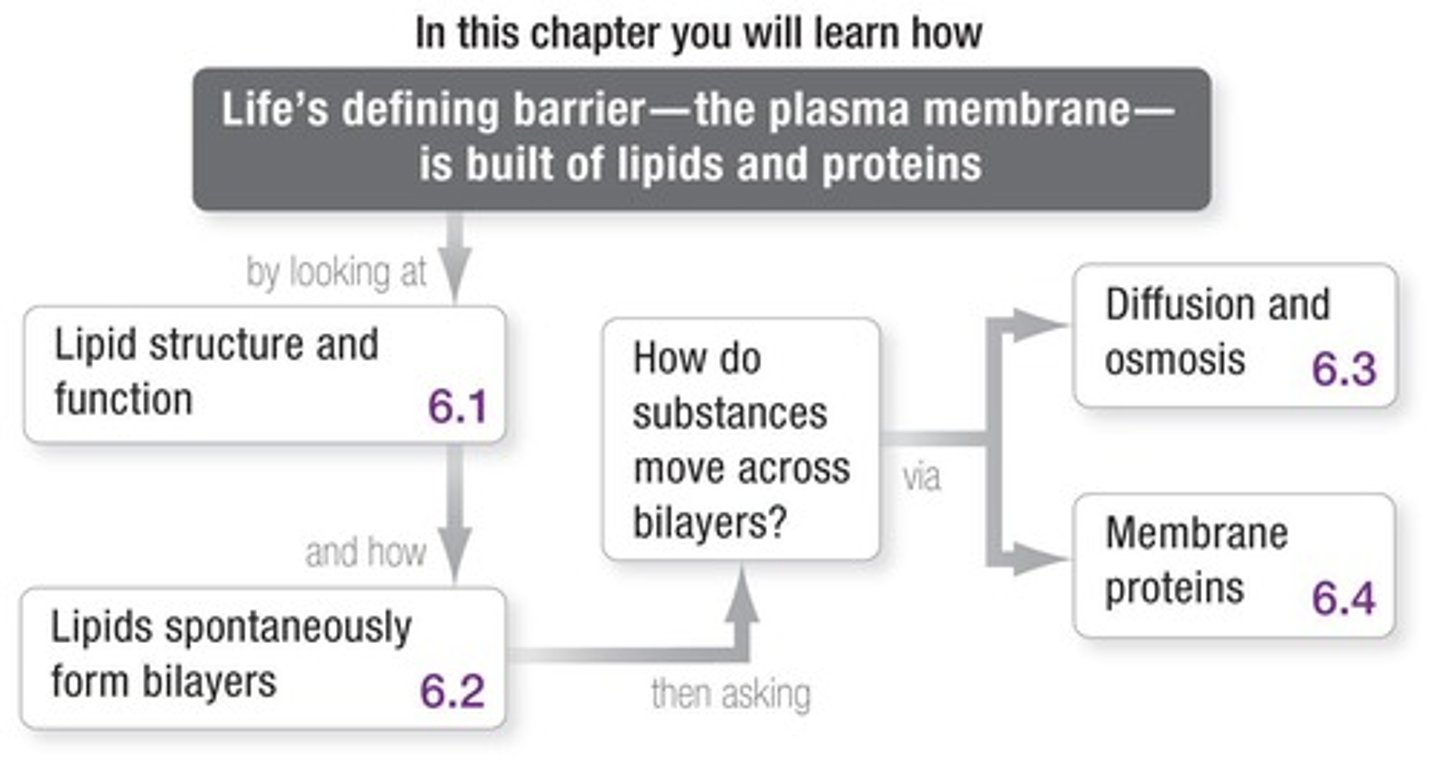
CH.6: Lipids, Membranes, and the First Cells
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Plasma membrane
Separates life from nonlife, selective barrier.
Selective barrier
Allows entry of needed materials, excludes harmful ones.
Chemical reactions
Facilitated by sequestering appropriate chemicals.
Lipids
Carbon compounds insoluble in water due to nonpolarity.
Hydrocarbons
Nonpolar molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen.
Hydrophobic
Repellent to water; does not mix with it.
Isoprenoid
Hydrocarbon chain, functions in pigments and hormones.
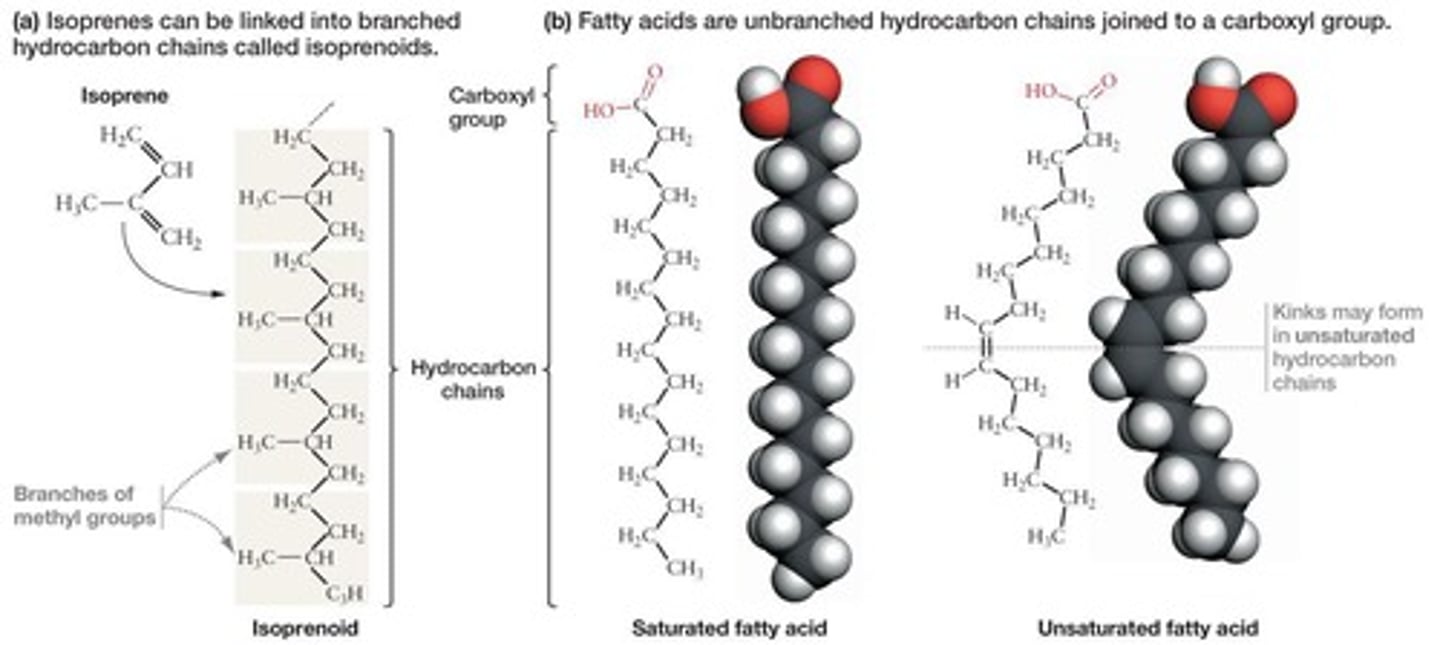
Fatty acid
Hydrocarbon chain bonded to a carboxyl group.
