IGCSE CIE - Geography
1/373
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
374 Terms
Birth Rate
The number of births per 1000 of the population per year.
Death Rate
The number of deaths per 1000 of the population per year.
Natural Change
The change (an increase or decrease) in population numbers resulting from the difference between the birth and death rates over one year. E.g. Natural increase or decrease.
Fertility rate
The number of children per woman on average in a country.
Life Expectancy
The number of years on average that a person is expected to live within a country.
Infant mortality rate
The number of deaths of children (under the age of one) per 1000 live births per year.
Migration
A process of people changing their place of residence, either within or between countries.
Immigrant
A person arriving in a country or region to live.
Emigrant
A person leaving a country or region to live somewhere else.
Ageing Population
A population with a rising average age. (Greying population)
Youthful Population
A population in which there is a high % of people under the age of 16.
Tipping Point
The point at which the momentum of a change becomes unstoppable.
Development
Economic and social progress that leads to an improvement in the quality of life for an increasing proportion of the population
Net migration
Average number of people moving to a country minus those moving out
Demographic transition model
Shows population change over time. It studies how birth rate and death rate affect the total population of a country.
DTM stage 1
High birth and death rate, low population
DTM stage 2
Falling death rate, high birth rate, rapid population increase
DTM stage 3
Declining death rate, falling birth rate, steady population increase
DTM stage 4
Low death rate, declining birth rate, slow population increase
DTM stage 5
Death rate overtakes birth rate, population decline
Reasons for falling birth rates
Education of women, contraception, reduction in infant mortality
Reasons for falling death rates
Improvement in medical facilities, improvements in sanitation, improvements in food production
Fertility
The number of live births per 1,000 women aged 15-49 in 1 year.
Infant Mortality
The number of deaths of children under the age of 1 year expressed per 1,000 live births per year
Population Density
The number of people in an area. The density of population is obtained by dividing the total population of a country (or region) by the total area of that country (or region)
Migration Rate
The rate of people moving into a country less the number of people moving out of the same country.
Pro natalista policies
A policy that encourages couples to have more children.
Pro natalista policy incentives
Cash payments.
Free to subsidised healthcare and education.
Free nurseries or subsidised childcare.
Reduced taxes.
Child benefits.
Free equipment.
Poster and advertising campaigns.
Anti-natalist policy
a policy that tries to reduce birth rates
Benefits of higher energy consumption
electricity makes tasks easier, transport systems use oil, industry uses energy to work

Problems with higher energy consumption
Will eventually run out of non-renewable energy sources soon. The burning of fossil fuels for energy is resulting in air pollution and accelerates the rate of global warming. Countries might conflict with each other over lack of energy supplies. Nuclear power not very safe.

renewable energy
Energy that can be reused over and over

fossil fuels
Coal, oil, natural gas, and other fuels that are ancient remains of plants and animals

oil
A liquid fossil fuel formed from marine organisms that is burned to obtain energy and used in the manufacture of plastics.

advantages of oil
Easy to transport by pipes/tankers(large vehicles.) Less polluting than coal when burnt. Can be used as raw material in chemical industry. Needs to be used for motor vehicles.

disadvantages of oil
Burning oil produces greenhouse gases which accelerate global warming. Oil spills from tanks/pipes can kill wildlife. Oil production is only in a small amount of countries, meaning they control the prices. Work on oil rigs can be dangerous.

petrochemical industry
The industry that uses the products of oil
refineries to manufacture products
like plastics.

hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
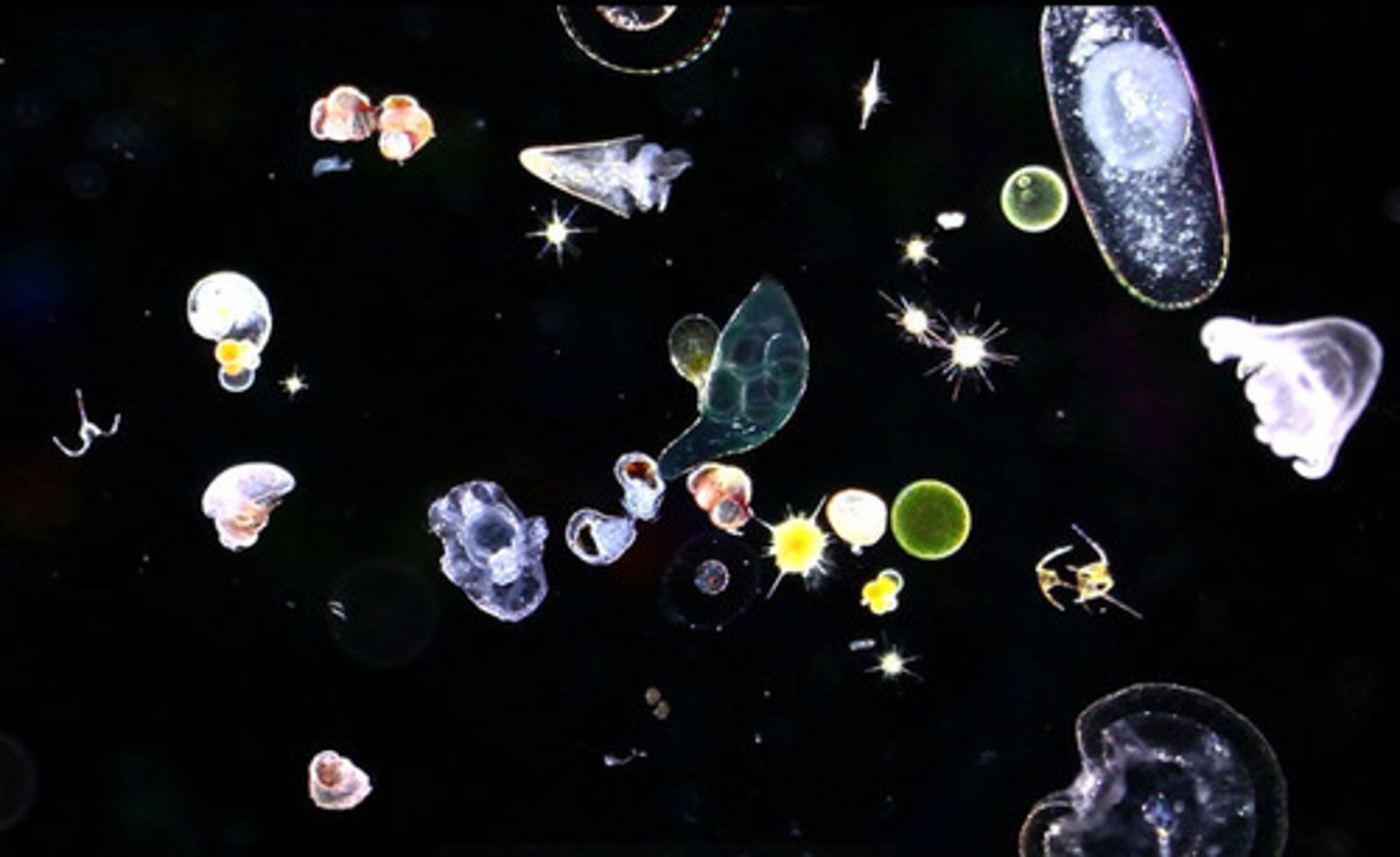
plankton
Drifting or weakly swimming organisms living suspended in the water column

