A&P unit 4 - Autonomic Nervous System
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
autonomic NS
-part of Efferent NS
-involuntary/unconscious
-control heart, smooth muscle, glands
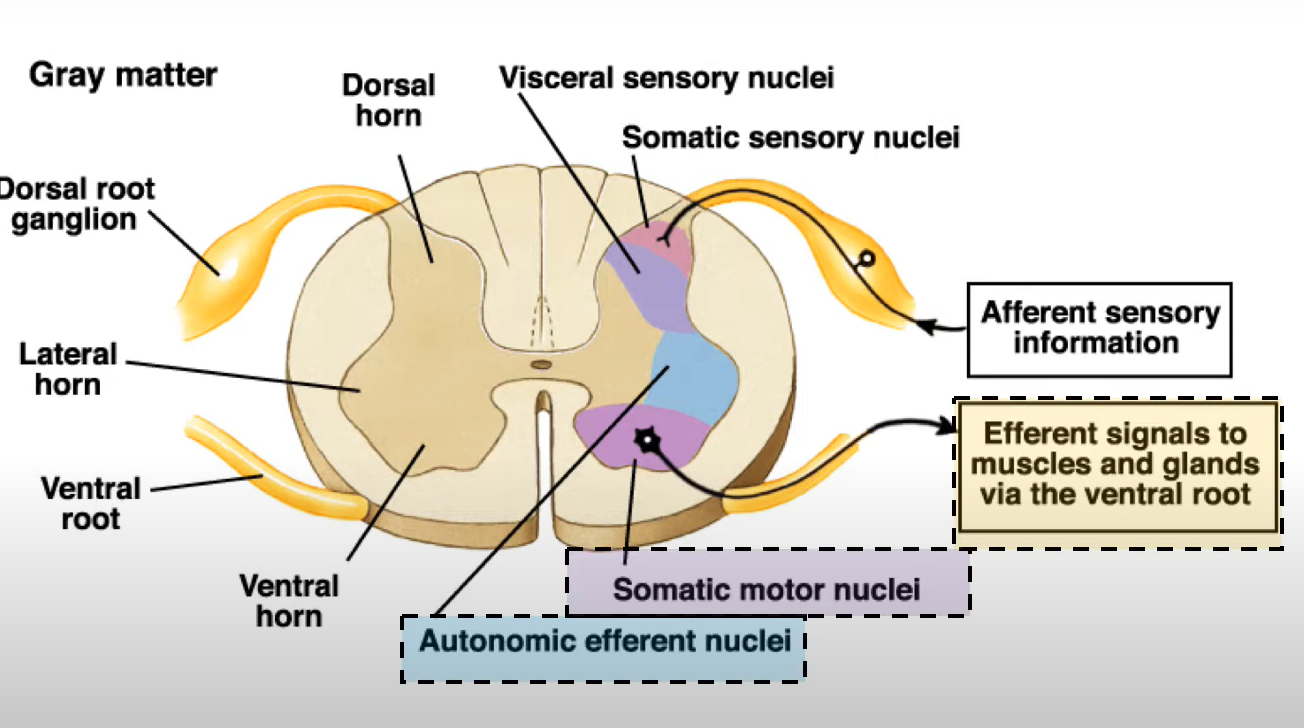
where in the spinal cord are the autonomic neurons?
