2 - ANATOMY OF THE BACK (BRS) 2025
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
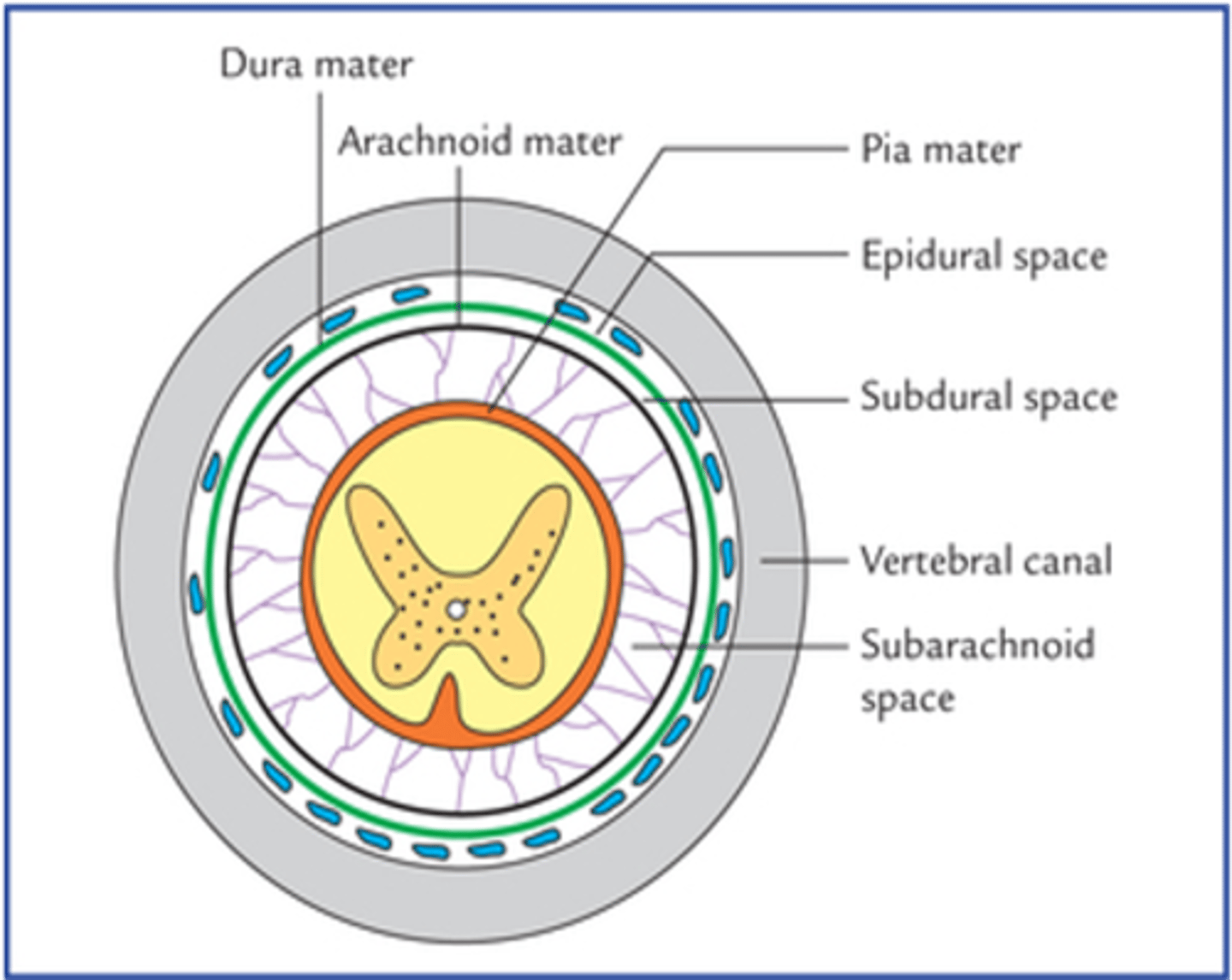
In what space can one obtain cerebrospinal fluid in a lumbar puncture procedure?
