Acids and Bases
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Acid
substances which can act as a proton (hydrogen ion) donor and are monoprotic or polyprotic depending on the number of protons available for donation
Electrolytes
form ions in solution
strong electrolytes
Fully ionise or dissociate (single arrow
strong acids fully ionise (very little acid remains in solution)
soluble ionic compounds e.g. strong bases fully dissociate
weak electrolytes
partially ionise (double arrows)
weak acids
weak bases
Bronsted Lowry theory of Acids and bases
acids are proton donors- usually resulting in H3O+ water
HCL + H2O → H3O+ +Cl
bases are proton acceptors - usually resulting in OH- water
NH3 + H2O →← OH- + NH4+
conjugate pairs
the result of swapping protons, in the case of reversible reactions a product which has accepted a proton can re-donate it and a product which has given a proton can re-accept it.
the weaker the acid the stronger it’s conjugate base
the weaker the base the stronger the conjugate acid
Amphoretic substances
can act as an acid or a base e.g. water
successive ionisation
the degree of ionisation of an acid decrease and the strength of the conjugate base increases
Autoionisation of water
since water is an amphoteric substance it is able to ionise itself (autoionization)
2H2O →← H3O(aq) + OH-(aq)
H2O (l) → ← H+ + OH-
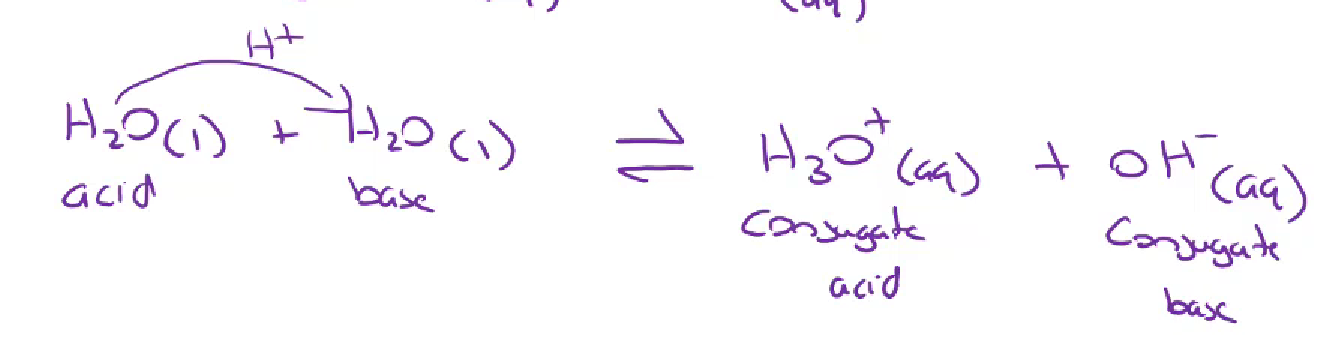
Kw
Kw = (H3O+) (OH-) = 1.0 × 10^-14
because water is a very weak electrolyte the equilibrium constant is very low
as temperature increases, the Kw value increases and vice versa
Strong acids
good conductors of electricity
HCL, H2SO4 and HNO3
weak acids
not good conductors of electricity
CH3COOH
H2CO3
H2SO3
H3PO4
Oxalic acid: HO2C2O2H
Acid Strength
determined by the concentration of H+ they produce in solution
Base strength
determined by the concentration of OH- they produce in solution
Strong bases
any soluble hydroxide
weak base
Ammonia: NH3
Hydrolysis/hydrolysis equations
when salts dissolve in water they may react with water to produce H+ or OH- theis is caled hydrolysis
a chemical breakdown of a compound due to a reaction with water
Hydrolysis equations show what happens when an acid or weak base dissolves in water
acidic species will donate a proton to water
base will accept a proton from water to form OH
Ka values
the equilibrium constant for ionisation of an acid, shows the extent to which the reaction occurs
a Large Ka value ( larger than 1) indicates that the acid will fully ionise in solution, strong acid
weak acids have low Ka value
Ka values of polyprotic acids
polyprotic acids have the potential to undergo multiple hydrolysis reactions, however the tendency decreases with each successive ionisation (Ka value decreases)
successive ionisations will not happen to completion, therefore the expected mols of H3O+ will not be produced.
