Exam 3 patho: Renal Failure
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Renal failure
When the kidneys fail to remove waste from the blood stream, and are unable to regulate fluid, electrolyte balance, and pH
Acute renal failure (ARF)
Rapid decline in kidney function
few hrs to days
Recoverable
Who is at risk for ARF?
Elderly
bc they are at risk for hypervalemia (excess K+ in BS)
Sepsis
this will take blood away from the kidneys and the BP will decrease and the kidneys won’t get the BF they need
Sock
Trauma
What is the result of acute renal failure?
Rapid decline in kidney function = inability to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance, and the ability to excrete it all
AKI manifestations
Azotemia
GFR decreases (glomerular filtration rate)
Azotemia
Accumulation of nitrogenous waste
3 types of renal failure, categorized by where the failure is occuring
Prerenal failure
Intrarenal failure
Post Renal failure
Prerenal failure
Decreased blood flow to the kidneys due to hypovolemia, hypotension, decreased CO, and decreased kidney perfusion
In prerenal failure, GFR is _____ from decreased BF, BUT renal tissue is _______
GFR is decreased from decreased BF, BUT renal tissue is undamaged
Manifestiatons of prerenal failure
Oliguria (Sharp decrease in urine output)
Decreased secretion of Na+
means that the kidneys are trying to hold onto Na+, meaning that H2O will stay behind to try and increase BP
Intrarenal failure
Damage to the structure of the kidney, resulting in kidney failure
Causes of intrarenal failure
Prolonged renal ischemia (ATN) (BP low for an extended period of time)
Rhabdomyolysis (intratubular obstruction)
Acute renal disease
Exposure to nephrotoxic drugs (ATN)
Acute tubular necrosis (most common)
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
Destruction of the tubular epithelial cells due to ischemia
Reversibility of Acute Tubular Necrosis
Reversible, but depends on the amount of injury the kidney has had overall and the ability of the body to rid itself of necrotic cells and create new tubular cells
In Acute Tubular Necrosis, does GFR improve with restoration of renal BF?
No
3 stages Acute Tubular Necrosis
Onset
lasting hrs to days
Maintenance
Decrease in GFR —> retention of metabolites and decrease in urine
Fluid retention observed
Prolonged oliguria
Recovery (1-3 wks)
Gradual increase in urine (diuresis)
Decrease in creatinine (indicates nephrons are recovering)
BUN, Cr, K+, and phosphorus may remain elevated, but will gradually decrease
Permanent damage to kidneys
How long does it take for a patient to recover from ATN?
3-12 months
Postrenal failure
obstruction of urine in ureter, bladder, or urethra
What is the most common cause of postrenal faiure?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
Enlarged prostate
Acute vs Chronic Renal Failure GFR
Acute RF has decreased GFR
chronic has severely decreased GFR
Who is at risk for ATN?
Those who already have renal insufficiency
Elderly
Diabetics
Patients receiving certain meds
Chronic RF
Permanent loss of nephrons and significant reduction of GFR
Most common cause for chronic renal failure (CRF) (2)
Diabetes
HTN
How is staging of CRF determined?
GFR measurements
What can early diagnosis of renal failure do?
Preserve kidney function and delay CRF
What classifies someone with chronic kidney disease?
When patients are in stages 3-4 for 3+ months
Kidney failure is when GFR is less than ____ ml/min, and patients will need ____
less than 15 ml/min
Patients will need dialysis
Renal function tests for Chronic Renal Failure
BUN and creatinine
GFR
Proteinuria
What will a proteinuria lab tell you when testing for CRF?