Subarachnoid space
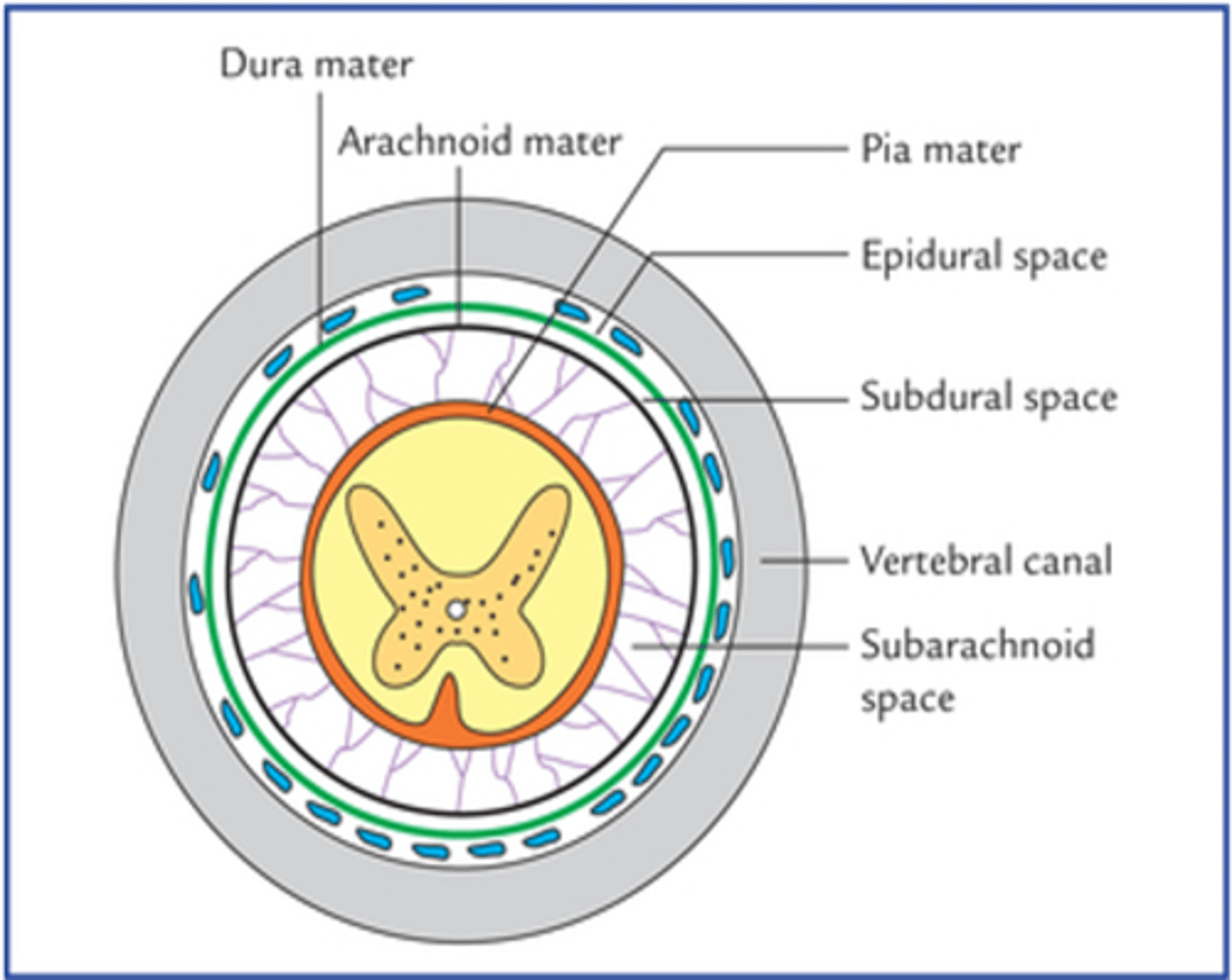
The internal vertebral venous plexus would rupture into what space around the spinal cord?