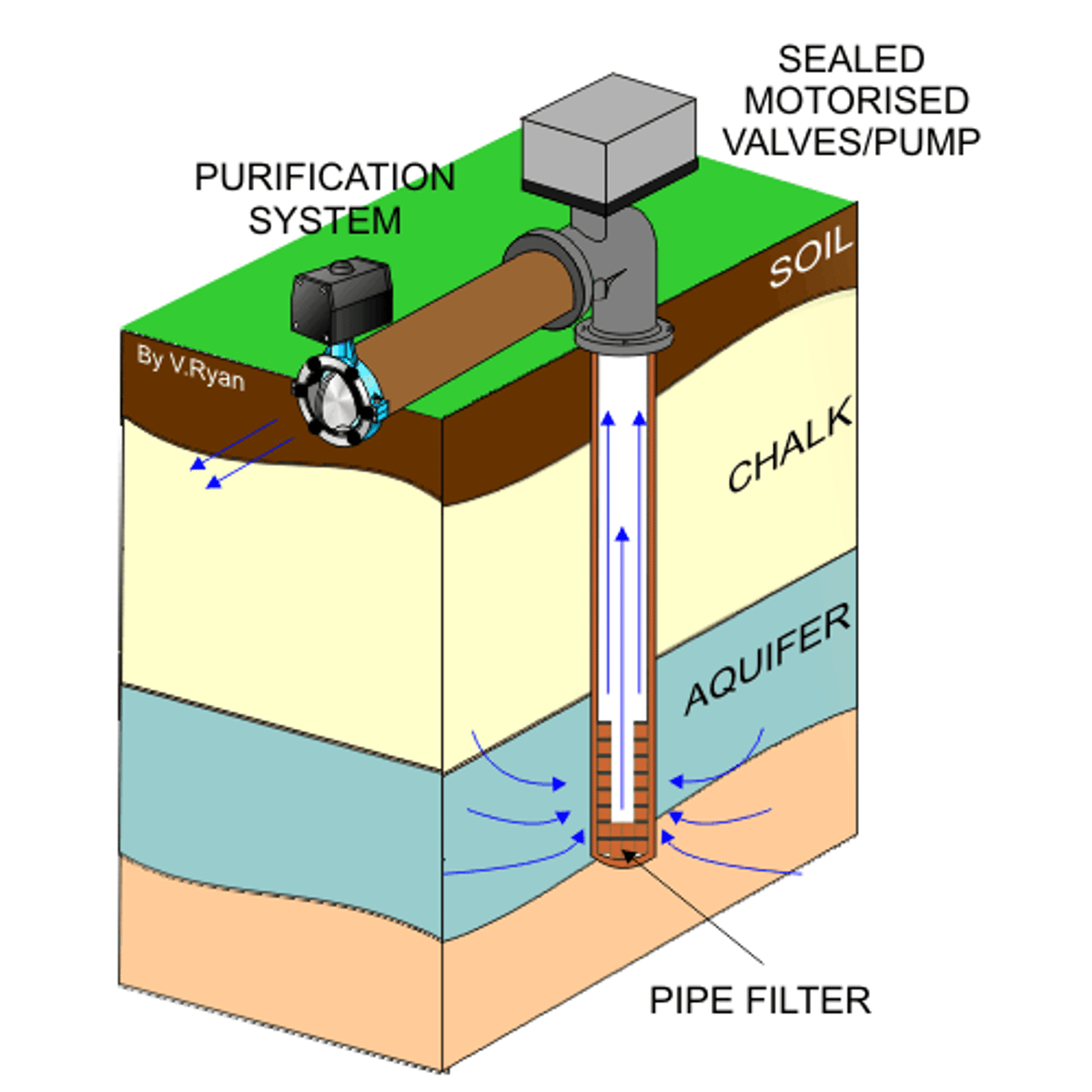
borehole
the generalized term for any narrow shaft bored in the ground, either vertically or horizontally. A borehole may be constructed for many different purposes, including the extraction of water or other liquid (such as petroleum) or gases
oil rigs
what are built in the water in order to get oil and natural gas that is beneath the ocean floor

coal
sedimentary rock that formed from trees growing in tropical swamp forests. burnt for energy.

sedimentary rocks
Formed when particles of broken rock and organic materials are pressed and cemented together to form new rocks. Sediments are mud, sand, pebbles, shells, bones, leaves, and stems. Some rocks of this type can be sandstone, limestone, and gypsum.

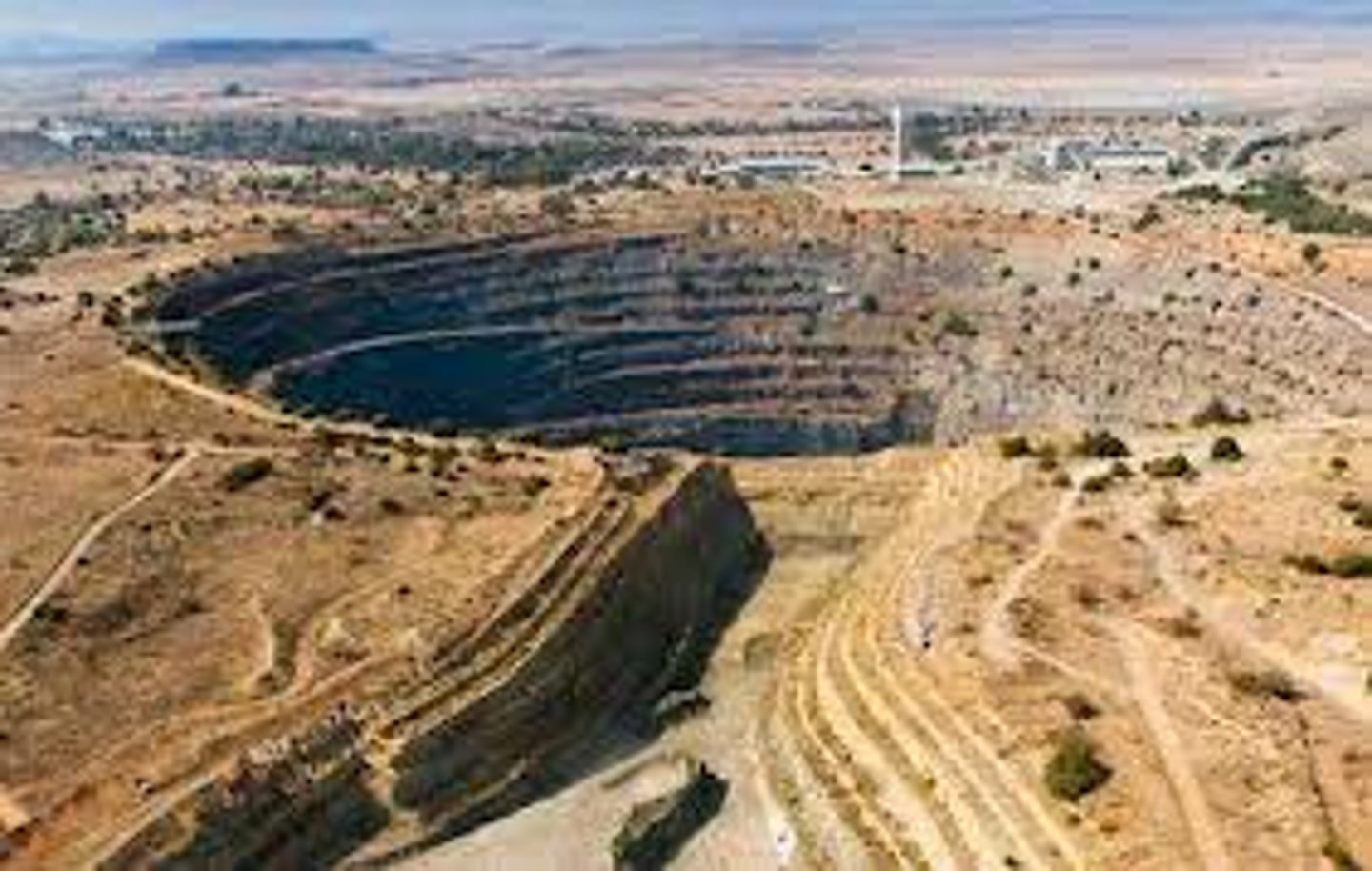
opencast mines
Mining at the surface by excavating an open pit.

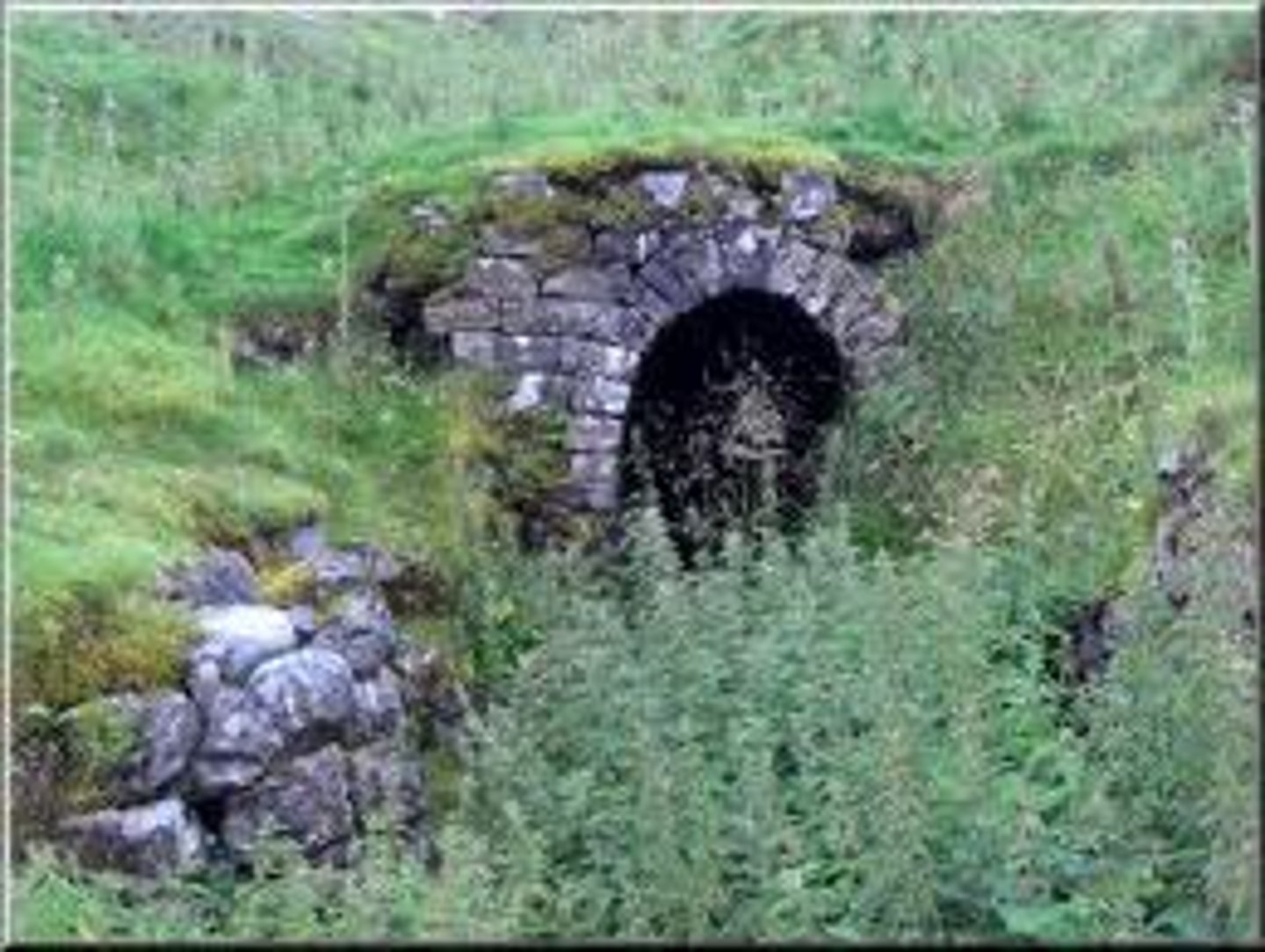
adit mines
A mine which is horizontal or nearly horizontal, driven into the side of a mountain/steep slope.

