Comparative Genomics + phylogenetics
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Comparative Genomics
the field of genomics in which genomic features (gene content, function and genome organisation) are compared across different species to understand evolutionary relationships and functions.
Molecular Phylogenetics
Applies a combination of molecular and statistical techniques to infer evolutionary relationships among organisms or genes eg analysing genetic data, enabling the construction of phylogenetic trees that depict the history of species evolution.
Evolutionary Relationships
Connections between organisms based on genetic data.
ACE2 and its significance
A gene encoding angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 which is a receptor that SARS-cov 2 binds to in human cells, playing a crucial role in the entry of the virus and influencing the severity of COVID-19.
Using comparative genomics we can see variations in ACE2 related to susceptibility to infection across different species.
Phylogenetics
Study of evolutionary relationships among biological entities.
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism)
Site in the genome where a single nucleotide differs between individuals of a species.
To be considered a SNP, it must reach a frequency of 1% in a population
Inherited as allelic variants in same way alleles produce phenotypic differences like blood types although SNPs don’t often produce phenotypic differences
Genetic Drift
Random changes in allele frequencies in a population.
Natural Selection
Process where organisms better adapted survive.
Genetic Engineering
Direct manipulation of an organism's genes.
Structural Genomics
Determines DNA sequences of entire genomes.
Human Genome Project
13-year project mapping the human genome.
Map-based Sequencing
Uses genetic maps to align sequenced fragments.
Whole-genome Shotgun Sequencing
Aligns fragments using sequence overlap.
Next-generation Sequencing
New technology for rapid genome data collection.
Bioinformatics Bottleneck
Challenge in processing vast genomic data.
Tree of Life
Universal tree representing all named species.
Myotis lucifugus
Little brown bat, key for evolutionary research.
Mammalian Genome Size
Bat has one of the smallest functional genomes.
Chromosomal Structure
Bat's chromosomes resemble ancestral mammalian state.
Metabolic Rate
Bat has highest rate among mammals, longevity.
Cancer-causing Free Radicals
Potentially managed by the little brown bat.
International Human Genome Consortium
Collaborative group for human genome sequencing.
Functional Elements
Coding and non-coding regions essential for research.
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history of a species or group.
Phylogenetic tree
Diagram representing evolutionary relationships.
Genealogical tree
Visual representation of lineage relationships.
Phylogenetic time
Chronological representation of evolutionary changes.
Systematics
Discipline classifying organisms by evolutionary relationships.
Taxonomy
Ordered division and naming of organisms.
Binomial Nomenclature
Two-part naming system for species.
Genus
First part of a species' scientific name.
Specific epithet
Unique second part of a species' name.
Hierarchical Classification
Grouping species into broad to narrow categories:
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Rhinolopus sp.
Genus of bats related to SARS-CoV-2.
Phylogenetic tree
Hypothesis about evolutionary relationships among species.
Branch point
Divergence point of two species in tree.
Sister taxa
Groups sharing an immediate common ancestor.
Rooted tree
Includes branch for last common ancestor.
Basal taxon
Diverges early near common ancestor of group.
Polytomy
Branch with more than two emerging groups.
Ancestral lineage
Lineage leading to common ancestor of taxa.
Phylogeny
Study of evolutionary history and relationships.
Common ancestor
Most recent ancestor shared by taxa.
Divergence
Separation of lineages from a common ancestor.
Minke whale
Species identified through phylogenetic analysis.
Humpback whale
Another species analyzed in phylogenetic studies.
Amino acid matrix
Data used for phylogenetic analysis of mammals.
Vertebrate outgroups
External taxa used to root phylogenetic trees.
Autocorrelated rates
Method for analyzing evolutionary rates in phylogeny.
Hard-bounded constraints
Limitations applied in phylogenetic analysis.
Whale meat
Identified species through phylogenetic methods.
Taxon
Group of one or more species in classification.
Evolutionary relationships
Connections between species based on ancestry.
Detection methods
Techniques used to identify species from samples.
Species identification
Determining species based on genetic analysis.