Epidural space
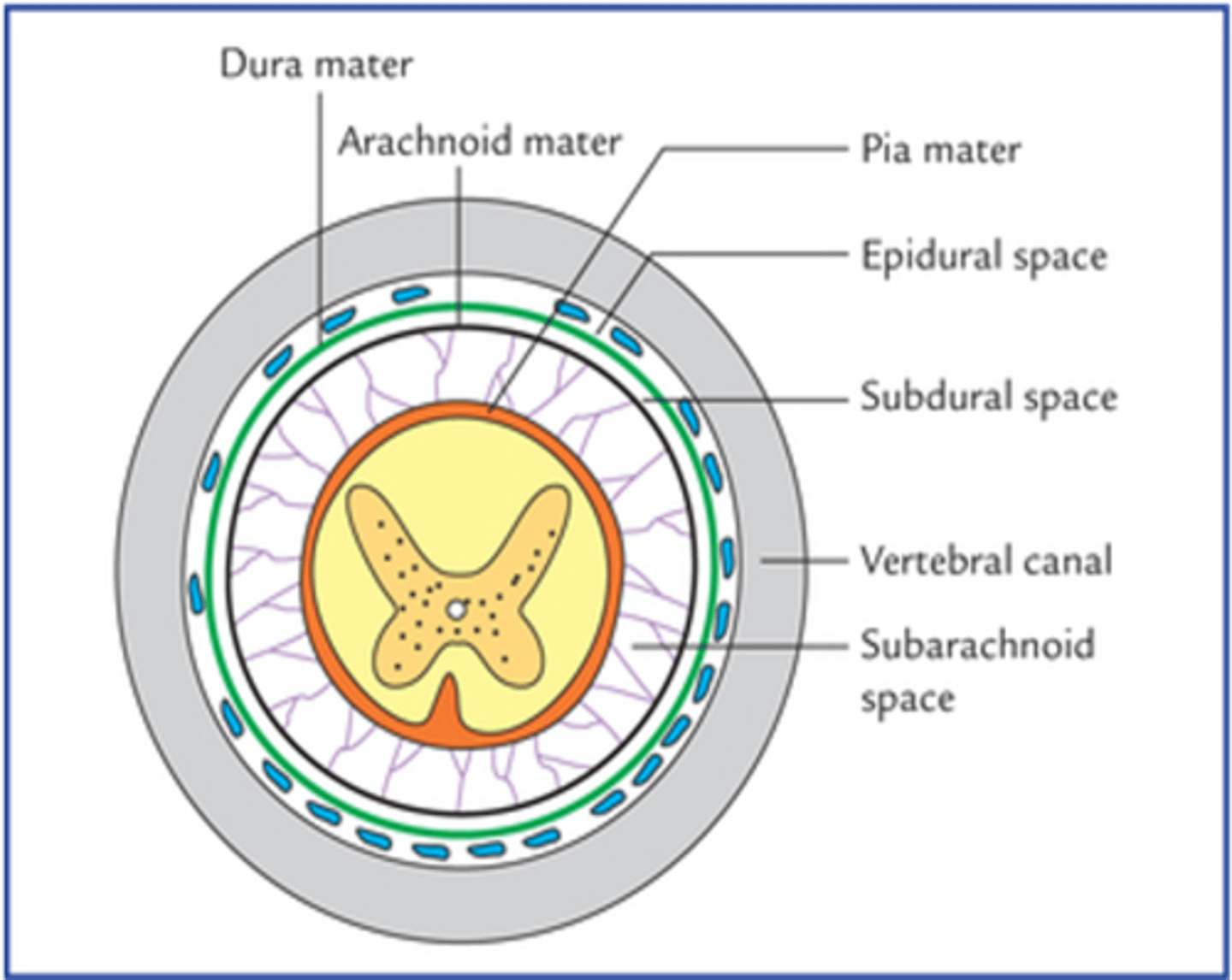
What is the space located between the vertebral canal and the dura mater?
