Section 1 Lecture Material
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Cranial
Toward the head
Opposite of caudal
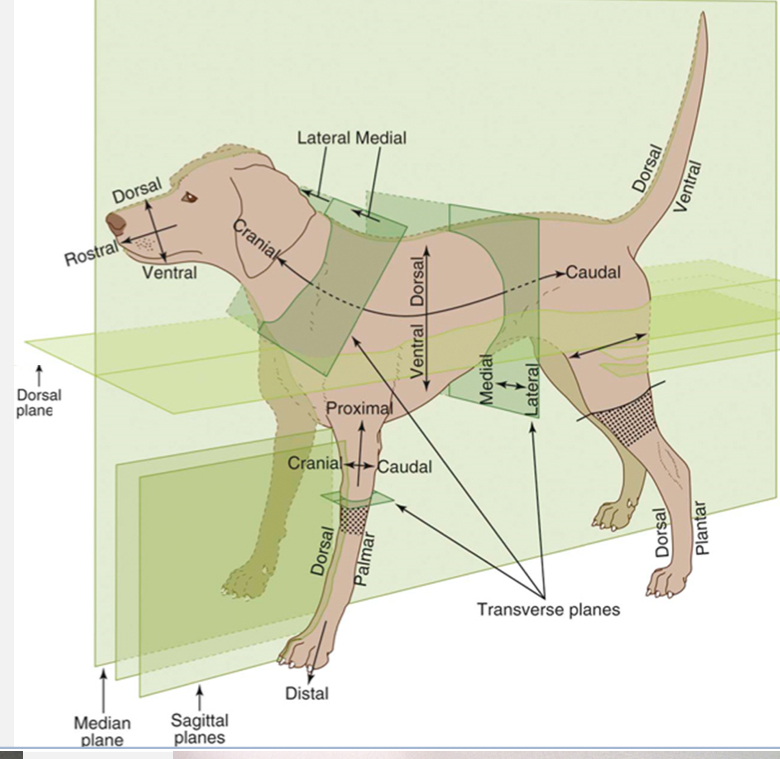
Caudal
Toward the butt
Opposite of cranial
Rostral
Toward the nose
Used with caudal when referring to areas on the head instead of using cranial
Dorsal
Toward the top of the back
Opposite of ventral
Ventral
Toward the belly
Opposite of dorsal
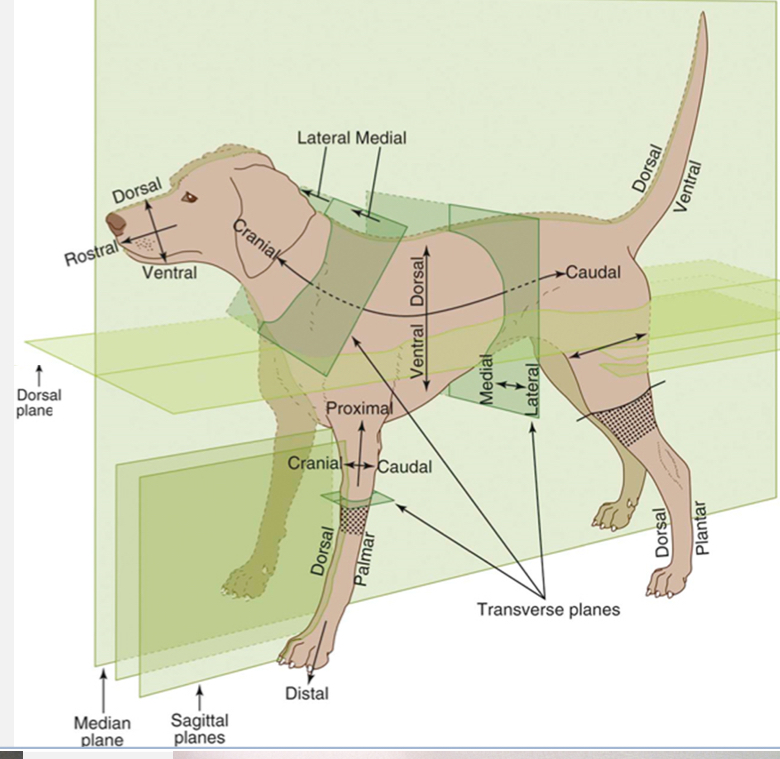
Palmar
the underside of the front feet
Used in conjunction with dorsal when referring to the front feet
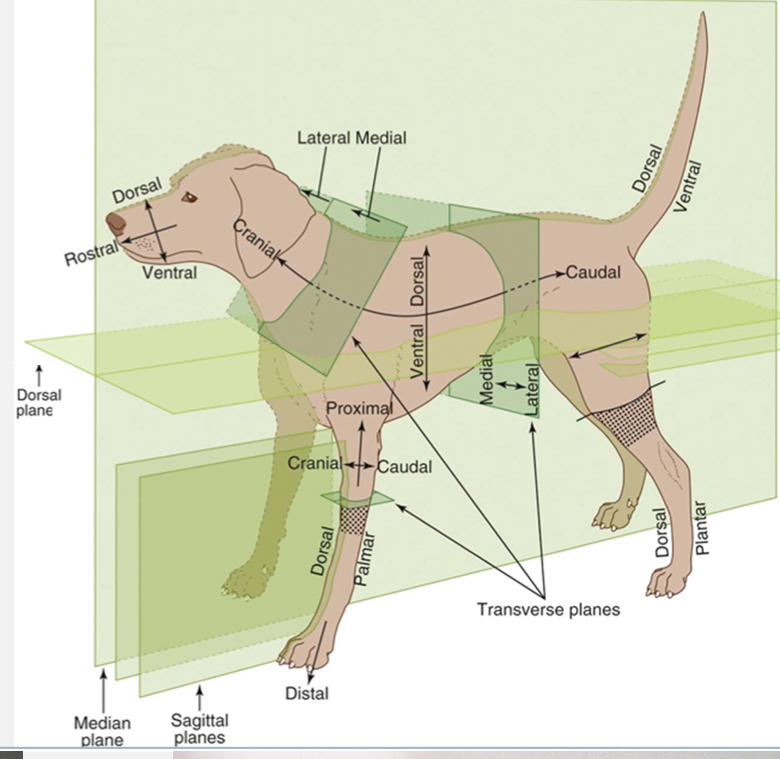
Plantar
The underside of the hind feet
Used in conjunction with dorsal when referring to the hind feet
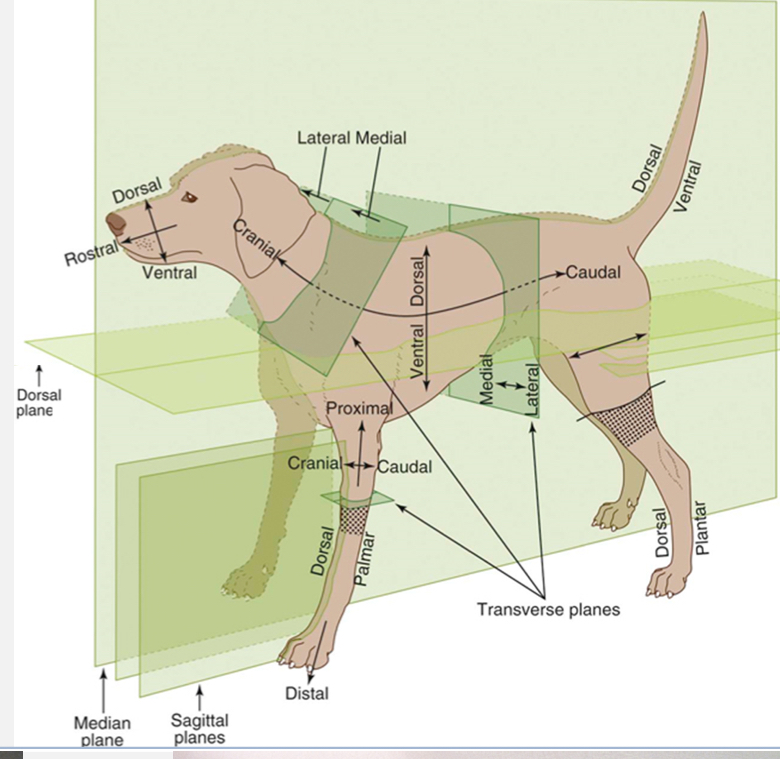
Proximal
Toward the trunk
Opposite of distal and used for appendages only
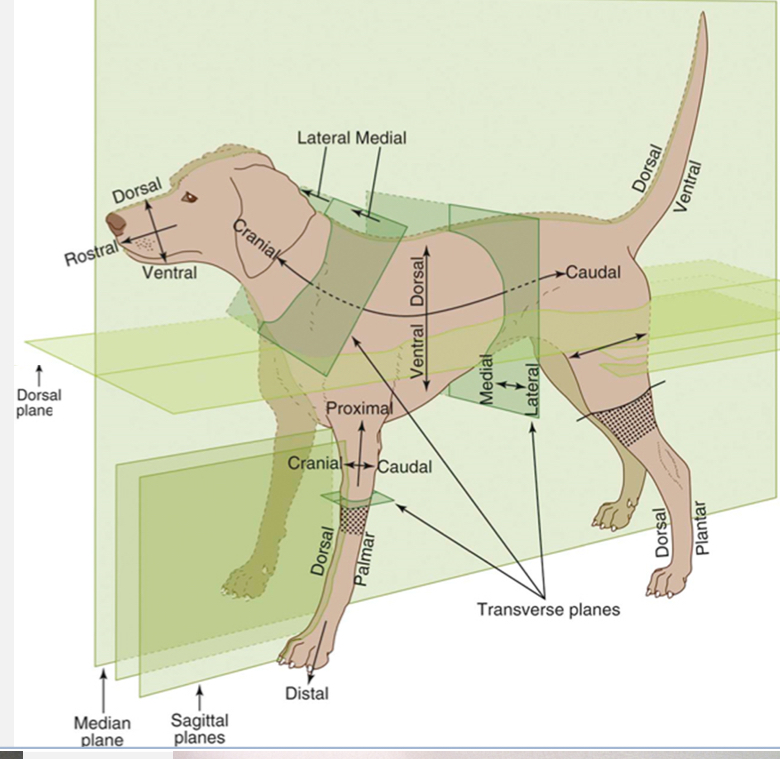
Distal
Away from the trunk
Opposite of proximal and used for appendages
Medial
Toward the midline
Opposite of lateral
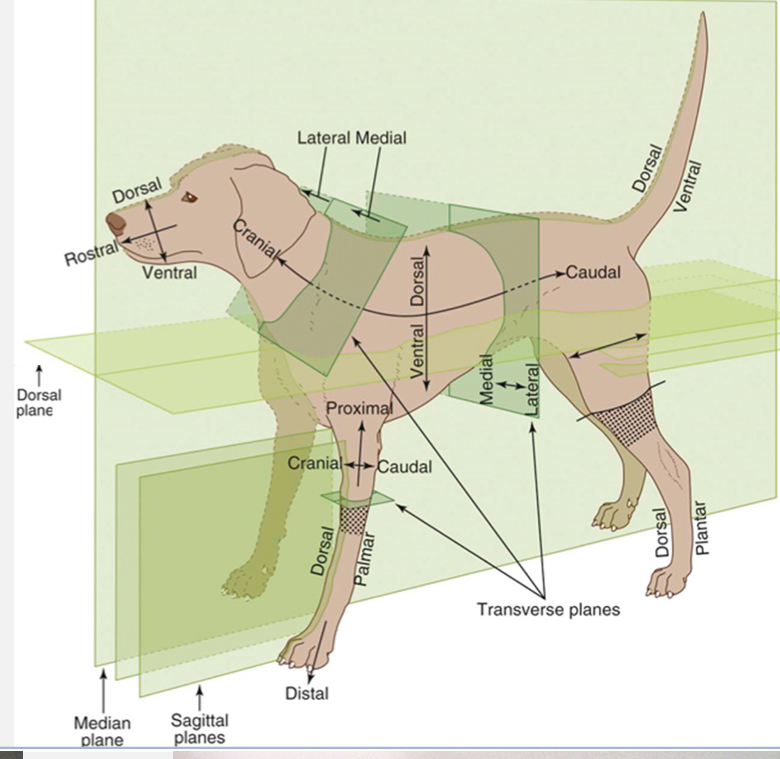
Lateral
Away from the midline
Opposite of medial
Ipsilateral
on the same side
Opposite of contralateral

Contralateral
on the opposite side
Opposite of ipsilateral

Superficial
closer to the surface
Opposite of deep
Deep
farther from the surface
Opposite of superficial
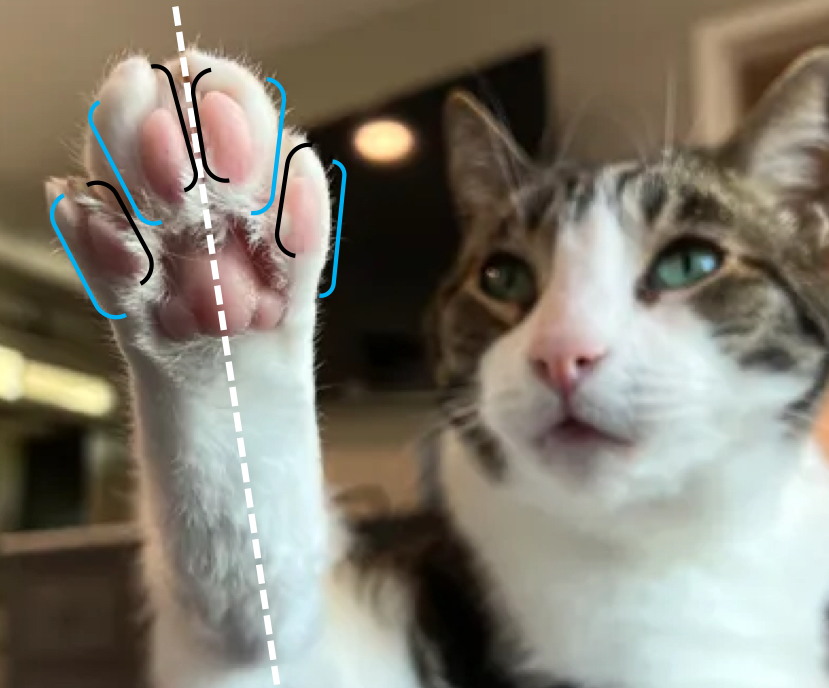
Axial
Toward the axis of the foot
Opposite of abaxial
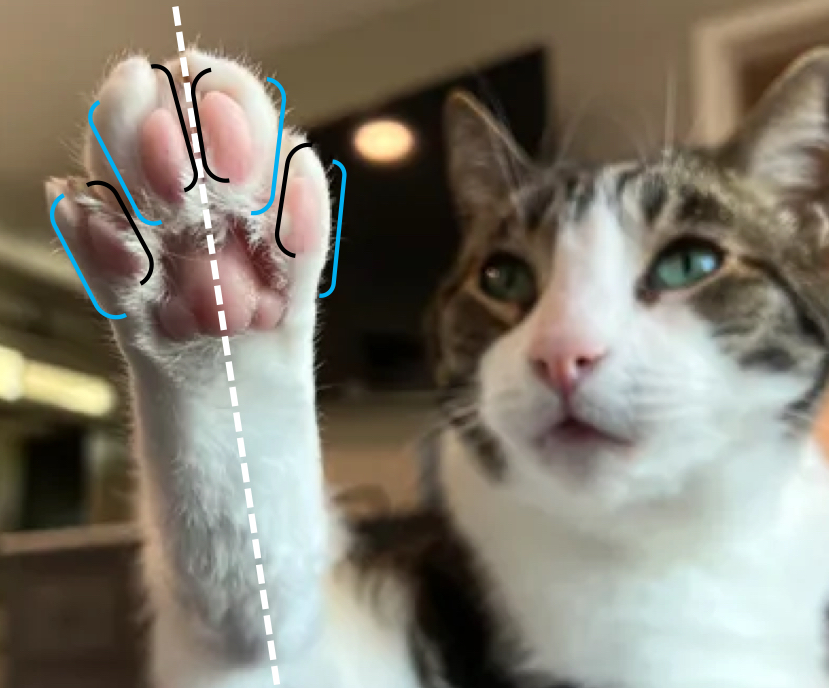

Abaxial
Away from the axis of the foot
Opposite of axial

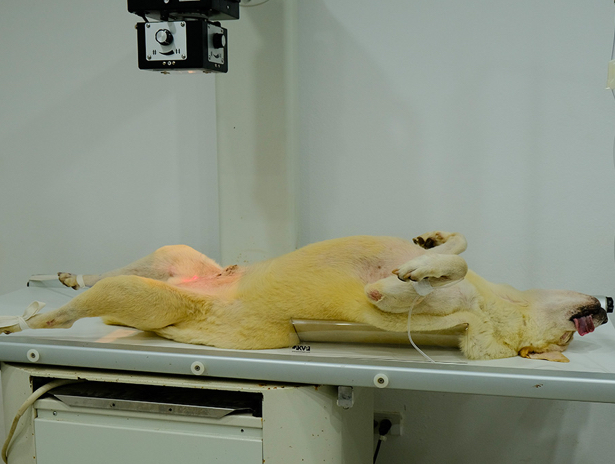
Dorsal Recumbency
The dog is placed on its dorsal side (laying on its back)

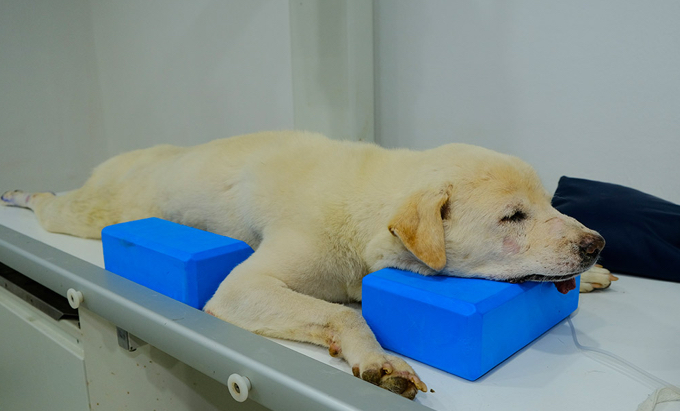
Sternal Recumbency
The dog is placed on its sternal side (laying on its belly)
Also known as ventral recumbency

Right and left lateral recumbency
The dog is placed on one of its lateral sides
Left lateral recumbency = laying on its left side
Right lateral recumbency = laying on its right side
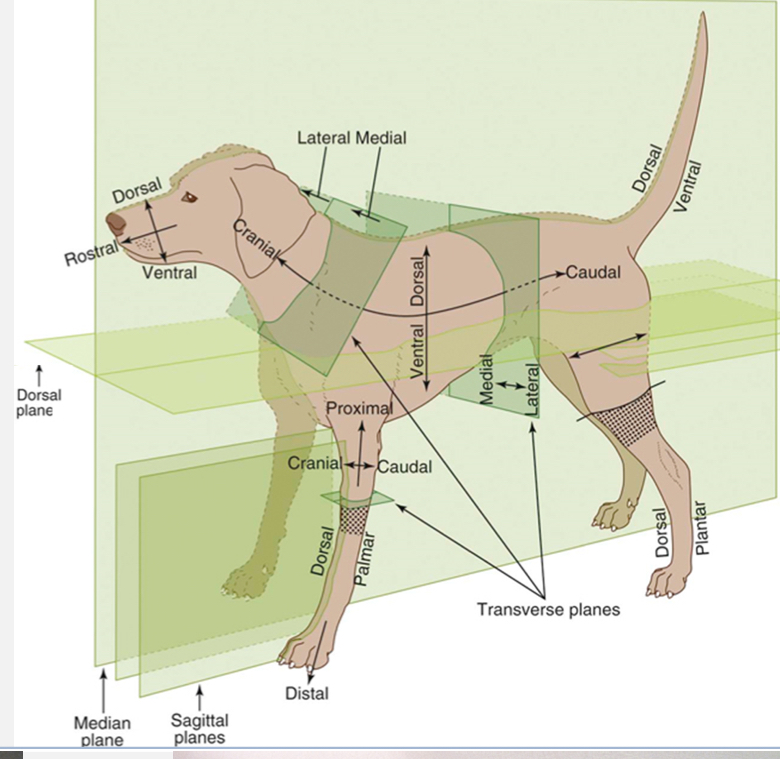
