Lec 8: Thorax, Lungs, and Respiratory
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
external respiration def
gas exchange at alveoli
internal respiration def
gas exchange at cellular level
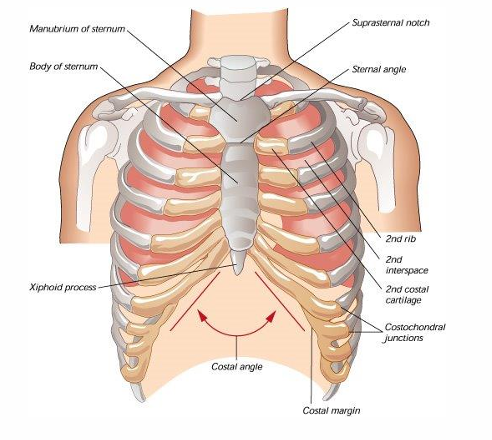
what makes up the thoracic cage
clavicles
manubrium (sternal angle at 2nd rib=angle of louis)
sternum, 12 pairs of ribs, 12 vertebra posteriorly
costal margin=inferior rib border
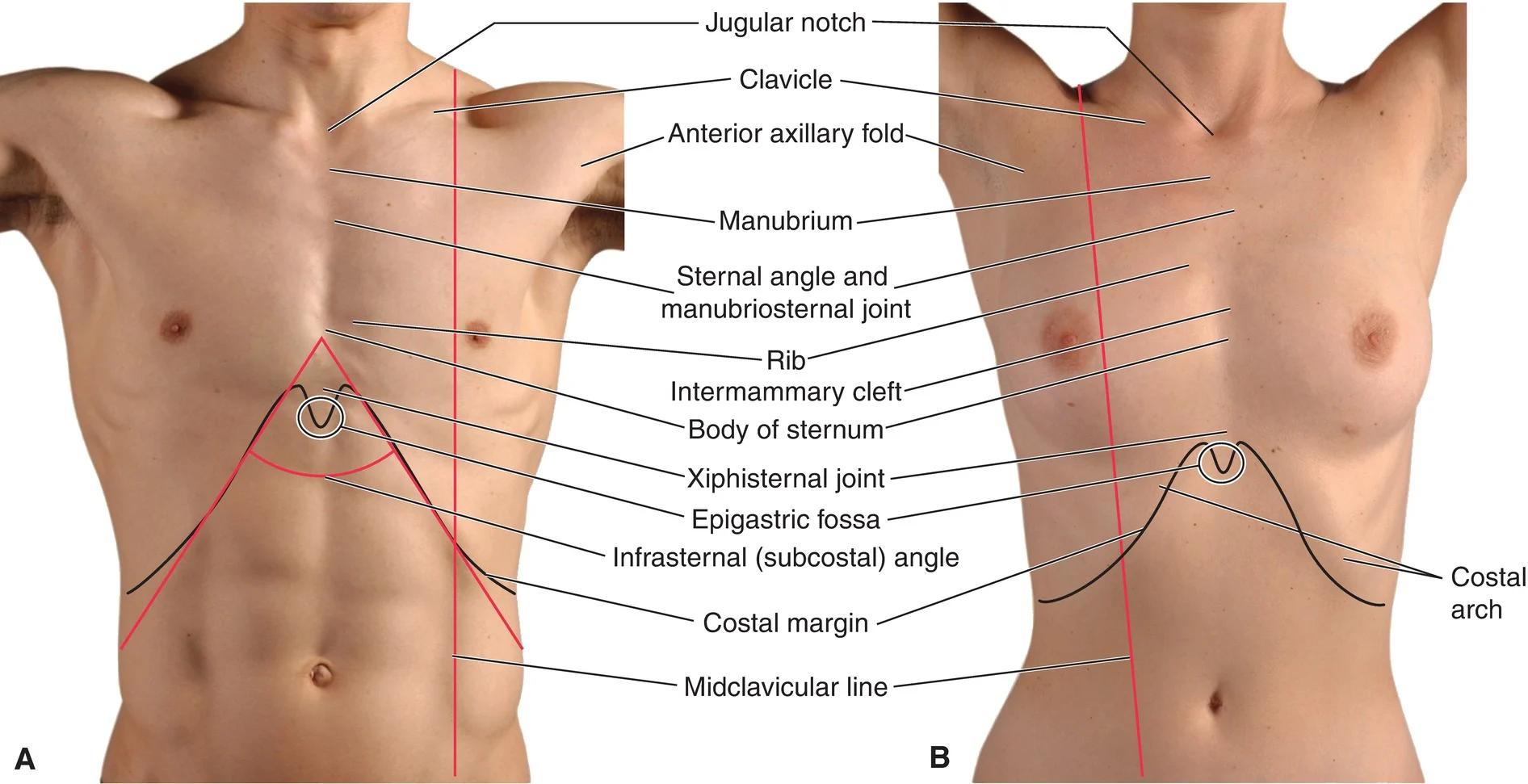
how do we count the intercostal/rib spaces
starting below the first rib
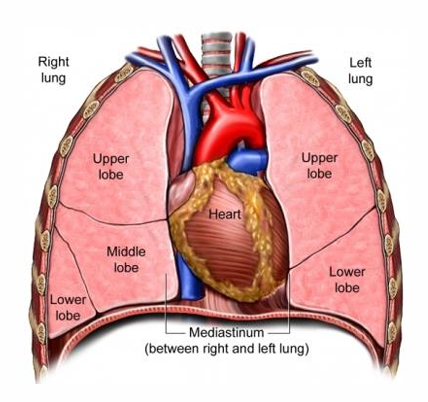
what makes up the thoracic cavity
heart
lungs
thymus
trachea
esophagus
aorta & great vessels
thymus
gland of immune system
shrinks post puberty, T-cell production
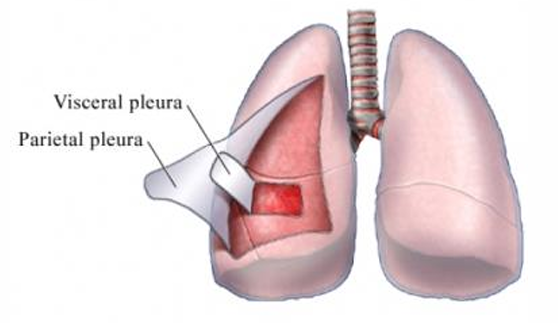
Visceral pleura
lines surface of lungs
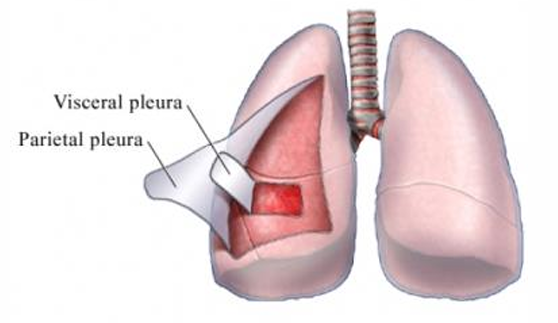
Parietal pleura
lines thoracic wall, mediastinum, diaphragm
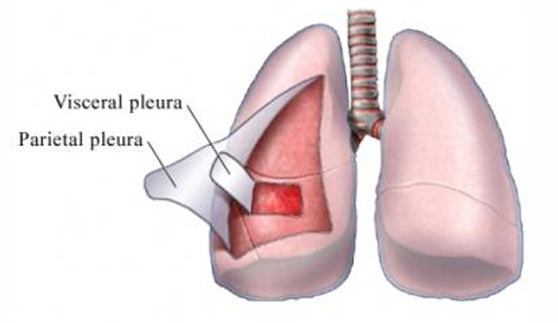
Pleural space
trauma can cause lung collapse (pneumothorax, hemothorax)
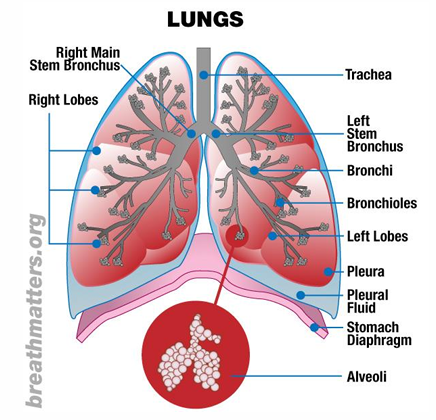
internal structures of the lungs
trachea bifurcates:
sternal angle (anteriorly)
T4 (posteriorly)
right main bronchus:
