College Biology Placement Test Practice
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Biology
The study of life
Cell Division
Process by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells
Sexual Reproduction
Cells from two parents unite to form the first cell of a new organism
Asexual Reproduction
Process by which a single parent reproduces by itself
Mitosis
cell division that results in two identical daughter cells
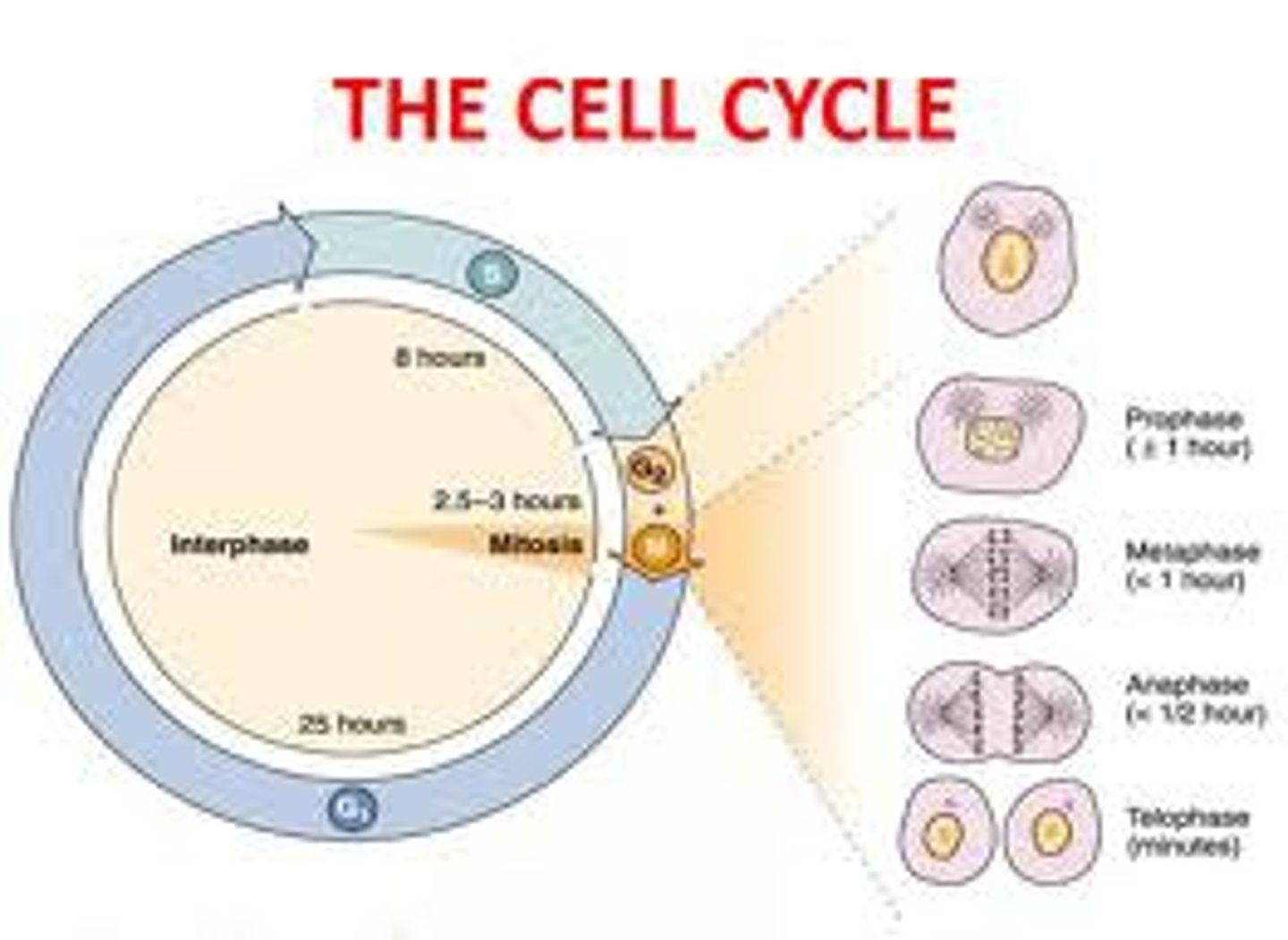
Cell Cycle
pattern of growth, DNA replication, and cell division that occurs in a eukaryotic cell
Chromosome
Tightly wound strand of genetic material or DNA
Genetics
The scientific study of heredity
Heredity
Passing of traits from parents to offspring
Gregor Mendel
Father of genetics

Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
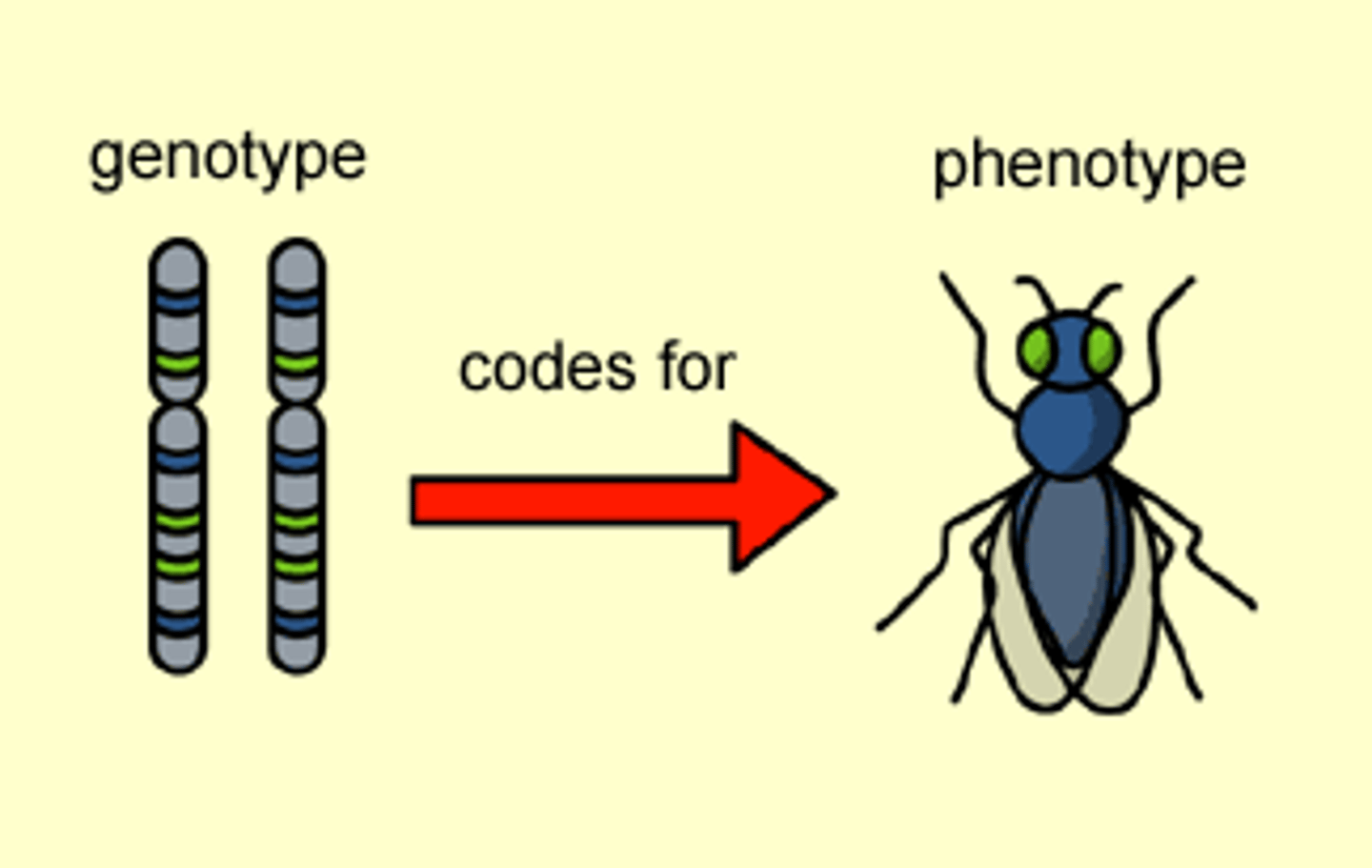
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
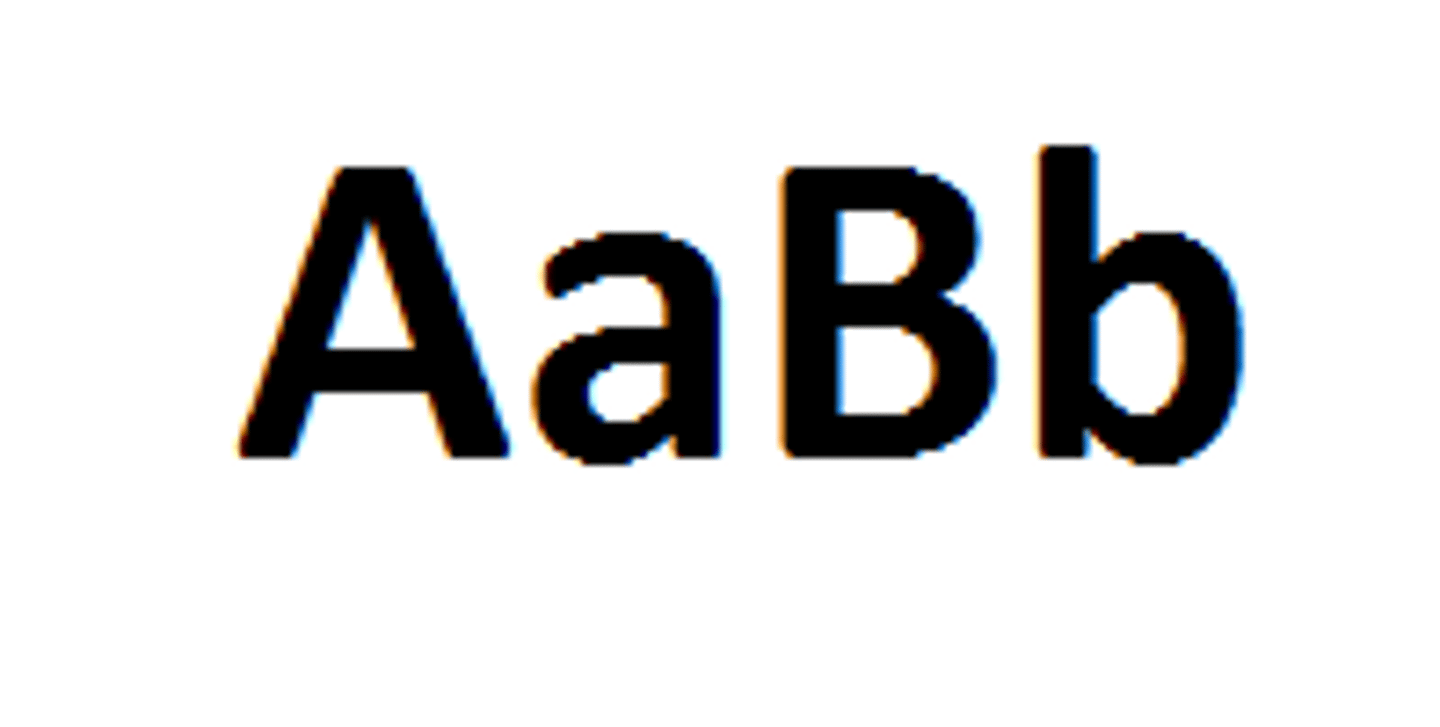
Recessive
trait of an organism that can be masked by the dominant form of a trait
Dominant
observed trait of an organism that mask the recessive form of a trait
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait

Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait

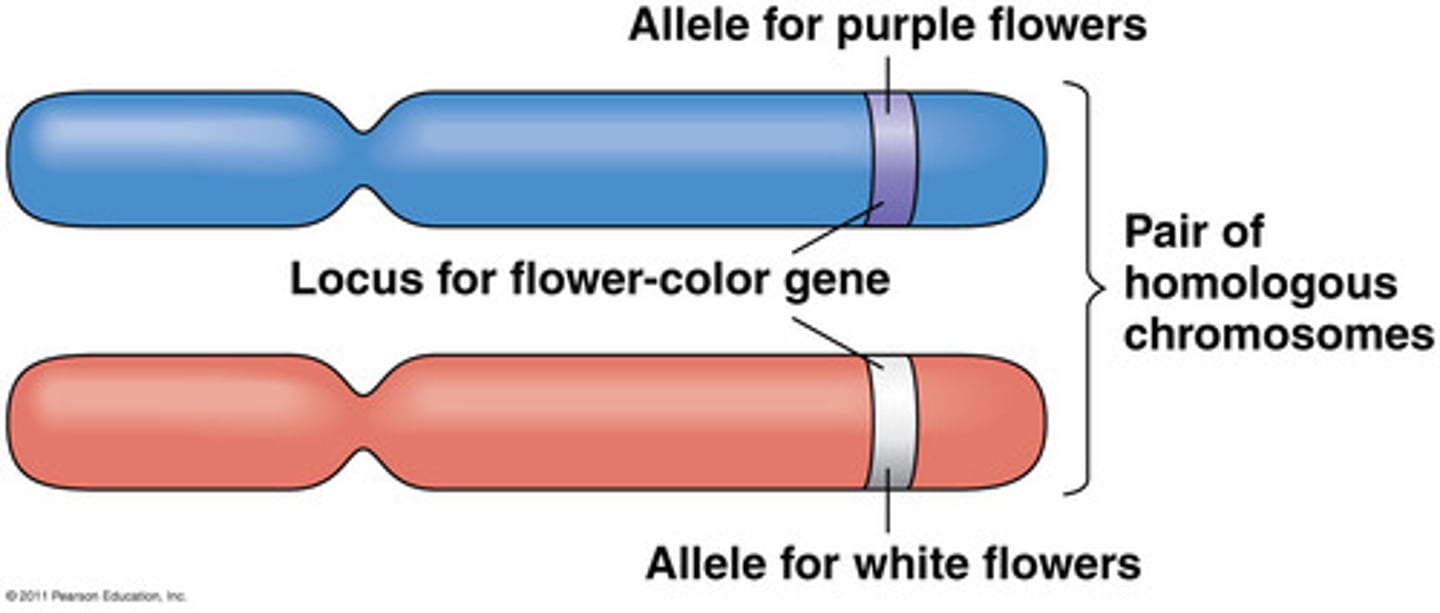
Allele
alternative forms of a gene for each variation of a trait of an organism
Law of independent assortment
The inheritance pattern of one trait will not affect the inheritance pattern of another
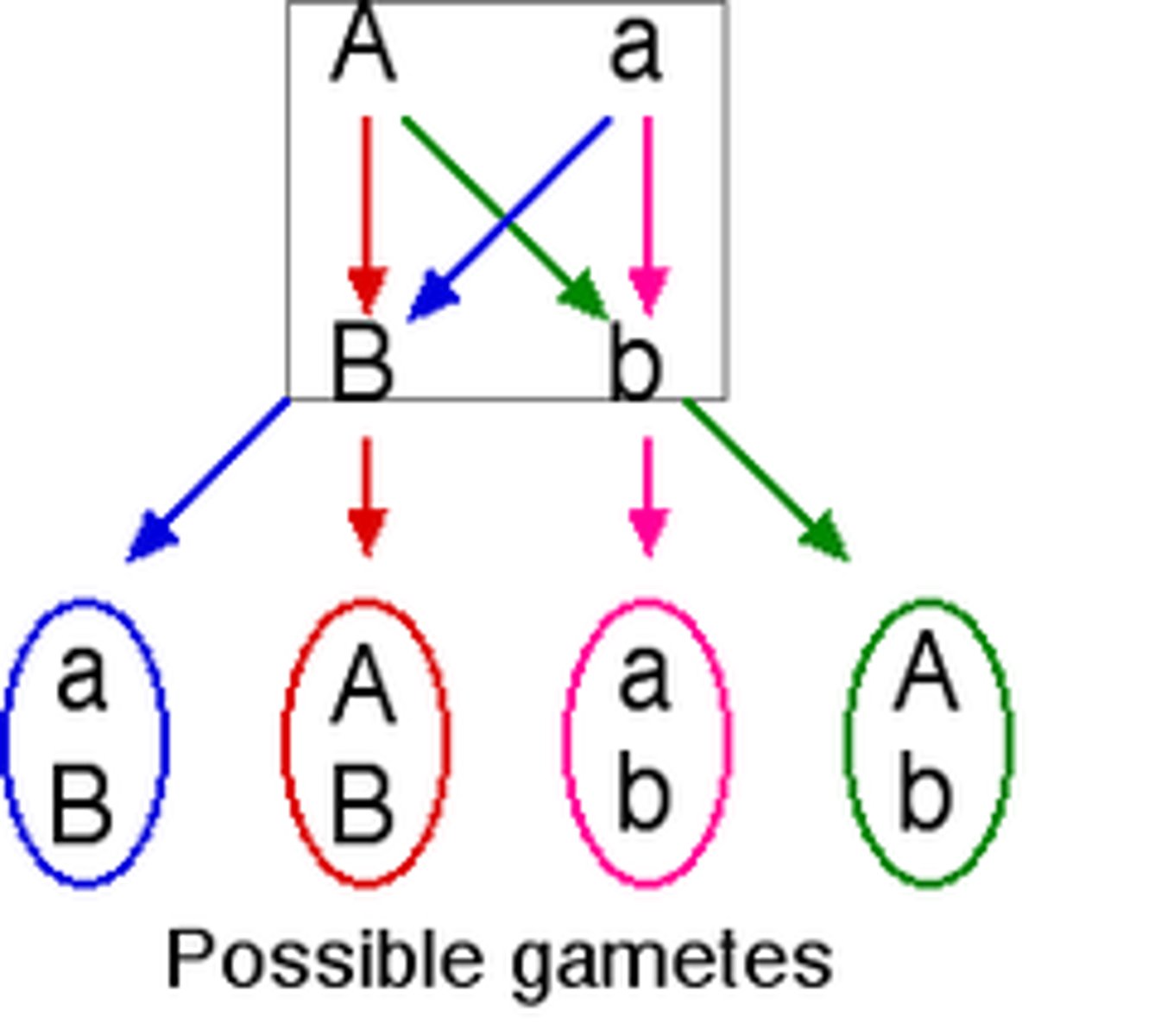
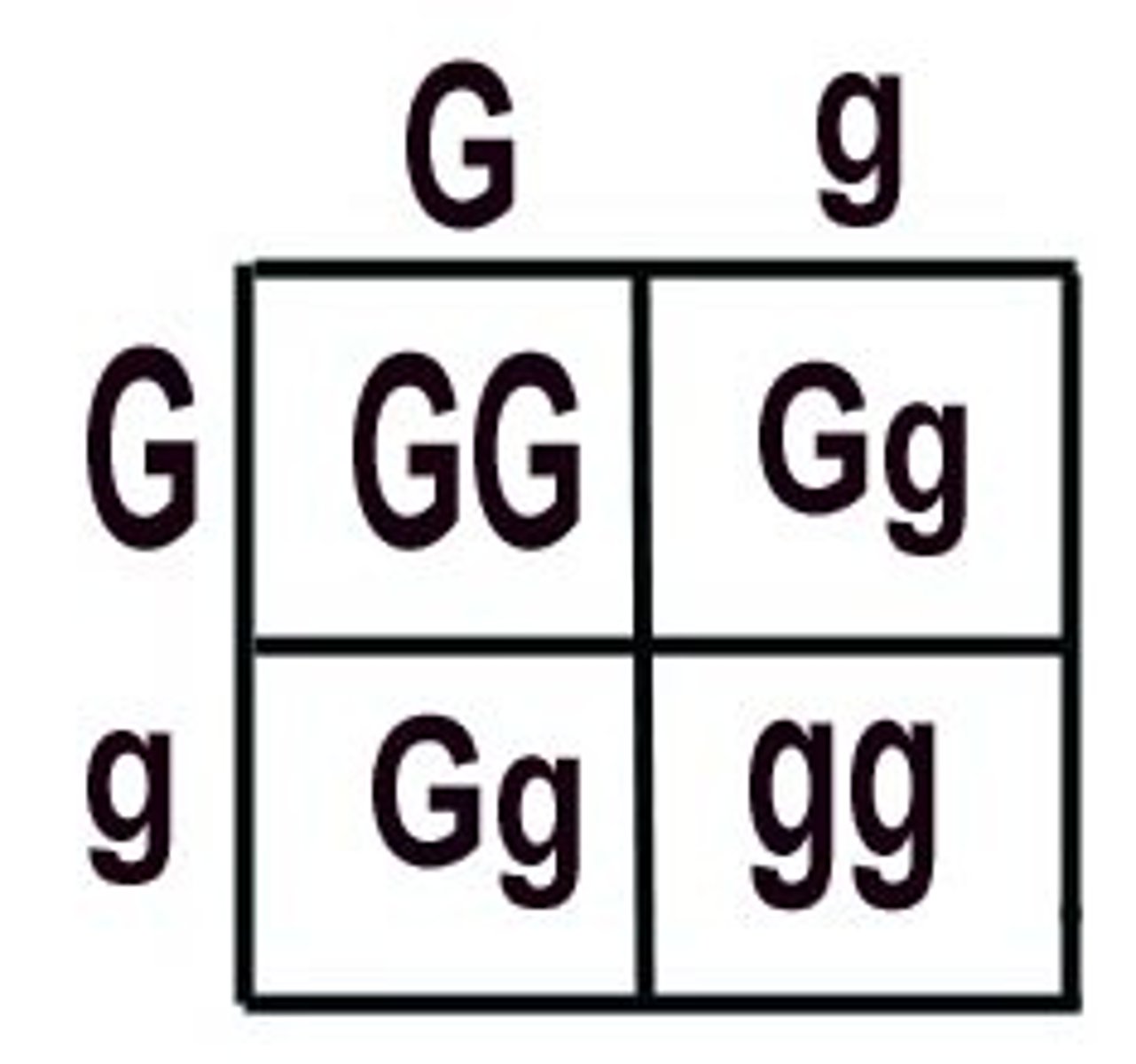
Punnett Square
diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross
Sex-Linked Trait
A trait associated with a gene that is carried only by the male or female parent.
