Digital Image Processing
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
is remotely sensed imagery valuable by itself
NO
what must happen to remote imagery to answer questions
it needs to be processed
what is the correlation between inputs and results
quality data = quality inputs = quality results
what are steps in digital image processing
preprocessing
image enhancement
image transformation
image classification and extraction
what are raw satellite images
images that have no corrections for atmosphere, topography, sensor irregularities and noise
what are the three levels of preprocessed data
level 0 = raw image
level 1 = some radiometric and geometric corrections
level 2 = some atmospheric corrections
what are radiometric corrections
correcting for sensor irregularities, unwanted sensor noise or atmospheric noise
what does preprocessing do
corrects data to represent the reflected or emitted radiation
what does radiometric corrections do
removes the influence of the atmosphere
what are two types of sensor irregularities
striping
dropped lines
what are three ways to correct atmospheric irregularities
ground target collection
pseudo invariant calibration sites
manufactured ground targets
how are geometric corrections done
linking unknown points with known ground control points
what are image mosaics
composite images consisting of at least two imagaes
what are benefits of image mosaics
increase the area covered
removes clouds
reduces off nadir angles
what must be considered for image mosaic analysis
time
why is image enhancement used
to improve the appearance of imagery to assist with visual interpretation
what are satellites designed to capture data from
a range of targets and conditions
what does image enhancement do
manipulates pixel values to display the optimum brightness rang and contrast for targets in the image
what is contrast enhancement
changing the original values so that more of the available range is used
what does contrast enhancement result in
increase in contrast between features
what is contrast
the difference in luminance or colour that makes object details distinguishable
what is the image histogram
the graphical representation of the brightness values that comprise an image
what is linear contrast stretch
identifies the minimum and maximum values of a histogram and stretches the data to fill the new range
what is histogram equalization stretch
assigns more display values (range) to frequently occurring portions of the histogram
why is histogram equalization stretching not linear
because it applies more values to areas with more points in an image
what is spatial filters
highlight or suppress specific features in an image based on spatial frequency
what is spatial frequency
variation in tone that appears in an image
contrast rough vs smooth spatial frequency
rough - textured area where changes in tone are ABRUPT
smooth - areas with little variation in tone (texture)
what describes high spatial frequency? low spatial frequency?
high = rough texture
low - smooth texture
contrast high vs low spatial frequency
high
data tends to look sharp and contain more detail
low
data tends to look smooth or blurry
what type of spatial filtering is used to remove elements from an image
low spatial frequency
contrast low vs high pass filters
low pass - smooths the data by reducing local variation and removing noise
high pass - sharpens the appearance of fine detail in an image
what are high pass filters used for
to highlight boundaries between features
what values does low pass filtering use from the window
mean or median values
what type of pass filtering removes extreme values from the data
low pass filtering
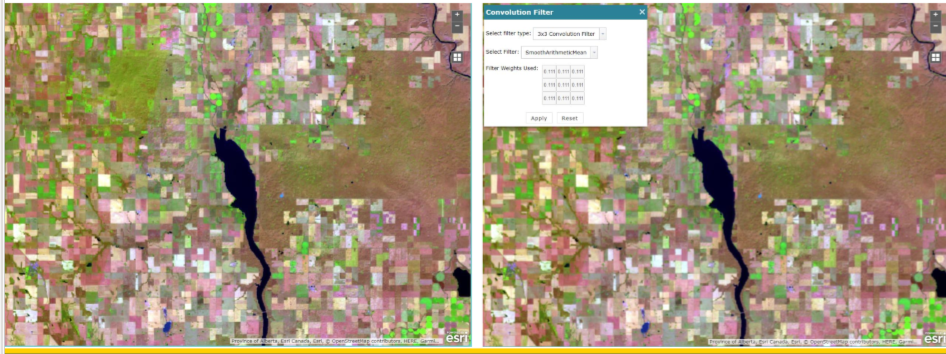
low or high pass filtering
low pass
what type of pass filters remove low frequency variation in cells
high pass filters
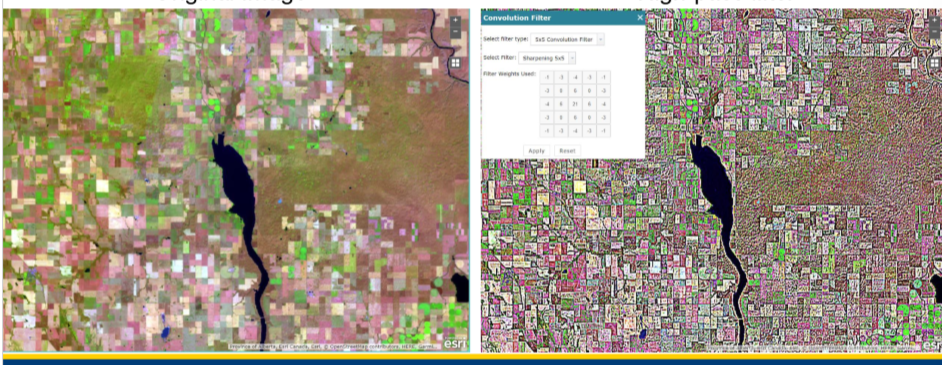
low or high pass filtering
high pass
what does edge detection filters do
highlights linear features such as roads, fields or boundaries
how do edge detection filters work
identify points in an image where brightness values change SHARPLY and use these points to create line segements
what is a directional filter
used to highlight features in a specific direction
what are directional filters used for
to detect linear features in geologic structures
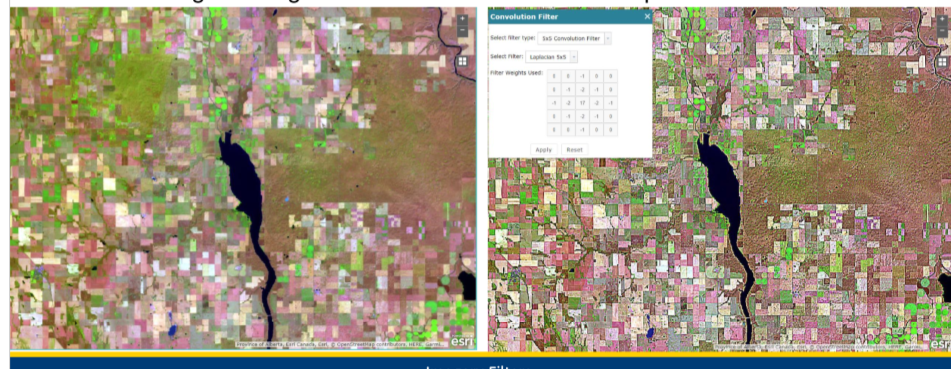
what filtering is this
edge detection filtering
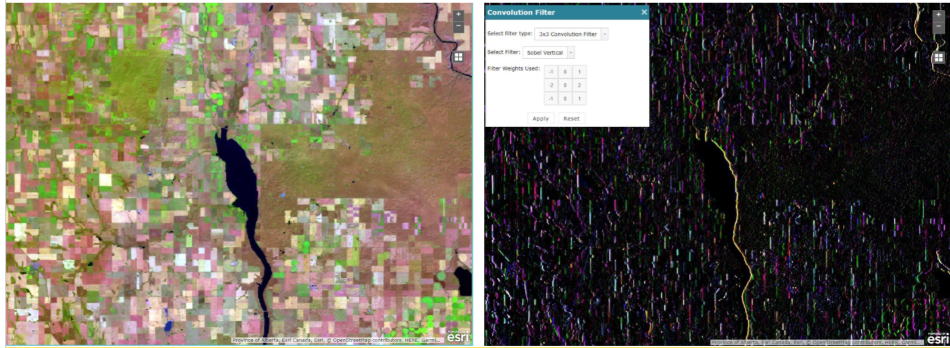
what type of filtering is this
directional filtering
what is image transformation
the generation of a new image from two or more sources and highlights a feature of intrest
what does image transformations involve
the combined processing of multiple spectral bands
where can the multiple spectral bands come from for image transformations
