Electronic Information
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
A circuit with only one path is a (an)___ circuit.
Series
What is the common term for electrical potential difference or electromotive force?
Voltage
Current will flow only if it can follow a(n)___ circuit.
Closed
Why is copper used as a conductor more frequently than is silver or aluminum?
Copper is much less expensive than silver and has a lower resistance than does aluminum.
What is the equation for frequency?
F = 1/T
Why are parallel circuits usually superior to series circuit?
If one path has a break or gap, the circuit will remain closed and current can flow.
What is the formula for the electrical power?
P = IV
If an element’s atoms have valence shells that are more than half full electrons, that element is a(n)___.
If an element’s atoms have valence shells that are more than half full electrons, that element is a(n)___.

Identify this symbol:
Fixed resistor
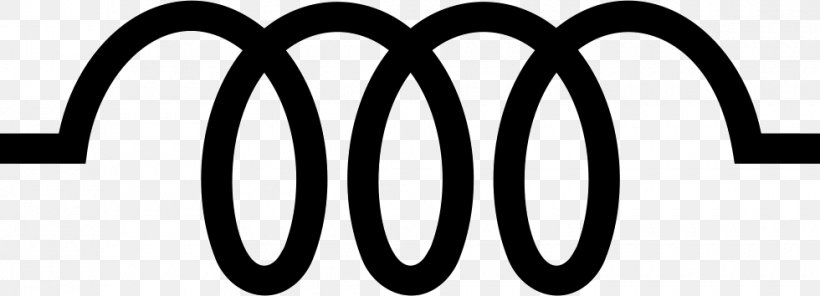
Identify this symbol:
Inductor
when a P-type semiconductor is joined to an N-type semiconductor, the result is a(n)___.
Diode
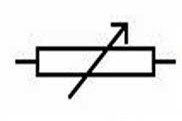
Identify this symbol:
Rheostat

Identify this symbol
Motor
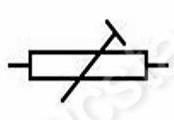
Identify this symbol:
Variable resistor
The name for the imaginary flow of positive charge, opposite to the actual flow of electrons, is___.
Conventional current
If the resistance provided by a load were to decrease, the current flowing through that circuit would___.
Increase
If an AC current is delivered at 20 Hz, what is it that happens 20 times per second in that circuit?
The voltage begins at zero, increases to a maximum level, decreases to zero again, switches direction and increases to a maximum level in that direction, and returns to zero again.
A(n)___ resists changes in current flowing through by applying a voltage that runs against increased current.
Inductor
A(n)___ is constructed of two metal plates and used to store electricity.
Capacitor (or condenser)
Poor conductors have___ resistance than good conductors.
Higher
What is voltage?
Voltage is the electric “pressure” produced by a large negative ghcarge.
The___ is a solid-state device that has revolutionized the construction of electronic devices.
Transistor
Capacitive reactance is measured in___.
Ohms
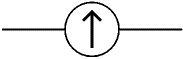
Identify this symbol:
Galvanometer
How can the magnetic field formed by a current-carrying wire be strengthened?
By winding the wire into a coil around a ferrous (iron) core
If multiple loads are connected in a series circuit, how is the overall voltage of the circuit calculated?
By adding the voltage drops across the various loads
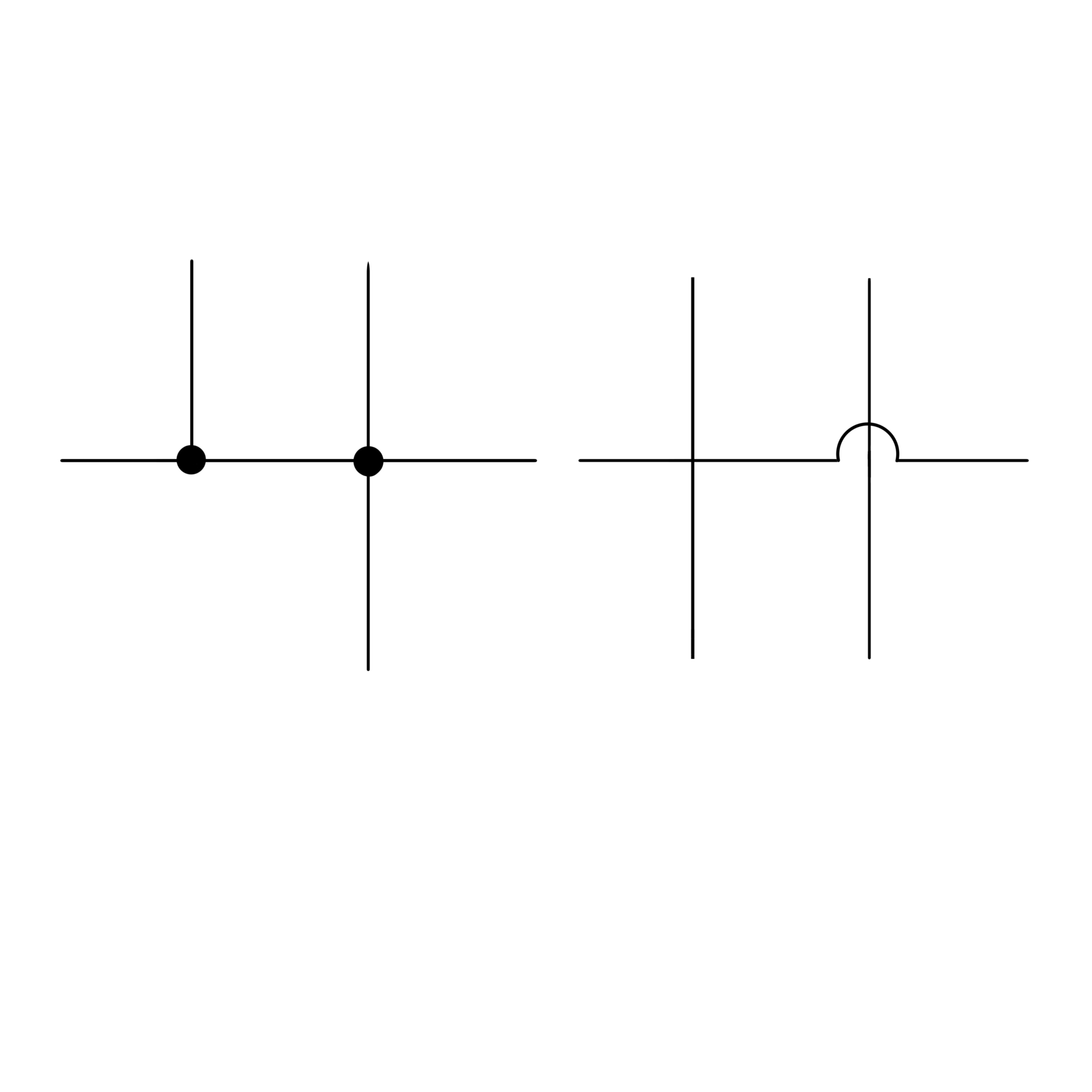
What is the difference between these connection symbols?
The left symbol indicates that the vertical wires are connected to the horizontal wire; the right symbol indicates they are not connected.
When silicon’s crystalline structure is doped with a five-electron element, the silicon crystal becomes a(n)___ material.
N-type
Why are transformers especially useful in the transmission of electricity from power plants to residences?