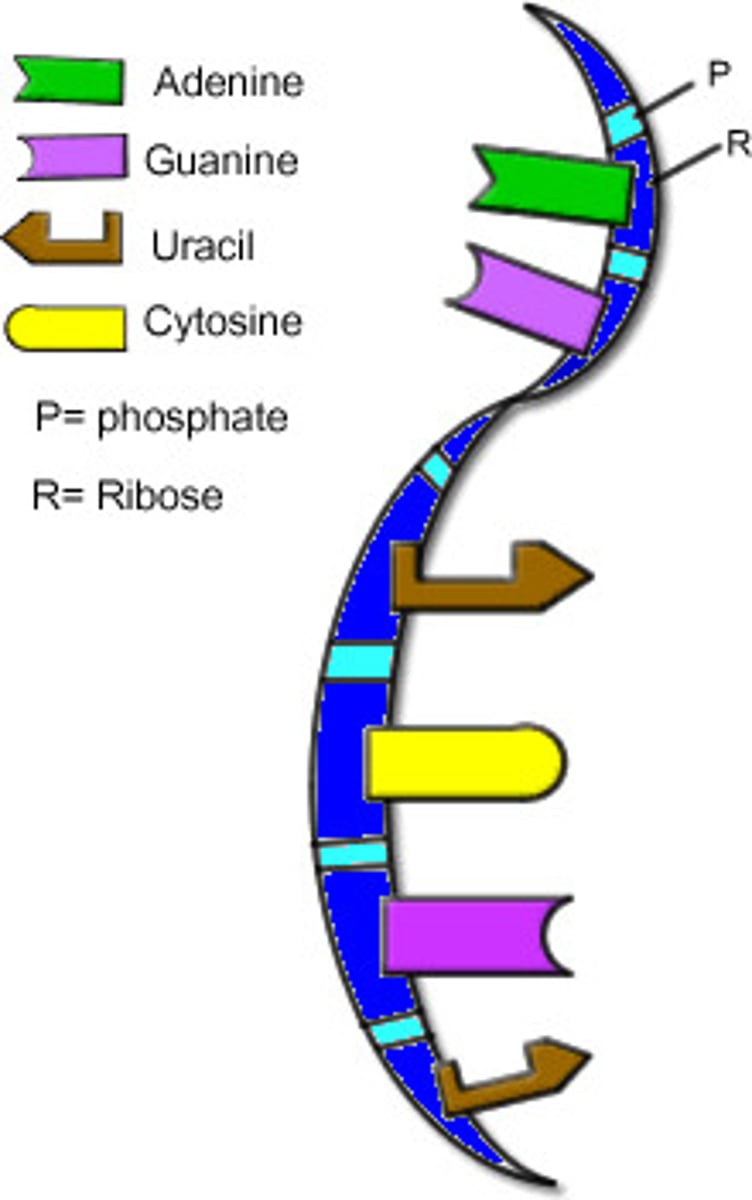
DNA
a complex molecule containing the genetic info that makes up the chromosomes
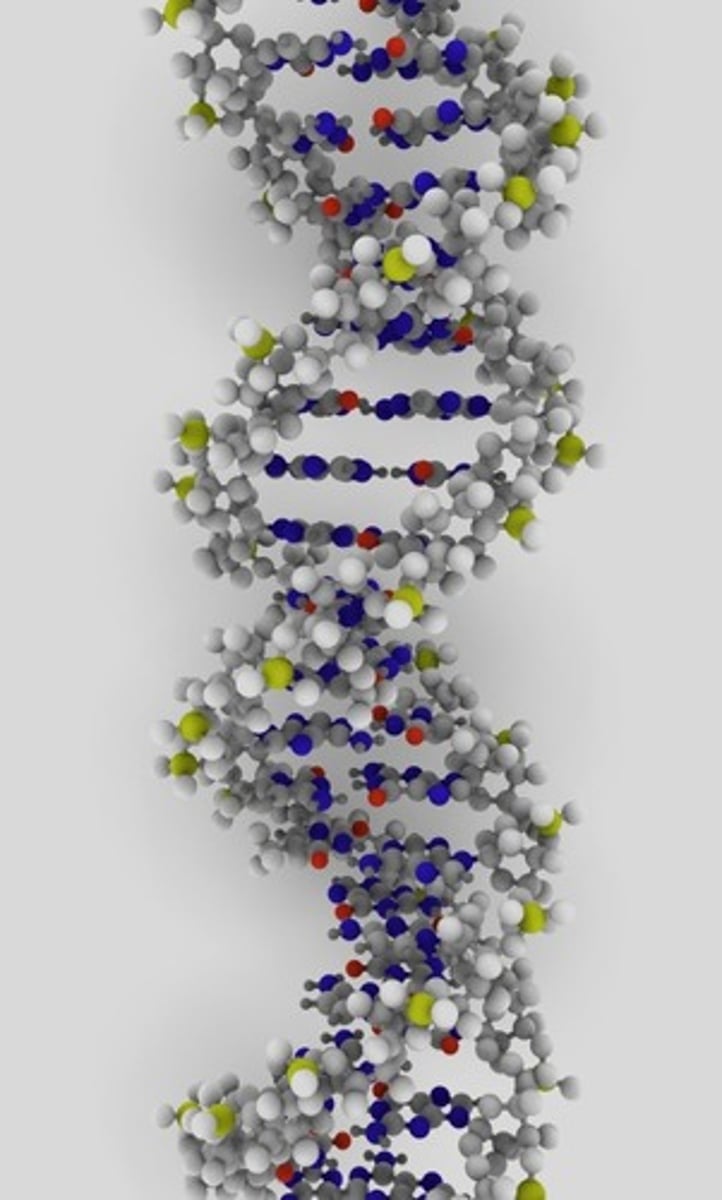
Watson and Crick
Developed the double helix model of DNA.

Nucleotide
Building blocks (monomer) of nucleic acid.
Codon
a sequence of three nucleotide bases that represents the code for one amino acid
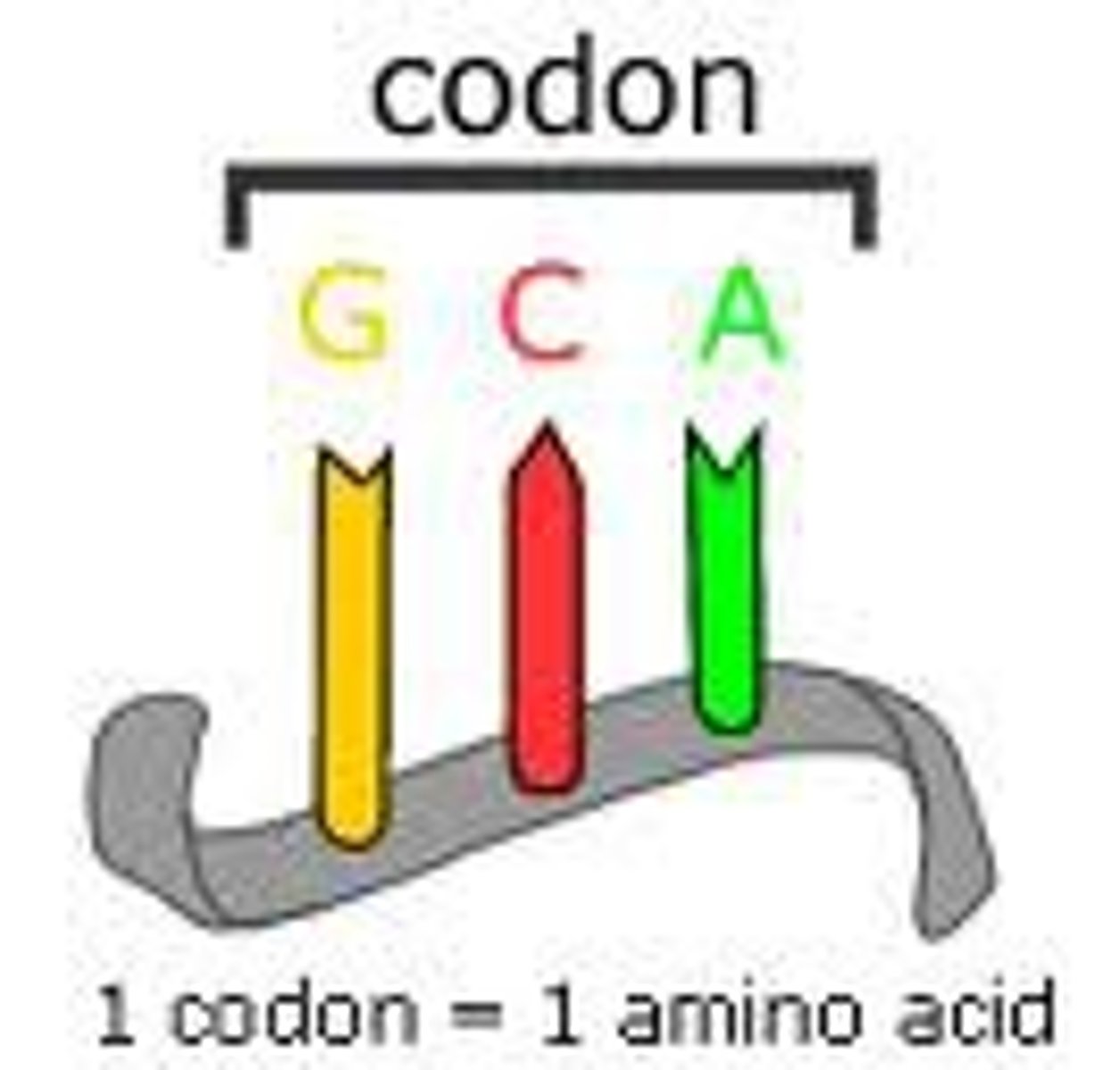
Amino Acids
Building blocks of protein
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages
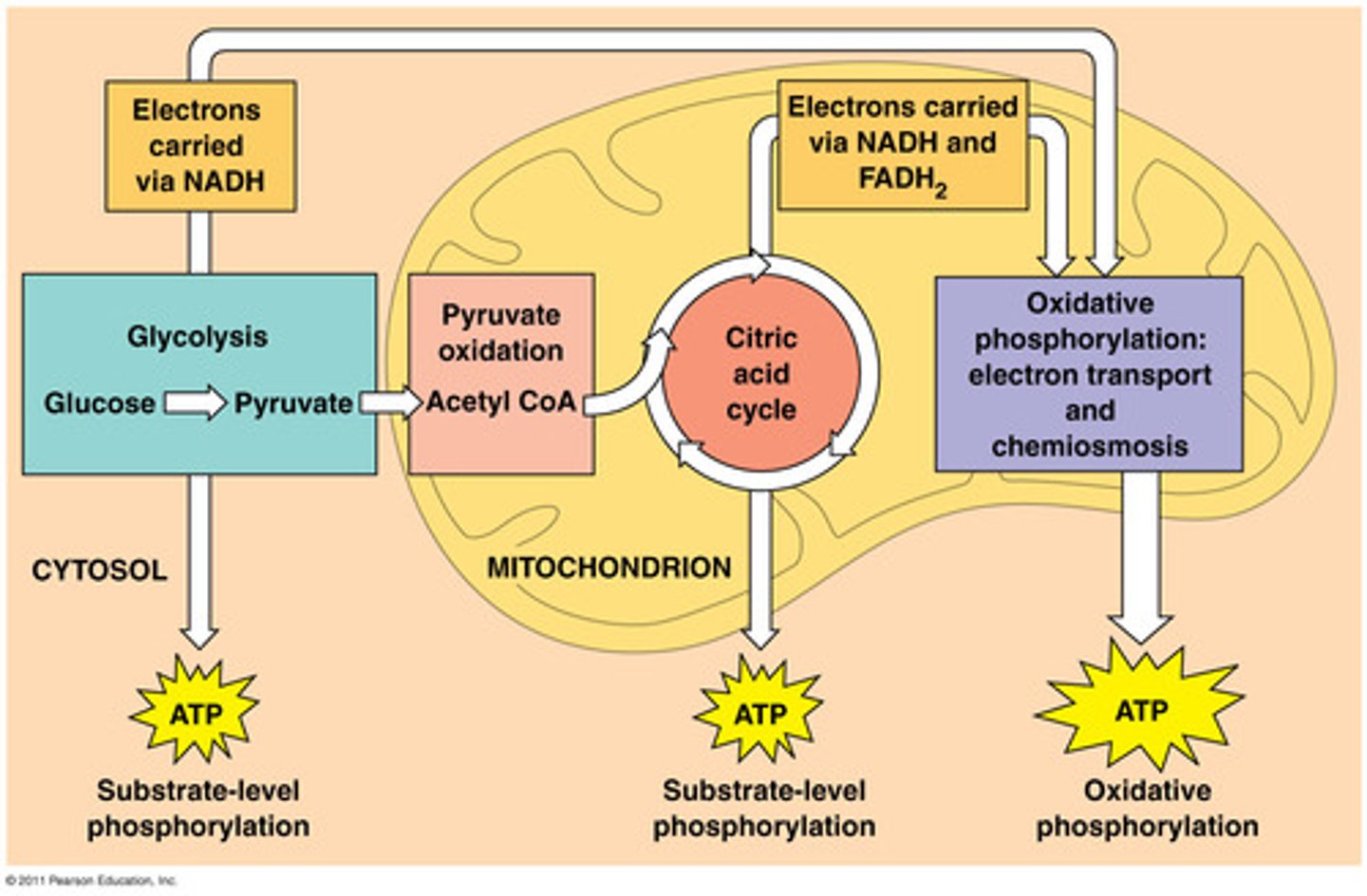
Cellular Respiration
The process of using sugar and oxygen to create carbon dioxide and water

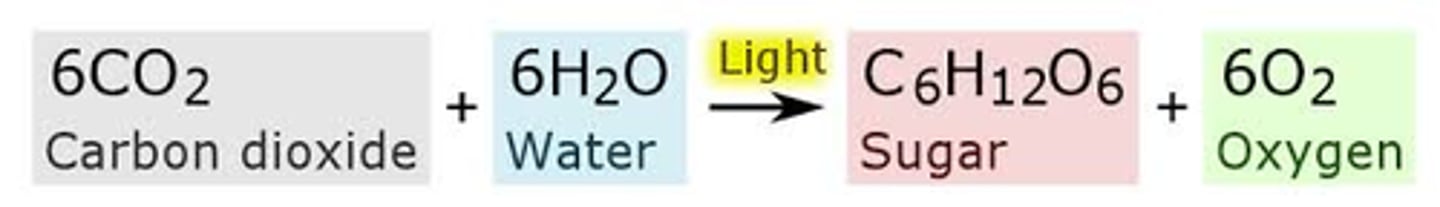
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars
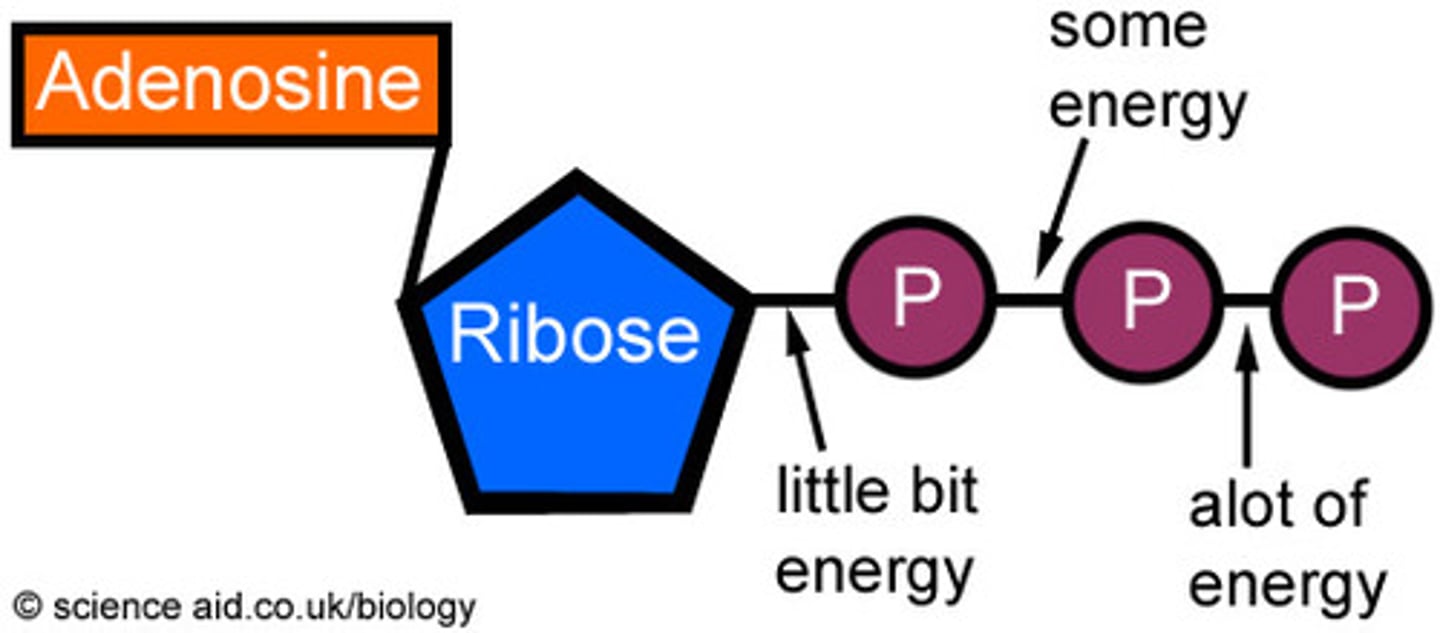
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
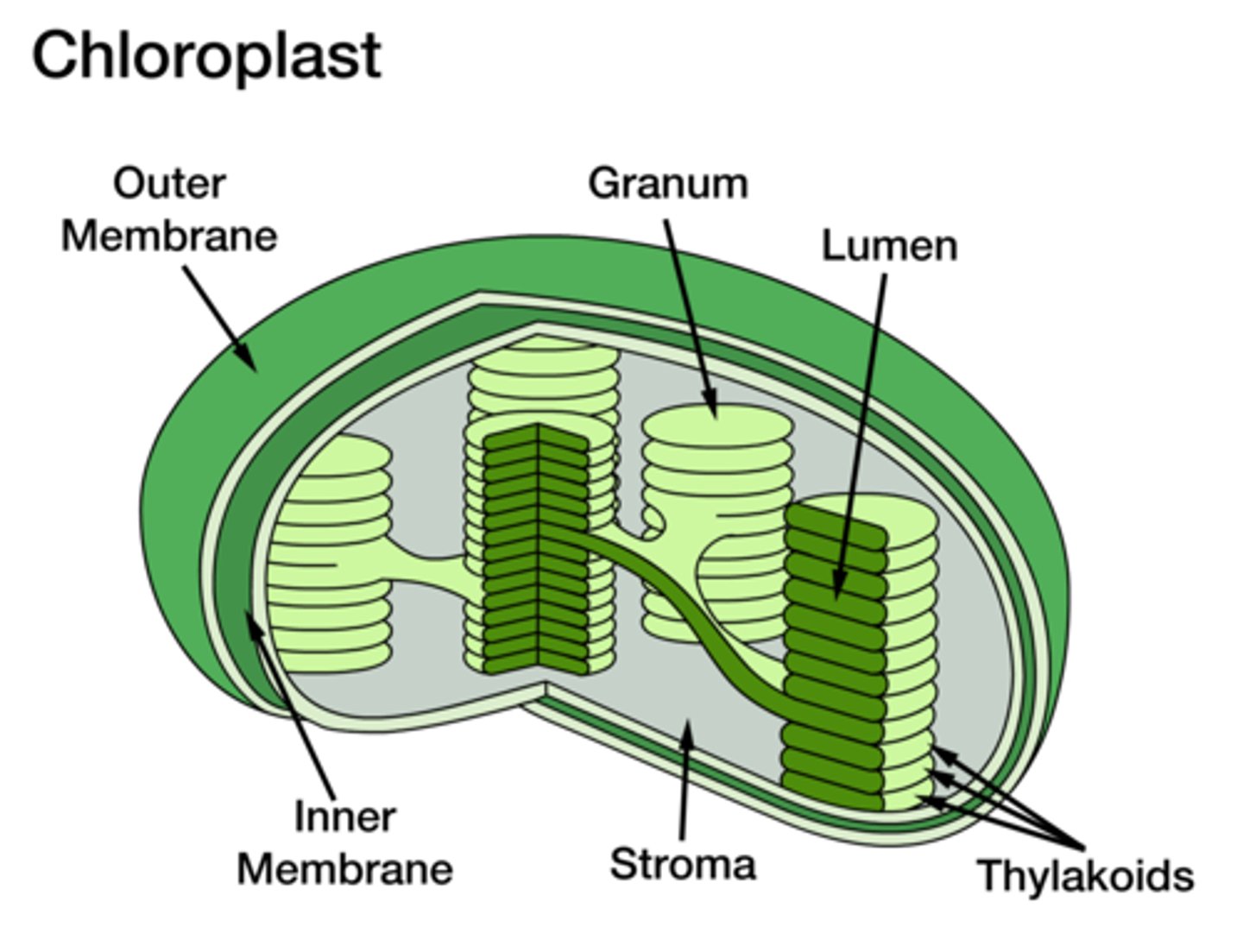
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
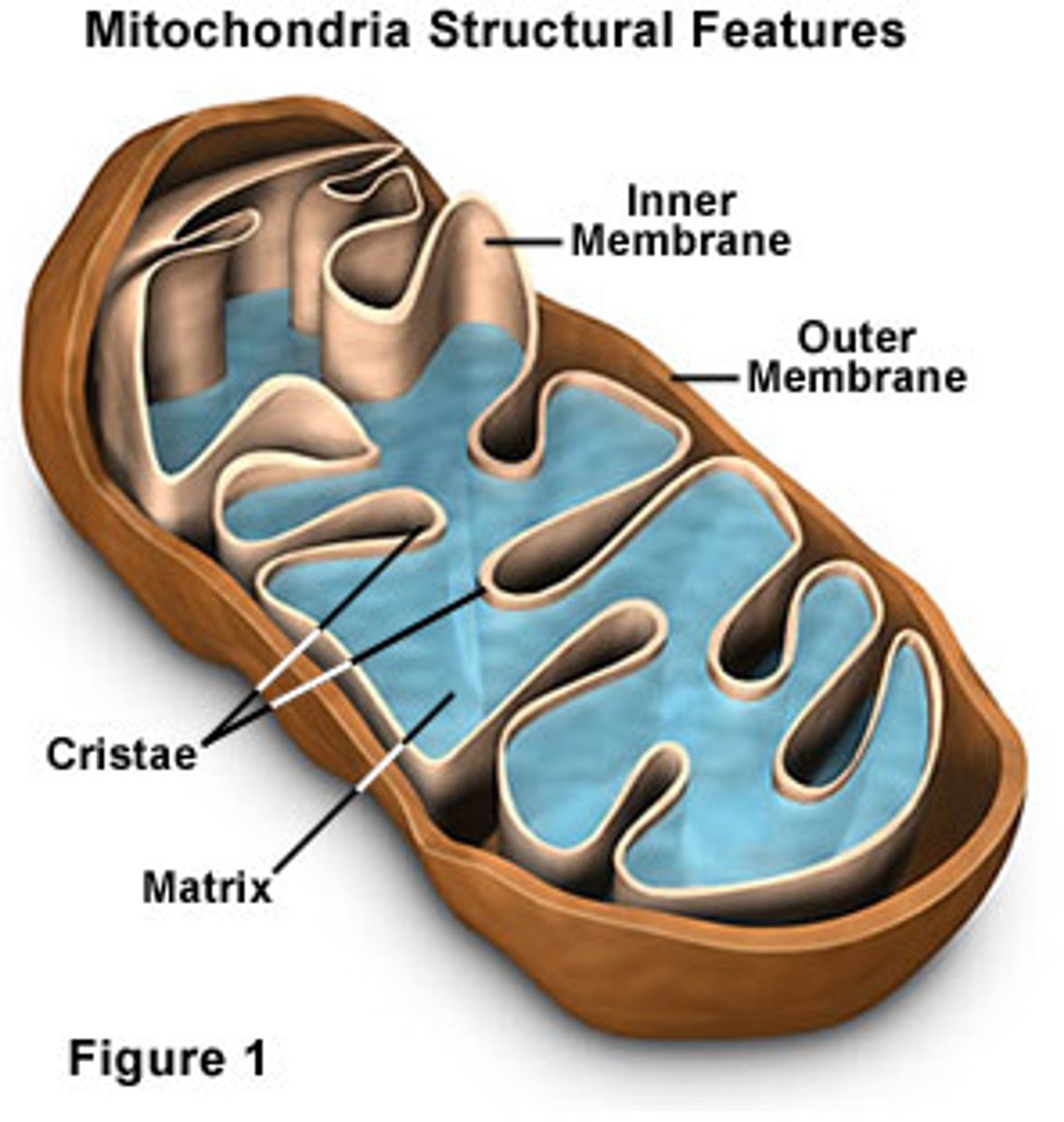
Mitochondria
site of cellular respiration
Scientific Theory
Hypothesis that has been tested and supported by evidence
Natural Selection
A natural process resulting in the evolution of organisms best adapted to the environment.