non-renewable energy
a source of energy that exsists in limited quantities and once used, cannot be replaced except over the course of millions of years

incline shafts
...A shaft which has been dug at an angle to the vertical to follow the depth of ore
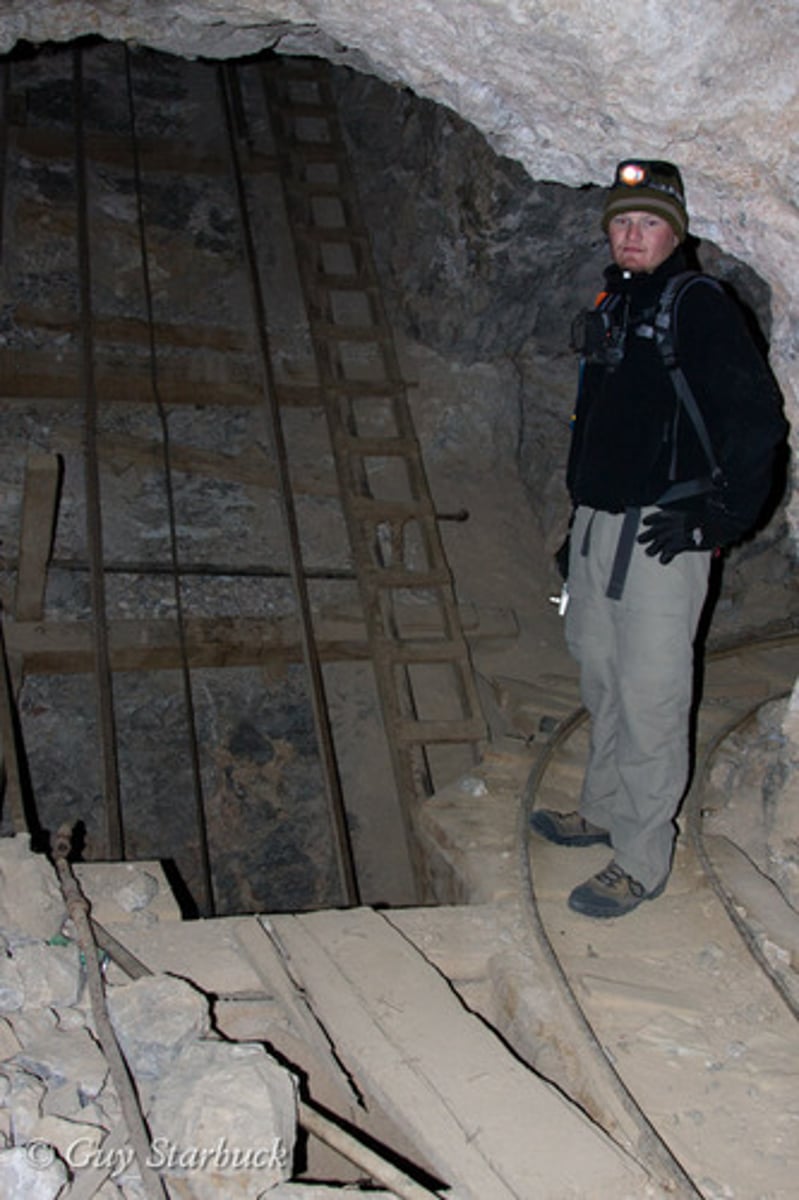

vertical mine shafts
a mine shaft which goes down vertically, and miners use lifts/elevators to go down the mine.
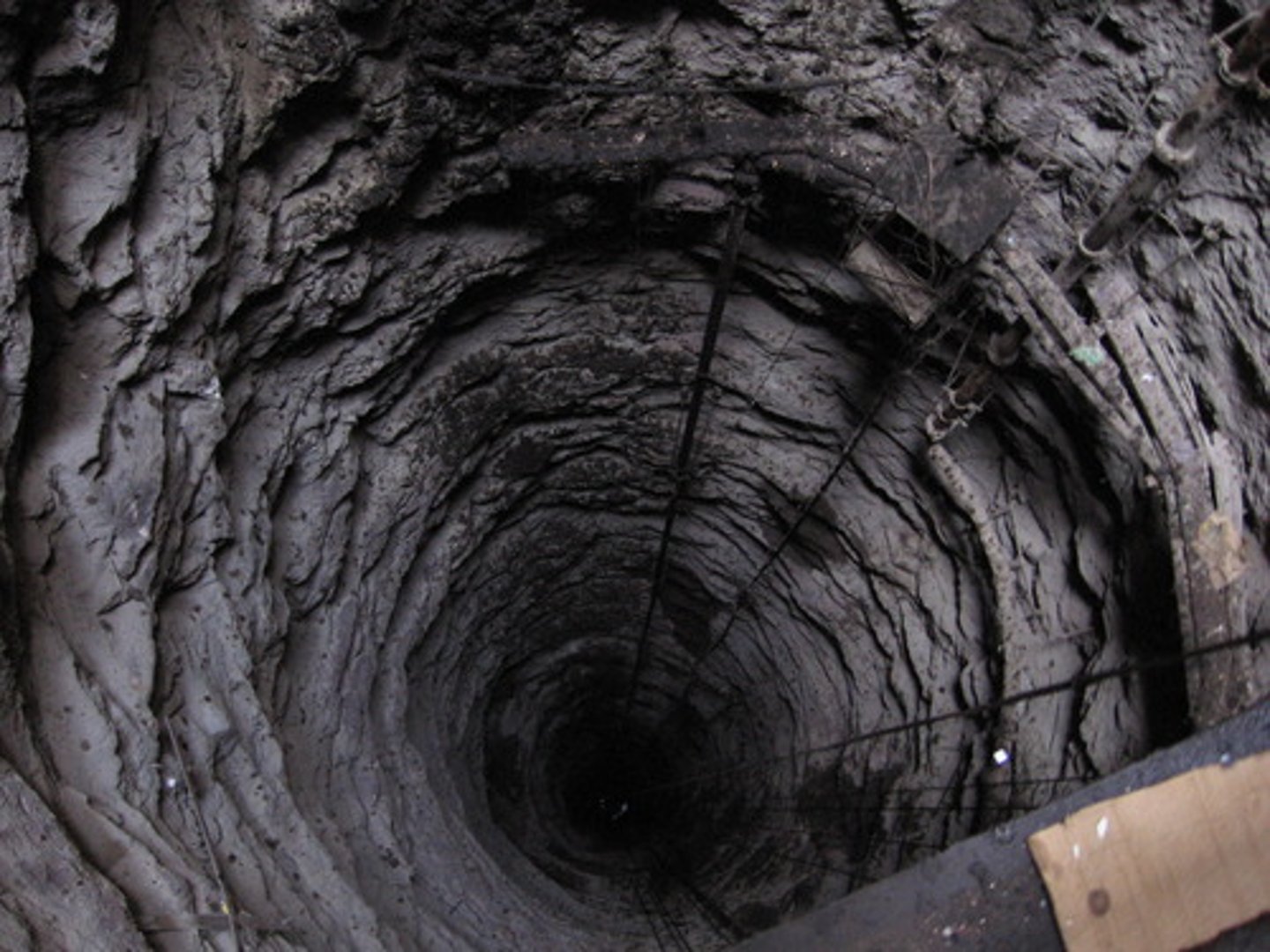

