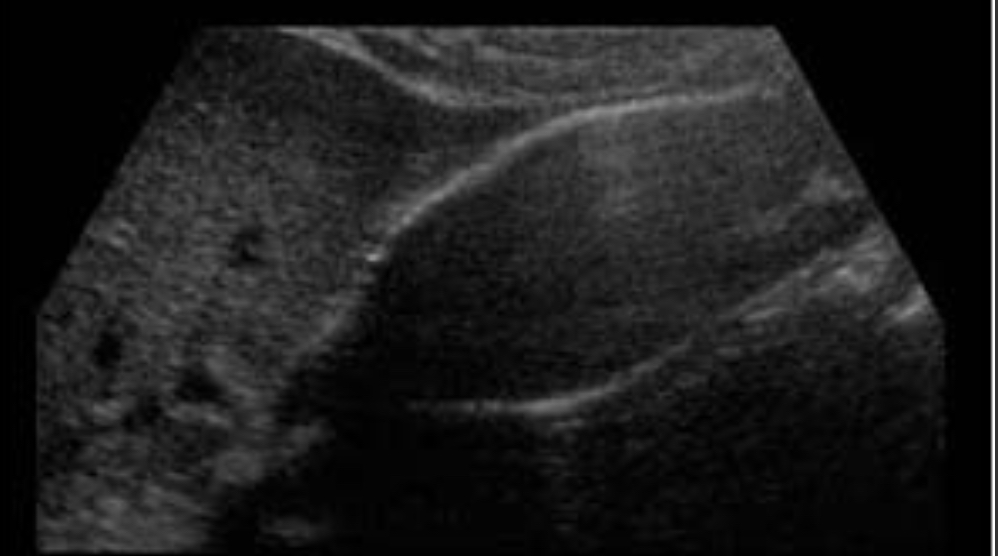
Courvoisier gallbladder
Enlarged painless GB due to distal biliary obstruction (usually pancreatic tumor)
Large distended GB; no stones; pancreatic head mass; dilated ducts
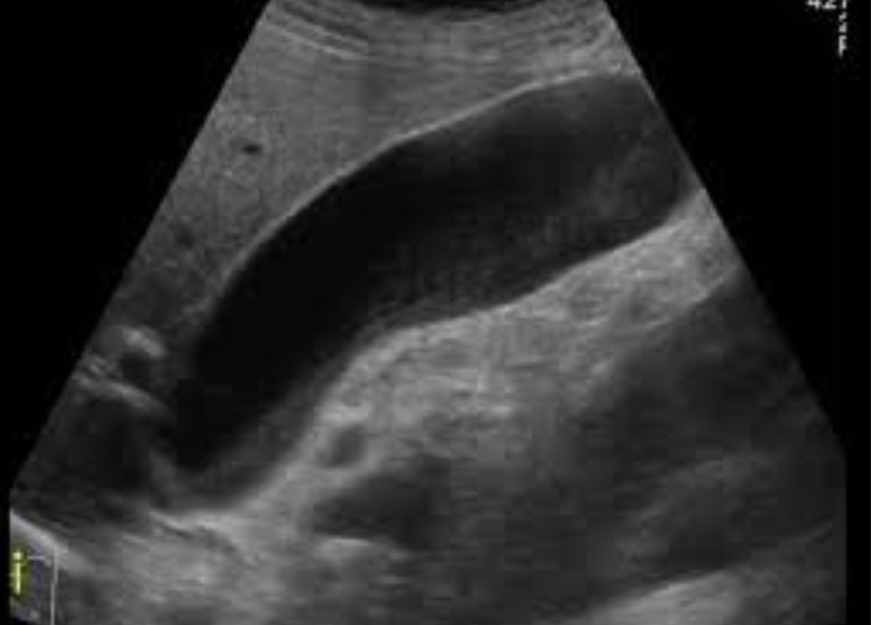
Biliary obstruction
Blockage in biliary outflow
Intrahepatic duct dilation; CBD>6mm; parallel channel sign; may see cause : stone, stricture, mass
Biliary stricture
Narrowing from surgery, trauma, or inflammation
Focal narrowing with proximal duct dilation; no vascular flow across narrowed segment
Cholesterolosis
“Strawberry GB”
Lipid deposition in mucosa
Echogenic foci in wall; diffuse or multiple small polyps; no shadowing; GB wall appears speckled
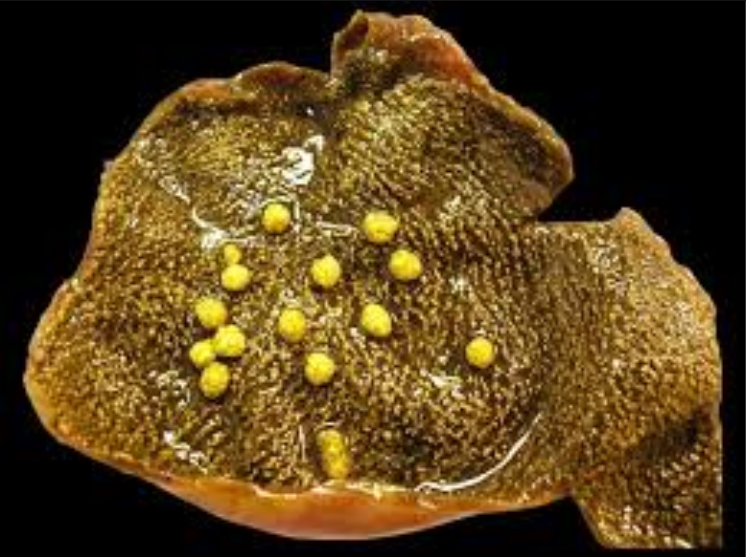
Adenomyomatosis
Hyperplasia of GB wall and mucosa with Rokitansky-Asschoff sinuses
Comet-tail artifacts; thickened wall; anechoic intramural spaces, especially in fundus
Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses
Intramural mucosal diverticula seen in adenomyomatosis
Small anechoic intramural cystic spaces; ring-down or comet-tail artifacts
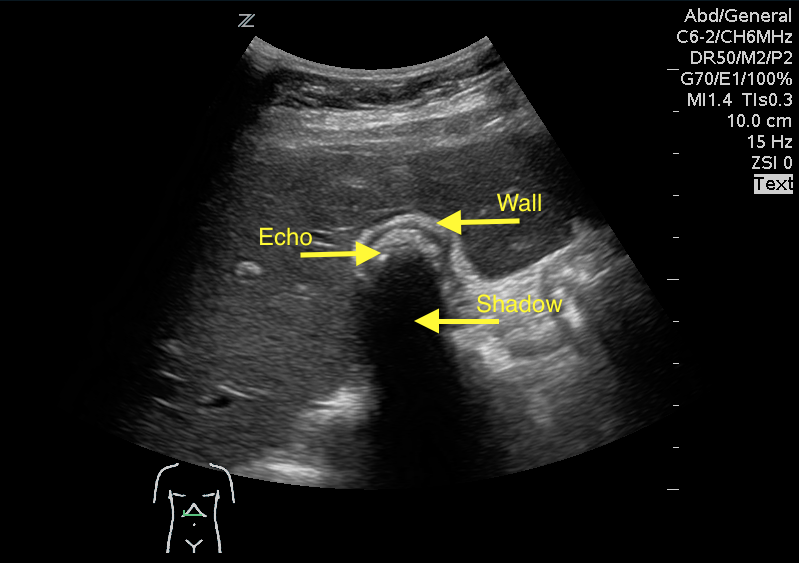
WES sign
Wall echo shadow : when GB is full of stones
Murphy’s sign
Clinical test used to diagnose conditions such as acute cholecystitis : inflammation of the GB
When pressure is applied to upper right abdomen while patient takes a deep breath = they experience pain and stops breathing due to discomfort
Comet-tail artifact
Reverberation seen in Adenomyomatosis
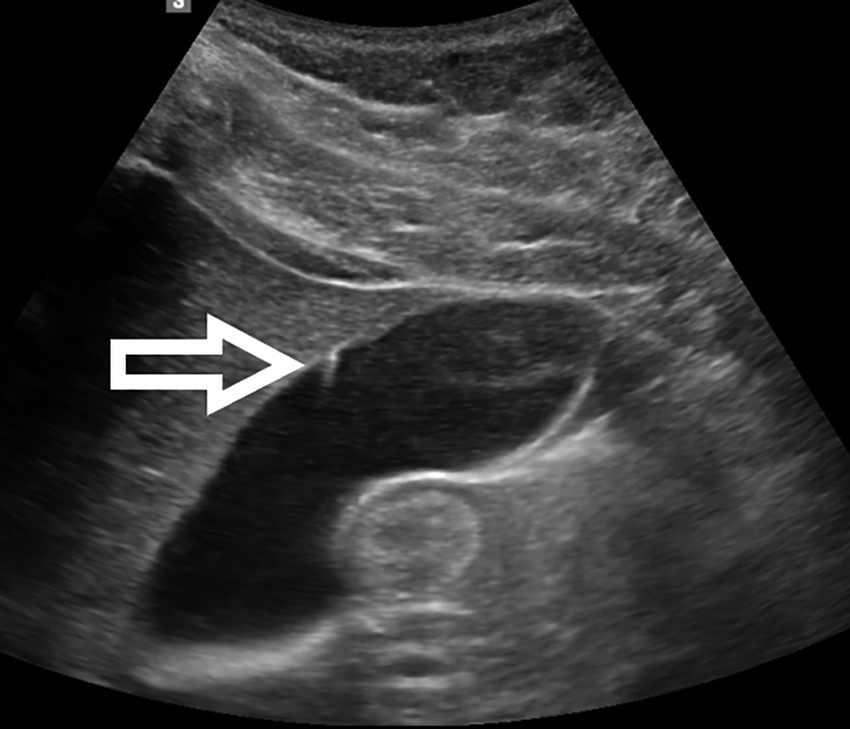
Triangular cord sign
Echogenic band at porta hepatic (biliary atresia)
Indicative of biliary atresia in infants, appearing as a triangular or tubular echogenic density near the portal vein bifurcation
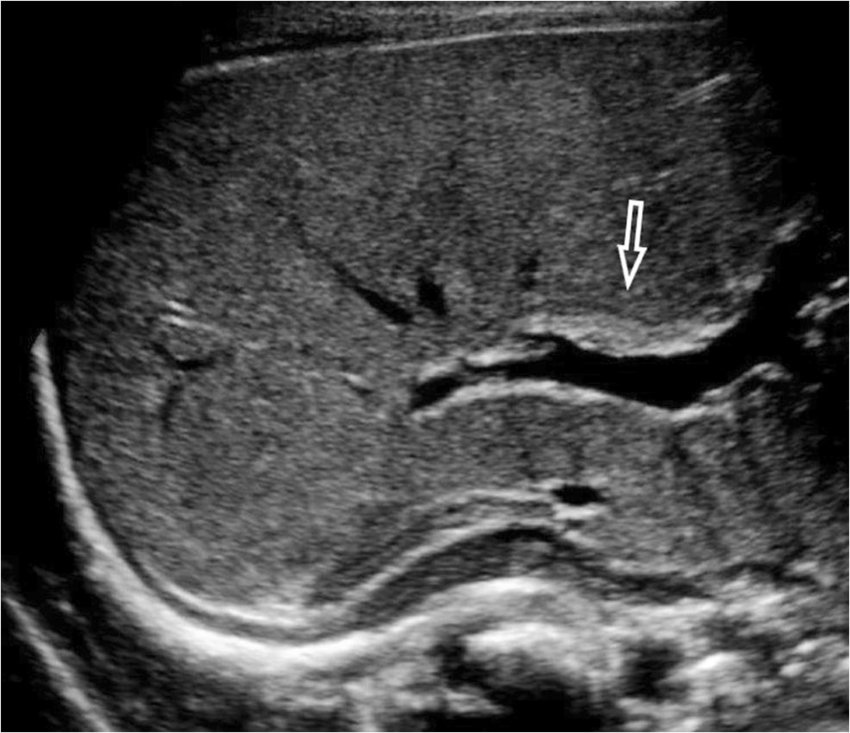
Parallel channel sign
Dilated bile duct and portal vein side by side (biliary obstruction)