It is more efficient to transmit high-voltage electricity, but most household appliances use low-voltage electricity.
What are the two types of transistors?
NPN transistor and PNP transistor
When a current is passed through a wire coiled around a ferrous material, the result is a(n)___.
Electromagnet
Do household electrical outlets in North America use AC or DC current?
AC
If an element’s atoms have valence shells that are less than half full of electrons, that element is a(n)___.
Conductor
If an element’s atoms have valence shells that are exactly half full of electrons, that element is a(n)___.
Semiconductor
What is the formula for Ohm’s law?
V = IR
What does an electrical ground do?
A ground provides a low-resistance path to guide excess electrical energy away from panels and loads, to protect them in the case of lightning or circuit failure.
The conversion of AC to DC is called___.
Rectification
What is the difference between direct current and alternating current?
Direct current flows in one direction only: alternating current changes its direction many times a second.
What do DC and AC stand for?
Direct current: alternating current
If multiple loads are connected in a parallel circuit, how is the overall resistance of the circuit calculated?
By adding the inverse of the resistance of the various loads, and then taking the inverse of the result
If multiple loads are connected in a series circuit, how is the overall resistance of the circuit calculated?
By adding the resistance of the various loads
Current and resistance are directly/ inversely proportional.
Inversely
Electrical current flowing through a conductor produces a(n)___field.
Magnetic
The basic unit of electrical charge is the___.
Coulomb (C)
In a series circuit, does the current vary alternate, or remain the same throughout the circuit?
Current remains the same
A(n)___is used to increase or decrease voltage in a circuit.
Transformer
Define electrical power.
Electrical power is the amount of energy delivered to and used by an electric circuit.
A(n)___is a thin wire that melts when current exceeds a certain amount.
Fuse
Resistance is measured in___.
Ohms (Ω)
If one battery’s terminal supplies greater voltage than that of another battery, the first battery terminal has more___.
Electrons (or negative charge)
Voltage and current are directly/inversely proportional.
Directly
A(n)___is used to raise or lower current in a circuit.
Resistor
Define load, as it relates to electrical systems.
In electricity, a load is a source of resistance that turns electrical energy into some other type of energy.
Induction is measured in___.
Henries
The process of adding impurities to silicon or germanium in order to improve its usefulness as a semiconductor is called___.
Doping
In North America, AC is delivered at___Hz.
60
What is a short circuit?
A short circuit occurs when a load is bypassed by a conductor, allowing more current to flow through the circuit.
What metal is most often used as a conductor in household electrical systems?
Copper
In most home electrical systems, loads are wired in parallel with a fuse wired in series/parallel.
Series
Electrical current is measured in___.
Amperes (A)