Epidural space
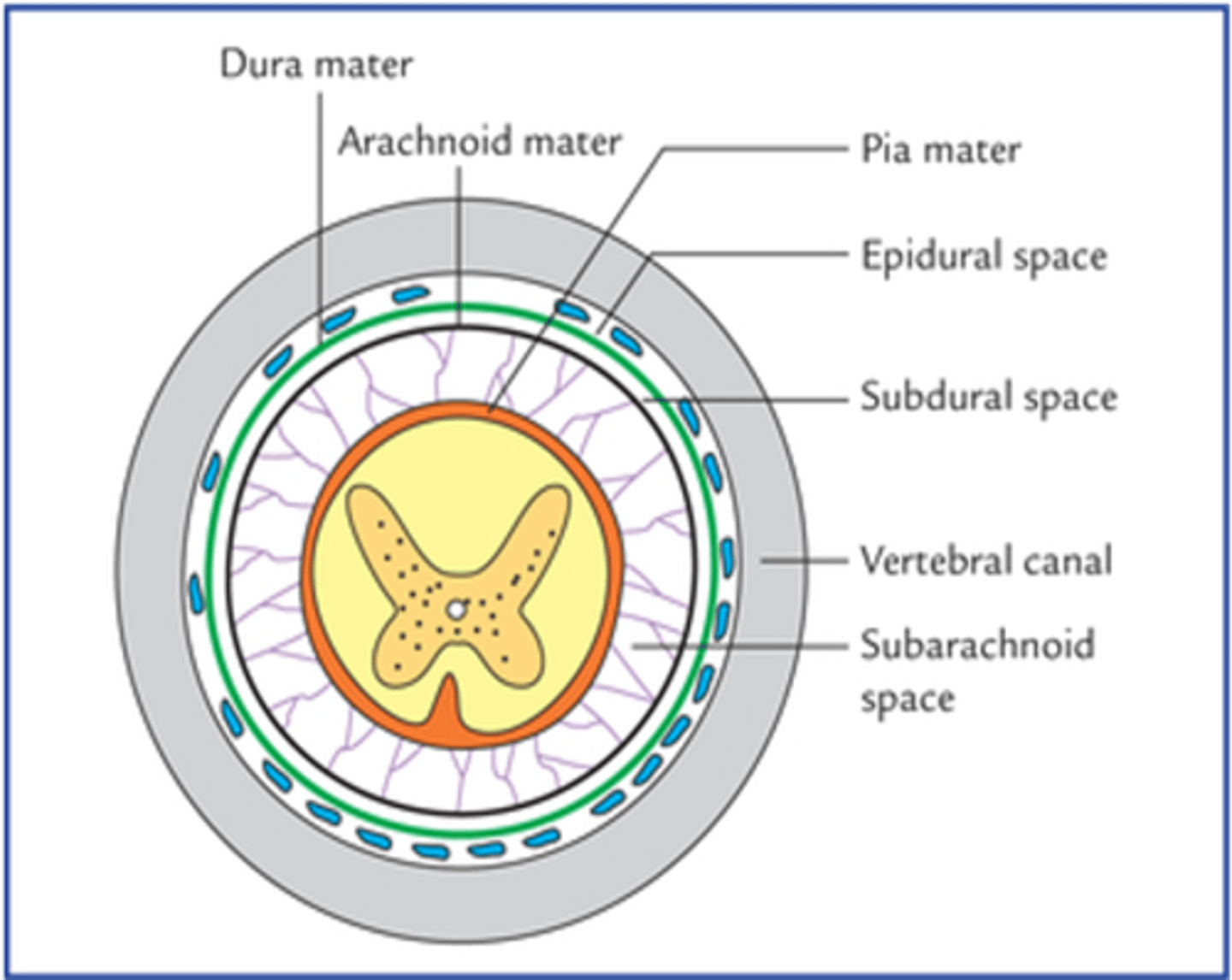
What is the space between the arachnoid and the dura maters of the spinal cord?