in the lateral horn (shown in blue)
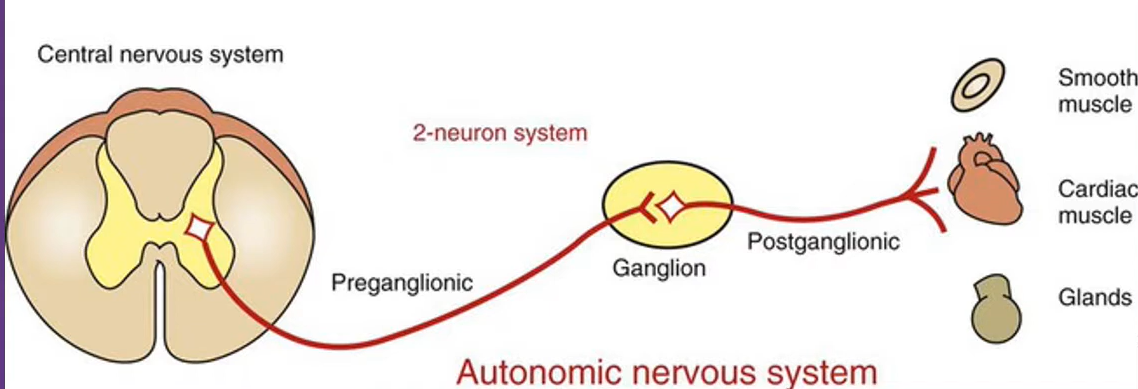
autonomic NS pathway
2-neuron pathway
-starts at spinal cord, ends at effector
-preganglionic neurons and postganglionic neuron
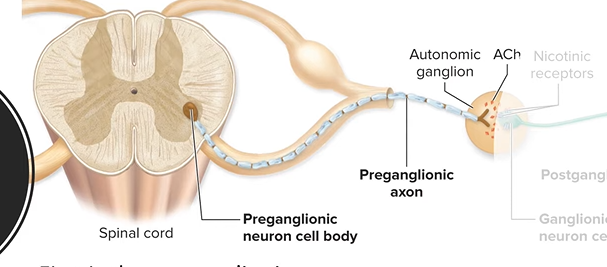
preganglionic neuron
-body is within spinal cord (lateral horn)
-thin, myelinated axon projects to autonomic ganglion in PNS
-releases Ach from syn. knob to excite 2nd neuron
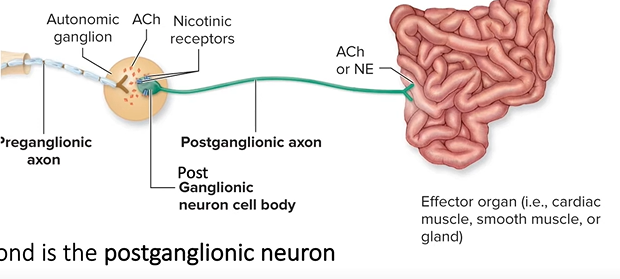
postganglionic neuron
-body is within autonomic ganglion
-very thin, unmyelinated axon projects to effectors
-releases Ach or norepinephrine from syn. knob to excite or inhibit effector depending on effector type
Why does the autonomic pathway involve a ganglion? Why not just have nerve go from spinal cord straight to effectors?
allows for neuronal convergence and divergence
-more control of response
-more areas of response
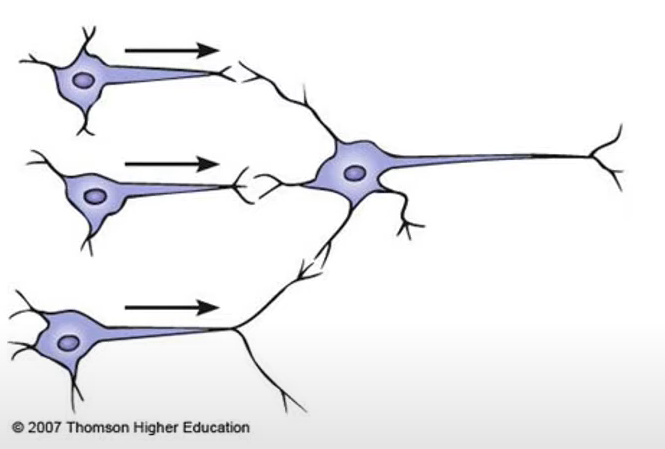
neuronal convergence
multiple preganglionic synapse onto one postganglionic neuron
-integration of signals
-fine tune response
-allow for one targeted, controlled response
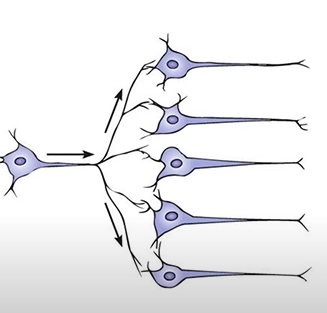
neuronal divergence
one preganglionic synapse with many postganglionic neurons
-increase effect by targeting many areas
-disperse areas that effectors are activated
Where are the control centers for the ANS?