shorter, wider, more vertical than left
risk for foreign body aspiration
Inspiration (what happens)
triggered by rise in blood co2
inspiratory muscles contract (external intercostals/diaphragm)
lung fields descend by 2 rib spaces
500-800 mL of air intake
Expiration compared to inspiration in length
longer (2x) & passive
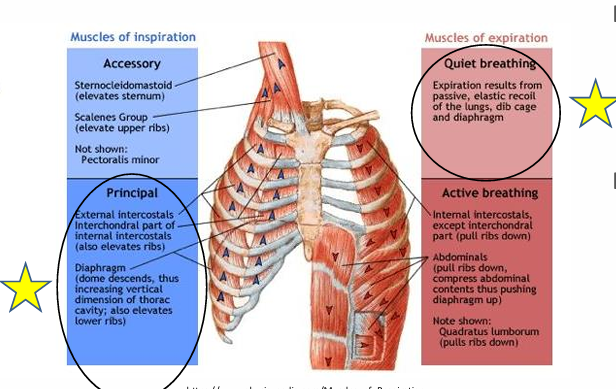
respiratory muscles for easy inspiration
external intercostal muscles
diaphragm
what is the diaphragm innervated by
phrenic nerve C3-C5, CN X
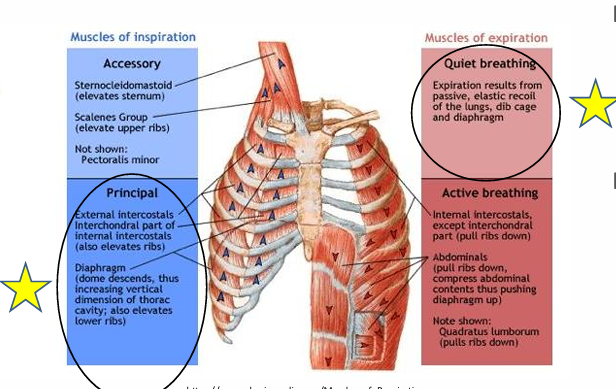
Easy Expiration
passive
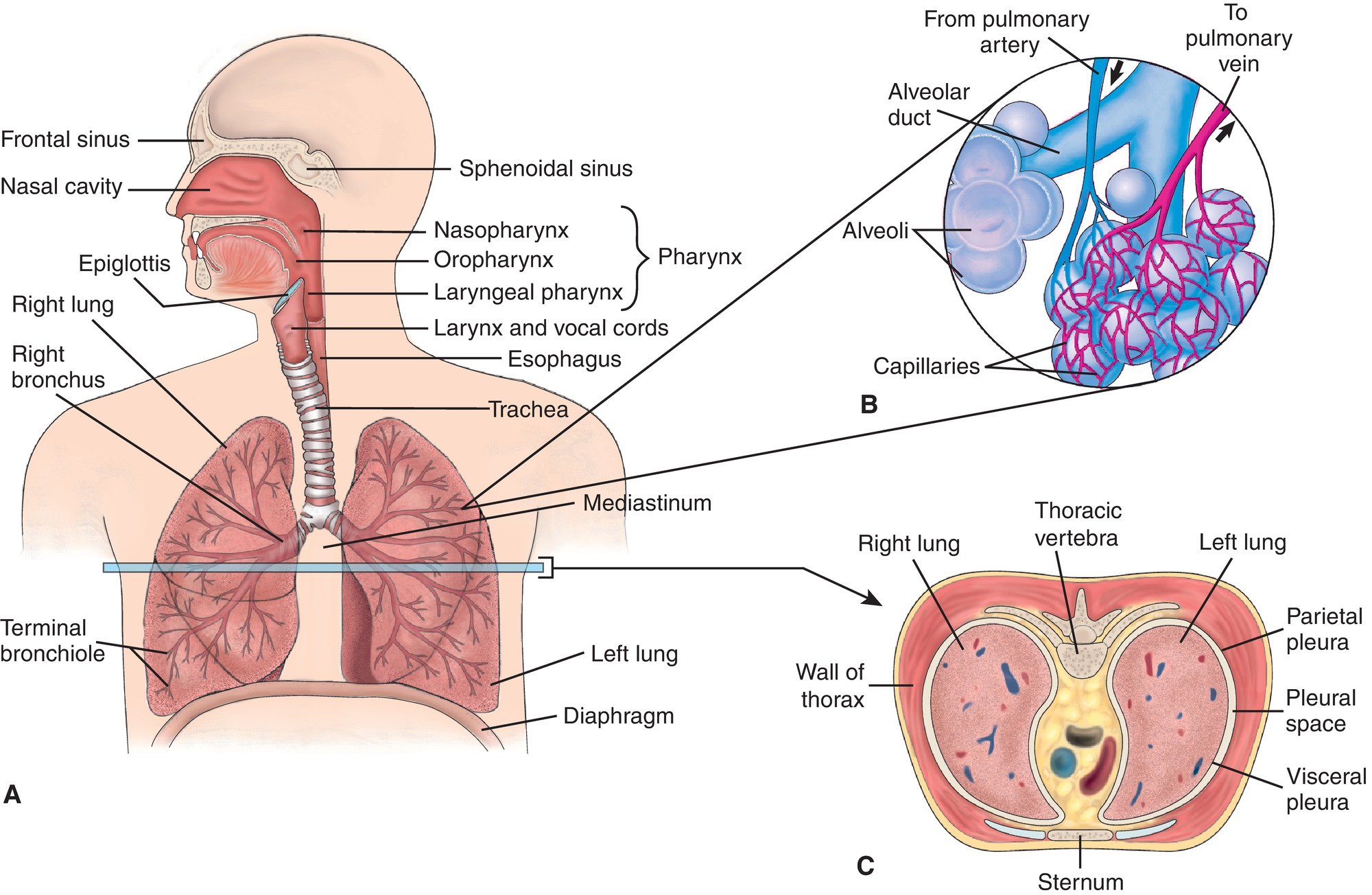
lower resp tract pic
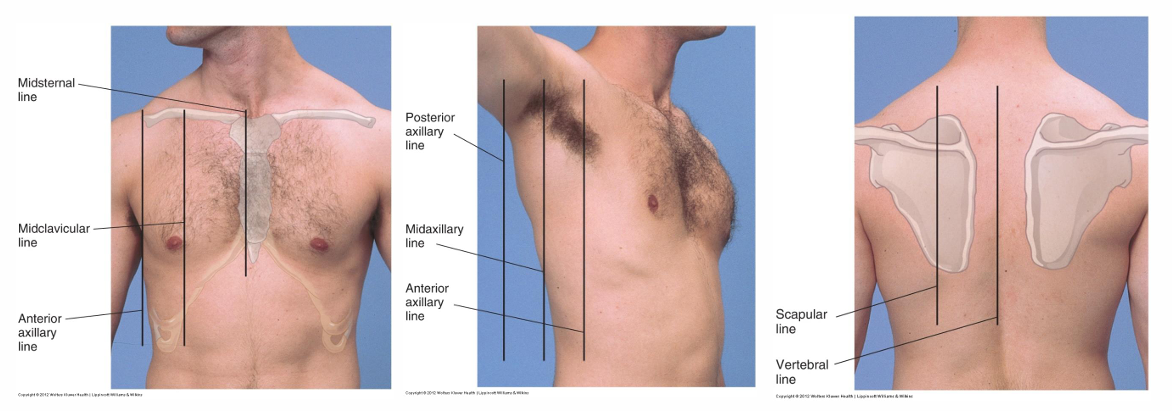
lung landmarking pic
midclavicular line=MCL
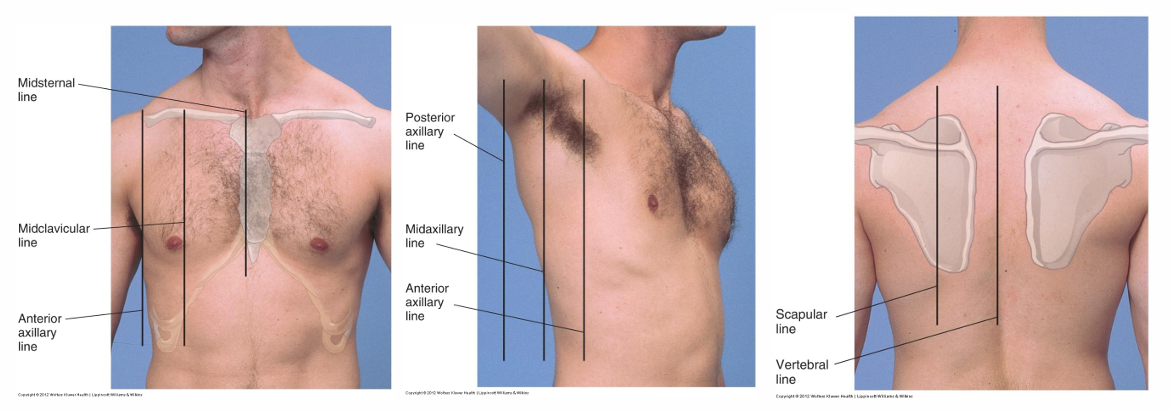
anterior Lung Fields:
base rests on:
supraclavicular=6th rib (midclavicular line)
8th rib (midaxillary line)
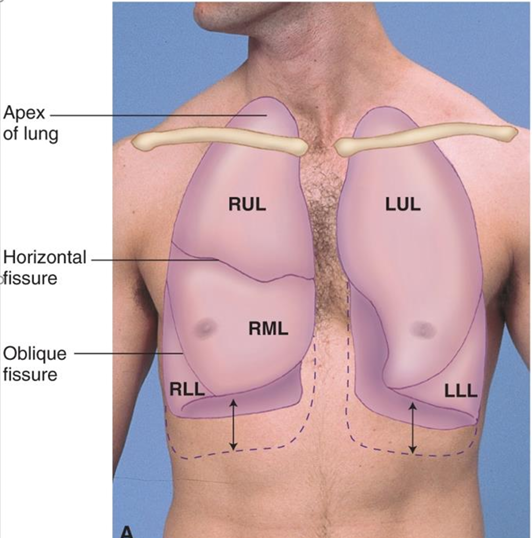
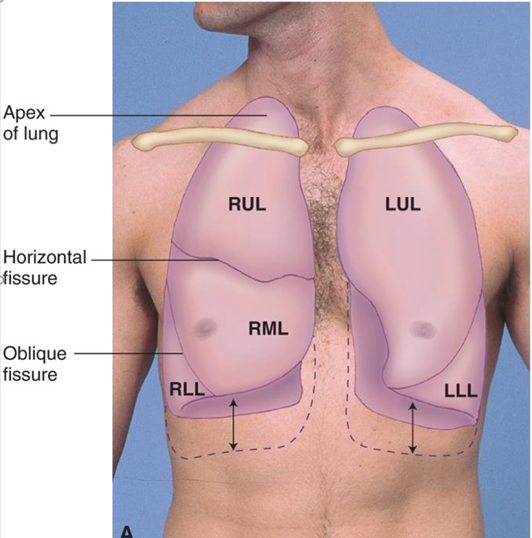
Right Upper Lobe (RUL) & Left Upper Lobe (LUL) dimensions
RUL apex 2.5 cm higher than LUL apex from liver displacing left lung
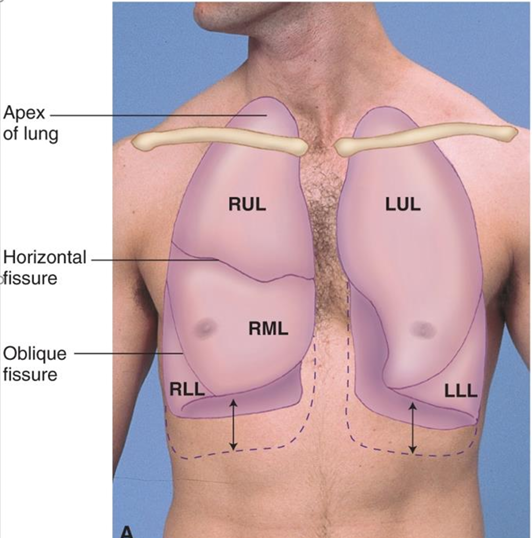
Right Middle Lobe (RML)
4th-6th rib (sternum), gives way to RLL at anterior axillary line