Adaptation
A trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
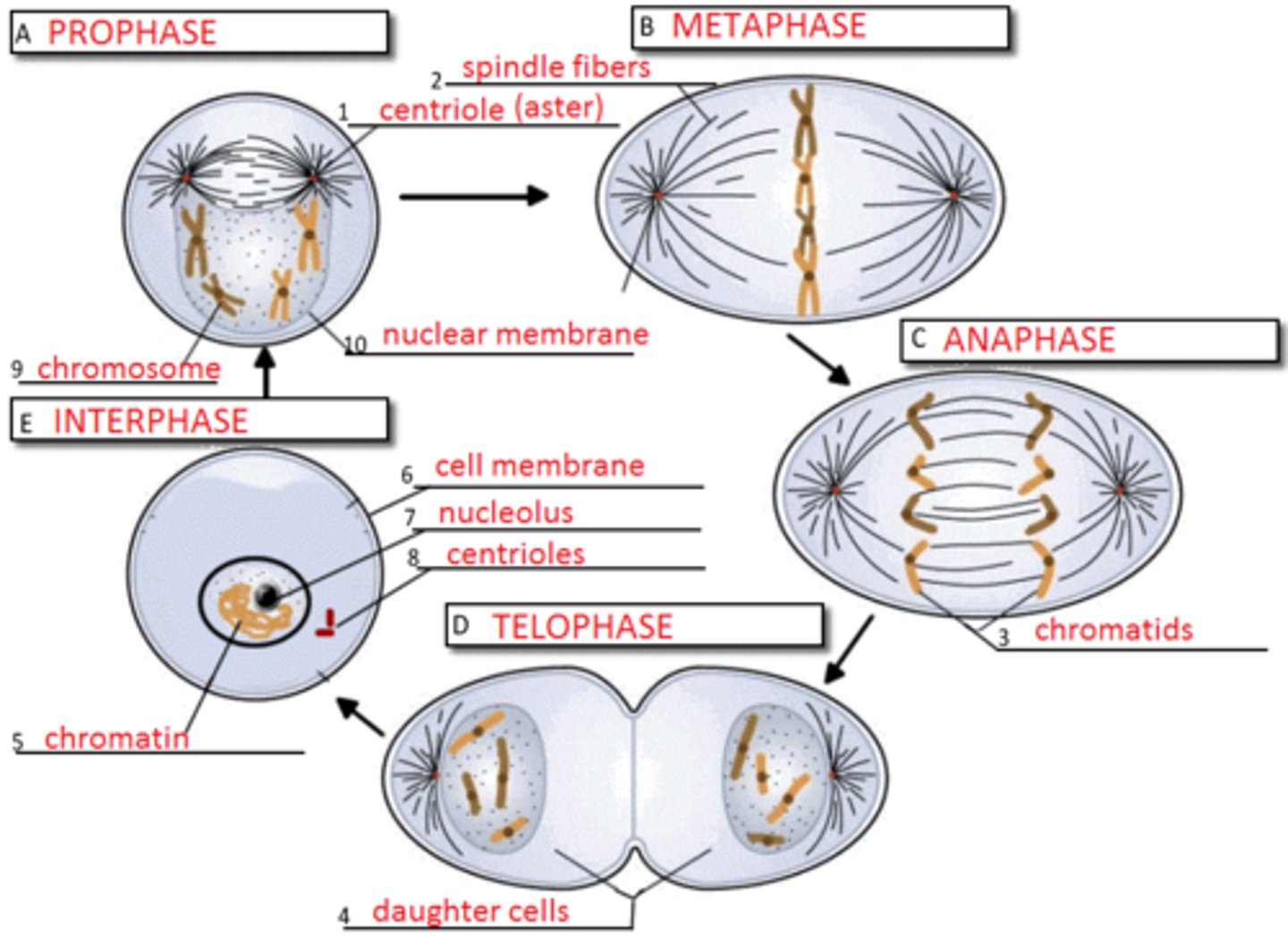
Prophase
Chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm of the cell
Atom
Smallest unit of an element that still retains the chemical and physical properties of an element.
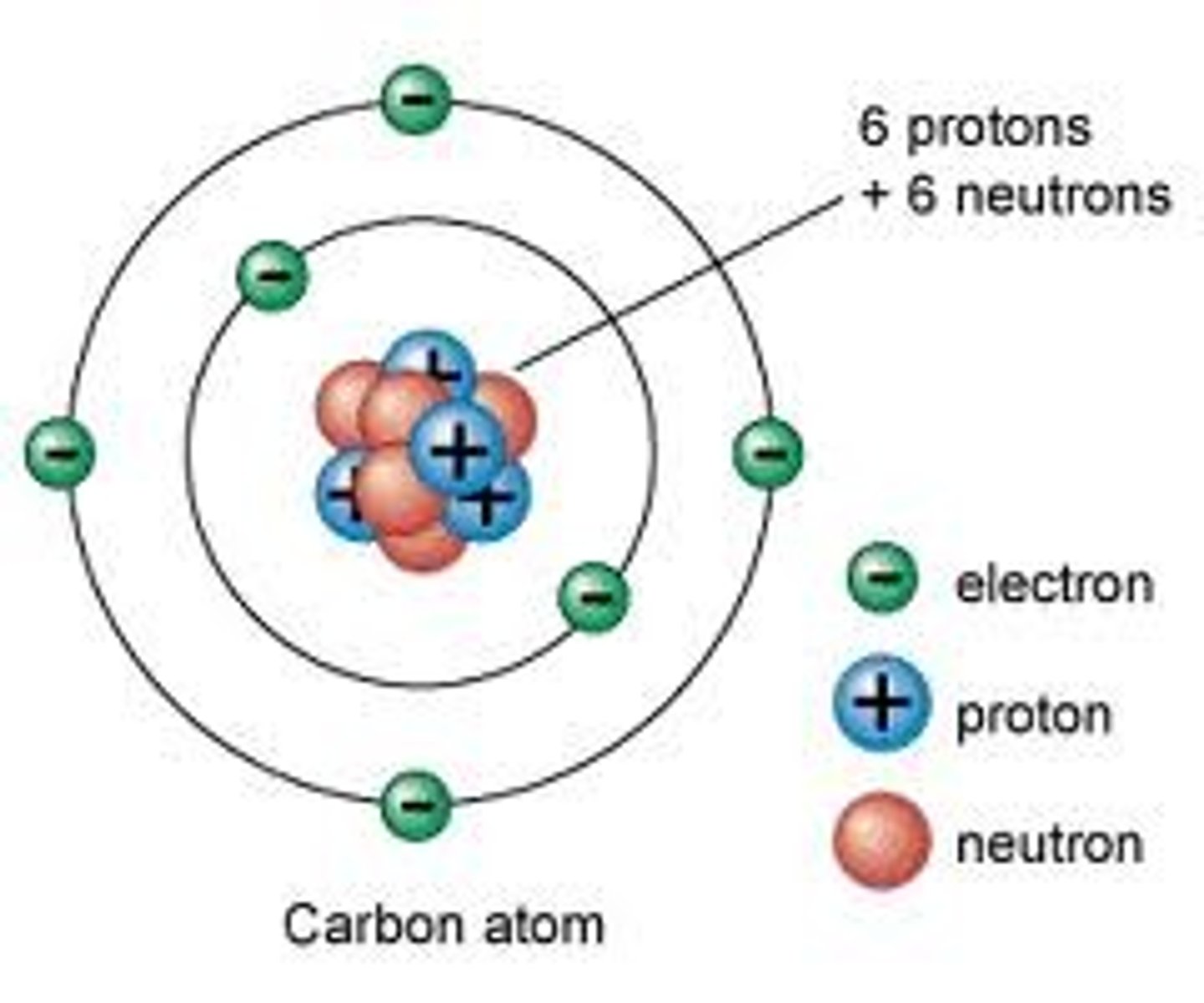
The three subatomic particles that makeup an atom are?
Protons (positively charged)
Neutrons (uncharged)
Electrons (negatively charged)

What is the circle around the nucleus of the atom?
Electron shell, which represents the average location of electrons.
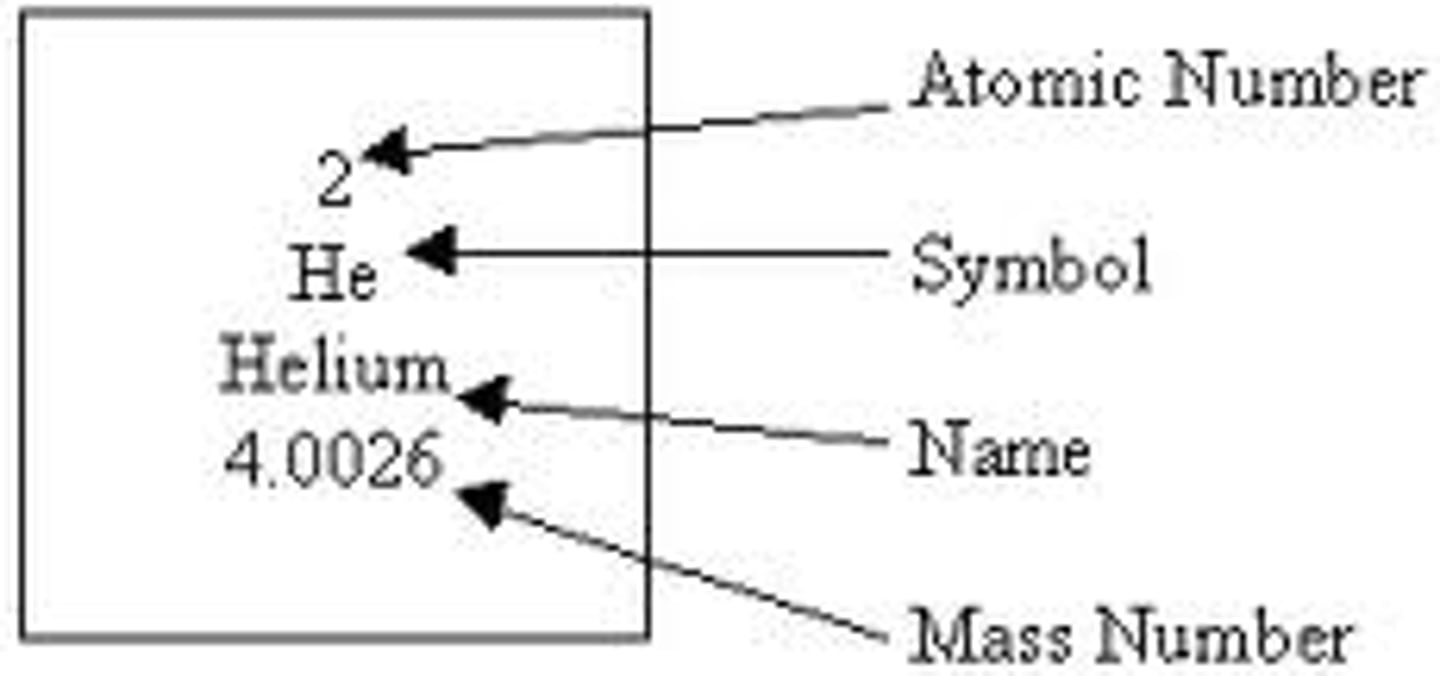
Atomic #?
# of protons
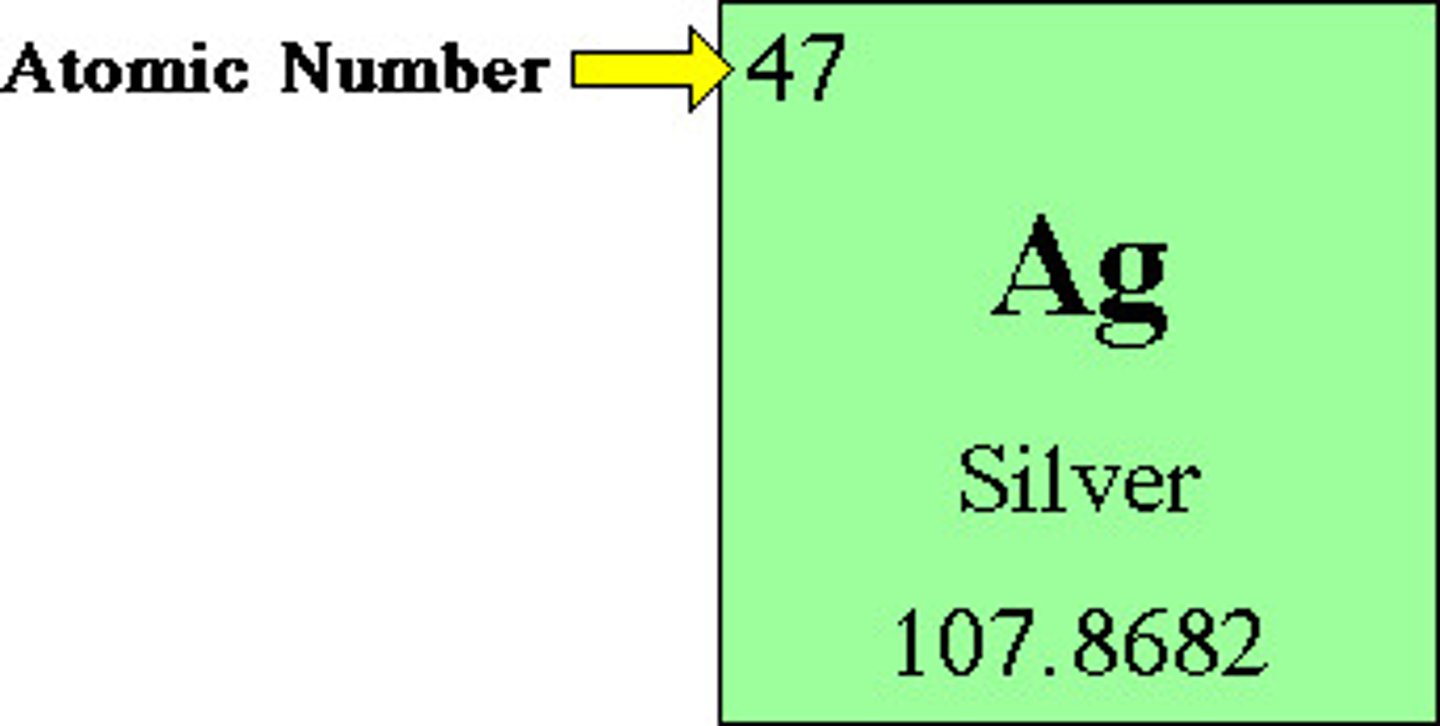
Mass #?
The sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
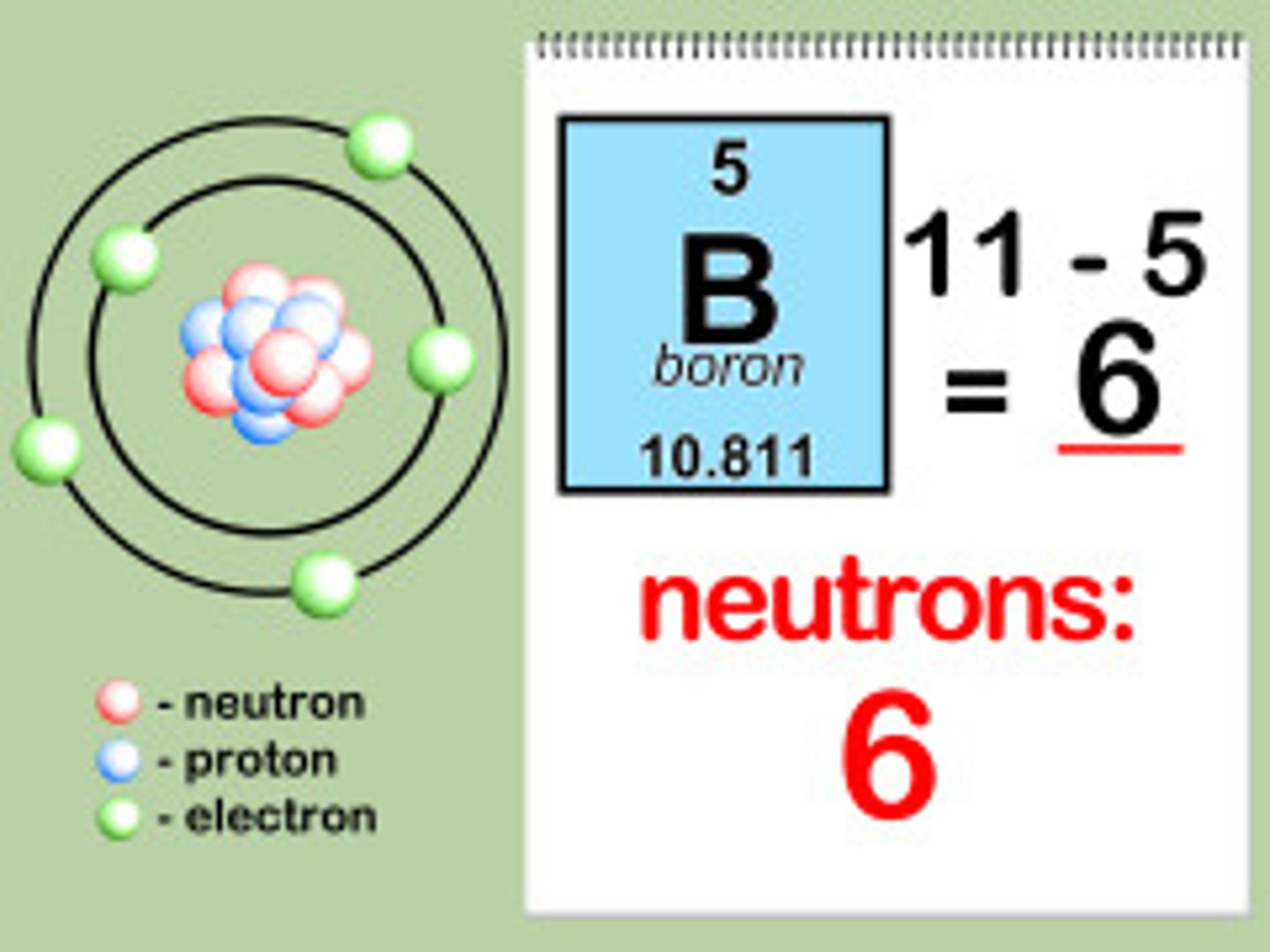
To determine the # of neutrons you?
Subtract the # of protons from the atomic mass, and take the closest whole #.
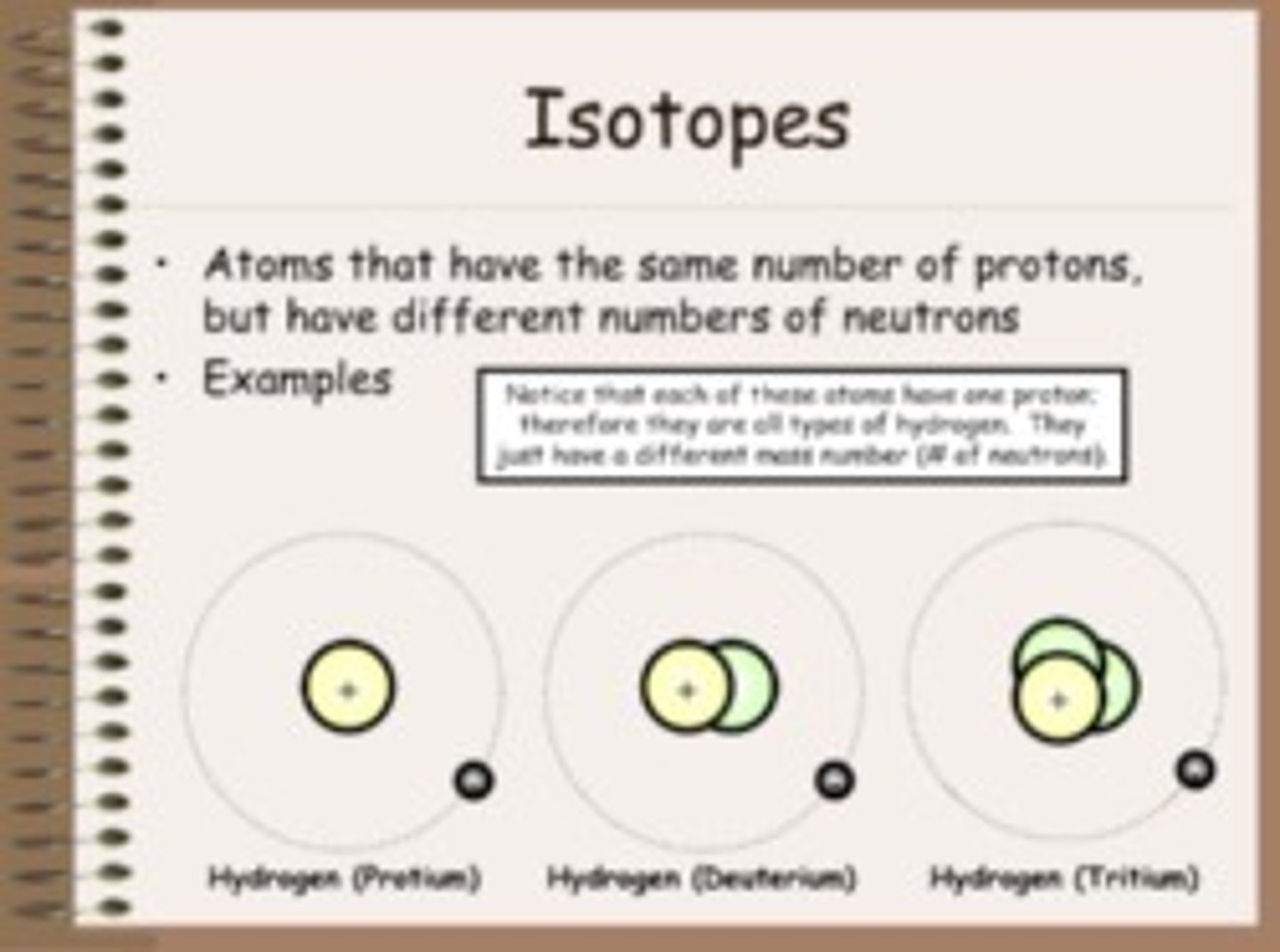
Isotope?
Same # of protons. Different number of neutrons.
Atoms bond with one another to form a chemical unit called?
Molecule
Atoms with more than one shell are most stable when the outer most shell also called ? contains eight electrons
Valence shell.
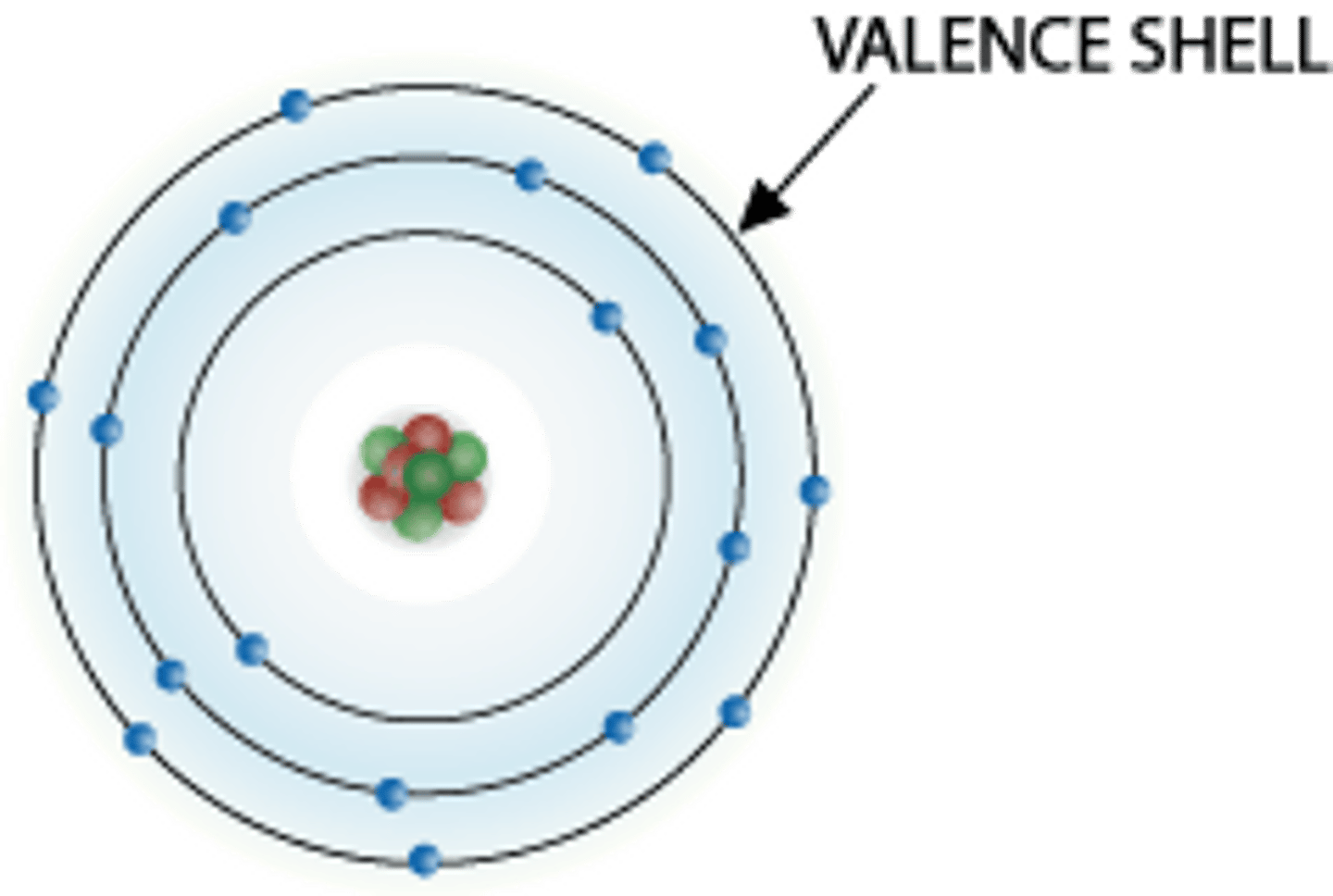
Ions
Particles that carry either a positive or negative charge.
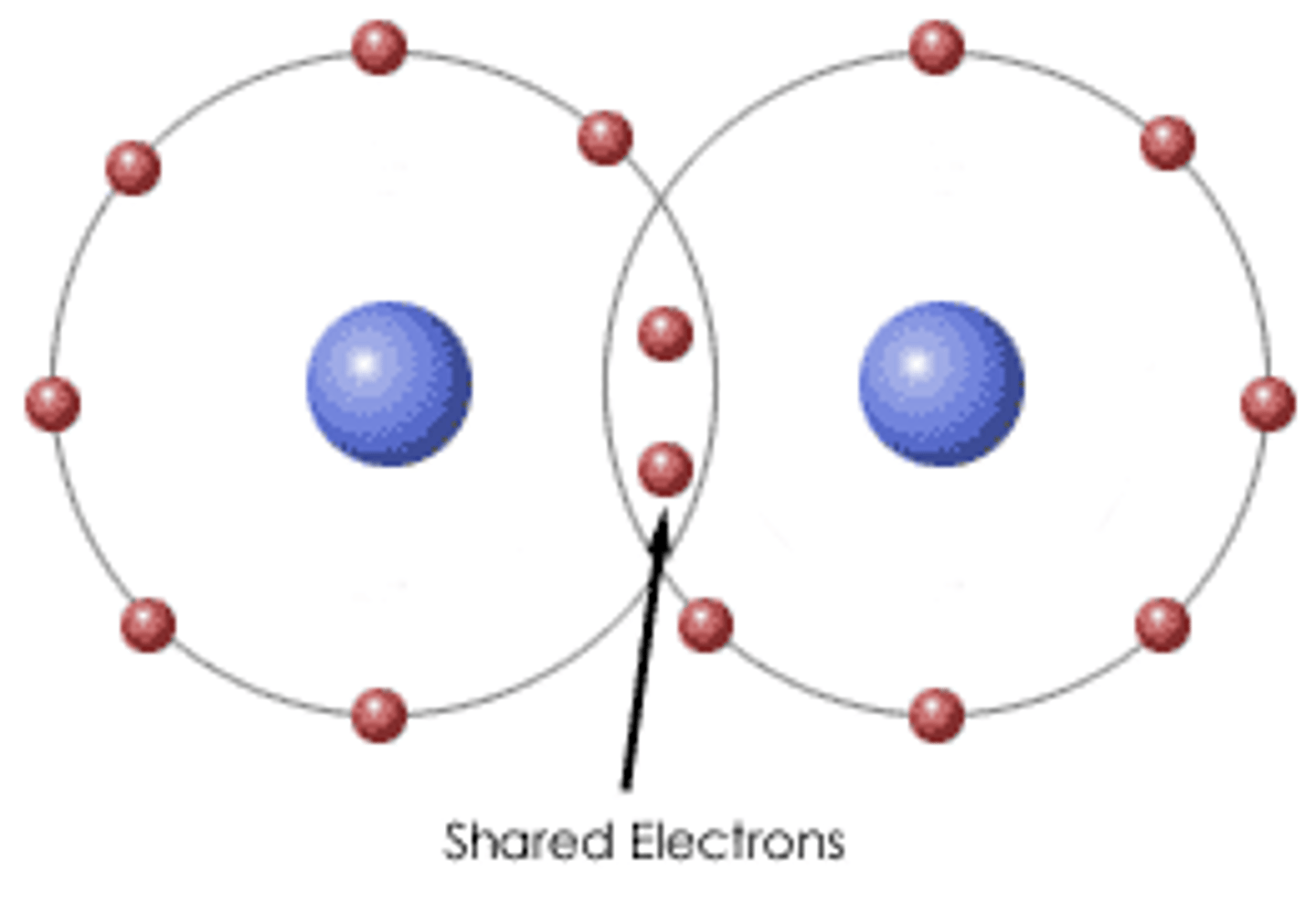
Covalent bond?
Atoms share electrons equally.
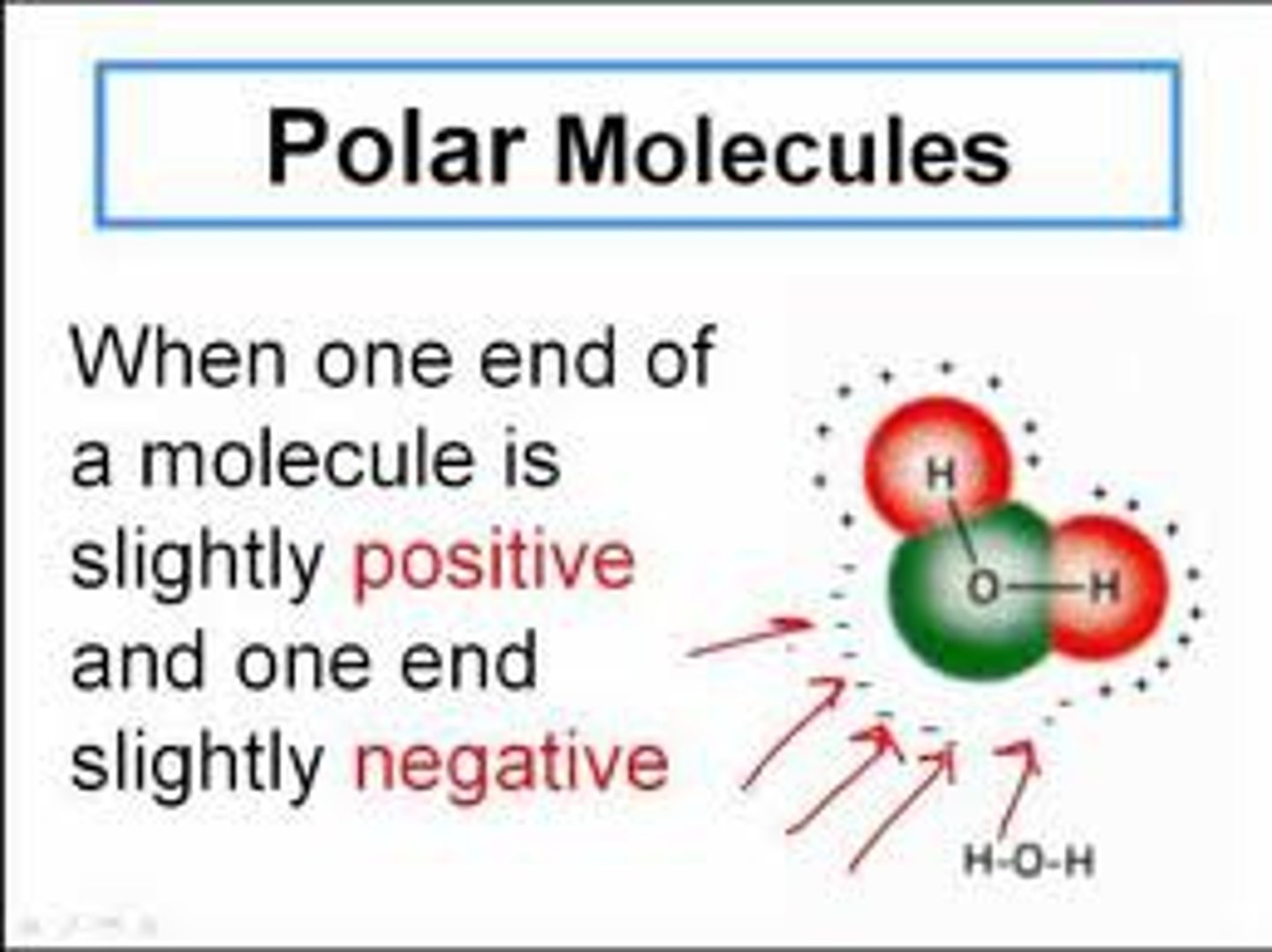
Polar molecule?
Its a covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally because the elements have different electronegtaives one end is slightly negative and the other is slightly positive. So they are considered partial charges and denoted by delta plus and delta minus.
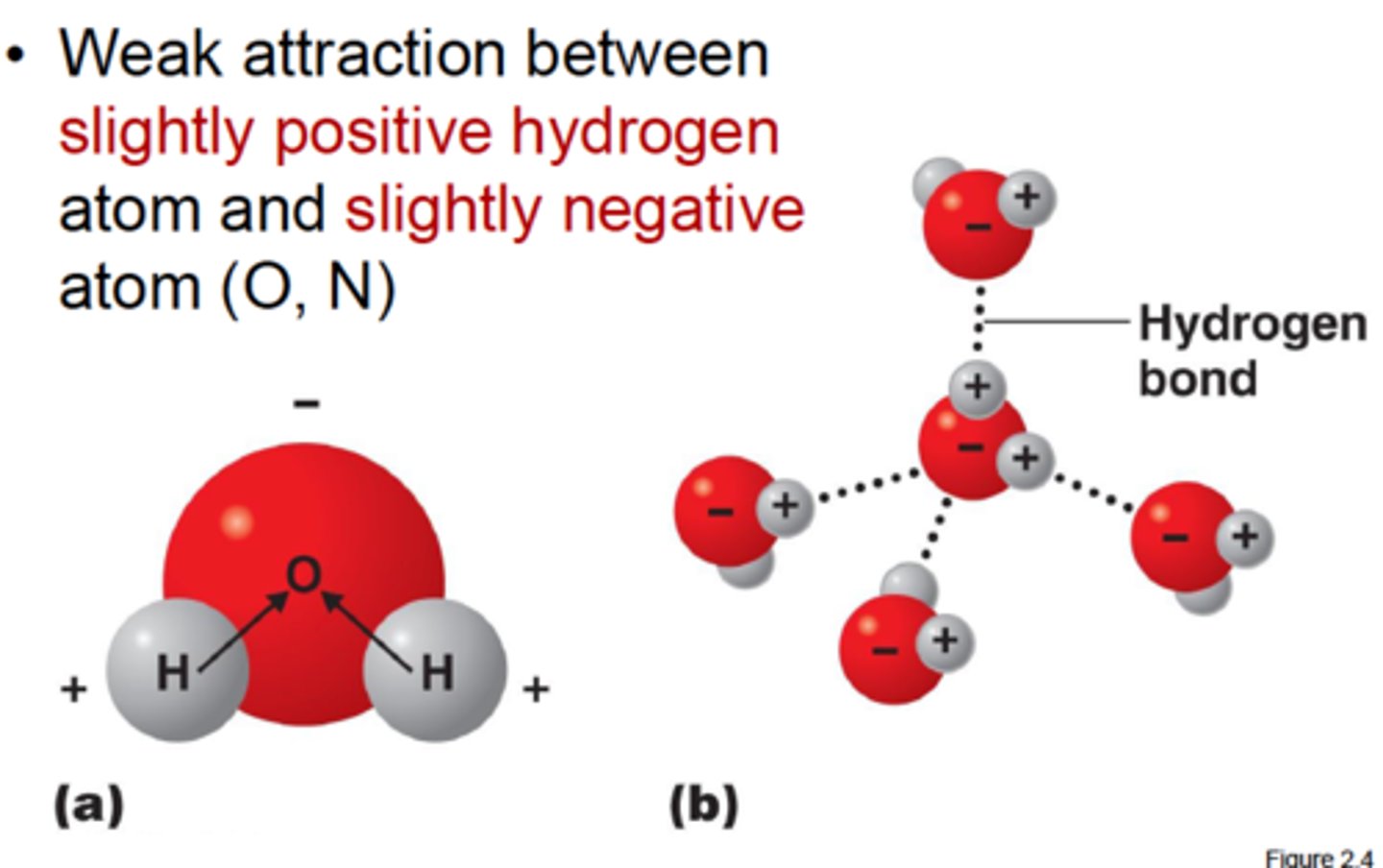
Hydrogen bond?