a single image OR multitemporal images
what is image subtraction
identifies changes that occur in the time between two images
what does image subtraction require
images to be geometrically registered
what is spectral rationing
ratioing data from two different spectral bands to enhance variation in the spectral reflectance between two spectral ranges
what do ratios reduce
the influence of variation in illumination
what are examples of spectral ratioing
NDVI and NBR
true or false: different multispectral bands are highly correlated and contain similar information
TRUE
what is principal component analysis
reduces redundancy and correlation between bands by compressing as much info as possible to reduce the number of bands
what are components
the new bands that result from statistical procedures (combo of correlated data in the image)
what is the benefit of PCA
maximizes the amount of information from the original data into FEWER bands
what is the relationship between features of interest and features that can be extracted
the middle ground (intersection) of the two will be the features available to work with
what are the three types of image extraction
pixel based classification
object oriented segmentation
deep learning
pixel classification
object detection
picture classification
what does pixel based classification result in
thematic map
what is pixel based classification
feature extraction based on the assumption that different features in an image have different spectral reflectance signatures
what is the preferred method doing pixel based classification
using reflectance (BUT DN values are also possible)
what is required for good pixel based classification
good spectral and radiometric calibration of sensors
contrast spectral and information classes in pixel based classification
spectral - groups of pixels that are uniform with respect to their brightness values in different spectral channels
information - categories of interest that are trying to be identified in the image (crop type, rock type…)
is matching spectral classes to information classes easy
NO
what is unsupervised pixel based classification
the clustering algorithms group pixels based on their properties but the classes DO NOT have labels
does the machine assign labels to the separated classes or the user in unsupervised pixel based classification
USER
what are pros and cons of unsupervised pixel based classification
pros
machine determines the different classes
simple method of classification
cons
unlabeled classes are not always easy to identify
results may be over or under classified
less accurate in complex landscapes
what is supervised pixel based classification
the analyst identifies features of each type of cover (water, trees, concrete…)
how does supervised pixel based classification work
the analyst identifies training samples for each type of cover and the classification process is used to assign class names to each pixel in the image
what is the output of a supervised pixel based classification
thematic raster
pros and cons of supervised pixel based classification
pros
considerable control over inputs
effective for distinguishing similar classes
high accuracy if data is selected well
cons
applied to the pixel level = output is noisy
accuracy is dependent on equality of training point s
subjective to human bias
what are object oriented approaches
groups pixels into representative polygons and the image is divided into homogeneous regions
how does object oriented approaches contrast from pixel based classifications
the classes are assigned to the ENTIRE object and NOT to individual pixels
can object oriented approaches be used in conjunction with only supervised classification
no - can be used with unsupervised as well
pros and cons of object oriented approaches
pros
incorporates shape, texture and contextual information
reduces noise that occurs using individual pixels
cons
computationally intensive
not effective for coarse resolution
requires a model
what is deep learning
based on neural networks, originating from research in AI
what is the primary technique for doing Deep learning
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
how is Deep learning done
labeled samples train the neural network by exposing the CNN to the samples and reinforcing connections that are correct and weaken those that are incorrect
what is the output of feature learning
raster with class for each pixel
pros and cons of deep learning
pros
incorporates spatial and spectral cues
pixel classification results are promising
cons
requires large number of samples for training
requires experienced data scientists
vulnerable to over and under training
what is data integration
the combining or merging of data from multiple sources to extract better/more information