Neuroscience and Cell Signaling: Action Potentials, Synapses, and Hormonal Communication
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What ion channels primarily contribute to the maintenance of the Resting Membrane Potential?
K+ channels
Action Potential Generation Order
1. All gated Na and K channels are closed;
2. Na+ channels open;
3. Na+ channels are inactivating, and K+ channels open;
4. Some K+ channels remain open, and Na+ channels reset.
Voltage gated potassium channels have one gate and alternate between how many different states?
Two
How does in increase in sodium influx affect an Action Potential?
More depolarisation, which opens more sodium channels, as a result ICF becomes less negative.
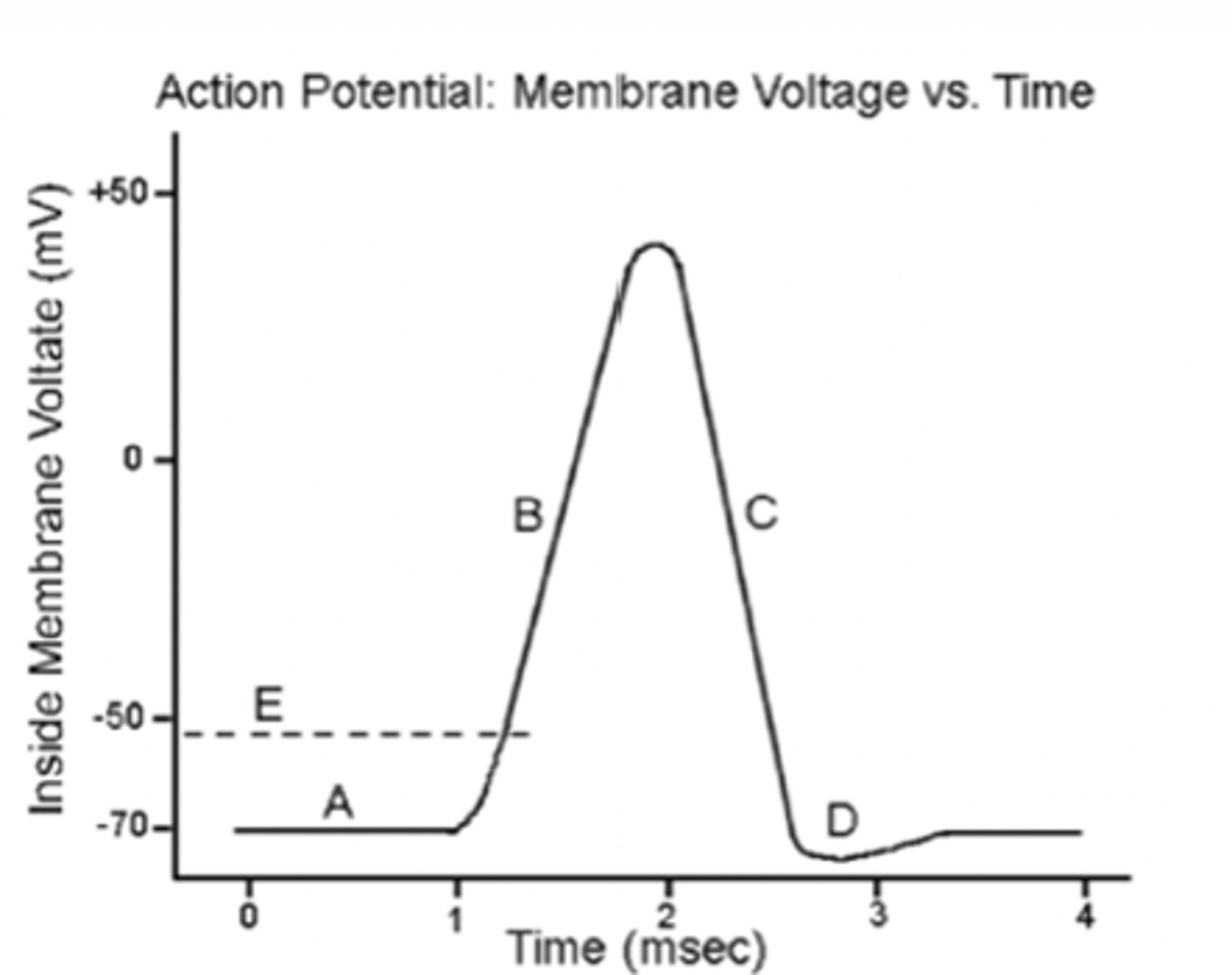
Action Potential Graph Events
A - Resting Membrane Potential;
B - Depolarisation;
C - Repolarisation;
D - Hyperpolarisation;
E - AP Threshold.