What is a genome
A genome is the complete set of biological information needed to build and maintain an organism
What molecule encodes the biological information in a genome
The biological information in a genome is encoded in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
What is the goal of Structural Genomics
To sequence entire genomes and understand their structure
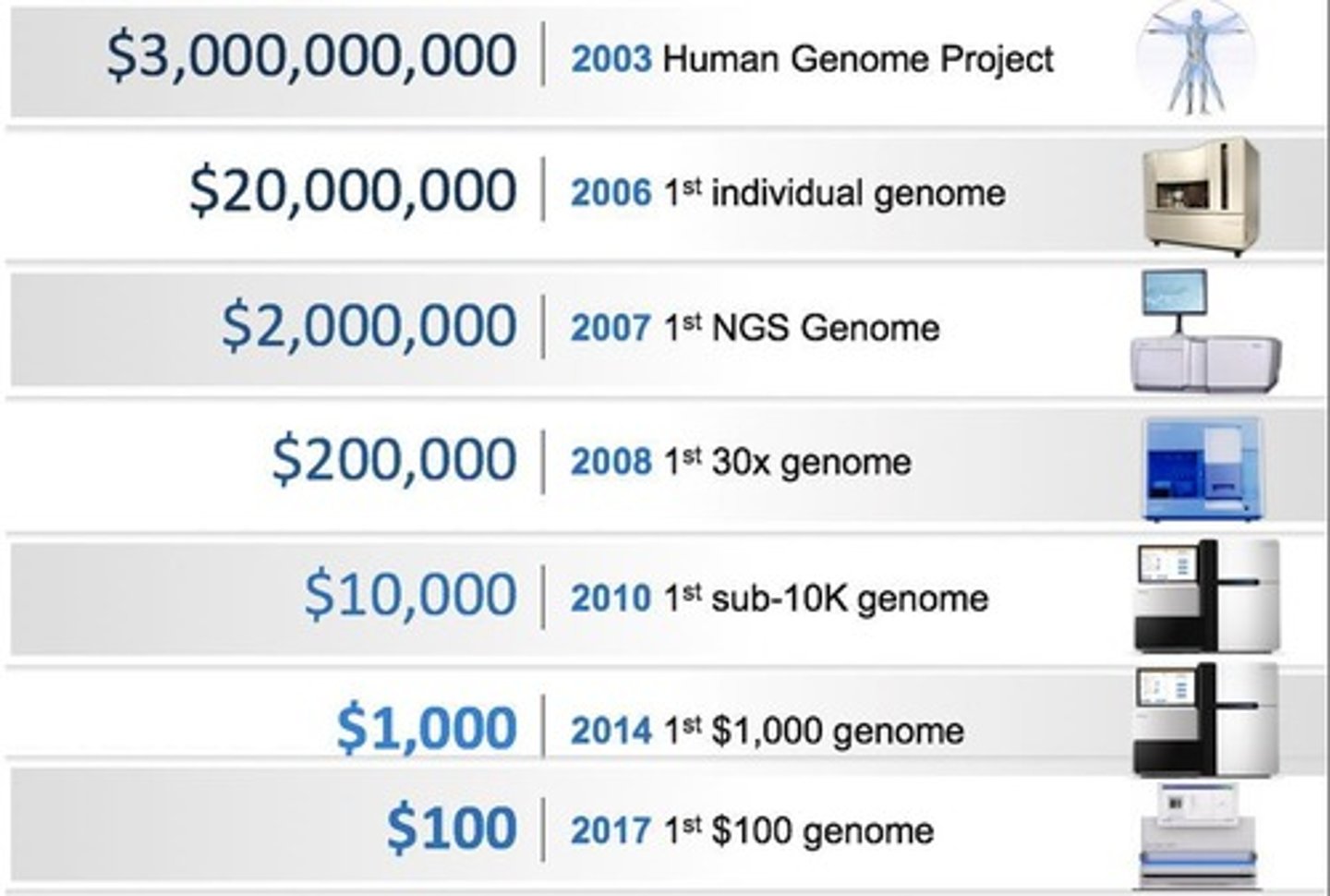
What major project aimed to sequence the human genome and what technologies helped lower the cost of human genome sequencing?
The Human Genome Project was a global scientific research initiative that aimed to map and understand all the genes of the human species, utilizing advancements in DNA sequencing technologies such as next-generation sequencing.
What are two main approaches used in genome sequencing
1. Map-based sequencing
2. Whole-genome shotgun sequencing
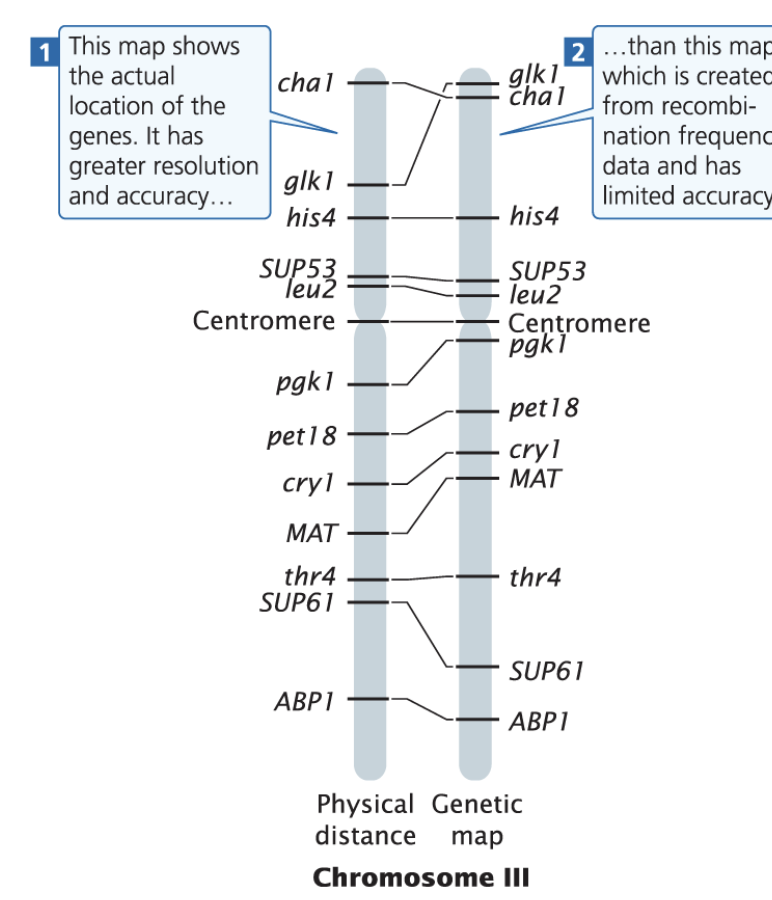
what are the differences b/w a genetic map and a physical map?
A genetic map shows the relative positions of genes based on recombination frequencies,
while a physical map provides the actual physical distances (kb,mb etc) between genes on a chromosome, measured in base pairs.