coal seams
coal is found in these layered formations

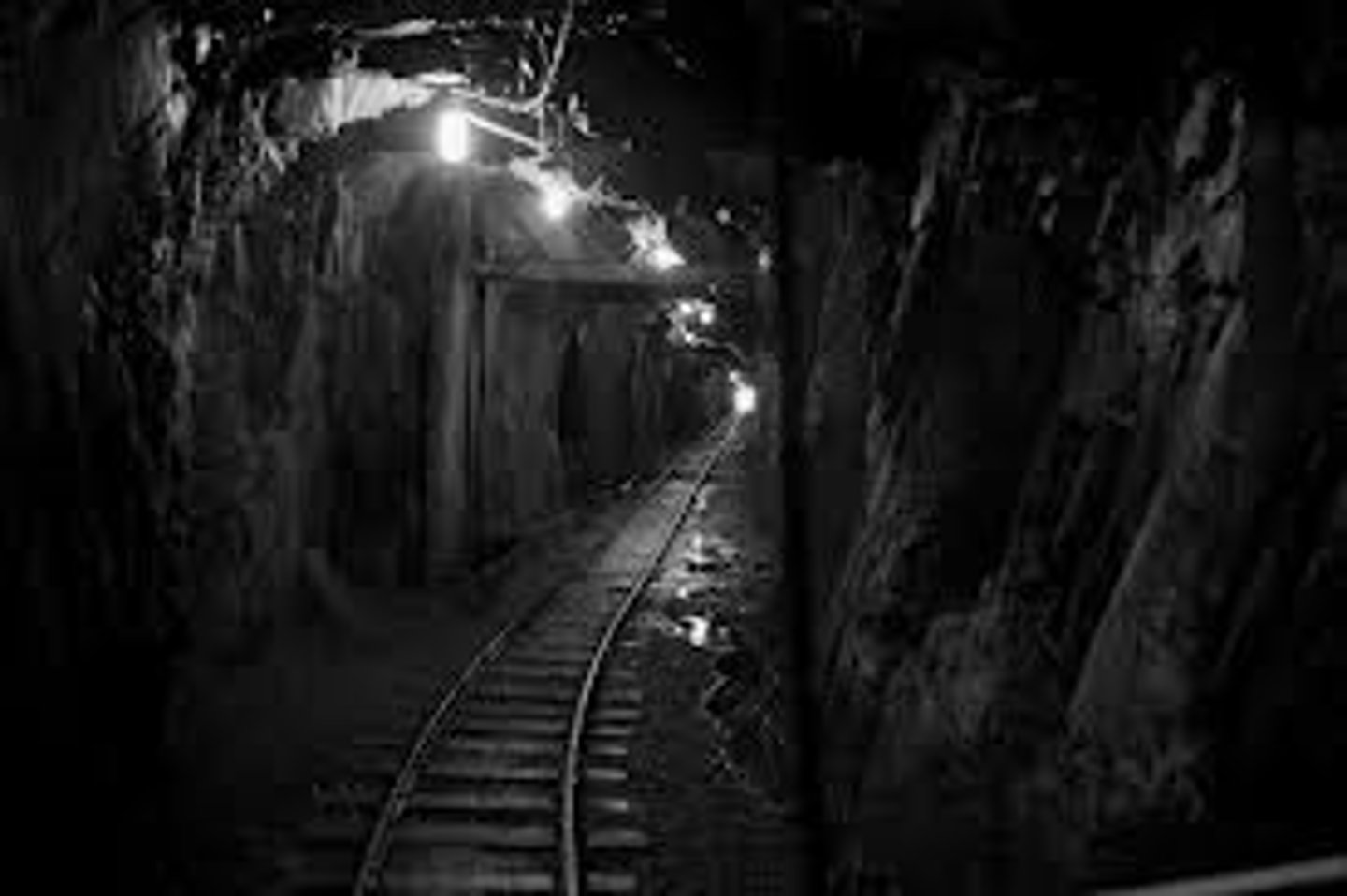
problems with deep mining
Visual pollution from coal storage, railway lines and mine buildings on surface. Possibility of subsidence, when surface collapses into old workings. Dangers to miners from accidents such as explosions/collapse of mine. Needs greater initial capital compared to opencast.

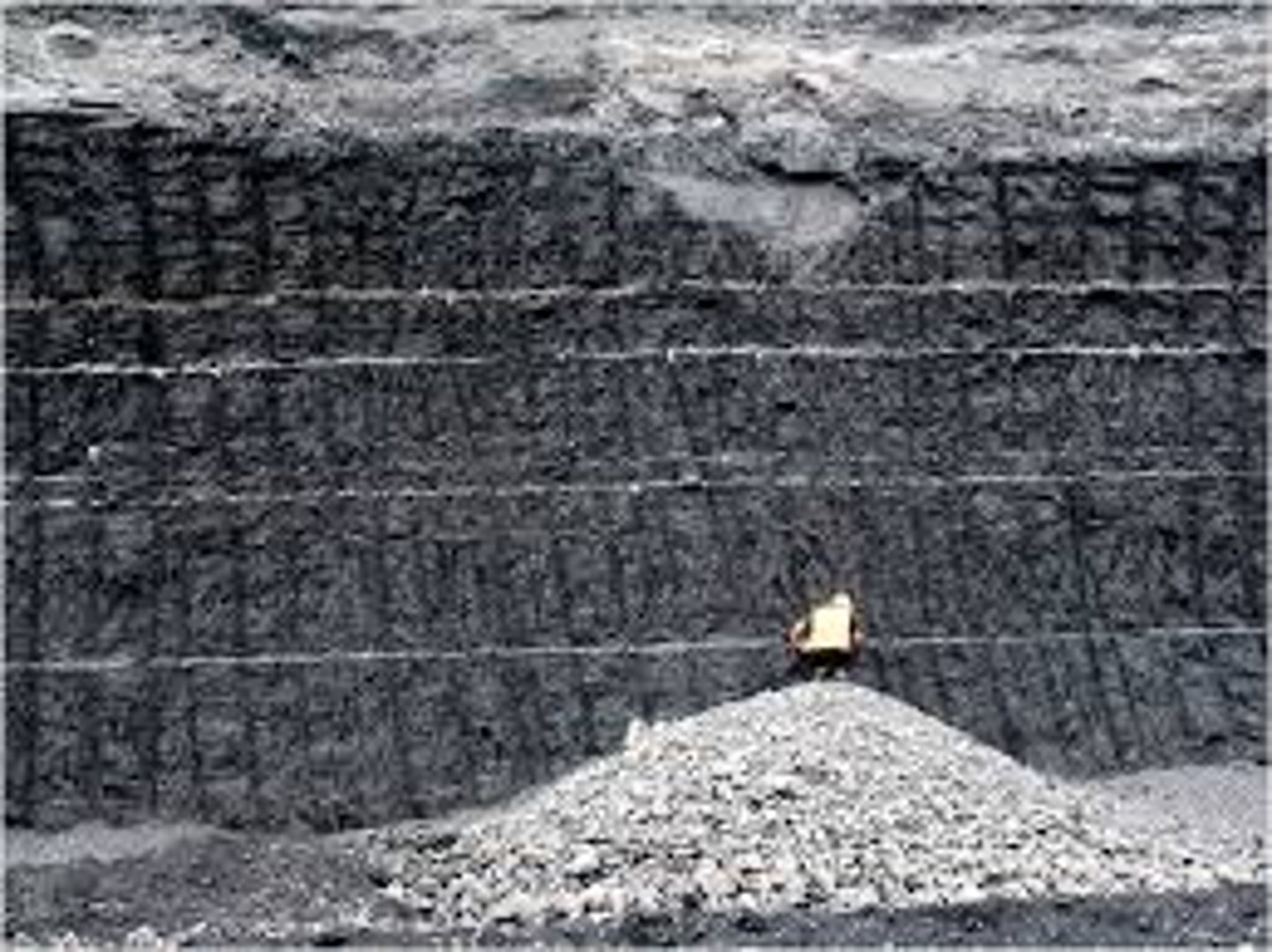
problems with opencast mining
Visual pollution from the big pit that's excavated. Temporary loss of land for other uses while mining happens. Noise from machinery/blasting. Dust, if pit becomes dry.

recession
A slowdown in economical activity

natural gas
A gas with high methane content, found along with various fossil fuels and is used as a fuel.