Dorsal Plane
divides the body into dorsal and ventral sides
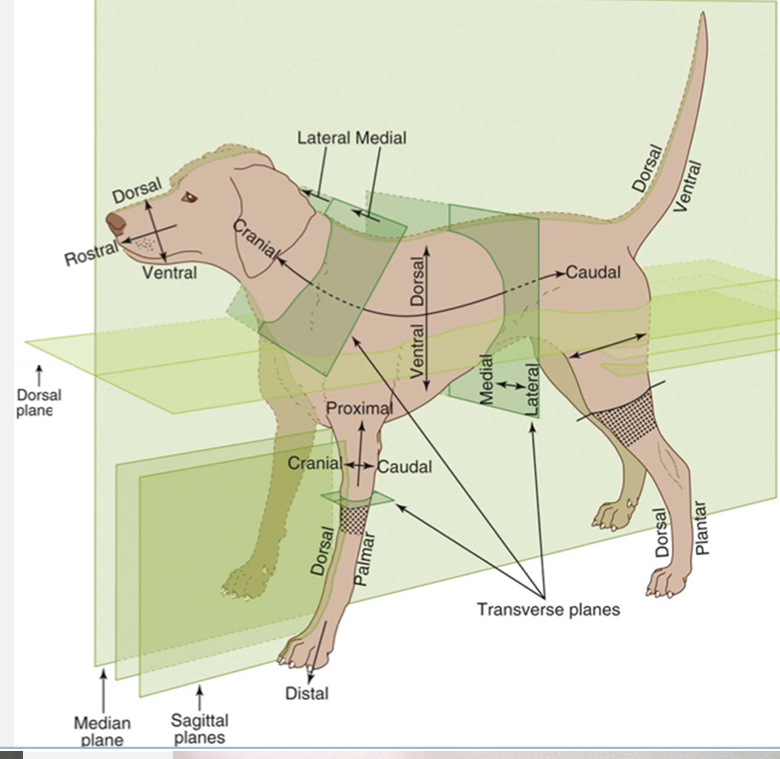
Sagittal Plane
divides the body into right and left sides (does not need to be equal and can have multiple sagittal planes
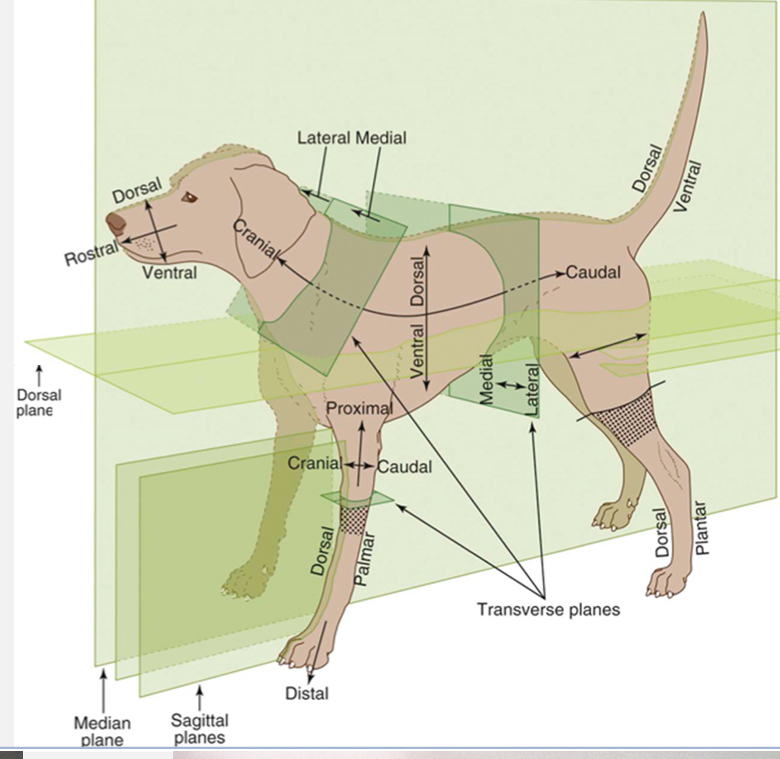
Median / Midsagittal Plane
divides the body into equal right and left halves
Midline
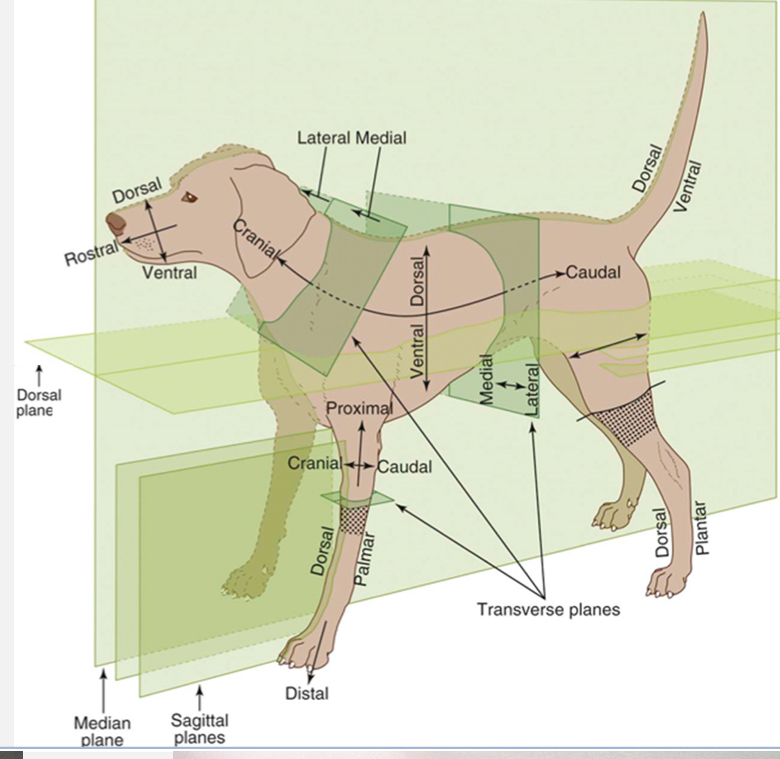
Transverse planes
create cross-sections (ex. Cranial and caudal; proximal and distal sides)
Tissues
A group of specialized cells working together to perform a common function
Organs
A somewhat independent part of the body that performs a particular functions
Usually composed of two or more basic tissues
4 types of basic tissues
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Nervous
Epithelial Tissue
Ex. Epidermis, endothelium
Lines internal body tubes and external body surfaces, forms glands
Connective Tissue
Ex. Adipose tissue (fat), blood, bone, cartilage, fibrous connective tissue
Connects and supports body components, movement, insulation, energy storage, repair, nutrition
Muscle Tissue
Ex. Skeletal, smooth, cardiac
Body movement, movement of blood, movement of ingesta
Nervous Tissue
Ex. Brain and spinal cord (CNS), Peripheral nerves, autonomic nervous system
Receives, integrates, and transmits external and internal stimuli between external and internal environments
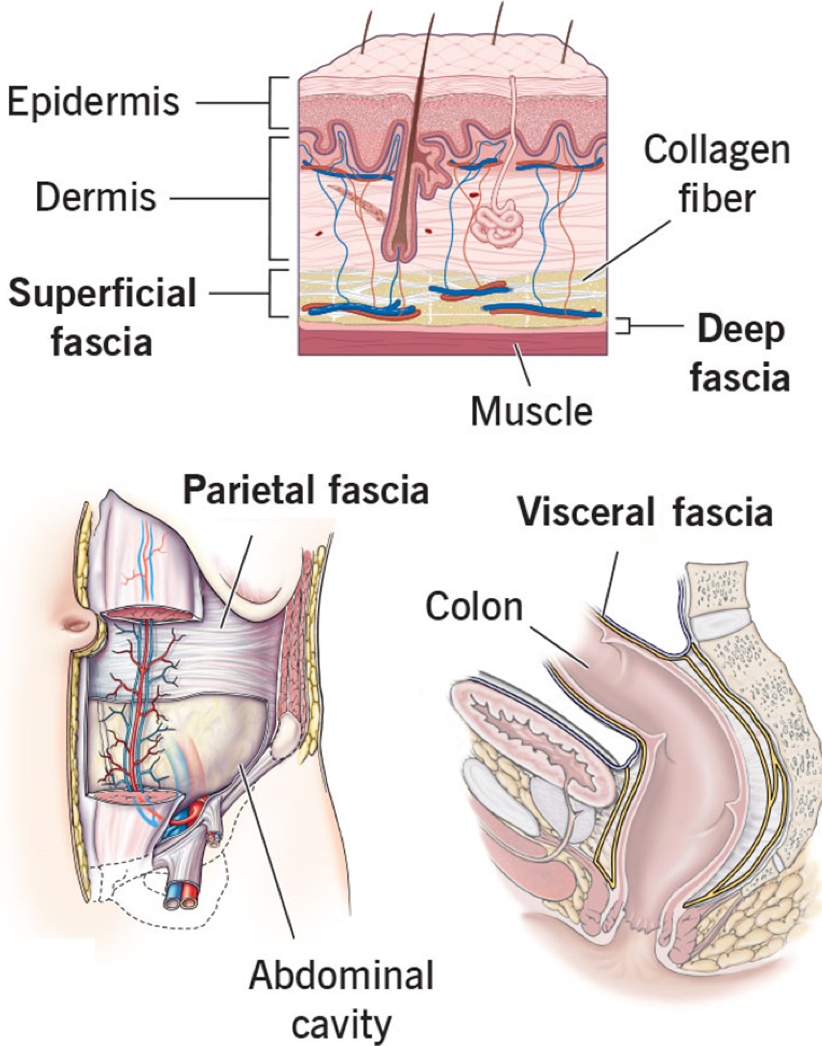
Fascia Functions
provides support and structure
Compartmentalizes and reduces friction, allowing muscles and organs to glide against each other
Transmits and distributes mechanical forces (ex. Muscle contractions, trauma)
Supports blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics
In some instances, it serves as muscle attachment
Important for proprioception, due to its network of mechanoreceptors
Fascia
A continuous, interconnected network of connective tissue that exists throughout the body