How does map-based genome sequencing work?
It relies on detailed genetic and physical maps to align sequenced fragments and reconstruct the genome by identifying overlapping sequences, effectively piecing together the entire genome from smaller segments.
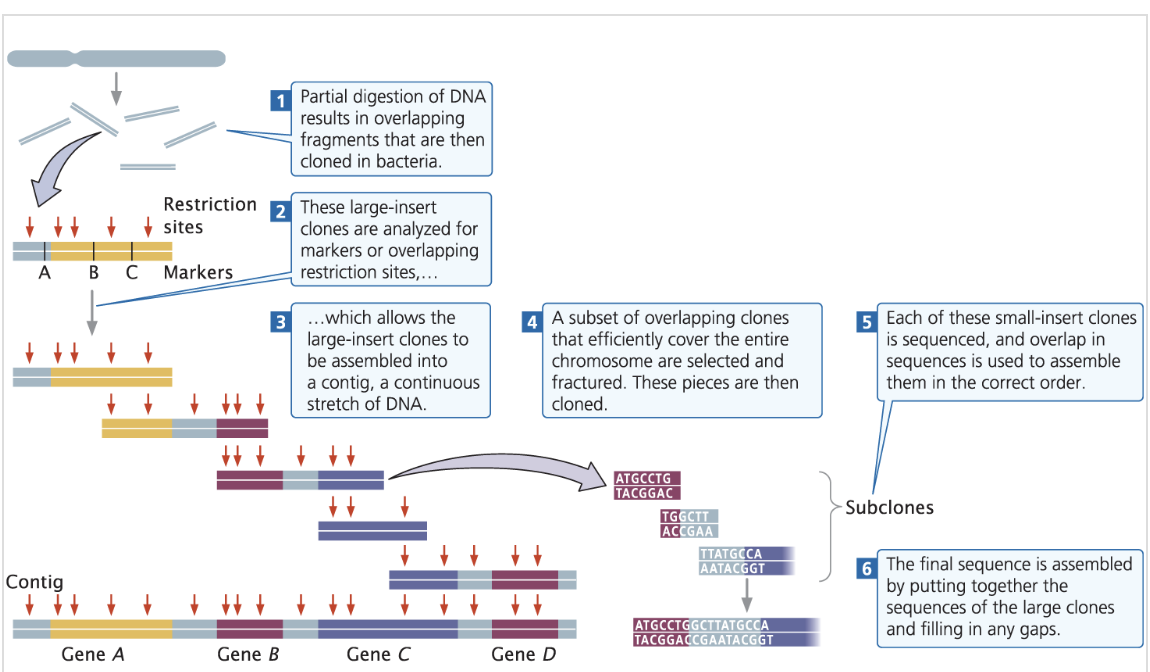
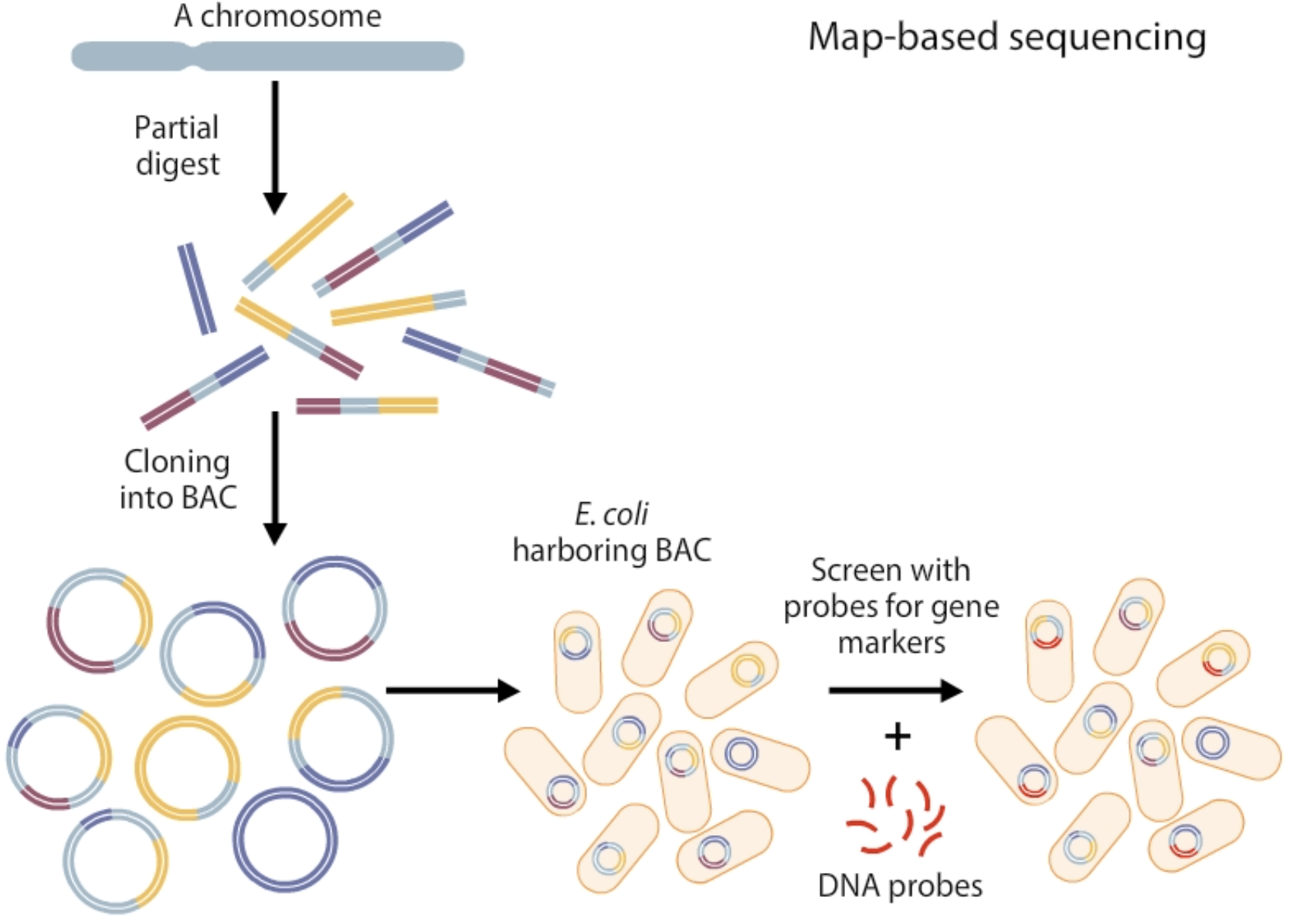
what are the 6 steps of map-based sequencing?
