Glial Cells - Neuroglia
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
What is a glial cell?
Cell which support and maintain the environment of neurones.
Involved in processes like providing nutrients, removing waste and forming myelin.
Primary types are astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia.
What is grey matter?
Consist of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and synapses. Involved in processing, cognition and primarily located in the outer layer of the brain (cortex)
What is white matter?
Composed primarily of myelinated axons
Responsible for transmitting electrical signals across different brain regions.
Myelin gives pale appearance to white matter
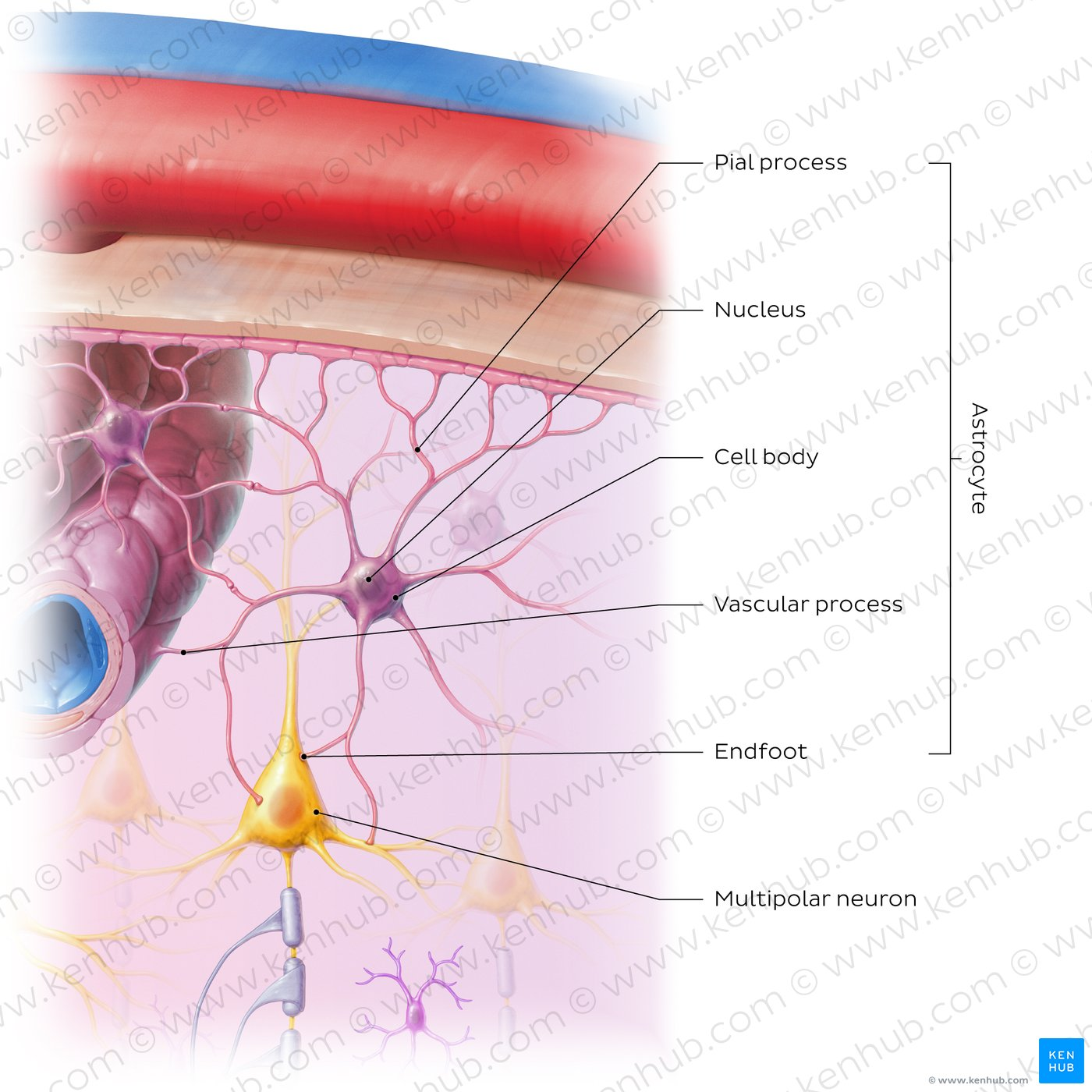
What is an astrocyte and what does it do?
Function
Provides structural and metabolic support for neurons.
Regulates blood-brain barrier and maintains extracellular environment (ion balance and neurotransmitter regulation).
Supports development of nerve cell and participates in synapse function + neuroplasticity.
Role in the brain
facilitates comms between neurons + contribute to remodelling + repair of neural networks.
Also involved in neurotransmitter uptake and recycling - e.g. glutamate + GABA.