It is composed of elastic fibers, collagen fibers, and fibroblasts
Types of fascia
Superficial - hypodermis
Deep - surrounds muscles, bones, nerves, vessels
Parietal - lines body cavities
Visceral - surrounds viscera
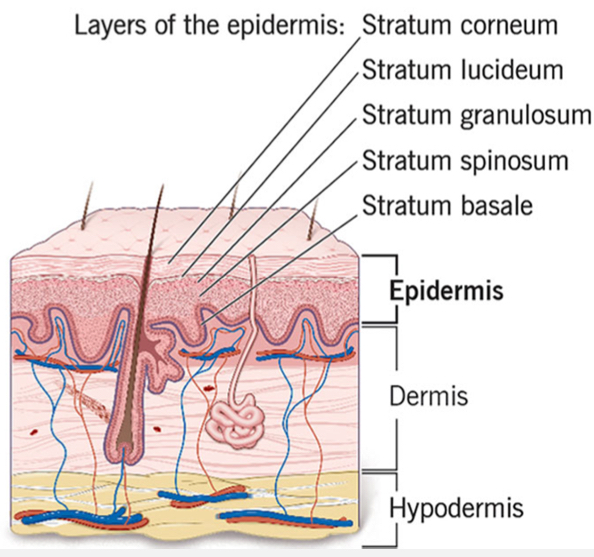
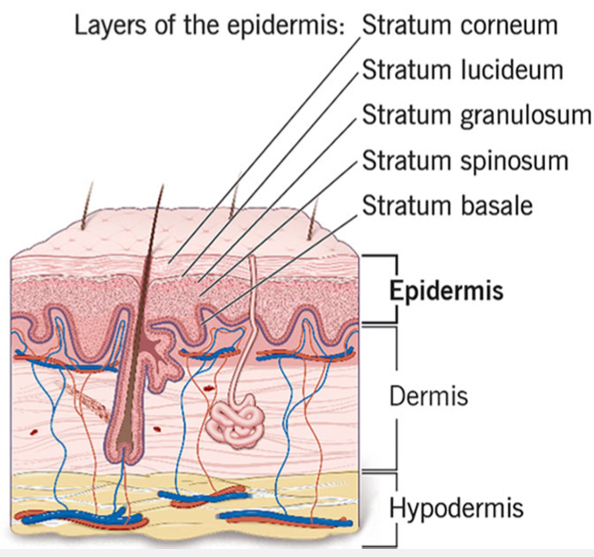
List the layers of the skin
Epidermis (cutis)
Dermis (corium)
Hypodermis (subcutis, superficial fascia layer)
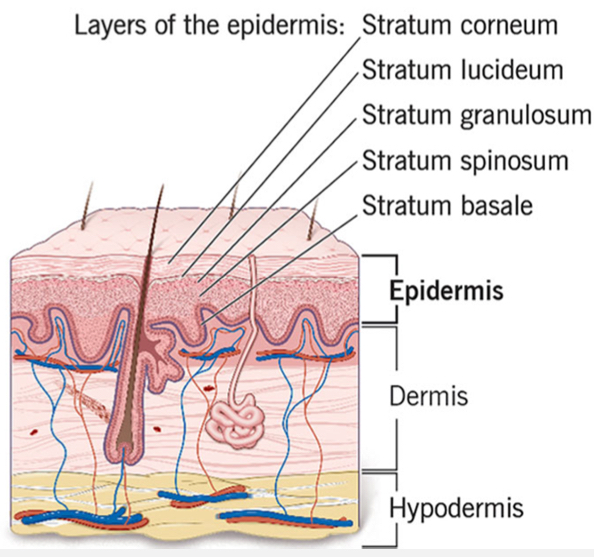
Epidermis (Cutis)
outermost layer of the skin
Composed of 5 layers of epithelial cells
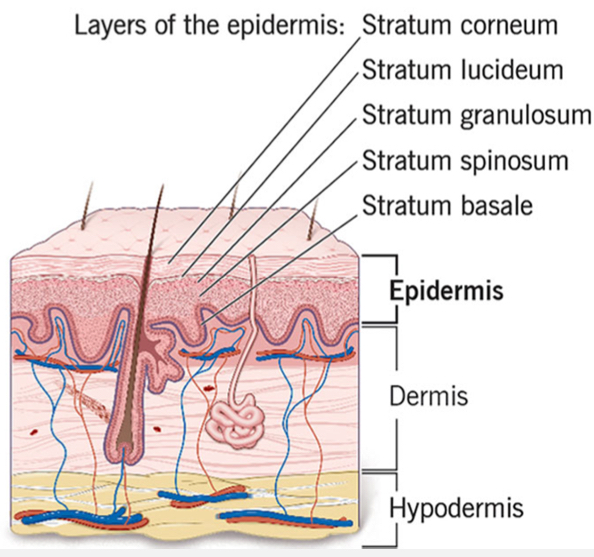
Dermis (corium)
Middle layer of the skin
Contains glands, hair follicles, nerves, blood vessels, CT fibers (collagen and elastin)
Hypodermis (subcutis, superficial fascia layer)
Deepest layer of the skin
Composed of loose areolar connective tissue and fat
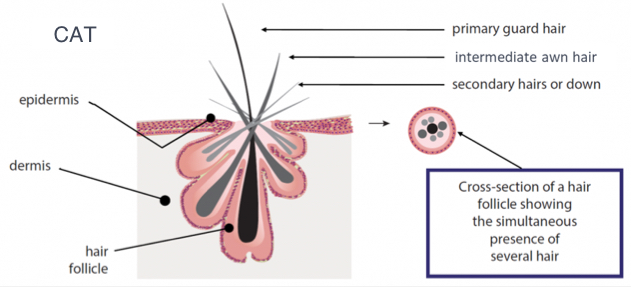
Hair
In dogs and cats, the follicles are simple shortly after birth, but are complex during adolescence and adulthood
Follicles in double coated dogs have one primary (guard) hair and multiple secondary (undercoat) hairs.
Cats have primary, intermediate, and secondary hairs
Vibrissa
Whiskers
Specialized hairs that are thicker and longer than primary hairs
Deeply rooted with follicles that sit within sinuses that are highly innervated with various sensory nerve endings
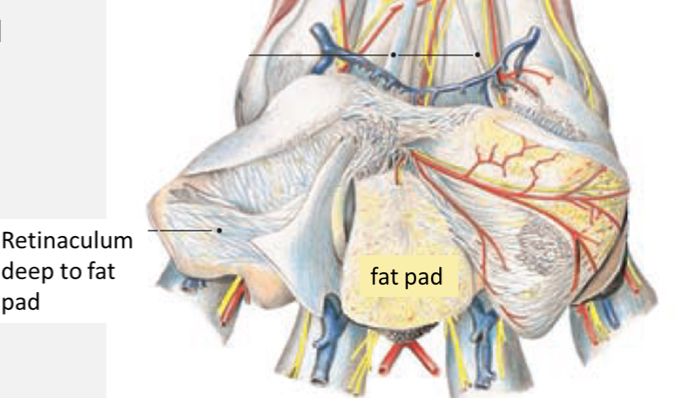
Pads
Specialized features of skin
Epidermis - keratinized and conical, often smoother in cats than dogs
Dermis - dense connective tissue and conical
Hypodermis - thick fat pad that interspersed with connective tissue fibers, eccrine sweat glands
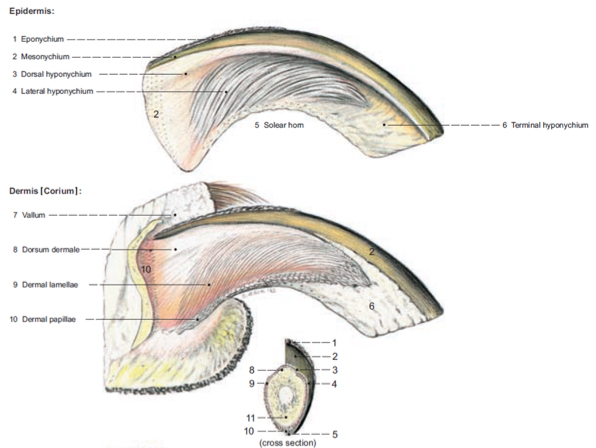
Nails
Specialized integument structures
Epidermis - outer cornified layer, grows from germinal epithelium aka living epidermis just superficial to the dermis
Dermis - the sensitive part of the nail which contains sensory nerve endings and blood vessels
Ungual process - bony process deep to the dermis