Create a genetic map by partial digestion of DNA resulting in overlapping fragments that are cloned into bacterial artifical chromosomes (BACs)
Analyse the large-insert clones for genetic markers i.e using DNA probes / overlapping restriction sites
Assemble the DNA sequences from BACs into contiguous sequences (contigs).
Select a subset of overlapping clones that efficiently cover the entire chromosome which are then fractured + cloned
Sequence each small-insert clone and use sequence overlap to assemble them in the correct order
Assemble the final sequence by putting together the large clones sequences together + fill any gaps
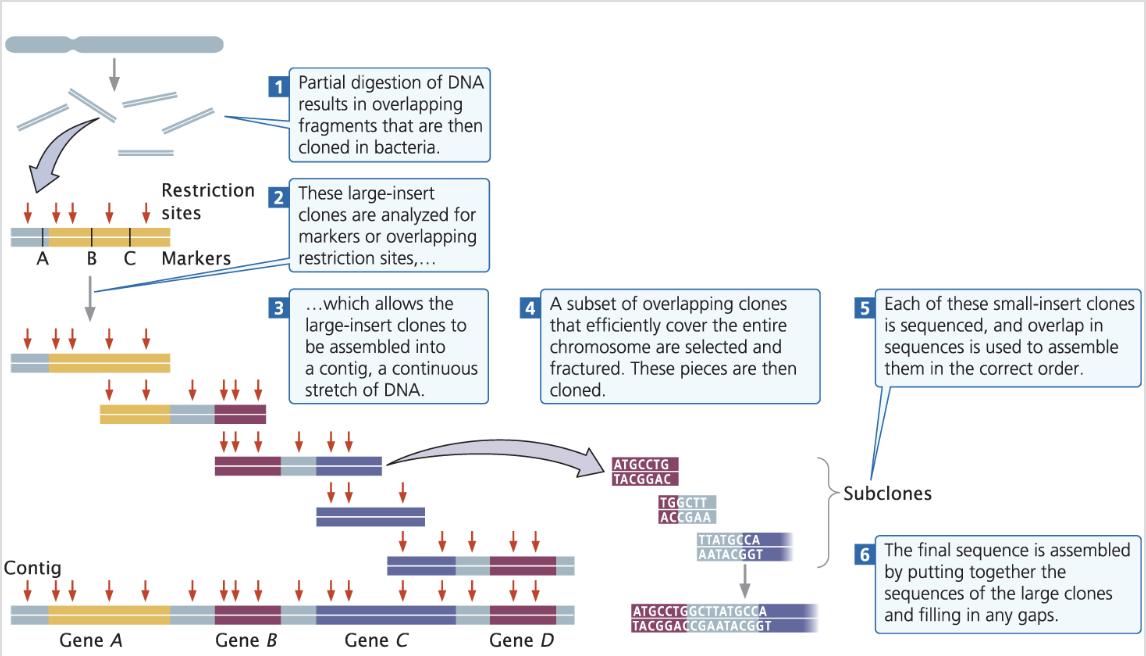
contig
is a continuous sequence of DNA that's constructed from overlapping DNA fragments.
Contigs are essential in genome assembly, as they represent the longest contiguous stretch of the DNA sequence from sequenced DNA fragments.