Subdural space
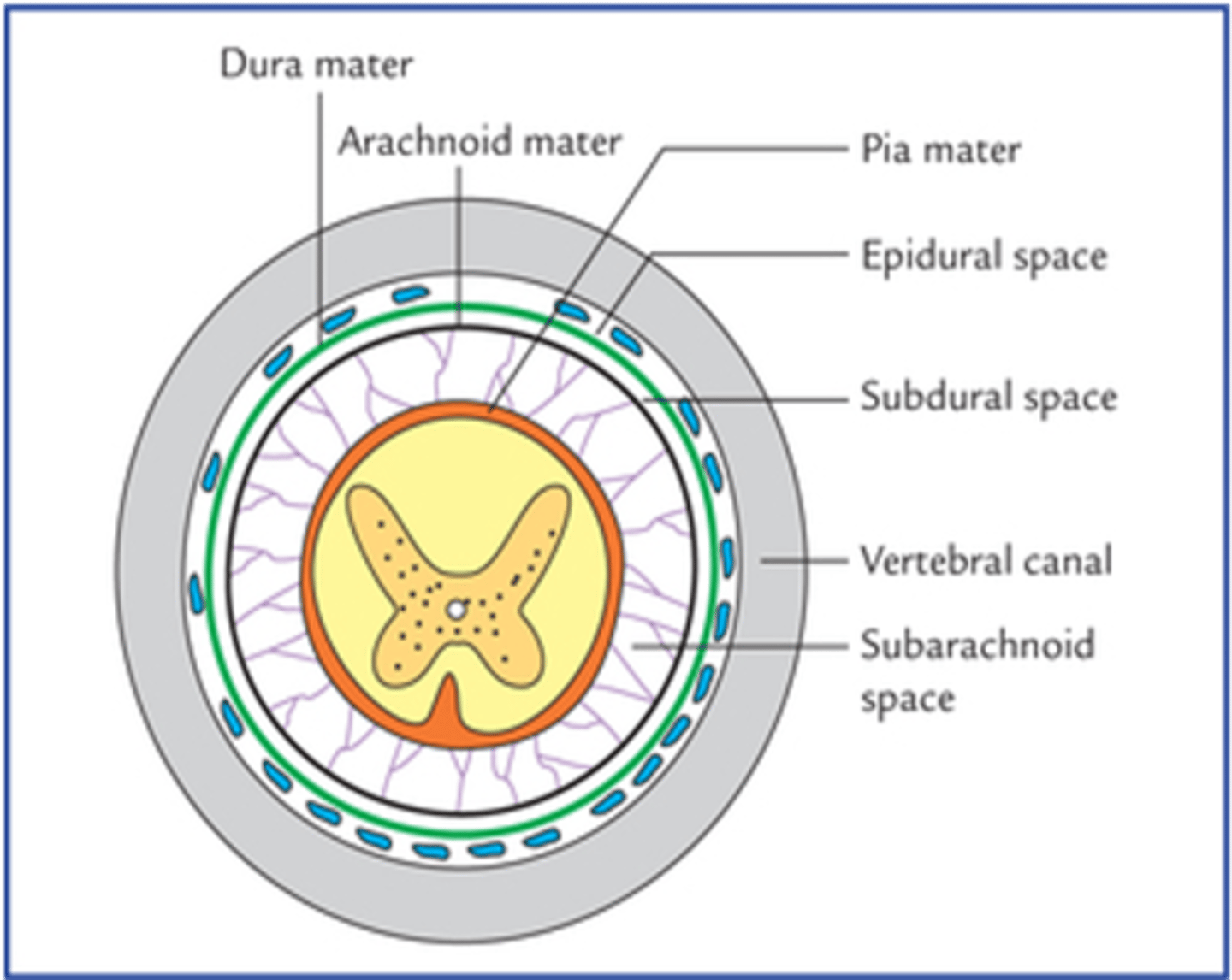
What fluid is located within the subarachnoid space around the spinal cord?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
A tumor in the intervertebral foramina between the fourth and fifth cervical vertebrae will damage what nerve?