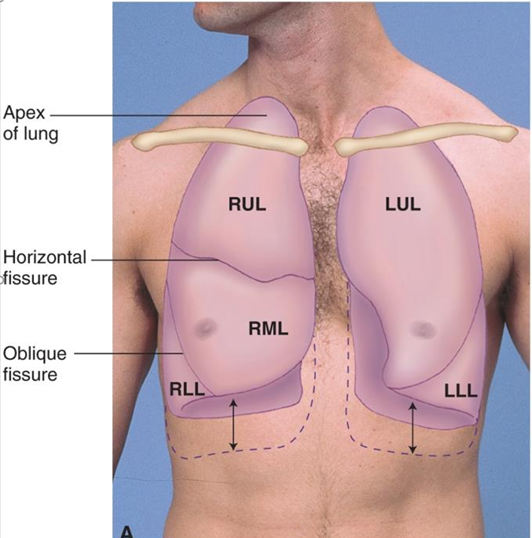
Lung fields aka where is the base and apex of the lungs approximately located
apex=C7
base=T10
with deep inspiration, base may extend to T12
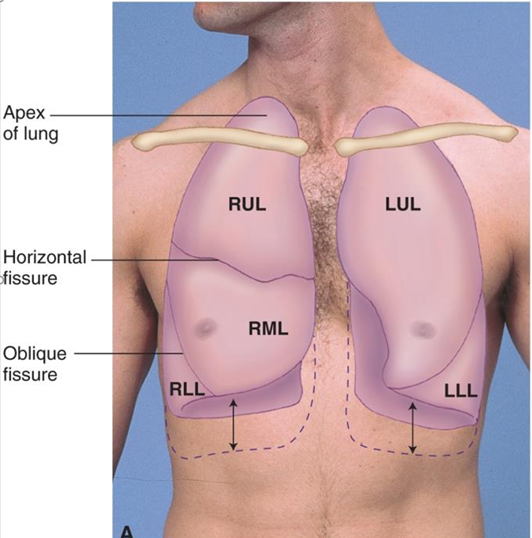
how can we calculate the size of the LUL
RUL + RML
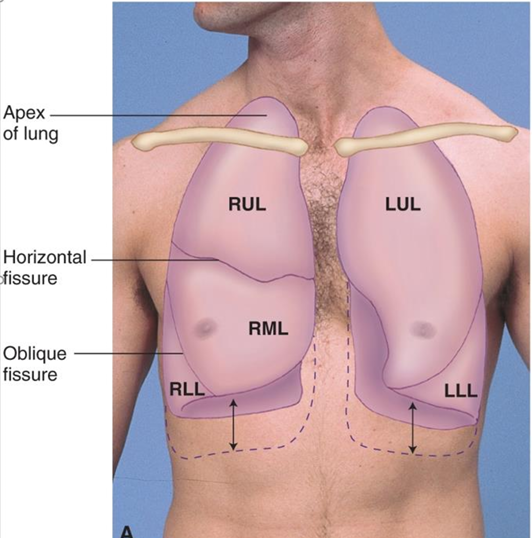
RLL size & position is …
equal to LLL size & position
LUL and RUL lung field
C7-T3
LLL and RLL field
T3-T10
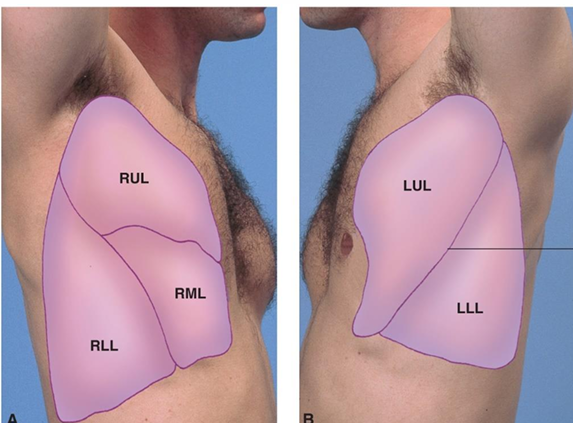
Lateral Lung Fields
upper/lower lobes bilaterally
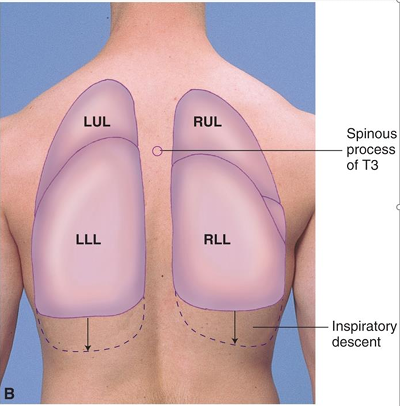
Posterior Lung Fields
assessment for upper/lower lobes bilaterally
what do we look for during health history
personal history
medications
family history
lifestyle/personal habits
occupational/environmental exposures
what do we look for during personal history
resp conditions=asthma, bronchitis, pneumonia, COPD, sleep apnea, TB
allergies
immunizations=influenza, pneumococcal
what do we ask about for lifestyle/personal habitss
smoking (cigarettes, cigars, vaping)
hobbies
Respiratory-Specific Symptoms we look for during ROS
tachypnea
dyspnea
shortness of breath
sleep apnea
pleuritic pain
cough
