Lecture 22- Hydrologic Cycle & Water Resources
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are the major water reservoirs on Earth?
Ocean - 97%
Ice Sheets and Glaciers
Groundwater - less than 1%
Lakes and rivers - 0.01%
Atmosphere - 0.001%
Biosphere - 0.0001%
Hydrologic cycle word definition
Earth’s water cycles between these reservoirs via the hydrologic cycle
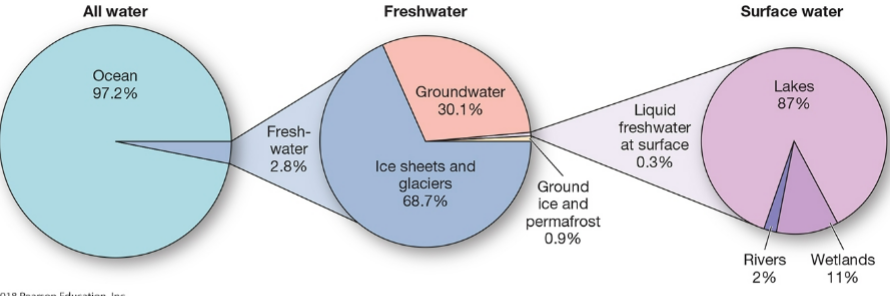
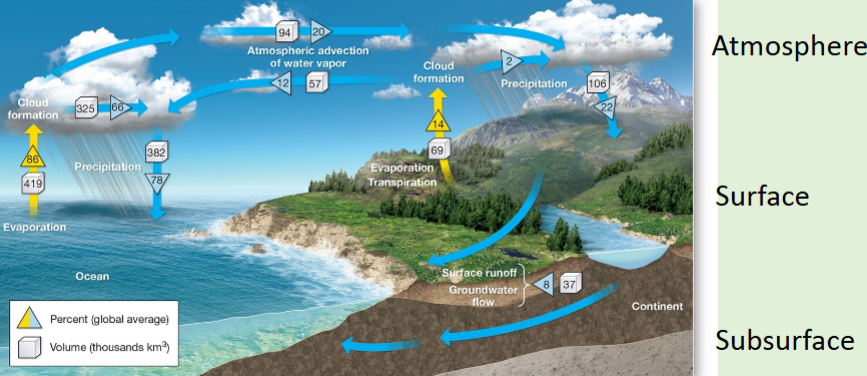
Image of hydrologic cycle
Role of the atmosphere
Solar energy and atmospheric circulation control precipitation patterns on Earth.
Where air rises → air moisture condenses → rain
Where air sinks → low moisture content → dry
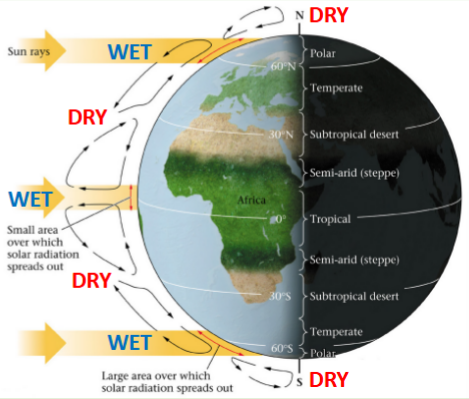
Role of the Atmosphere image
Surface Water
After precipitation, water may follow several pathways
Runoff: when water remains on top of the soil and flows downhill (eventually into streams/lakes)
Infiltration: some of the precipitation will soak into the soil moisture zone (into subsurface)
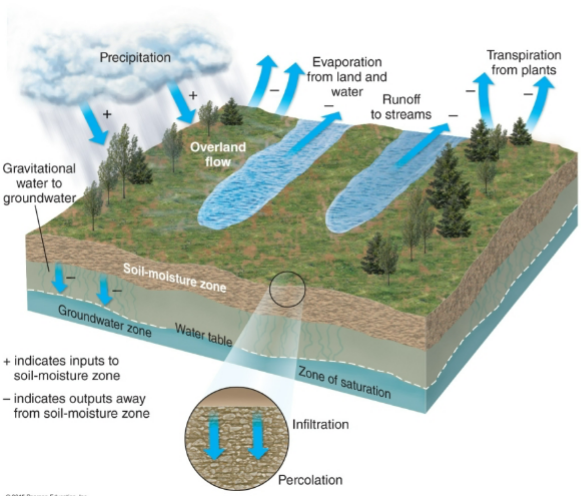
Subsurface Water
Upon infiltration: transpiration by plants → returns to atmosphere
May percolate downwards
Water percolating down can join the groundwater (saturated zone of soils & bedrock)
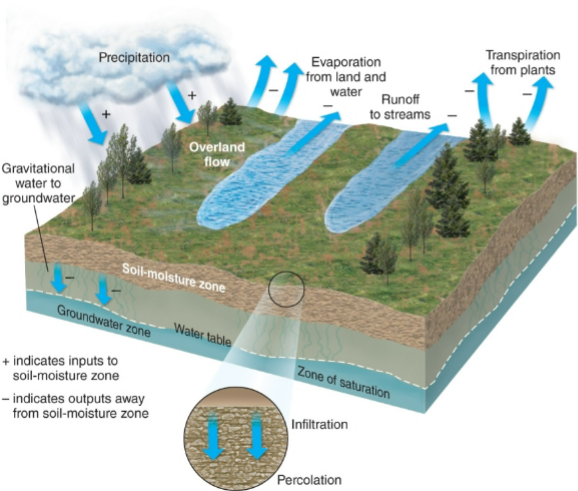
Two types of water resources that society uses:
Surface water (Streams, lakes, reservoirs)
Groundwater.
Put together, fresh water resources account for less than 1% of earth’s water - but has to supply the needs of people and terrestrial plants/animals (most of earth’s freshwater is frozen in icecaps and glaciers)
US household water use
over 80 gallons per person per day
Majority used for toilet and showers
Personal household use accounts for about 10% of this total
The thermoelectric power (usually recycled), irrigation, public supply are the industries using the most water.
Sufarce-water withdrawals
Total water withdrawals reflect the multiple uses of the nation’s water supplies
Increases with population, irrigation demands
Surface water supplies much of the West’s water use
Dams built by Bureau of Reclamation store water in reservoirs to keep continuous supply available
Major resources include the Rio Grande, Sacramento and Colorado rivers
Surface water case study: Colorado River
30+ million people depend on the water and electricity from the Colorado River system
Colorado River Compact, 1922: Agreement that regulates water distribution in the SW US.
CA’s Imperial Valley, east of San Diego, is desert country - rainfall averages to 3 inches per year
Aqueduct from Colorado River flows through and permits irrigation
The Colorado River often doesn’t make it to the sea today
Southwest water balance
Southwest US has been drying out
People continue to use water from reservoirs
Lake Mead- reservoir behind Hoover Dam
Water level has dropped 150 feet since 2000
Minimum elevation for power generation is 950 ft
Californio received enormous amounts of rain and snow in January and February 2017 via an atmospheric river
The rainfall diminished the drought in 2017, but dry summers bring it back
Drought
A period of shortage in water supply
May be due to decreased precipitations, increased heat & evaporation, or both