Free Energy and Thermodynamics
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Spontaneous Process
Process occurs without any ongoing outside influence
Non-spontaneous process
Occurs only with a continuous outside influence
Formal Definition of Entropy
Is a thermodynamic function that increases with the number of energetically equivalent ways to arrange the components of a system in a particular state
Formal Definition of Entropy
Entropy is a measure of the energy randomization, or energy dispersal, within a system
State of a System
A state is a description of a system at a given time
Microstates
Describes the exact arrangement of the components within a system
The second Law of Thermodynamics
A spontaneous process increases the entropy of the universe
Phase Transition
Both states of matter are present during a phase change
Melting
Phase change from a solid to a liquid
Freezing
Phase change from a liquid to a solid
Vaporization
Phase change from a liquid to a gas
Condensation
Phase change from a gas to a liquid
Sublimation
Transition from solid to gas
Deposition
Transition from gas to solid
System
Thing that is under investigation
Surroundings
Everything else with which the system can exchange energy
Entropy changes for system and surroundings
the second law of thermodynamics tells us that a spontaneous process increases the entropy of the universe
The entropy of the system can decrease as long as it is accompanied by a greater increase in the entropy of the surrounding
What is the equation for Entropy Changes in Surroundings
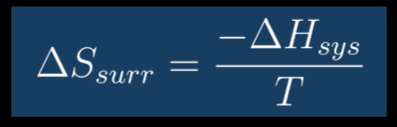
What is the Gibbs Free Energy equation?

Negative Delta G
Process is spontaneous
Positive Delta G
Process is not spontaneous
Gibbs Free Energy as Chemical Potential
Is useful because it is analogous to mechanical potential
systems tend toward lower free energy
Standard states
Are reference conditions for a given material
a degree sign is used to designate standard state conditions
What are the standard state conditions for a gas?
pure gas with a pressure of 1 bar
The pressure of a gas in its standard state used to be 1 atm, both standard are now in common use
What are the standard state conditions for a solids, and liquid?
Pure substance in its most stable form at a pressure of 1 atm and at the temperature of interest (usually 25 degrees)
What is the Standard Enthalpy Change for a Reaction ( Delta H rxn) equation?

Standard Molar Entropies
A measure of the energy dispersed into one mole of a substance at a particular temperature
Third Law of Thermodynamics
the entropy of a perfect crystal at absolute zero (0 K) is zero
What is the equation for Standard Entropy Changes for a Reaction (Delta S rxn) ?

What is the Calculations for Standard Free Energy Changes Using Equation for Gibbs Free Energy?

Standard Free Energy changes using Equation for Gibbs Free Energy
Standard enthalpies of formation standard molar entropies can be used to calculate the standard free energy changes using of a reaction