advantages of natural gas
Electricity generation using natural gas is less expensive to build than oil. Gas fired generating plants are less expensive to build than other plants e.g. coal/nuclear. Easy to transport by pipes/tankers(large vehicles.) Less polluting than coal when burnt. Can be used as raw material in chemical industry.
disadvantages of natural gas
Burning gas produces greenhouse gases which accelerate global warming. gas leaks from tanks/pipes can kill wildlife. Gas production is only in a small amount of countries, meaning they control the prices. Work on rigs can be dangerous.

fuelwoods
Wood used for fuel, for cooking/keeping warm etc.

problems with fuelwoods
Natural woodland is being cut faster than it can regenerate, so families have to walk farther to get wood, resulting in time lost-children might miss out on education. Deforestation lead to exhaustion of soil, so the forest can't grow back. Burning wood in confined spaces on inefficient stoves leads to respiratory (breathing) problems.

development of fuelwoods
Planting more trees, and constantly planting them. Managing woodland and carefully pruning/thinning to encourage growth. Introduction of fast-growing species. Fuel efficient stoves, which cause less smoke.

renewable energy supplies
Hydroelectricity, geothermal power, wind power, solar power & bio fuels.

reasons for growth of renewable energy
Anticipated increase in oil prices. Environmental impacts of fossil fuels (global warming.) Concerns over the sustainability of fossil fuels. Government incentives to increase use of renewable energy.

geothermal energy
Energy extracted from hot rocks beneath the earth's surface.
volcanic sources
Groundwater is heated by magma, up to 1000 degrees Celsius. Groundwater is under pressure so it doesn't boil and evaporate. Borehole is then sunk into the rocks, and the hot groundwater rushes up and turns into steam due to the reduction in pressure. This steam is then used to drive turbines or heat water to drive turbines. The condensed water is then pumped back into the ground.
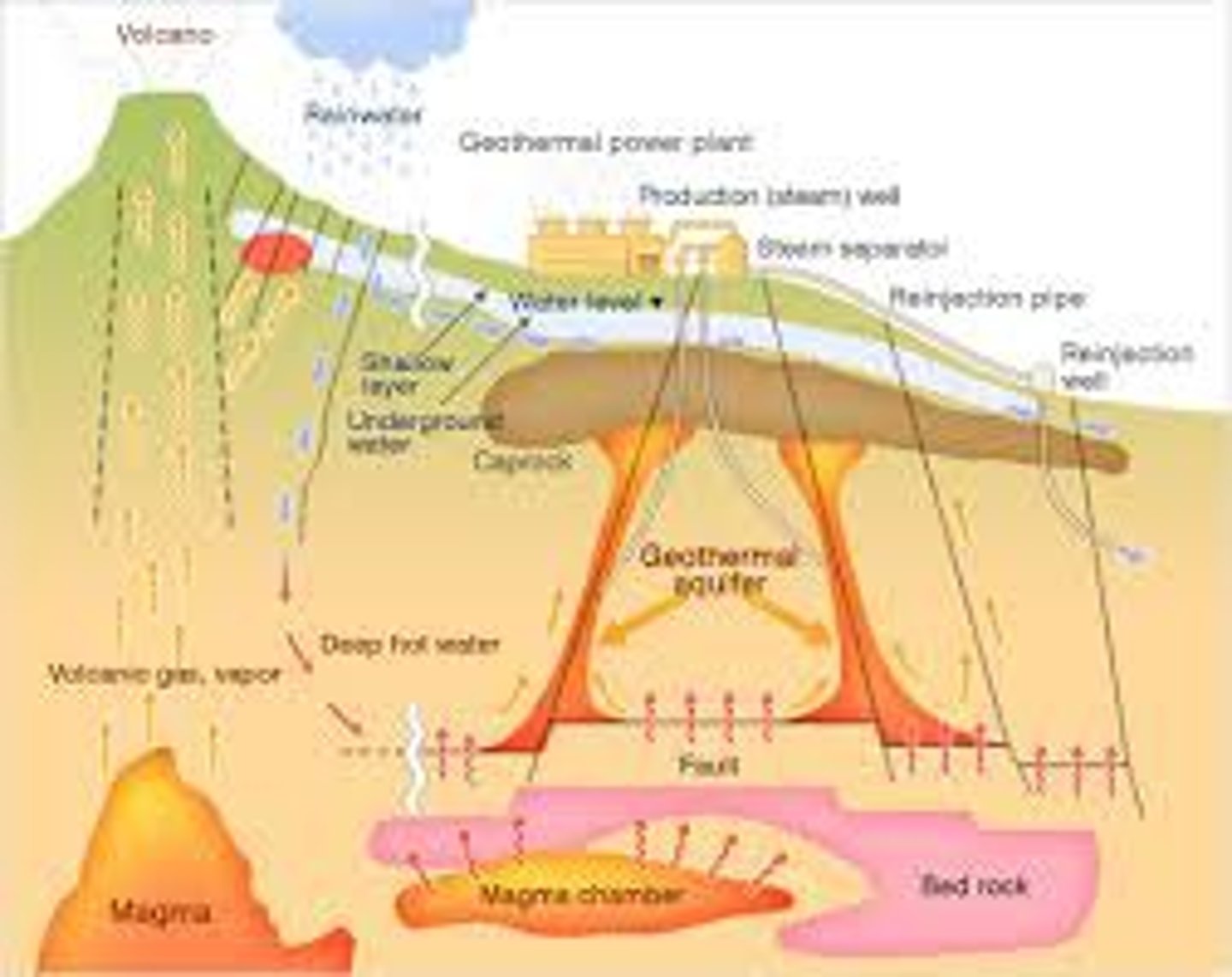
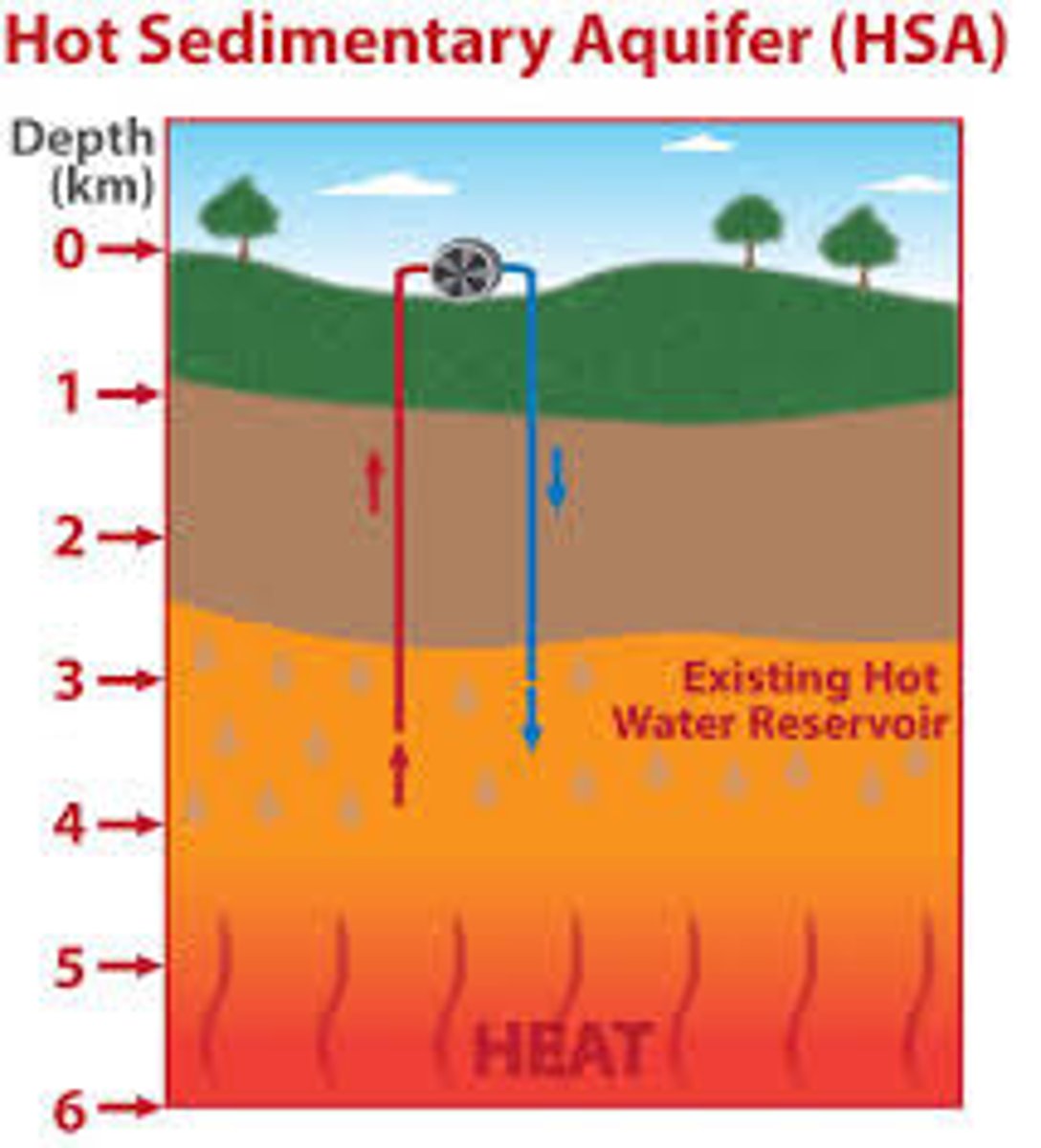
geothermal aquifers
Layers of rocks which contain hot water. The hot water is pumped out and a heat exchange extracts the heat. The cold water is then pumped back into the ground.
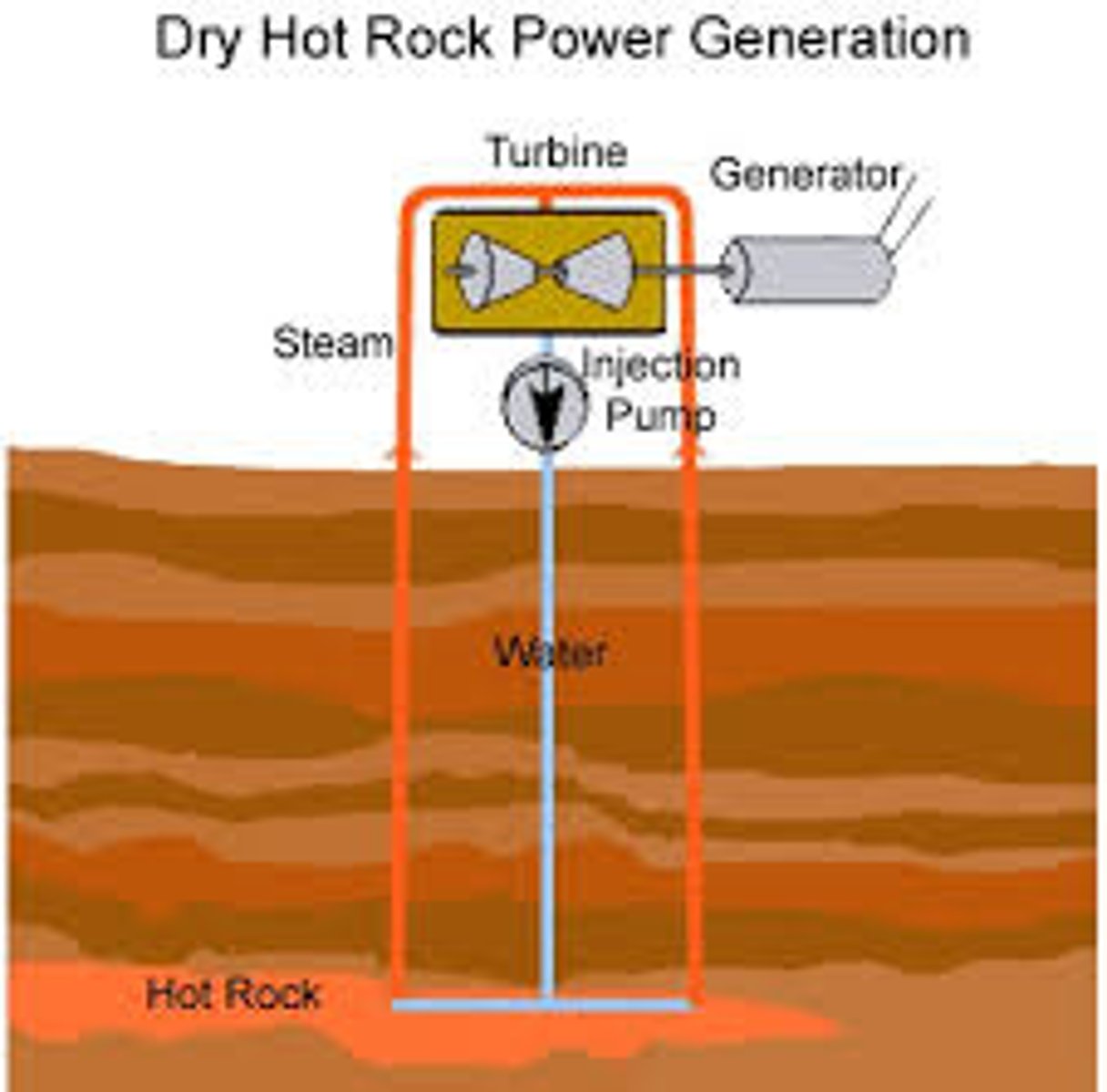
hot dry rocks
aka enhanced geothermal system (EGS), it generates geothermal electricity without the need for natural convective hydrothermal resources.
advantages of geothermal power
Almost entirely emission free
Zero carbon
The process can scrub out sulfur that might have otherwise been released
No fuel required (no mining or transportation)
Not subject to the same fluctuations as solar or wind
Smallest land footprint of any major power source
Virtually limitless supply
Inherently simple and reliable
Can provide base load or peak power
Already cost competitive in some areas
Could be built underground
Some level of geothermal energy available most places
New technologies show promise to utilize lower temperatures