Saturated fatty acid
Only single bonds between carbons, maximum hydrogens.
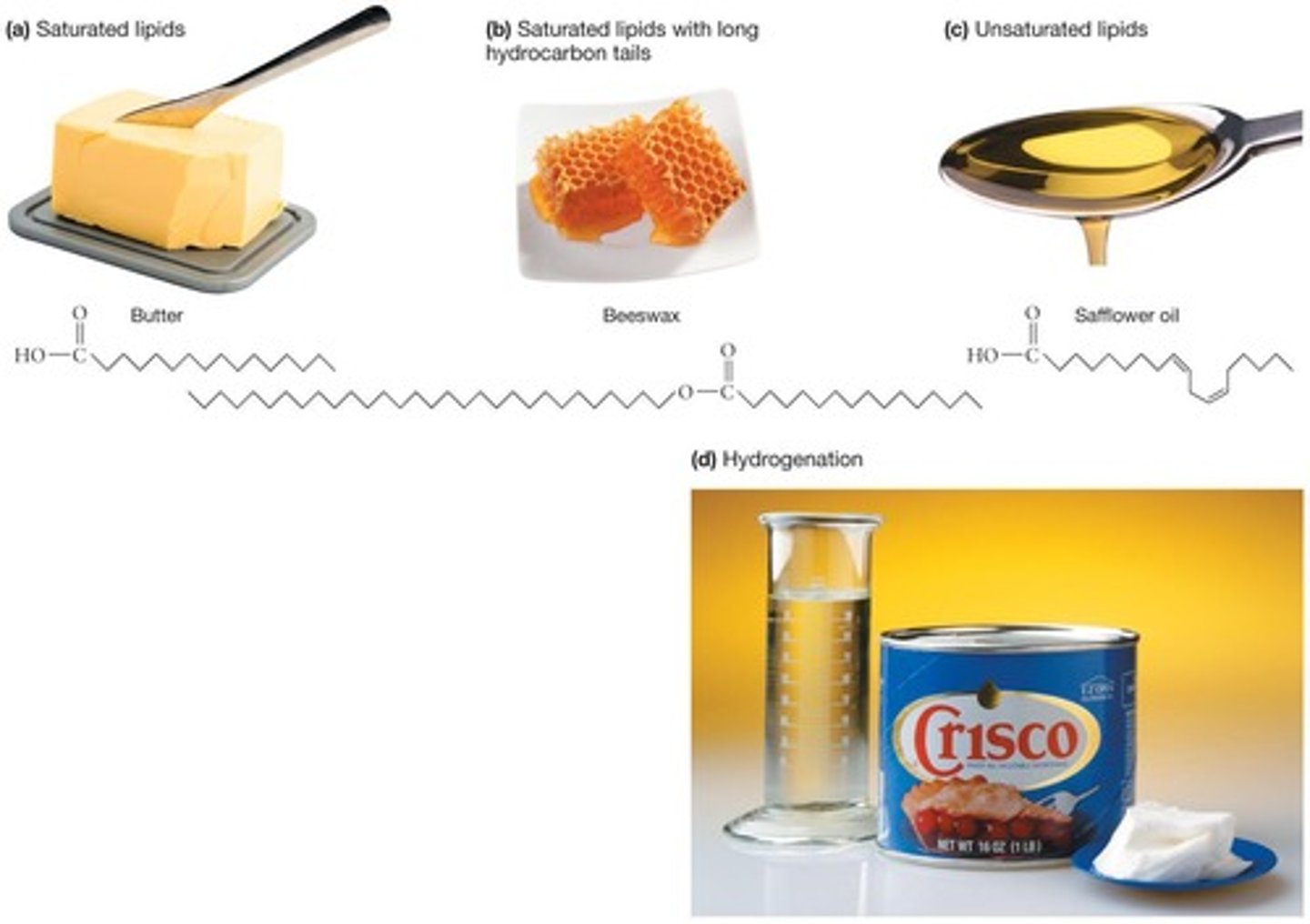
Unsaturated fatty acid
Contains one or more double bonds, creates kinks.