sputum: (mucoid? purulent? tenacious? – color, quality, quantity)/hemoptysis
wheezing
stridor
in what order do we conduct physical examination of the lungs
inspection
palpation
percussion
auscultation
f the patient has acute shortness of breath, immediate assessments include:
RR
pulse
BP
o2 saturation
lungs are auscultated
o2 administered
what do we look for with inspection
LOC
skin/mucus membranes
facial expression
posture
shape of thorax
resp movement/effort
rate, rhythm, depth, quality (VS)
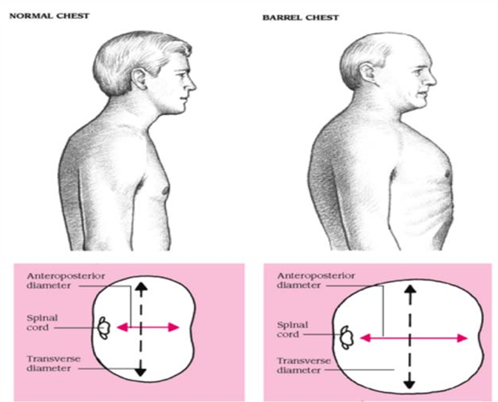
Thorax Shape expected findings
anterior-posterior (AP or sagittal) diameter should be less than transverse
ratio of AP:transverse=between 1:2-5:7
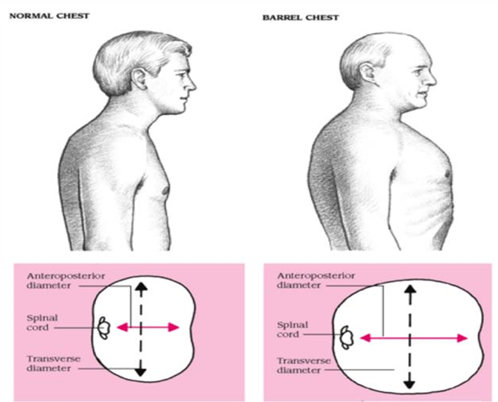
what are the findings indicative of a barrel chest
1:1 AP/transverse ratio
COPD
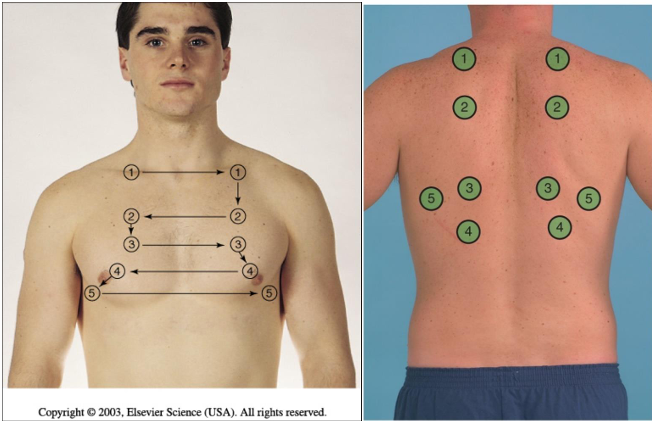
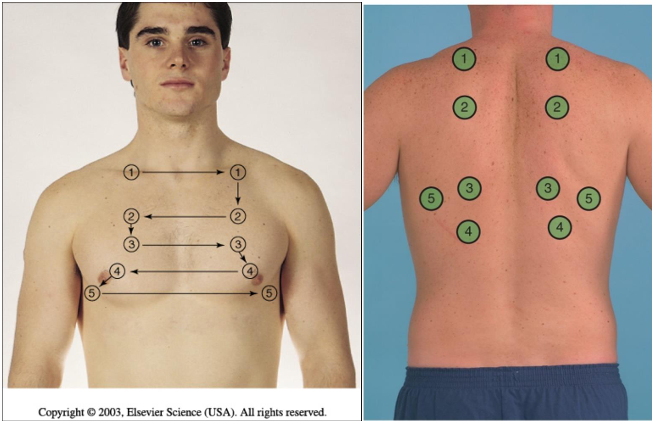
how do we conduct palpation of the chest
superior to inferior
1,2,3,4,5, pattern
left and right sides consecutively
anterior & posterior assessment
what do we note during palpation
tenderness
masses
lesions
crepitus=bubble wrap sensation=air trapping
when do we palpate for tactile fremitus
when there are concerns about lung disease