A sonographic finding observed during U/S of the biliary tree
Appears as 2 parallel lines representing dilated intrahepatic bile ducts alongside the adjacent portal vein branches
Sign is often associated with obstructive jaundice particularly when there is mild bile duct dilation
Whirlpool sign
Twisting of pedicle in GB torsion
The whirlpool sign of the mesentery, also known as the whirl sign, is seen when the bowel rotates around its mesentery leading to whirls of the mesenteric vessels
It represents the swirling appearance of the mesentery and superior mesenteric vein around the superior mesenteric artery
Ring-down artifact
Air/gas reverberation in emphysematous cholecystitis
Ring down artifact is a special type of resonance artifact
Appearance is similar to the ladder-like reverberation of comet-tail artifact but it is produced by a completely different mechanism
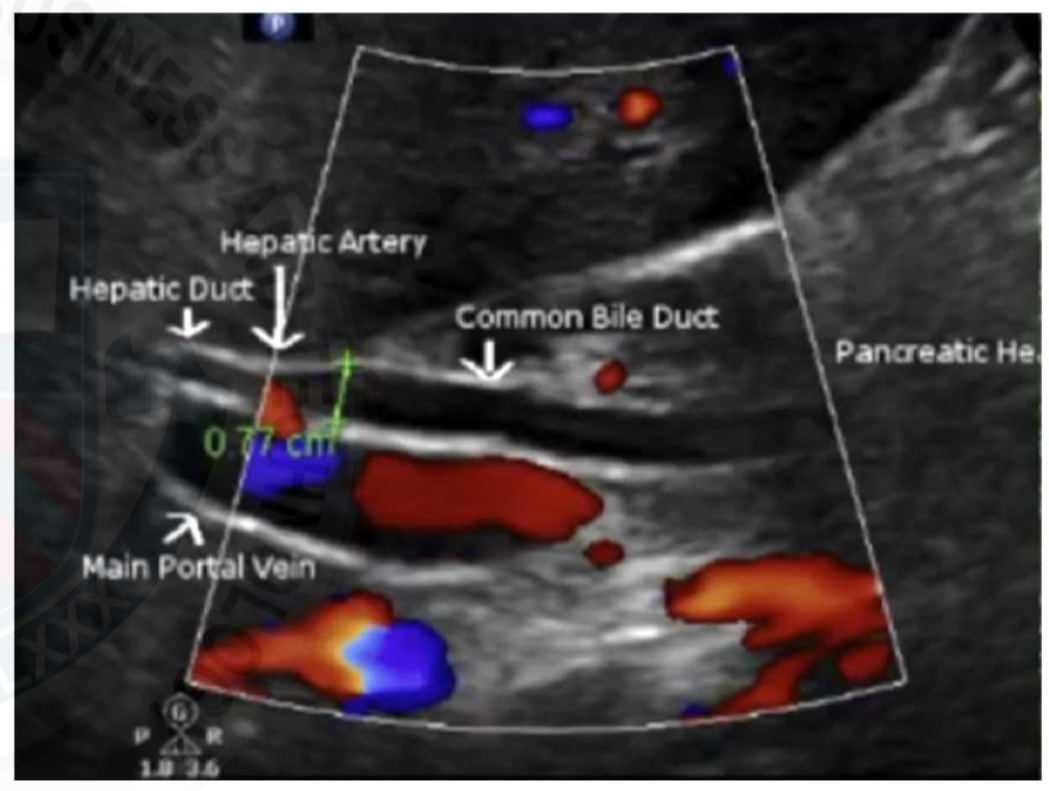
