Metabolism and Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Metabolism
Collection of all biochemical reactions in organisms.
Oxidation
Reaction involving loss of electrons.
Reduction
Reaction involving gain of electrons.
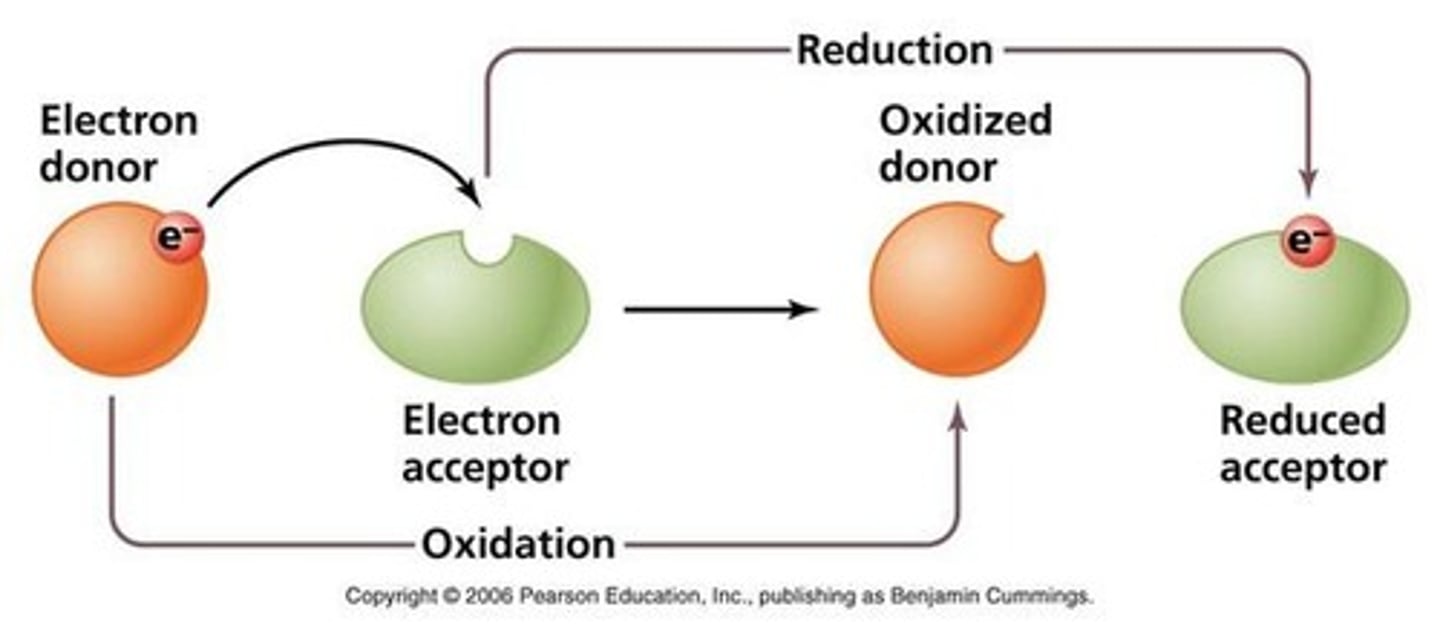
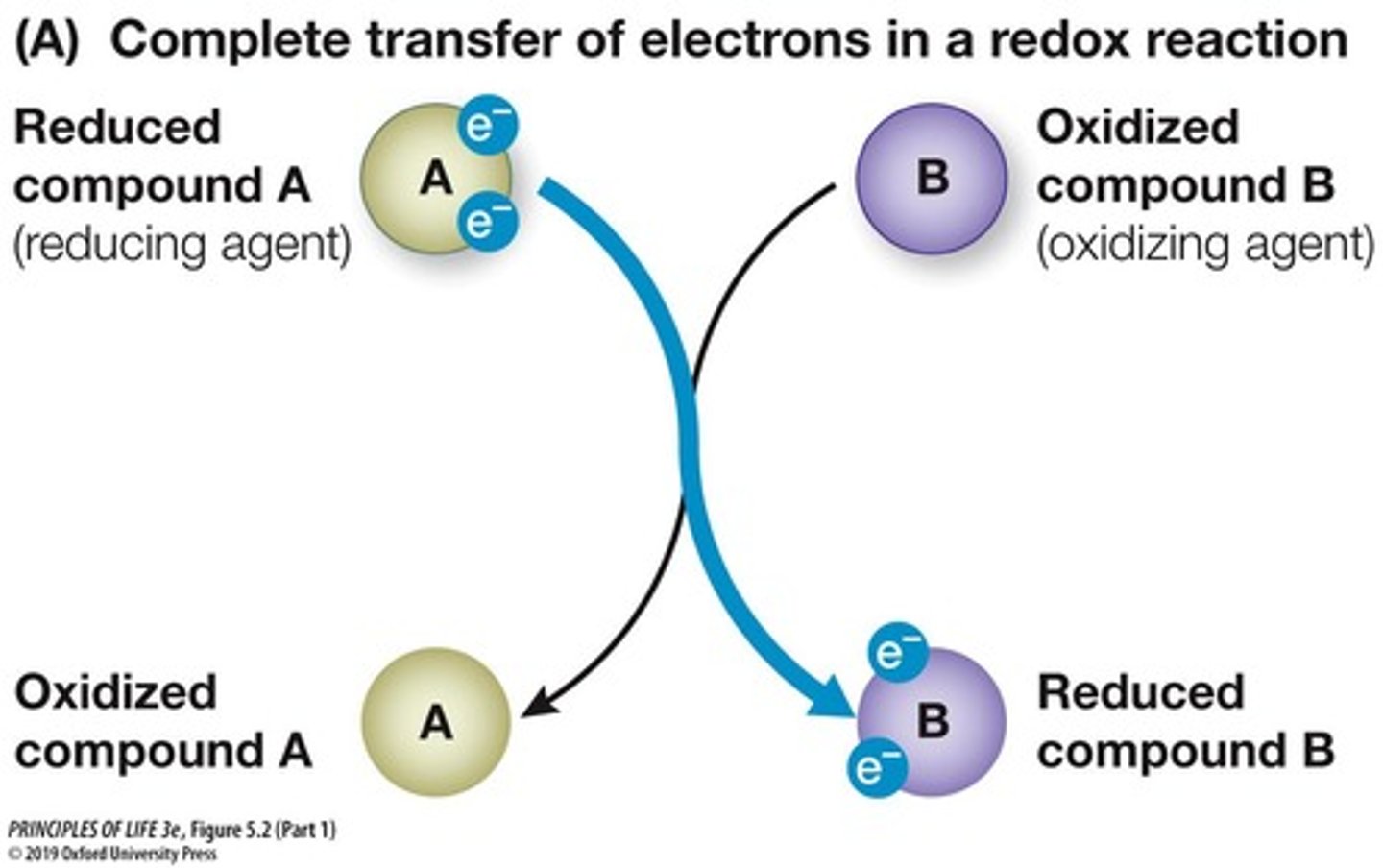
Redox Reactions
Reactions involving electron transfer between reactants.
Exergonic Reaction
Reaction that releases energy, e.g., combustion.
Combustion
Rapid chemical combination with oxygen.
Energy Storage
Energy stored in glycogen, starch, and lipids.
Potential Energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds.
Covalent Bonds
Bonds formed by electron sharing.
OIL RIG
Mnemonic: Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain.
LEO the Lion says GER
Mnemonic: Loss Equals Oxidation, Gain Equals Reduction.
Combustion of Glucose
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 686,000 cal/mol.
Electron Transfer
Movement of electrons between reactants in reactions.
Hydrogen Reduction
e- + H+ → H, more hydrogens indicate reduction.
Oxidation of Cellular Fuel
C6H12O6 oxidized to CO2, releasing energy.
Rule of Redox
Oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
Example of Redox
Na + Cl → Na+ + Cl-; Na oxidized, Cl reduced.
Energy Release
Excess energy released when electrons rearranged.