The attraction of a partially positive covalently bonded hydrogen to a partially negative atoms in the vicinity. Not as strong as a ionic or covalent bond. It is a weak bond that can break easily. It will bond to anything that is more electronegative (electron greedy) than it is so it can form a hydrogen bond.
Molecules that can attract water are said to be?
Hydrophilic
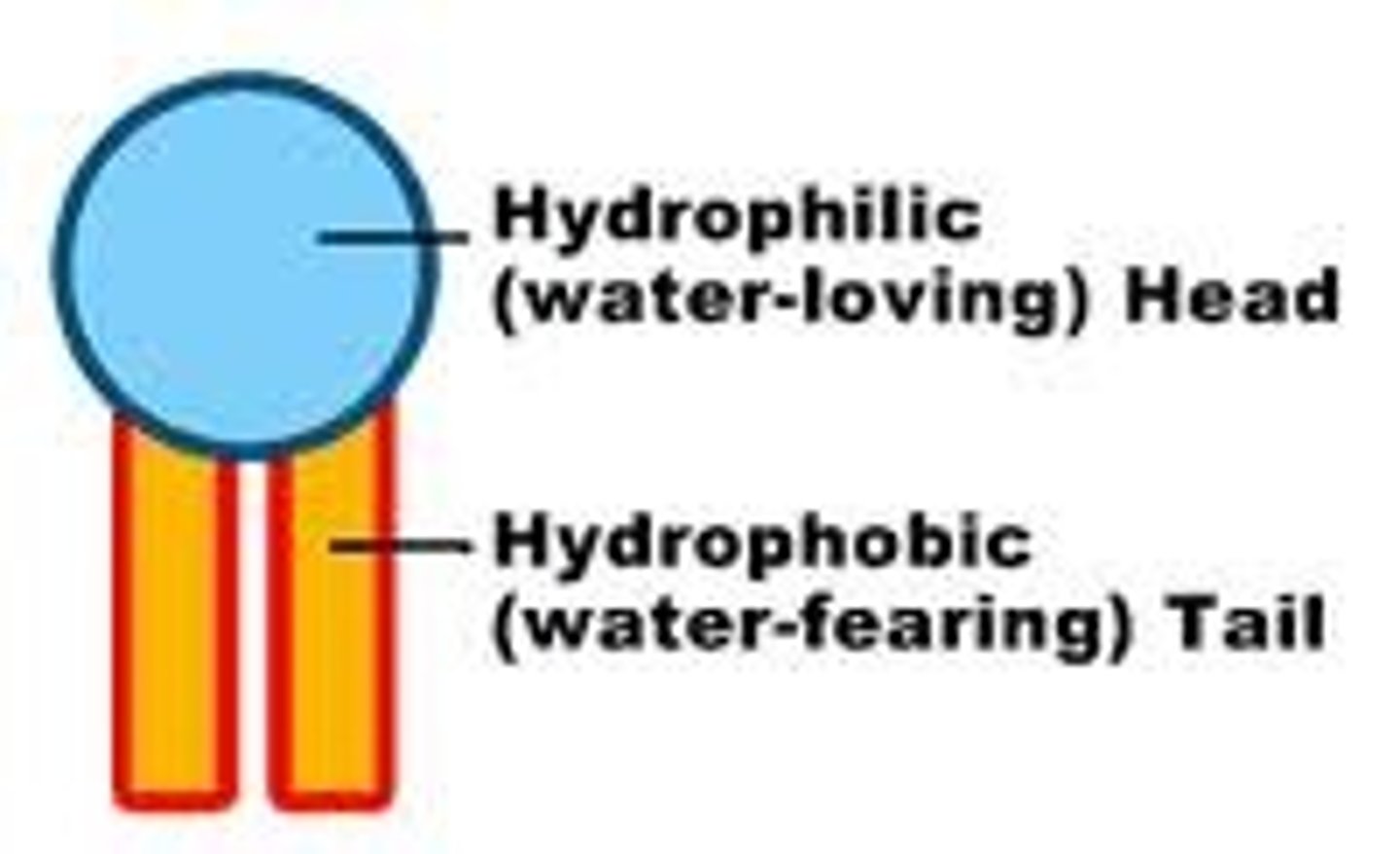
Molecules that cannot attract water are said to be?
Hydrophobic
Hydrophobic molecules tend to attract other?
non polar molecules
Example of polar molecules and non polar molecules?
1. Water is polar
2. Oils like vegetable oils. Which is why it does not mix well in water.
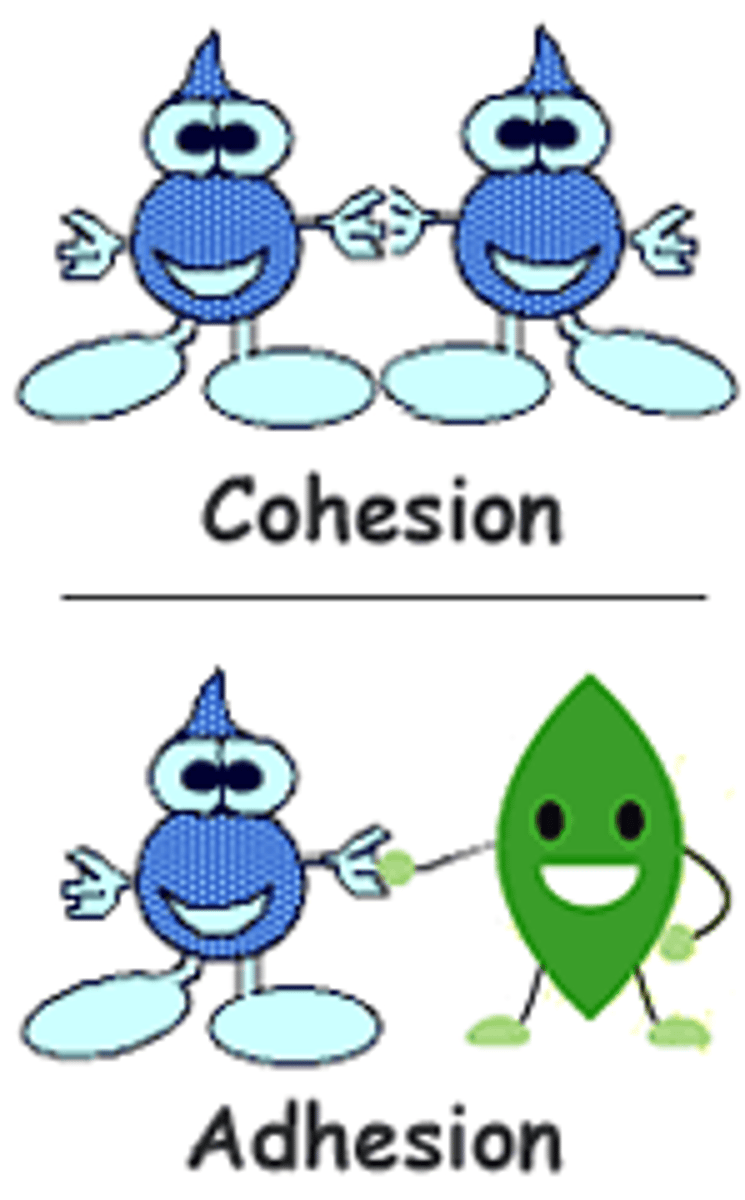
Cohesion
The ability of water molecules to cling to each other due to hydrogen bonding
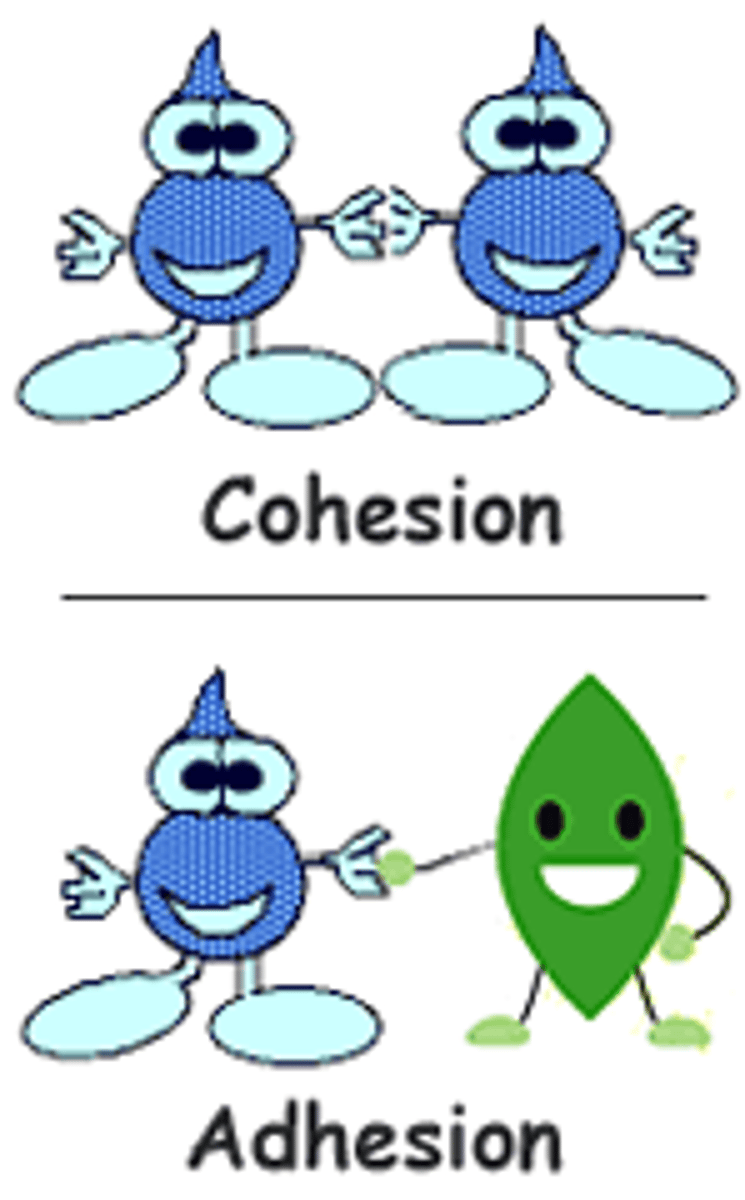
Adhesion
Refers to the ability of water molecules to cling to other polar surfaces. This is a result of water polarity.
Surface tension
caused by the attraction between the molecules of the liquid by various intermolecular forces.
Acids
Substances that dissociates (proton donor) in water releasing hydrogen ions (H+)
Bases
Substances that either take up hydrogen ions or release hydroxide ions (OH-). (proton acceptor).
PH scale?
Indicate the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a solution.

Buffer?
Controls Ph through dissolved compounds. Prevents sudden changed in Ph.
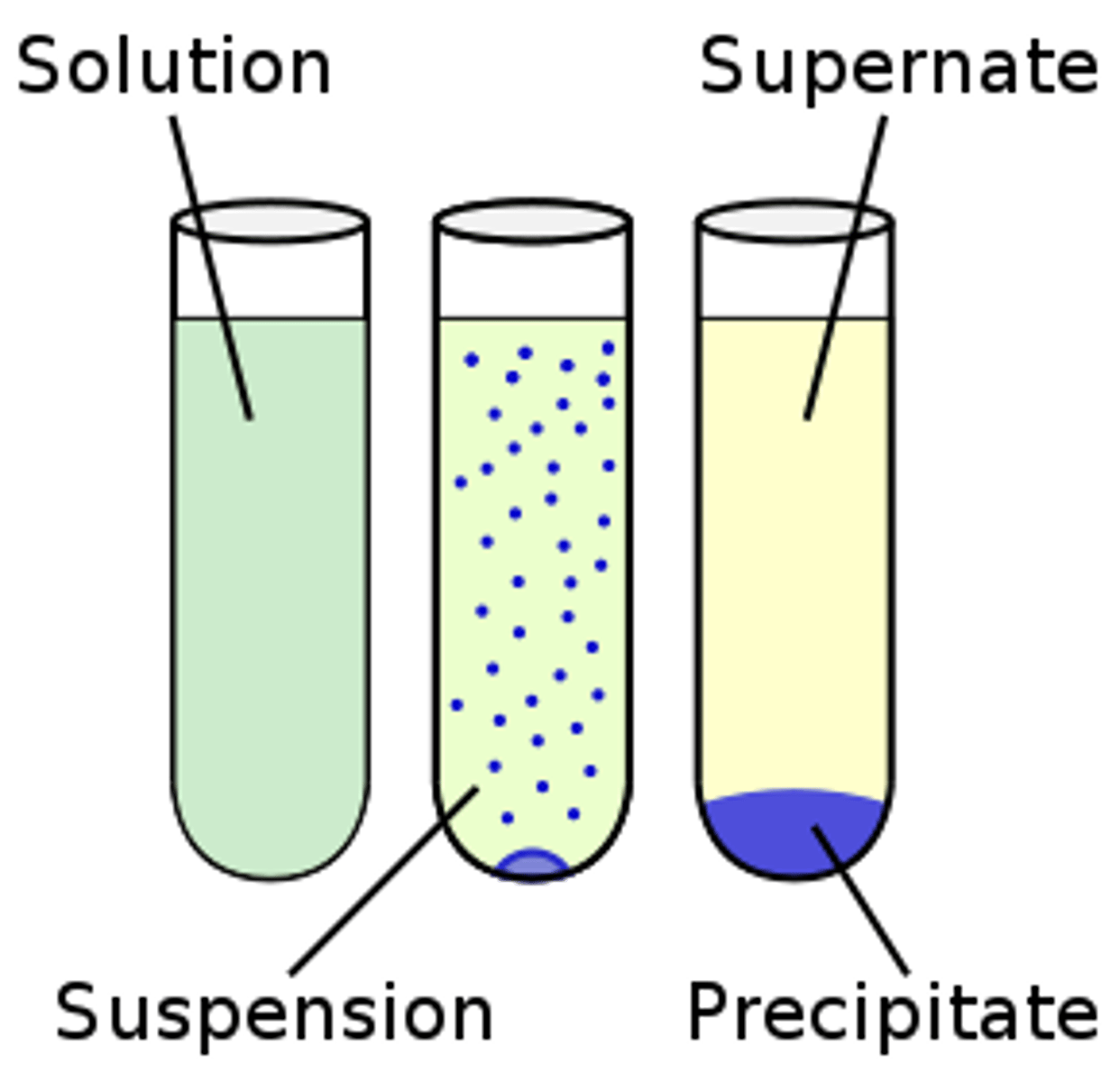
Suspension
Mixtures of water and non dissolved material.
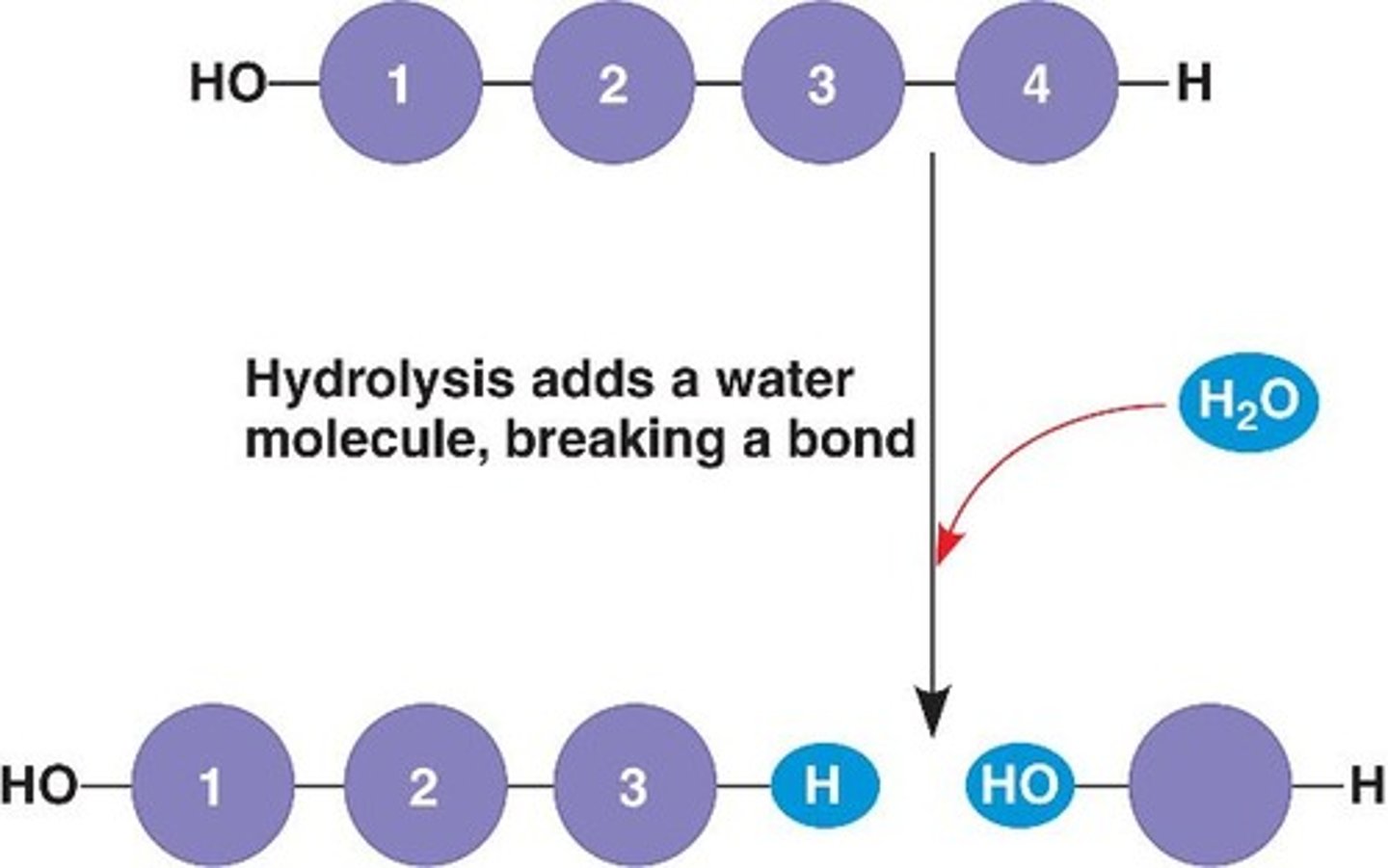
Hydrolysis reaction?
In which the components of water are added during the breaking of the bond between the molecules.
WHAT EUKARYOTIC CELL HAS A CELL WALL?
The plant cell. The cellulose commonly called fiber is found in a plant cell walls.
DNA and RNA are?