disadvantages of geothermal power
Prime sites are very location-specific
Prime sites are often far from population centers
Losses due to long distance transmission of electricity
Water usage
Sulfur dioxide and silica emissions
High construction costs
Drilling into heated rock is very difficult
Minimum temperature of 350F+ generally required
Care must be taken to manage heat and not overuse it

wind power
The use of a windmill to drive an electric generator

advantages of wind power
-It does not cause air pollution, global warming or acid rain.
-It has very little effect on the local ecosystem, except very occasionally killing birds that get caught in the blades.
-In Europe, the wind is strongest in winter, when demand for electricity peaks.
-After the initial capital input, production is cheap because the fuel is free.
-Wind farms may provide a small source of income for farmers.

disadvantages of wind power
-It cannot e used during calm periods or storms.
-Many people consider wind farms to be a form of visual pollution-especially in areas of natural beauty.
-The technology is relatively new and at present very large numbers of turbines are needed to generate fairly modest amounts of electricity.

solar power
energy from the sun that is converted into thermal or electrical energy

advantages of solar power
-It is safe and pollution-free
-After the initial capital input, production is cheap because the fuel is free.
-It can be used effectively for low-power uses, such as heating swimming pools or central heating.
-Its greatest potential is in warm and sunny countries, or in LEDC's where people live in locations that are isolated from the national effectively grids

disadvantages of solar power
-The initial capital input in high
-It is not as effective in cloudy countries
-It is less effective in high-latitude countries, where more power is needed in the winter but the days are shorter and the sun is lower in the sky-giving lees light.
- It is less effective for high-output uses, such as powering colour TVs.

solar panels - photovoltaic cells
When more solar energy is generated than is being used, it can be stored in a battery or exported to the national utility grid

biofuels
Fuels, such as ethanol or methanol, that are created from the fermentation of plants or plant products.

bioethanol
Bioethanol is an alcohol made by fermentation from carbohydrates

biodiesels
a vegetable oil- or animal fat-based diesel fuel consisting of long-chain alkyl

biogas
Biogas typically refers to a mixture of gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen.

solid biofuels
Can be used in power stations and in the heating systems of houses and other building. Special fuels and boilers are needed to make use of this energy source.

advantages of biofuels
-Prices could be more stable than world oil prices.
-Suppliers can be more secure and reduce reliance on imported fuels.
-Fewer pollutants are produced than by than fossil fuels.
-They are "carbon-neutral", because the growing source crops absorb carbon dioxide from the air which balances the emissions from the burning fuel.

disadvantages of biofuels
-IN the period from 2008-2011, some land previously used for the production of food was changing to produce crops for biofuel production instead. This led to increases in world food prices and decreases in the food supply.

power stations
The places where electricity is generated.