Fifth Cervical Nerve (C5)
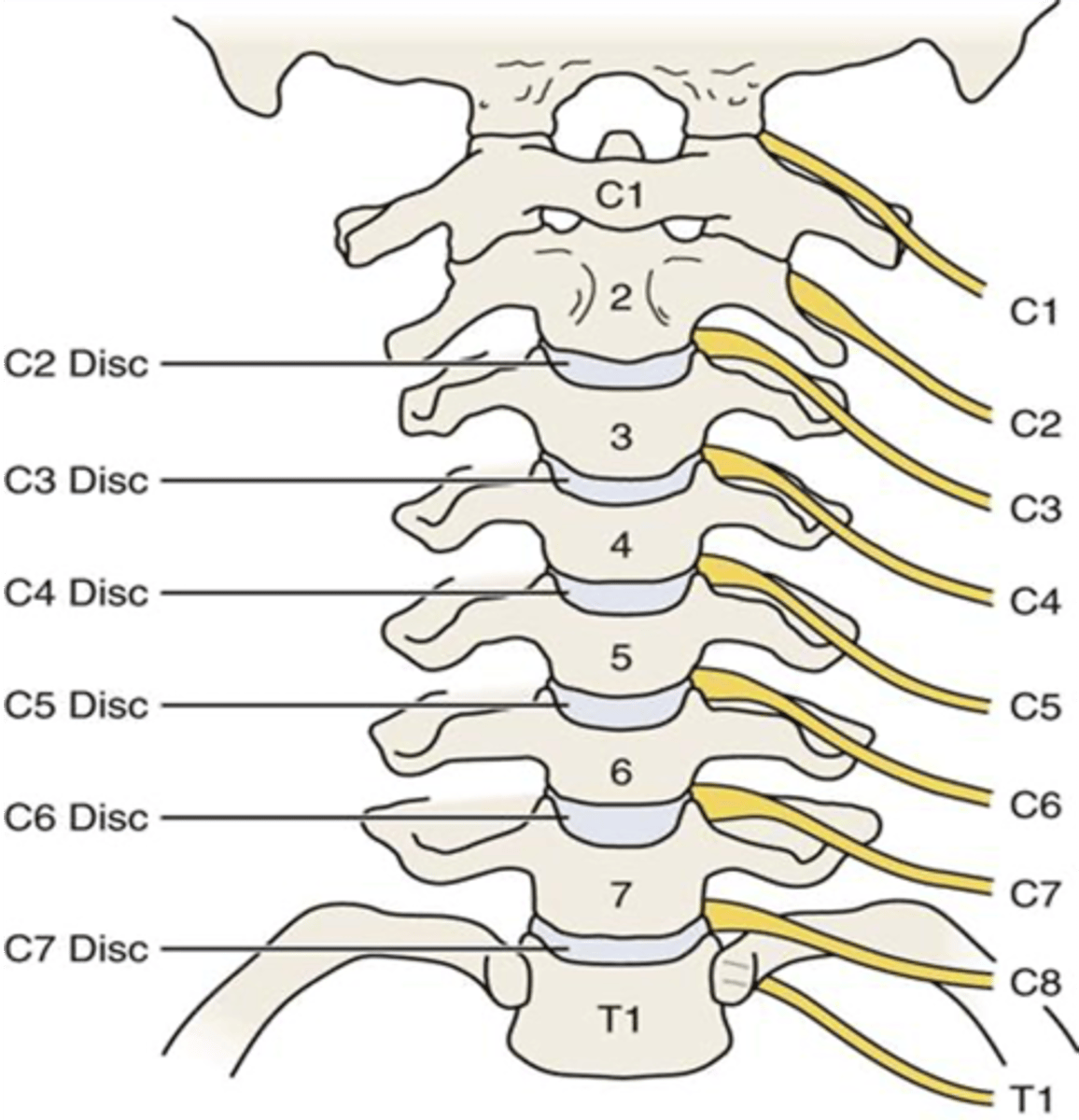
A tumor in the intervertebral foramina between the fourth and fifth thoracic vertabrae will damage what nerve?