Nucleic acids
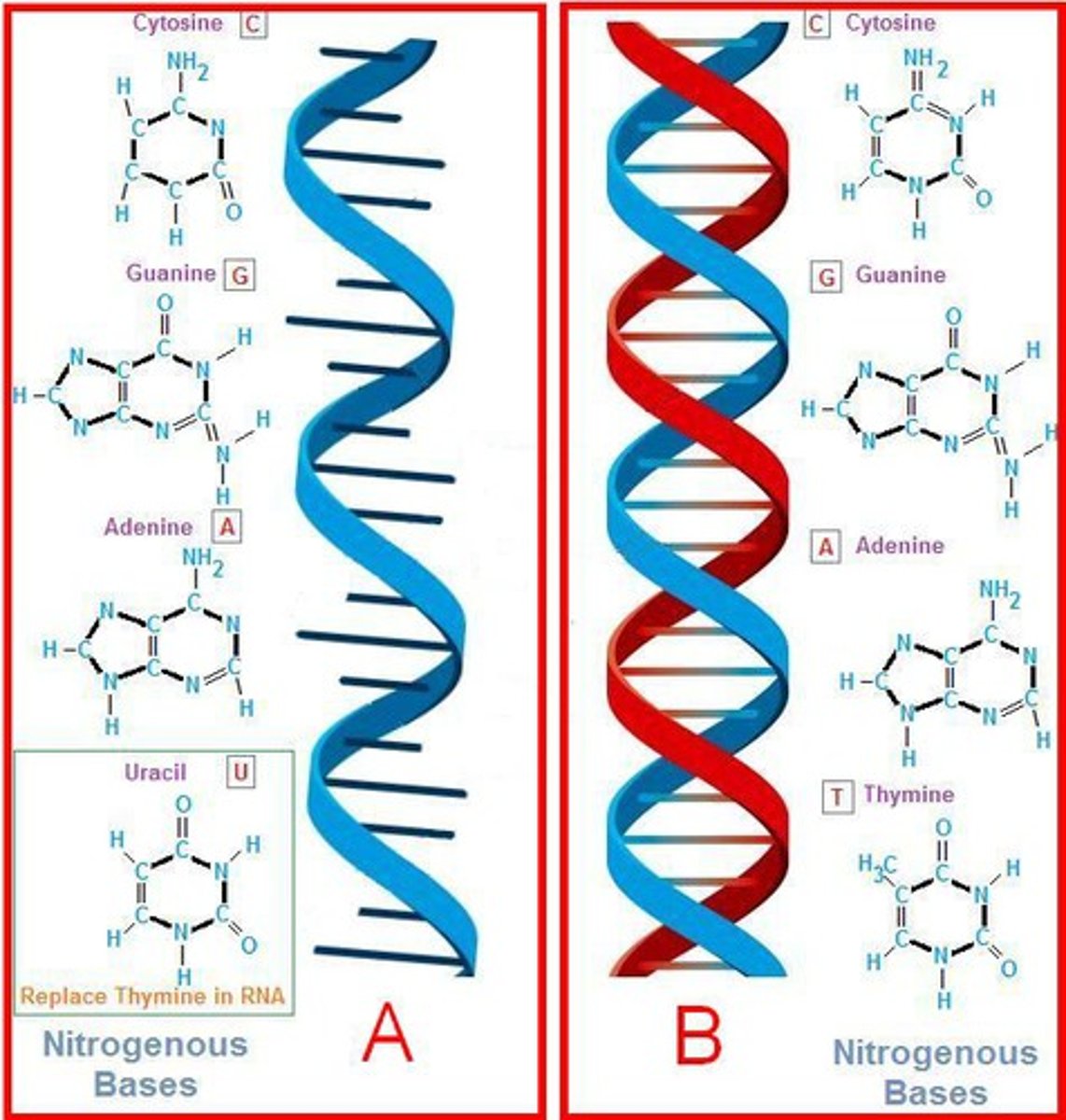
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, stores information about how to copy or replicate itself but also specifies the order in which amino acids are to be joined to make a protein.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid. Working copy of a single gene. Involved in one job-protein synthesis.
Transfer RNA
tRNA, necessary in synthesizing proteins and helps translate the sequence of nucleic acids in a gene into the correct sequence of amino acid during protein synthesis.
Ribosomal RNA
rRNA works as an enzyme to form the peptide bonds between amino acids in a polypeptide.
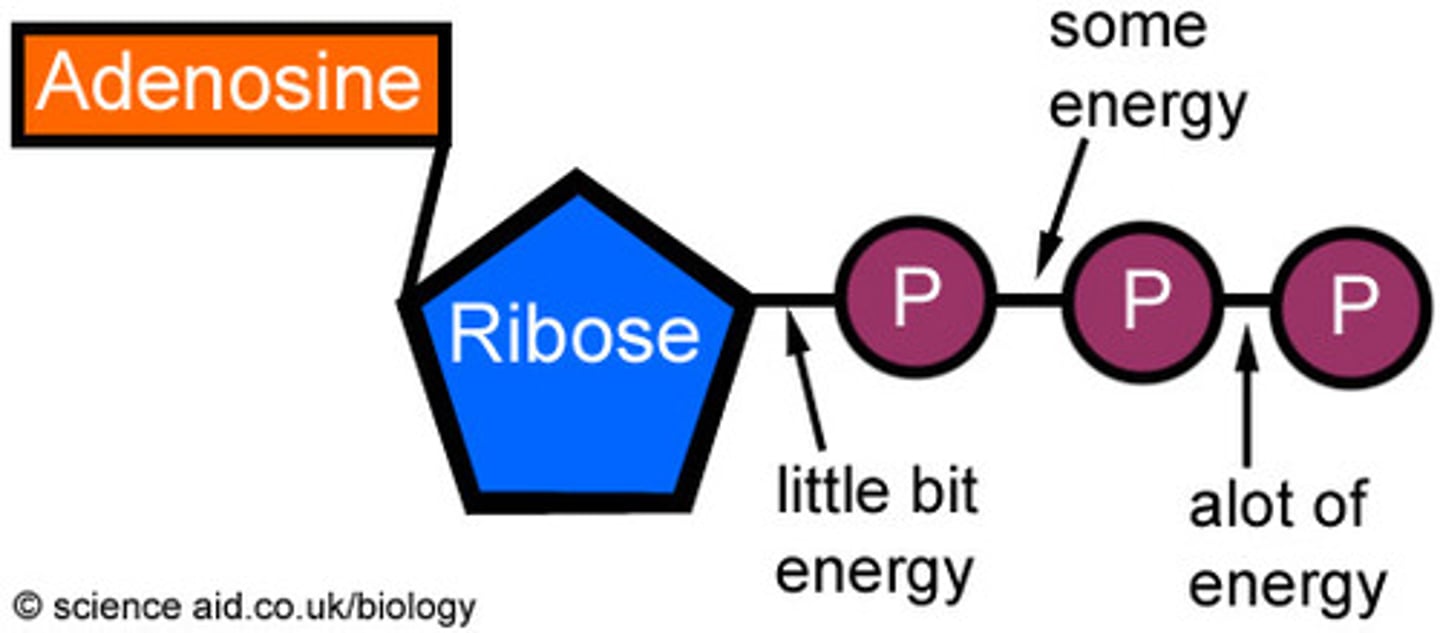
ATP
Adenosinetriphosphate is a nucleotide that stores large amounts of energy needed for synthetic reactions and for various other energy requiring processes in cells.
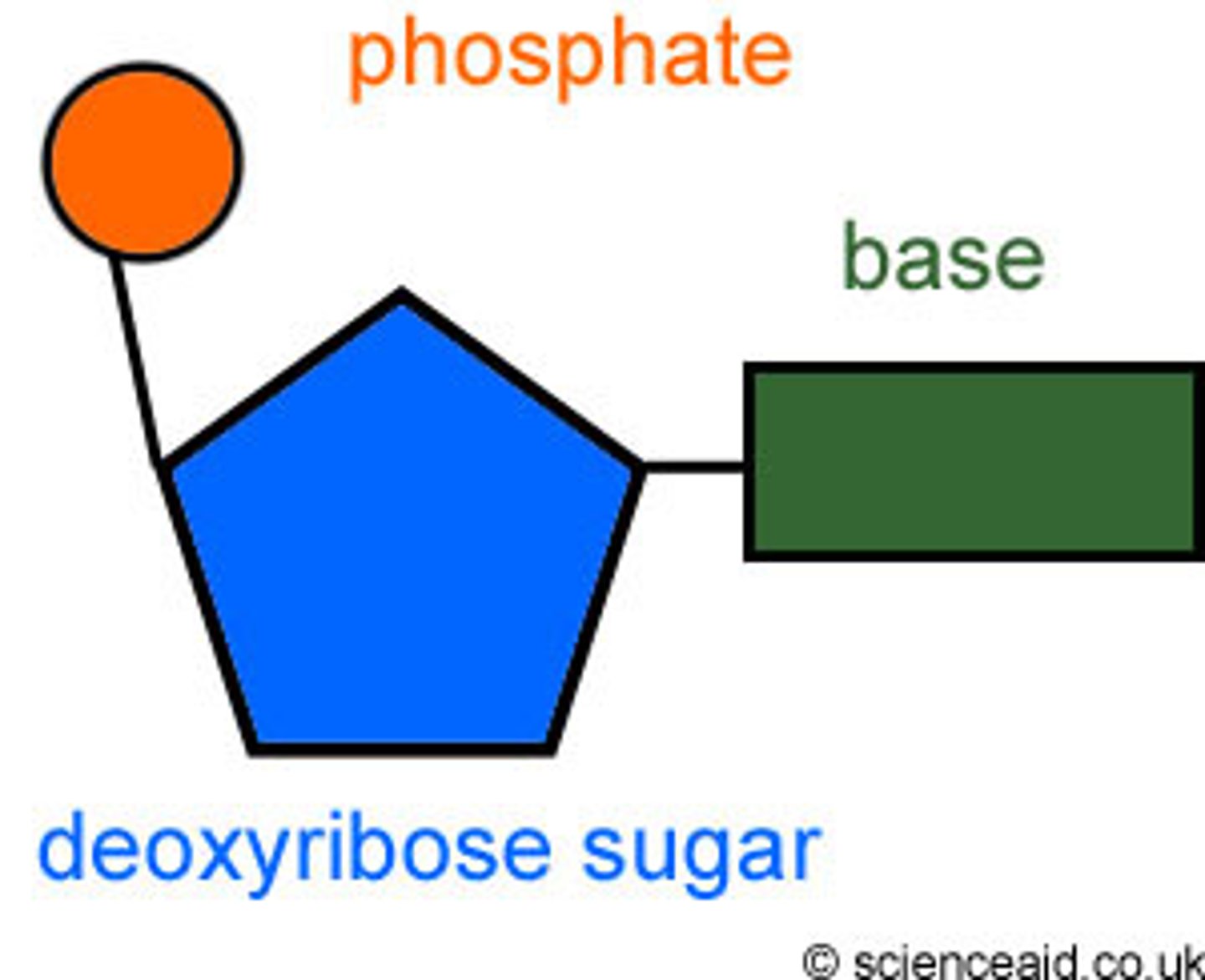
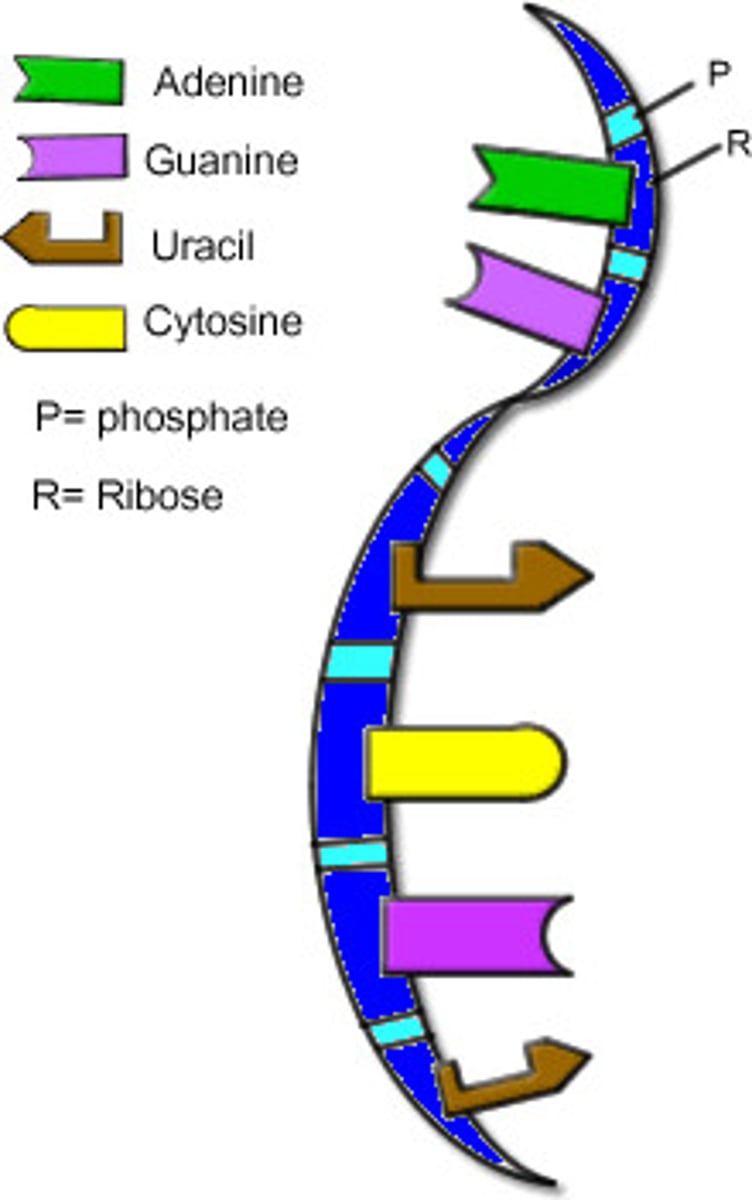
The nucleotides in DNA contain?
1. The sugar deoxyribose
2.Phosphate group
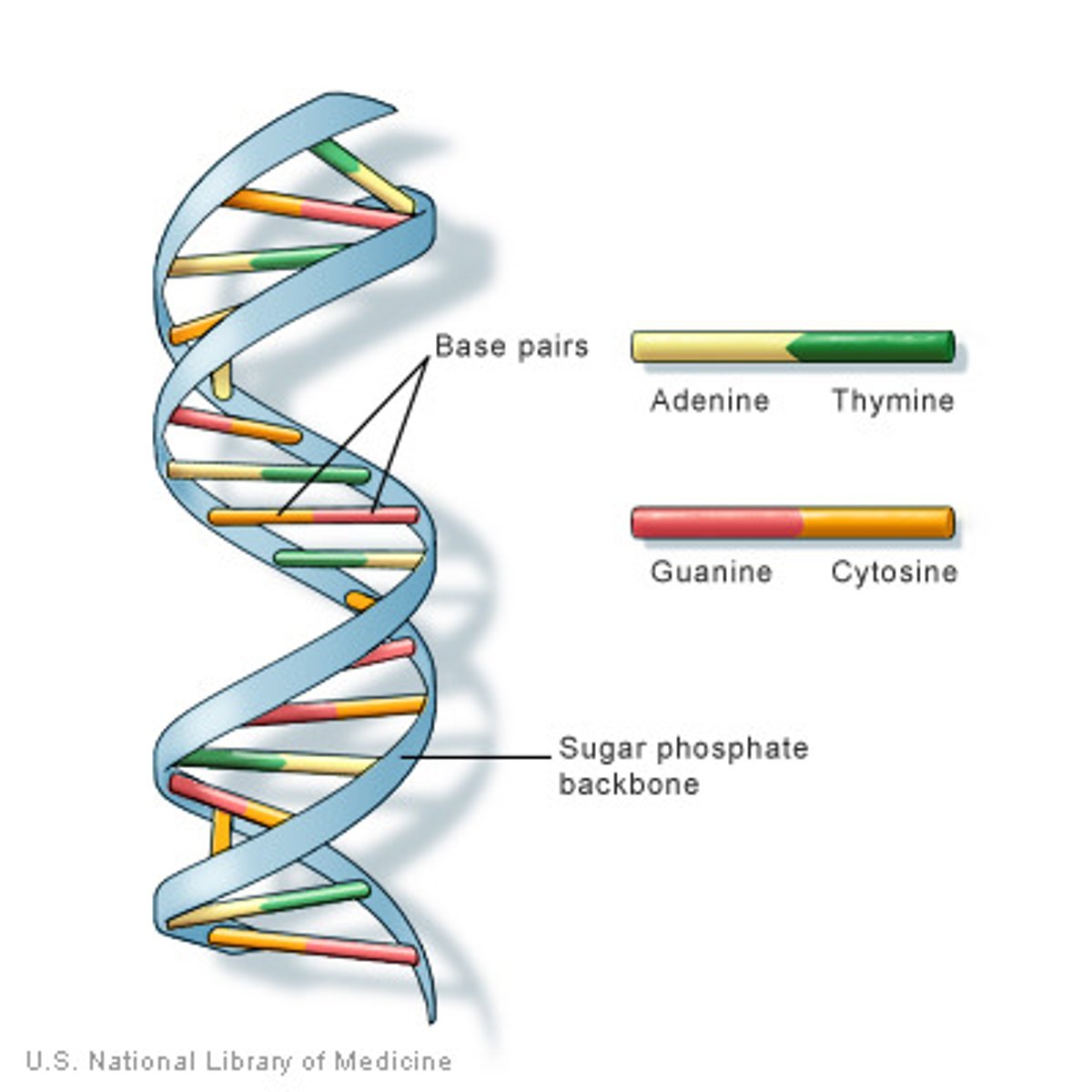
3.4 kinds of nitrogenous bases called Adenine and thymine. Guanine and cytosine.
The nucleotides in RNA contain?
1. The sugar ribose
2. A phosphate group
3.Rna contains uracil instead of thymine. So Adenine and uracil. Guanine and cytosine.
Two of the nitrogenous bases adenine and guanine belong to a group of compounds known as?
Purines (two ring in their structures)
The remaining two bases cytosine and thymine are known as?
Pyramidines (one ring)
Guanine and cytosine are hard to denature because?
Adenine and thymine are easier to denature because?
They have 3 hydrogen bonds.
They have 2 hydrogen bonds which makes it easier to break down.
When ADP is modified by the addition of three phosphate groups it is known as?
ATP (energy carrier in cells).
