Exam 3: Viruses, prions_18.pdf
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
General Virus Characteristics
• Obligatory intracellular parasites
-Require living host cells to multiply
• Nucleic acid (DNA or RNA)
-ss OR ds
• Capsid
• Envelope
• No ribosomes
• No ATP-generating mechanism
•Range from 20 nanometer to 1000nanometer in length
Viral Structure, Terminology
• Virion-complete, fully developed viral particle
• Nucleic acid
• Capsid (capsomeres- subunits)
• Envelope
• Spikes
General Viral Morphology
• Helical
• Polyhedral (icosahedral)
• Enveloped viruses
• Complex viruses
Key Terms
• Host range: what host cells (species) a virus can infect
-Usually only 1 type of cell in a species
-Determined by specific host attachment sites and cellular factors
• Tropism: range of cells/tissues virus can infect
General Virus Life Cycle: 5steps
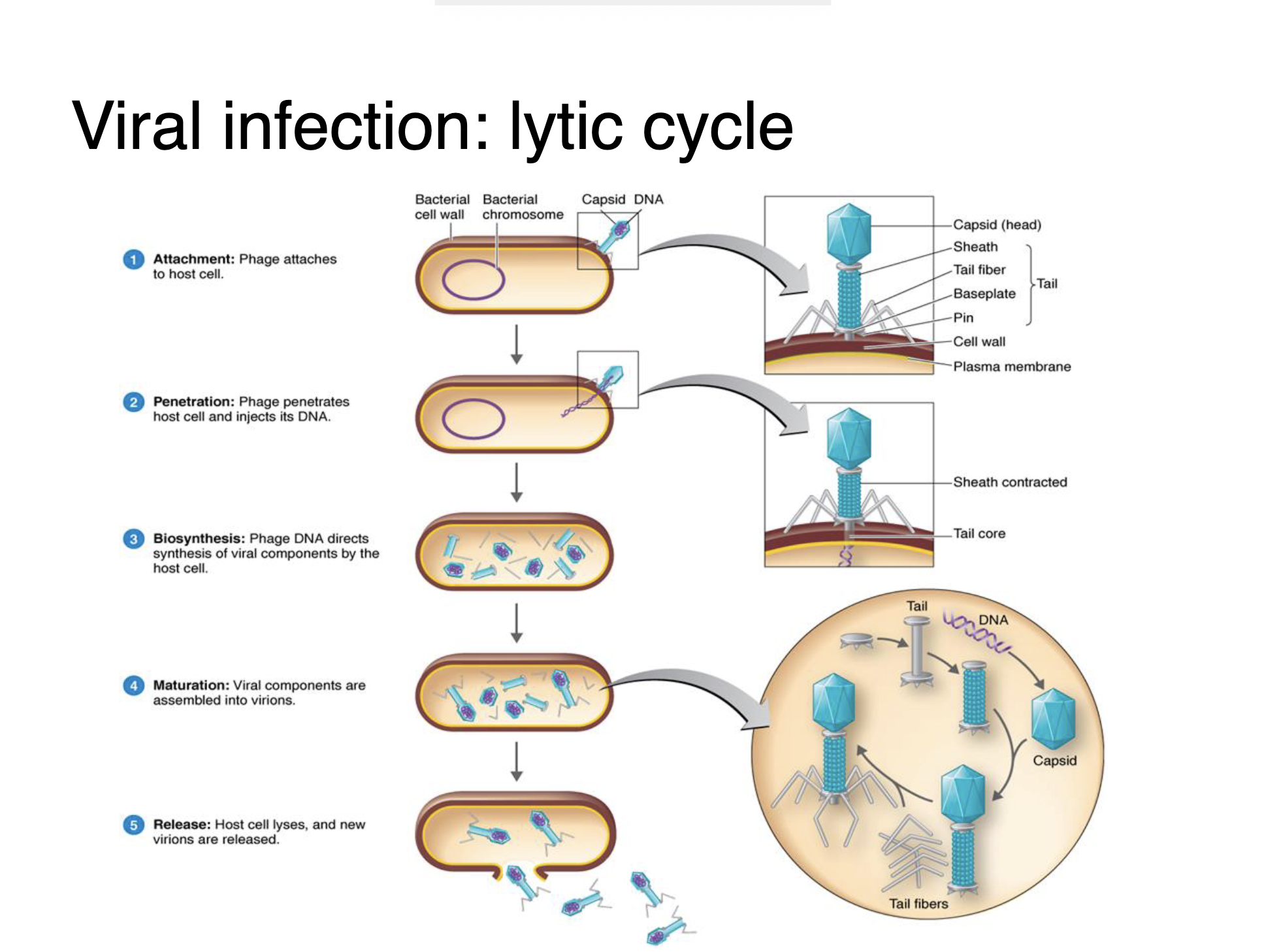
1. Attachment
2. Entry
3. Synthesis
4. Assembly
5. Release
1. Attachment
• Interaction between molecule on virion surface (ligand) and on host cell (receptor)
• Why have viral tropism
• Example: phage to LPS incell wall
2. Entry
• Genome or entire nucleocapsid enters cytoplasm
• Penetration/uncoating may occur at same time
1. Fusion of envelope with host PM
2. Endocytic pathway
3. Synthesis
•Virus factories
-May occur in host cytoplasm (viroplasms)
-May rearrange host cell membrane (replication complexes): protects from host cell immune system
• Strong regulation
-Early, middle, late genes
4. Assembly
• Form independent subassembly lines
• Lines eventually converge
• Packasome and terminase to move DNA into prohead
5. Release
• Lysis of host cell
• May release by budding (enveloped)
• Note: some move directly from 1 host cell to another by cell division, mating
Viral infection: lytic cycle
Viral infection: lysogenic
• Lysogeny: phage remains latent
• Phage DNA incorporates into host cell DNA
-Prophage: genetic material phage inserted into bacterial chromosome