hypothalamus = regulate many autonomic processes, sleep, involved in emotions
brain stem = major reflex centers, digestion, cardiovascular, respiratory
spinal cord = reflex centers for defecation and urination → these reflexes become controlled as we get older
sympathetic NS
-fight or flight
-needed for exercise, excitement, emergency
thoracolumbar outflow
in sympathetic, nerve fibers originate in chest and abdominal regions of the spinal cord
-lateral horns of T1-L2
-preganglionic fibers are short and branched (allow for divergence), postganglionic are long
parasympathetic NS
-rest and digest
-maintain homeostasis when resting
craniosacral outflow
in parasymp, nerve fibers originate in brain and lower spinal cord
-brainstem nuclei, and S2-S4
-preganglionic fibers are long, postganglionic are short
terminal ganglion vs intramural ganglion
terminal = if ganglion lies close to the effector
intramural = if ganglion lies within the effector
parasympathetic activation vs sympathetic activation
sympathetic = mass activation → branched preganglionic allow many effectors to be activated at once
parasymp = localized reponse → ganglion close to effectors allow for only one or a few structures activated at a time
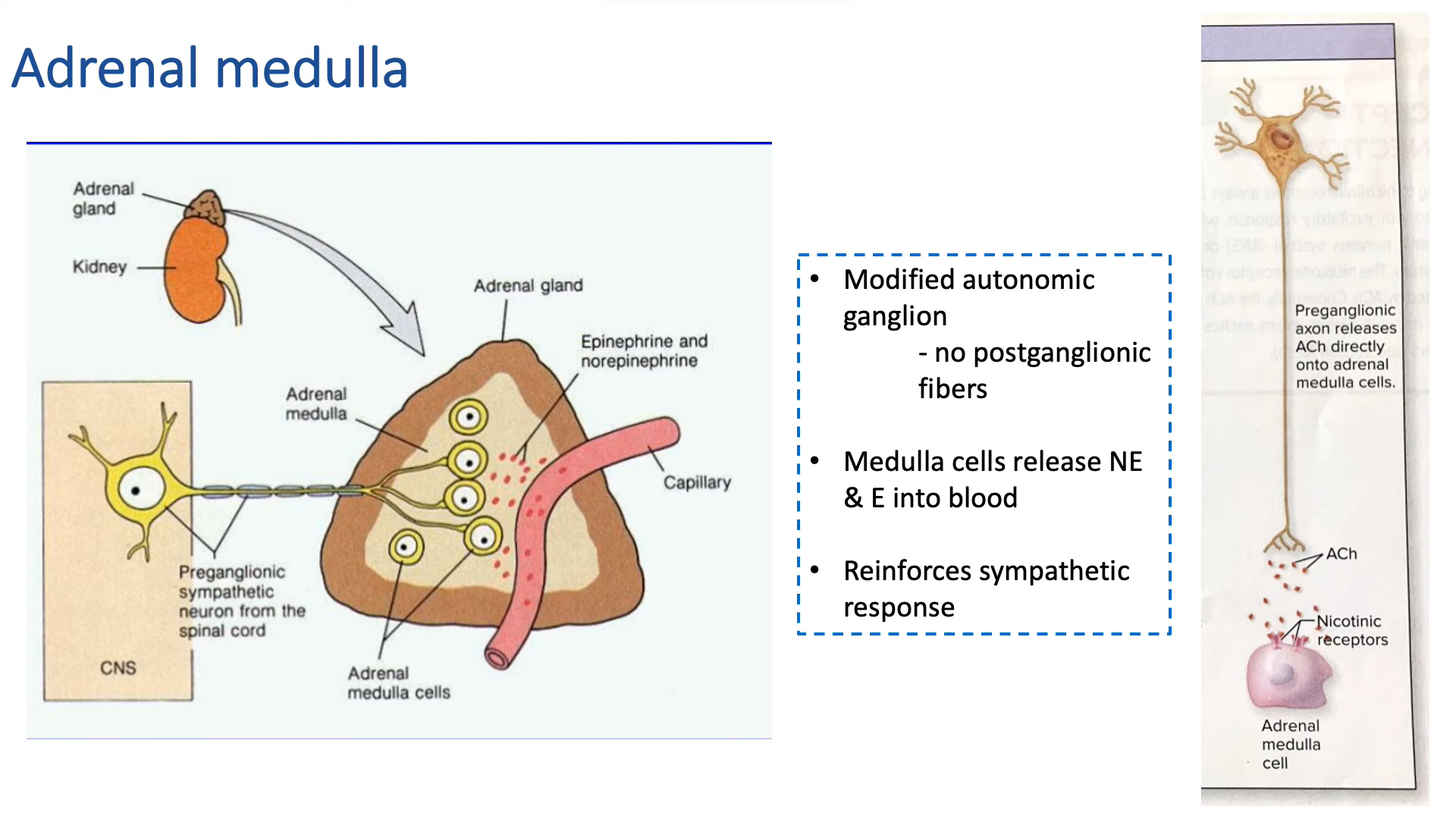
adrenal medulla role in sympathetic mass activation
-adrenal glands are on top of kidneys
-when stimulated, releases epinephrine (E) and norepinephrine (NE) into blood
-now the hormones flow thru blood and reach many targets
Adrenal medulla
-modified autonomic ganglion, NO postganglionic fibers
-medulla release NE and E into blood, reinforces sympathetic response
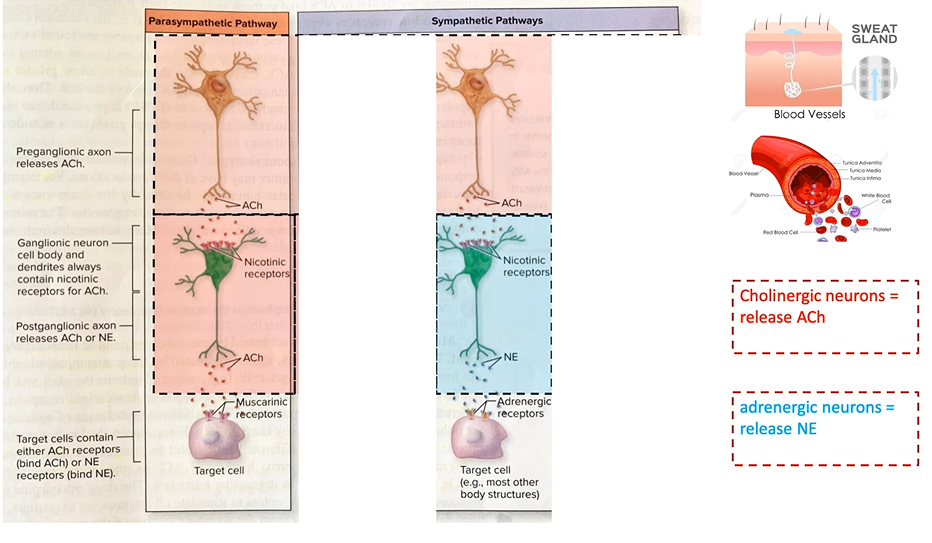
cholinergenic vs adrenergenic fibers
cholinergenic = release Ach. more common in parasymp
-includes nicotinic and muscarinic
adrenergenic = release NE. more common in sympathetic
-includes alpha and beta receptors
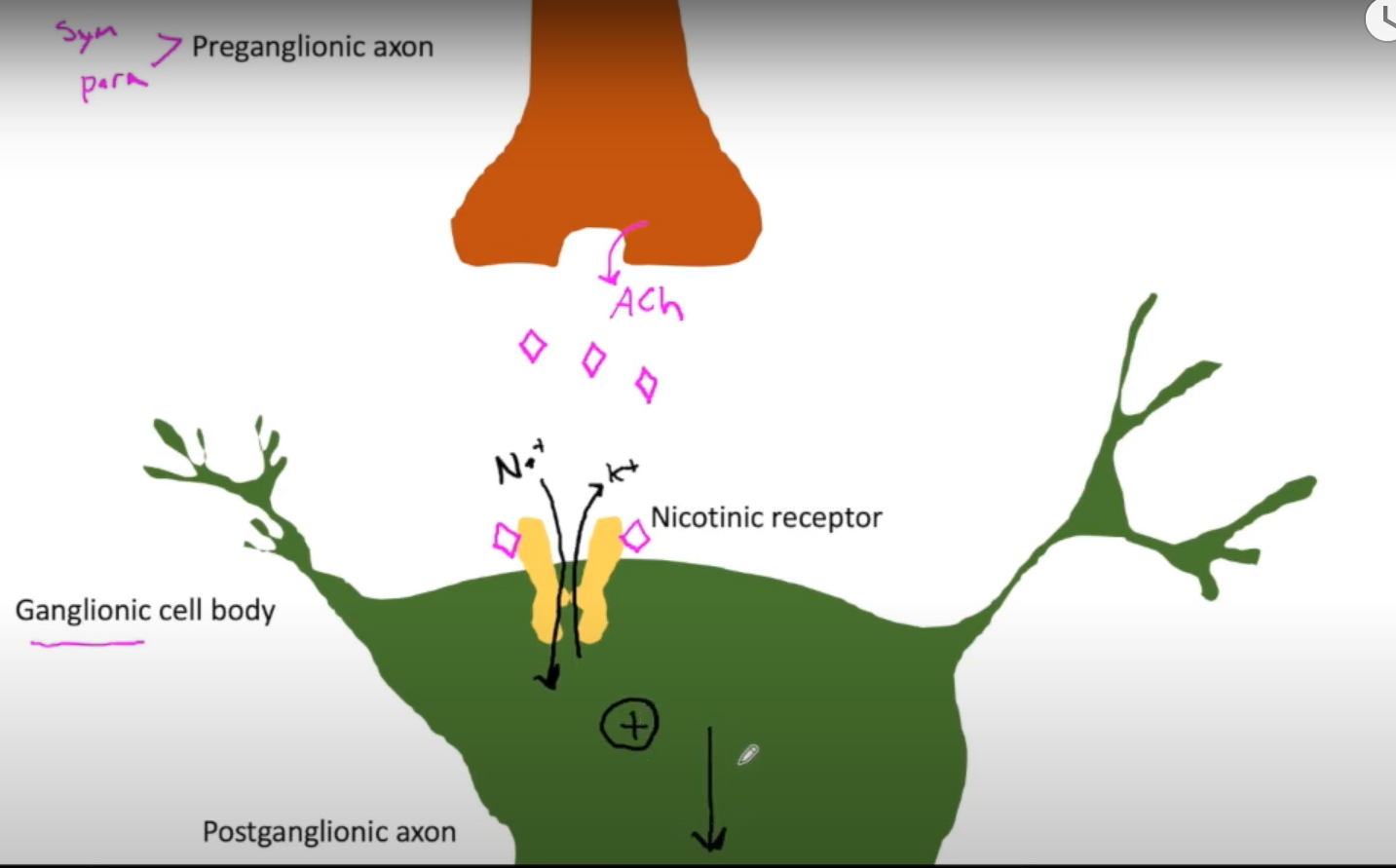
nicotinic receptors