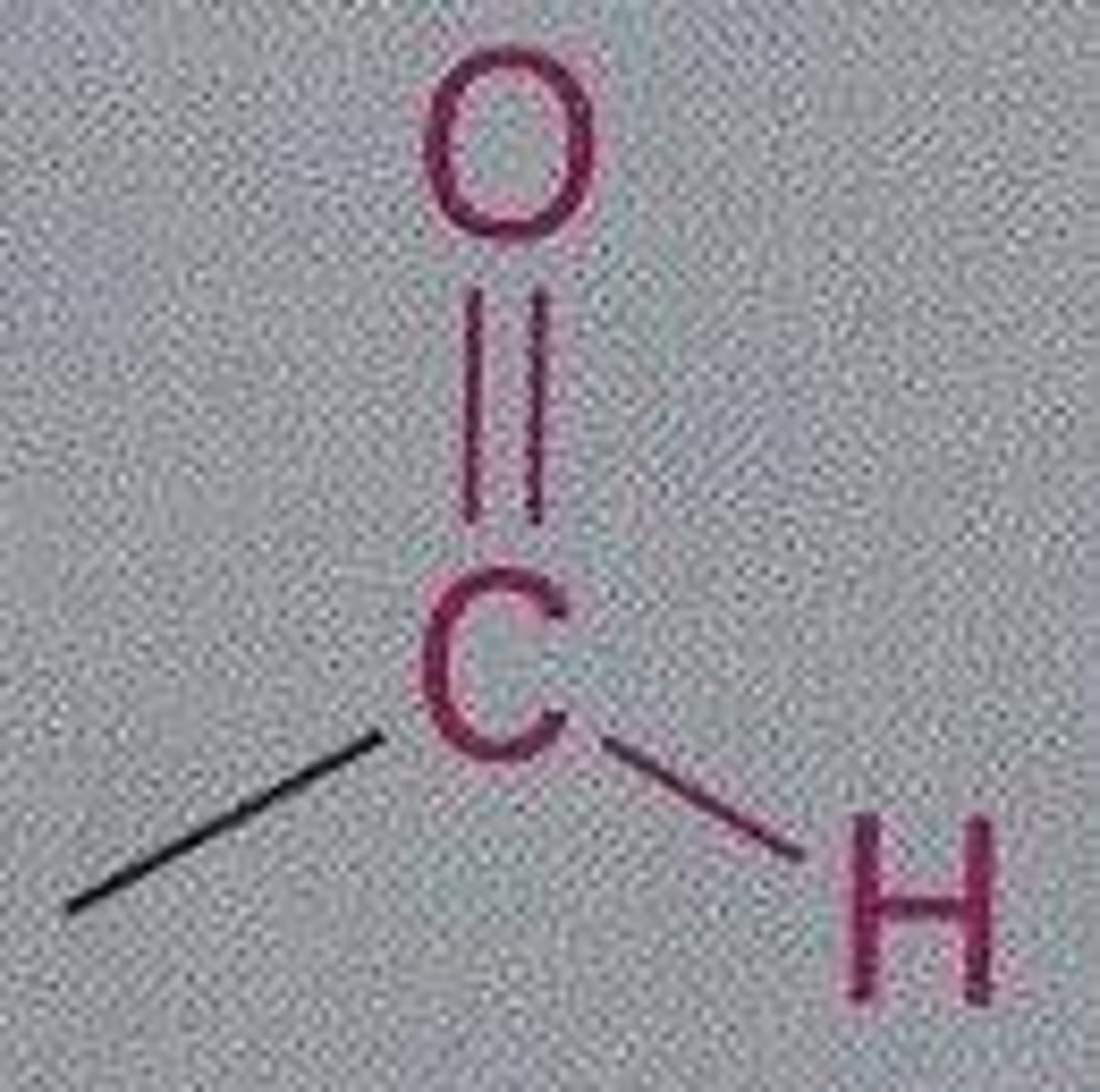
Aldehyde
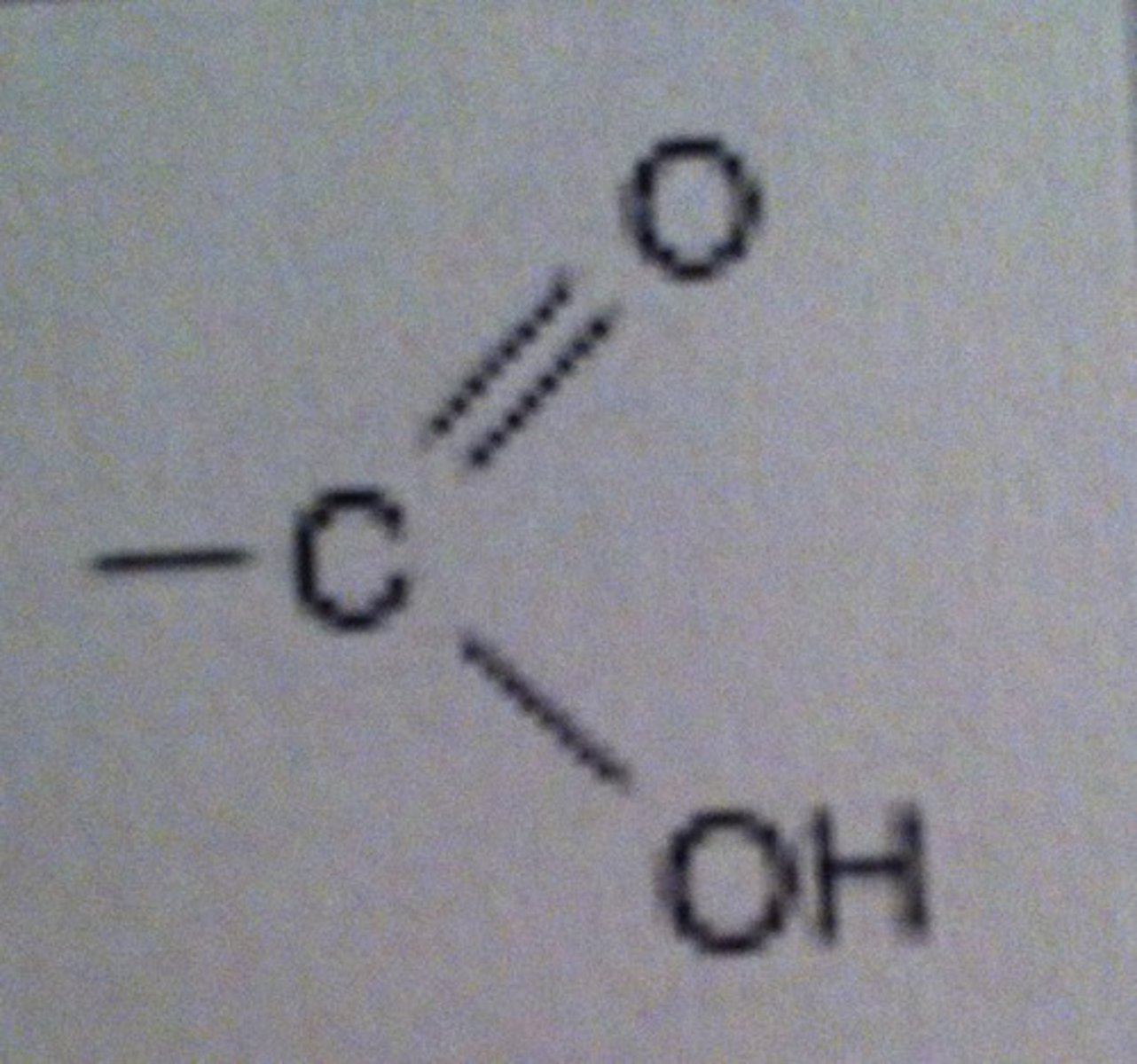
Carboxylic acid
Ester
In the red only
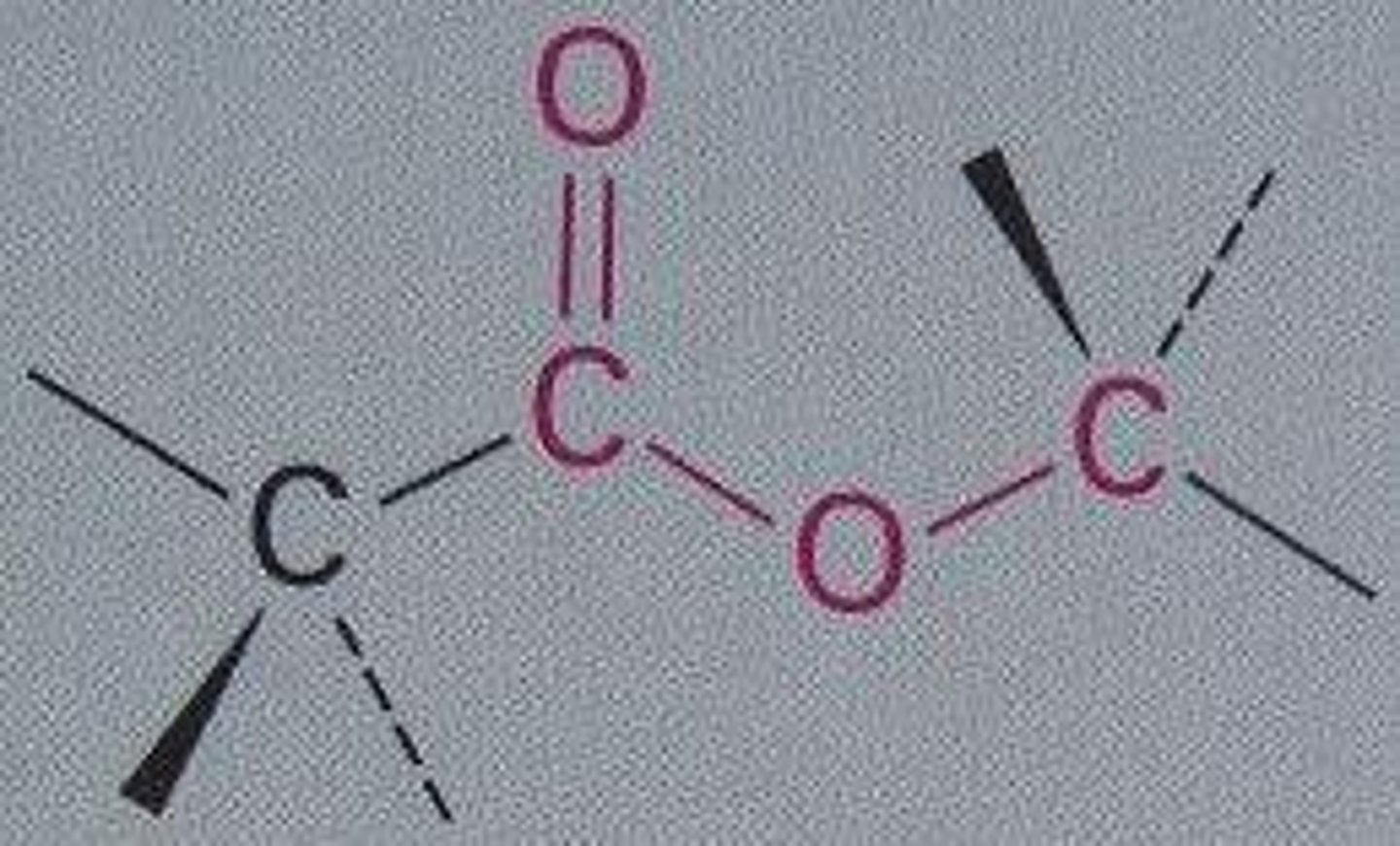
Phosphate
-PO4
COMPOUNDS CONTAINING CARBON ARE CALLED?
Organic molecules
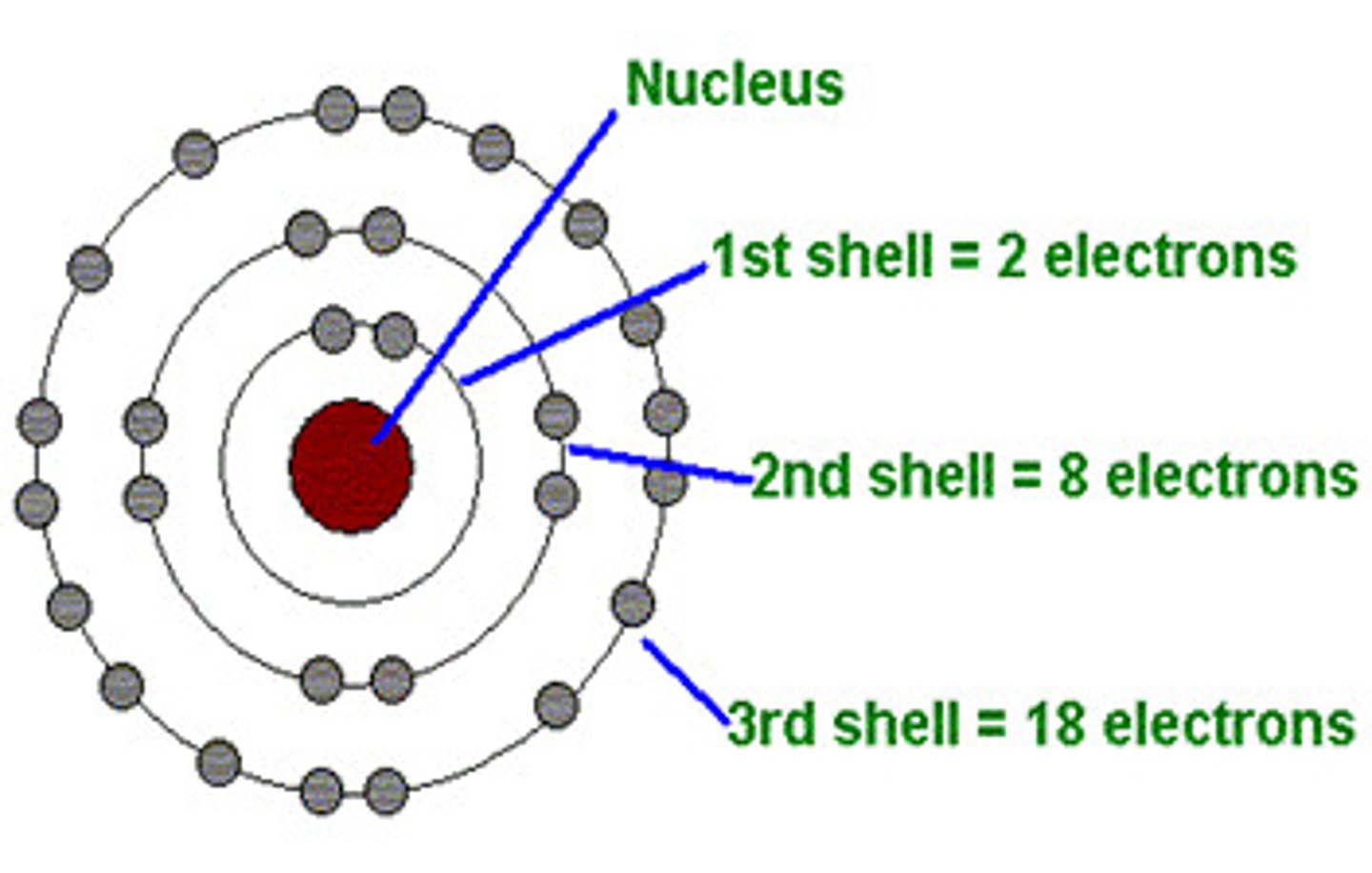
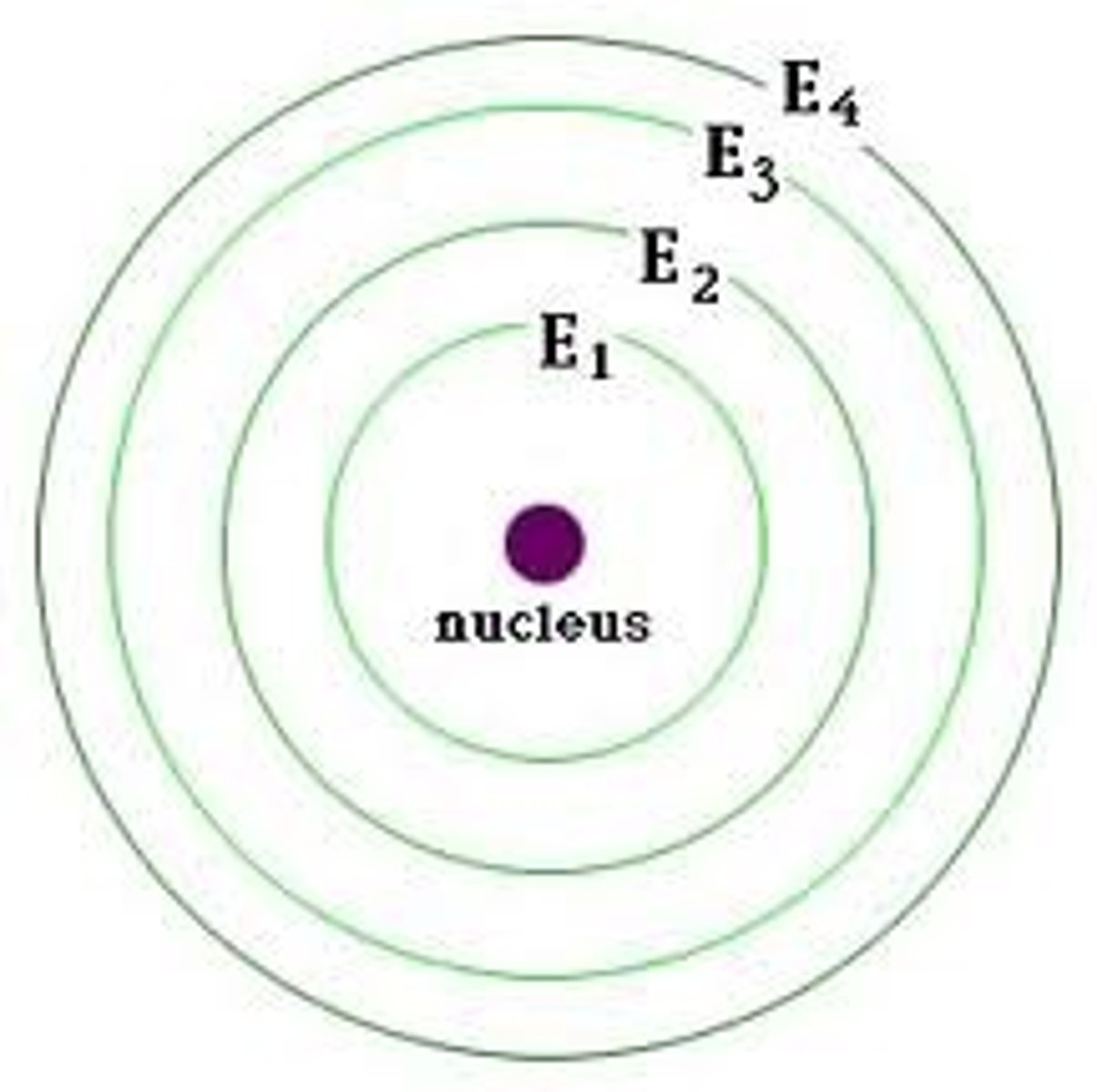
Energy levels
Level 1 = s-orbital which = 1s =2e
Level 2= 2s and 2 p= 2+6 e= 8 e
Level 3= 3s,3p,3d = 2+6+10= 18 e.
What is an example of a prokaryote ?
Bacteria
Examples of eukaryote ?
Humans, animals, plants, fungi and protists
What is a organelle?
Little organ. Internal compartments that have specialized functions.
Both the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain a?
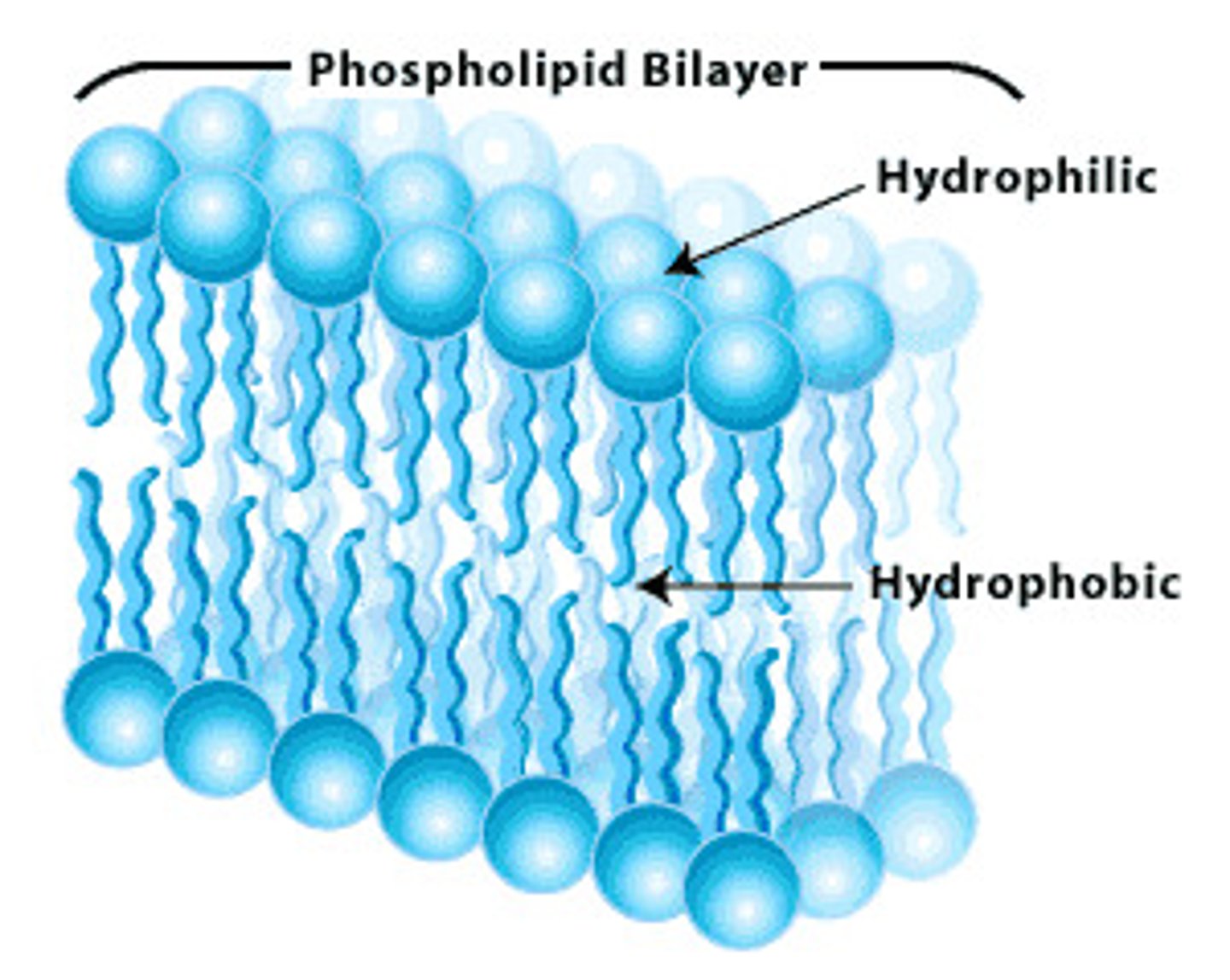
Plasma membrane
PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER
It is selectively permeable meaning it allows certain molecules to enter but not others.