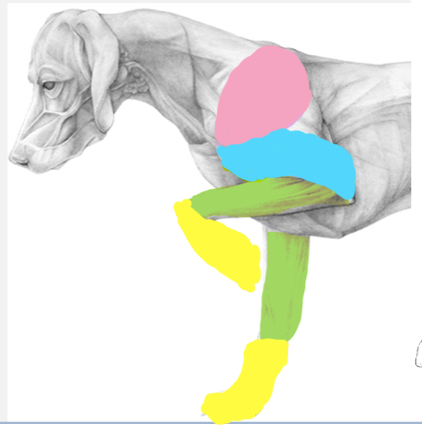
Regions of the forelimb
Scapular (pink) - scapula and surrounding features
Brachium (yellow) - region between shoulder and elbow joints
Antebrachium (green) - region between elbow and carpal joints
Manus (blue) - carpus and distal
Axilla (armpit) - cavity between the forelimb and thorax
Skeletal functions
provides a frame for the body
Movement (acts as attachment sites for muscles)
Protection of vital organs
Source of minerals (calcium and phosphorus)
Hematopoiesis (making red blood cells)
Parts of the skeleton
Axial - skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternebrae
Appendicular - limbs
Heterotropic - bone development in the soft tissue
Vertebral formula for cats and dogs
C7 T13 L7 S3 Cd20-23
Types of bones
long - humerus, radius, ulna
Short - carpals
Flat - scapula, skull
Irregular - vertebrae
Sesamoid (embedded in tendons) - palmar and dorsal sesamoids, patella
Pneumatic (contain air spaces) - mammalian skull bones with paranasal sinuses or bird bones
Visceral / heterotopic (within soft tissue) - ossa cordis, os penis, os rostrale
Types of bone composition
woven
Lamellar
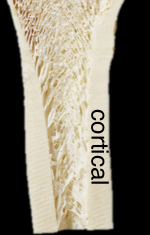
Cortical / compact
Cancellous / trabecular
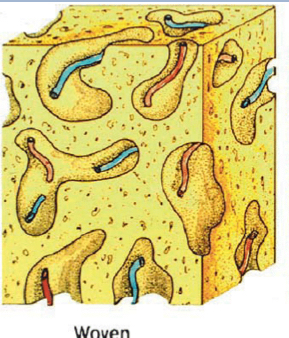
Woven Bone
Arrangement of immature bone
Found in juvenile/developing bones and early fracture repair
Lamellar bone
Highly ordered arrangement of mature bone
Circular structure
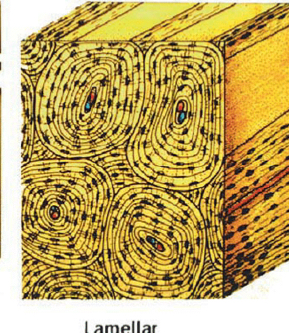
Cortical / compact bone
Dense layers of lamellar bone
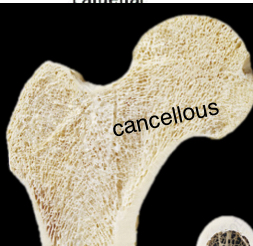
Cancellous / trabecular bone
Lattice arrangement of bony spicules deep to cortical bone
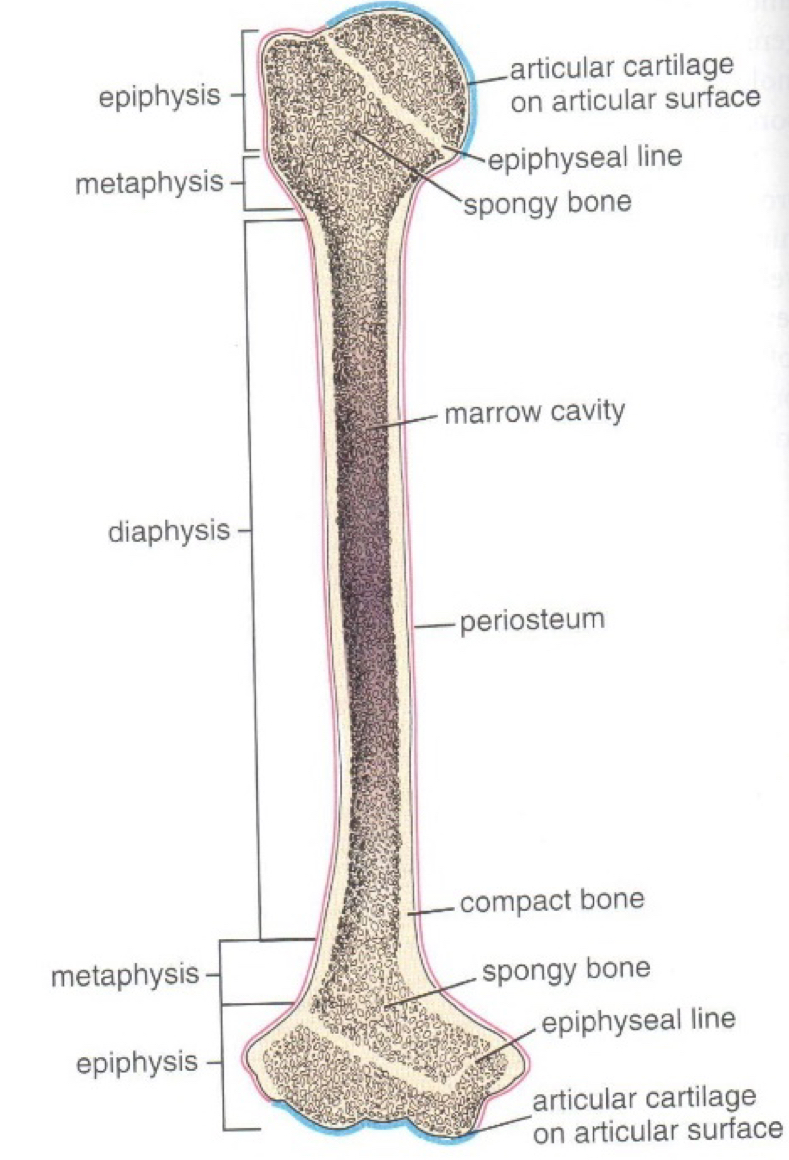
Identify the regions of a lone bone
Epiphysis - enlarged proximal and distal ends
Diaphysis / body - elongated central portion, contains marrow cavity
Metaphysis - between epiphysis and diaphysis