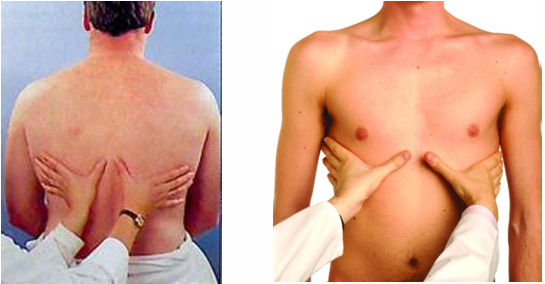
how do we palpate for tactile fremitus
ulnar surface of hand on chest wall to feel vibrations
pt repeats 99
variations in expected findings:
usually reduced at bases
most intense between scapulae
what does the finding of increased fremitus indicate
denser or inflamed lung tissue ex pneumonia
what does the finding of decreased fremitus indicate
air or fluid in pleural space ex pneumothorax
decrease in lung tissue density ex COPD, asthma
when do we palpate for chest expansion
concerns about lung volume from:
muscle weakness, fracture, infection, resp disease
combine with percussion for diaphragmatic excursion
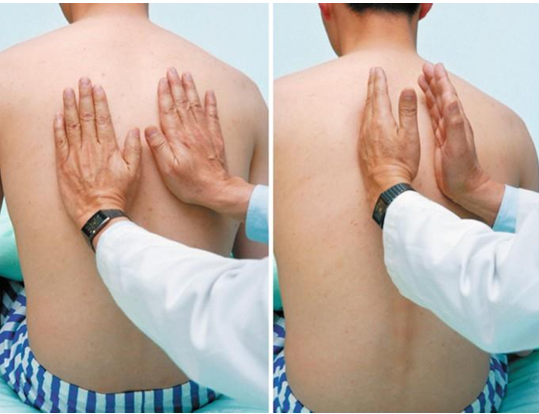
how do we palpate chest expansion posteriorly
place palm of hands at level of T9 and T10 posteriorly
slide thumbs medially to raise a skin fold between
ask pt to inhale deeply
skin fold should expand/disappear
note symmetry
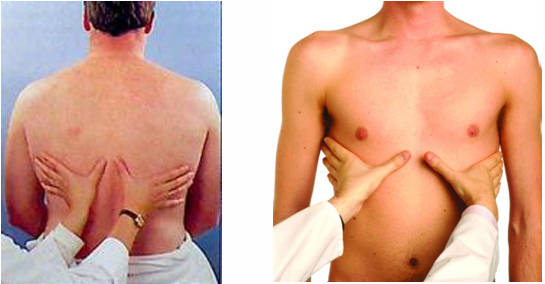
how do we palpate chest expansion anteriorly
hands at costal margin
what are the unexpected findings when testing chest expansion
low/asymmetrical
thumbs should move 5-10 cm
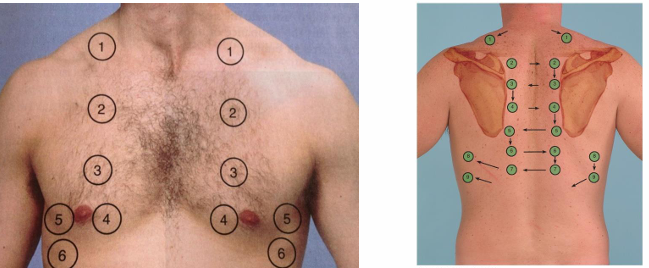
how do we conduct percussion
