Formulas For Final
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is the Hall Petch equation?
What does it do?
See figure
σyield = yield stremgth
σo = Stress for dislocation movement
ky = strengthening coefficient
d = diameter
Shows how smaller grains make materials stronger
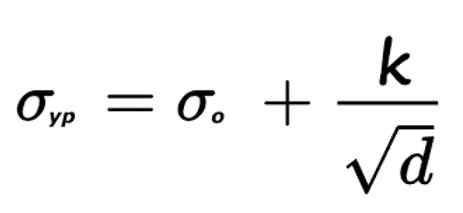
What is the cold work equation?
What does it do?
See figure
%CW = cold work percentage
Ao = Original cross sectional area
Ad = Cross sectional area after deformation
measures the percentage change in the cross-sectional area of a material after cold working
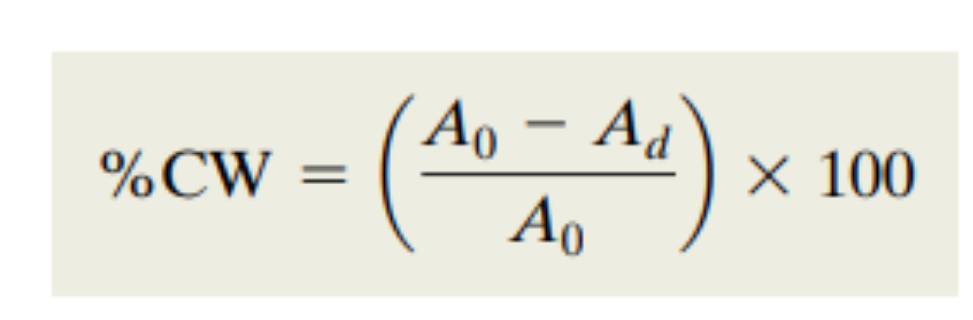
What is the Griffith equation?
What does it do?
See figure
σm = stress at crack tip [Pa]
σo = applied stress [Pa]
pt = radius of curvature [m]
a = one half length of internal crack [m]
predicts the critical stress required for a crack to propagate in a brittle material
![<p>See figure</p><p><span>σm = stress at crack tip [Pa]</span></p><p><span>σo = applied stress [Pa]</span></p><p><span>pt = radius of curvature [m]</span></p><p><span>a = one half length of internal crack [m]</span></p><p>predicts the critical stress required for a crack to propagate in a brittle material</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/df820111-b3a4-49df-921e-8a3011101b6a.png)
Stress concentration factor?
Whats it used for?
See figure
σm = max stress at crack tip
σo = average applied stress
quantifies the stress concentration at a point of discontinuity in a structure
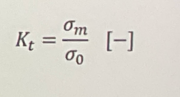
What is the critical stress formula?
What is it used for?
See figure
σc = critical stress [Pa or MPa]
E = Youngs modulus [Pa]
ys = specific surface energy [J/m²]
a = one half length of internal crack [m]
for ductile materials replace ys with ys+yp where yp is the plastic deformation energy
predicting the stress required to propagate a crack in a brittle material.
![<p>See figure</p><p><span>σc = critical stress [Pa or MPa]</span></p><p><span>E = Youngs modulus [Pa]</span></p><p><span>ys = specific surface energy [J/m²]</span></p><p><span>a = one half length of internal crack [m]</span></p><p><span>for ductile materials replace ys with ys+yp where yp is the plastic deformation energy</span></p><p><span>predicting the stress required to propagate a crack in a brittle material.</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bafdf857-8655-4647-8380-ca4405273024.png)
What is the formula for fracture toughness?
What is it used for?
See figure
Kc = Fracture toughness [MPa sqrt m]
Y = Dimensionless parameter
σc = critical stress [MPa]
a = one half length of internal crack [m]
Measures the materials resistance to brittle fracture when a crack is present
For thick samples replace Kc with KIC which is plane strain fracture toughness
![<p>See figure</p><p>Kc = Fracture toughness [MPa sqrt m]</p><p>Y = Dimensionless parameter</p><p>σc = critical stress [MPa]</p><p>a = one half length of internal crack [m]</p><p>Measures the materials resistance to brittle fracture when a crack is present</p><p>For thick samples replace Kc with KIC which is plane strain fracture toughness</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dd21a4b3-1eb7-46bc-bdff-dde82c59d77f.png)
What is the mean stress for cyclic loading equation?