Physis / growth plate / epiphyseal plate - after closure of the physis, an ossified epiphyseal line remains
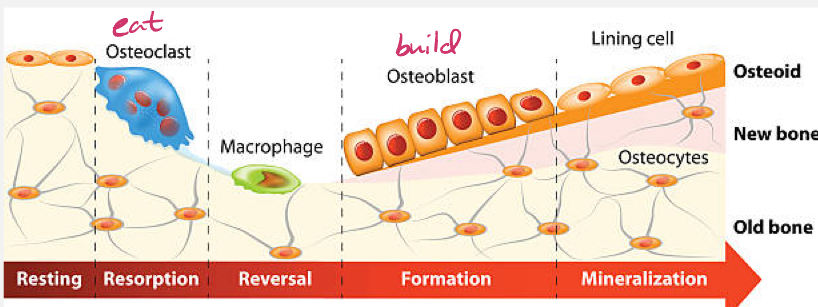
Bone remodeling
The reformation of existing bone due to normal biomechanical forces, damage / trauma, diet, or hormones (ex. Parathyroid, calcitonin, calcitriol, estradiol)
Remodeling is a constant, dynamic process involving bone resorption by osteoclasts and bone formation by osteoblasts
Bone linings
Hyaline cartilage - lines the superficial surface of subchondral bone
Periosteum - lines the superficial surface of non-articular areas
Endosteum - lines the deep surface of compact bone
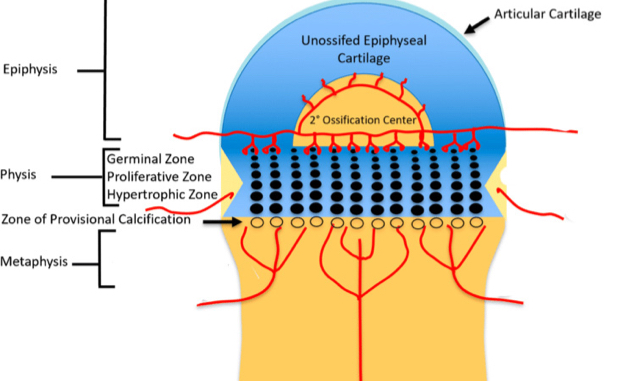
Physes / growth plate / epiphyseal plate
Area at which long bones increase in length
Cartilaginous portions of long bones that exist between separate centers of ossification
Chondrocytes in a collagen matrix mature and are replaced by osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes (cartilage becomes bone)
Medullary cavity
Consists of cancellous bone interspersed throughout either red or yellow marrow
Bone marrow can be samples from any area with red marrow (ribs, sternum, ilium, femur, tibia, humerus) or can be used for intraosseous (IO) access
Proximal humerus, proximal femur, and proximal tibia are most commonly used
Yellow bone marrow
Medullary cavities of adults contain predominantly yellow marrow, which contains a great deal of adipose tissue
The color is due to carotenoids in fat cells
During times of need, yellow marrow can be converted back to red marrow
Red bone marrow
Young animals have primarily red marrow, which has a great deal of hematopoietic tissue and is highly vascularized
The color is due to hemoglobin in erythroid cells
Red marrow is normally present in some adult bones, including ribs, sternum, ilium, femur, tibia, and humerus
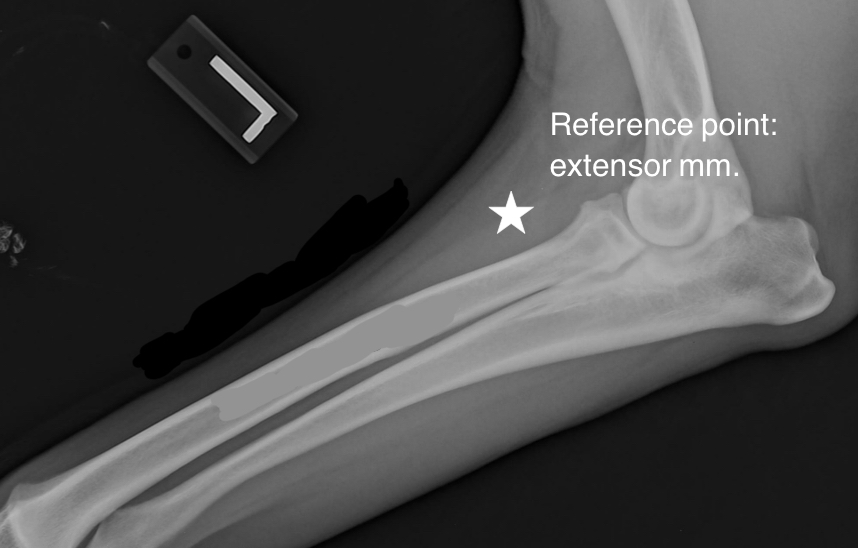
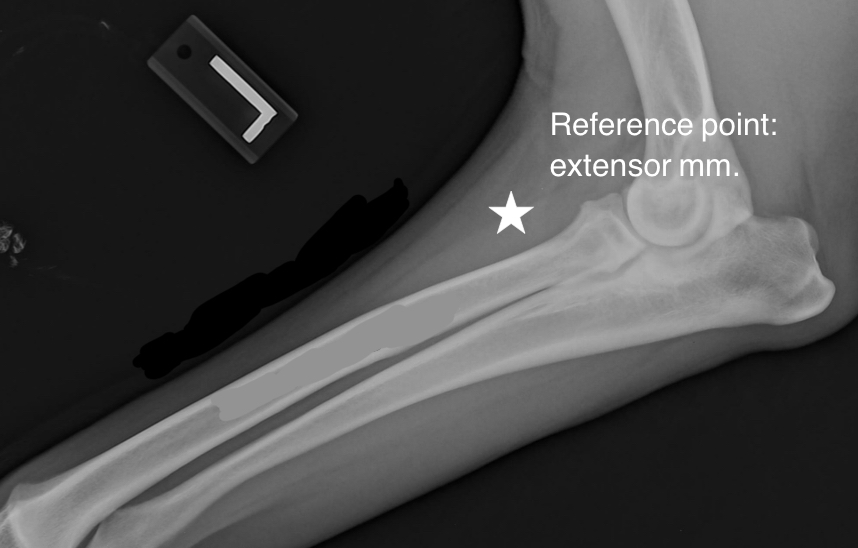
What area is usually used for IO access in the forelimb?