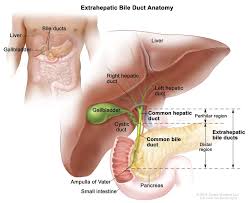
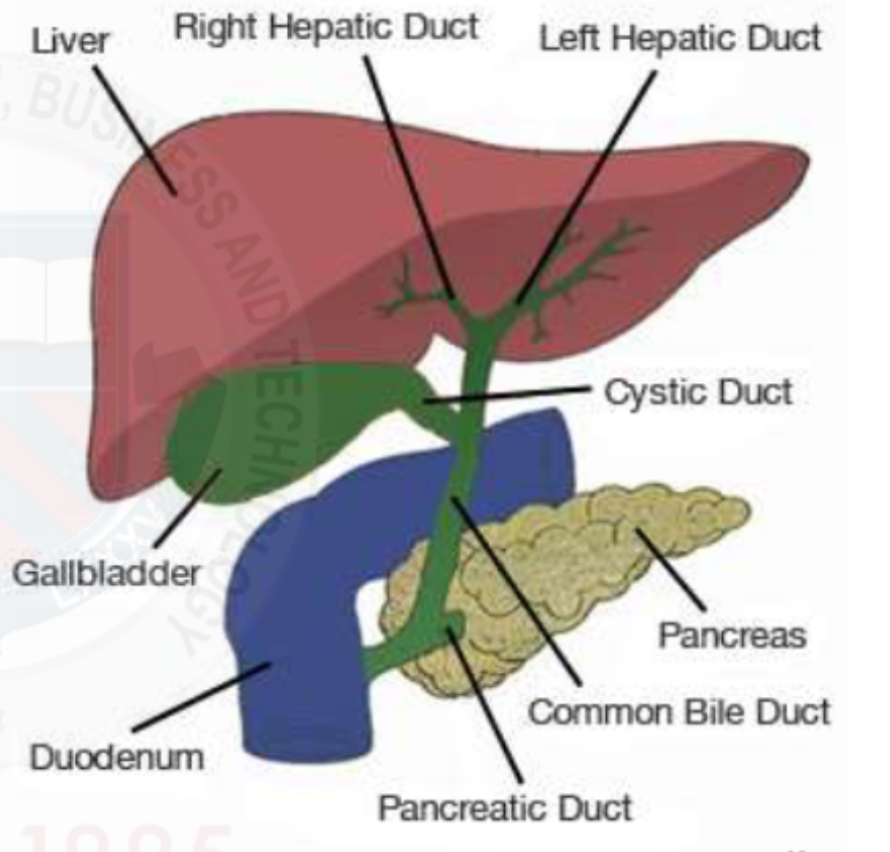
Biliary system
R&L hepatic ducts
Common hepatic duct
Common bile duct
Pear-shaped gallbladder
Cystic duct
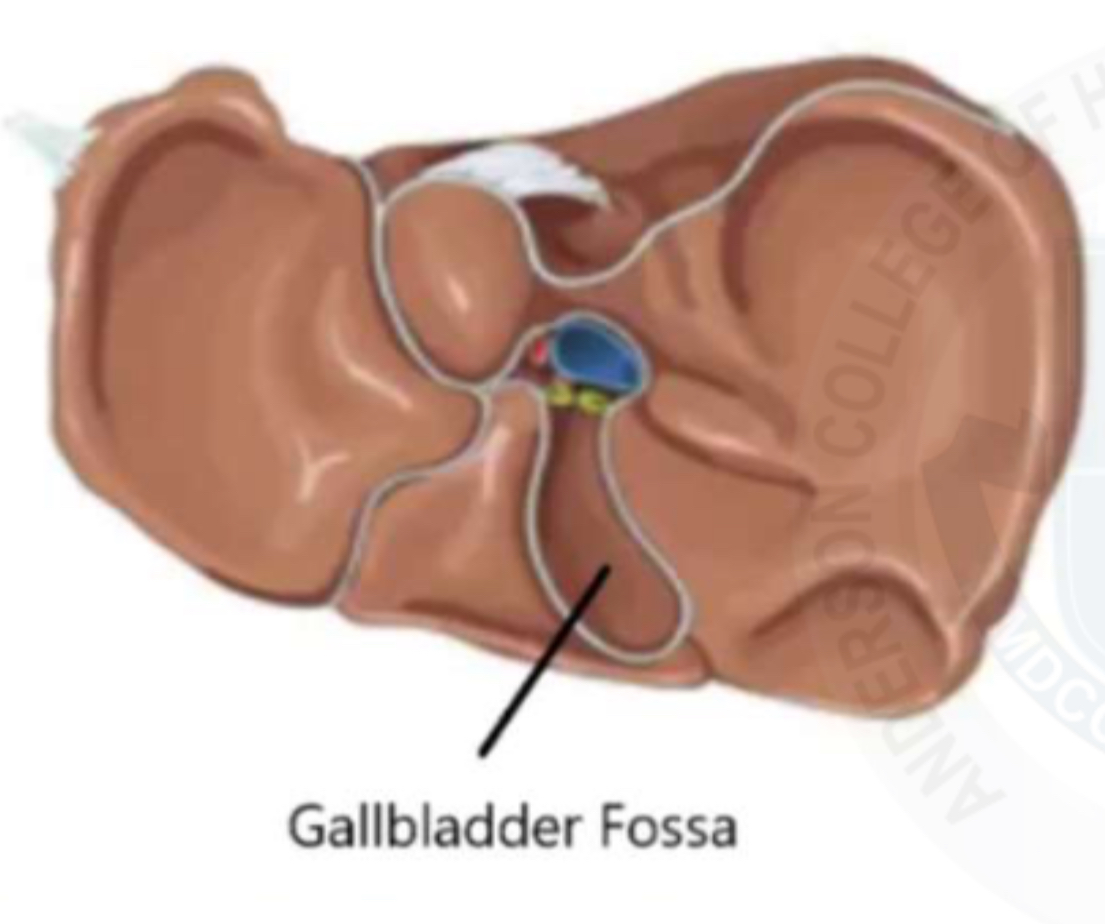
Location of GB
Gall bladder fossa
Posteroinferior side of liver
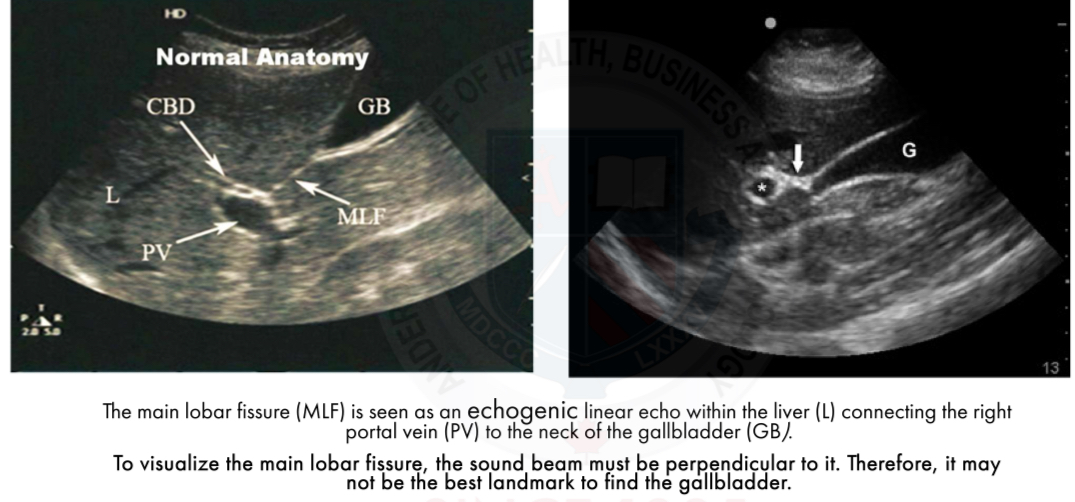
Look for the Main Lobar Fissure(MLF) as a landmark
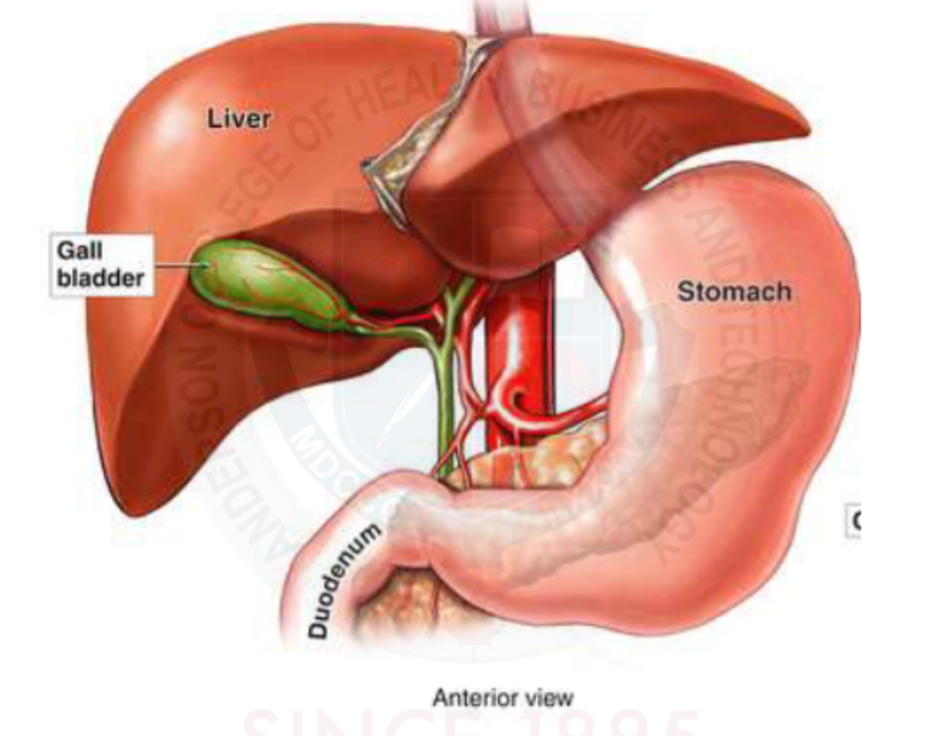
Anterior view of GB anatomy
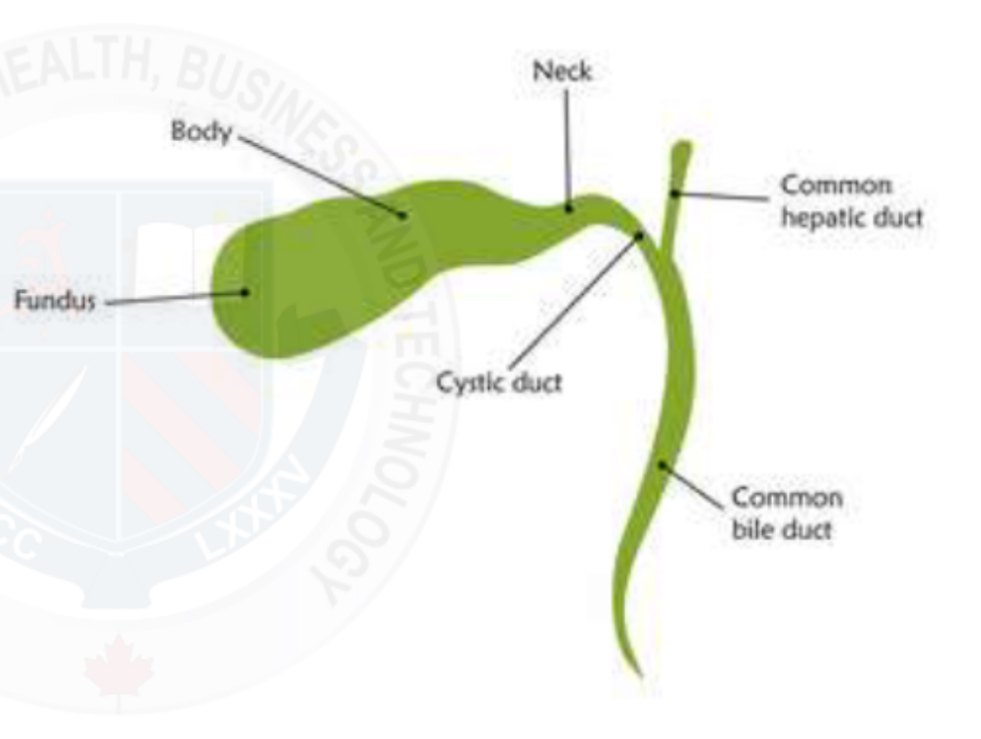
Gallbladder anatomy
Pear shaped
Divided into : fundus, body, neck
Joins with the cystic duct
Gallbladder
Serves as a reservoir for bile
Sores and concentrates bile during the fasting state
Contracts upon eating
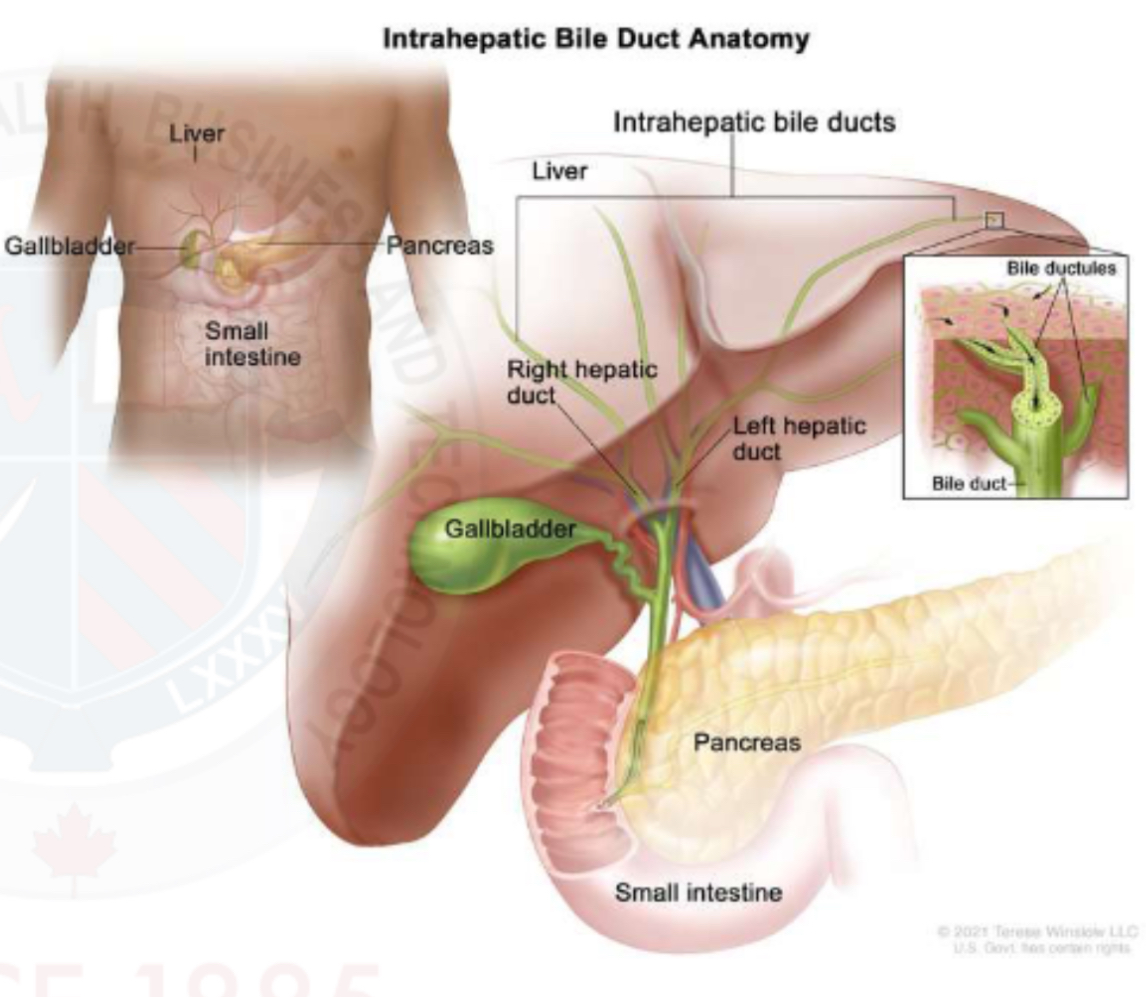
Location of bile ducts
Part of the portal triad, running with the portal veins and hepatic arteries, intrasegmentally
Intrahepatic ducts are separated from extrahepatic ducts by the porta hepatis