Voltage-gated sodium channels
The Japanese puffer fish, commonly known as Fugu, possesses sufficient tetrodotoxin (TTX) to potentially kill 30 individuals. Which type of channel does this toxin block?
What are the effects of Tetrodotoxin (TTX) toxin (from the puffer fish)?
TTX toxin is 1000 times stronger than cyanide, and impedes nerve function. This can paralysis, respiratory difficulties, and immobility.
Death occurs due to respiratory failure.
What factors affect the duration required for a nerve impulse to travel through a neuron?
1. presence or absence of Nodes of Ranvier,
2. degree of myelination,
3. diameter of the axon
True or False: The length of the axon affects the duration required for a nerve impulse to travel through a neuron?
False. The length has no effect.
What's the role of local anaesthetics in nerve function?
Blocking action potential propagation
The change in membrane potential that does not reach the threshold for an action potential is called___?
Subthreshold potential
Which Ion channels are affected in multiple sclerosis?
Sodium and potassium channels
What happens to Ion channels during hyperpolarisation?
Voltage-gated K+ channels are open, while voltage-gated Na+ channels are closed.
Relative refractory period vs absolute refractory period
Neurons require a stronger stimulus to generate an AP during the relative refractory period.
Which option accurately describes fast cell-to-cell communication?
Occurs within milliseconds to seconds
3 multiple choice options
Hormonal signaling
Involves hormones that travel through the bloodstream
Duration of action in hormonal signaling
Typically has a longer duration of action
Electrical signaling
Relies on direct electrical connections between cells
Speed of electrical signaling
Occurs within milliseconds to seconds
Temporal summation in a neuron