The proximal humerus is usually used with specific interest in the flat area of the proximal lateral humerus just distal to the greater tubercle
List the bones of the thoracic girdle
scapula
Clavicle (cats only)
List the bones in the brachium
humerus
List the bones in the antebrachium
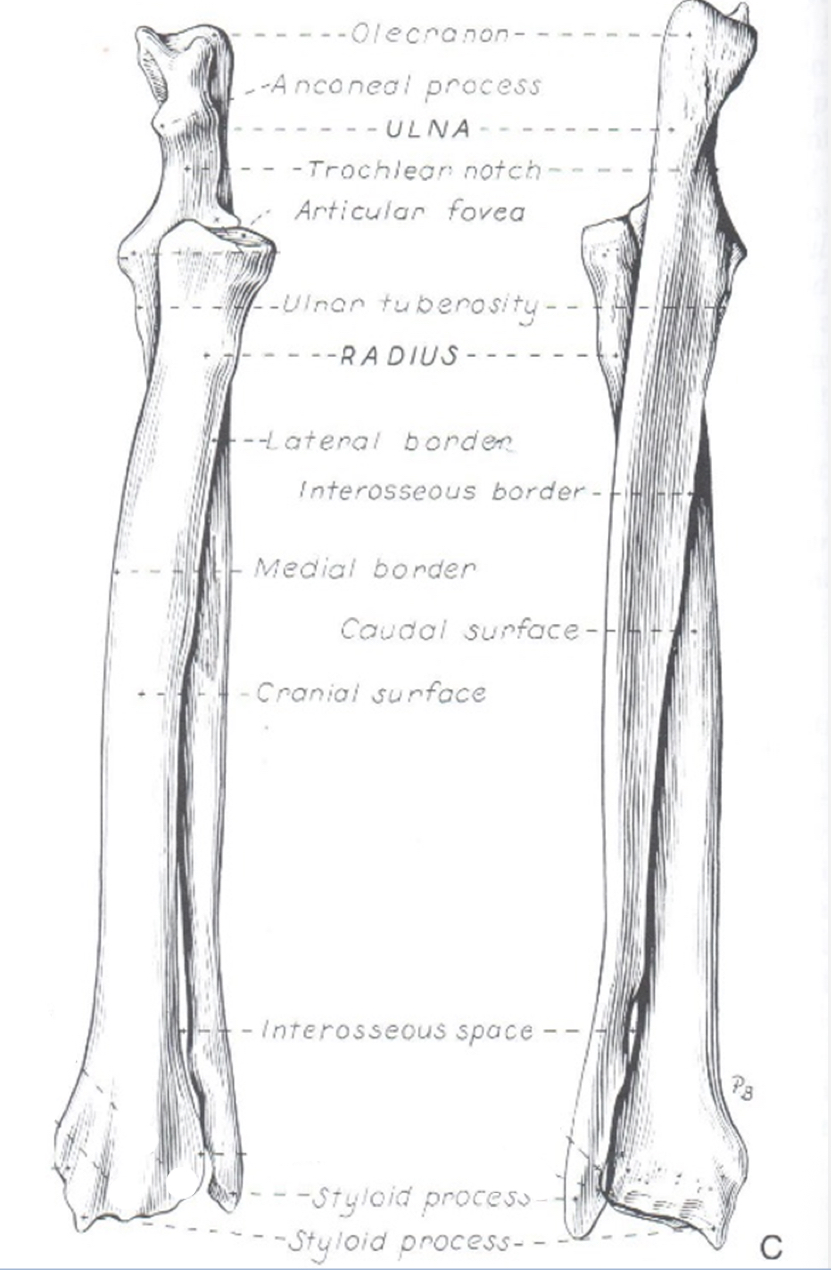
radius
Ulna
List the bones in the manus
carpus
Metacarpus
Digits
Identify the physes of the scapula
supraglenoid
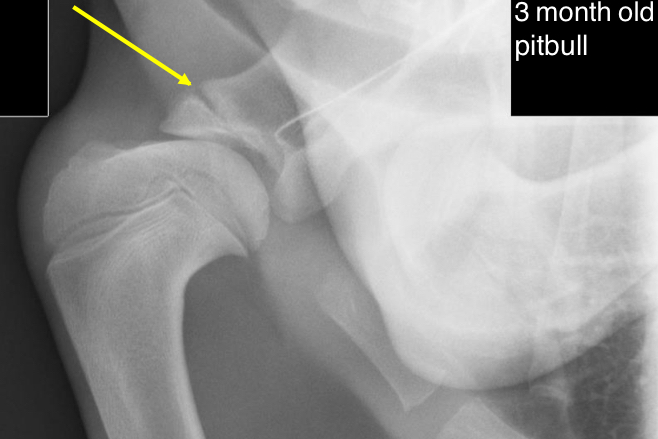
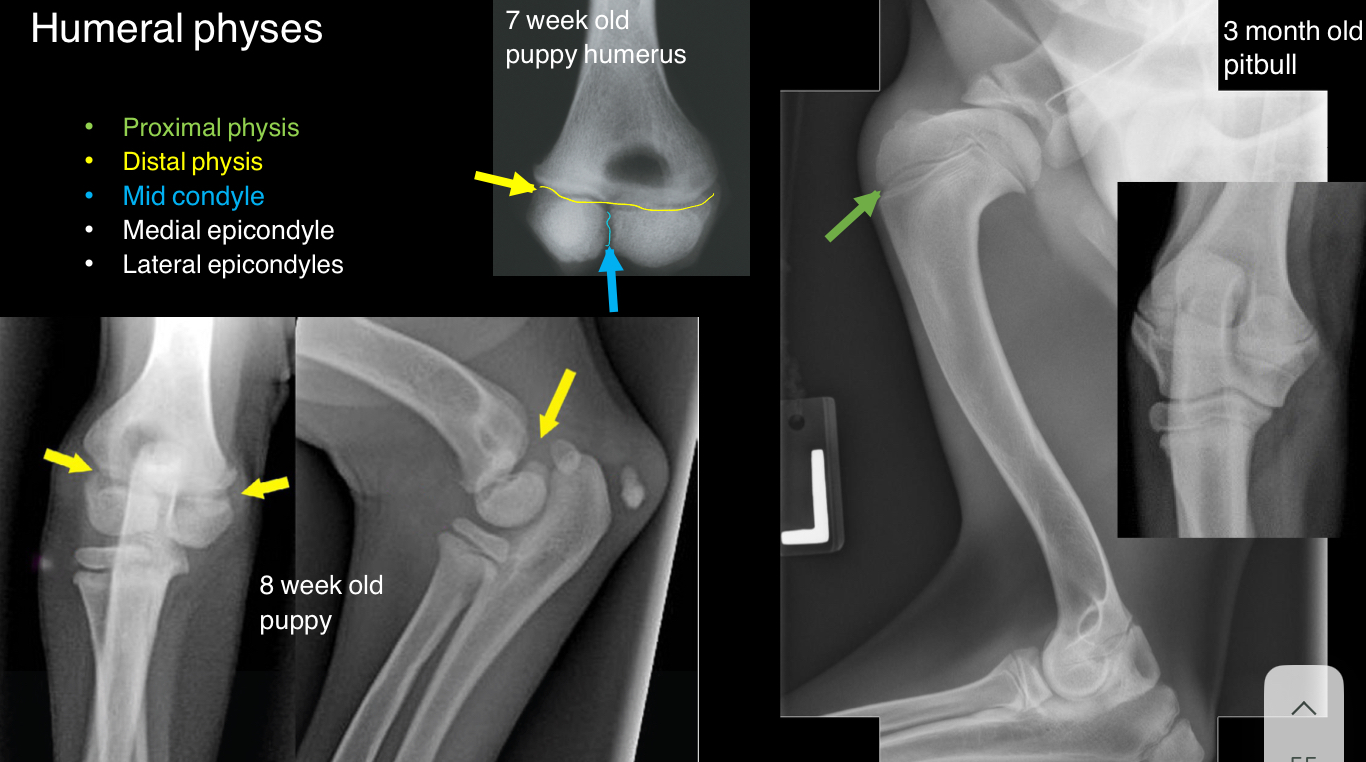
Identify the physes of the humerus
proximal
Distal
Mid-condyle
Medial epicondyle
Lateral epicondyle
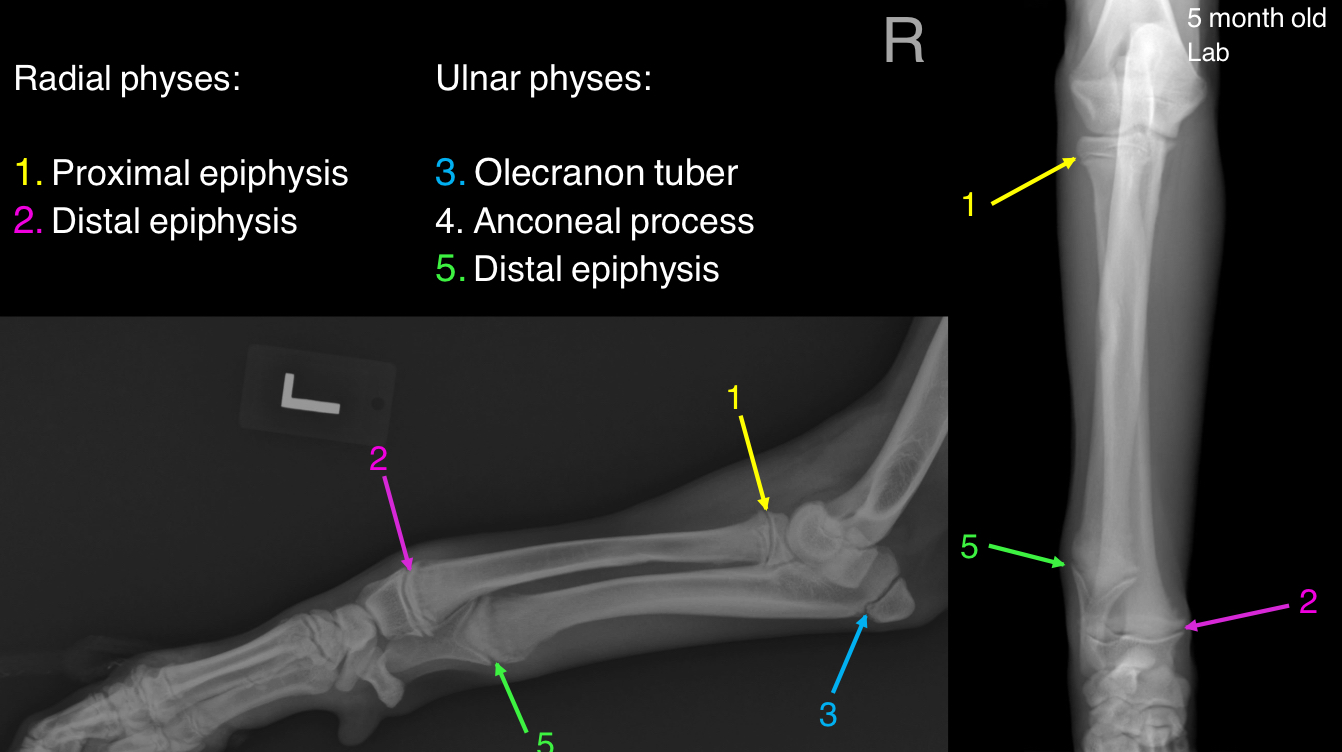
List the physes of the radius
proximal
Distal
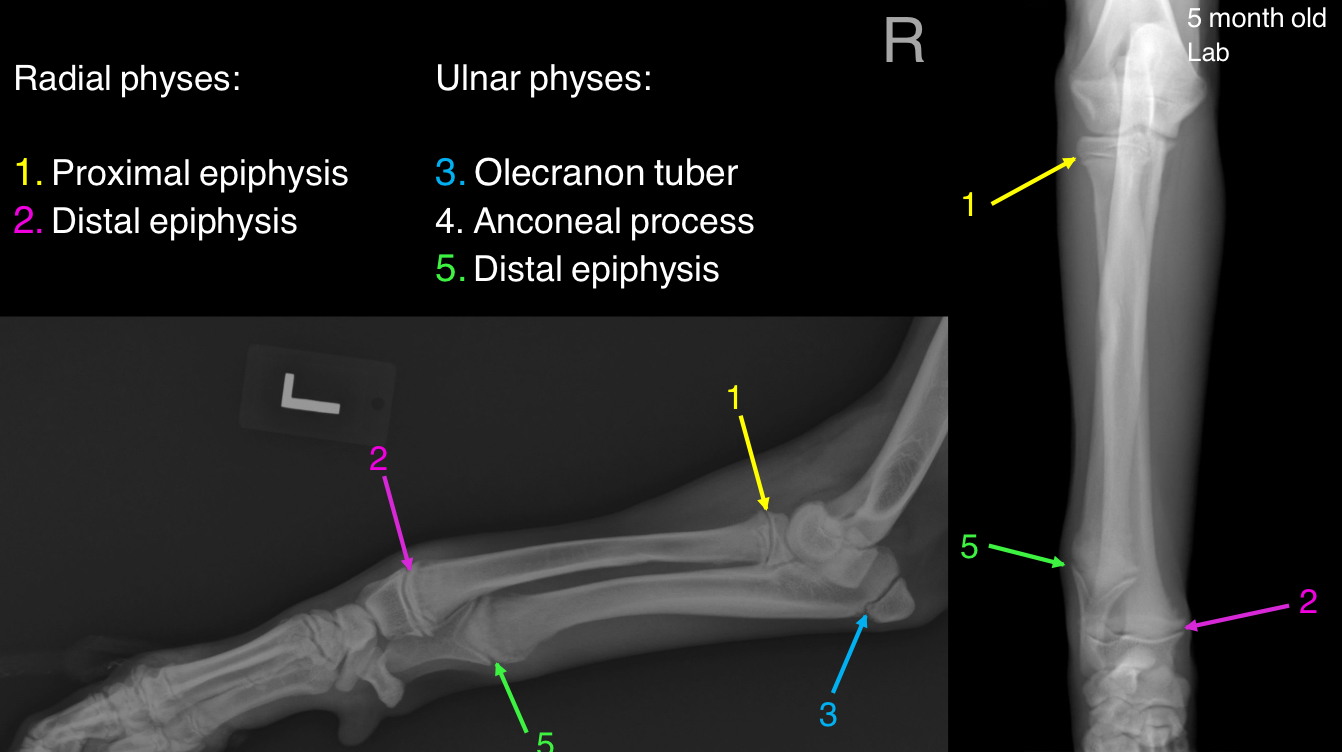
List the physes of the ulna
olecranon tuber
Anconeal process
Distal
What passes through the supracondylar foramen in cats?
through this hole passes the brachial artery and the median nerve
It is situated on the medial surface of the distal humerus
Fractures can occur in this area, surgeons must take great care to not cause further damage to these features
Explain the relationship between the radius and ulna
The radius is craniomedial to the ulna proximally and craniomedial to the ulna distally
Joint
The union between two or more bones by fibrous, elastic, cartilaginous, or a combination of tissue
3 types of joints: fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
Synsarcosis - a type of joint wherein bones are joined to one another via muscle (ex. Scapular attachment to the thorax by extrinsic muscles)
Fibrous joints
Relatively immovable joints with bones united by dense connective tissue
Suture - between flat bones of the skull
Syndesmosis - ex. Distal radioulnar joint
Gomphosis - tooth in alveolar socket
Cartilaginous joints
Slightly moveable joints with bones united by cartilage, many are transient
Synchondrosis (hyaline cartilage) - growth plates, costochondral junctions