Intrahepatic ducts
Each hepatic ducts is formed by the unions of bile canaliculi from the liver lobules
Intrasegmental ducts grow larger as they converge towards the porta hepatis
Cystic duct
Contains the spiral valves of Hester
Small folds with the cystic duct that contain some muscle
Regulate the release of bile
CBD
Extrahepatic(outside liver)
Created when the cystic duct(CD) and common hepatic duct (CHD) unite
Length variation
CD and CHD may join more distally
= CBD will be shorter
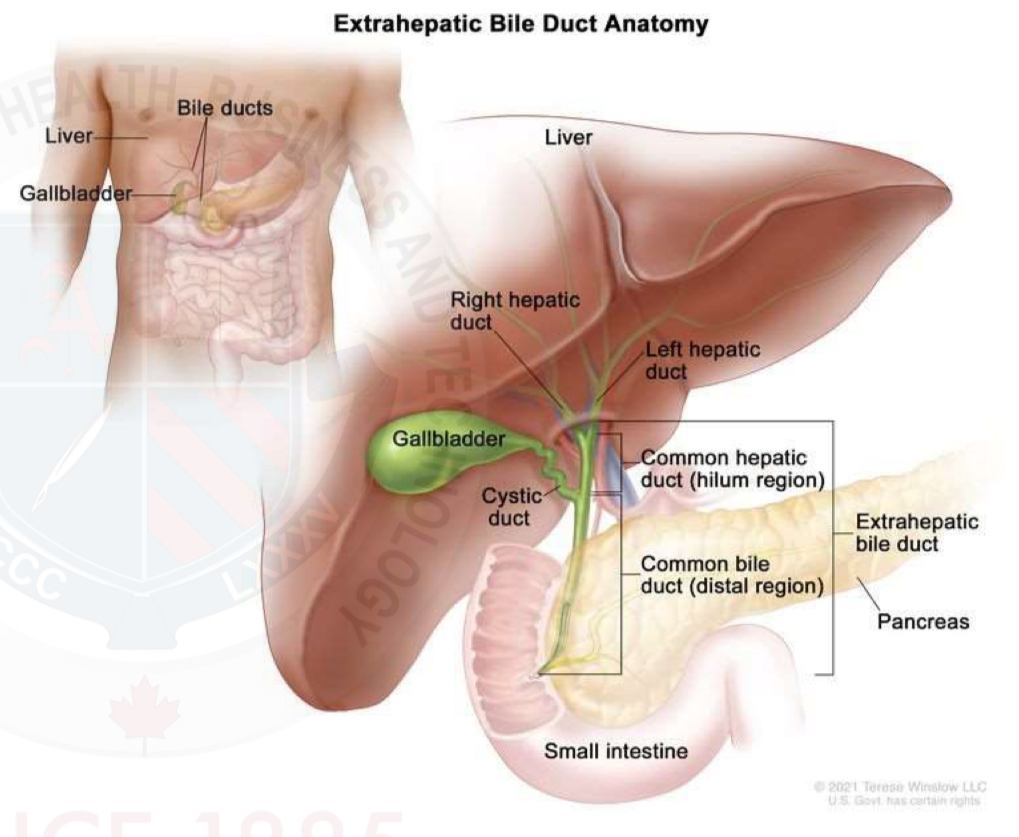
Common bile duct measurement
Normal common bile duct has a diameter of up to 6 mm
Length variation
- CD and CHD may join more distally
- CBD will be shorter

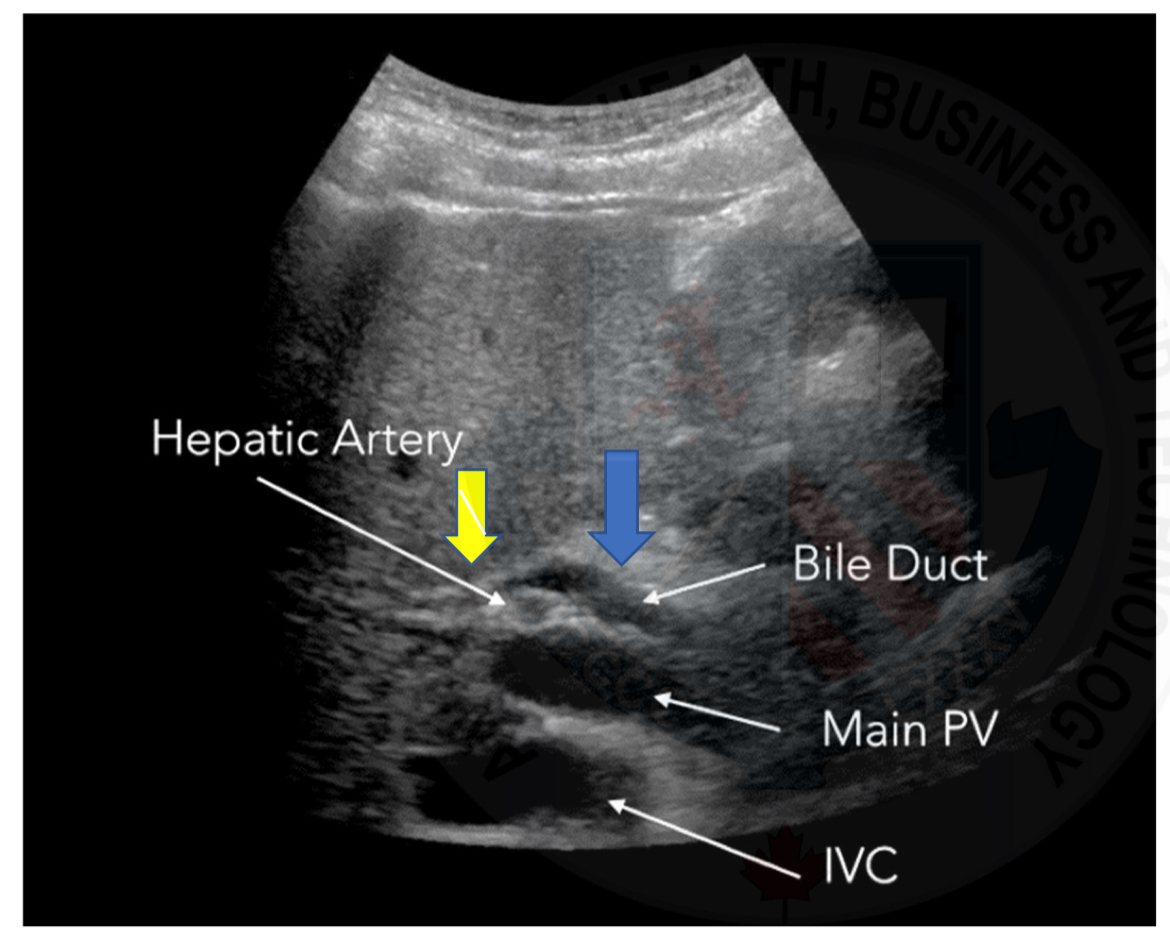
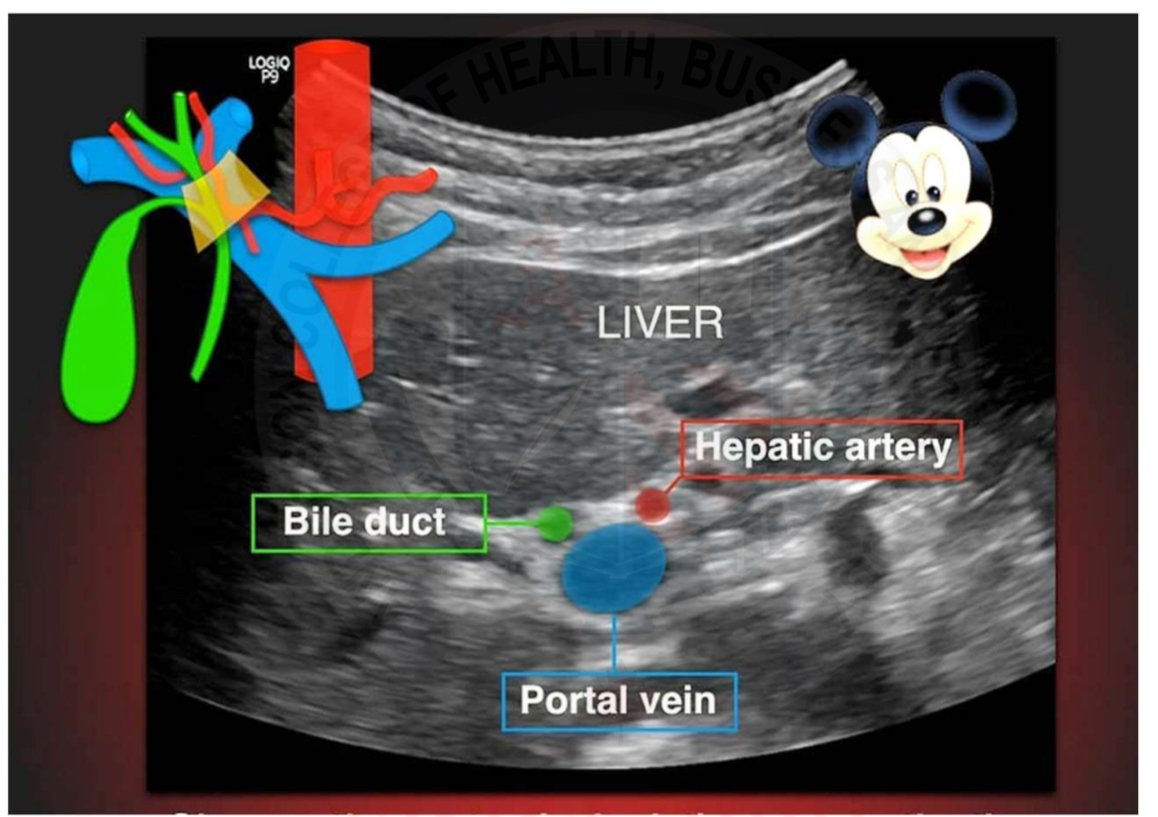
Vasculature - Gallbladder
Cystic artery originates from the right hepatic artery
Venous drainage of the gallbladder is by the way of the hepatic portal system