Addition of graded potentials generated at the same location on the neuron rapidly over time
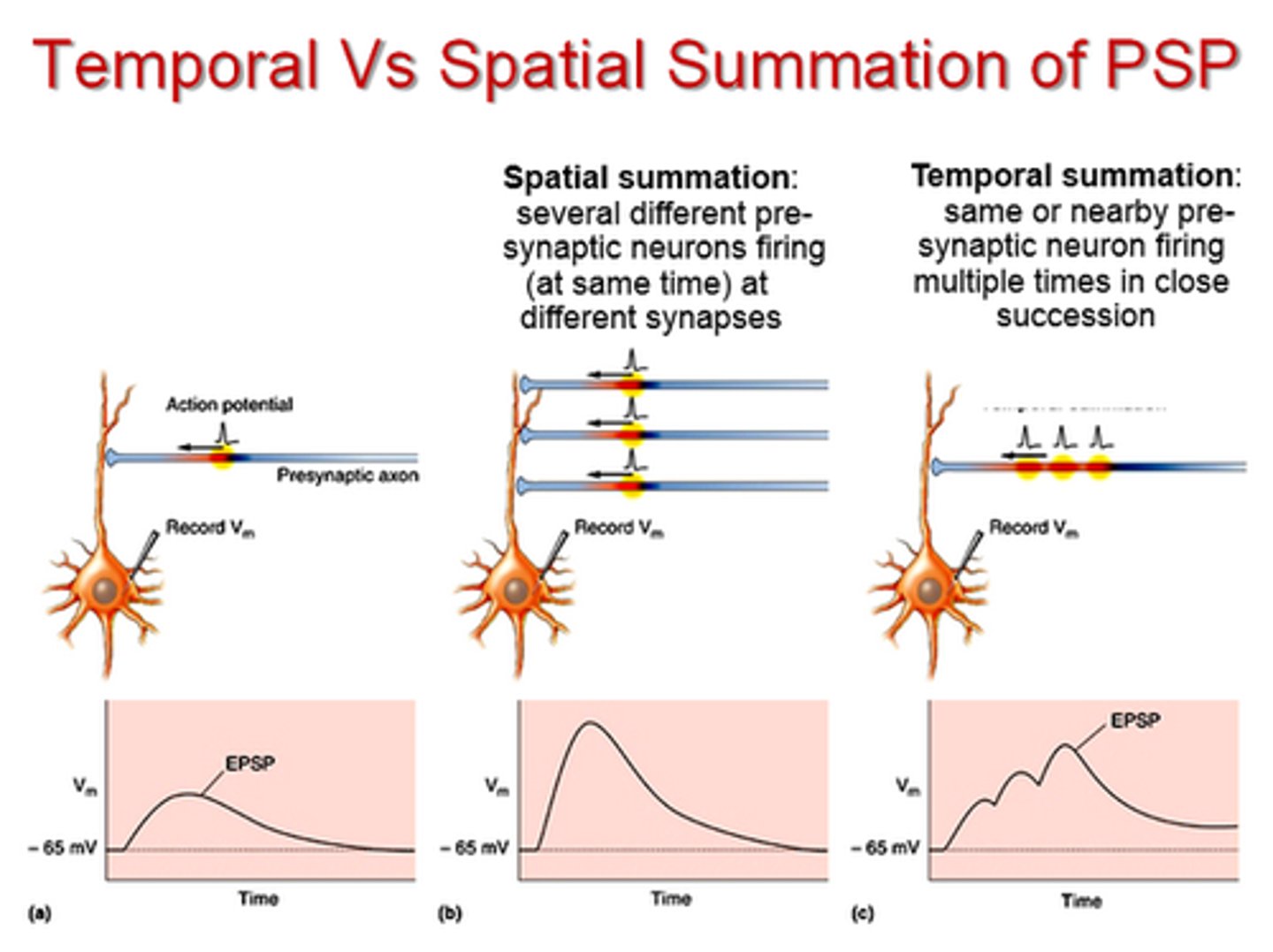
Spatial integration
Spatial integration of signals from multiple neurons
Action potential generation
The process of generating an action potential from a single graded potential
What is a structural characteristic of a Chemical synapse?
Axon terminals separated by a synaptic cleft
What is the neural pathway for the efferent impulse to the hamstring in the patella reflex?
Sensory neuron > interneuron > motor neuron
The neurotransmitter involved in the neuromuscular junction is: ?
Acetylcholine
What factor influences how much neurotransmitter is released at the axon terminal?
The frequency of the action potentials
What type of neural circuit would be involved in the sleep wake cycle?
Reverberating
Describe the effect of organophosphates on synaptic transmission.
Inactivates ACh-esterase, resulting in elevated levels of ACh remaining in the cleft. (because it has not been broken down by ACh-esterase)
Describe the symptoms of organophosphates as well as a potential treatment for this condition.
Symptoms: Convulsions, twitching, pupil contraction.
Treatment: Atropine – ACh receptor blocker
Inhibitory synapses
Synapses in which an axon terminal connects directly to the soma of the post-synaptic neuron are usually ___?
Order of synaptic transmission events
1. Impulse reaches synapse from the axon.
2. Impulse stimulates synaptic vesicles to move to presynaptic membrane.
3. Synaptic vesicles dump neurotransmitter substance into synaptic cleft.
4. Neurotransmitter substance diffuses across the cleft.
5. Neurotransmitter substance fits into receptor sites on postsynaptic membrane.
An enzyme cleaves the neurotransmitter substance & clears out the synaptic cleft.