Symphysis (articular cartilage connected via fibrocartilage - mandibular symphysis, pelvic symphysis
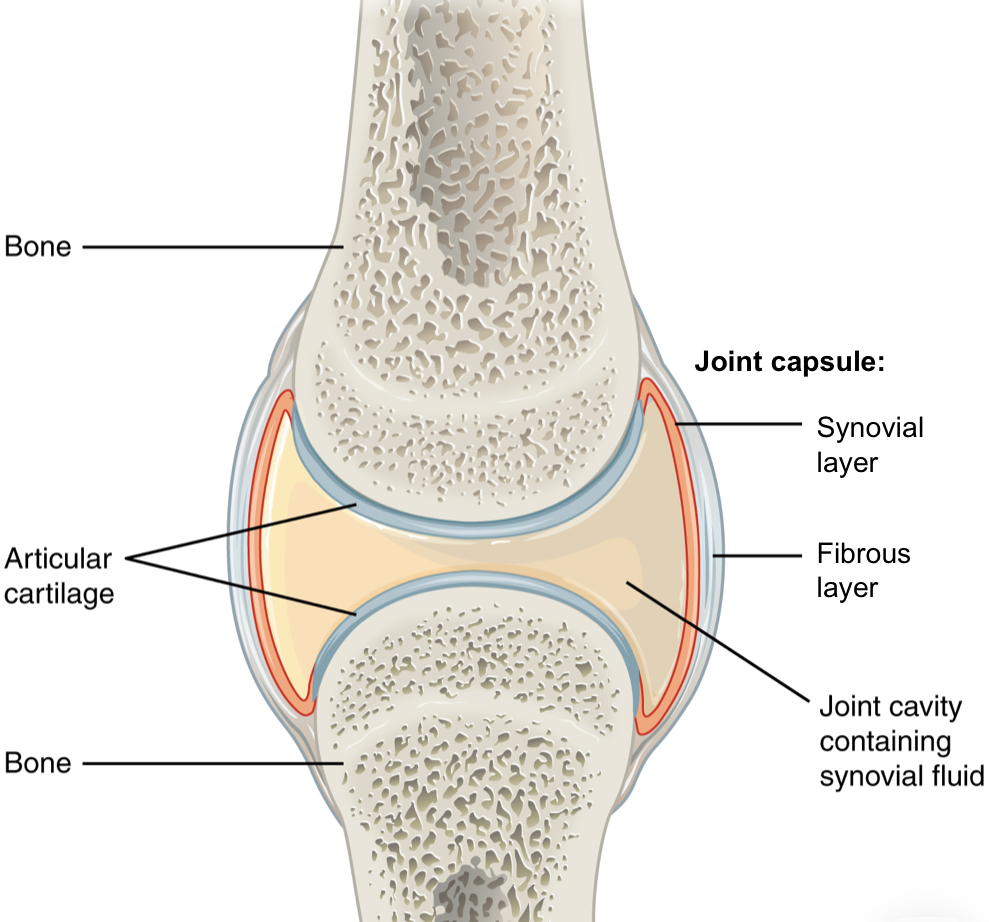
Synovial joints
Apposing surfaces of bones are covered with hyaline articular cartilage, which act as shock absorbers during weight bearing and impact
Bones are connected by a joint capsule, which has two layers:
fibrous layer - superficial layer, DFCT, attaches to apposing bones
Synovial layer - deep layer, specialized CT, secretes synovial fluid (nutrition), attaches at the bone / cartilage junction
Other synovial structures (bursae, tendon sheaths) have the same structure of fibrous and synovial layers
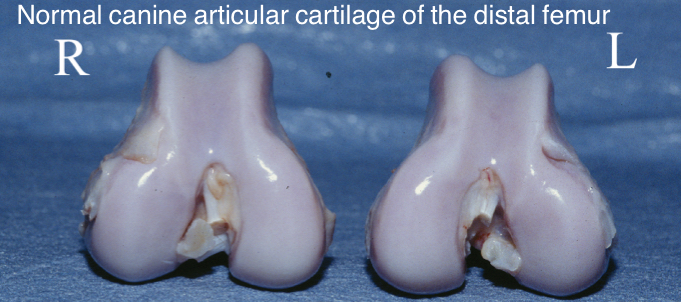
Hyaline articular cartilage
One of three types of cartilage
Normal hyaline cartilage is smooth, shiny, and glaucous
As cartilage is damaged, it erodes, thus exposing subchondral bone, articular cartilage has limited ability to repair itself and areas of wear are eventually replaced with fibrocartilage which lacks hyaline’s resistance to compressive forces
Synovial fluid
A filtrate of plasma concentrated by synoviocytes
Function:
lubrication - reduces friction between apposing surfaces
Nutrition - hyaline cartilage, menisci, labrum, etc. are avascular; nutrients to these structures are supplied by synovial fluid via diffusion
Functional types of synovial
ball and socket joint
Hinge joint
Ellipsoid joint
Saddle joint
Pivot joint
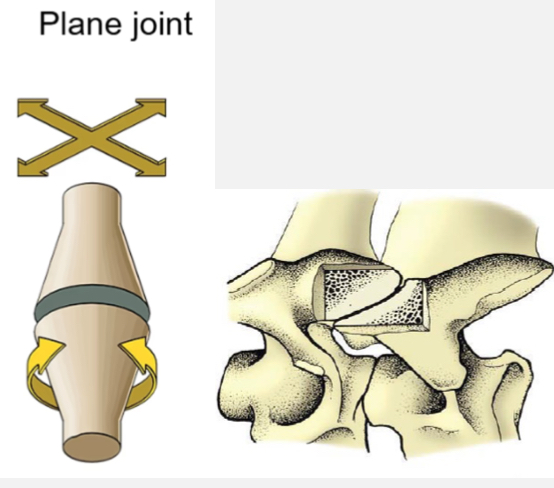
Plane joint
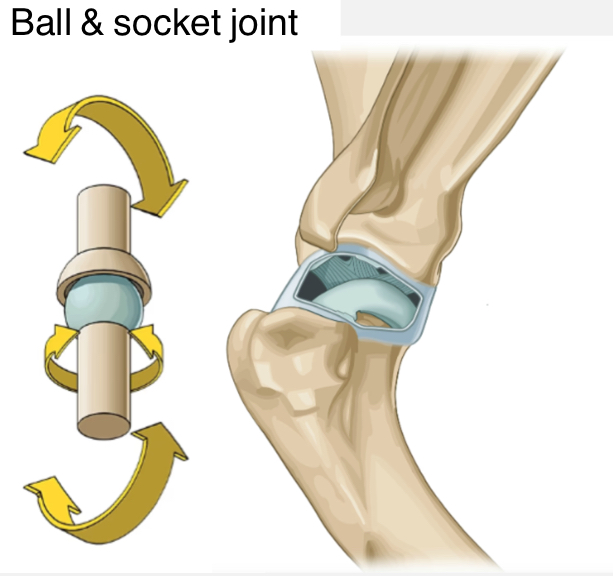
Ball and socket joint
Ex. Glenohumeral
Movement - in many planes: flexion/extension, internal/external rotation, side-to-side
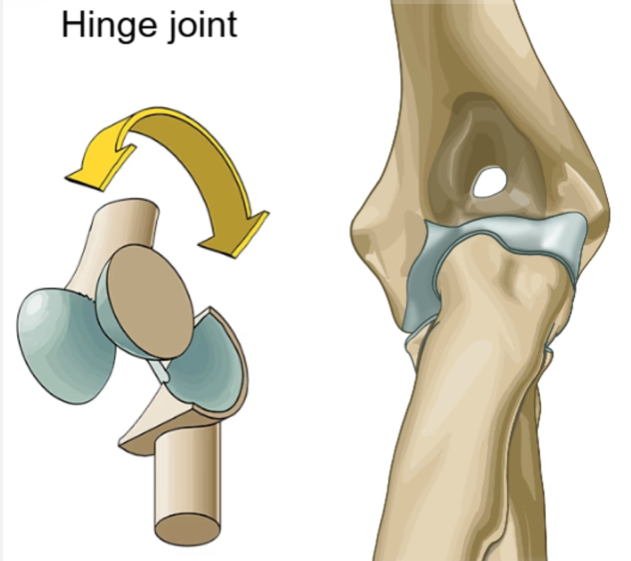
Hinge joint
Ex. Umeroradial and humeroulnar
Movement - flexion and extension
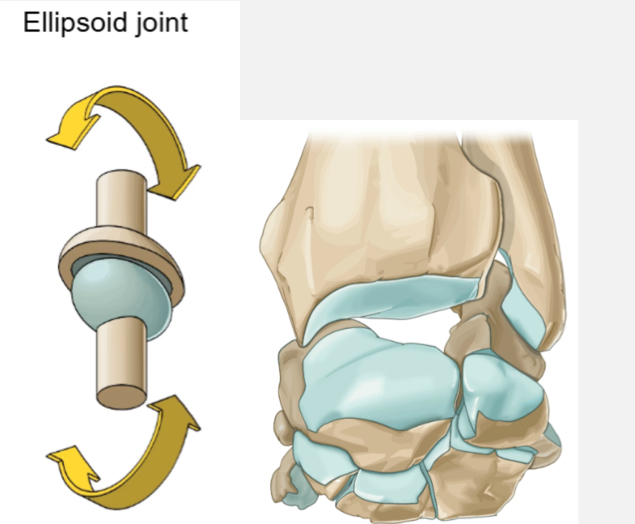
Ellipsoid joint
Ex. Carpus, metacarpophalangeal, prox. Interphalangeal
Movement - primarily flexion and extension, with some medial to lateral movement