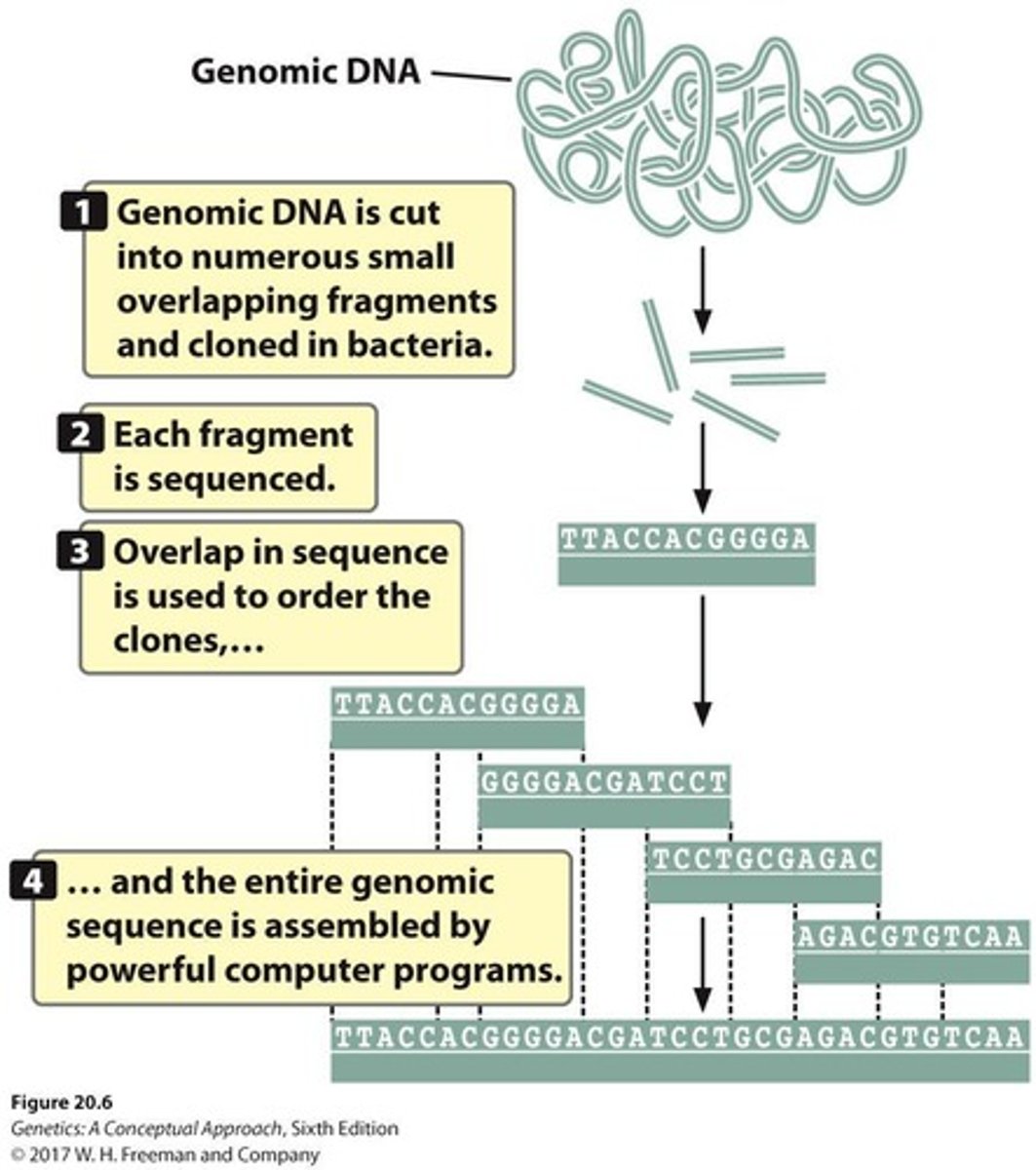
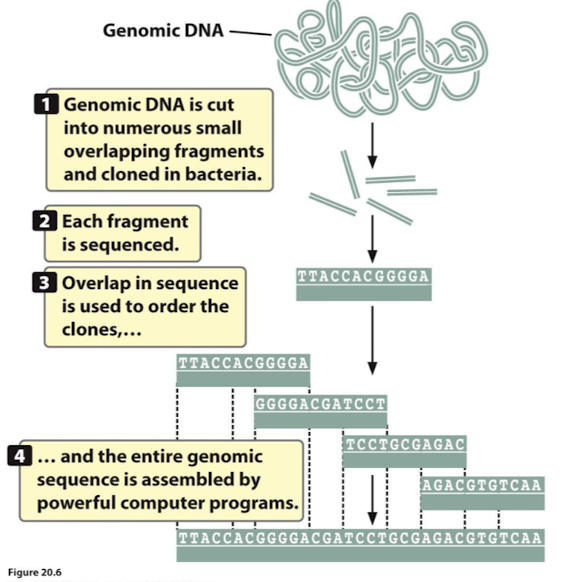
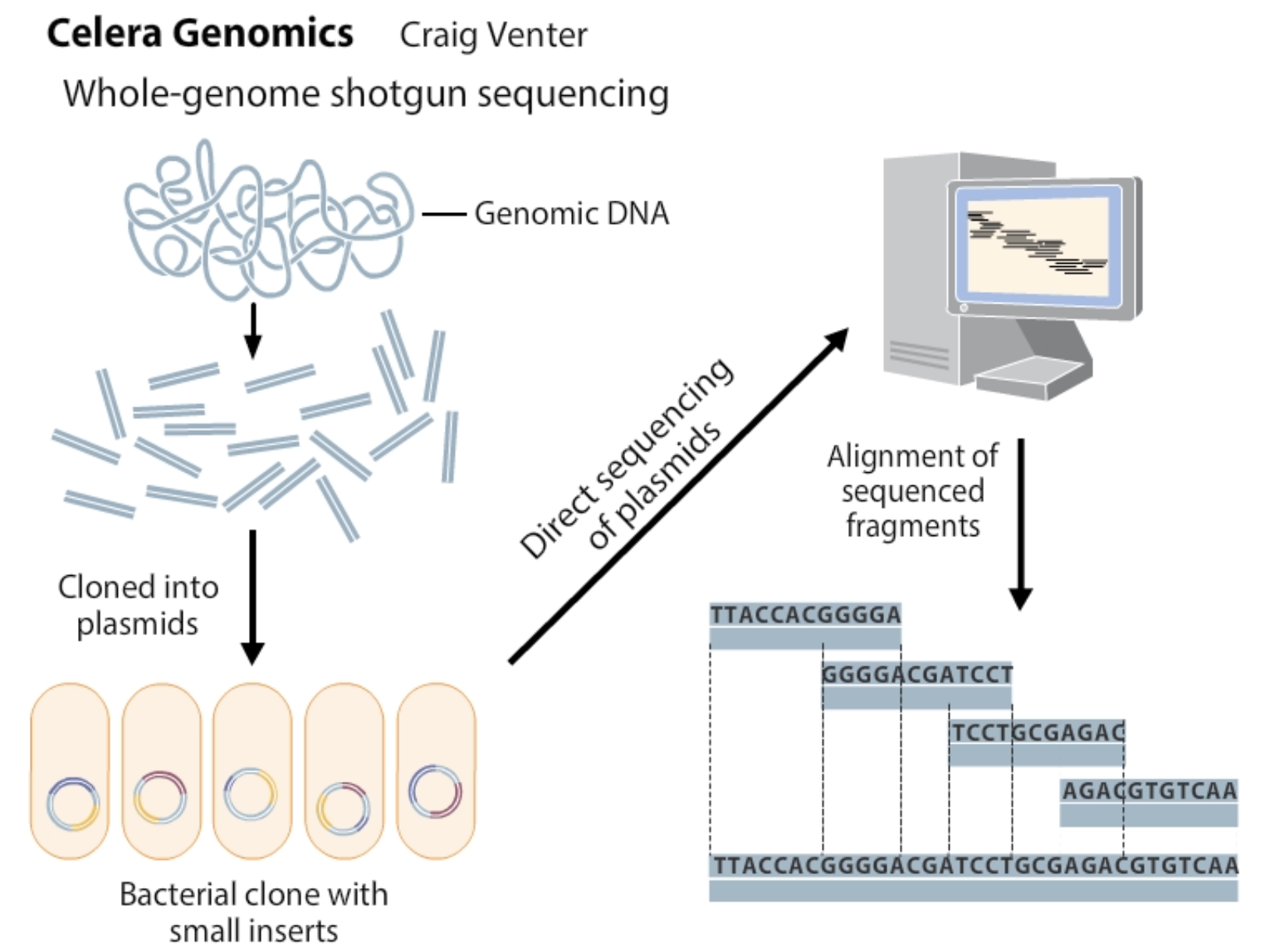
How does whole-genome shotgun sequencing work
It uses sequence overlap to align sequenced fragments
what are the 4 steps of whole-genome shotgun sequencing
Fragment the genome into small pieces using physical or enzymatic methods.
Clone the fragments into vectors to create a library of cloned DNA.
Sequence the fragments using high-throughput sequencing technologies.
Assemble the overlaps between fragments to reconstruct the original genome using powerful computer software
How has the genome revolution impacted biology and medicine
New technologies, like next-generation sequencing, generate vast amounts of data that transform biological research and medicine
What is the biomedical importance of comparative genomics
Comparative genomics helps identify functional elements in the human genome, including coding and non-coding regions, by comparing genomes across species.
This approach leverages 100 million years of evolutionary history to advance biomedical research
Why is identifying functional elements in the human genome important for biomedical research
Functional elements, including both coding and non-coding regions, are key to understanding human biology and disease
How does comparative genomics aid biomedical research
It helps identify functional elements in the human genome by comparing it with other mammalian genomes
What is one of the most powerful ways to discover functional elements in the human genome
Cross-species comparisons with other mammalian genomes
What is the Darwin Tree of Life Project