Regulates vessel constriction + dilation (can sense metabolic rate of adjacent nerve cells)
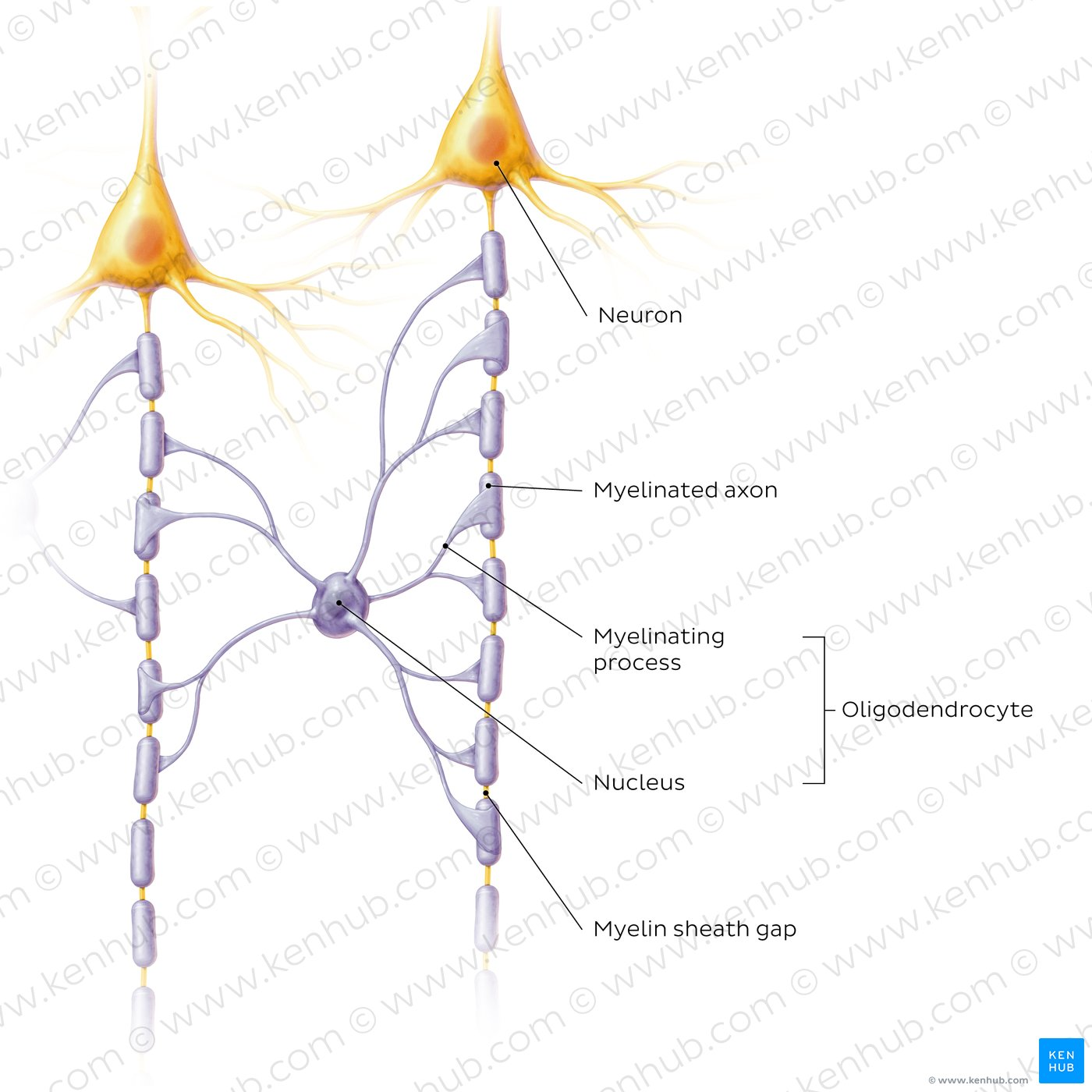
What are oligodendrocytes and what do they do? What does it look like?
Function
produce myelin in the CNS - this insulates axons and speeds up electrical signal transmission via saltatory conduction.
Each oligodendrocyte myelinates multiple axons, making up to 50 myelin sheaths
Oligodendrocyte body does not attach to the axon
Found in higher numbers on white matter
Appearance
round + dense nucleus
small cytoplasm with multiple orcesses
What is the difference between myelination in the PNS and the CNS?
in the CNS:
each oligodendrocyte extends multiple processes - helps to support up to 50 diff processes, can be distant or on the same axon
cell body + nucleus remain distant from the sheath it forms
Support is maintained by astrocytes - gives stable chem environment
in the PNS:
Schwann cell creates 1 myelin sheath
This attached cell body + nucleus directly to the axolemma - so no extended processes
Connective tissue and basal lamina gives support for myelin sheaths.