Fourth Thoracic Nerve (T4)
What is the only cervical nerve without a corresponding vertebra?
C8
A herniated intervetebral disk between L4 and L5 vertebrae will likely affect nerve roots from whcih spinal nerves?
Fifth Lumbar Nerve Root (L5)
Spinal nerves generally exit BELOW their corresponding vertebra, EXCEPT for what spinal nerves?
C1 - C7
What structures in the brain are responsible for the absorption of CSF?
Arachnoid villi
Arachnoid granulations
CSF is produced by what structures located inside the ventricles?
Choroid plexus
What muscle originates from the transverse processes of the upper cervical vertebrae and insert on the medial border of the scapula?
Levator scapulae
The heads of the sixth and seventh ribs articulate with the vertebral body at what vertebral level?
T6
Which part of the vertebra articulates with the tubercle of the corresponding rib?
Transverse process
This congenital disorder is characterized by the protrusion of the meninges and a pathologic tubular cavity in the spinal cord or brain
Syringomyelocele
What B vitamin is shown to prevent neural tube defects?
Folic acid (Vitamin B9)
The deep muscles of the back are innervated by what nerves?
Dorsal primary rami of the spinal nerves
The superficial muscles of the back are innervated by what nerves?
Ventral primary rami of the spinal nerves
What muscles are innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve?
-Levator scapulae
-Rhomboid minor
-Rhomboid major
What structures are penetrated by the spinal needle during a lumbar puncture procedure? (From the most superficial structure)
-Skin
-Subcutaneous tissue
-Supraspinous ligament
-Interspinous ligament
-Ligamentum flavum
-Epidural space
-Dura mater
-Subdural space
-Arachnoid mater
-Subarachnoid space
What space is located between the arachnoid and pia mater?
Subarachnoid space
The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is located within what space?
Subarachnoid space
The lateral horn of the spinal cord containing sympathetic preganglionic neuron cell bodies is present at what levels of the spinal cord?
T1-L2
The lateral horn of the spinal cord containing parasympathetic preganglionic neuron cell bodies is present at what levels of the spinal cord?
S2-S4
What structures pass through the intervertebral foramen?
Dorsal and ventral primary rami of the spinal nerves
Local anesthetic agents are injected via what foramen located between the sacral cornua to block the spinal nerves in the epidural space?
Dorsal and ventral primary rami of the spinal nerves
What structure lies within the vertebral canal?
Spinal cord
The suboccipital nerve supplies what muscles?
-Rectus capitis posterior major
-Obliquus capitis superior
-Obliquus capitis inferior
-Semispinalis capitis
What nerve supplies the rectus capitis posterior major, obliquus capitis superior, obliquus capitis inferior and semispinalis capitis muscles?
Suboccipital nerve
What muscle is innervated by the dorsal primary rami of the middle and lower cervical nerves?
Splenius capitis
The atlantoaxial joint of the cervical vertebrae is responsible for what movement of the neck?
Rotation
This ligament interconnects vertebral bodies and intervertebral disks posteriorly and runs anterior to the spinal cord within the vertebral canal
Posterior longitudinal ligament
This ligament is formed by supraspinous ligaments extending from the seventh cervical vertebra to the external occipital protuberance and crest
Ligamentum nuchae
This ligament interconnects vertebral bodies and intervertebral disks anteriorly
Anterior longitudinal ligament
The transverse foramina is present up to what cervical vertebrae level?
C6
What structures occupy the transverse foramina?
Vertebral artery and vein
The vertebral artery and vein passes through what foramen to enter/exit the skull?
Transverse foramina
This structure is the enlargement of the subarachnoid space between the inferior end of the spinal cord and the inferior end of the subarachnoid space
Lumbar cistern
The anterior part of the external vertebral venous plexus lies in front of what structure?
Vertebral column
The posterior part of the external vertebral venous plexus lies on what structure?