-type of cholinergenic receptor (binds Ach) in parasymp
-found on all postganglionic cell bodies in ANS (parasym and sym)
-found on neuron, not effector organ
-when Ach binds, it opens cation channel. more Na in than K out leads to cell depolarization, AP
agonist vs antagonist
both refer to a foreign molecule
agonist = binds to a receptor and has same response as NT would
antagonist = binds, but in doing so prevents NT binding/response
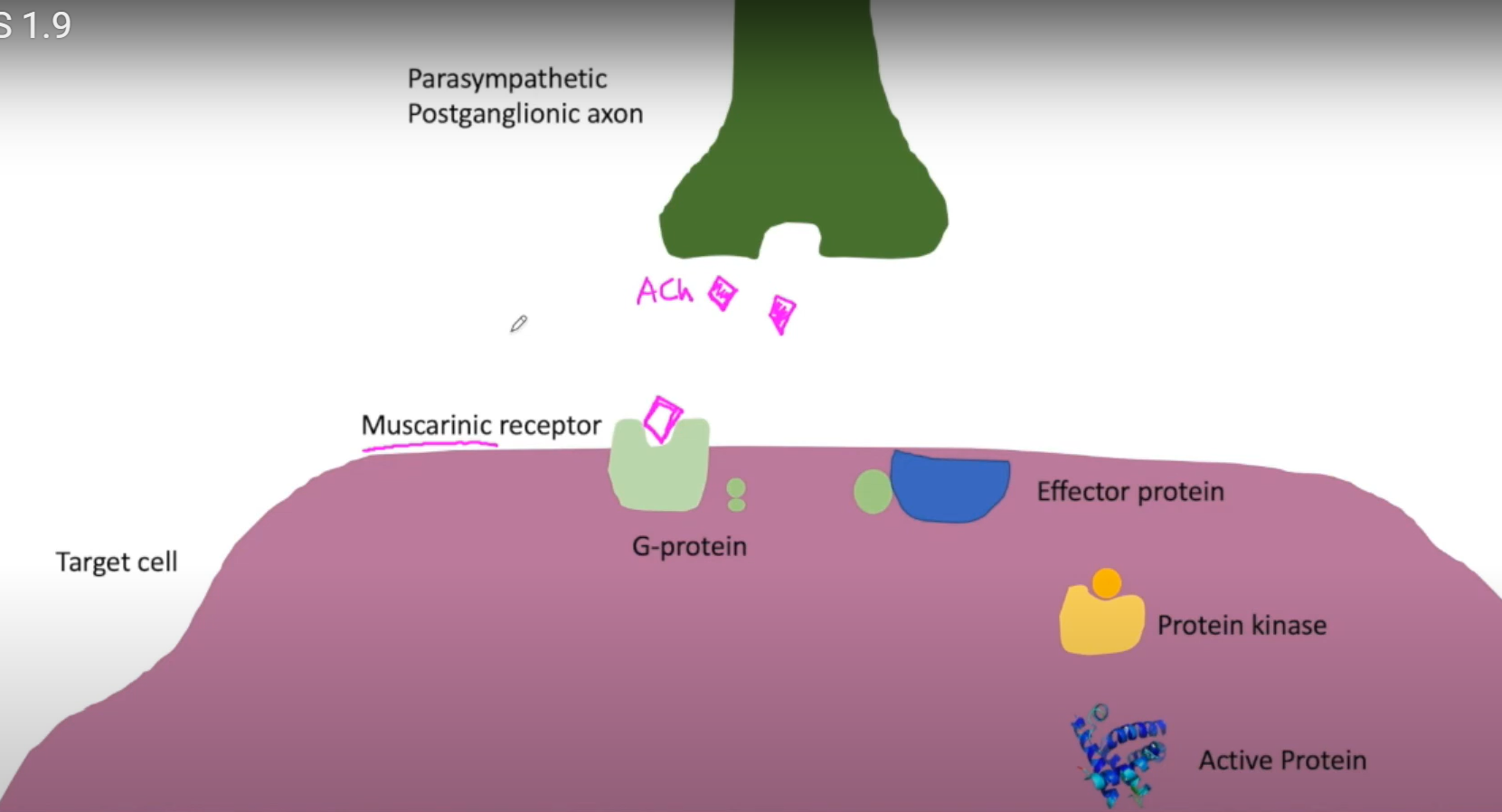
muscarinic receptors
-type of cholinergenic receptor (binds Ach) in parasymp
-found in all target organs of parasymp, AND sweat glands and blood vessels of symp
-found on effector organ, not neuron
-when Ach binds, activates GPCR, that leads to kinase activating a protein in the effector cell
alpha and beta receptors
-type of adrenogenic receptor (binds E and NE) in sympathetic
-most commonly found on effector organ
-all have GPCR pathway, but pathway is diff based on subtype
-A1, A2, B1, B2
-in general, A/B1 is excitatory and A/B2 is inhibitory
alpha 1 receptors (A1)
-most common adrenogenic
-greater affinity for NE than E
-activation excites effector organ
alpha 2 receptors (A2)
-on mainly digestive organs
-greater affinity for NE than E
-activation inhibits effector (stop digestion for fight or flight)
beta 1 receptors (B1)
-in heart
-equal affinity for E and NE
-excitatory response (heart pump faster)
beta 2 receptors (B2)
-in small blood/airway vessels
-affinity for E
-activation is mostly inhibitory (relax smooth muscle walls, BV dilate)
dual innervation
when organ can receive input from both parasymp and symp
-ability to produce opposite effects in the organ
-allows for precise control of organ, functions can change depending on situation needed
Nicotinic mnemonic
nicotinic = all post-ganglionic
No Alligators Prowl Gracefully
muscarinic mnemonic
muscarinic = parasympathetic targets
Mice Prefer Treats
adrenergic mnemonic
adrenergic = sympathetic targets
A Swift Tiger