Biology - Paper 1 - Cells
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is an overview of the paper1 biology topic “cells”. This however doesn’t contain any of the required practicals but you can find that on my profile if you go to: Profile -> Biology -> RP paper1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Name all 5 things in animal cell
cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes.
Example idiom:
"Clear Minds Recognize New Chances" :)
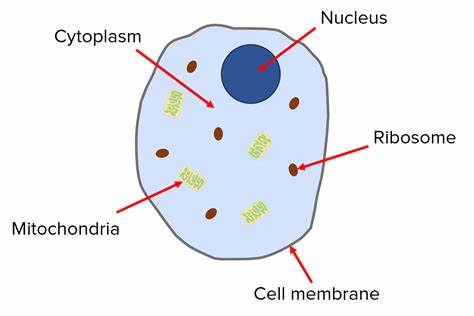
What does the mitochondria do?
Aerobic respiration to release energy
What does the nucleus do?
Holds all genetic information
Name all 8 things in a plant cell
A plant cell contains the cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, chloroplasts, and vacuole.
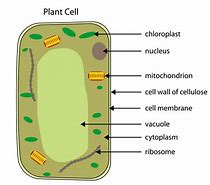
There is 3 extra things in a plant cell, what are they?
Vacuole
Cell wall
Chloroplasts
What does the vacuole do?
Holds the cell sap to give support to the cell
What does chloroplasts do?
They conduct photosynthesis
What is an Organelle?
Structure inside a cell that does a specific job.
E.g- Mitochondria or ribsomes
What organalle the cell appear green?
Chloroplasts
Name some features of Eukaryotic cells
They contain a nucleus
Large
They’re in multi-celled organisms.
Name some features in Prokaryotic cells
They don’t contain a nucleus
Smaller
Not multi-celled
(Basically the opposite if you cant remember them both just remember one and the other is just the opposite 🙂 )
Name all 8 things in a bacteria cell
Cell membrane, cell wall, slime capsule, plasmids , DNA , ribosomes, cytoplasm and flagella
What do the plasmids do?
Hold the ‘special’ genes
Which give the information for:
-Antibiotic resistance: Helps bacteria survive antibiotics.
-Toxin production: Makes bacteria more harmful
What is the slime capsule for?
Protection and too stick to things
What is a specialized cell?
A cell adapted for a specific job
E.g- A sperm cell or a red blood cell
What does it mean for a cell to differentiate?
When a cell changes to become a specialized cell.
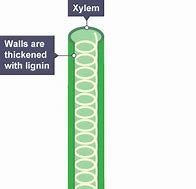
What does the xylem do?
Carries water + mineral ions
Can you name the 2 main features of a xylem cell?
-A hollow tube
-Lignin spirals
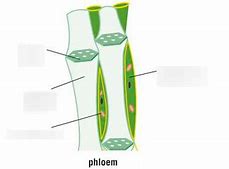
What does the Phloem cell do?
Carries sugar
You can say ‘food’ but its better to be specific
Name features in a phloem tube.
Sieve tube
Companion cell
Sieve end plate
What unit would we use to measure a cell?
Micrometres
What does a root hair cell do?
Absorbs water + mineral ions
What does ‘passive process’ mean?
A process that doesn’t require energy from the cell.
E.g Diffusion
What is diffusion?
When molecules move from a region of high to low concertation
What is an active process?
Where does it take place?
A process that requires energy from the cell
In the membrane
What is active transport?
The movement of molecules from low to high concentration against their concentration gradient.
Where does energy come from in active processes?
Cellular respiration (mitochondria)
What is osmosis?
The movement of water from high to low concertation across partially permeable membrane
What is partially permeable membrane?
Semi-selective membrane
Only some molecules can pass through.
What is a isotonic solution
When solutions have the same amount of solutes and water.
When orange squash has the same amount of cordial and water.
What is hydrotonic?
When solutions have less solutes but more water.
When orange squash has more water then cordial.
Its DILUTE.
What is hypertonic?
When solutions have more solutes and less water
When orange squash has more cordial then water.
Its CONCENTRATED
In a experiment, you have a sugar solution and water.
What would you measurement would you measure the sugar solution with?
What would you measurement would you measure the water with?
Sugar solution- M
e.g- 0.5m
Water- cm3
e.g- 10cm3
What’s the equation for percentage change?
( (New value - old) / old value ) x 100
What is the calculation for magnification?
Image size / actual size = magnification
A common error is people say ‘zoom’.
What’s the correct way to say ‘zoom’?
Increasing the focus or magnification
Light magnification are uses by shining __?__ through a thin specimen
Electron microscopes use __?__ to see through a thin specimen.
Light magnification are uses by shining light through a thin specimen
Electron microscopes use electrons to see through a thin specimen.
Wow bet you didn’t see that coming sherlock.
What does it mean when you increase magnification?
Increasing the size of how the object looks in the microscope
What does it mean when you increase resolution?
Increasing the sharpness/quality of how the specimen looks in the microscope
bro im so tired 😒😒😒😒😒😒😒