percuss from lung apex to lung base (avoid the clavicle and ribs)
compare side to side
anterior and posterior assessment
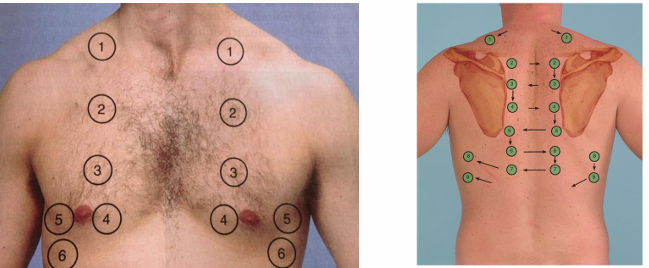
what are the expected findings of percussion
resonance throughout
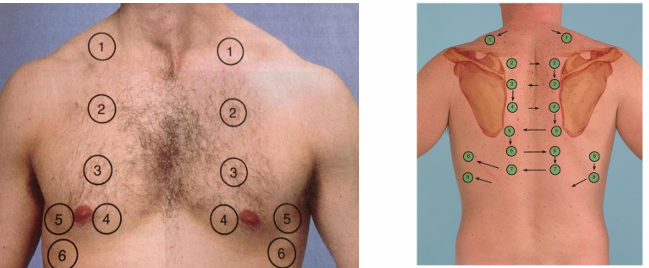
what are the unexpected findings of percussion
hyperresonance=air trapping ex COPD
dullness=fluid ex pneumonia, effusion
when do we percuss for diaphragmatic excursion
concerns with chest expansion
helps estimate how much diaphragm moves between inhalation/expiration
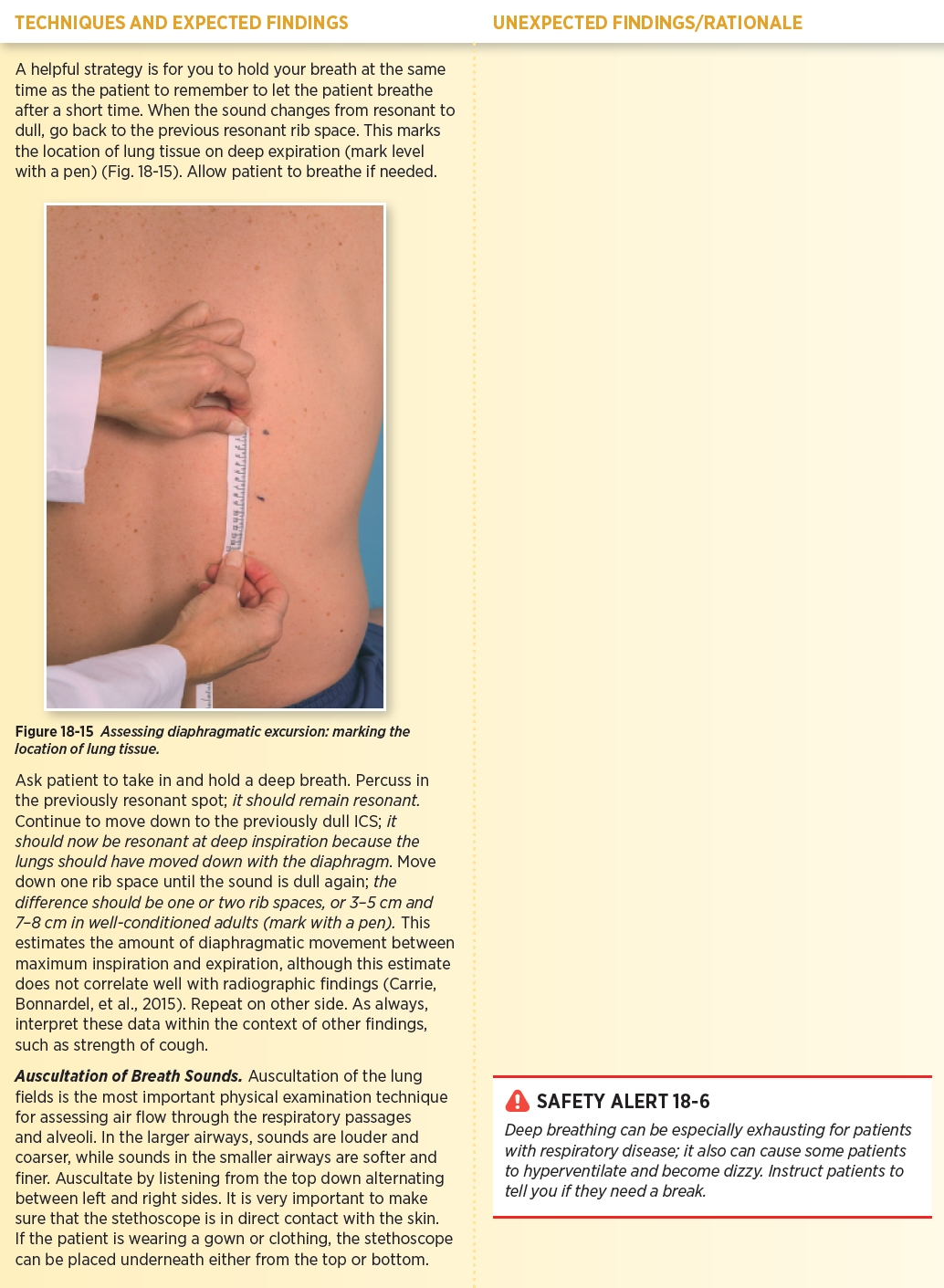
how do we percuss for diaphragmatic excursion
instruct to exhale and hold
percuss down mid-scapular line intercostal spaces
mark change to dullness
break (breath normally)
instruct to inhale and hold
percuss from first line down
should be at least 1-2 rib spaces (3-5 cm)
repeat on other side (can have unilateral paralysis)
what do we assess for during auscultation
intensity/pitch
quality
duration
adventitious sounds
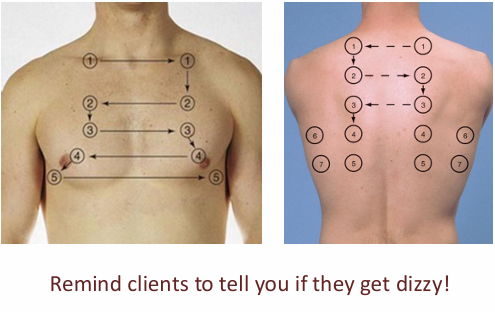
what tips should we remember for auscultation
not over clothing
diaphragm of stethoscope
ask pt to breath a little more deeply than normal, through their mouth