LMW globulins
indicates tublulointestinal disease
Albumin
Present due to chronic kidney disease, due to HTN or diabetes mellitus
Affects of CKD on the body (flow chart)
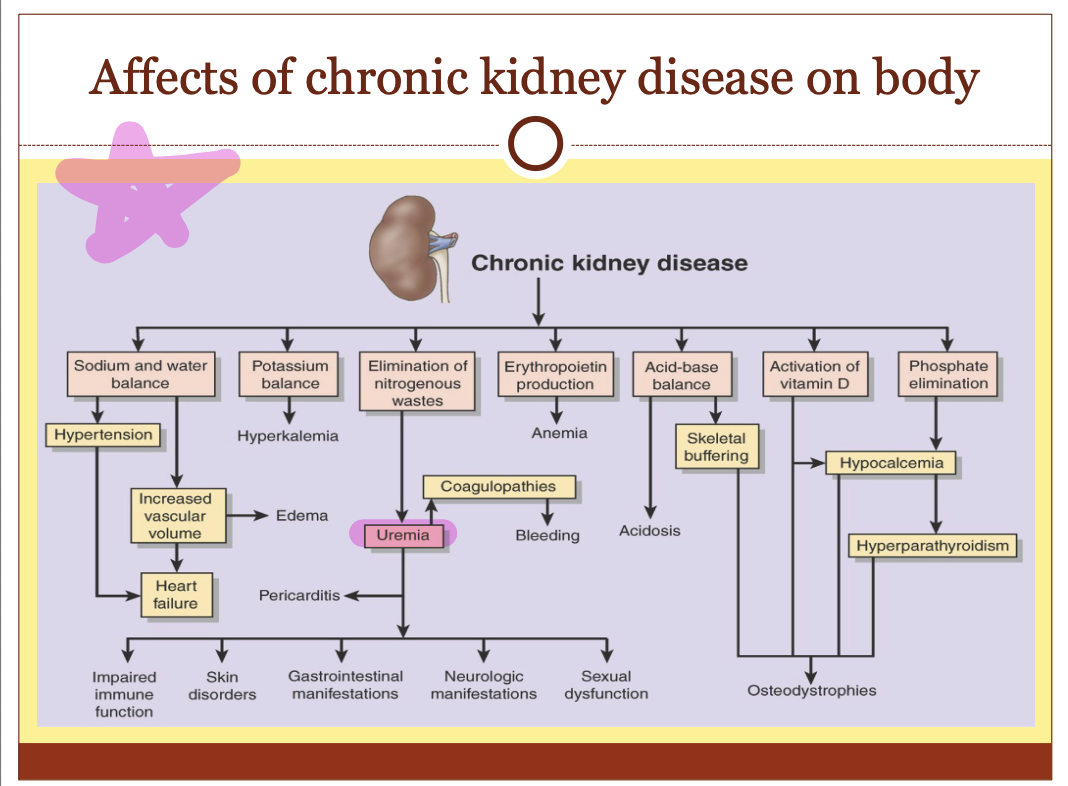
What is uremia? What are the symptoms?
Organic waste in the blood
Symptoms:
weakness
fatigue
nausea
apathy
Clinical manifestation of CRF (7)
Fluid/electrolyte balance
Acid/base balance
Hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia
Renal osteodystrophy
Hematologic complications
Cardiovascular
Nitrogenous waste conditions
Fluid imbalance due to CRF
Early symptom is isosthenuria (polyuria)
Urine is almost isotonic with plasma
Which electrolytes imbalanced due to CRF?
Na+
K+
Na+ imbalance due to CRF
kidneys lose the ability to regulate Na+
salt-wasting: body loses a lot of Na+
excreted in urine —> osmotic diuresis —> dehydration
Others have Na+ retained
Results in HTN and HF
K+ imbalance due to CRF
As the kidney starts to fail, the body tries to find other ways to get rid of excess K+ to maintain homeostasis
How can K+ be removed from body when kidney starts to fail? What happens when constipated?
Removed through GI tract
Constipation will result in decreased amounts of K+ being excreted from the body
Why does hyperkalemia occur?