reasons for growth in electricity
LEDCs. As their standards of living begin to rise, there will be an increasing demand for home appliances(like televisions)as well as services(offices)- all which consume electricity

hydroelectric power
Electricity generated by flowing water
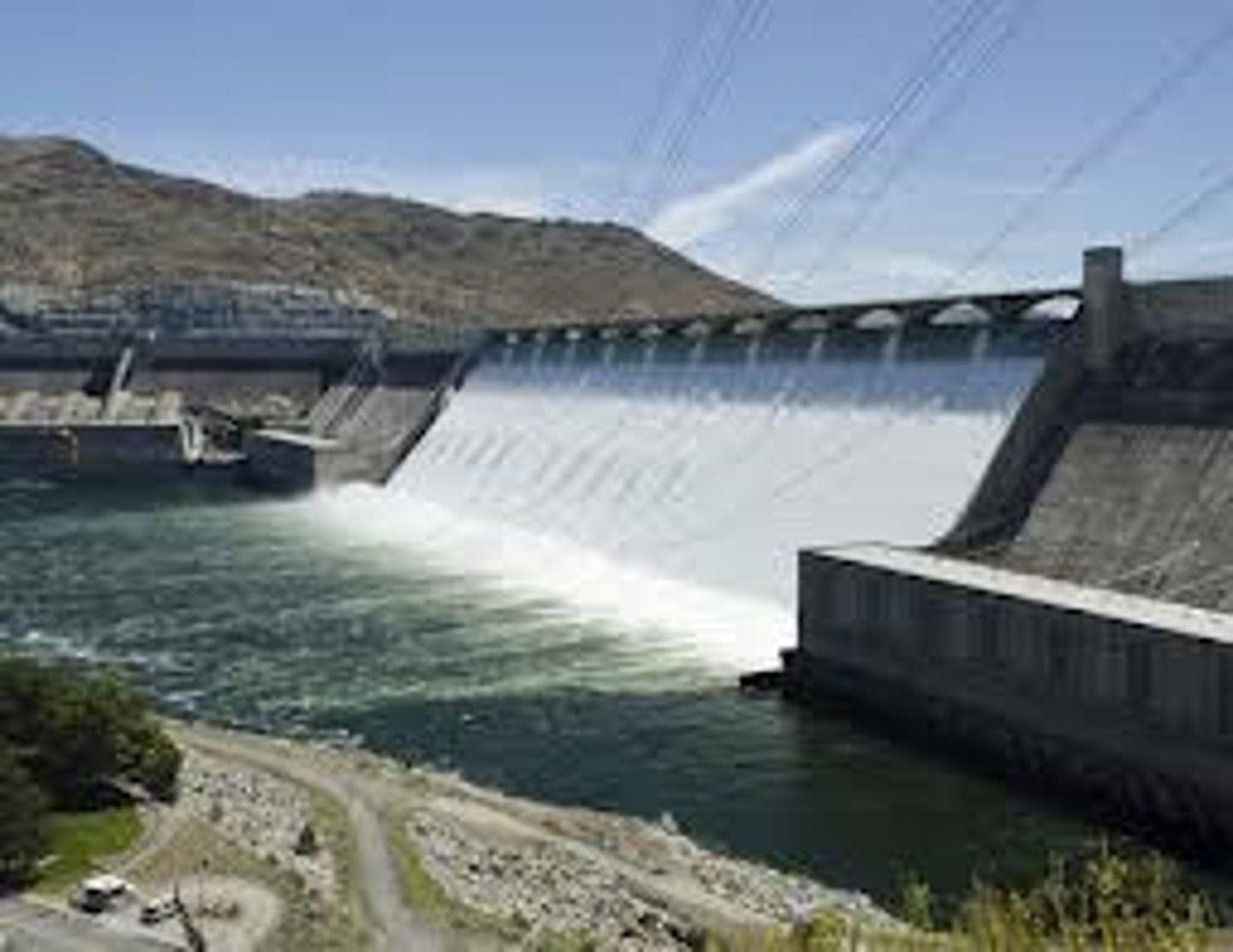

sites for hydroelectric power stations
-a large river
-a large falling distance(head) of water
-a constant flow of water throughout the year
-a narrow valley to provide a good dam site

penstock
A tube bringing the water to the turbine
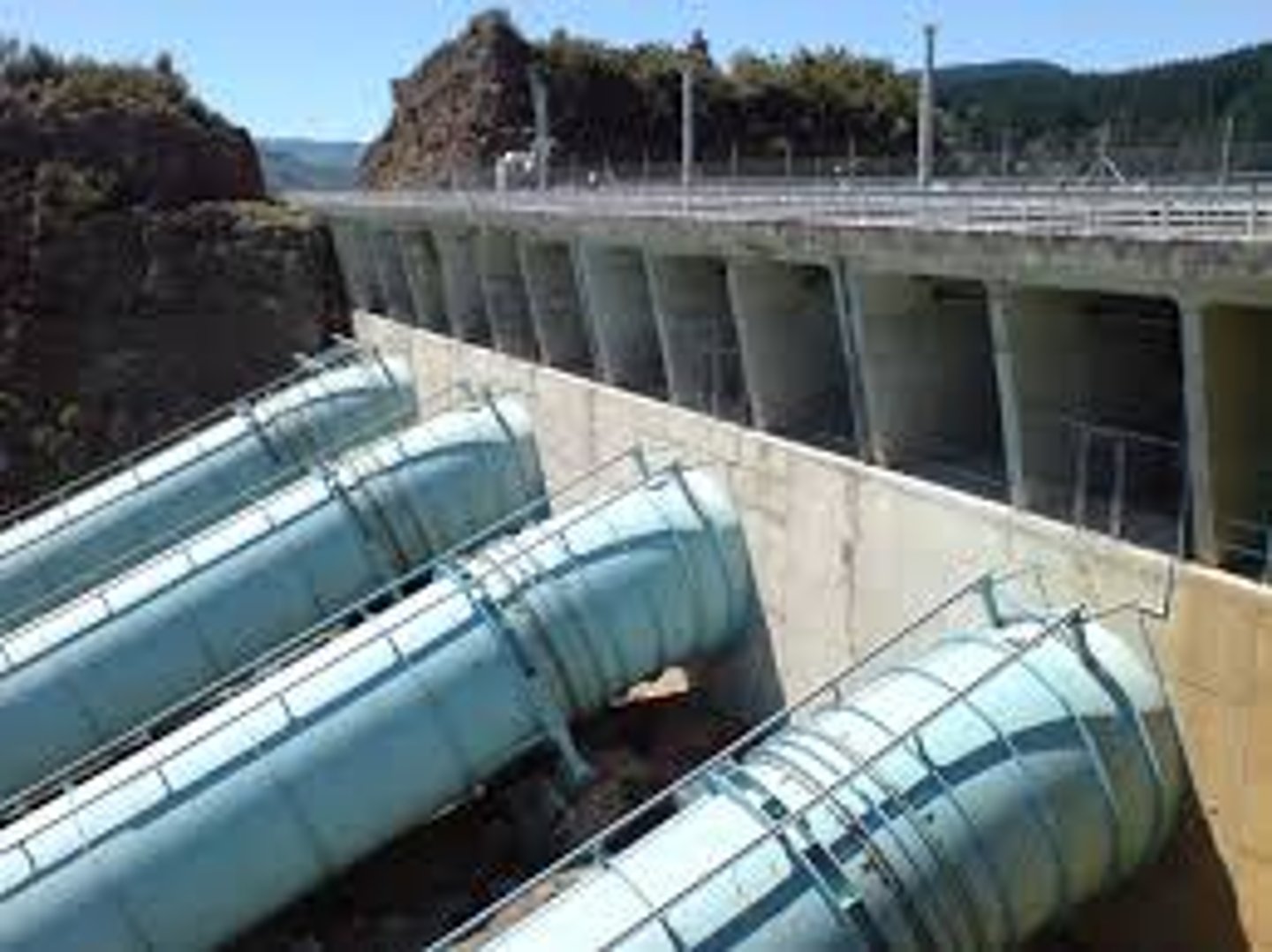

advantages of hydroelectric power stations
-Once a dam is construed, electricity can be produced at constant rate.
-The power stations can respond quickly to changing demand, as explained above.
-There are no fuel costs.
-The reservoir that forms behind the dam can be user for water sported and leisure activities.
-The stored water can also used for irrigation and other purposes.
-There is no atmosphic.

disadvantages of hydroelectric power stations
-Dams are extremely expensive to build, and they must operate for many decades to make a profit
-The flooding of large areas of land means that the environment is destroyed, along with natural habitats and historical or archaeological features.
-People living in the villages and towns of the valleys to be flooded must move. In some countries, people are forcibly removed so that hydroelectric power schemes can go ahead.