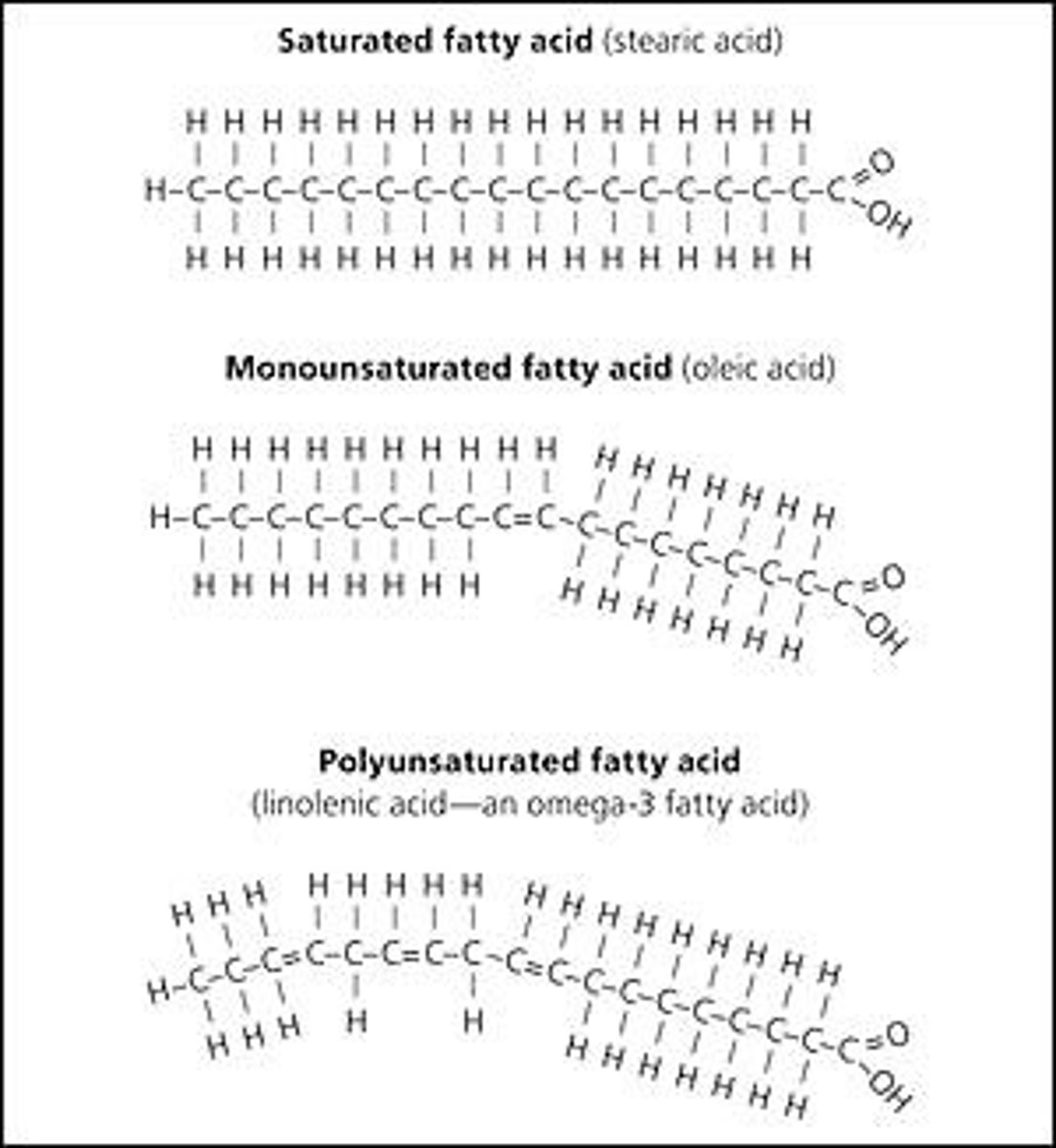
Polyunsaturated fatty acid
Multiple double bonds in hydrocarbon chain.
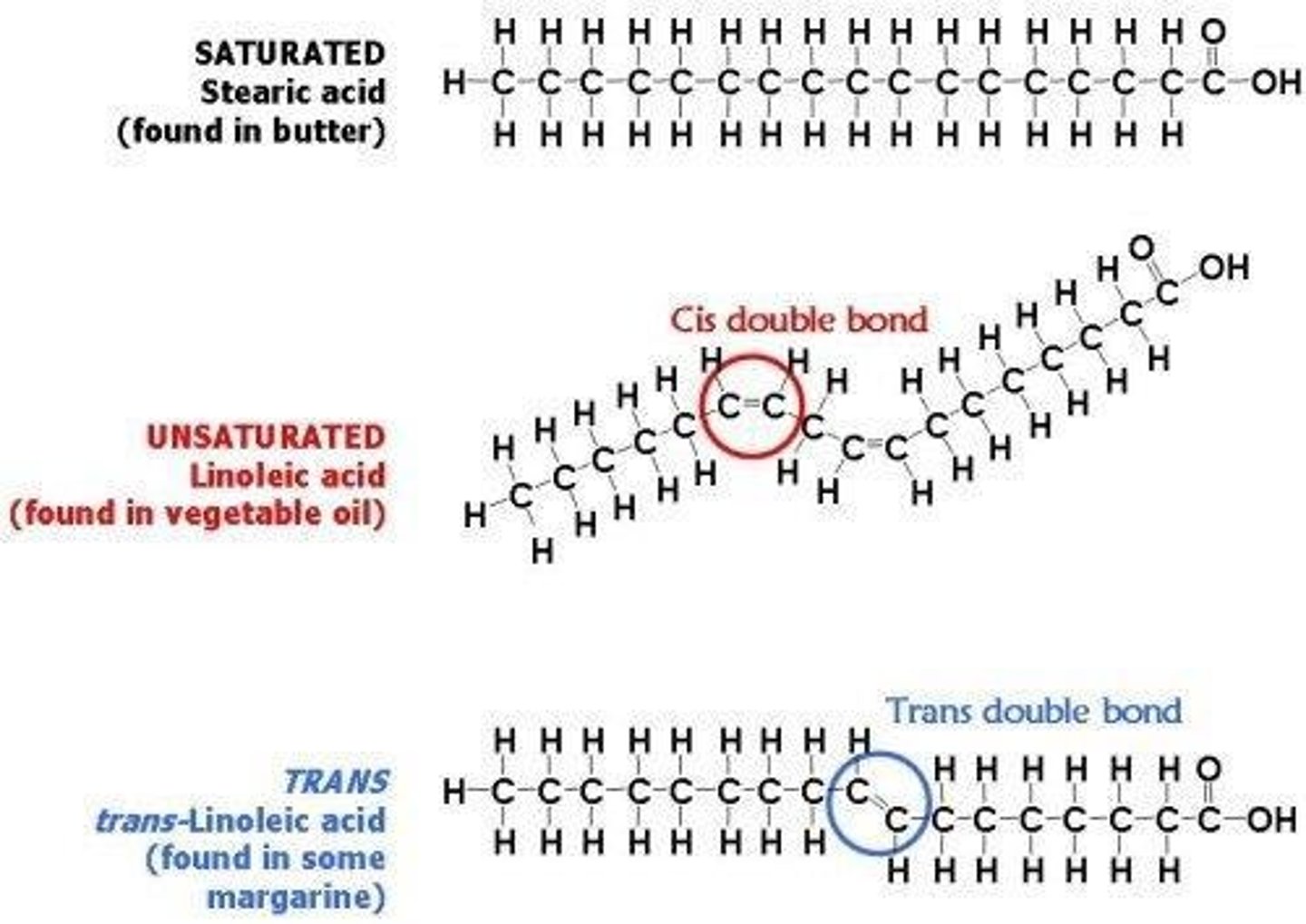
Saturation
Affects physical state; influences healthiness of lipids.
Solid lipids
Highly saturated, stiff at room temperature.