listen to one full breath per location
move side to side to compare symmetry
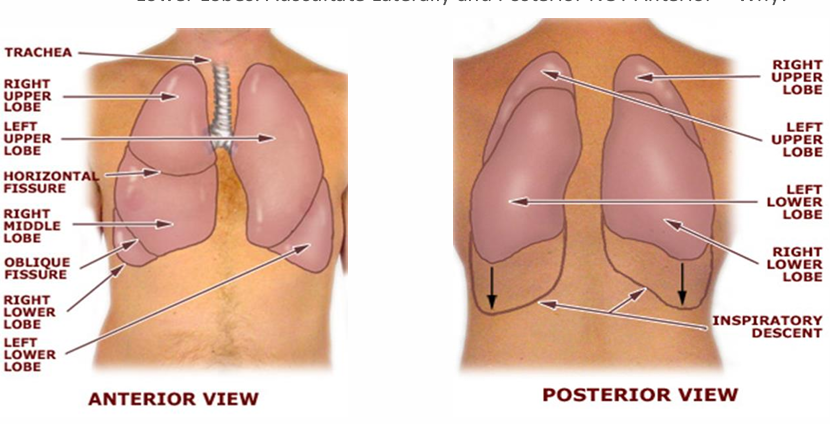
what do have to keep in mind when auscultating the lower lobes
auscultate laterally and posterior not anterior
because lower lobes make up majority of posterior
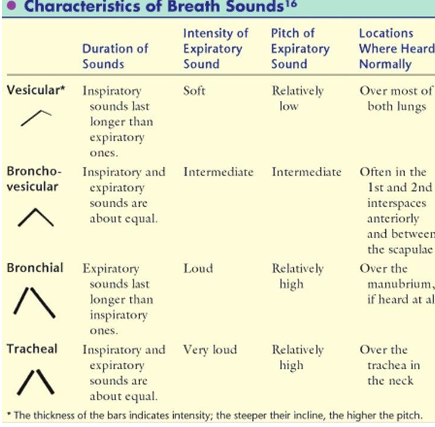
what are the diff normal breath sounds
tracheal
bronchial
bronchovesicular
vesicular
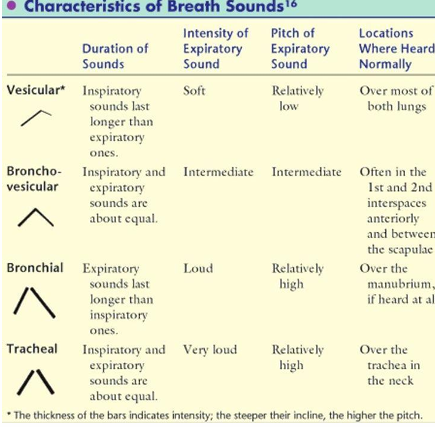
tracheal breath sound location
heard over trachea
I=E
very loud intensity
high pitch
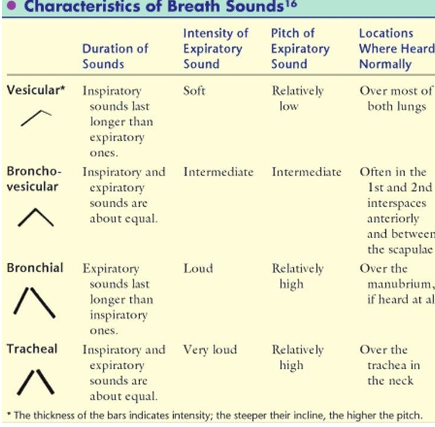
Bronchial breath sound
heard over sternum
I:E=1:2 or 1:3 aka expiratory longer
loud intensity
high pitch
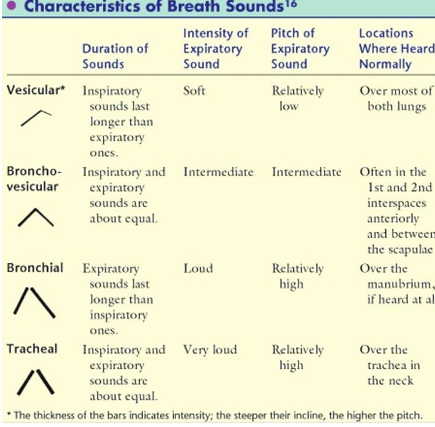
Bronchovesicular breath sound
heard 1st & 2nd intercostal space
I=E
medium intensity/pitch
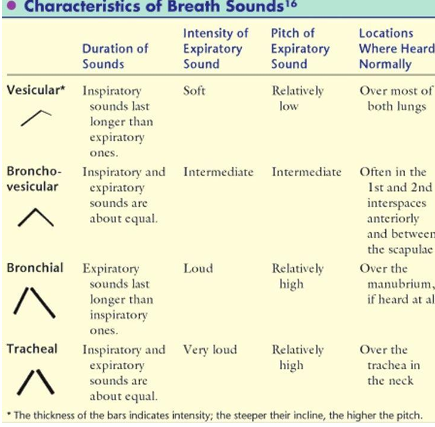
Vesicular breath sounds
heard over most lung fields
I:E = 3:1 or 4:1 aka inspiratory longer
soft intensity
low pitch
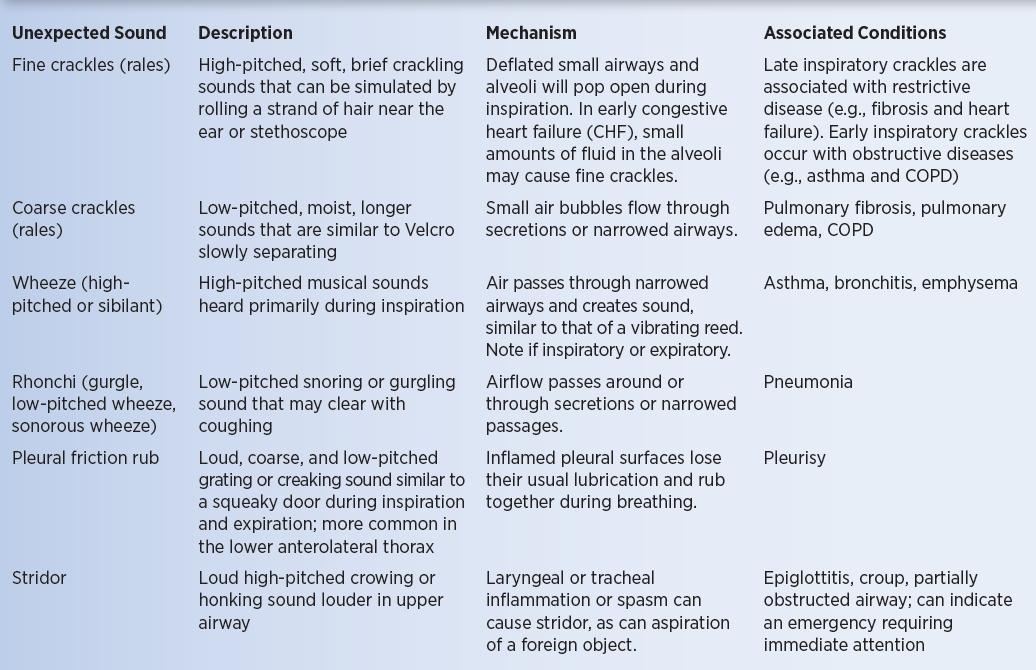
what are the adventitious Lung Sounds
wheezes
crackles
stridor
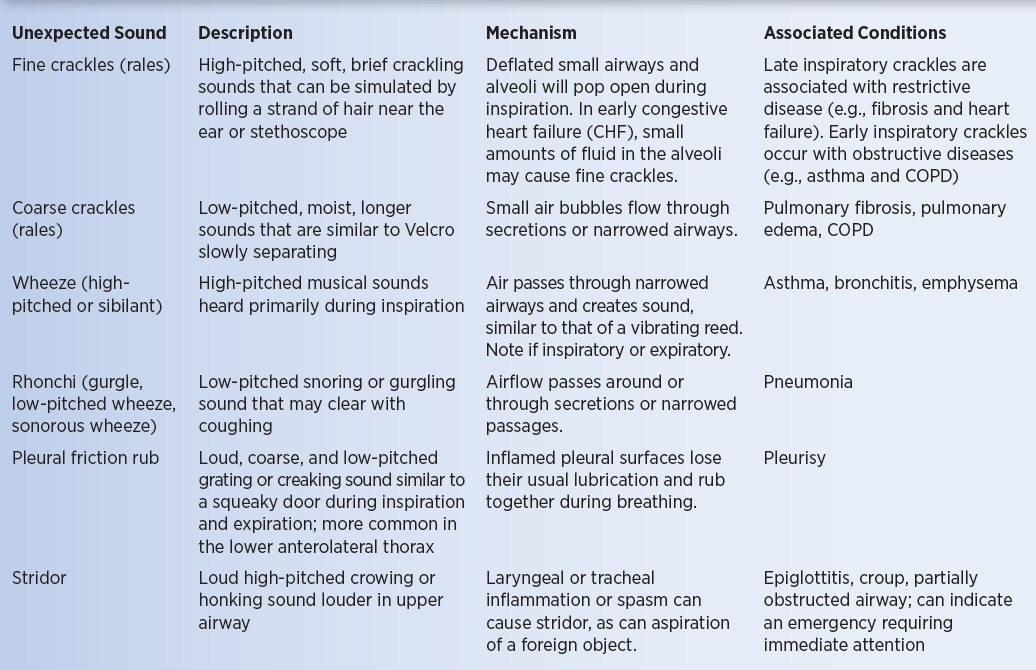
wheezes
continuous sound, high or low
more pronounced on expiration?