thermal power stations
electrical generating station that uses thermal energy to produce steam to drive turbines; sources of thermal energy include coal, natural gas, and nuclear energy
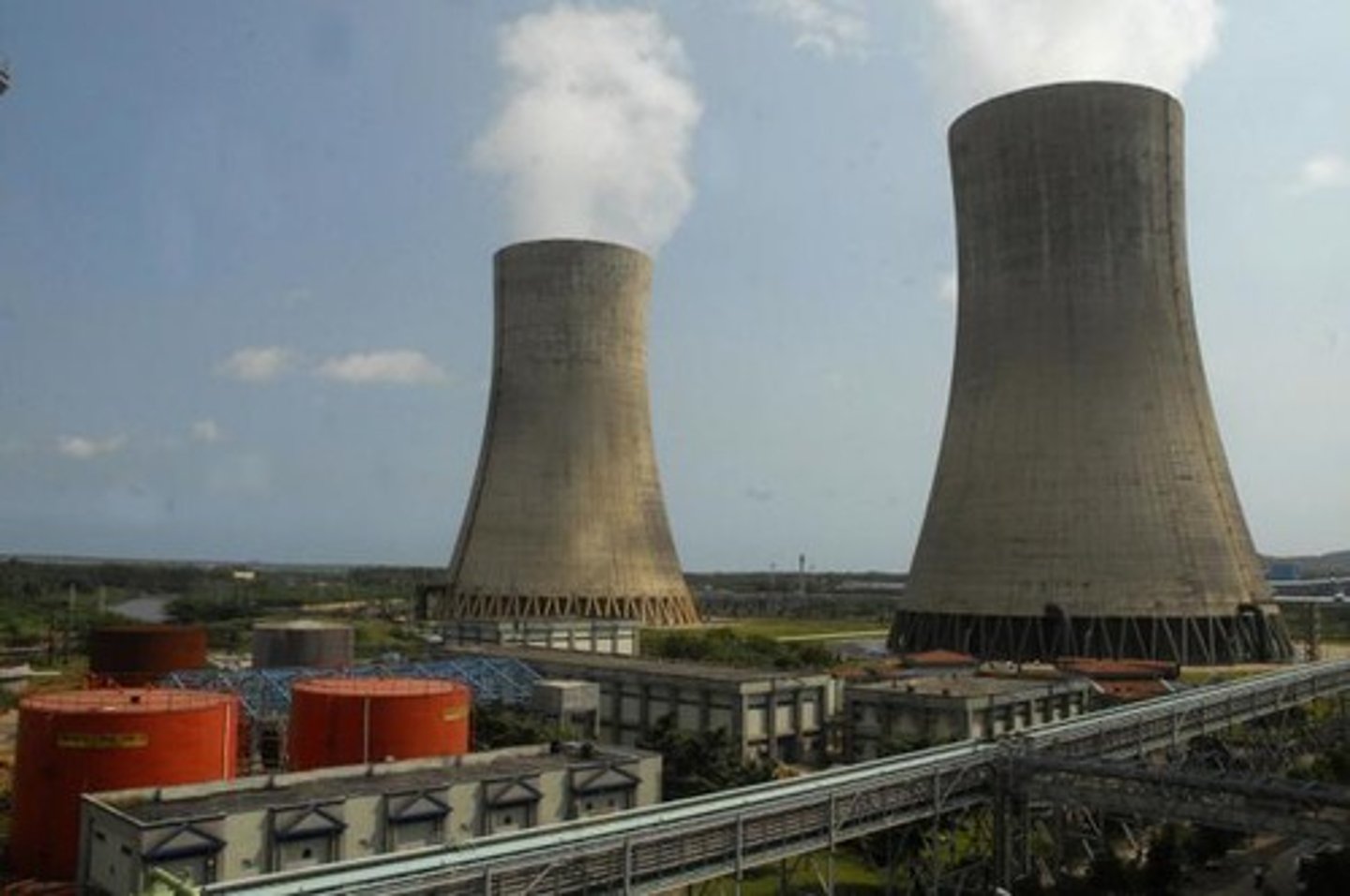

factors effecting location of thermal power stations
-Coal is bulky and is normally transported by rail. For this reason, coal-fired power stations re often located close to the coal mines.
-Oil and gas can be transported relatively easily by pipeline, so their power stations do not needed to be located close to the oil and gas wells. Nevertheless oil-importing countries often locate oil fired power stations at oil refineries close to the port where the oil arrives in the country.
advantages of thermal power
-Many countries still have large reserves of fuel.
-Coal is also used to make coke for the steel industry, and oil is the basis of the petrochemical industry
-Oil and gas can transported efficiently by pipeline.

disadvantages of thermal power
-World coal reserves may only last for another 300 years, and oil and gas for an even an shorter time.
-Deep mining is dangerous and careful health and safety measures are repuired
nuclear power stations
Power station generating electricity from the energy stored inside atoms - energy is released by the controlled splitting apart of large atoms (nuclear fission)

factors affecting the location of nuclear power stations
-Like other power stations. Large flat sites are needed for the plant and for cooling towers.
-The volume of raw material is so small that this is not a factor.
-Pure water is need for cooling. Sea water will not do, unless it is desalinated. However, sea water has been used in emergencies.
advantages of nuclear power
-Only very small amounts of uranium are needed to produce large amounts of energy.
-Uranium ore will not ran out in the foreseeable.
-It does not produce greenhouse gases and acid rain.
-The safety record of nuclear power stations has improved and the industry is high regularly

disadvantages of nuclear power
-The earthquake in Japan in March 2011 caused an explosion and leakage of radioactive material at the Fukushima nuclear power stations. This raised questions about the safety of nuclear power stations in earthquake zones.
-Nuclear power stations produce material that is also the raw material of nuclear weapons, so there can be serious security concerns.

water supply
Storage and regulation of water.

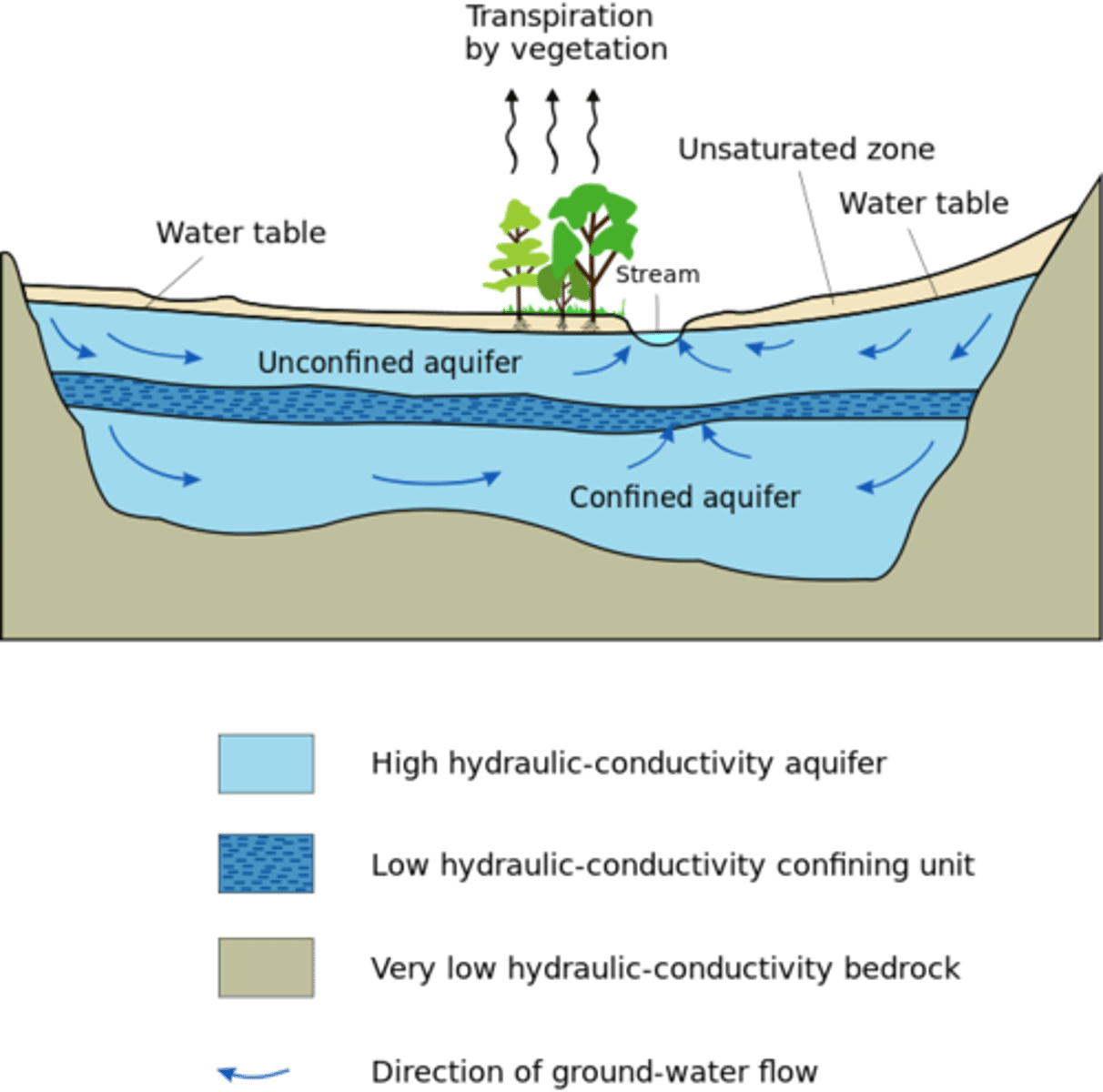
surface water
Water above the surface of the land, including lakes, rivers, streams, ponds, floodwater, and runoff.

groundwater
water that fills the cracks and spaces in underground soil and rock layers

aquifers
Subterranean, porous, water-holding rocks that provide millions of wells with steady flows of water.
agriculture use
Areas of the world where the rainfall is so low that it's difficult, or even impossible, to grow crops without irrigation