Test 1 - Karlee
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Problems I missed or need more practice on
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
pH of an acid
below 7, indicating higher concentration of hydrogen ions.
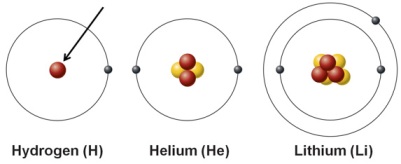
What is the arrow pointing to
Proton
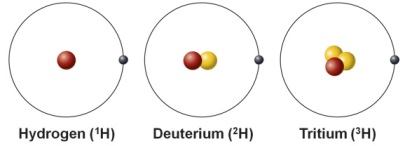
The three atoms shown represent three different
Isotopes ( same number or protons different number of neutrons )
pH of a base
above 7,indicating lower concentration of hydrogen ions.
Monomer of DNA
Nucleotides
Monomer of triglycerides
Fatty acids and glycerol
Monomer of proteins
Amino acids that link together to form proteins.
Monomer of Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides that serve as the building blocks for carbohydrates.
What are the 4 basic elements that compose approximately 96% of a humans body weight?
They are oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen.
Atomic Number
is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the chemical element and its properties.
Isotopes have the same number of - , but differ in the number of -
same number of protons, differ in number of neutrons
If the pH or temperature of the environment that contains a protein is altered dramatically, then the protein may
become denatured (looses shape and function)
Atoms of any given element differ from others due to
physical and chemical properties
Buffers
stabilize pH by resisting changes in acidity or alkalinity.
Universal solvent in the body
water
What type of mixture is a Colloid (emulsion)
Heterogeneous. A mixture where fine particles are dispersed throughout a liquid or gas and do not settle out.
Ionic bond
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond where one atom gives an electron to another atom. This creates two oppositely charged ions that stick together like magnets.
synthesis reaction
A type of chemical reaction where two or more reactants combine to form a single product. Ex: Hydrogen (H₂) + Oxygen (O₂) → Water (H₂O)
Acids vs Bases (physical properties)
acids are substances that produce hydrogen ions (H⁺) in solution, while bases produce hydroxide ions (OH⁻). Acids typically taste sour, whereas bases taste bitter and feel slippery.
What are the three basic steps involved in enzyme action?
The three basic steps in enzyme action are:
Substrate binding to the enzyme's active site,
Formation of the enzyme-substrate complex, and
Catalysis, leading to the production of products.
What is the major function of RNA?
to carry out genetic instructions for protein synthesis
What are the two fundamental roles of DNA?
to store genetic information and to replicate for cell division
What is the primary energy-transferring molecule in cells?
Adenosine Triphosphate
tight junctions
prevent molecules from passing through the extracellular space between adjacent cells
desmosomes
anchor junctions found in areas subjected to pulling forces
gap junctions
specialized intercellular connections that facilitate communication and the transfer of ions and small molecules between adjacent cells.
Osmosis
the diffusion of water across a membrane, passive membrane transport process
Endocytosis
active membrane transport processE
Exocytosis
active membrane transport process
Diffusion
Passive membrane transport process
Primary active transport
involves the direct use of ATP to move substances against their concentration gradient across a membrane.
Secondary active transport
involves the use of an electrochemical gradient created by primary active transport to move substances across a membrane.
Pinocytosis
“Cell Drinking”, Pinocytosis helps the cell take in fluids and dissolved nutrients from the outside environment.
The cell forms small vesicles to sip extracellular fluid.This process allows cells to sample their external environment and obtain necessary solutes for cellular function.
Phagocytosis
“Cell Eating”, allows cells to engulf and digest large particles ex: white blood cells digesting bacteria by trapping them in a vesicle and breaking them down with enzymes
DNA is replicated during the
S Phase
A Gene is best defined as
A segment of DNA that carries instruction for the production of one polypeptide chaini
DNA is used as a template to make
RNA during transcription
atomic number
number of protons
How do you tell if an element is chemically inert?
if it has a full valence shell of electrons.
mass number(protons+neutrons) - atomic number(protons) =
number of neutrons
in a solution, the solute is the substance present in
the least amount, the smallest quantity.
mixture vs compound
no chemical bonding occurs between the components of a mixture
colloid
A colloid is a mixture where tiny particles are spread out evenly, but they don’t settle to the bottom like in a suspension.
Examples of Colloids:
Milk (fat droplets in water)
Whipped cream (air in cream)
Fog (water droplets in air)
Gelatin (protein in water)
solution
A solution is a homogeneous mixture where one substance (the solute) is completely dissolved in another (the solvent).
Example:
Salt water = salt (solute) + water (solvent)
The salt dissolves completely into the water.
Each shared pair of electrons represents a
single covalent bond