-When the host cell replicates its chromosome, it also replicates prophage DNA
-phage conversion-the host cell exhibits new properties
Viral infection: animal cells
• Cytocidal: cell death
• Persistent infections
• Cytopathic effects: observable changes
•Cell rounding
•Cell detachment
• Inclusion bodies
• Alter cell metabolism
• transformation
Latent Viral Infections
• Latent virus : in asymptomatic host cell for long periods
• May reactivate due to changes in immunity
- Cold sores, shingles
Persistent Viral Infections
• A persistent viral infection occurs gradually over a long period; is generally fatal
- Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (measles virus)
Viruses and Cancer
• Multiple cancers caused by viruses
- May develop long after a viral infection
- Cancer is not contagious
• Oncogenes transform normal cells into cancerous cells
• Oncogenic viruses become integrated into the host cell's DNA and induce tumors
Baltimore Classification: based on viral genome
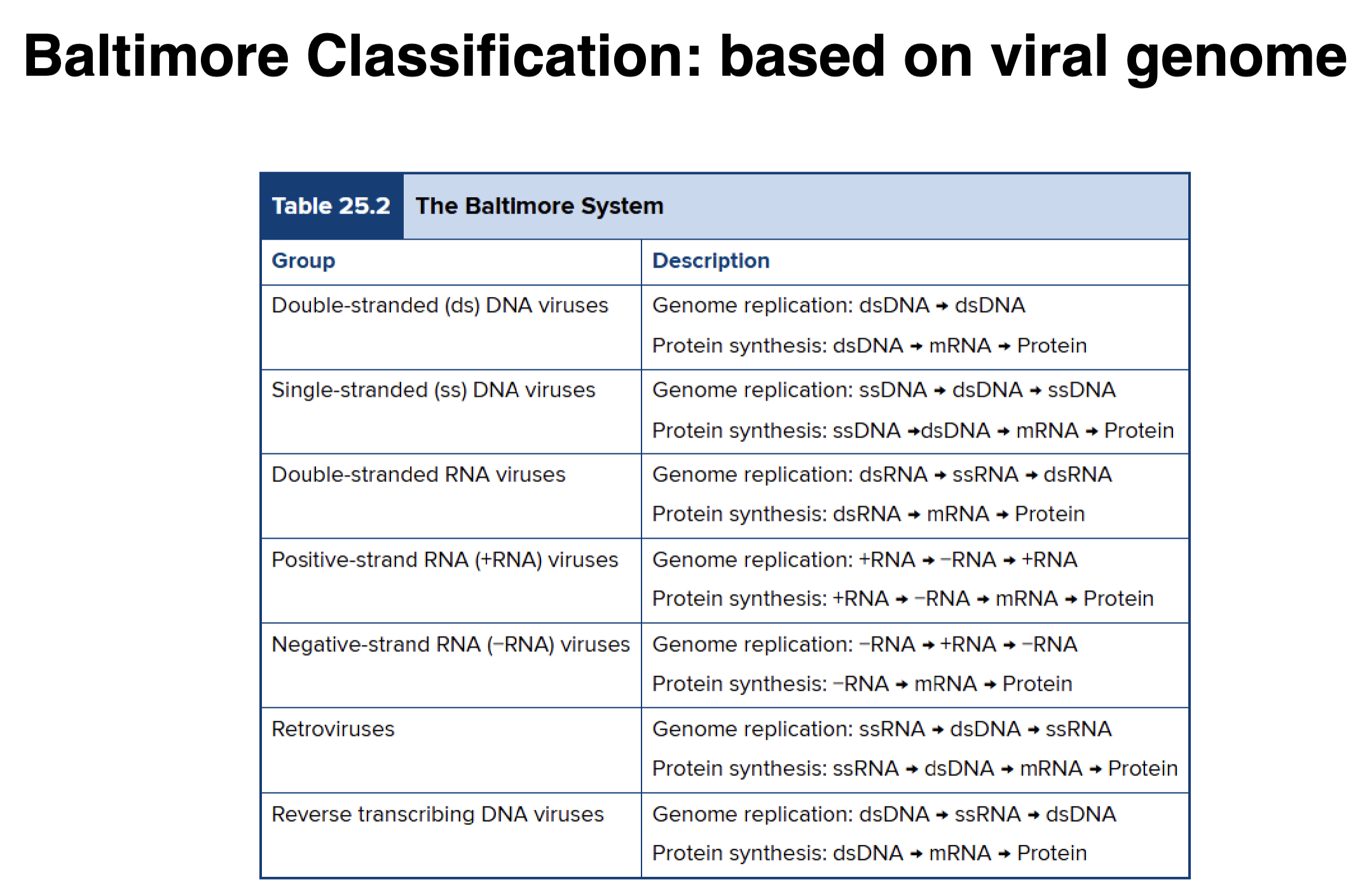
dsDNA Viruses
• DNA viruses replicate their DNA in the nucleus of the host using viral enzymes
• Synthesize capsid in the cytoplasm using host cell enzymes
• Bacteriophages, archael viruses, insect viruses, vertebrates (herpesvirus, poxvirus)
•Varicella-zoster (chickenpox)
ssDNA Viruses
• Use dsDNA intermediate in life cycle
• Uses host cell enzymes
• Positive strand OR negative strand
• Examples: Pseudomonas virus Pf1, parvoviruses
dsRNA Viruses
• Must produce RNA-dep RNA polymerase (RdRp)
-Acts as replicase, transcriptase
• Example: rotaviruses (stomach flu, gastroenteritis)
ssRNA positive strand Viruses
• Translated upon entry
• Genomes act as mRNA
• Must make RdRp
• Examples: coronaviruses, Zika, hepatitis A
•Microcephaly from Zika virus infection early in pregnancy
ssRNA negative strand Viruses
• Must bring RdRp
• Viral RNA is transcribed to a + strand to serve as mRNA for protein synthesis
• Examples: Rabies, Ebola, Measles, mumps, influenza