A project aimed at sequencing the genomes of all eukaryotic living species in the UK and Ireland to create a comprehensive tree of life
Why is Myotis lucifungus (little brown bat) important for human health and evolutionary research
The little brown bat plays a role in human health by helping control insect populations, particularly mosquitoes.
It is also important in evolutionary research due to its unique immune system and adaptations to hibernation, providing insights into aging, disease resistance, and environmental adaptation
Why is sequencing the genome of Myotis lucifungus (little brown bat) important
Bats represent 25% of all mammalian diversity and have one of the smallest mammalian genome sizes, providing insights into the minimal DNA required for a functional mammalian genome
Why is sequencing the genome of Myotis lucifungus (little brown bat) important in terms of chromosomal structure
This bat's chromosomal structure is very similar to the putative ancestral mammalian chromosomal state, making it valuable for studying mammalian evolution
Why is sequencing the genome of Myotis lucifungus (little brown bat) important for understanding metabolism and aging
This bat has the highest metabolic rate of all mammals yet can live over 34 years, suggesting it may have an unusual way of dealing with cancer-causing free radicals
Why is sequencing the genome of Myotis lucifungus (little brown bat) important for studying immunity
Bats may have immunity to certain diseases, and by understanding their genome, we can identify immune system genes that could offer insights into natural immunity
What is phylogeny
Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a species or group of species.