Occurs when the output of K+ decreases (excretions from body)
Manifestations of hyperkalemia
Weakness
T-wave changes on an EKG
Acid-base imbalance results in metabolic acidosis, which results in:
losing the ability to eliminate H+ ions (bc the tubules can’t move H+ back and forth within the filtrate very well)
Unable to reabsorb bicarbonate (HCO3-)
Ammonia cannot be produced (aids in buffering H+)
Hyperphosphatemia and hypocalcemia due to CRF
Hyperphosphatemia: elevated PO4- in the BS; kidney’s inability to excrete
Hypocalcemia: decreased Ca2+ in the BS
Due to the kidney’s inability to synthesize and activate vit D, resulting in Ca2+ binding to excess PO4-
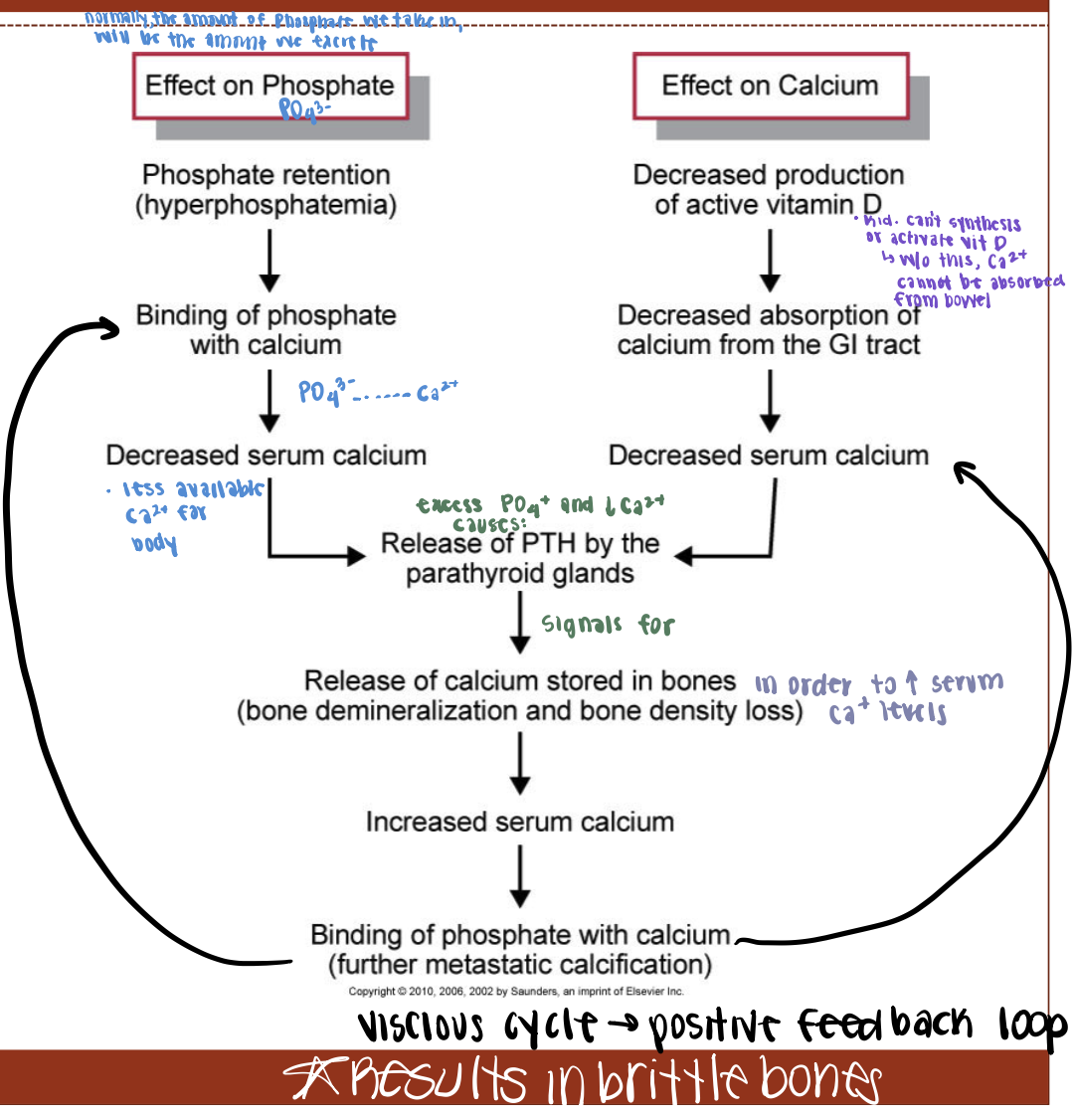
What is the end result of increased phosphates and decreased calcium? Why?