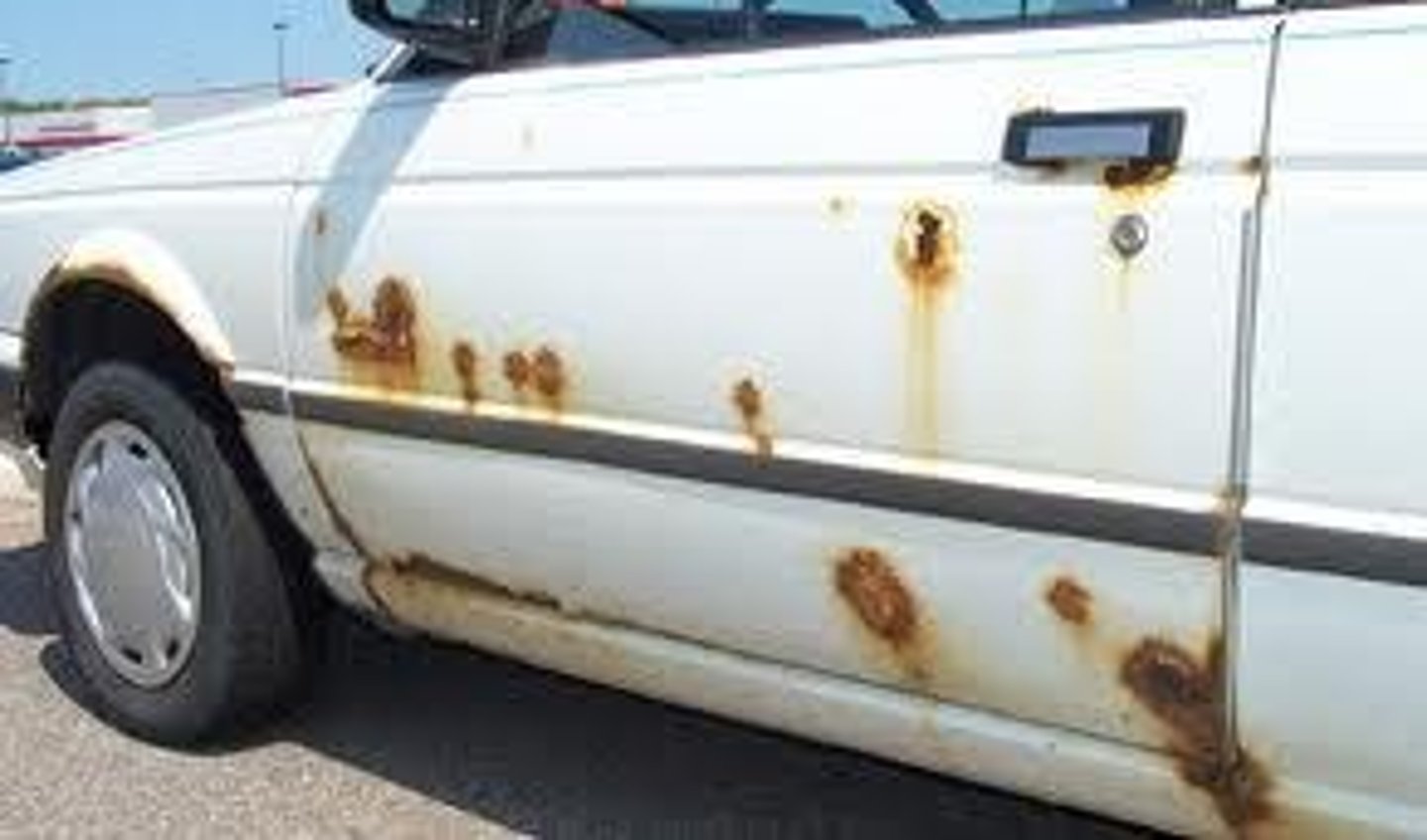
Rust Formation
Oxidation of iron, a slow combustion process.

ATP Synthesis
Driven by released free energy from reactions.
Electron Energy Loss
Electrons lose energy with each transfer.