Biology - Microbiology (George)
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What is a microbe?
Microscopic organisms, including bacteria, fungi and protoctista as well as viruses that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
How many cells do bacteria have?
They are unicellular. They have one cell.
How do bacteria reproduce?
By binary fission
Bacteria can survive in…
very harsh conditions
Some bacteria photosynthesise to make…
their own carbohydrate, but most live in or on their food.
Examples of harmful bacteria are…
E.coli, Pneumococcus, Lactobacillus
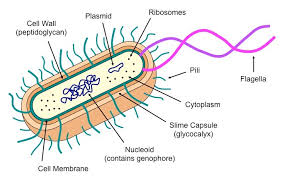
What type of microbe is this?
Bacteria
Viruses are living organisms. True or False?
False. Viruses are not living organisms.
What is the only characteristtic of life viruses display?
Reproduction although this is only carried out inside a host cell.
Viral infections can only occur in animals. True or False?
False. Viral infections can occur in all types of living organisms.
What are some examples of viruses?
Influenza, Human papillomavirus (HPV), Covid-19, HIV
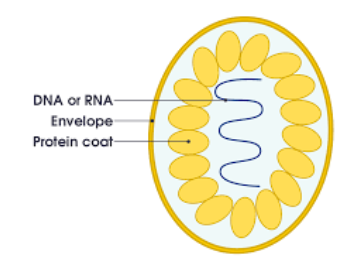
What microbe’s structure is this?
Virus
What is the difference between the terms ‘Covid-19’ and SARS-CoV-2?
Covid-19 is the disease and SARS-CoV-2 is the virus.
How much smaller is SARS-CoV-2 compared to a grain of salt?
x10,000
Where do coronaviruses get their name from?
The spikes around the outside of the viruses which look like crowns, corona meaning crown-like
What do the spikes do in a SARS-CoV—2 infection?
Enable the viruses to stick to molecules on the surface of your body.
What does the word genome mean?
The complete set of its genes.
What is the genome of SARS-CoV-2 made of?
RNA
How many proteins does SARS-CoV-2 have?
25
What do the viral proteins in SARS-CoV-2 do?
They hijack the cell’s machinery to turn it into a virus-producing factory. Switch off many of the cell’s defences to speed up the replication.
How does SARS-CoV-2 spread?
Spreads by droplet infection when you sneeze or cough and somebody breathes in the infected droplets.
What does zoonotic mean?
Means the virus can jump from animals to humans.
Where is SARS-CoV-2 most likely to have come from?
A bat
What animal was suggested as a host species for SARS-CoV-2? Why do we think this is not the case
The Pangolin although the coronavirus they carry is not entirely genetically similar to SARS-CoV-2.
Name a unicellular fungi
Yeast
Name a multicellular fungi
Mushrooms
What is a fungi’s cell wall made from?
Chitin
How do fungi feed?
Extracellularly (outside their cells) by releasing digestive enzymes onto their food.
What is the way fungi feed called?
Saprophytic Nutrition. Fungi are saprophytes.
What diseases can fungi cause?
Athletes foot, ringworm
What can yeast be used to make?
Bread and beer
What does Penicillium produce?
The antibiotic Penicillin.
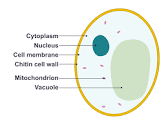
What type of fungi is this?
A yeast cell
Some Protoctista resemble animal cells and take in then digest solid food. Give an example
Amoeba
Some Protoctista possess chloroplast and photosynthesise like plants. Give an example
Seaweeds and single-celled algae such as Euglena or Chlorella.
Some Protoctista can cause diseases. Give an example.