from narrowed airways
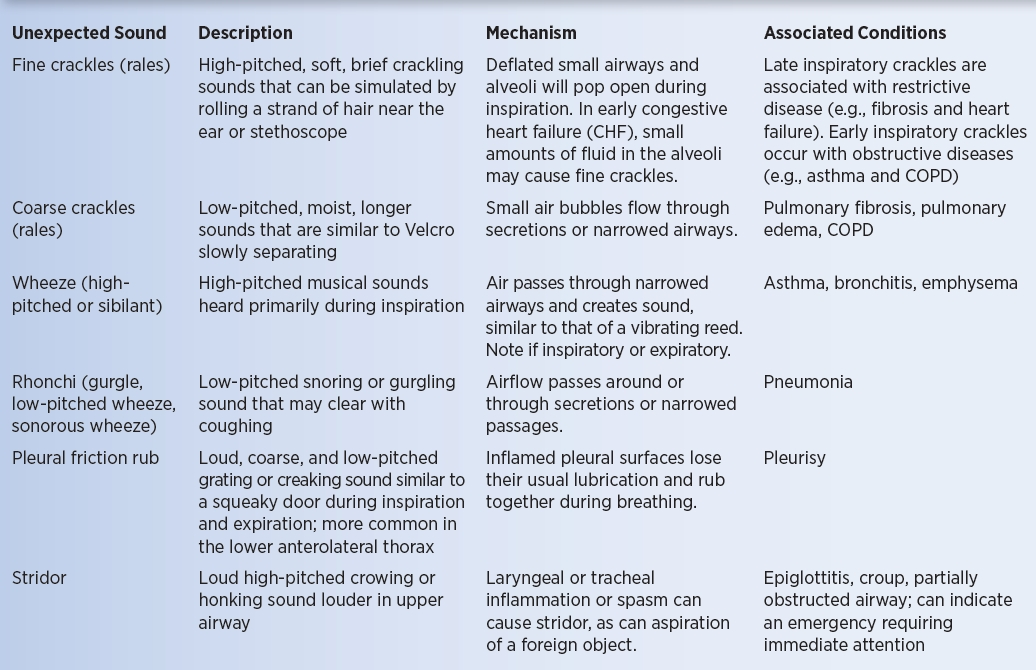
crackles
discontinuous brief popping sounds
more common during inspiration (small airways snapping open)
fine vs coarse
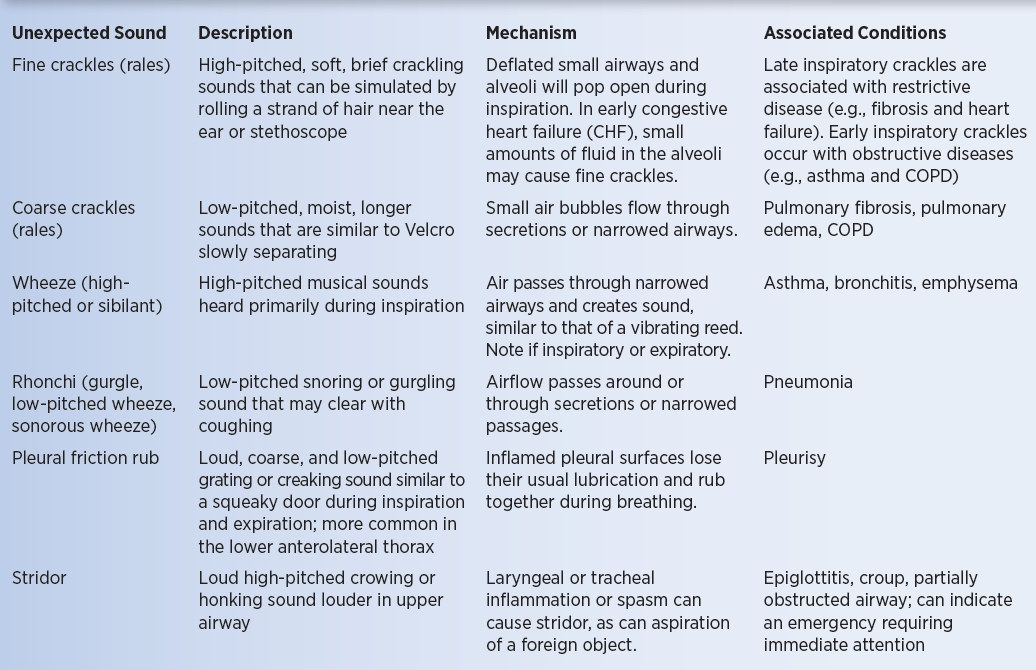
stridor
dont need stethoscope to hear it
from laryngeal/tracheal inflammation or foreign object
Respiratory Distress (Red Flags!)
short sentences, few words
irritability
positioning
work of breathing
irritability red flag
LOC alterations
unable to focus
positioning red flag
leaning forward
standing
sitting, tripod position
Work of breathing red flag
mouth breathing
pursed lips
nasal flaring
accessory muscle use (neck & intercostal muscles)
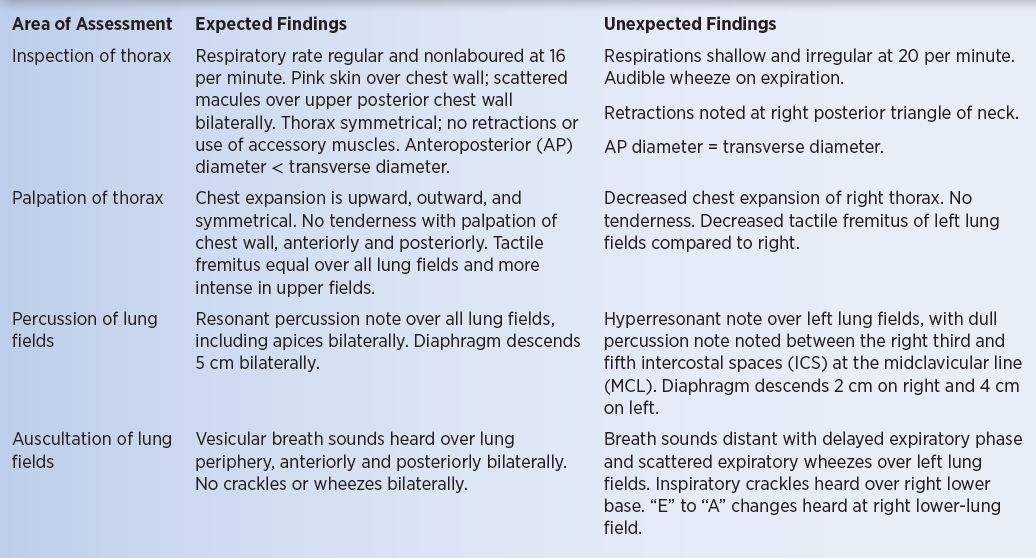
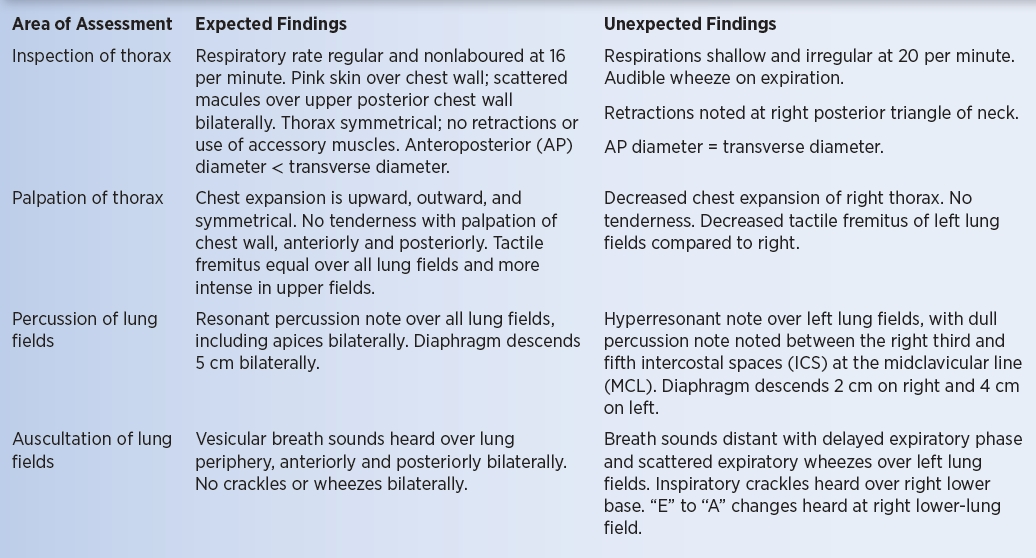
expected findings pic
what does mucoid sputum indicate, what does it look like
clear, white or grey=bronchitis
what does purulent sputum indicate, what colour is it
yellow or green=presence of WBC and bacterial infection
what does tenacious sputum indicate
thick from dehydration/cystic fibrosis
what does bloody sputum indicate
lung cancer or TB
what does sputum from heart failure look like
thin, frothy, slightly pink