See figure
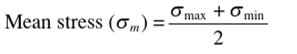
What is the range of stress equation?
See figure
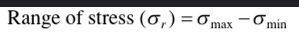
What is the stress amplitude equation?
See figure
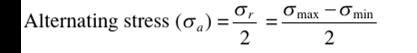
What is the stress ratio equation?
See figure
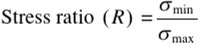
Weight percent and atom percent formula?
See figure
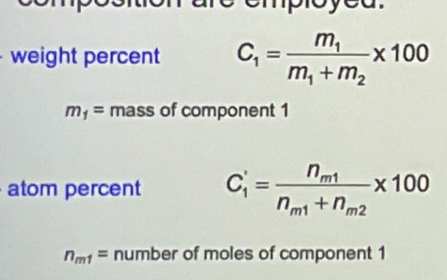
Burgers Vector Calculation for BCC and FCC lattices?
For SC lattices?
See figure
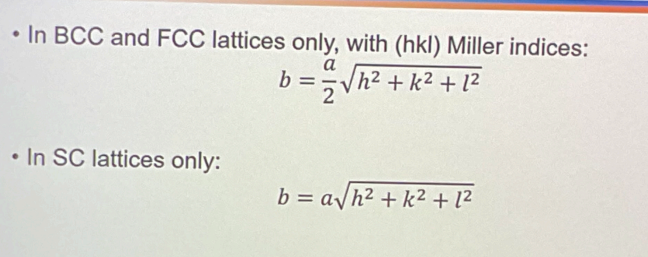
Vacancy concentration formula?
See figure
Nv = number of defects [atom/m³]
N = total number of atomic sites [atom/m³]
Qv = activation energy [J/atom] or [eV/atom]
k = boltszman’s constant [1.38×10^-23 J/atom] or [8.62×10^-5 eV/atom K]
T = temp [K]
![<p>See figure</p><p>Nv = number of defects [atom/m³]</p><p>N = total number of atomic sites [atom/m³]</p><p>Qv = activation energy [J/atom] or [eV/atom]</p><p>k = boltszman’s constant [1.38×10^-23 J/atom] or [8.62×10^-5 eV/atom K]</p><p>T = temp [K]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e3951dd0-57b1-458c-8e78-6dd96f27c987.png)
Fick’s 2nd Law?
See figure
∂C/∂t = The rate of change of concentration with respect to time
D = The diffusion coefficient
∂²C/∂x²: The second derivative of concentration with respect to position
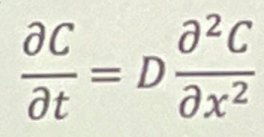
Arrhenius equation for diffusion?
See figure

Ficks 1st Law of Diffusion?
J = -D [(dC)/(dx)]
D = Diffusion coefficient [m²/s]
J = Flux = [moles or mass diffusing] / [surface area times times] in mol/cm²s or kg/m²s
Poissons ratio
v = ex/ey
Relationship for isotropic materials for elastic shear?
See figure
tau = Gy
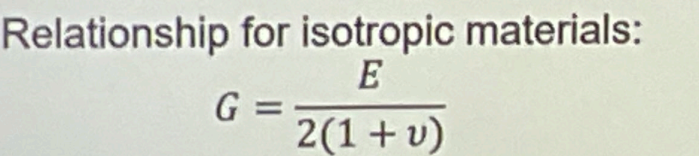
Relationship for isotropic materials for elastic bulk?
See figure
P = -K [delta V / Vo]
![<p>See figure</p><p>P = -K [delta V / Vo]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7241c95b-bf02-43d4-9e0f-8e01bcd8c57d.png)
Percent elongation?
Percent reduction in area?
See figure

Resilience equation?
Ur = ½ σy ey