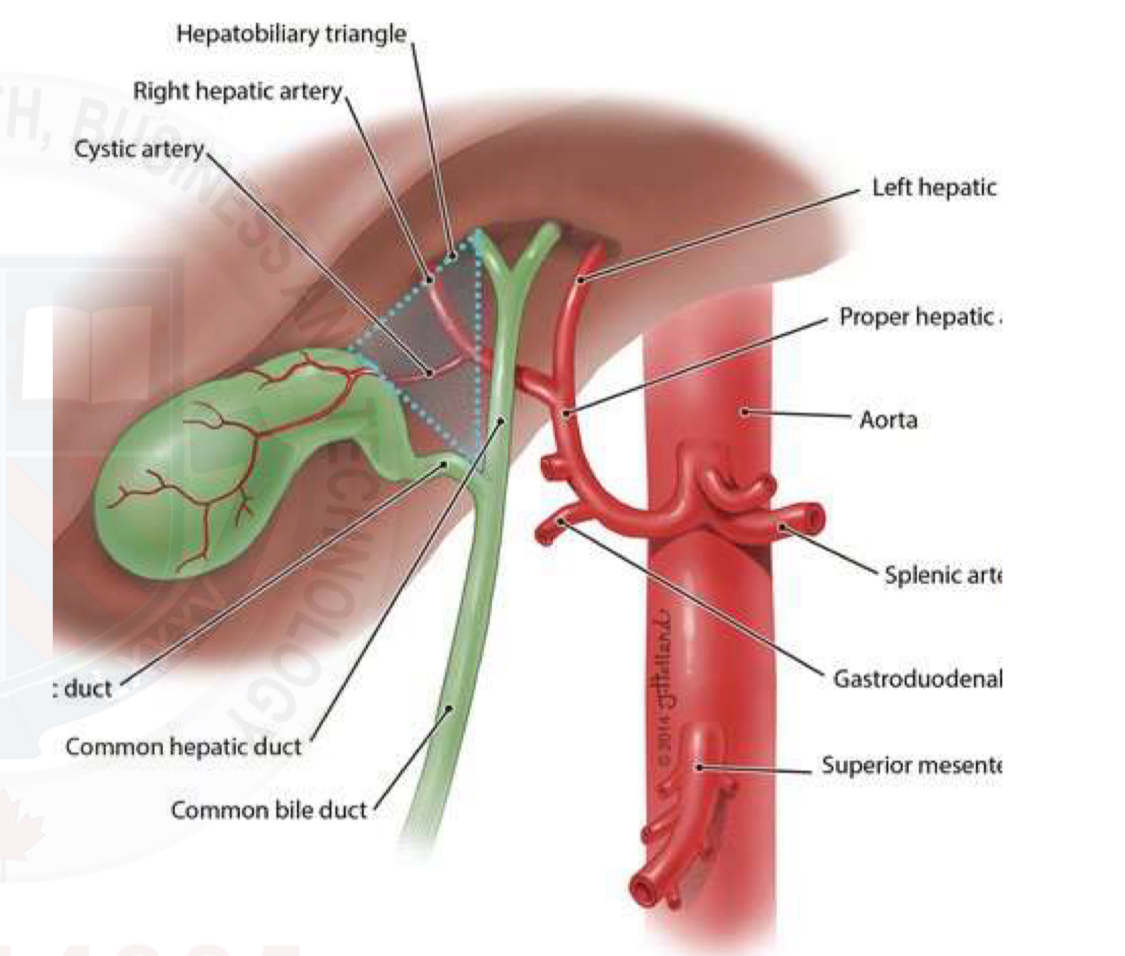
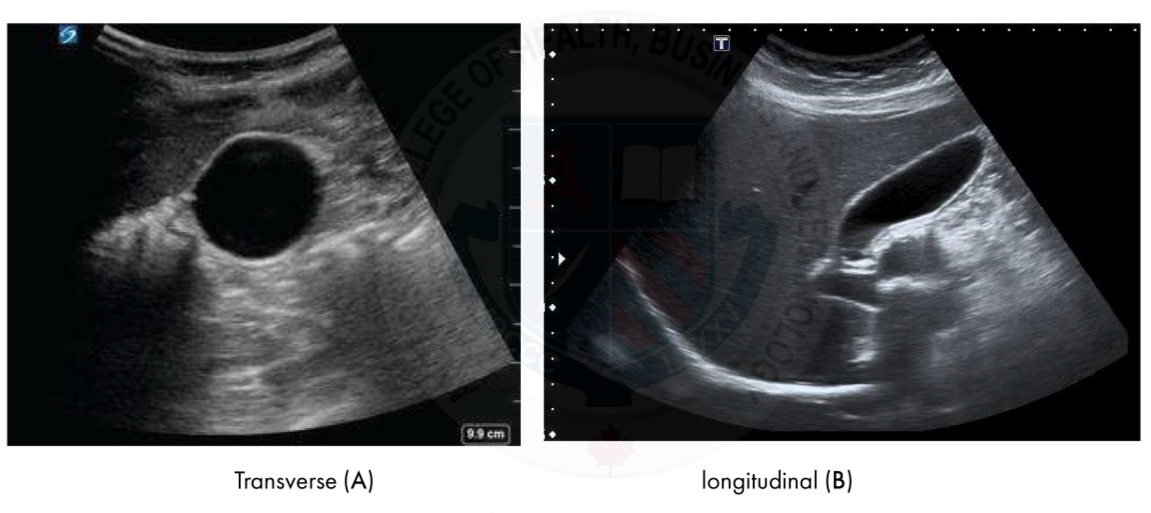
Normal gallbladder U/S
Main Lobar Fissure (MFL)
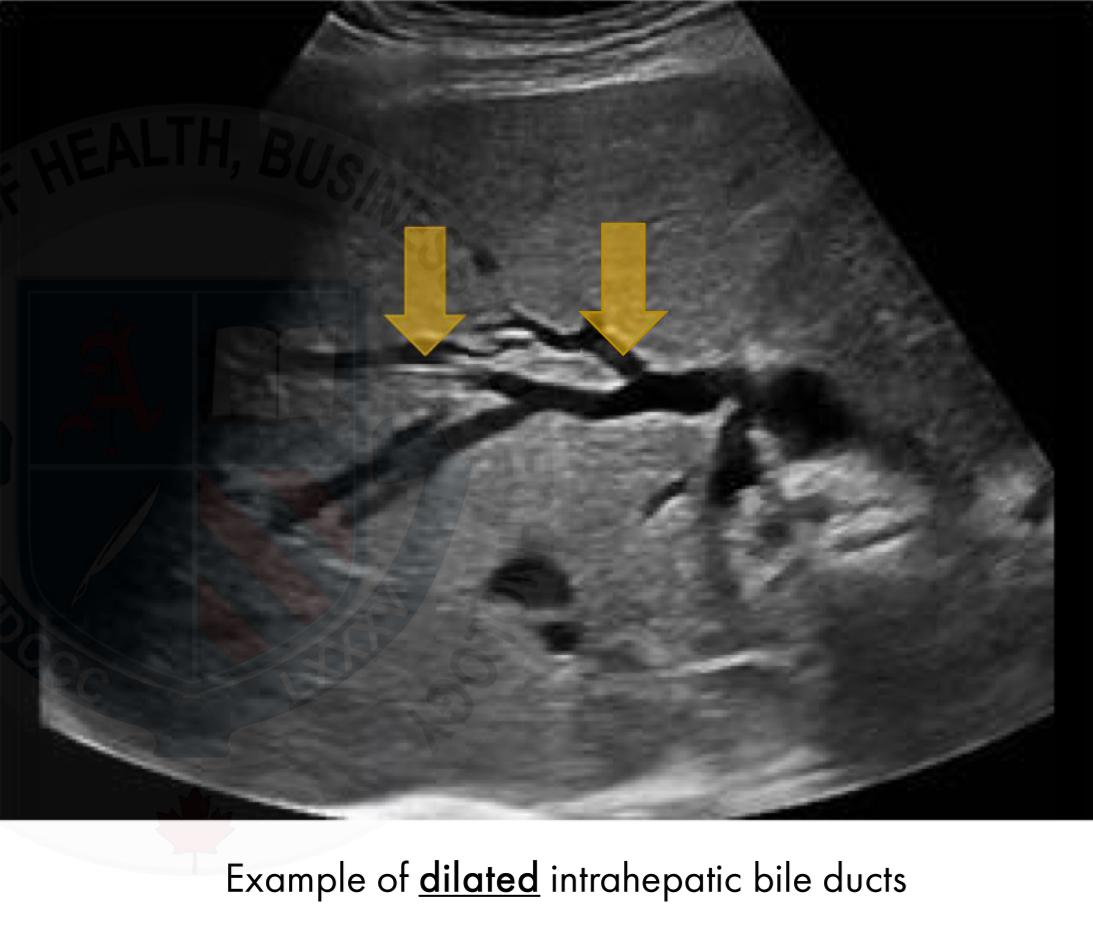
Intrahepatic ducts
NOT seen in normal patients
Small ducts that join together into larger ducts, ending in the left and right hepatic ducts
Common hepatic duct
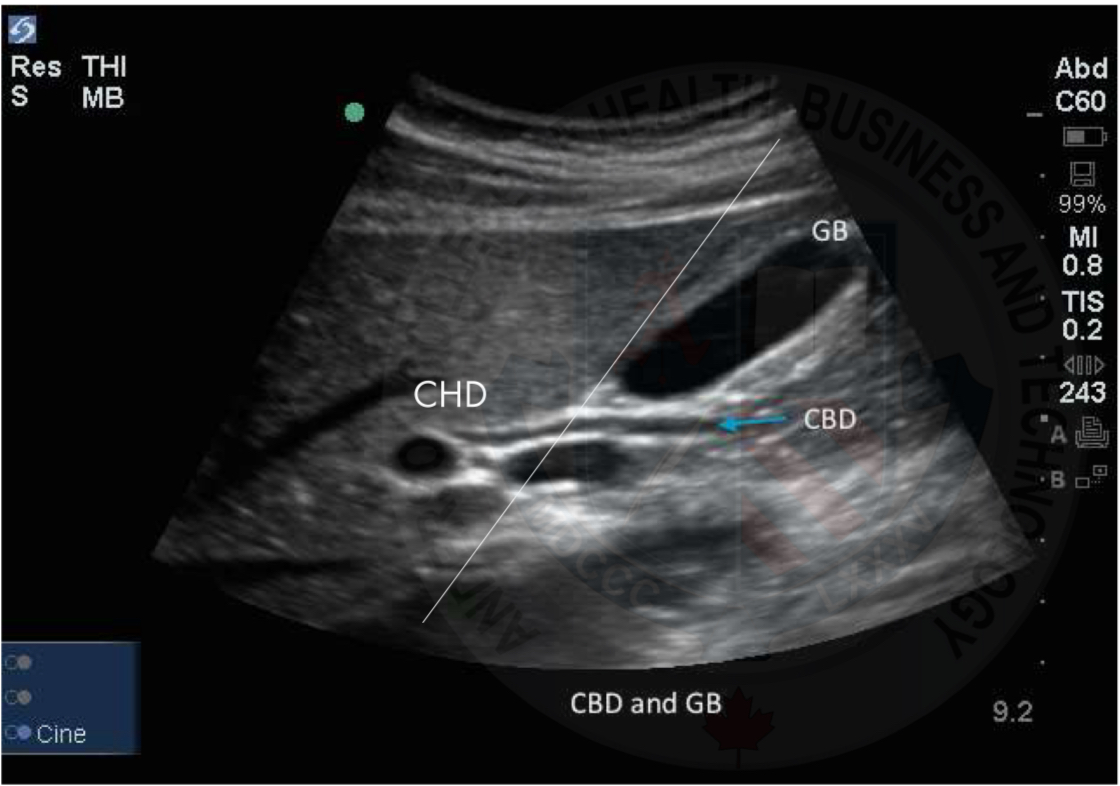
Cystic duct
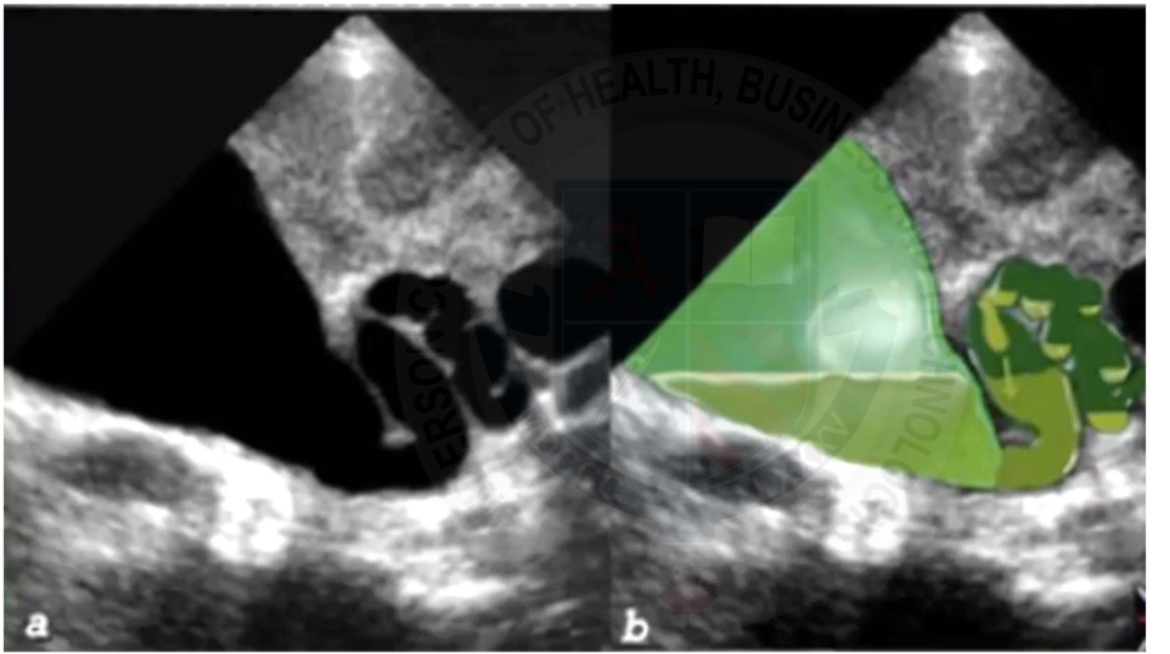
CHD vs CBD
Normal size biliary tree
CHD < 4mm
CBD < 6mm
Anatomic variations GB
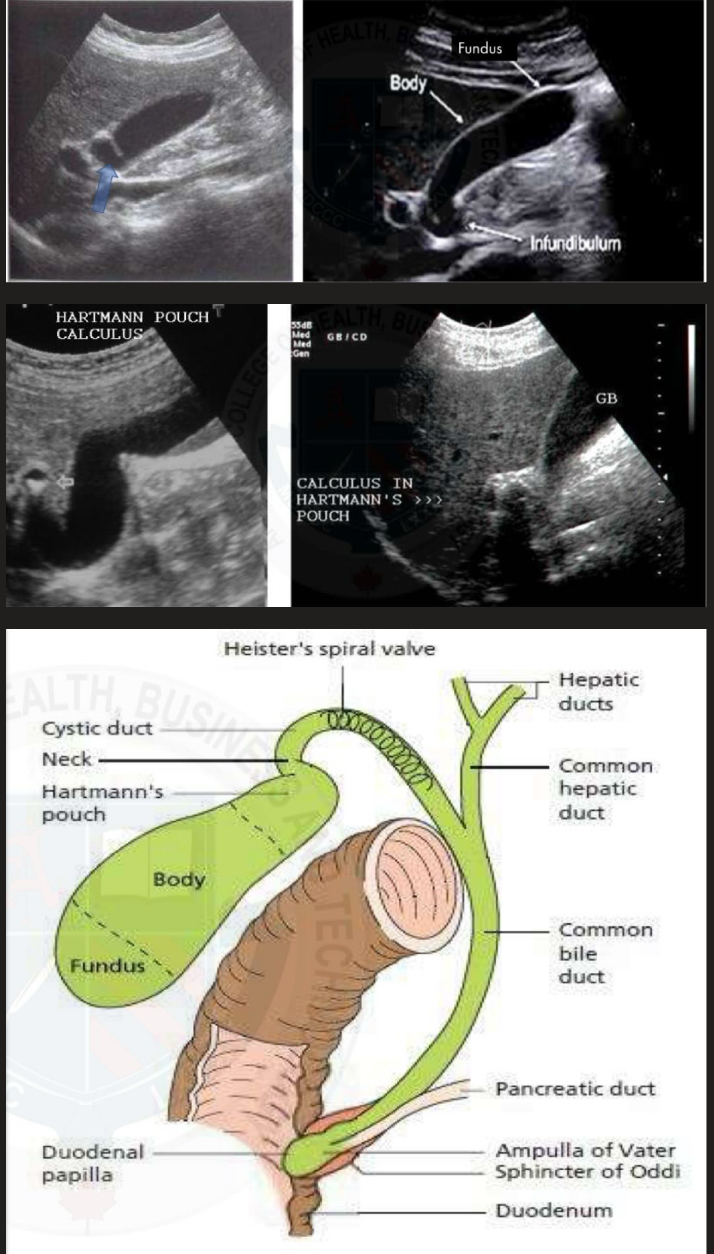
Gallbladder may fold back on itself at the neck, forming Hartmann’s pouch
Folding of the fundus = Phrygian cap
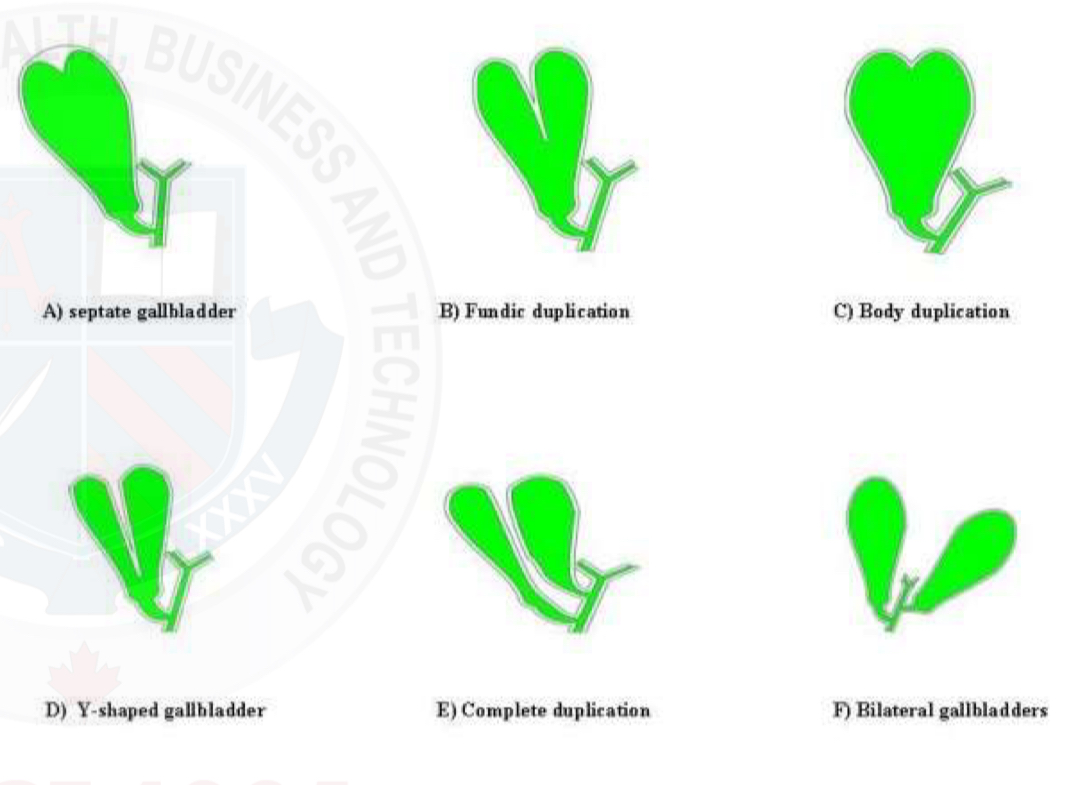
Partial septation
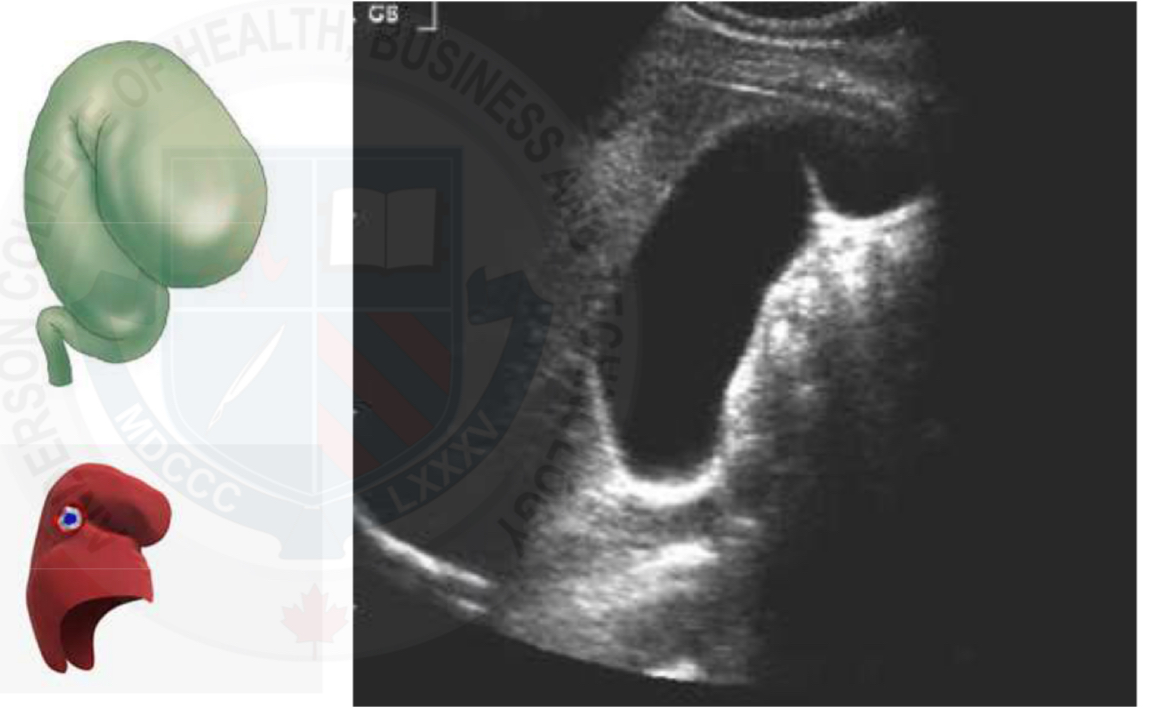
Complete septation (double gallbladder)
GB duplication
Ectopic GB
GB agenesis
Mickey Mouse sign
Hartmann’s Pouch
Seen at the neck fo the gallbladder