Liquid lipids
Highly unsaturated, remain liquid at room temperature.
Triglycerides
Type of lipid made from glycerol and fatty acids.
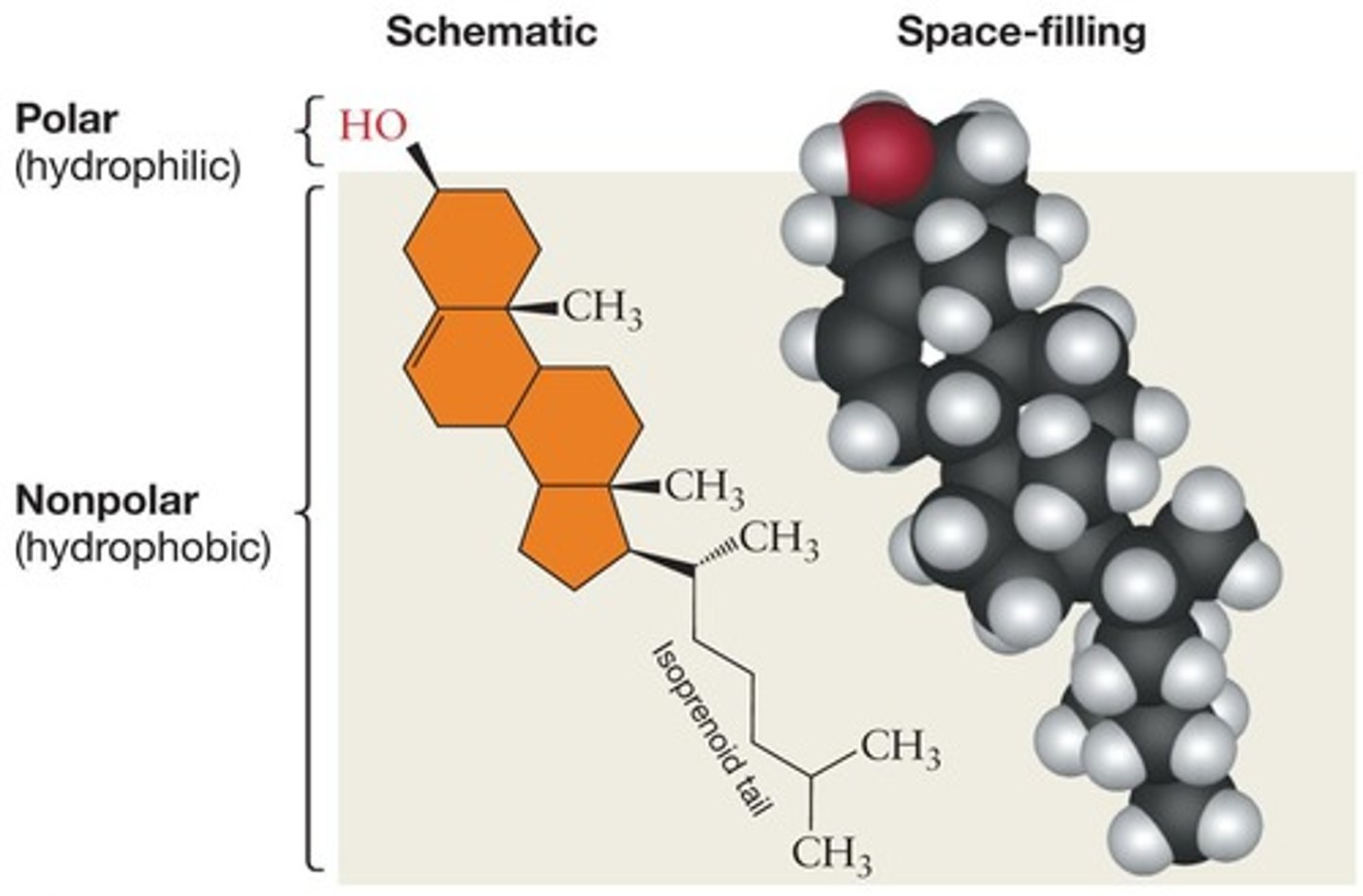
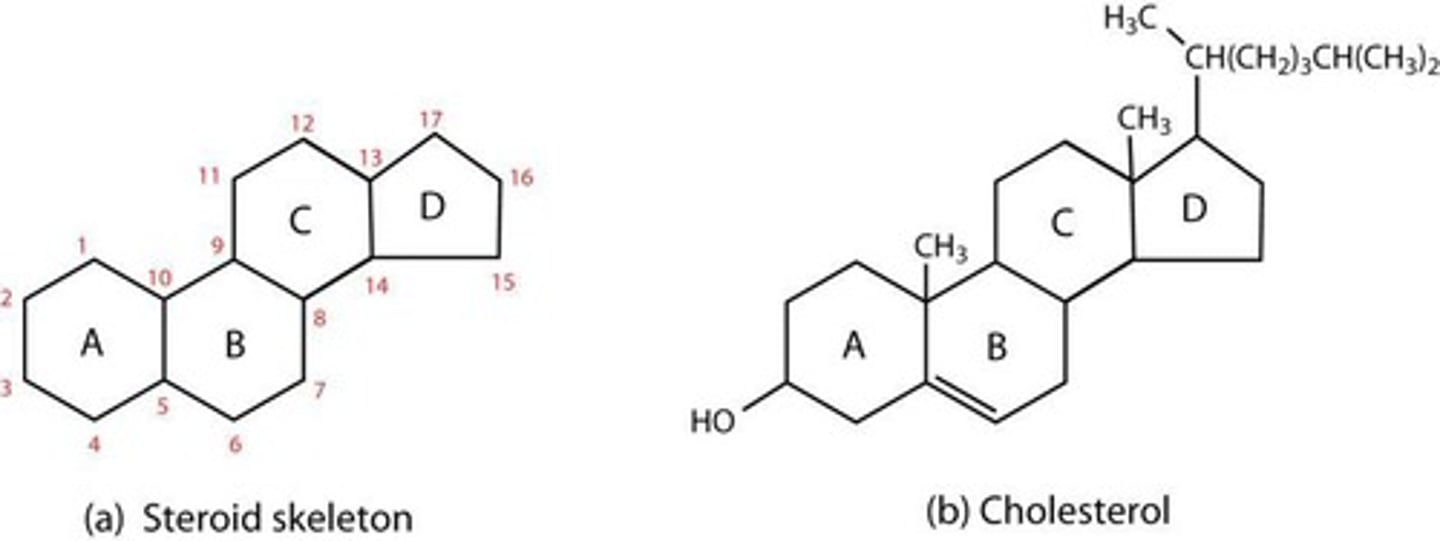
Steroids
Lipids with a four-ring carbon structure.