Brittle bones because Ca2+ stored in bones is released to maintain serum Ca2+
Renal osterodystrophy due to CRF results from:
Occurs due to Secondary Paraythyroidism (chronic stimulation of PTH) and vitamin D deficiency
Causes of Renal Osteodystrophy
Abnormal bone reabsorption
Defective bone remodeling
Symptoms of Renal Osteodystrophy
Softening of bones results in:
skeletal abnormailities
Bone pain
Fractures
Muscle weakness
Metastatic calcifications
Hematologic complications due to CRF
Anemia
Impaired platelet formation
Hypercoagulability (altered clotting factors)
Why can anemia occur due to CRF?
This happens because:
EPO production decreased
Decreased half life of RBCs
BM suppression from uremia
Iron deficiency from diet and restriction and anorexia
How are platelets impaired?
Defective platelet aggregation and impaired adhesions to endothelium
Cardiovascular issues due to CRF
Hypertension And diabetes mellitus
Dyslipidemia (due to uremia)
Endothelial cell dysfunction and Ca2+ deposits
Pericarditis
What is the most common cause of death among those with kidney disease?
Cardiovascular issues
What is the endothelial cell dysfunction and Ca2+ deposits due to CRF?
Loss of vessel elasticity and vascular calcifications
Increased risk of ischemic heart disease, LVH, CHF, stroke, and PVD
Pericarditis due to CRF
Occurs in 20% of chronic dialysis patients
Caused by inflammatory process and uremic toxins
Mild to severe chest pain and pericardial friction rub
Nitrogenous waste conditions due to CRF
Neuromuscular
GI
Infection and immune
Sexual
Skin
Neuromuscular disorders associated with nitrogenous waste of CRF
PNS and CNS dysfunctions
Neuropathies
Restless leg syndrome
Uremic encephalopathy
Motor dysfunction
Neuropathies
Related to demylinization of nerve fibers, likely due to renic-toxins that the body cannot get rid of
Restless leg syndrome
Creeping/prickling sensation at rest in legs
Uremic encephalopathy due to neuromuscular disorders of CRF
When the uremia affect the brain tissue
Patients less alert, impaired judgement, and have memory loss
Can get to the point where it causes seizures and coma
Motor dysfunction due to neuromuscular disorders of CRF
From muscle weakness
If you have peripheral nerve damage patients might have burning to the feet
GI dysfunction associated with nitrogenous waste of CRF
Loss of appetite due to nausea bc of uremia:
Anorexia
Nausea and vomiting
Metallic taste
Uremic factor
GI bleeding and ulceration
Infection and immune disorders associated with nitrogenous waste of CRF
Suppression from urea & waste
Impaired skin & mucosal barriers
Malnutrition contributes to immunosuppression
Skin issues associated with nitrogenous waste of CRF
Dry skin
Pruritus
Uremic frost
Sexual issues associated with nitrogenous waste of CRF
Multifactual
has a lot to do with urinary toxins and neuropathy and some medications patients are on
Disorders of Drug Elimination (4)
Phosphate binding drugs
Drugs may contain unwanted (Nitrogen, K, Na, Mg)
Decreased Elimination & Metabolism
Low plasma proteins levels
Many drugs bind with plasma proteins
Unbound drugs can be harmful
Phosphate binding drugs
can interfere with absorption of other drugs
Diet for those with CRF
Protein — decrease (high protein can lead to high BUN)
Na+ — decrease
Fluid — decrease to 500-800 mL/day
K+ — increase when GFR drops significantly
Why would someone need to decrease their sodium intake if they have CRD?
Glomerular origin causes Na+ retention
Tubular dysfunction causes salt wasting
Where is phosphorous found in food? (3) What is the impact on poor patients?
Found in processed foods, instant products, and beverages
this makes it harder for POOR patients to adhere to decreased phosphorous
Where is K+ found in food? (4)
Salt substitutes
Fruits
Fruit juices
Chocolate
Medical management for Chronic Renal Failure
Peritoneal dialysis
Hemodialysis
Kidney transplant
Peritoneal dialysis
Catheter is inserted into abdomen and it uses the lining of your abdomen to filter blood inside the body
works very well but need to be dedicated
Hemodialysis
circulating the blood outside the body through a machine that filters out toxins and returns the cleansed blood to the patient
needs needles in arms 3x per week