How can the evolutionary history of a group of organisms be represented
It can be represented in a diagram called a phylogenetic tree
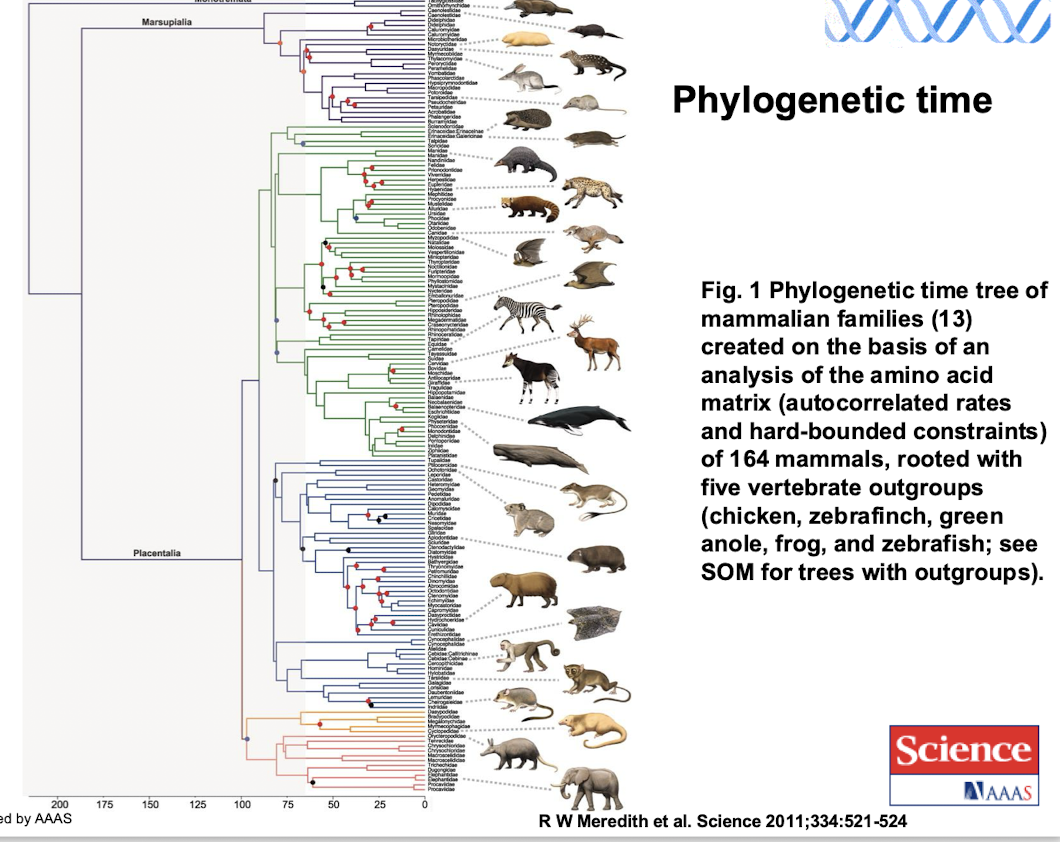
What is a phylogenetic time tree
A phylogenetic time tree is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships and timelines of species, such as the mammalian families based on amino acid matrix analysis.
How was the phylogenetic time tree of mammalian families created
It was created based on an analysis of the amino acid matrix of 164 mammals, with constraints on autocorrelated rates and rooted with five vertebrate outgroups (chicken, zebrafinch, green anole, frog, and zebrafish).
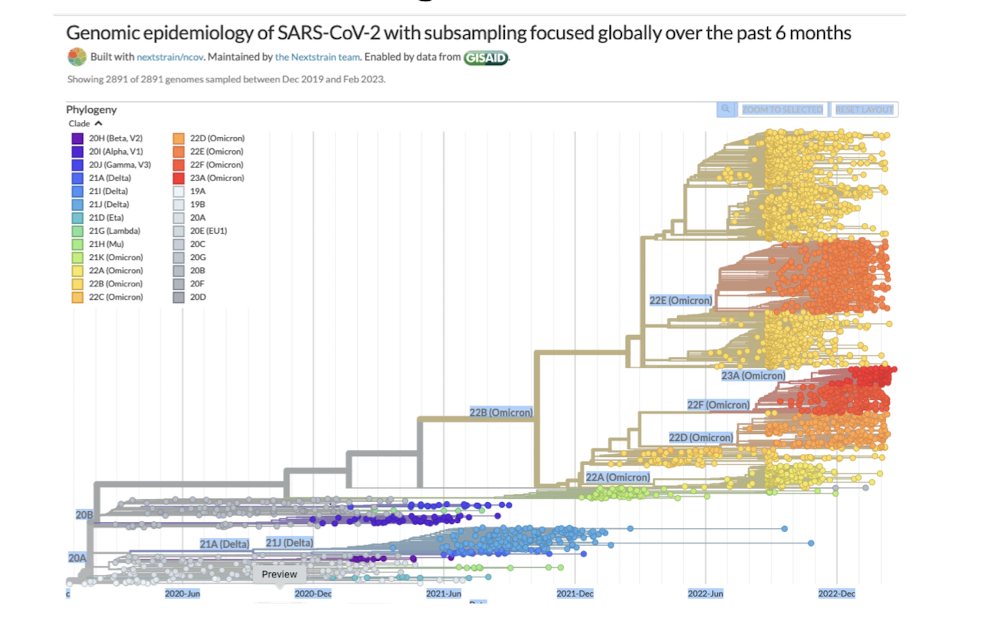
how can phylogenetic trees be used in studying epidemiology?
Can be used to follow the transmission of Covid-19 around the globeby tracing viral lineages and understanding how the virus spreads between populations.
What does phylogeny show
Phylogeny shows the evolutionary history of a species or group of species
What is the discipline of systematics
Systematics classifies organisms and determines their evolutionary relationships
What data does systematics use to infer evolutionary relationships
Systematics uses fossil, molecular, and genetic data to infer evolutionary relationships
What is taxonomy
Taxonomy is the ordered division and naming of organisms
What are the two key features of Linnaeus' system of taxonomy
The two key features are two-part names for species and hierarchical classification
What is the two-part scientific name of a species called
It is called a binomial
What does the first part of a binomial name represent
The first part represents the genus
What is the second part of a binomial name called
The second part is called the specific epithet, which is unique for each species within the genus
How should a binomial name be written.