Fats
Energy storage lipids, composed of triglycerides.
Hydrocarbon tails
Long chains in lipids affecting their state.
Chemical structure of lipids
Varies widely, allowing diverse functions.
Carboxyl group
Functional group in fatty acids, polar.
Kink in chain
Caused by double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids.
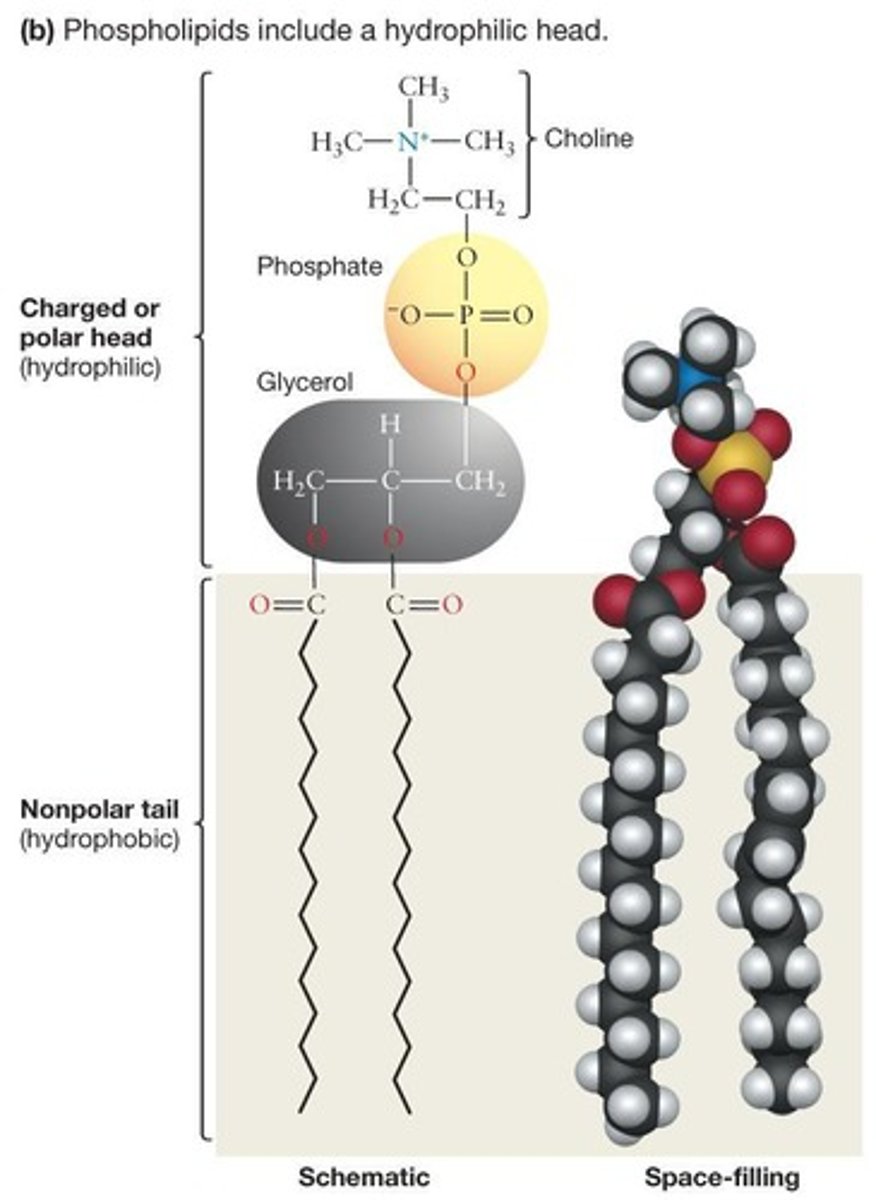
Phospholipids
Glycerol linked to phosphate and two hydrocarbon chains.
Steroids
Lipids with a bulky four-ring structure.
Testosterone
Hormone steroid important for male development.
Estrogen
Hormone steroid important for female development.
Cholesterol
Component of plasma membranes, a type of steroid.
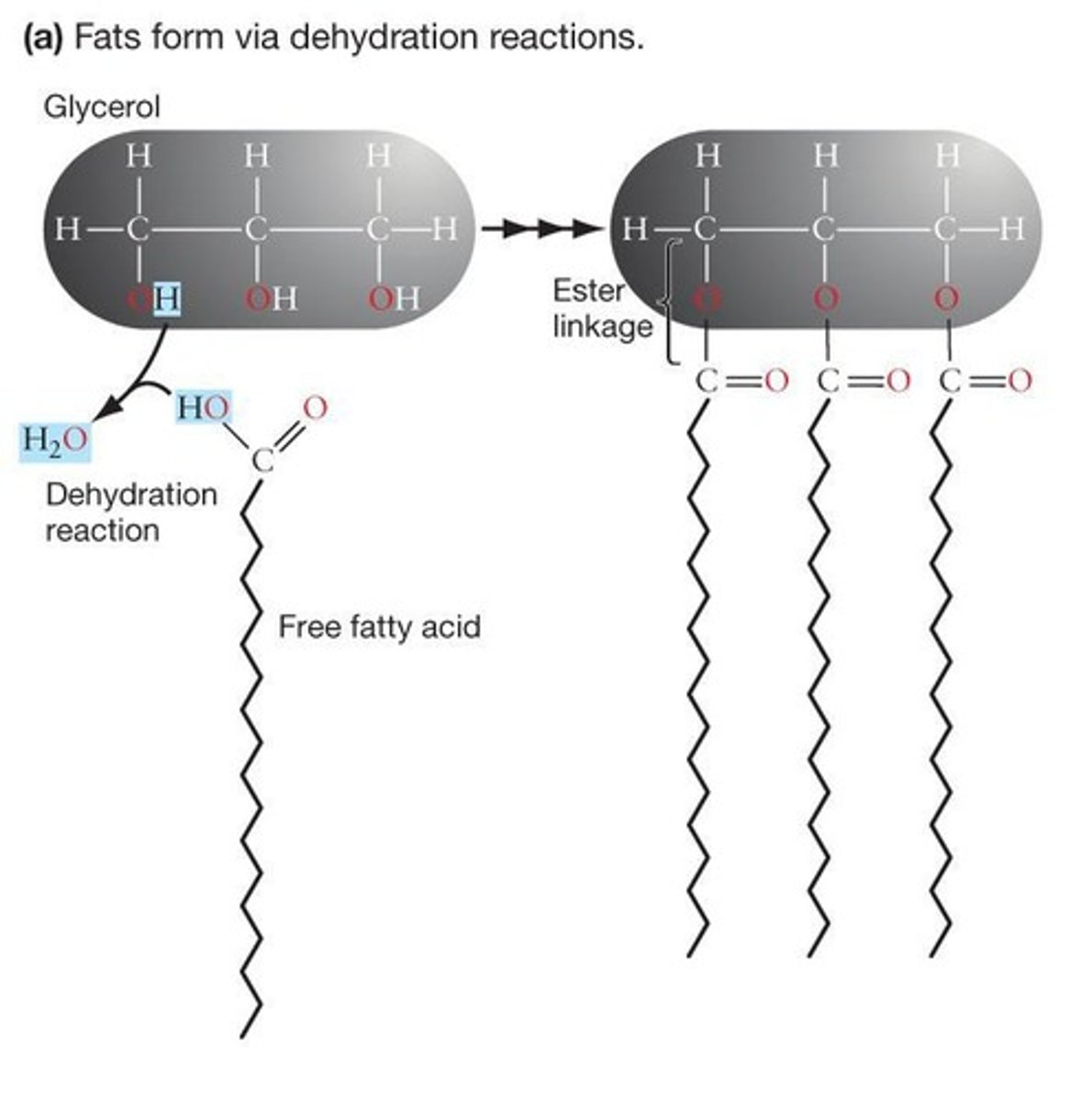
Fats
Composed of three fatty acids linked to glycerol.