Malaria (caused by Plasmodium) and dysentery (caused by Amoeba)
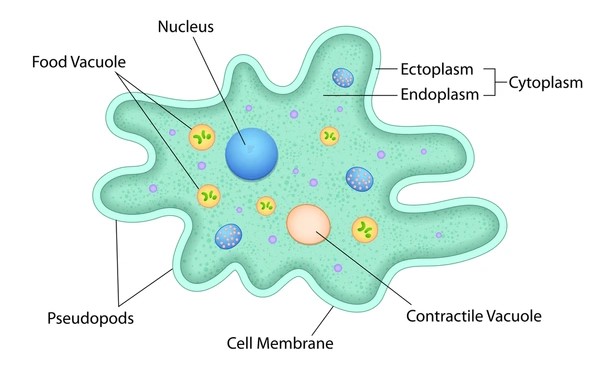
What type of Protoctista is this?
An Amoeba
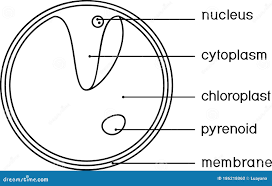
What type of Protoctista is this?
Chlorella
Who made the microscope that enabled Louis Pasteur do his research?
Joseph Jackson Lister
What material helped Lister make the microscope for Louis Pasteur?
Better quality glass
How much magnification did Lister’s new microscope provide?
1000x
What is pasteurisation?
Killing bacteria growing in beer by heating it.
Why did the winemakers and brewers of Lille ask Louis Pasteur to help?
They wanted to know why their beer was going sour.
How did Pasteur resolve the problem of the winemakers and brewers in Lille?
He heated their beer to 55 degrees C to kill the bacteria.
What was the special equipment Pasteur used to disprove spontaneous generation?
Swan-necked flask
What did the swan-necked flask allow Pasteur to show?
That things only rotted because tiny microorganisms had got into them.
What did the swan-necked flask help Pasteur to disprove?
Spontaneous generation - the idea that living things can appear from non-living material.
If conditions are favourable, how frequently can bacteria reproduce asexually?
Every 20 minutes
What do bacteria have that balances their fast reproduction rate?
A high death rate
Why should you not seal a petri dish completely?
Because microbes need oxygen to grow
What does pathogenesis mean?
How a disease develops
What does sterile mean?
Free from bacteria or other living microorganisms
Why shouldn’t you take the lid off the petri dish once the microbes have grown?
The microbes could be harmful and contaminate the air and surfaces around us
Fungi are…
furry
Bacteria are…
shiny
What works best in combating a virus?
White blood cells
What is a disease?
A sickness of the body or mind
What are infectious diseases caused by?
Microbes that invade the body
What are diseases that exist in an area permanently called?
Endemic
What is an epidemic?
An outbreak of a disease which attacks many people at the same time and may spread through several communities
What are pandemics?
Diseases that spread over the while world
Name 2 infectious diseases?
Chickenpox, Influenza (flu)
Name 2 inherited diseases?
MND, Cystic Fybrosis
Name 2 diseases caused by a poor diet?
Scurvy, Type 2 diabetes
Name 2 diseases caused by harmful chemicals?
Asthma, Lung cancer
What are antibiotics?
A medicine that kill bacteria
What does it mean if a bacteria has developed antibiotic resistance?
It has the ability to defeat the drugs taken to kill it.
What is the zone of inhibition?
An area where no bacteria grows
What are disinfectants?
Used to kill microbes on inert surfaces. Bleach would be an example. Humans shouldn’t ingest them.
What are antiseptics?
Used to kill microbes on living tissue and prevent infections. Humans shouldn’t ingest them.
What are antivirals?
Target viruses by stopping them from reproducing. Humans can ingest these.
What is sepsis?
A condition where parent’s wounds would rot
What did von Leibig think sepsis was caused by?
Exposing flesh to oxygen.
What did Lister think sepsis was caused by?
Microbes in the air
What is an amputation?
When an infected limb is chopped off to stop further infection.
Why were so many amputations needed in Lister’s time (19th century)
Because they didn’t know how to treat the infections. The hospitals were a lot dirtier which causes the infections.
Why did Lister use carbolic acid on his patients infected wounds?
Because he saw it stopped cattle getting infections from sewage so it might do the same for humans.
Why do we now refer to carbolic acid as antiseptic?
Because it kills the sepsis microbes and stops them from spreading to other body parts.