• measles in children
Retroviruses
• Positive strand, uses Reverse transcriptase
-RNA-dep DNA polymerase
-DNA-dep DNA polymerase
-Ribonuclease
-Lacks proofreading
• Integrates into host cell's DNA
• Example: HIV
Reverse transcribing DNA viruses
• Reverse transcriptase to replicate genome
• Integrate into host genome
• Example: hepatitis B virus
Isolation, cultivation
• Viruses must be grown in living cells
• Bacteriophages are grown in bacteria
• Animal viruses: grown in embryonated eggs, cell/tissue culture
Antivirals
• Small molecules
• Inhibit virus-specific enzymes
• Target replication processes
• Limits duration of illness, severity
Prions
...
Prions
• Proteinaceous infectious particles
• Inherited and transmissible by ingestion, transplant, and surgical instruments
• Difficult/impossible to eradicate/eliminate:
- Resistant to disinfectants - Autoclaves, medical sterilization no effect
- *cooking actually concentrates the prions
-Long latency
- Remain in environment
Prions Spongiform encephalopathies
- "Mad cow disease"
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)
- Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome
- Fatal familial insomnia
- Sheep scrapie
- Kuru
- Chronic wasting disease (CWD)
Prions Continued...
• Scrapie: sheep and goats
• PrPC: normal cellular prion protein, on the cell surface
• PrPSc: scrapie protein; accumulates in brain cells, forming plaques
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy
• "mad cow disease"
• Can be spread from diseased cattle to humans (Creutzfield-Jakob)
• Degeneration of nervous system
Kuru
Papa New Guinea (1950s)
• Fore tribe
• Out of love, respect would ingest every part of deceased family members (endocannibalism)
-Women/children ate the brain
-Return life force
• Tremors, loss of coordination
Chronic wasting disease...now in GA!
• "zombie deer disease"
• cervid family — elk, deer, reindeer, caribou, and moose
• Potential for spillover to humans...
• No plan if spillover occurs