Triacylglycerols
Another name for fats or triglycerides.
Ester Linkage
Bond formed between glycerol and fatty acids.
Hydrophobic Region
Non-polar tail of phospholipids, repels water.
Hydrophilic Region
Polar head of phospholipids, interacts with water.
Phospholipid Bilayers
Lipid bilayers formed by phospholipids in water.
Micelles
Spherical aggregates formed by free fatty acids.
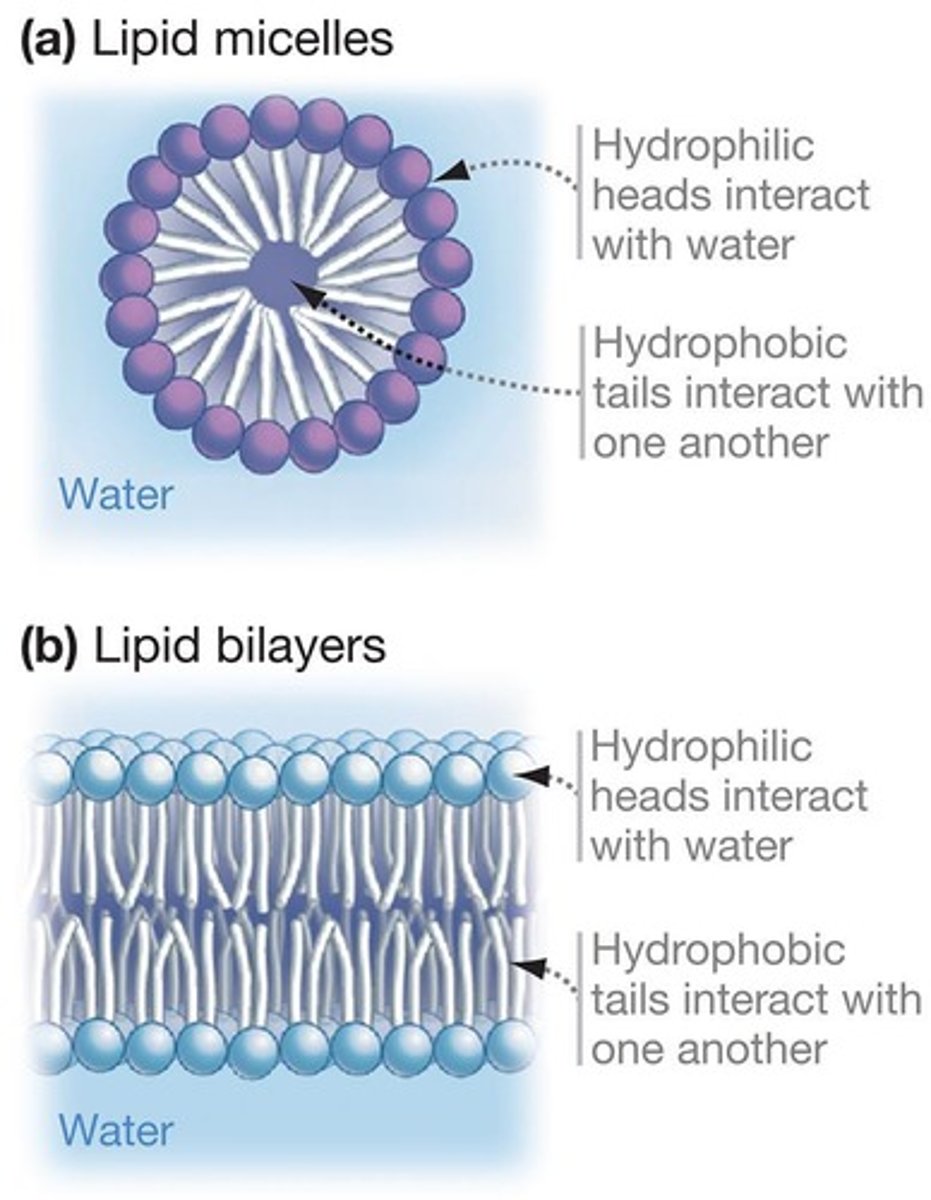
Lipid Bilayers
Paired sheets of lipid molecules in membranes.