The first letter of the genus is capitalized, and the entire species name is italicized
What is an example of a binomial name
Homo sapiens
Are broader taxa comparable between lineages
No, broader taxa are not comparable between lineages.
For example, an order of snails has less genetic diversity than an order of mammals
How do systematists depict evolutionary relationships?
Systematists depict evolutionary relationships in branching phylogenetic trees
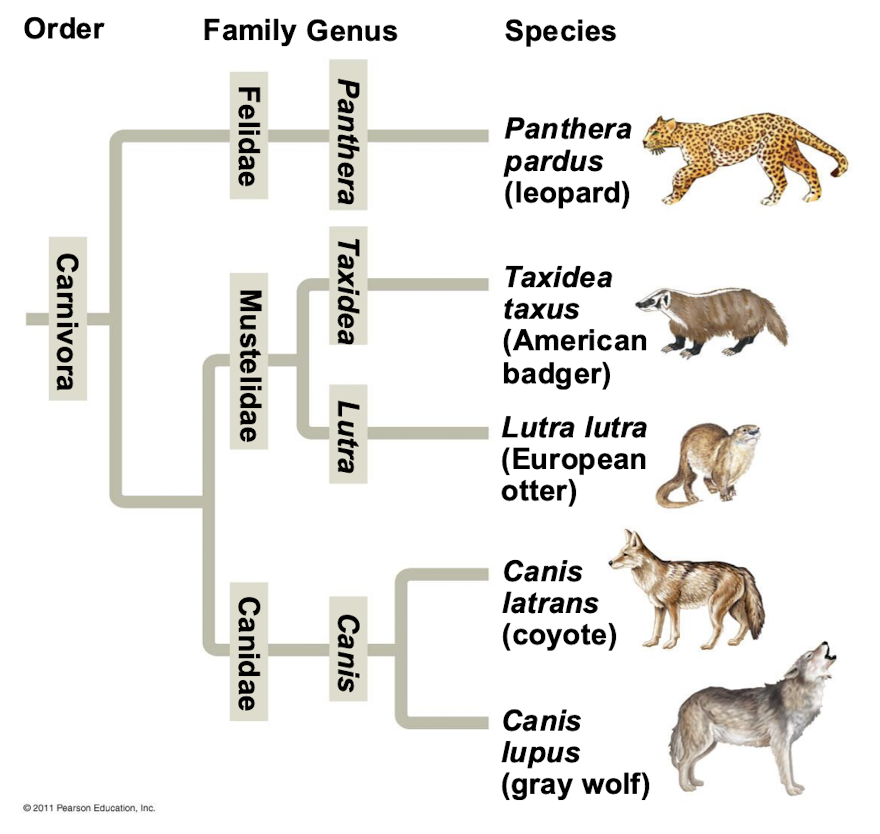
Can Linnaean classification and phylogeny differ from each other
Yes, Linnaean classification and phylogeny can differ from each other because classification is based on shared characteristics while phylogeny is based on evolutionary history.
What does a phylogenetic tree represent
A phylogenetic tree represents a hypothesis about evolutionary relationships
What does each branch point on a phylogenetic tree represent
Each branch point represents the divergence of two species
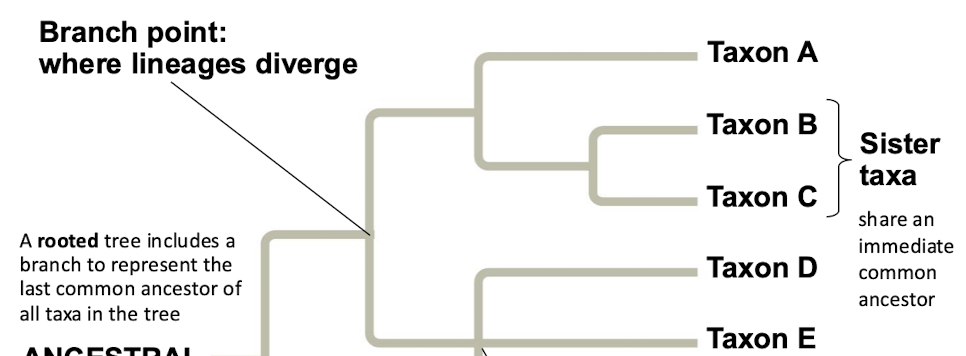
What are sister taxa
Sister taxa are groups that share an immediate common ancestor
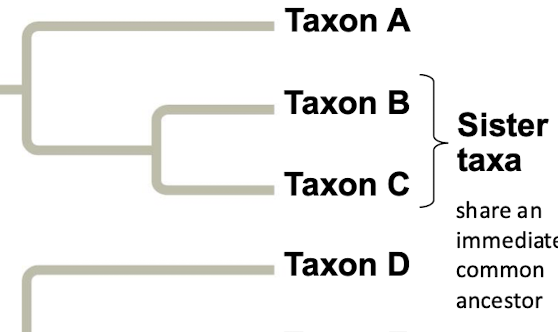
What does a rooted phylogenetic tree include
A rooted tree includes a branch to represent the last common ancestor of all taxa in the tree
What is a basal taxon
A basal taxon diverges early in the history of a group and originates near the common ancestor of the group