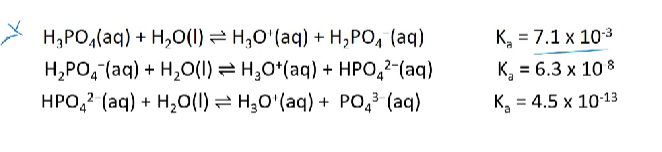
Salts
produced when a acid and a bases are reacted together
neutral salts
salts which have been produced by a strong acid and a strong base, therefore neither component of the salt will undergo hydrolysis with water
Basic salt
produced when a weak acid and a strong base are reacted together
basic salt completely dissociate in water
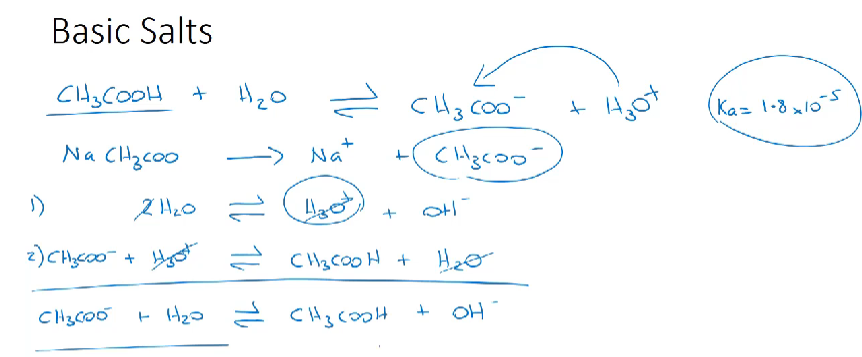
Acidic salts-
strong acids and weak bases react
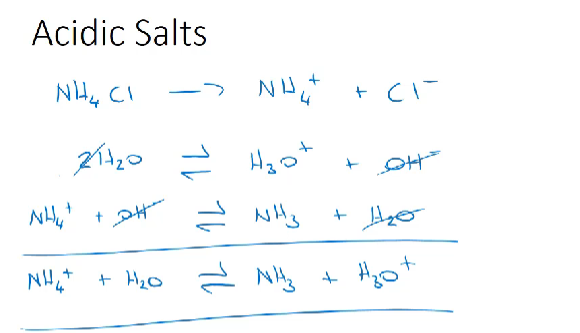
Arrhenius theory of acids and bases
an acid will ionise to form hydrogen ions in solution, and will increase the conc of H+
A base will form hydroxide in solution; it will increase the concentration of OH- in solution
Why do hydrogen ions form hydronium ions in solution
Protons are not stable by themselves in water
limitations of Arrhenius
limited to interactions in aqueous solution
e.g. Hcl, HNO3, and H2SO4 are not acids under arrhenius definition as they do not dissolve in water
it doesn’t explain why some salts are acidic and basic
Davy Theory
acids contain hydrogen ions which could be replaced metals and bases are substances which react with acids to form salts

polyprotic acids
acids that can donate two or more protons
become less acidic as they lose protons/with every successive ionisation the degree of ionisation of the acid decreases
why are only some substances that contain hydrogen acidic under normal conditions
hydrogen atoms will only be acidic if they already have a slight positive charge, generally only happens if they are bonded to a highly electronegative atom such as oxygen or chlorine.
what does an acid and a base produce
salt + water
what are the formulas involved in pH calcullations
Kw=(H+)(OH)=1.0 x 10^-14 for any aqueous solution at 25C
pOH= -log(OH)
pH= -log(H+)
pH= 14 - pOH
(H+)= 10^-pH