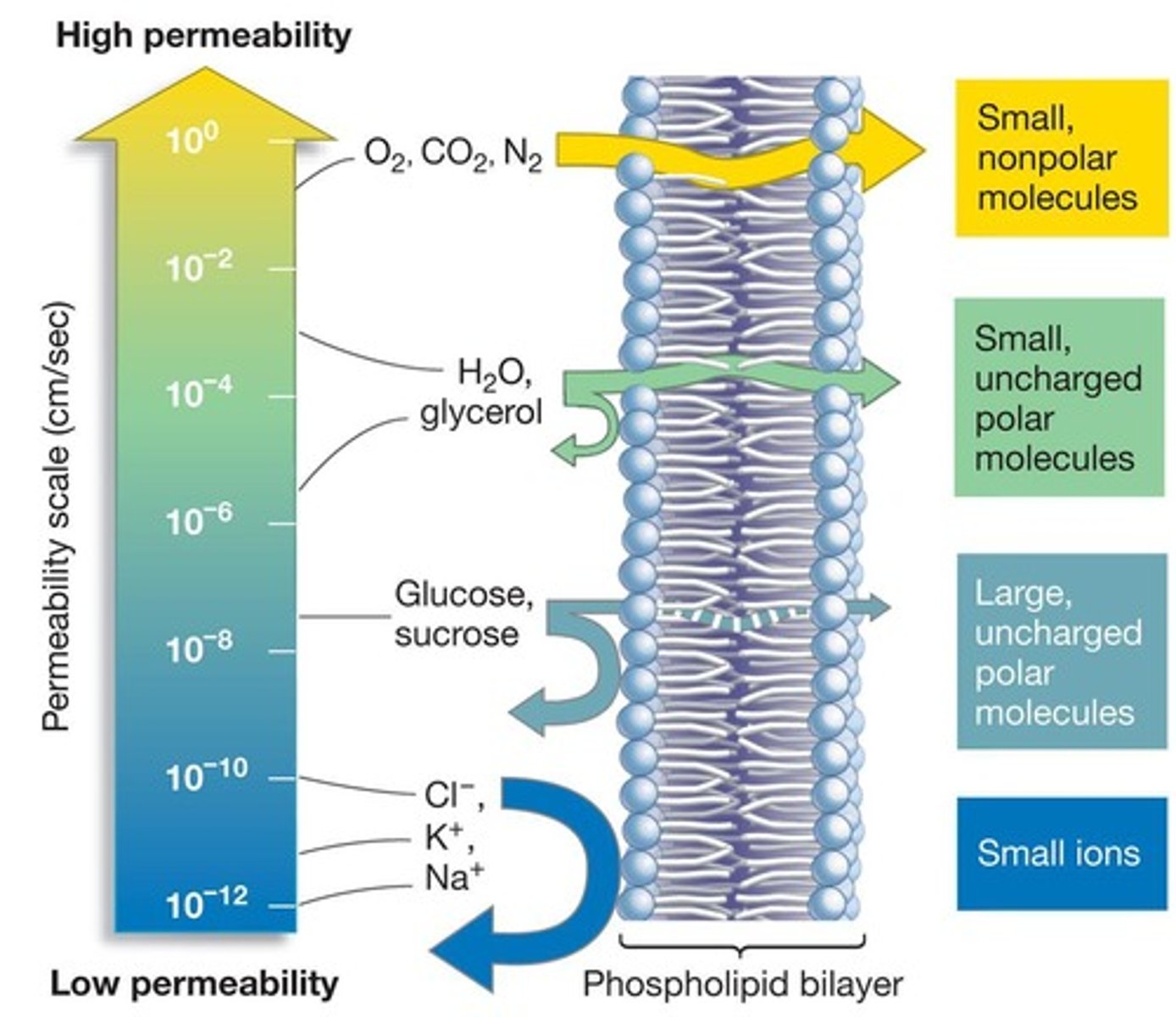
Selective Permeability
Ability of membranes to control substance passage.
Small Nonpolar Molecules
Cross bilayers quickly due to size and polarity.
Large Polar Molecules
Cross bilayers slowly, if at all.
Dehydration Reaction
Process linking glycerol and fatty acids to form fats.
Amphipathic Lipids
Molecules with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
Artificial Membranes
Lab-created lipid structures for experimental purposes.
Liposomes
Artificial vesicles formed from phospholipids.
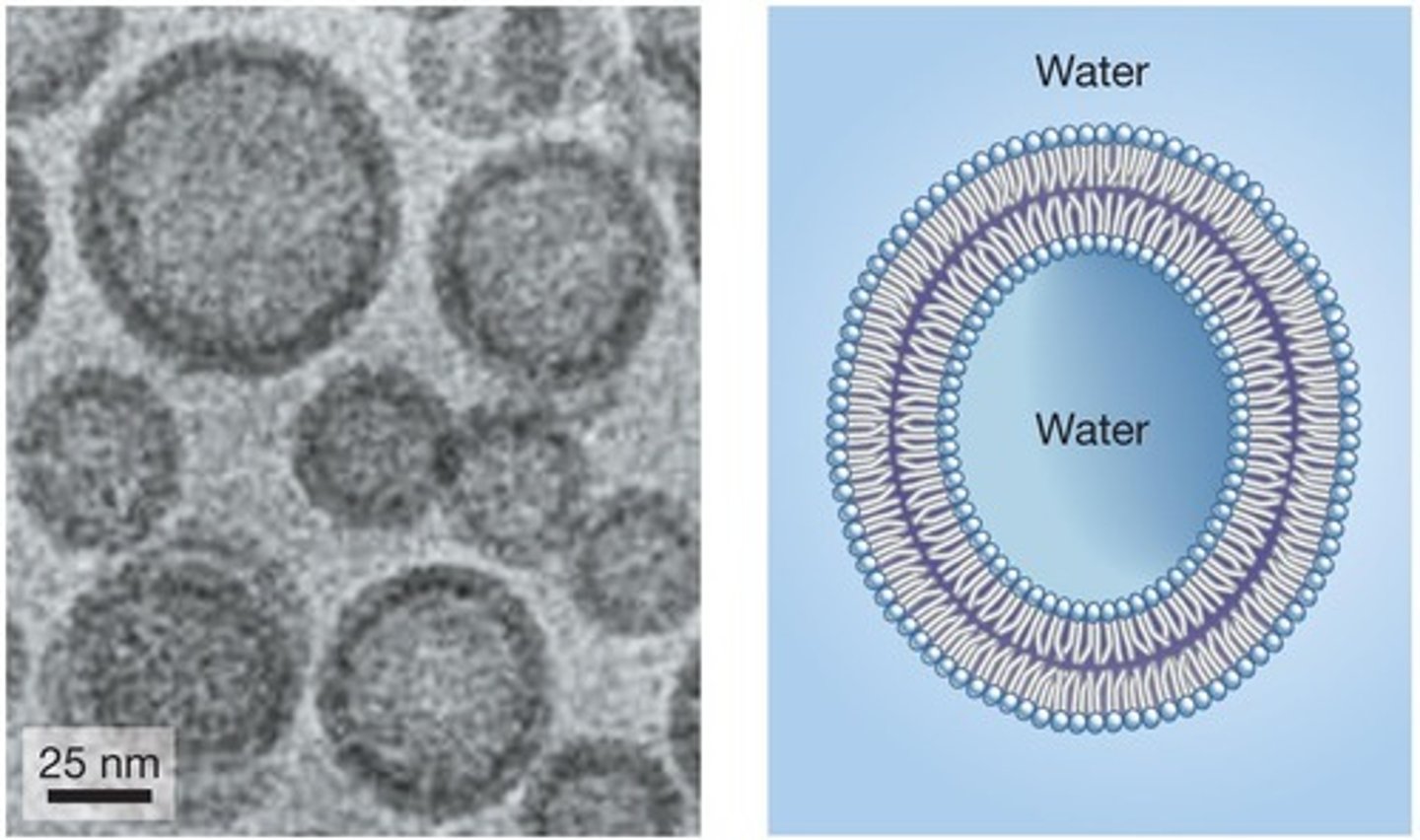
Planar Bilayers
Lipid bilayers across openings in glass/plastic.