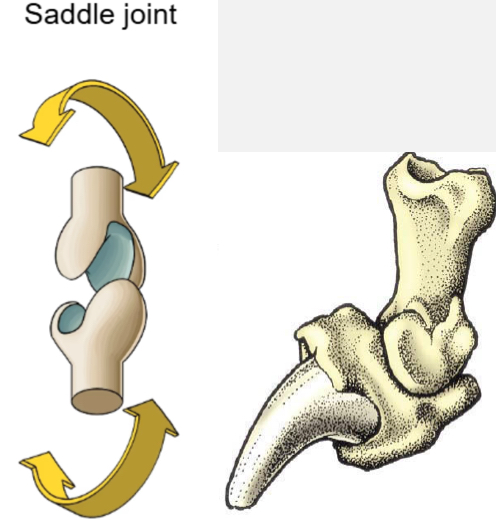
Saddle joint
Ex. Distal interphalangeal joint
Movement - primarily flexion and extension, with some medial to lateral movement
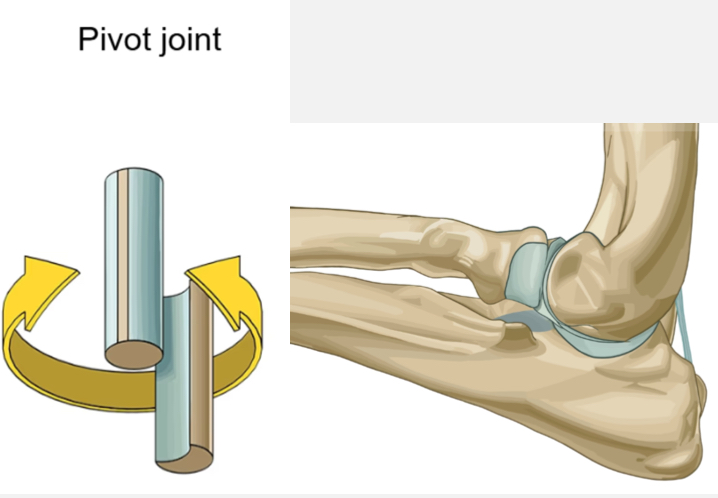
Pivot joint
Ex. Proximal radioulnar joint
Movement - rotation
Plane joint
Ex. Articular surfaces between vertebrae
Movement - flat joints that slide against each other
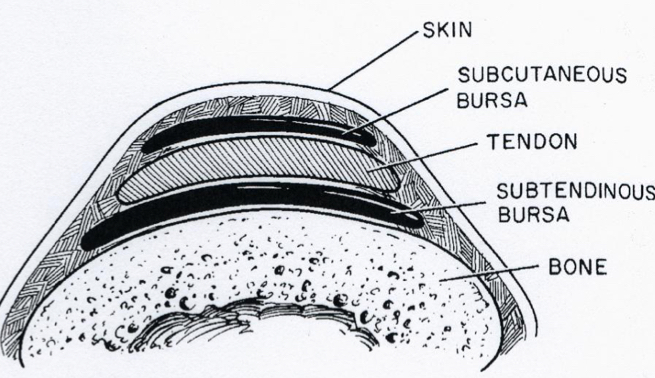
Synovial bursa
A small sac containing synovial fluid
Like joint capsules, there is an outer fibrous layer and an inner synovial layer
Bursae are located between highly mobile structures and structures under high tension (usually between tendon and bone, but may also be between fascia and skin) Thus, they act like cushions and reduce friction to prevent damage to said structures
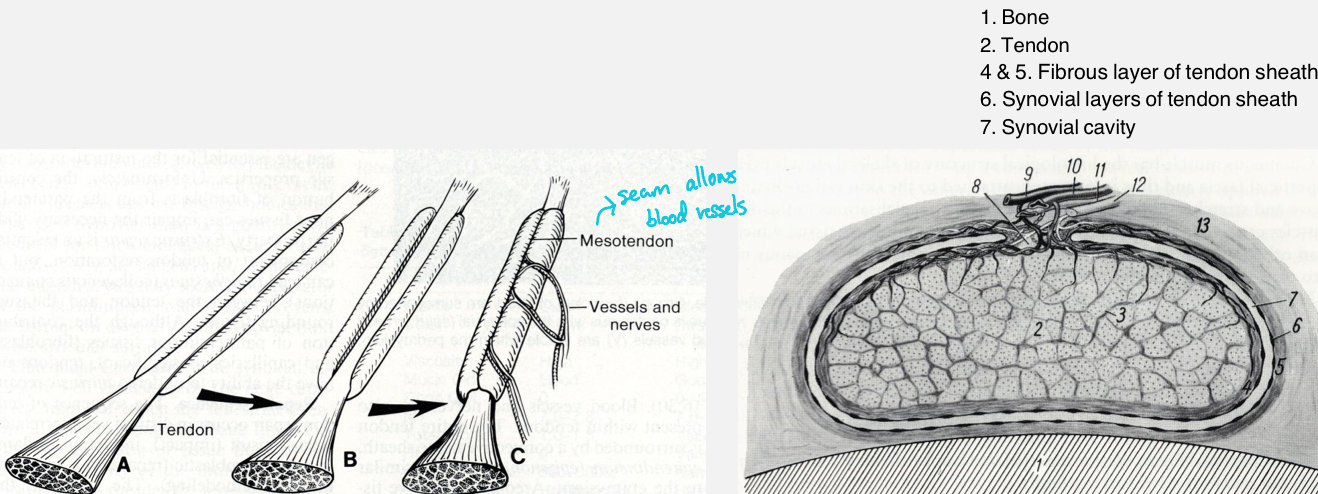
Synovial tendon sheaths
Tube-like structures surrounding a tendon or tendons
They provide lubrication and reduce friction
Ex. Proximal tendon of biceps brachii m. Or distal tendons of superficial and deep digital flexor mm.
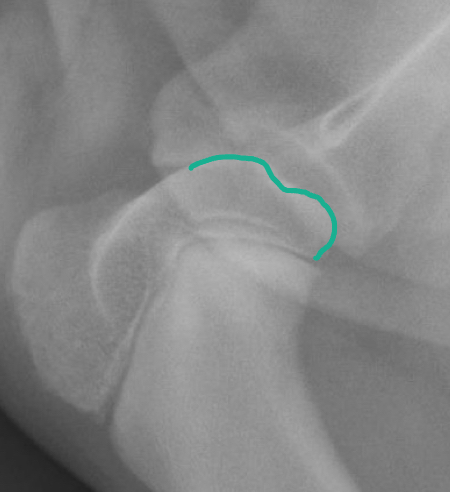
Osteochondritis dessicans (OCD)
Osteochondrosis is a group of disorders of bone development most commonly in large dog breeds on the humeral head (followed by femoral condyles)
It is caused by epiphyseal ischemia, which results in defective growth of the subchondral bone
The overlying articular cartilage becomes excessively stressed and tears, resulting in the formation of a cartilage flap
Flexion
Bending a joint
Ex. Decreasing angle of the flexor surface
Extension
Straightening a joint
Ex. Increasing the angle of the flexor surface
Rotation
Moving in a circular motion (external or internal)
Supination - movement of palmar or plantar surface upward
Pronation - movement of palmar or plantar surface to neutral
Abduction
Moving away from the midline
Adduction
Moving toward the midline
Protraction
Moving the limb cranially
Retraction
Moving the limb caudally