Vertebral arch
This condition is characterized by an abnormally increased thoracic curvature
Kyphosis/ Hunchback/ Humpback
This condition is characterized by the abnormal accentuation of the lumbar curvature
Lordosis
This condition is the failure of the vertebral arch to fuse (bony defect only)
Spina bifida occulta
This congenital condition is characterized by protrusion of the meninges through the unfused arch of the vertebra
Meningocele
Injury caused by force that hyperextends the cervical vertebrae after driving the trunk forward with the head lagging behind
Whiplash injury
This condition is a lateral deviation of the vertebrae resulting from unequal growth of the spinal column
Scoliosis
This is a fracture of the neural arch through the pedicle of the axis due to hanging or motor vehicle accidents
Hangman fracture
This congenital condition is characterized by protrusion of the spinal cord and its meninges through a defect at the back
Meningomyelocele
This condition occurs when the nucleus pulposus is protruded through the annulus fibrosus
Herniated disk
What muscle originates from the posterior tubercle of the atlas and inserts on the occipital bone (below the inferior nuchal line)
Rectus capitis posterior minor
This ligament extends from the apex of the dens to the medial side of the occipital bone
Alar ligament
This ligaments extends from the dens of the axis to the anterior aspect of the foramen magnum of occipital bone
Apical ligament
This muscle originates from the transverse processes and insert onto the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae
Semispinalis cervicis
This muscle originates from the spine of the axis and inserts on to the transverse process of the atlas
Obliquus capitis inferior
Lateral extensions of the pia mater in the spinal cord
Denticulate ligament
This structure is an inferior extension of the pia mater from the tip of the conus medullaris
Filum terminale (internum)
This structure is the filum of the dura and extends from the tip of the dural sac to the coccyx
Coccygeal ligament or Filum terminale externum
This membrane is an upward extension of the posterior longitudinal ligaments from the body of the axis to the basilar part of the occipital bone
Tectorial membrane
The tectorial membrane is an upward extension of what ligament of the back?
Posterior longitudinal ligaments
What is the action of the rhomboid major muscle?
Adducts the scapula
The dorsal scapular nerve arises from ventral ramus of which cervical nerve?
C5
The latissimus dorsi forms boundaries of what 2 triangles of the back?
Auscultation and Lumbar triangles
The trapezius muscle forms a boundary of which triangle of the back?
Auscultation triangle
What artery supplies the levator scapulae, rhomboid minor, trapezius muscles
Transverse cervical artery
The splenius capitis muscle receives blood from what 2 arteries?
Occipital artery
Transverse cervical artery
The trapezius muscle receives blood from what artery?
Transverse cervical artery (superficial branch)
The latissimus dorsi receives blood from what artery?
Thoracodorsal artery
The rhomboid major muscle receives blood from what artery?
Transverse cervical artery (deep/descending branch)
The multifidus and longissimus capitis muscles receive blood from what arteries?
Segmental arteries
What is found in the epidural space around the spinal cord that is not found in the cranial epidural space?
Epidural fat
The internal vertebral venous plexus lies in what space around the spinal cord?
Epidural space
What venous plexus is located inside the epidural space of the spinal cord?
Internal vertebral venous plexus
What structure located at the caudal end of the spinal cord is formed by dorsal and ventral roots of the lumbar and sacral nerves?
Cauda equina
What do you call the conical end of the spinal cord?
Conus medullaris
The adult conus medullaris terminates at what vertebral level?
L2
What is the central mucoid substance in the intervertebral disk?
Nucleus pulposus
What is the fibrous tissue and fibrocartilage surrounding the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disk?
Annulus fibrosus
What structure produces cerebrospinal fluid?
Choroid plexus
After exiting the ventricles of the brain, the cerebrospinal fluid proceeds to circulate within what space around the brain and spinal cord?
Subarachnoid space
The choroid plexuses are located within what CSF-filled structures of the brain?
Ventricles
After passing through the subarachnoid space, CSF is filtered into the venous system by what structures?
-Arachnoid villi
-Arachnoid granulations
What is another term for subarachnoid space in the lumbar area?
Lumbar cistern