Appear as a little pocket and can often catch gallstones within
Phrygian cap
Seen at a fold/kink in the fundus of the gallbladder
Common finding
Gallbladder folds
Folds are commonly seen and are normal
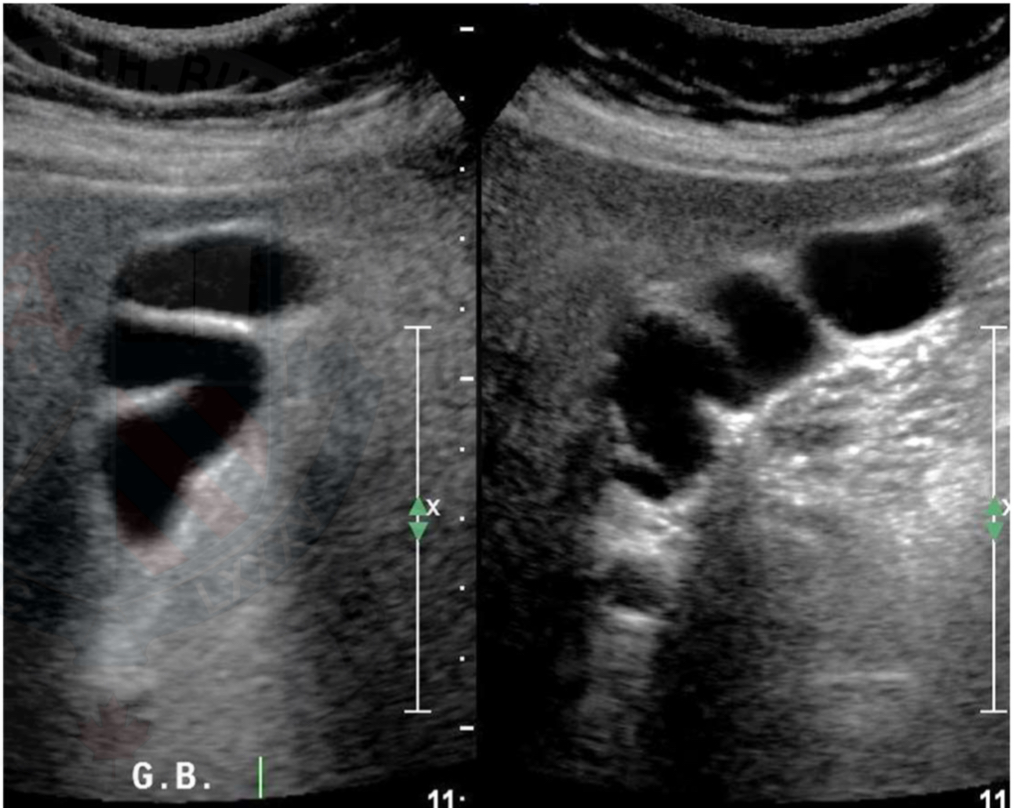
Gallbladder septations
Lumen of gallbladder fails at being completely open
Results in strands of tissue crossing through the lumen
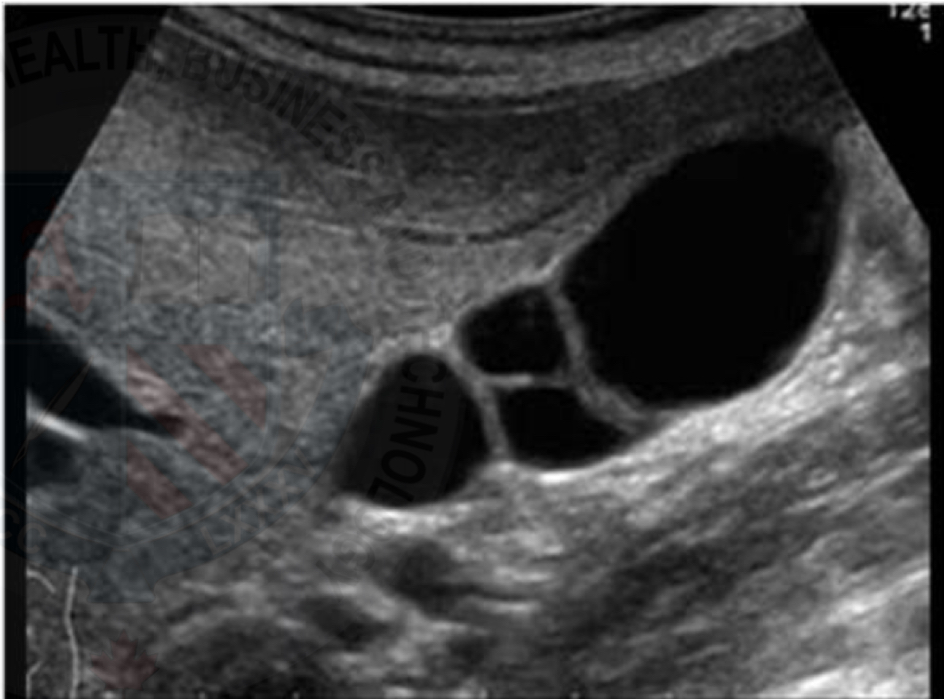
Double gallbladder (GB duplication)
Full septations/2 gallbladders
Very rare
Can’t confirm by ultrasound
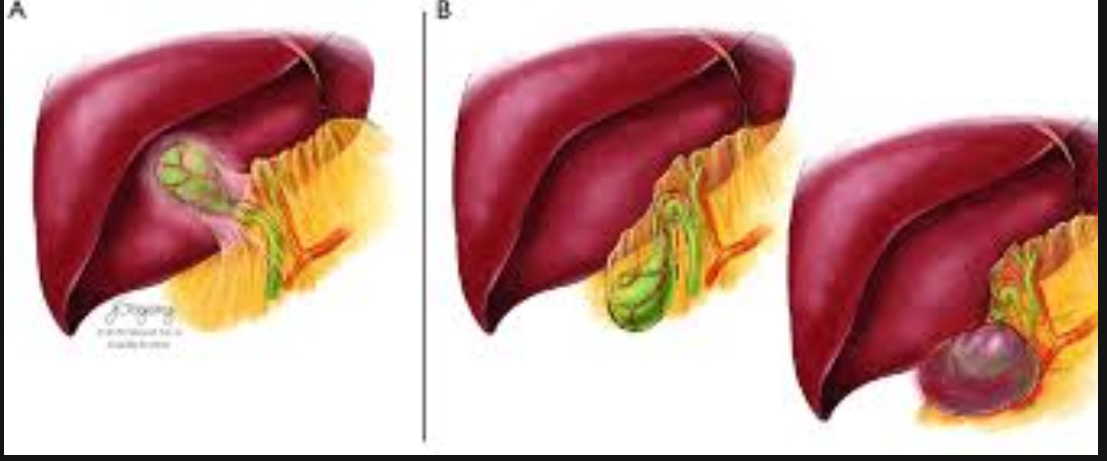
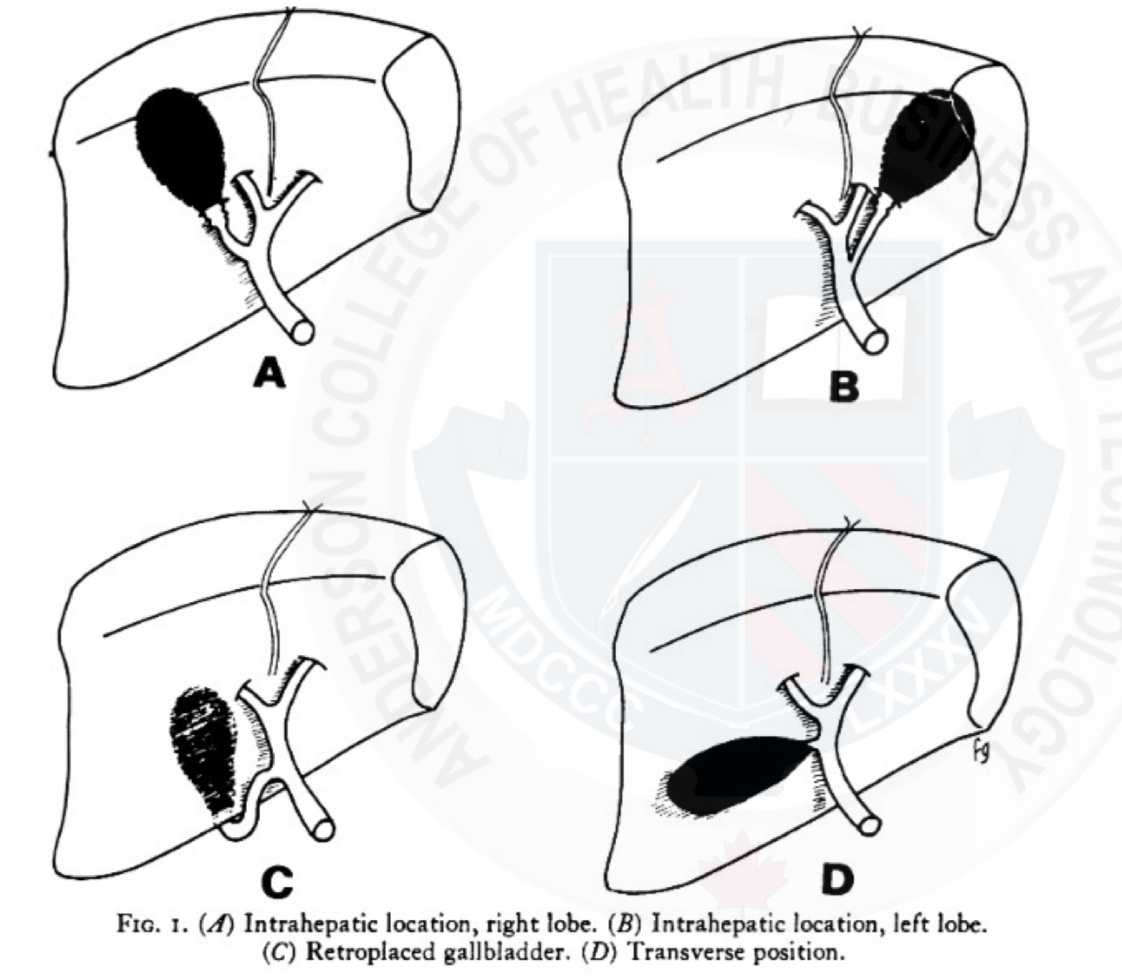
Ectopic gallbladder
Rare
Can be located in a variety of anomalous positions :
Intrahepatic
GB completely surrounded by liver parenchyma
May complicate the clinical diagnosis of acute cholecystitis because of a paucity of peritoneal signs resulting from the long distance between the GB and peritoneum
Anomaly also makes cholecystectomy more difficult
Suprahepatic
Retrohepatic
Supradiaphragmatic
Retroperitoneal
Gallbladder agenesis
Rare
Asymptomatic
Jaundice may be present with a dilated common bile duct
High incidence of choledocholithiasis
Intrinsic thickening of GB wall
Cholecystitis
Gallbladder perforation
Sepsis
Hyperplastic cholecystosis
Gallbladder carcinoma
AIDS cholangiography
Sclerosing cholangitis
Extrinsic thickening of gallbladder wall
Hepatitis and cirrhosis
Hypoalbuminemia
Renal failure
Right heart failure
Ascites
Multiple myeloma
Portal node lymphatic obstruction
Removal of the gallbladder - cholecystectomy
Bile is no longer retained in the bile ducts; it is free to flow into the duodenum during fasting and digestive phases
Extrahepatic bile ducts dilate, usually less than 1 cm
Presbyductia
Dilation of CBD
Increase of CBD size by 1mm per decade over 50 years old considered normal
Also after a cholecystectomy
Not considered dilated until greater 10 mm