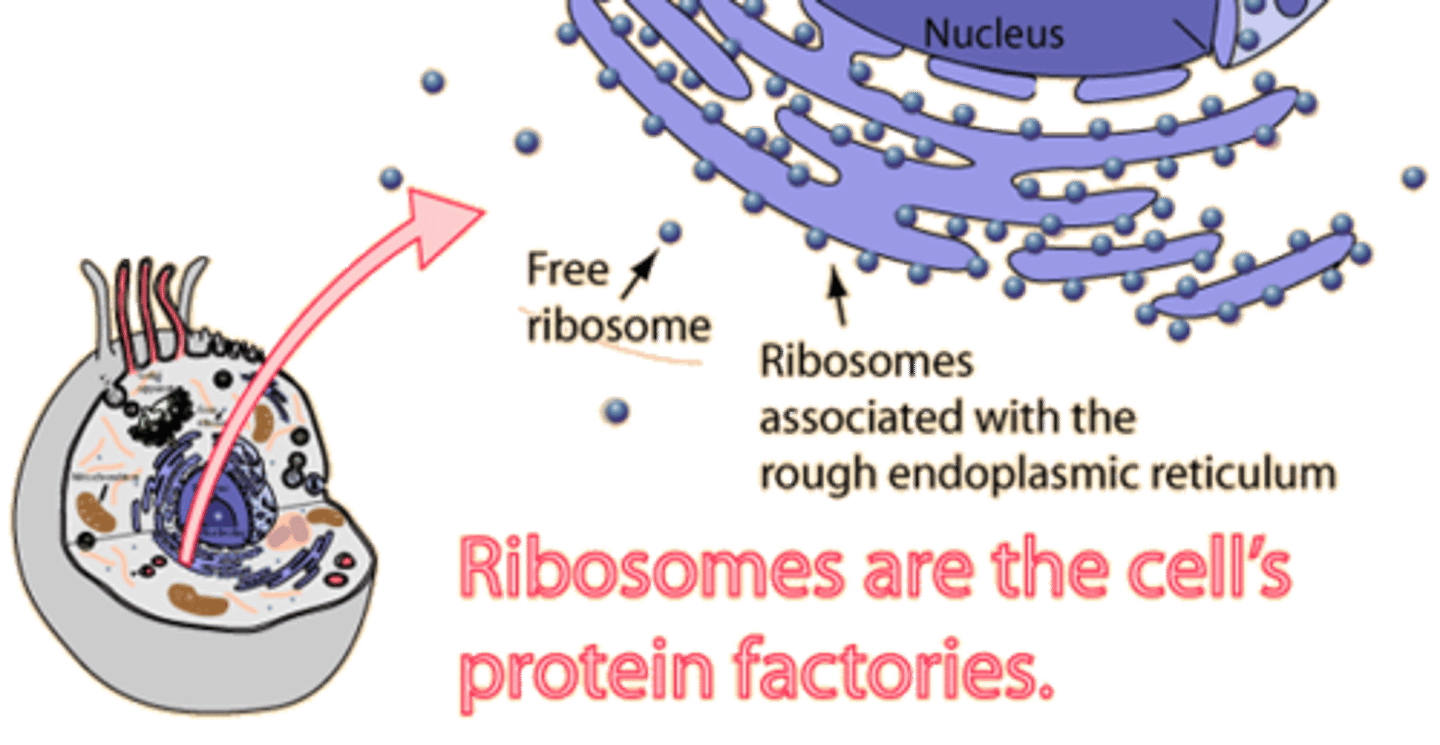
Where do you find ribosomes?
Rough ER and cytoplasma floating around.
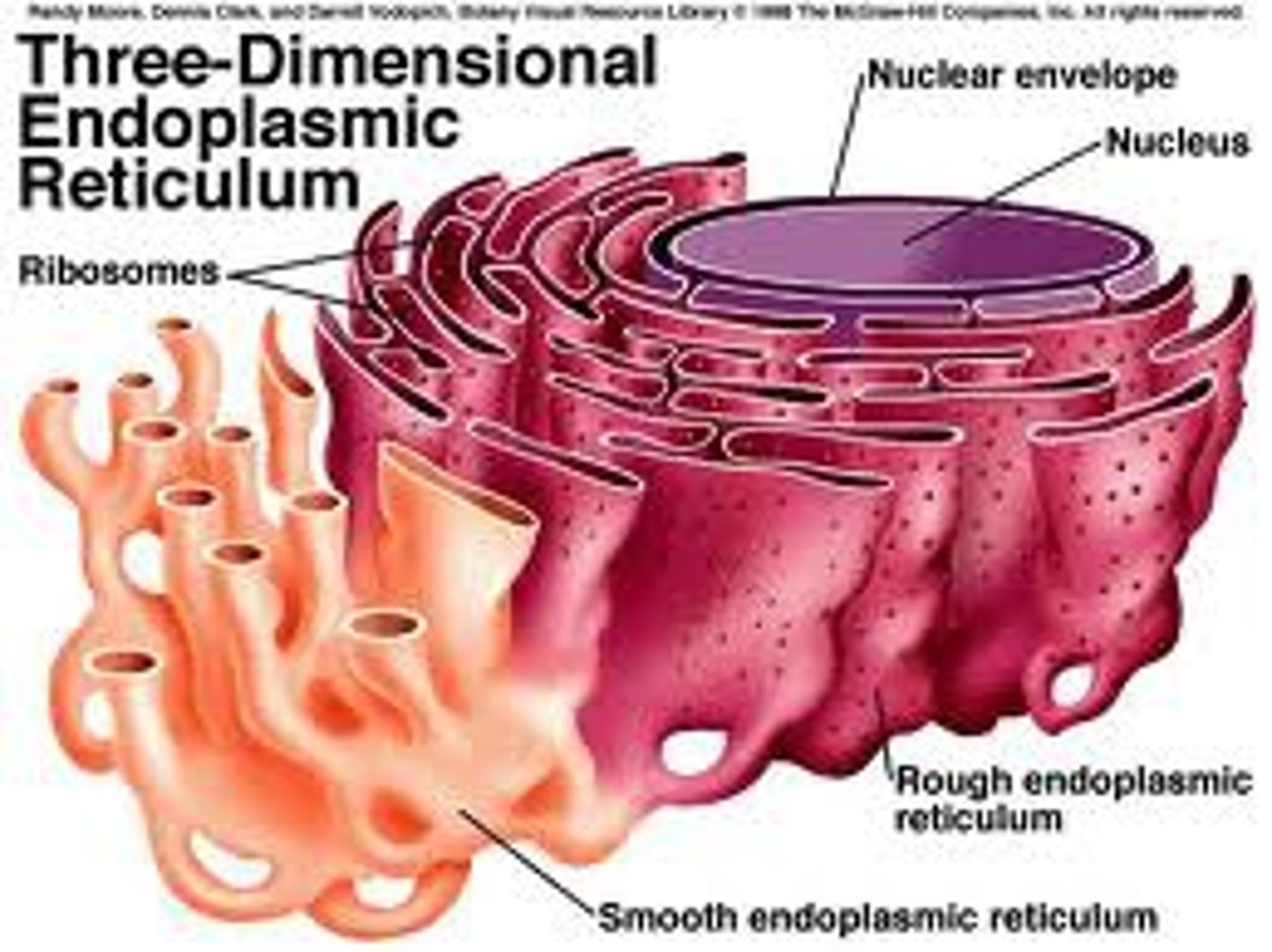
2. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ORGANELLE)
Has two portions the rough ER and smooth ER.
The rough ER is studded with ribosomes. The smooth ER does not have ribosomes attatched.
4. Vacule
Sac like structure. Store materials such as water, salts, proteins and carbohydrates.
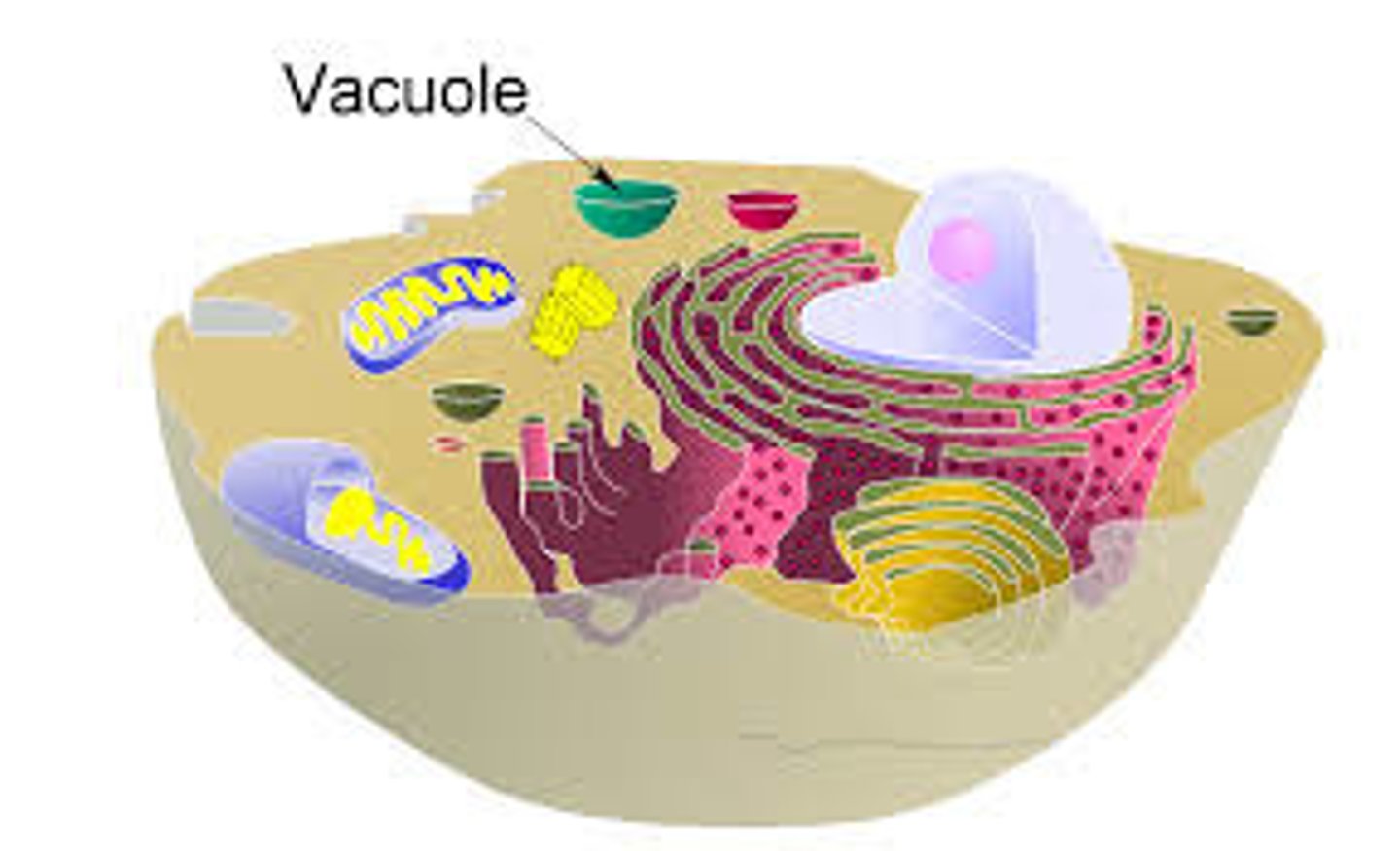
Eukaryotic cells have a structure called?
The cytoskeleton.
Cytoskeleton?
Network of protein filaments that helps the cell to maintain its shape.
Isotonic solution
Same solute concentration as in the cell.
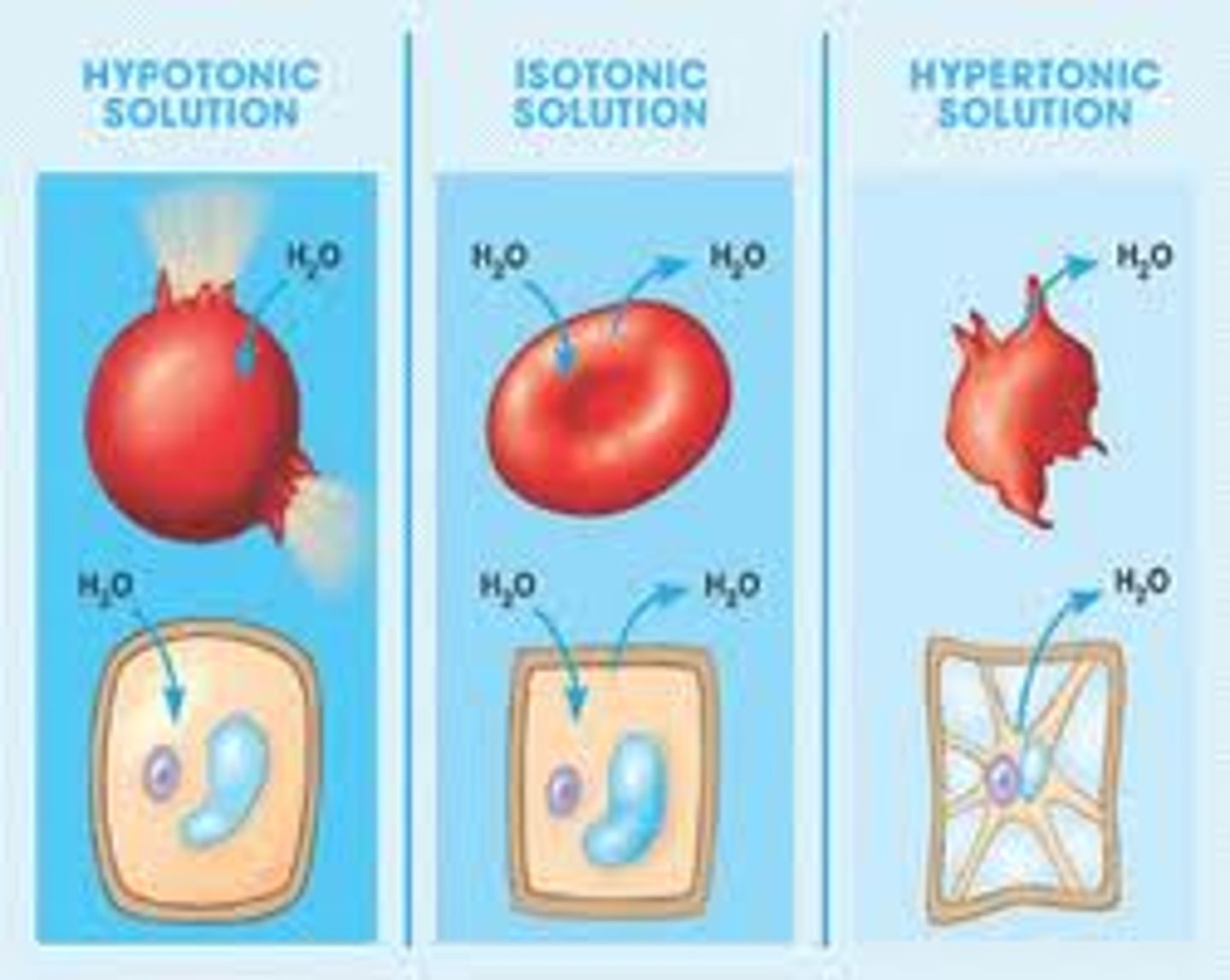
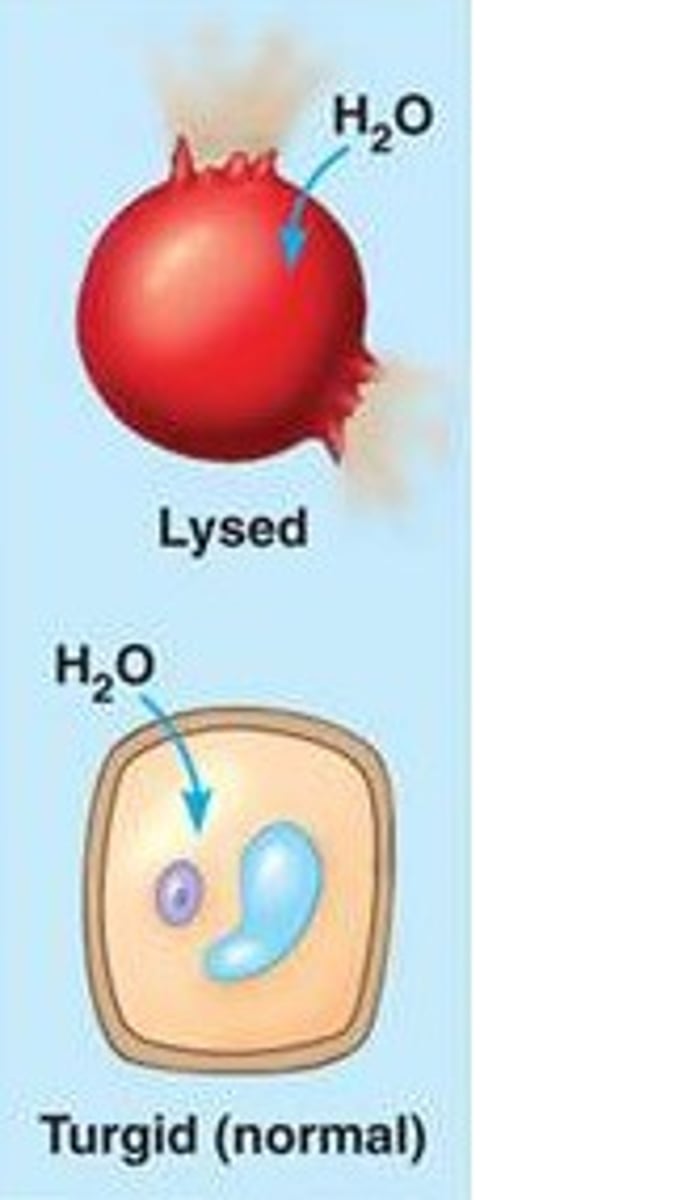
Hypotonic solution
Lower solute concentration than in the cell. They swell and burst. Example placing a RBC (red blood cell) in a hypotonic solution causes it to burst or (hemolysis)
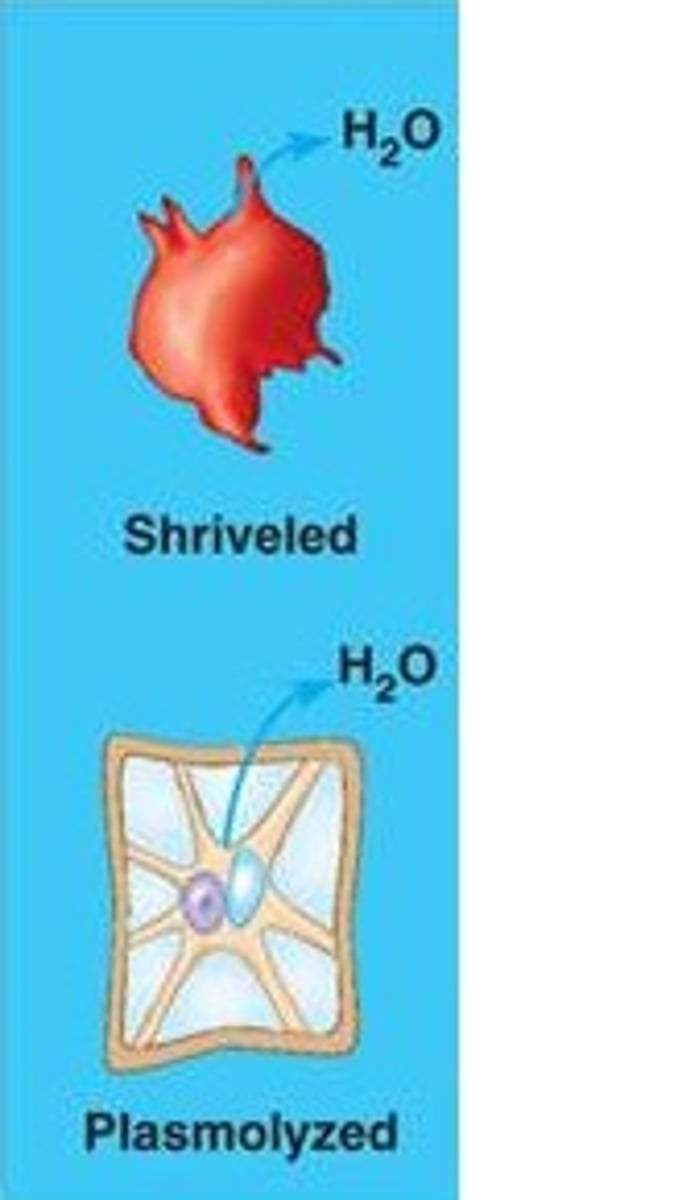
Hypertonic solution
Higher solute concentration than in the salt.
When you place a RBC in a hypertonic solution this causes the cell to shrink and shrivel due to loss of water. This term is called crenation when a RBC shrinks.
Facilitated transport?
A molecule is transported across the plasma membrane from the side of higher concentration to the side of lower concentration. This is a passive means of transport. No cellular energy required.
Proteins involved in active transport are called?
Pumps.
What are the 3 stages of cellular respiration?
1. Glycolysis
2. Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)
3. ETC (electron transport chain)