AP is stimulated at the postsynaptic membrane & impulse travels down dendrite.
What’s the role of calcium in synaptic transmission?
Allowing synaptic vesicles to fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane.
Neurotransmitters exert their effects of on their target cells by … ?
By binding to the appropriate gated channel in the post synaptic membrane at the synapse.
Which ion is crucial for neurotransmitter release at the axon terminal?
Calcium.
What type of gated channel binds to the neurotransmitter on the post-synaptic membrane?
Receptor-mediated.
Where are inhibitory synapses normally located on a neuron?
Cell body
Where are the Ach receptors located in the neuromuscular junction?
Sarcolemma
What does IPSP stand for?
Inhibitory Post-Synaptic Potential
The patellar reflex is an automatic response that produces the same effect every time when hitting the __?
The patella ligament leading to a stretch reflex in the quadriceps
Paracrine signalling
Locally acting chemicals which affect nearby cells.
Prostaglandin
An eicosanoid that acts as a signaling molecule.
Peptide and amine hormones
Hydrophilic and cannot diffuse through cell membranes.
Steroids
Have a slow onset and longer duration of effect.
Target cell activation influences
Blood levels of the hormone, relative number of receptors on the target cell, the affinity of the hormone for the receptors, and the affinity of the receptors for the hormone.
Hormonal permissiveness
When one hormone cannot exert its effects without another hormone being present.
Antidiuretic hormone
Also known as vasopressin.
Up-regulation
When hormone levels are persistently low, target cells form more receptors.
Noradrenaline
A neurotransmitter that can bind to both α and β receptors, causing blood vessels to either constrict or dilate depending on the receptor type it binds to.
α receptors
Receptors that, when bound by noradrenaline, stimulate smooth muscle contraction in blood vessels.
β receptors
Receptors that, when bound by noradrenaline, inhibit smooth muscle contraction in blood vessels, leading to vasodilation.
Ligand
Any molecule that binds to a cell receptor.
Agonist
An agent that binds to cell receptors and elicits a response, activating the receptors.
Antagonist
An external agent that binds to a cell receptor to prevent it from responding.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers of the nervous system.
Endocrine system
A system that responds to stimuli, but not as rapidly as the nervous system.
Lipid soluble hormones
Hormones that can diffuse through the plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptors.
Water soluble hormones
Hormones that bind to extracellular receptors on the plasma membrane, activating cytoplasmic second messengers.
Hormonal stimulation
A type of stimulation where one gland secretes hormones that stimulate other endocrine glands to secrete hormones.
Catecholamines
A class of hormones that includes adrenaline and noradrenaline.
Na+/K+ ATPase
An enzyme whose synthesis is stimulated by hormones like thyroxine, insulin, glucagon, and adrenaline.
Permissiveness
A phenomenon where one hormone requires another hormone to exert its full effect.
Synergism
A situation where two hormones work together to produce a greater effect.
Antagonism
A situation where one hormone opposes the action of another hormone.
Agonism
The action of a substance that mimics the effect of a hormone.
β2 receptors
Receptors predominantly found in airways that bind to noradrenaline.
β1 receptors
Receptors predominantly found in the heart that bind to noradrenaline.
α receptors in blood vessels
Receptors that bind to noradrenaline, leading to vasoconstriction.
Secretory vesicles
Structures that can store lipid soluble hormones.
Cytoplasmic second messenger
A molecule activated by water-soluble hormones that triggers a cascade of intracellular reactions.
Receptor-hormone complex
The structure formed when a lipid-soluble hormone binds to its intracellular receptor.
Hormonal response element
The specific DNA sequence where the receptor-hormone complex binds to initiate transcription.