Biol121 Midterm 2 Lecture 9-W 2025
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Nucleic Acid
DNA/RNA
Central Dogma
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
Transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template, first step of gene expression
RNA polymerase
RNA synthesis
sigma factor (sigma 70), "The housekeeping sigma factor"
recognizes promoter at -10 to -35 region, guides core enzyme to initiate transcription, responsible for transcribing most genes in bacteria like E. Coli
Holoenzyme
Core enzyme + sigma factor
Consensus sequences of sigma 70
TTGAT TATT
Other sigma factors
Operate under variable conditions, perform same job as sigma 70.
Sigma factor binding step 1
1) Bind to DNA
Sigma factor binding step 2
2) Recruits core enzyme, scans for promoter
Sigma factor binding step 3
3) Unwinds DNA at promoter
Sigma factor binding step 4
4) Sigma factor released
Direction and explanation of RNA synthesis
5' to 3', bases complementary to DNA template, has the same sequence as non template, but with U's instead of T's
Rho-dependent transcription termination
Rho factor binds to mRNA, acts as a helicase, breaks off polymerase and mRNA off of DNA-> offers more precise control over termination
Rho-independent transcription termination
polymerase slows at pause site, GC Rich sequence forms hairpin loop on mRNA, U-A base pairs located downstream of pause site, very unstable, polymerase released, mRNA breaks off DNA
mRNA
tRNA
rRNA
sRNA
messenger RNA transfer RNA--> carries information from DNA to protein
Ribosomal RNA(Structural, non coding)
Small RNA-->postranscriptional regulation of specific Mrna into protein
Translation
Decoding of RNA to protein
The Genetic code is degenerate
• There are 64 codons, but only 20 amino acids, multiple codons can code for the same amino acid
Open Reading Frame(ORF)
Each codon has three different possible reading frames, Reading can start at the first, second or third nucleotide of the RNA. Stop codon is in the same reading frame as the start codon
transfer RNA
binds individual amino acids--> have 3 base anticodon, base pair to codons in mRNA,
aminoacyl tRNA transferases
Attach amino acid to tRNA-->"Charge the tRNA
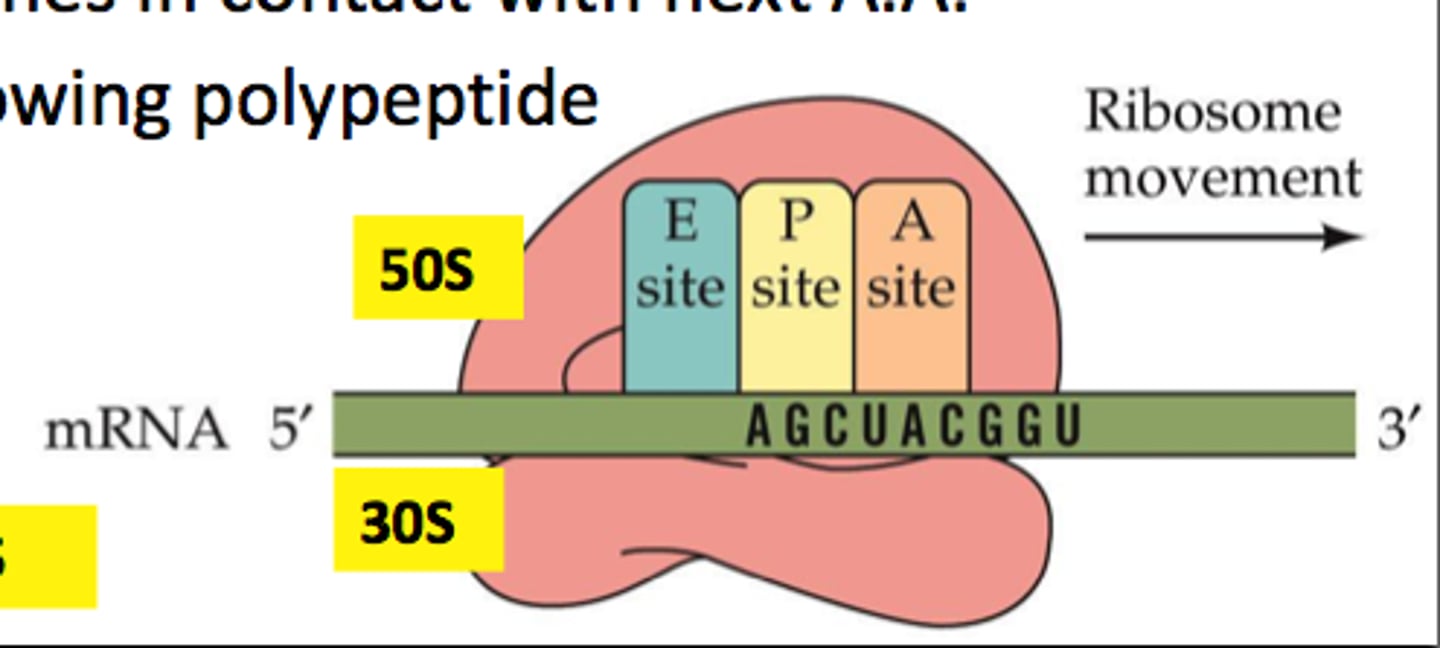
Ribosomes
2 subunit composition--> 30S(small), 50S(big) , bind 1 mRNA and 3 tRNA
Transcription and Translation in Prokaryotes
Both are coupled, nothing separating the two processes. Ribosomes bind mRNa while mRNA still being synthesized, multiple ribosomes can bind to mRNA--> super fast protein synthesis
Ribosome sites
A site: binds free Aminoacyl- tRNA
P Site: binds Peptidyl-tRNA
E Site: Exit site,
(Not really talked about this in depth in class)
translation intiation
Shine-Dalgarno sequence on mRNA, ALLOWS binding to 30S subunit., IF3 DOES the actual binding, IF1 blocks A site, IF2 brings in formylmethionine for start codon-Formyl, specific to bacteria, first codon tRNA binds directly to P site.
Way to remember what IF1 and IF2 do-->
- First site of ribosome is A site, we can call this site 1, therefore IF1 acts on site 1
-IF2 acts on site 2(P site), bringing in formylmethionine.
Think since the exam is multiple choice this might help even if you forget specifically what IF1 and IF2 actually do.
Translation elongation
1) Aminoacyl trna binds to A site
2)Peptide bond formed between new amino acid and growing peptide chain in P site
3) Ribosome shifts mRNA one codon
Translation Termination
Stop codon on mRNA enters A site, Protein release factor enters A site(NO trna), peptidyl transferase activated, releases completed proteins, Ribosome recycling factor enters A site and ribosome falls apart.