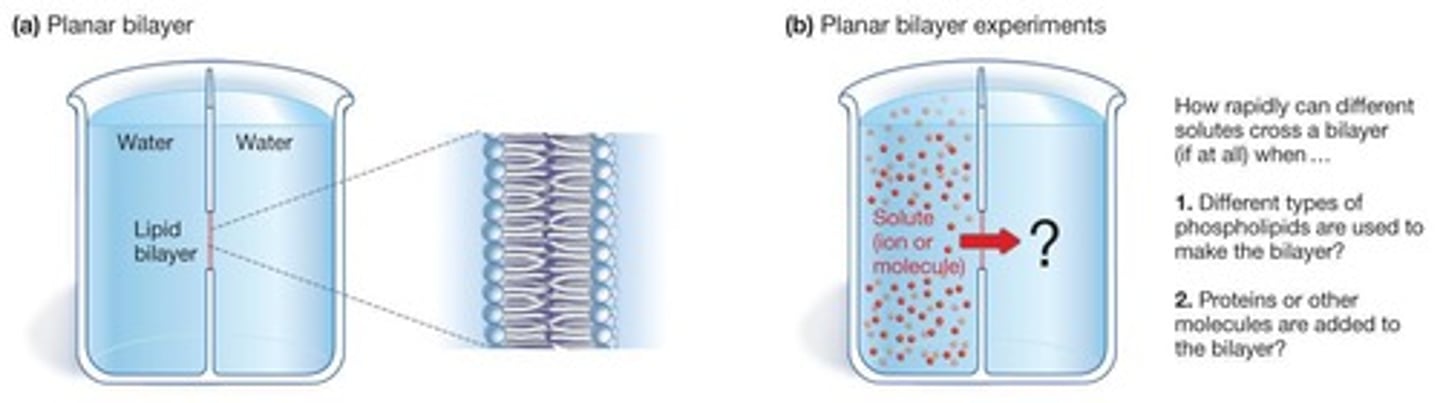
Energy Storage
Primary role of fats due to high-energy bonds.
Entropy in Lipid Organization
Spontaneous processes decrease entropy at lipid level.
Phospholipids
Molecules forming cell membranes, varying in properties.
Hydrocarbon Tails
Fatty acid chains affecting membrane fluidity and permeability.
Saturation
Presence of double bonds in hydrocarbon tails.
Unsaturated Tails
Contain double bonds, causing kinks in structure.
Saturated Tails
No double bonds, leading to tighter packing.
Cholesterol
Steroid that increases membrane density and reduces permeability.
Membrane Permeability
Ability of substances to cross the membrane.
Hydrophobic Interactions
Forces holding tails together in membranes.
Temperature Effect
Lower temperatures decrease membrane fluidity and permeability.
Diffusion
Movement from high to low concentration regions.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in solute concentrations across a space.
Equilibrium
State where molecules are evenly distributed, no net movement.
Passive Transport
Substances cross membranes without energy input.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across selectively permeable membranes.
Hypertonic Solution
Higher solute concentration outside the cell.
Hypotonic Solution
Lower solute concentration outside the cell.
Isotonic Solution
Equal solute concentrations inside and outside the cell.
Cell Swelling
Occurs in hypotonic solutions due to water influx.
Cell Shrinking
Occurs in hypertonic solutions due to water efflux.
Entropy
Measure of disorder, increased by diffusion.
Fluidity
Ability of phospholipids to move within the bilayer.
Packing Density
Tightness of phospholipid tails affecting permeability.
Selective Permeability
Membrane's ability to allow certain substances to pass.
Osmosis
Movement of water across a semipermeable membrane.
Protocells
Simple vesicle-like structures containing nucleic acids.
Lipid Bilayers
Double layer of lipids forming cell membranes.
Ribonucleotides
Building blocks of RNA, negatively charged.
Phospholipids
Basic structural components of cell membranes.
Fluid-Mosaic Model
Membrane structure with dynamic proteins and lipids.
Integral Membrane Proteins
Proteins that span the entire membrane.
Peripheral Membrane Proteins
Proteins that bind to membrane surfaces.
Ion Channels
Membrane proteins that allow ion passage.
Electrochemical Gradients
Concentration and charge differences across membranes.
Channel Proteins
Selective proteins facilitating ion or molecule diffusion.
Aquaporins
Channel proteins specifically for water transport.
Gated Channels
Channels that open or close in response to signals.
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive transport assisted by membrane proteins.
Carrier Proteins
Proteins that transport substances across membranes.
GLUT-1
Carrier protein that transports glucose into cells.
Active Transport
Movement of substances against their concentration gradient.
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Active transport mechanism for Na+ and K+ ions.
Na+/K+-ATPase
Pump using ATP to transport sodium and potassium.
Secondary Active Transport
Transport driven by electrochemical gradients.
Selective Permeability
Membrane's ability to control substance passage.
Passive Transport
Movement of substances without energy input.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in substance concentration across a membrane.
Transmembrane Proteins
Proteins that extend across the lipid bilayer.
Hydrophilic Residues
Amino acids that attract water inside channel pores.
Dynamic Mosaic
Fluid arrangement of proteins and lipids in membranes.
Membrane Structure
Arrangement of lipids and proteins in biological membranes.
Transport Mechanisms
Processes for moving substances across cell membranes.